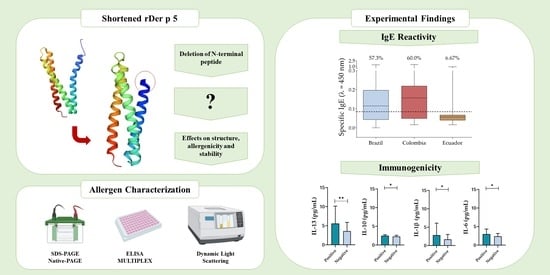
Removal of N-Terminal Peptide Impacts Structural Aspects of an IgE-Reactive Recombinant Der p 5
Highlights
- We managed to successfully express a shortened recombinant allergen of Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus, rDer p 5, which was strongly stable and a major allergen in Brazil and Colombia.
- N-terminal peptide deletion enhanced rDer p 5 thermal stability likely due to increased dimerization, but it still displayed a high IgE binding capacity.
- Although dimerization is expected to influence the allergenicity of molecules, this feature did not significantly change IgE reactivity to rDer p 5, considering that in Brazil and Colombia, the allergen was classified as major.
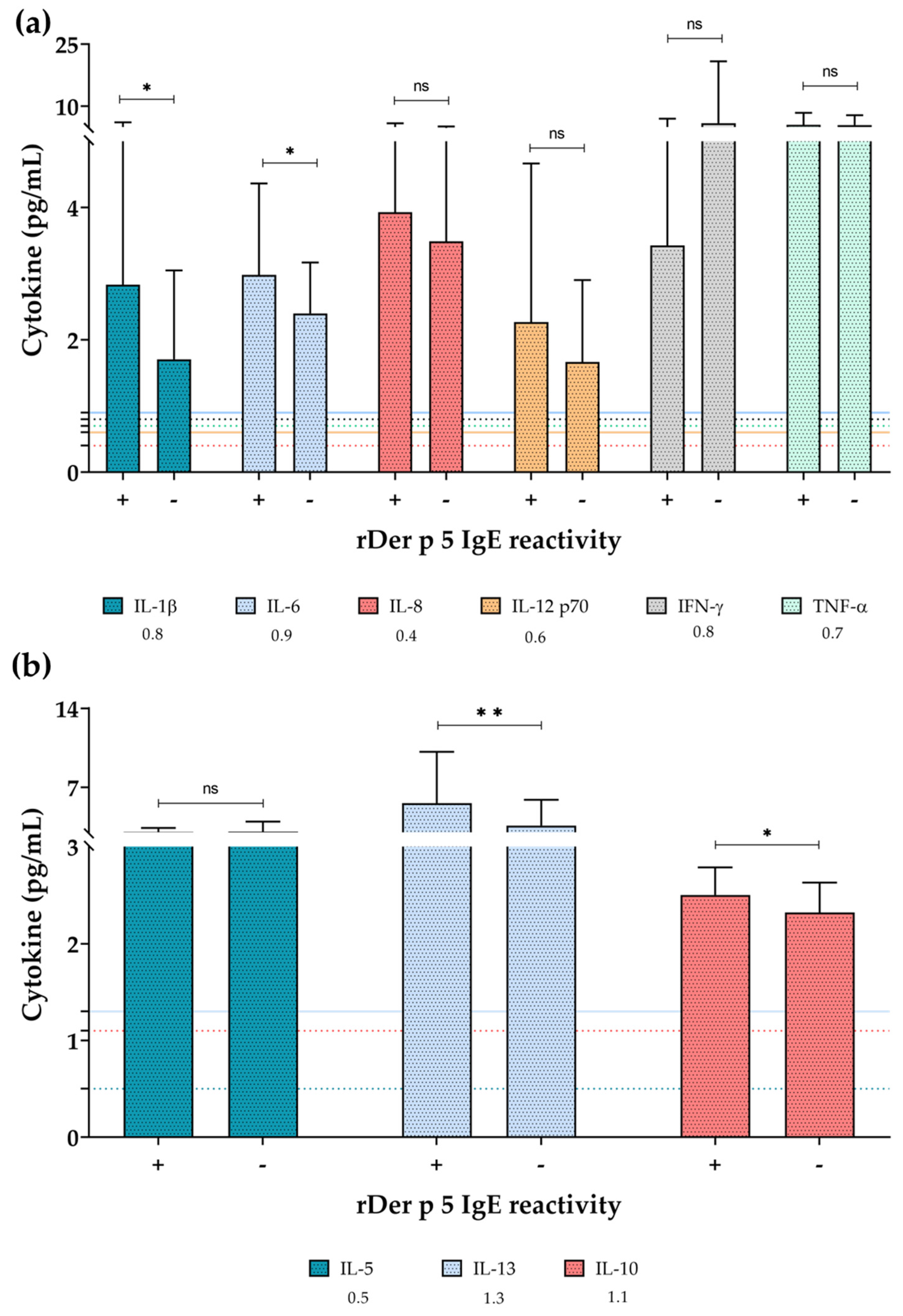
- Inflammatory interleukins related to allergic responses, such as IL-6 and IL-13, were more present in sera of rDer p 5 reactive patients.
