Abstract
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) and atopic dermatitis (AD) are both inflammatory dermatoses that can significantly impact patient quality of life, however, limited research exists regarding their association. The purpose of this comprehensive review is to compare the inflammatory pathogenesis of HS and AD, explore the associations between these diseases, and discuss standalone and concomitant disease treatment options. Although HS and AD are understood to be primarily driven by the Th1 and Th2 inflammation pathways, respectively, these conditions both utilize the Janus Kinase/Signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT) pathway to promote inflammation. Newer research also suggests that IL-36 and IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 (IRAK4) may be two additional inflammatory signals shared between the HS and AD disease pathways. These shared mechanisms are reflected in patient presentations as HS and AD are often concomitantly present and demonstrate a bidirectional association in the current literature. Treatment options for concomitant disease are limited, but leverage the shared immune pathogenesis of both diseases. Dupilumab has been reported to improve both HS and AD symptoms in select patients. JAK inhibitors are currently FDA-approved for the treatment of AD, and early trials have suggested benefits from JAK inhibitors such as upadacitinib, povorcitinib, and topical ruxolitinib for HS. Possible future avenues for research on treating both HS and AD include IRAK-4 inhibitors such as zabedosertib and BAY1830839, and diet and gut microbiome modifications.
1. Introduction
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a debilitating chronic inflammatory condition characterized by recurrent abscesses, nodules, and tunnels in skinfold areas like the underarms, buttocks, and groin [1]. Atopic dermatitis (AD) is an inflammatory skin disease characterized by the presence of eczematous, dry, scaly, and pruritic skin patches [2]. Although prior literature has explored the pathogenesis of HS and AD, there is a paucity of information regarding the associations of HS with AD. Furthermore, although for some patients, HS is often comorbid with AD, suitable treatment approaches for patients with both remain unclear. The purpose of this review is to discuss the current state of the literature regarding the role of the immune system for HS and AD, explore their associations, and discuss management options for patients with concomitant disease.
2. The Role of the Immune System in Atopic Dermatitis and Hidradenitis Suppurativa
AD is understood to be caused by the combination of dysregulated immune response and skin barrier impairment [3,4,5,6]. AD is primarily understood to be a Th2-dominated inflammatory process with skin barrier defects, which allows infiltration of allergens and microbes, leading to Th2 cell sensitization that subsequently leads to cytokine release [7,8]. However, recent data suggests that chronic AD is more biphasic with an initial Th2 response in the acute phase, leading to lesion development via Th17 and Th22 responses in the chronic phase [8,9,10]. Some of the cytokines implicated in AD include IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 [11,12,13,14]. IL-4 and IL-13 are both thought to bind to IL-4 receptor alpha (IL-4Ra). They are responsible for the production of the extracellular matrix and can cause skin micro-epidermal fissuring and epidermal water loss through kallikrein 7 production (Figure 1). IL-17, another proinflammatory cytokine, is also thought to play a role in AD pathogenesis. Damaged keratinocytes in AD produce IL-17E that subsequently stimulates IL-5 and IL-13 production while inhibiting the release of filaggrin, important for skin barrier maintenance [15] (Figure 1).
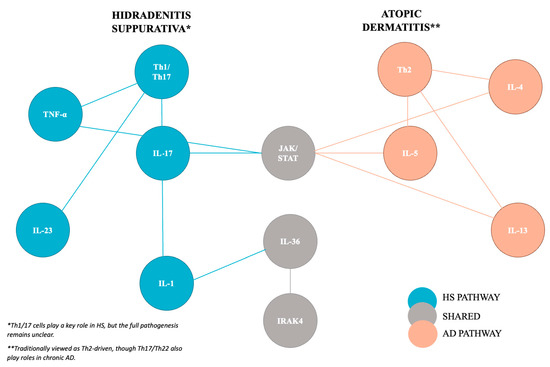
Figure 1.
Key inflammatory cytokines involved in the pathogenesis of Hidradenitis suppurativa and atopic dermatitis with an emphasis on shared pathways.
The pathogenesis of HS is incompletely understood; however, newer research suggests that the immune system plays a pivotal role. Th1/17 cells are important for HS pathogenesis, subsequently leading to the release of numerous proinflammatory cytokines. Key cytokines of interest include IL-17, IL-23, IL-1, Tumor Necrosis Factor-a (TNF-a), and IL-12, which are elevated in patient lesional HS skin [16,17]. TNF-α promoted T-cell proliferation and CD8+ cytotoxic T-cell stimulation and was expressed in higher levels in HS skin and positively correlated to increased disease severity [18,19]. IL-23 participates in the activation of TH17 cells, which induces the production of IL-17A, IL-17F, TNF-α, and IL-16 [15,20] (Figure 1).
The Janus Kinase/Signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT) pathway presents perhaps the clearest overlap in inflammatory mechanisms between HS and AD and is currently an important target for therapeutics related to inflammatory or autoimmune dermatoses. The transmembrane receptor JAK, once activated, phosphorylates both itself and the cytoplasmic STAT. STAT subsequently travels to the nucleus as a transcription factor regulating gene expression [21]. Different inflammatory cytokines induce JAK expression, including IL-4, IL-5, and IL-31 [22,23,24]. Multiple components of the JAK/STAT pathway have been implicated in AD. In the IL-4 pathway, IL-4 binds to its corresponding receptor and induces phosphorylation of JAK1 and JAK3, which subsequently activate IL-4Ra and STAT6 [22]. Alternatively, IL-4 and IL-13 may also bind the IL-4 receptor and strongly phosphorylate JAK1 and TYK2. This causes downstream STAT3 and STAT6 phosphorylation that can lead to skin barrier dysfunction and increased accumulation of TSLP, IL-25, and IL-33 in keratinocytes [25]. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), a Th2-related immune factor associated with inflammatory diseases, also contributes to the JAK/STAT pathway by binding the TSLP receptor and IL-7 receptor alpha (IL-7Rα) and subsequently phosphorylating JAK1 and JAK2. IL-5 can also phosphorylate JAK1 and JAK2, resulting in the activation of STAT1, STAT3, and STAT5 [23] (Figure 1).
The JAK/STAT pathway is also closely involved with multiple inflammatory markers associated with HS, including TNF-α and IFN-γ [26]. This pathway may also contribute to inflammatory cytokine accumulation in HS lesions, as demonstrated by a quantitative analysis of JAK/STAT pathway signaling by Dermirci et al., who found an overexpression of all cytokines except STAT6 in HS skin compared to controls [27]. JAK1 inhibitors have been evaluated in HS with promising initial results [28].
