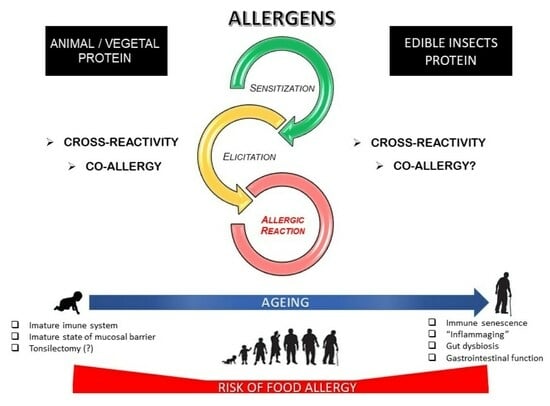
Edible Insects and Allergy Risks: Implications for Children and the Elderly
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Emerging Allergy Risks from Edible Insect Consumption
2.1. Food Allergies: An Overview of Allergic Diseases and Food Allergy Development
2.2. Food Allergies and Insects: An Interconnected Perspective
2.3. Food Allergen Characteristics: Implications for Allergenicity
3. The Impact of Processing on Edible Insect Allergenicity
3.1. The Influence of the Food Matrix on Allergenicity
3.2. The Effect of Processing on Food Allergenicity
4. Edible Insects and Allergies: A Focus on Vulnerable Individuals
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. Edible Insects-Future Prospects for Food and Feed Security; FAO Forestry Paper No. 171; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2013; E-ISBN 978-92-5-107596-8. [Google Scholar]
- Dunkel, F.V.; Van Hui, A. Edible insects: A neglected and promising food source. In Susteinable Protein Sources, 2nd ed.; Nadathur, S., Wanasundara, J.P.D., Scanlin, L., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 515–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, T.-K.; Shin, D.-M. Edible insects in food. In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Toldrá, F., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; Volume 108, pp. 223–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colamatteo, I.; Bravo, I.; Cappelli, L. Insect-based food products: A scoping literature review. Food Res. Int. 2024, 200, 115355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, M. Novel foods: Insects—Safety issues. In Encyclopledia of Food Security and Sustainability, Ferranti, P., Berry, E.M., Anderson, J.R., Ed.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2019; Volume 1, pp. 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukutomi, Y.; Kawakami, Y. Respiratory sensitization to insect allergens: Species, components and clinical symptons. Allergol. Int. 2021, 70, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, S.; Prescott, S.L. The origins of allergic disease. In Middleton’s Allergy Essentials; O’Hehir, R.E., Holgate, S.T., Sheikh, A., Eds.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2017; pp. 29–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicherer, S.H.; Leung, D.Y.M. Advances in allergic skin disease, analphylaxis, and hypersensitivity reactions to foods, drugs, and insects in 2012. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 131, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguori, B.; Sancho, A.I.; Poulsen, M.; Lindholm Bøgh, K. Novel foods: Allergenicity assessment of insect proteins. EFSA J. 2022, 20, e200910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larouche, J.; Campbell, B.; Hénault-Éthier, L.; Banks, I.J.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Preyer, C.; Deschamps, M.-H.; Vandenberg, G.W. The edible insect sector in Canada and the United States. Anim. Front. 2023, 13, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeckx, K.C.M.; den Heijer, Y. Food allergy to edible insects. In Encyclopedia of Food Allergy, 1st ed.; Sicherer, S.H., Ed.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2024; pp. 391–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.L.; Baumert, J.L. Food allergies, sensitivies, and intolerances. In Present Knowledge in Nutrition, 11th ed.; Marriott, B.P., Birt, D.F., Stallings, V.A., Yates, A.A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopko, C.; Garthoff, J.A.; Zhou, K.; Meunier, L.; O’Sullivan, A.J.; Fattori, V. Are alternative proteins increasing food allergies? Trends, drivers and future perspectives. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 129, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downs, M.; Johnson, P.; Zeece, M. Insects and their connection to food allergy. In Insects as Sustainable Food Ingredients; Dossey, A.T., Morales-Ramos, J.A., Rojas, M.G., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Looking at Edible Insects from a Food Safety Perspective. Challenges and Opportunities for the Sector; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anvari, S.; Jennifer, M.; Yeh, C.-Y.; Davis, C.M. IgE-mediated food allergy. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 57, 244–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, M.; Assa’ad, A. Food allergy: Definitions and overview. In Encyclopedia of Food Allergy; Sicherer, S.H., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, J.F.E.; Jiménez-Saiz, R.; Jordana, R. An overview of the fundamental immune mechanisms of food allergy. In Encyclopedia of Food Allergy, 1st ed.; Sicherer, S.H., Ed.