- The enhanced structural stability of the shortened rDer p 5 may extend its shelf life, making it a highly appealing candidate for biotechnological applications in allergy diagnostics and immunotherapy.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
| Country 1 | Frequency (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Australia | 46.5 | [27] |
| Austria | 61.5 | [28] |
| Austria | 41.3 | [29] |
| Belgium | 12.5 | [30] |
| China | 17.7 | [31] |
| China | 17.8 | [13] |
| Colombia | 37.8 | [32] |
| Germany | 32.1 | [33] |
| Germany | 39.2 | [12] |
| Italy | 26.4 | [34] |
| Singapore | 90.0 | [20] |
| Singapore | 11.0 | [35] |
| Spain | 83.3 | [36] |
| Thailand | 69.2 | [17] |
| United States of America | 47.4 | [12] |
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Transformation of Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) Star Strain
2.2. Heterologous Expression of Der p 5 and Solubility Test
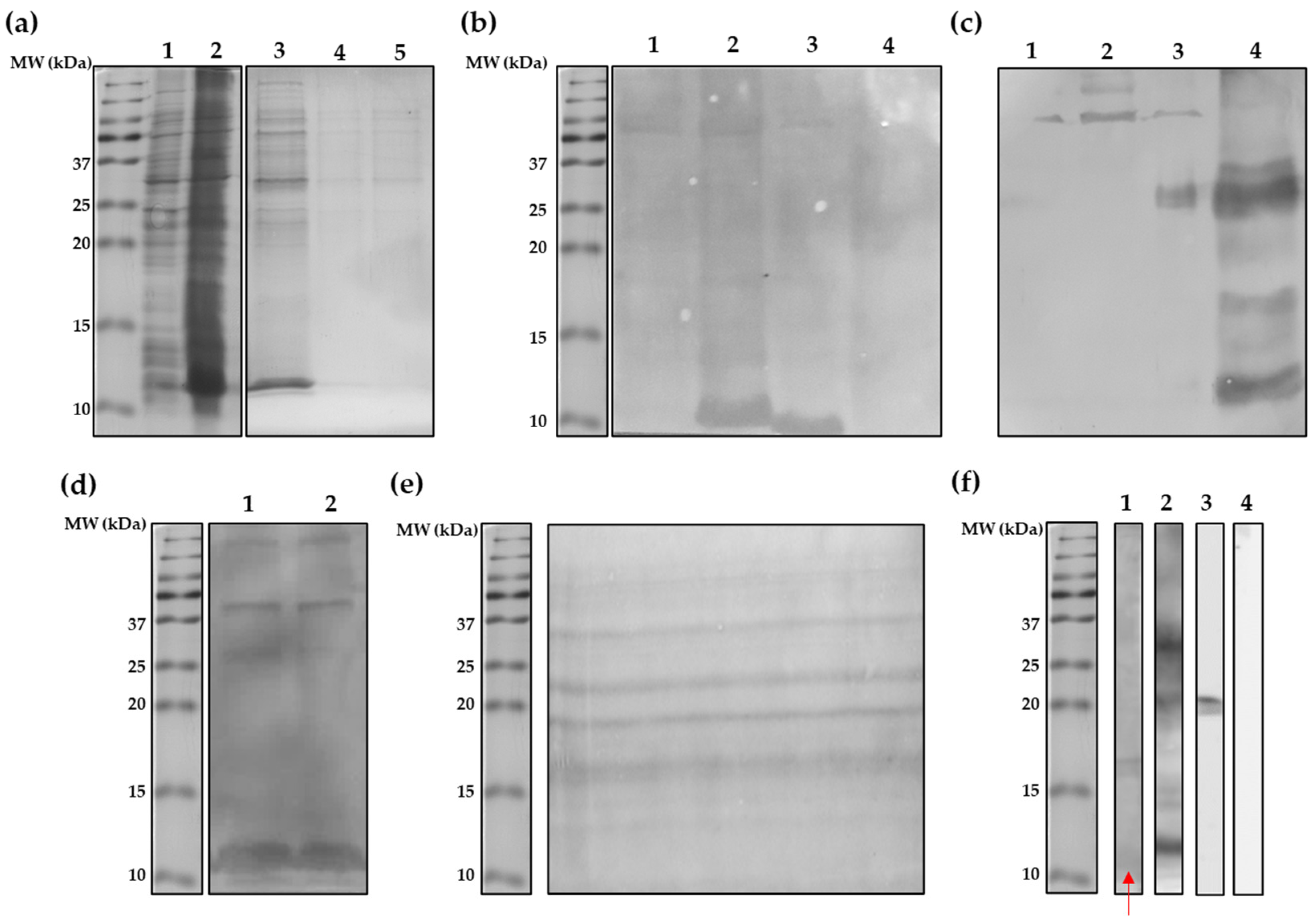
2.3. Immunodetection of rDer p 5 Using Western Blot Analyses
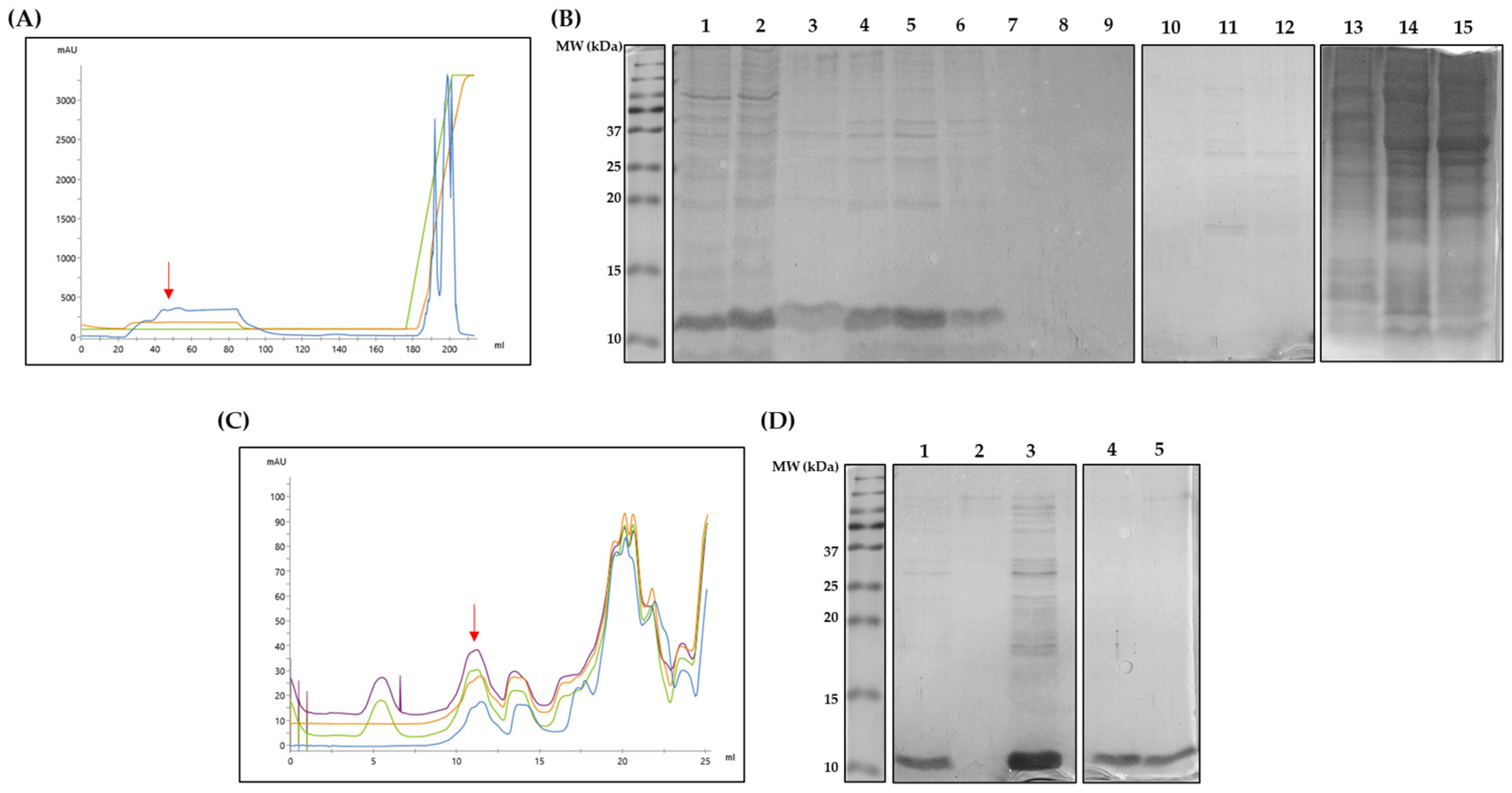
2.4. Purification of rDer p 5
2.5. In Silico and In Vitro Caracterization of rDer p 5 Structural Aspects
2.6. Individuals and Sera