IL-36 is a member of the IL-1 cytokine family whose role in inflammatory skin conditions has been explored in recent years (Figure 1). It is comprised of three agonists (IL-36α, IL-36β, and IL-36γ) and one antagonist (IL-36Ra). IL-36α and IL-36γ are proinflammatory. While IL-36Ra is understood to be anti-inflammatory, the role of IL-36β remains incompletely understood, but is thought to induce antimicrobial peptides, matrix metalloproteinases, and IL-8 expression in keratinocytes [29,30]. In allergic contact dermatitis, a disease that frequently co-occurs with AD, IL-36 promotes disease, with overexpression of IL-36α, IL-36β, and IL-36γ occurring in areas of active lesions and positive skin patch test results [30,31]. A study exploring lesional AD transcriptomics using RNA sequencing demonstrated increased expression of IL-36 cytokine in AD skin lesions compared to non-lesional skin [32]. Tsoi et al. also found a marked increase in IL-36 in chronic compared to acute AD lesions, suggesting its potential role in the progression from acute to chronic AD in humans. They postulate regarding the potential efficacy of anti-IL-36 treatments for AD but acknowledge that data supporting this hypothesis is lacking [33]. A phase IIa randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of an anti-IL-36 antibody, Spesolimab, failed to produce statistically significant differences in Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) scores at Week 16 from baseline compared to placebo [34].
IL-36 expression is also pertinent to HS, with multiple studies demonstrating increased epidermal expression of all IL-36 cytokines in lesional compared to healthy skin [35,36,37]. In the immunohistochemistry and mRNA analysis of IL-36 in lesional HS versus healthy and psoriatic skin, Thomi et al. demonstrated that IL-36α was statistically significantly increased in HS skin versus healthy skin. However, although all IL-36 isomers were elevated in HS skin compared to healthy skin, expressions were significantly lower compared to psoriatic skin, raising questions about the significance of their role in HS and its viability as a therapeutic target [37] (Figure 1). A proof-of-concept, randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled study of Spesolimab for moderate-to-severe HS did not result in a significant difference in the primary endpoint of abscess and nodule (AN) count between Spesolimab treatment and placebo. However, Spesolimab did decrease overall disease severity as measured by other validated tools, including the International Hidradenitis Suppurativa Severity (IHS4), Hidradenitis Suppurativa Area and Severity Index (HASI-R), Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response (HiSCR50), and draining tunnel count, suggesting future therapeutic potential, especially for patients with multiple draining tunnels [38].
Finally, IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 (IRAK4) is also thought to contribute to the shared pathogenesis of HS and AD by acting as a key regulator of our innate immunity [39,40,41,42]. IRAK4 is a part of the complex called the myddosome, whose kinase functions enable the signaling of toll-like receptors (TLR) and interleukin-1 receptors (IL-1Rs), contributing to an inflammatory state [43,44] (Figure 1). Inhibition of IRAK4 has been shown to reverse pathogenic molecular signatures by affecting central mediators of atopic dermatitis, such as IL-4 and IL-13 [45].
Our current understanding of the pathogenesis of HS and AD suggests both are fundamentally inflammatory processes, albeit with distinct pathways. Nevertheless, a few common inflammatory cytokines are found to be pertinent to both diseases, leading to new potential targets for concomitant disease. These current and future therapeutic options are discussed in further detail below.
3. Associations of AD and HS
HS has long been associated with inflammatory pathways involving cytokines like IL-1β, TNFα, IFN-γ, and IL-17/22. However, a recent meta-analysis has challenged the clear distinction between HS and other conditions like atopic dermatitis, suggesting these diseases may share more in common than previously thought [46]. Furthermore, one study pointed to a potential relationship between increased apoptosis of TH1 cells, which are known for producing elevated levels of IFN-γ, and the dominant TH2 immune response typically seen in atopic disorders. This finding hints at overlapping immune mechanisms between these conditions, highlighting the possibility of shared pathways in their pathogenesis [47,48].
Moreover, a bidirectional association between HS and atopic dermatitis (AD) has been observed, suggesting that individuals with HS are at a higher risk of developing AD, and vice versa [49]. A study investigating this relationship found that patients with AD had a 5.57-fold increased odds ratio of having HS compared with those who did not have AD [50]. Another Mendelian randomization study exploring the relationship between AD and HS using genome-wide association data found a causal connection of AD on HS (OR: 1.78, p = 0.006) [51]. Rick et al. discuss their experience observing this trajectory of concomitant AD and HS, with uncontrolled AD featuring prominent xerosis and ichthyosis vulgaris presenting early in childhood and persisting as patients reach early adulthood and develop HS symptoms [52].
Such associations may extend to others in the atopic triad as well, with Kridin et al. reporting 1.4-fold greater odds of HS in patients with a history of asthma in their age, sex, and ethnicity-matched longitudinal study [53]. Interestingly, the inverse relationship of patients with HS developing new-onset asthma was not statistically significant. A case-control study using the All of Us Research Program by Chen et al. further supports such an association between HS and asthma and allergic rhinitis. In their multivariable analysis, HS was significantly associated with allergic rhinitis (OR: 1.68, 95%CI: 1.47–1.92, p < 0.001) and asthma (OR: 1.73, 95%CI: 1.52–1.97, p < 0.001) even after controlling for multiple patient characteristics, including BMI, smoking, eczema, and food allergy [54].
Several hypotheses have been proposed to explain the connection between HS and atopic diseases. One suggests that deficient notch signaling may lead to epidermal barrier defects, resulting in increased inflammation in both conditions, as a disrupted skin barrier can fuel ongoing inflammatory responses. Another theory points to the dysregulation of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), which may enhance inflammatory activity in both HS and AD. Genetic susceptibility is another potential factor, with shared genetic predispositions potentially connecting the two diseases [50]. Coates et al. in their analysis of HS skin transcriptomics found S100A7A (also known as S100A15, Koebnerisin) to be the most significantly upregulated gene in HS lesional skin [55]. Interestingly, the S100A7A gene has also been found to be upregulated in other skin conditions, including psoriasis and, notably, atopic dermatitis [56,57]. Additionally, alterations in sphingolipid metabolism have been proposed as a mechanism contributing to immune dysregulation in HS [58]. These hypotheses suggest a complex interplay of immune dysregulation, genetic susceptibility, and barrier dysfunction that may underlie the co-occurrence of HS and atopic diseases [59,60,61,62]. However, multiple unanswered questions remain, including (1) if patients with concomitant AD and HS follow a similar disease trajectory as those with standalone disease; (2) if these patients are more likely to have other atopic and follicular diseases; and whether (3) immunomodulation to treat either HS or AD contributes to the pathogenesis of the other [52]. Therefore, further research is necessary to elucidate these shared pathways and to improve therapeutic approaches for individuals affected by these conditions.