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2024; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renz, H.; Allen, K.; Sicherer, S.; Sampson, H.A.; Gideon, L.; Beyer, K.; Oettgen, H. Food allergy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 17098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedé, S.; Berin, M.C. Applications of Mouse Models to the Study of Food Allergy. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2223, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheehan, W.J.; Taylor, S.L.; Phipatanakul, W.; Brough, E.A. Environmental Food Exposure: What Is the Risk of Clinical Reactivity from Cross-Contact and What Is the Risk of Sensitization. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2018, 6, 1825–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, H.A. Update on food allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 113, 805–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, F.J. Gastrointestinal digestion of food allergens: Effect on their allergenicity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2007, 61, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulten, V.; Lauer, I.; Scheurer, S.; Thalhammer, T.; Bohle, B. A food matrix reduces digestion and absorption of food allergens in vivo. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 1484–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Lin, S.; Sun, N. How does food matrix components affect food allergies, food allergens and the detection of food allergens? A systematic review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 127, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzolino, D.; Verdi, L.; Perna, S.; Baldassari, I.; Cesari, M.; Lucchi, T. Food allergies in older people: An emerging health problem. WAO J. 2024, 17, 100967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Ho, H.-E.; Bunyavanich, S. The gut microbiome in food allergy. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019, 122, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesemann, D.R.; Nagler, C.R. The Microbiome, Timing, and Barrier Function in the Context of Allergic Disease. Immunity 2016, 44, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, O.L.; Wang, K.Y.; Kim, E.H.; Moran, T.P. Common food allergenss and cross-reactivity. J. Food Allergy 2020, 2, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamath, S.D.; Bublin, M.; Kitamura, K.; Matsui, T.; Ito, K.; Lopata, A.L. Cross-reactive epitopes and their role in food allergy. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 151, 1178–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, A.L.; Gupta, M. Cross reactivity and co-allergy in food allergy. In Encyclopedia of Food Allergy, 1st ed.; Sicherer, S.H., Ed.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2024; pp. 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoni, C.; Volpicella, M.; Dileo, M.C.G.; Gattulli, B.A.R.; Ceci, L.R. Chitinases as Food Allergens. Molecules 2019, 24, 2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xia, Z.; Wu, Y.; Xia, Q.; Chen, J.; Roux, K.H. Identification and characterization of an arginine kinase as a major allergen from silkworm (Bombyx mori) larvae. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2009, 150, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phiriyangkul, P.; Srinroch, C.; Srisomsap, C.; Hokchaichamnankit, C.; Punyarit, P. Effect of food thermal processing on allergenicity proteins in Bombay Locust (Patanga succincta). Int. J. Food Eng. 2015, 1, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Reese, G.; Ayuso, R.; Lehrer, S.B. Tropomyosin: An invertebrate pan-allergen. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 1999, 119, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leni, G.; Tedeschi, T.; Faccini, A.; Pratesi, F.; Folli, C.; Puxeddu, I.; Migliorini, P.; Gianotten, N.; Jacobs, J.; Depraeteres, S.; et al. Shotgun proteomics, in-silico evaluation and immunoblotting assays for allergenicity assessment of lesser mealworm, black soldier fly and their protein hydrolysates. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinroch, C.; Srisomsap, C.; Chokchaichamnankit, D.; Punyarit, P.; Phiriyangkul, P. Identification of novel allergen in edible insect, Gryllus bimaculatus and its cross-reactivity with Macrobrachium spp. allergens. Food Chem. 2015, 184, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, G.; Shivalingaiah, A.H.; Vijayeendra, A.M.; Sarkar, N.; Nagaraj, C.; Masthi, N.R.R. Sensitization to silk allergen among workers of silk filatures in India: A comparative study. Asia Pac. Allergy 2016, 6, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- de Las Marinas, M.D.; Cerdá, J.C.; López-Matas, M.A.; González-Ruiz, A.; Martorell, C.; Felix, R.; Alvariño, M.; Carnés, J. Hexamerin-like protein 2, a cricket allergen involved in occupational and food allergy. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2021, 6, 858–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayuso, R.; Reese, G.; Leong-Kee, S.; Plante, M.; Lehrer, S.B. Molecular basis of arthropod cross-reactivity: IgE-binding cross-reactive epitopes of shrimp, house dust mite and cockroach tropomyosins. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2002, 1, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyanasundaram, A.; Santiago, T.C. Identification and characterization of new allergen troponin C (Pen m 6.0101) from Indian black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 240, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Itterbeeck, J.; Pelozuelo, L. How Many Edible Insect Species Are There? A Not So Simple Question. Diversity 2022, 14, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongema, Y. List of Edible Insects of the World (April 1, 2017). Available online: https://www.wur.nl/en/research-results/chair-groups/plant-sciences/laboratory-of-entomology/edible-insects/worldwide-species-list.htm (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Ji, K.; Chen, J.; Li, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhan, Z.; Wu, X.; Xia, Q. Anaphylactic shock and lethal anaphylaxis caused by food consumption in China. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 20, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pekar, J.; Ret, D.; Untersmayr, E. Stability of allergens. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 100, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiteneder, H.; Mills, E.N. Molecular properties of food allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomés, A.; Schulten, V.; Glesner, J.; da Silva Antunes, R.; Sutherland, A.; Bacharier, L.B.; Beigelman, A.; Busse, P.; Frazier, A.; Sette, A. IgE and T Cell Reactivity to a Comprehensive Panel of Cockroach Allergens in Relation to Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 621700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barre, A.; Pichereaux, C.; Simplicien, M.; Burlet-Schiltz, O.; Benoist, H.; Rougé, P. A Proteomic- and Bioinformatic-Based Identification of Specific Allergens from Edible Insects: Probes for Future Detection as Food Ingredients. Foods 2021, 10, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlüter, O.; Rumpold, B.; Holzhauser, T.; Roth, A.; Vogel, R.F.; Quasigroch, W.; Vogel, S.; Heinz, V.; Jäger, H.; Bandick, N.; et al. Safety aspects of the production of foods and food ingredients from insects. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 6, 1600520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeckx, K.C.M.; van Broekhoven, S.; den Hartog-Jager, C.F.; Gaspari, M.; de Jong, G.H.A.; Wichers, H.J.; van Hoffen, E.; Houben, G.F.; Knulst, A.C. House dust mite (Der p 10) and crustacean allergic patients may react to food containing Yellow mealworm proteins. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 65, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak-Wegrzyn, A.; Fiocchi, A. Rare, medium, or well done? The effect of heating and food matrix on food protein allergenicity. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 9, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarahi, M.; Aghababaei, F.; McClements, D.J.; Pignitter, M.; Hadidi, M. Bioactive peptides derived from insect proteins: Preparation, biological activities, potential applications, and safety issues. Food Chem. 2025, 465, 142113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, T.; Vasiljevic, T.; Ramchandran, L. Effect of processing on conformational changes of food proteins related to allergenicity. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 49, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, X.; Sun, Y.; Fu, G.; Wu, Z.; Cheng, J. Effect of processing on soybean allergens and their allergenicity. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 118, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, P.J.; Williams, S.C. Protein modification by thermal processing. Allergy 1998, 53, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadrado, C.; Sanchiz, Á.; Linacero, R. Nut Allergenicity: Effect of Food Processing. Allergies 2021, 1, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeckx, K.; Broekman, H.; Knulst, A.; Houben, G. Allergenicity assessment strategy for novel food proteins and protein sources. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 79, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.C.; Cunha, L.M.; Sousa-Pinto, B.; Fonseca, J. Allergic risks of consuming edible insects: A systematic review. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1700030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Li, L.; Kuang, Z.; Luo, G.; Li, B. Proteomic and immunological identification of two new allergens from silkworm (Bombyx mori L.) pupae. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 40, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broekman, H.; Knulst, A.; den Hartog Jager, S.; Monteleone, F.; Gaspari, M.; de Jong, G.; Houben, G.; Verhoeckx, K. Effect of thermal processing on mealworm allergenicity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 1855–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Broekhoven, S.; Bastiaan-Net, S.; de Jong, J.W.; Wichers, H.J. Influencie of processing and in vitro digestion on the allergic cross-reactivity of three mealworm species. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jongh, H.H.J.; de Jong, G.A.H.; Apostolovic, D.; Taylor, S.L.; Baumert, J.L.; Koppelman, S.J. Effect of heat treatment on the conformational stability of intact and cleaved forms ofthe peanut allergen Ara h 6 in relation to its IgE-binding potency. Food Chem. 2020, 326, 127027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, K.; Morrow, E.; Li, X.M.; Bardina, L.; Bannon, G.A.; Burks, A.W.; Sampson, H.A. Effects of cooking methods on peanut allergenicity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 107, 1077–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmoteleb, M.; Zhang, C.; Furey, B.; Kozubal, M.; Griffiths, H.; Champeaud, M.; Goodman, R.E. Evaluating potential risks of food allergy of novel food sources based on comparison of proteins predicted from genomes and compared to www.AllergenOnline.org. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 147, 111888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Park, J. “Human-like” is powerful: The effect of anthropomorphism on psychological closeness and purchase intention in insect food marketing. Food Qual. Prefer. 2023, 109, 104901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuso, A.; Leni, G.; Prandi, B.; Lolli, V.; Caligiani, A. Novel foods/feeds and novel frauds: The case of edible insects. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 147, 104457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Nutrition; Novel Foods and Food Allergens; Turck, D.; Bohn, T.; Castenmiller, J.; De Henauw, S.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Maciuk, A.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; et al. Safety of Acheta domesticus powder as a Novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA J. 2024, 22, e8919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasza, G.; Izsó, T.; Szakos, D.; Nugraha, W.S.; Tamimi, M.H.; Süth, M. Insects as food—Changes in consumers’ acceptance of entomophagy in Hungary between 2016 and 2021. Appetite 2023, 188, 106770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, G.; Lee, S.; Mazmanian, S. Gut biogeography of the bacterial microbiota. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spolidoro, G.C.I.; Azzolino, D.; Cesari, M.; Agostinin, C. Diet diversity through the life-course as na opportunity toward food allergy prevention. Front. Allergy 2021, 2, 711945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, V.; Zanconato, S.; Carraro, S. Timing of Food Introduction and the Risk of Food Allergy. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claesson, M.J.; Cusack, S.; O’Sullivan, O.; O’Toole, P.W. Composition, variability, and temporal stability of the intestinal microbiota of the elderly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4586–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsunenko, T.; Rey, F.; Manary, M.; Trehan, I.; Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Baldassano, R.N.; Anokhin, A.P.; et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature 2012, 486, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Bornhorst, G.M.; Henrick, B.M.; German, J.B. Protein Digestion of Baby Foods: Study Approaches and Implications for Infant Health. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1700231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, O.; Plaza, A.M.; Alvaro, M. Relationship Between Atopic Dermatitis and Food Allergy. Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2020, 16, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hanache, H.; Perennec, T.; Beaumont, P.; Puillandre, E.; Schwender, D.; Louis Donguy, F.; Froidefond, C.; Jarlot, S.; Petit, N.; Nootens, C.; et al. Food anaphylaxis in the elderly: Analysis of allergy vigilance network data from 2002 to 2021. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2023, 53, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen-Jarolim, E.; Jensen, S.A.F. Food allergies in the elderly: Collecting the evidence. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2016, 117, 472–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diesner, S.C.; Untersmayr, E.; Pietschmann, P.; Jensen-Jarolim, E. Food allergy: Only a pediatric disease? Gerontology 2011, 57, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardona, V.; Guilarte, M.; Luengo, O.; Labrador-Horrillo, M.; Sala-Cunill, A.; Garriga, T. Allergic diseases in the elderly. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2011, 17, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, I.; Muller, C.E.; Walter, J. Long-Term Temporal Analysis of the Human Fecal Microbiota Revealed a Stable Core of Dominant Bacterial Species. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faith, J.J.; Guruge, J.L.; Charbonneau, M.; Subramanian, S.; Seedorf, H.; Goodman, A.L.; Clemente, J.C.; Knight, R.; Heath, A.C.; Leibel, R.L.; et al. The long-term stability of the human gut microbiota. Science 2013, 341, 1237439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Faria, A.M.; Ficker, S.M.; Speziali, E.; Menezes, J.S.; Stransky, B.; Silva Rodrigues, V.; Vaz, N.M. Aging affects oral tolerance induction but not its maintenance in mice. Mech. Ageing Dev. 1998, 102, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoreux, K.; Owen, R.L.; Schmucker, D.L. Intestinal lymphocyte number, migration and antibody secretion in young and old rats. Immunology 2000, 101, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laia-Dias, I.; Lozoya-Ibáñez, C.; Skypala, I.; Gama, J.M.R.; Nurmatov, U.; Lourenço, O.; Taborda-Barata, L. Prevalence and risk factors for food allergy in older people: Protocol for a systematic review. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e029633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, C.; Bovin, N.V.; Bram, L.V.; Flyvbjerg, E.; Erlandsen, M.; Vorup-Jensen, T.; Petersen, E. Age is an important determinant in humoral and T cell responses to immunization with hepatitis B surface antigen. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2013, 9, 1466–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahluwalia, N.; Sun, J.; Krause, D.; Mastro, A.; Handte, G. Immune function is impaired in iron-deficient, homebound, older women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aranow, C. Vitamin D and the immune system. J. Investig. Med. 2011, 59, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, M.; Cryer, B.; McArthur, K.E.; Huet, B.A.; Lee, E. Effects of aging and gastritis on gastric acid and pepsin secretion in humans: A prospective study. Gastroenterology 1996, 10, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakos, N.; Schöll, I.; Szalai, K.; Kundi, M.; Untersmayr, E.; Jensen-Jarolim, E. Risk assessment in elderly for sensitization to food and respiratory allergens. Immunol. Lett. 2006, 107, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, J.; Katelaris, C.H. Food allergy in adolescents and adults. Intern. Med. J. 2009, 39, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Laguna, L.; Sarkar, A. Aging-related changes in quantity and quality of saliva: Where do we stand in our understanding? J. Texture Stud. 2019, 50, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byars, S.G.; Stearns, S.C.; Boomsma, J.J. Association of Long-Term Risk of Respiratory, Allergic, and Infectious Diseases with Removal of Adenoids and Tonsils in Childhood. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 144, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwaru, B.I.; Hickstein, L.; Panesar, S.S.; Muraro, A.; Werfel, T.; Cardona, V.; Dubois, A.E.; Halken, S.; Hoffmann-Sommergruber, K.; Poulsen, L.K.; et al. EAACI Food Allergy and Anaphylaxis Guidelines Group. The epidemiology of food allergy in Europe: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Allergy 2014, 69, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, M.T.; Scichilone, N.; Gelardi, M.; Patella, V.; Ridolo, E. Management of allergic disease in the elderly: Key considerations, recommendations and emerging therapies. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 11, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Romero, A.d.C. Edible Insects and Allergy Risks: Implications for Children and the Elderly. Allergies 2025, 5, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies5020015
Romero AdC. Edible Insects and Allergy Risks: Implications for Children and the Elderly. Allergies. 2025; 5(2):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies5020015
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomero, Alessandra de Cássia. 2025. "Edible Insects and Allergy Risks: Implications for Children and the Elderly" Allergies 5, no. 2: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies5020015
APA StyleRomero, A. d. C. (2025). Edible Insects and Allergy Risks: Implications for Children and the Elderly. Allergies, 5(2), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies5020015