4. Current Treatment Landscape of HS and AD
4.1. Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis treatment strategies vary depending on the severity and location of the disease, but often start with regular emollients alongside topical treatments such as corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors. Recent approvals for topical formulations of the JAK inhibitor ruxolitinib, aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist tapinarof, and phosphodiesterase-4 antagonist roflumilast have opened up a new variety of non-steroid topical treatment options. Lifestyle adjustments, such as regular bleach baths, may be necessary for moderate-to-severe cases, but are not recommended for mild disease. For widespread disease or topical treatment failures, systemic biologics such as dupilumab (dual inhibitor of IL-4 and IL-13) or tralokinumab (IL-13 inhibitor) should be added [63]. These biologics represented a major step forward in AD management and were followed by the FDA approval of Janus Kinase (JAK) inhibitors upadacitinib and abrocitinib, which are also highly efficacious [64,65]. The IL-31 antagonist nemolizumab was also recently approved for moderate-to-severe AD [66] (Table 1). The 2023 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology/American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology Joint Task Force guidelines recommend against the use of prescription moisturizers or methotrexate/azathioprine, given lower levels of supporting evidence [63].

Table 1.
Available treatment modalities for Hidradenitis suppurativa, atopic dermatitis, and concomitant HS and AD.
4.2. Hidradenitis Suppurativa
The current treatment landscape for HS involves a multidisciplinary approach aimed at managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Lifestyle modifications include weight loss, smoking cessation, and managing comorbidities. For mild-to-moderate cases, topical treatments, including antiseptics and antibiotics, are commonly used [67]. In more severe cases, systemic antibiotics are prescribed not only for their antimicrobial properties but also for their anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects. Biologic therapies are increasingly employed for moderate-to-severe HS, targeting specific inflammatory pathways. In advanced cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to remove affected tissue and prevent further complications. This comprehensive approach allows for personalized treatment plans based on disease severity and patient needs [67] (Table 1).
Adalimumab was the first FDA-approved biologic for the treatment of moderate-to-severe HS. It is a fully humanized anti-TNF-α monoclonal antibody that has been shown to reduce the number of abscesses and inflammatory nodules in HS patients [68]. Secukinumab, an IL-17A antagonist, and bimekizumab, an IL-17A/F dual antagonist, were approved for the treatment of HS in 2023 and 2024, respectively [69,70,71,72]. Other biologics with potential benefits from HS treatment include infliximab (a chimeric anti-TNF-α monoclonal antibody), ustekinumab (interleukin-12/23 (IL) receptor antagonist), and anakinra (IL-1 receptor antagonist) [73,74,75] (Table 1).
5. Approach to Treatment of Overlapping HS and AD
For patients with both HS and AD, the goal of current therapeutic research is to identify treatments that may offer the greatest benefit for both conditions. However, it is important to note that comorbid HS and AD is relatively rare, and a single treatment alone may be insufficient to manage both diseases. Despite a paucity of data to support a specific treatment algorithm for concomitant HS and AD, some therapeutic suggestions based on the current literature are provided below.
Corticosteroids may be employed, given the inflammatory nature of both HS and AD; however, different delivery vehicles may have varying levels of efficacy. While topical corticosteroids are commonly used for mild-to-moderate AD, they seemingly have minimal efficacy for HS, likely due to inadequate lesion penetration. Intralesional steroids are commonly employed for HS instead; however, the data regarding their efficacy is mixed. While a few small studies have found intralesional triamcinolone (ILT) to improve patient symptoms and reduce lesion burden in HS, a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial by Fajgenbaum et al. found no statistically significant difference between varying concentrations of triamcinolone and placebo for the treatment of HS lesions [76,77,78]. Finally, systemic corticosteroids may be employed for recalcitrant HS or AD; however, alternative treatments are preferred given the low certainty of evidence for oral corticosteroid use for AD and concern for systemic side effects with prolonged exposure for HS [79] (Table 1).
Dupilumab, an IL-4/13 inhibitor primarily used for AD, has also shown success in treating HS in a few patients with concomitant HS and AD [48,58,80,81]. However, it is important to note that HS is primarily considered a T1/T17-mediated inflammatory disease, while dupilumab targets T2-mediated inflammation, suggesting dupilumab may not be a long-term treatment option for patients with severe HS and AD (Table 1).
Other small-molecule inhibitors commonly employed for AD, particularly Janus Kinase (JAK) inhibitors such as upadacitinib and abrocitinib, can also be therapeutic for HS and AD. In a randomized clinical trial, upadacitinib was found to be superior in improving AD compared to dupilumab in a head-to-head comparison [82]. The data on upadacitinib for the treatment of HS is less comprehensive, but initial results remain promising. Two open-label, phase II trials of upadacitinib 15/30/60/90 mg once daily versus placebo for HS found moderate efficacy, with an increasing proportion of HS patients achieving HiSCR 50 with increased dose (15 mg: 43%, 30 mg: 56%, 60 mg: 56%, 90 mg: 88%) [83]. However, concerns remain given the small sample size and high percentage of HS patients (70% and 81%) reporting at least one treatment-related adverse effect. A novel JAK inhibitor, povorcitinib, was recently evaluated in a Phase 2b study of 209 subjects with HS randomized to daily doses of 15 mg, 45 mg, 75 mg, or placebo. Treatment arms all showed improved efficacy relative to placebo, and phase 3 trials are currently underway for both povorcitinib and upadacitinib [84]. Smaller, single-center, real-world efficacy studies and case reports also found similar results, suggesting JAK inhibitors as potentially important therapeutic options for concomitant HS and AD [85,86,87,88]. The topical JAK inhibitor ruxolitinib has also been the subject of early clinical trials that suggest it may be effective for patients with mild-to-moderate HS [89] (Table 1).
IL-17 inhibitor biologics such as secukinumab, commonly used for moderate-to-severe HS, have also been minimally investigated for AD, albeit with poor results. A phase 2 randomized, double-blind study by Ungar et al. found minimal improvement with secukinumab, questioning the validity of IL-17 as a therapeutic target for AD [90]. Furthermore, a few case reports suggest IL-17 inhibitors may instead cause an AD-like reaction in some patients with psoriasis [91,92,93]. Hence, the authors recommend against using IL-17 inhibitors for concomitant HS and AD, although further research is needed to validate these findings (Table 1).
6. Future Directions
Multiple other avenues for HS and AD treatment are currently being explored. IRAK-4, important for toll-like receptor and IL-1 receptor signaling, has been implicated in multiple inflammatory conditions and is currently being explored as a therapeutic target with promising initial results. The oral IRAK4 inhibitors zabedosertib and BAY1830839 were found to significantly reduce inflammatory response via reduction in serum TNF-a, IL-6, and IL-8 [94]. An initial double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 1 trial by Ackerman et al. demonstrated excellent tolerability and improvement in skin lesions in both HS and AD, with minimal side effects, making it a future potential therapeutic target [95].
Modification of nutrition also continues to be a topic of interest for the treatment of inflammatory conditions such as AD and HS. The relationship between dietary restriction and AD improvement remains unclear, with data suggesting that severe dietary restrictions, often undertaken by patients with medical advice, do not work and instead may reduce growth in pediatric patients with AD [96]. However, a study by Finch et al. found the incidence of AD in pediatric patients dropped significantly if their mothers received prophylactic administration of prenatal Lactobacillus. Breastfeeding may also have a protective effect against AD [97].
Dietary modifications are also often undertaken by HS patients, although data regarding their efficacy remains limited. A cross-sectional study surveying more than 1400 HS patients found that a diet high in sugars, fat, and alcohol was reported as a common HS flare trigger [98]. Multiple dietary modifications have been proposed, including weight loss, a dairy and brewer’s yeast-free diet, and the addition of zinc and vitamin D supplementation [99]. However, very little evidence and no randomized control trials exist to support these findings; hence, nutrition poses a possible frontier for future personalized medicine research.
The role of gut microbiota in multiple systemic inflammatory conditions is already being evaluated and may present another avenue for future research regarding inflammatory dermatoses. The mechanism behind the gut’s influence on skin disease remains unclear; however, the common coexistence of other inflammatory GI disorders, such as inflammatory bowel disease, with inflammatory skin conditions may provide an initial clue. Furthermore, initial research postulates that high-fat diets may induce HS lesion development by increasing matrix metalloproteinase levels [100]. HS patients were found to have lower levels of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and increased E. coli, although the effect of this difference on disease progression and severity remains unclear [101,102,103].
The influence of gut microbiome on AD has also been explored minimally, and multiple pathways have been proposed. Dysbiosis of a subspecies of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii was found in the fecal samples of patients with AD [104]. Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), thought to be important for epithelial barrier maintenance, were also found at lower levels in AD patient fecal samples. Overall, these dysbioses are thought to cause toxins and harmful gut microbiota to penetrate the epithelial barrier, causing significant Th2-type inflammation [105,106,107]. Regardless of the mechanism of action, personalized medicine focused on changing gut microbiota to address systemic inflammation continues to be an exciting area of future research.
7. Conclusions
In conclusion, HS and AD can be frequently concomitant in dermatology patients, with their associations highlighting shared mechanisms of immune dysregulation, barrier dysfunction, and genetic susceptibility. The overlap between Th1/Th17 inflammation in HS and Th2-driven responses in atopic conditions suggests a complex relationship. While multiple treatment options exist for both, modalities that treat both can be difficult to find but may include JAK inhibitors such as upadacitinib and abrocitinib, and IL-4/13 inhibitors such as dupilumab. The future landscape of treatment of concomitant HS and AD may include IRAK-4 degraders and personalized nutrition and gut microbiota therapy that reduce the inflammatory burden, although significant additional research is needed to validate these potential therapies.
Author Contributions
R.B.S.: Conceptualization, methodology, data curation, writing—original draft, writing—reviewing and editing. H.S.P.: Writing—original draft, writing—reviewing and editing. C.J.S.: Conceptualization, validation, writing—reviewing and editing, supervision, project administration. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
R.B.S. and H.S.P. report no conflicts of interest. C.J.S. reports being an investigator for AbbVie, Astrazeneca, ChemoCentryx, Incyte, InflaRx, Novartis, and UCB Pharma; receiving consultancy fees from AbbVie, Astrazeneca, Alumis, Astrazeneca, InflaRx, Sandoz, Sanofi, Incyte, Logical Images, Sonoma Biotherapeutics, and UCB Pharma; and serving as a speaker for AbbVie and Novartis.
References
- Goldburg, S.R.; Strober, B.E.; Payette, M.J. Hidradenitis suppurativa: Epidemiology, clinical presentation, and pathogenesis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, 1045–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortz, C.G.; Andersen, K.E.; Dellgren, C.; Barington, T.; Bindslev-Jensen, C. Atopic dermatitis from adolescence to adulthood in the TOACS cohort: Prevalence, persistence and comorbidities. Allergy 2015, 70, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campione, E.; Lanna, C.; Diluvio, L.; Cannizzaro, M.V.; Grelli, S.; Galluzzo, M.; Talamonti, M.; Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli, M.; Mancini, M.; Melino, G.; et al. Skin immunity and its dysregulation in atopic dermatitis, hidradenitis suppurativa and vitiligo. Cell Cycle 2020, 19, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutten, S. Atopic dermatitis: Global epidemiology and risk factors. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 66 (Suppl. S1), 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glinskii, A.B.; Ma, J.; Ma, S.; Grant, D.; Lim, C.-U.; Sell, S.; Glinsky, G.V. Identification of intergenic trans-regulatory RNAs containing a disease-linked SNP sequence and targeting cell cycle progression/differentiation pathways in multiple common human disorders. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 3925–3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardini, S.; Gravina, P.; Croce, N.; Perricone, R.; Knight, R.A.; Valentini, A.; Melino, G.; Federici, G. Itch gene polymorphisms in healthy population and in patients affected by rheumatoid arthritis and atopic dermatitis. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 3607–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salava, A.; Lauerma, A. Role of the skin microbiome in atopic dermatitis. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2014, 4, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittler, J.K.; Shemer, A.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Fuentes-Duculan, J.; Gulewicz, K.J.; Wang, C.Q.F.; Mitsui, H.; Cardinale, I.; de Guzman Strong, C.; Krueger, J.G.; et al. Progressive activation of T(H)2/T(H)22 cytokines and selective epidermal proteins characterizes acute and chronic atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 1344–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datsi, A.; Steinhoff, M.; Ahmad, F.; Alam, M.; Buddenkotte, J. Interleukin-31: The “itchy” cytokine in inflammation and therapy. Allergy 2021, 76, 2982–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esaki, H.; Brunner, P.M.; Renert-Yuval, Y.; Czarnowicki, T.; Huynh, T.; Tran, G.; Lyon, S.; Rodriguez, G.; Immaneni, S.; Johnson, D.B.; et al. Early-onset pediatric atopic dermatitis is TH2 but also TH17 polarized in skin. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 1639–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neis, M.M.; Peters, B.; Dreuw, A.; Wenzel, J.; Bieber, T.; Mauch, C.; Krieg, T.; Stanzel, S.; Heinrich, P.C.; Merk, H.F.; et al. Enhanced expression levels of IL-31 correlate with IL-4 and IL-13 in atopic and allergic contact dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 118, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howell, M.D.; Kim, B.E.; Gao, P.; Grant, A.V.; Boguniewicz, M.; DeBenedetto, A.; Schneider, L.; Beck, L.A.; Barnes, K.C.; Leung, D.Y.M. Cytokine modulation of atopic dermatitis filaggrin skin expression. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124 (Suppl. S2), R7–R12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.E.; Leung, D.Y.M.; Boguniewicz, M.; Howell, M.D. Loricrin and involucrin expression is down-regulated by Th2 cytokines through STAT-6. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 126, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittmann, M.; McGonagle, D.; Werfel, T. Cytokines as therapeutic targets in skin inflammation. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014, 25, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, S.; Ying, S.; Tang, S.; Ding, Y.; Li, Y.; Qiao, J.; Fang, H. The IL-23/IL-17 Pathway in Inflammatory Skin Diseases: From Bench to Bedside. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 594735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlapbach, C.; Hänni, T.; Yawalkar, N.; Hunger, R.E. Expression of the IL-23/Th17 pathway in lesions of hidradenitis suppurativa. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2011, 65, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, G.; Hughes, R.; McGarry, T.; Born, M.; Adamzik, K.; Fitzgerald, R.; Lawlor, C.; Tobin, A.M.; Sweeney, C.M.; Kirby, B. Dysregulated cytokine expression in lesional and nonlesional skin in hidradenitis suppurativa. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 173, 1431–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozeika, E.; Pilmane, M.; Nürnberg, B.M.; Jemec, G.B.E. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha and matrix metalloproteinase-2 are expressed strongly in hidradenitis suppurativa. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2013, 93, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Zee, H.H.; de Ruiter, L.; van den Broecke, D.G.; Dik, W.A.; Laman, J.D.; Prens, E.P. Elevated levels of tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-10 in hidradenitis suppurativa skin: A rationale for targeting TNF-α and IL-1β. Br. J. Dermatol. 2011, 164, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langrish, C.L.; Chen, Y.; Blumenschein, W.M.; Mattson, J.; Basham, B.; Sedgwick, J.D.; McClanahan, T.; Kastelein, R.A.; Cua, D.J. IL-23 drives a pathogenic T cell population that induces autoimmune inflammation. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, J.J.; Schwartz, D.M.; Villarino, A.V.; Gadina, M.; McInnes, I.B.; Laurence, A. The JAK-STAT pathway: Impact on human disease and therapeutic intervention. Annu. Rev. Med. 2015, 66, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, T.; Kawahara, A.; Fujii, H.; Nakagawa, Y.; Minami, Y.; Liu, Z.-J.; Oishi, I.; Silvennoinen, O.; Witthuhn, B.A.; Ihle, J.N.; et al. Functional Activation of Jak1 and Jak3 by Selective Association with IL-2 Receptor Subunits. Science 1994, 266, 1045–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, N.A.; Bennett, B.L.; Graham, N.M.H.; Pirozzi, G.; Stahl, N.; Yancopoulos, G.D. Targeting key proximal drivers of type 2 inflammation in disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Salvo, E.; Ventura-Spagnolo, E.; Casciaro, M.; Navarra, M.; Gangemi, S. IL-33/IL-31 Axis: A Potential Inflammatory Pathway. Mediators Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 3858032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furue, M. Regulation of Skin Barrier Function via Competition between AHR Axis versus IL-13/IL-4‒JAK‒STAT6/STAT3 Axis: Pathogenic and Therapeutic Implications in Atopic Dermatitis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.Y.; Armstrong, A.W. Janus-kinase inhibitors in dermatology: A review of their use in psoriasis, vitiligo, systemic lupus erythematosus, hidradenitis suppurativa, dermatomyositis, lichen planus, lichen planopilaris, sarcoidosis and graft-versus-host disease. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2023, 90, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci Yildirim, T.; Kahraman, A.; Köken Avşar, A.; Onen, F.; Akar, S.; Sari, İ. Quantitative analysis of JAK/STAT signaling pathway in patients of inflammatory skin disorders. Rheumatol. Int. 2023, 44, 3009–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, J.G.; Frew, J.; Jemec, G.B.E.; Kimball, A.B.; Kirby, B.; Bechara, F.G.; Navrazhina, K.; Prens, E.; Reich, K.; Cullen, E.; et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: New insights into disease mechanisms and an evolving treatment landscape. Br. J. Dermatol. 2024, 190, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, A.; Xing, X.; Guzman, A.M.; Riblett, M.; Loyd, C.M.; Ward, N.L.; Wohn, C.; Prens, E.P.; Wang, F.; Maier, L.E.; et al. IL-1F5, -F6, -F8, and -F9: A novel IL-1 family signaling system that is active in psoriasis and promotes keratinocyte antimicrobial peptide expression. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 2613–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Alam, M.A.; Ansari, A.W.; Jochebeth, A.; Leo, R.; Al-Abdulla, M.N.; Al-Khawaga, S.; AlHammadi, A.; Al-Malki, A.; Al Naama, K.; et al. Emerging Role of the IL-36/IL-36R Axis in Multiple Inflammatory Skin Diseases. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2024, 144, 206–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattii, M.; Ayala, F.; Balato, N.; Filotico, R.; Lembo, S.; Schiattarella, M.; Patruno, C.; Marone, G.; Balato, A. The balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines is crucial in human allergic contact dermatitis pathogenesis: The role of IL-1 family members. Exp. Dermatol. 2013, 22, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Ungar, B.; Correa da Rosa, J.; Ewald, D.A.; Rozenblit, M.; Gonzalez, J.; Xu, H.; Zheng, X.; Peng, X.; Estrada, Y.D.; et al. RNA sequencing atopic dermatitis transcriptome profiling provides insights into novel disease mechanisms with potential therapeutic implications. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 1218–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoi, L.C.; Rodriguez, E.; Stölzl, D.; Wehkamp, U.; Sun, J.; Gerdes, S.; Sarkar, M.K.; Hübenthal, M.; Zeng, C.; Uppala, R.; et al. Progression of acute-to-chronic atopic dermatitis is associated with quantitative rather than qualitative changes in cytokine responses. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 1406–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissonnette, R.; Abramovits, W.; Saint-Cyr Proulx, É.; Lee, P.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Zovko, E.; Sigmund, R.; Willcox, J.; Bieber, T. Spesolimab, an anti-interleukin-36 receptor antibody, in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: Results from a multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase IIa study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2023, 37, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessam, S.; Sand, M.; Gambichler, T.; Skrygan, M.; Rüddel, I.; Bechara, F.G. Interleukin-36 in hidradenitis suppurativa: Evidence for a distinctive proinflammatory role and a key factor in the development of an inflammatory loop. Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 178, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Caprio, R.; Balato, A.; Caiazzo, G.; Lembo, S.; Raimondo, A.; Fabbrocini, G.; Monfrecola, G. IL-36 cytokines are increased in acne and hidradenitis suppurativa. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2017, 309, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomi, R.; Kakeda, M.; Yawalkar, N.; Schlapbach, C.; Hunger, R.E. Increased expression of the interleukin-36 cytokines in lesions of hidradenitis suppurativa. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, 2091–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, A.; Prens, E.P.; Kimball, A.B.; Frew, J.W.; Krueger, J.G.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Gao, H.; Ranganathan, U.; Ivanoff, N.B.; Hernandez Daly, A.C.; et al. Proof-of-concept study exploring the effect of spesolimab in patients with moderate-to-severe hidradenitis suppurativa: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. Br. J. Dermatol. 2024, 191, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möbus, L.; Rodriguez, E.; Harder, I.; Stölzl, D.; Boraczynski, N.; Gerdes, S.; Kleinheinz, A.; Abraham, S.; Heratizadeh, A.; Handrick, C.; et al. Atopic dermatitis displays stable and dynamic skin transcriptome signatures. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte-Händel, E.; Wolk, K.; Tsaousi, A.; Irmer, M.L.; Mößner, R.; Shomroni, O.; Lingner, T.; Witte, K.; Kunkel, D.; Salinas, G.; et al. The IL-1 Pathway Is Hyperactive in Hidradenitis Suppurativa and Contributes to Skin Infiltration and Destruction. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 1294–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Rick, J.; Hsiao, J.; Shi, V.Y. A review of IL-36: An emerging therapeutic target for inflammatory dermatoses. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2022, 33, 2711–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, A.; Karnik, R.; Campbell, V.; Davis, J.; Chavoshi, S.; Slavin, A.; Sharma, K.; Gollob, J.; Alavi, A. IRAK4 Is Overexpressed in Hidradenitis Suppurativa Skin and Correlates with Inflammatory Biomarkers. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2025, 145, 323–333.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balka, K.R.; De Nardo, D. Understanding early TLR signaling through the Myddosome. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2019, 105, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, M.; Gazzinelli, R.T. Regulation of innate immune signaling by IRAK proteins. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1133354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavazais, S.; Jargosch, M.; Dupont, S.; Labéguère, F.; Menet, C.; Jagerschmidt, C.; Ohm, F.; Kupcsik, L.; Parent, I.; Cottereaux, C.; et al. IRAK4 inhibition dampens pathogenic processes driving inflammatory skin diseases. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eabj3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gau, S.-Y.; Chan, W.L.; Tsai, J.-D. Risk of Atopic Diseases in Patients with Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Dermatology 2023, 239, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.-C.; Lin, C.-Y.; Guo, Y.-C.; Lu, H.-Y.; Lee, C.-Y.; Wu, M.-C.; Gau, S.-Y. Association between hidradenitis suppurativa and atopic diseases: A multi-center, propensity-score-matched cohort study. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2024, 21, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.K.; Shin, J.U.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, H.J. Severe atopic dermatitis and concurrent severe hidradenitis suppurativa successfully treated with dupilumab. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2022, 47, 2303–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, S.; Kridin, K.; Bitan, D.T.; Leshem, Y.A.; Hodak, E.; Cohen, A.D. Hidradenitis suppurativa and atopic dermatitis: A 2-way association. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 85, 1473–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaakati, R.N.; Tanaka, J.; Liu, B.; Ward, R.; Macleod, A.S.; Green, C.L.; Jaleel, T. Atopic dermatitis is associated with hidradenitis suppurativa diagnosis: A single institution retrospective cohort study. JAAD Int. 2021, 4, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Shen, M.; Man, X. Association between atopic dermatitis and hidradenitis suppurativa: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study. J. Dermatol. 2023, 50, e287–e288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rick, J.W.; Alavi, A.; Hsiao, J.L.; Yosipovitch, G.; Shi, V.Y. Atopic dermatitis and hidradenitis suppurativa: An under-recognized pair. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 85, e387–e388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kridin, K.; Shihade, W.; Weinstein, O.; Zoller, L.; Onn, E.; Cohen, A.; Solomon-Cohen, E. A history of asthma is associated with susceptibility to hidradenitis suppurativa: A population-based longitudinal study. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2023, 315, 2845–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.F.; Cohen, J.M.; Eisenstein, A. Associations between hidradenitis suppurativa and asthma and allergic rhinitis: A case-control study in the All of Us research program. Int. J. Dermatol. 2024, 63, e74–e75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, M.; Mariottoni, P.; Corcoran, D.L.; Kirshner, H.F.; Jaleel, T.; Brown, D.A.; Brooks, S.R.; Murray, J.; Morasso, M.I.; MacLeod, A.S. The skin transcriptome in hidradenitis suppurativa uncovers an antimicrobial and sweat gland gene signature which has distinct overlap with wounded skin. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, R.; Mirmohammadsadegh, A.; Walz, M.; Lysa, B.; Tartler, U.; Remus, R.; Hengge, U.; Michel, G.; Ruzicka, T. Molecular cloning and characterization of alternatively spliced mRNA isoforms from psoriatic skin encoding a novel member of the S100 family. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 1969–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinquan, T.; Vorum, H.; Larsen, C.G.; Madsen, P.; Rasmussen, H.H.; Gesser, B.; Etzerodt, M.; Honoré, B.; Celis, J.E.; Thestrup-Pedersen, K. Psoriasin: A novel chemotactic protein. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1996, 107, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, S.; Tazudeen, N.; Garden, B.C. Is Exploration of Alternate Immune Pathways Needed in Hidradenitis Suppurativa? A Case of Atopic Dermatitis and Concurrent Hidradenitis Suppurativa Responding to Dupilumab. Case Rep. Dermatol. Med. 2023, 2023, 5189034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, Y.; Guan, Y.; Deliu, L.; Humphrey, E.; Frontera, J.K.; Yang, Y.J.; Zamler, D.; Kim, K.H.; Mohanty, V.; Jin, K.; et al. KLF5 governs sphingolipid metabolism and barrier function of the skin. Genes Dev. 2022, 36, 822–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Broadaway, K.A.; Edmiston, S.N.; Fajgenbaum, K.; Miller-Fleming, T.; Westerkam, L.L.; Melendez-Gonzalez, M.; Bui, H.; Blum, F.R.; Levitt, B.; et al. Genetic Variants Associated With Hidradenitis Suppurativa. JAMA Dermatol. 2023, 159, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, V.W.; Bundgaard Vad, O.; Holgersen, N.; Paludan-Müller, C.; Meseguer Monfort, L.; Beyer, A.F.; Jemec, G.B.E.; Kjærsgaard Andersen, R.; Egeberg, A.; Thyssen, J.P.; et al. Genetic Susceptibility to Hidradenitis Suppurativa and Predisposition to Cardiometabolic Disease. JAMA Dermatol. 2025, 161, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budu-Aggrey, A.; Kilanowski, A.; Sobczyk, M.K.; 23andMe Research Team; Shringarpure, S.S.; Mitchell, R.; Reis, K.; Reigo, A.; Estonian Biobank Research Team; Mägi, R.; et al. European and multi-ancestry genome-wide association meta-analysis of atopic dermatitis highlights importance of systemic immune regulation. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AAAAI/ACAAI JTF Atopic Dermatitis Guideline Panel; Chu, D.K.; Schneider, L.; Asiniwasis, R.N.; Boguniewicz, M.; De Benedetto, A.; Ellison, K.; Frazier, W.T.; Greenhawt, M.; Huynh, J.; et al. Atopic dermatitis (eczema) guidelines: 2023 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology/American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology Joint Task Force on Practice Parameters GRADE- and Institute of Medicine-based recommendations. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2024, 132, 274–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meher, B.R.; Mishra, A.; Behera, B.; Ponnusamy, S. Efficacy and Safety of Upadacitinib in Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis: A Meta-Analysis. Cureus 2024, 16, e64488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverberg, J.I.; Simpson, E.L.; Thyssen, J.P.; Gooderham, M.; Chan, G.; Feeney, C.; Biswas, P.; Valdez, H.; DiBonaventura, M.; Nduaka, C.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Abrocitinib in Patients With Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2020, 156, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverberg, J.I.; Wollenberg, A.; Reich, A.; Thaçi, D.; Legat, F.J.; Papp, K.A.; Stein Gold, L.; Bouaziz, J.-D.; Pink, A.E.; Carrascosa, J.M.; et al. Nemolizumab with concomitant topical therapy in adolescents and adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2): Results from two replicate, double-blind, randomised controlled phase 3 trials. Lancet 2024, 404, 445–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alikhan, A.; Sayed, C.; Alavi, A.; Alhusayen, R.; Brassard, A.; Burkhart, C.; Crowell, K.; Eisen, D.B.; Gottlieb, A.B.; Hamzavi, I.; et al. North American clinical management guidelines for hidradenitis suppurativa: A publication from the United States and Canadian Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundations: Part I: Diagnosis, evaluation, and the use of complementary and procedural management. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 81, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimball, A.B.; Okun, M.M.; Williams, D.A.; Gottlieb, A.B.; Papp, K.A.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Armstrong, A.W.; Kerdel, F.; Gold, M.H.; Forman, S.B.; et al. Two Phase 3 Trials of Adalimumab for Hidradenitis Suppurativa. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimball, A.B.; Jemec, G.B.E.; Alavi, A.; Reguiai, Z.; Gottlieb, A.B.; Bechara, F.G.; Paul, C.; Giamarellos Bourboulis, E.J.; Villani, A.P.; Schwinn, A.; et al. Secukinumab in moderate-to-severe hidradenitis suppurativa (SUNSHINE and SUNRISE): Week 16 and week 52 results of two identical, multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind phase 3 trials. Lancet 2023, 401, 747–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA Approves Novartis Cosentyx® as the First New Biologic Treatment Option for Hidradenitis Suppurativa Patients in Nearly a Decade. Novartis. Available online: https://www.novartis.com/news/media-releases/fda-approves-novartis-cosentyx-first-new-biologic-treatment-option-hidradenitis-suppurativa-patients-nearly-decade (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- Glatt, S.; Jemec, G.B.E.; Forman, S.; Sayed, C.; Schmieder, G.; Weisman, J.; Rolleri, R.; Seegobin, S.; Baeten, D.; Ionescu, L.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Bimekizumab in Moderate to Severe Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A Phase 2, Double-blind, Placebo-Controlled Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2021, 157, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UCB Receives U.S. FDA Approval for BIMZELX[®] (Bimekizumab-Bkzx) as the First IL-17A and IL-17F Inhibitor for Adults with Moderate to Severe Hidradenitis Suppurativa | UCB. Available online: https://www.ucb.com/newsroom/press-releases/article/ucb-receives-us-fda-approval-for-bimzelxr-bimekizumab-bkzx-as-the-first-il-17a-and-il-17f-inhibitor-for-adults-with-moderate-to-severe-hidradenitis-suppurativa (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- Grant, A.; Gonzalez, T.; Montgomery, M.O.; Cardenas, V.; Kerdel, F.A. Infliximab therapy for patients with moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover trial. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2010, 62, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, R.; Seivright, J.; Grogan, T.; Atluri, S.; Hamzavi, I.; Hogeling, M.; Shi, V.Y.; Hsiao, J.L. Ustekinumab in Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Dermatol. Ther. 2024, 14, 1901–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzanetakou, V.; Kanni, T.; Giatrakou, S.; Katoulis, A.; Papadavid, E.; Netea, M.G.; Dinarello, C.A.; van der Meer, J.W.M.; Rigopoulos, D.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J. Safety and Efficacy of Anakinra in Severe Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2016, 152, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garelik, J.; Babbush, K.; Ghias, M.; Cohen, S.R. Efficacy of high-dose intralesional triamcinolone for hidradenitis suppurativa. Int. J. Dermatol. 2021, 60, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, P.; García-Martínez, F.J.; Poveda, I.; Pascual, J.C. Intralesional Triamcinolone for Fistulous Tracts in Hidradenitis Suppurativa: An Uncontrolled Prospective Trial with Clinical and Ultrasonographic Follow-Up. Dermatology 2020, 236, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajgenbaum, K.; Crouse, L.; Dong, L.; Zeng, D.; Sayed, C. Intralesional Triamcinolone May Not Be Beneficial for Treating Acute Hidradenitis Suppurativa Lesions: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Dermatol. Surg. 2020, 46, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, A.W.L.; Wong, M.M.; Rayner, D.G.; Guyatt, G.H.; Díaz Martinez, J.P.; Ceccacci, R.; Zhao, I.X.; McMullen, E.; Srivastava, A.; Wang, J.; et al. Systemic treatments for atopic dermatitis (eczema): Systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized trials. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 152, 1470–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinelli, E.; Sapigni, C.; Simonetti, O.; Radi, G.; Gambini, D.; Maurizi, A.; Rizzetto, G.; D’Agostino, G.M.; Offidani, A. Successfully and safety use of dupilumab in the management of severe atopic dermatitis and concomitant moderate-to-severe hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambardella, A.; Calabrese, G.; Di Brizzi, E.V.; Alfano, R.; Argenziano, G. A case of Atopic dermatitis and Hidradenitis Suppurativa successfully treated with Dupilumab. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, e284–e286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blauvelt, A.; Teixeira, H.D.; Simpson, E.L.; Costanzo, A.; De Bruin-Weller, M.; Barbarot, S.; Prajapati, V.H.; Lio, P.; Hu, X.; Wu, T.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Upadacitinib vs Dupilumab in Adults With Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2021, 157, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, A.; Hamzavi, I.; Brown, K.; Santos, L.L.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, H.; Howell, M.D.; Kirby, J.S. Janus kinase 1 inhibitor INCB054707 for patients with moderate-to-severe hidradenitis suppurativa: Results from two phase II studies. Br. J. Dermatol. 2022, 186, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirby, J.S.; Okun, M.M.; Alavi, A.; Bechara, F.G.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Brown, K.; Santos, L.L.; Wang, A.; Bibeau, K.B.; Kimball, A.B.; et al. Efficacy and safety of the oral Janus kinase 1 inhibitor povorcitinib (INCB054707) in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa in a phase 2, randomized, double-blind, dose-ranging, placebo-controlled study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2024, 90, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Liang, J.; Li, C.; Li, Q.; Liu, W.; Zhu, J.; Chen, W.; Zhang, X. Abrocitinib as a Novel Treatment for Multiple Skin Disorders: 3 Case Reports and a Scoping Review. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2024, 17, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ok, M.T.; Googe, P.B.; Sayed, C.J.; Burkhart, C.; Gulati, A.S.; Nieman, E.L. The Successful Use of Upadacitinib as Monotherapy for Hidradenitis Suppurativa and Ulcerative Colitis in the Setting of Refractory Disease. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2025, 42, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martora, F.; Scalvenzi, M.; Ruggiero, A.; Potestio, L.; Battista, T.; Megna, M. Hidradenitis Suppurativa and JAK Inhibitors: A Review of the Published Literature. Medicina 2023, 59, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozera, E.; Flora, A.; Frew, J.W. Real-world safety and clinical response of Janus kinase inhibitor upadacitinib in the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa: A retrospective cohort study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 87, 1440–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schell, S.L.; Sennett, M.L.; Feehan, R.P.; Wallace, T.E.; Meiszberg, E.C.; Longenecker, A.L.; Helm, M.F.; Kirby, J.S.; Nelson, A.M. Pilot study of topical ruxolitinib demonstrates efficacy and blunting of heterogeneous inflammatory processes in mild hidradenitis suppurativa. Br. J. Dermatol. 2025, 192, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungar, B.; Pavel, A.B.; Li, R.; Kimmel, G.; Nia, J.; Hashim, P.; Kim, H.J.; Chima, M.; Vekaria, A.S.; Estrada, Y.; et al. Phase 2 randomized, double-blind study of IL-17 targeting with secukinumab in atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes Roncada, E.V.; Brambilla, V.R.; Freitas Filitto, B.; Genta, M.P.; Morgado de Abreu, M.A.M. Atopic Dermatitis as a Paradoxical Effect of Secukinumab for the Treatment of Psoriasis. Case Rep. Dermatol. 2021, 13, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlando, M.; Cozzani, E.; Russo, R.; Parodi, A. Atopic-like dermatitis after secukinumab injection: A case report. Dermatol. Ther. 2019, 32, e12751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zundell, M.P.; Gottlieb, A.B.; Stanger, R. Atopic Dermatitis as a Paradoxical Reaction to Secukinumab in a Patient With Plaque Psoriasis. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2024, 23, 97–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jodl, S.J.; Ten Voorde, W.; Klein, S.; Wagenfeld, A.; Zollmann, F.S.; Feldmüller, M.; Klarenbeek, N.B.; de Bruin, D.T.; Jansen, M.A.A.; Rissmann, R.; et al. The oral IRAK4 inhibitors zabedosertib and BAY1830839 suppress local and systemic immune responses in a randomized trial in healthy male volunteers. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2024, 17, e13771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, L.; Acloque, G.; Bacchelli, S.; Schwartz, H.; Feinstein, B.J.; La Stella, P.; Alavi, A.; Gollerkeri, A.; Davis, J.; Campbell, V.; et al. IRAK4 degrader in hidradenitis suppurativa and atopic dermatitis: A phase 1 trial. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 3127–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, D.; Jamil, A.; Md Nor, N.; Kader Ibrahim, S.B.; Poh, B.K. Food restriction, nutrition status, and growth in toddlers with atopic dermatitis. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2020, 37, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finch, J.; Munhutu, M.N.; Whitaker-Worth, D.L. Atopic dermatitis and nutrition. Clin. Dermatol. 2010, 28, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, R.B.; Sayed, C.J. Patient-reported exacerbating factors for hidradenitis suppurativa: A cross sectional study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2024, 91, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamgochian, M.; Alamgir, M.; Rao, B. Diet in Dermatology: Review of Diet’s Influence on the Conditions of Rosacea, Hidradenitis Suppurativa, Herpes Labialis, and Vitiligo. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2023, 17, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, J.; Mallonee, C.J.; Stanisic, D.; Homme, R.P.; George, A.K.; Singh, M.; Tyagi, S.C. Hidradenitis Suppurativa and 1-Carbon Metabolism: Role of Gut Microbiome, Matrix Metalloproteinases, and Hyperhomocysteinemia. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintoff, D.; Borg, I.; Pace, N.P. The Clinical Relevance of the Microbiome in Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A Systematic Review. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eppinga, H.; Sperna Weiland, C.J.; Thio, H.B.; Van Der Woude, C.J.; Nijsten, T.E.C.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Konstantinov, S.R. Similar Depletion of Protective Faecalibacterium prausnitzii in Psoriasis and Inflammatory Bowel Disease, but not in Hidradenitis Suppurativa. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2016, 10, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polkowska-Pruszyńska, B.; Gerkowicz, A.; Krasowska, D. The gut microbiome alterations in allergic and inflammatory skin diseases—An update. Acad Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.H.; Kim, J.W.; Park, H.-J.; Hahm, D.-H. Comparative Analysis of the Microbiome across the Gut-Skin Axis in Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purchiaroni, F.; Tortora, A.; Gabrielli, M.; Bertucci, F.; Gigante, G.; Ianiro, G.; Ojetti, V.; Scarpellini, E.; Gasbarrini, A. The role of intestinal microbiota and the immune system. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 17, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salem, I.; Ramser, A.; Isham, N.; Ghannoum, M.A. The Gut Microbiome as a Major Regulator of the Gut-Skin Axis. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Kim, H.S. Microbiome of the Skin and Gut in Atopic Dermatitis (AD): Understanding the Pathophysiology and Finding Novel Management Strategies. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).