2.7. IgE Reactivity Assays and Descriptive Analysis
2.8. Determination of Cytokine Amount in Sera and Statistical Analyses
2.9. Culture of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
3. Results
3.1. Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) Star Strain Is a Suitable rDe p 5 Expression Vector
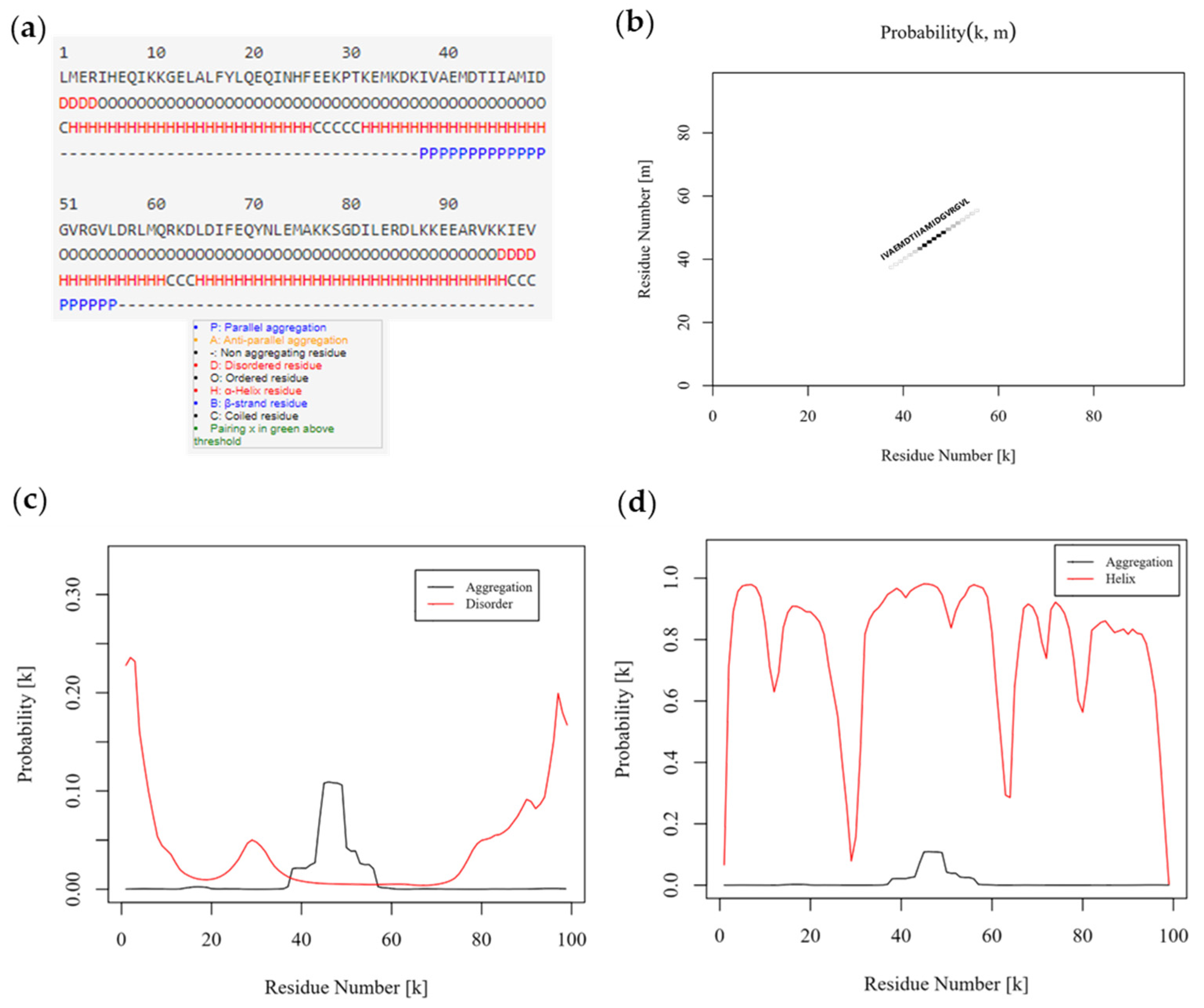
3.2. Shortened rDer p 5 Is Structuarally Stable but Agregates
3.3. Shortening of rDer p 5 Does Not Change Its Aggregation Behavior
3.4. Shortened rDer p 5 Is IgE-Reactive
3.5. Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Were More Present in Sera of rDer p 5-Reactive Patients
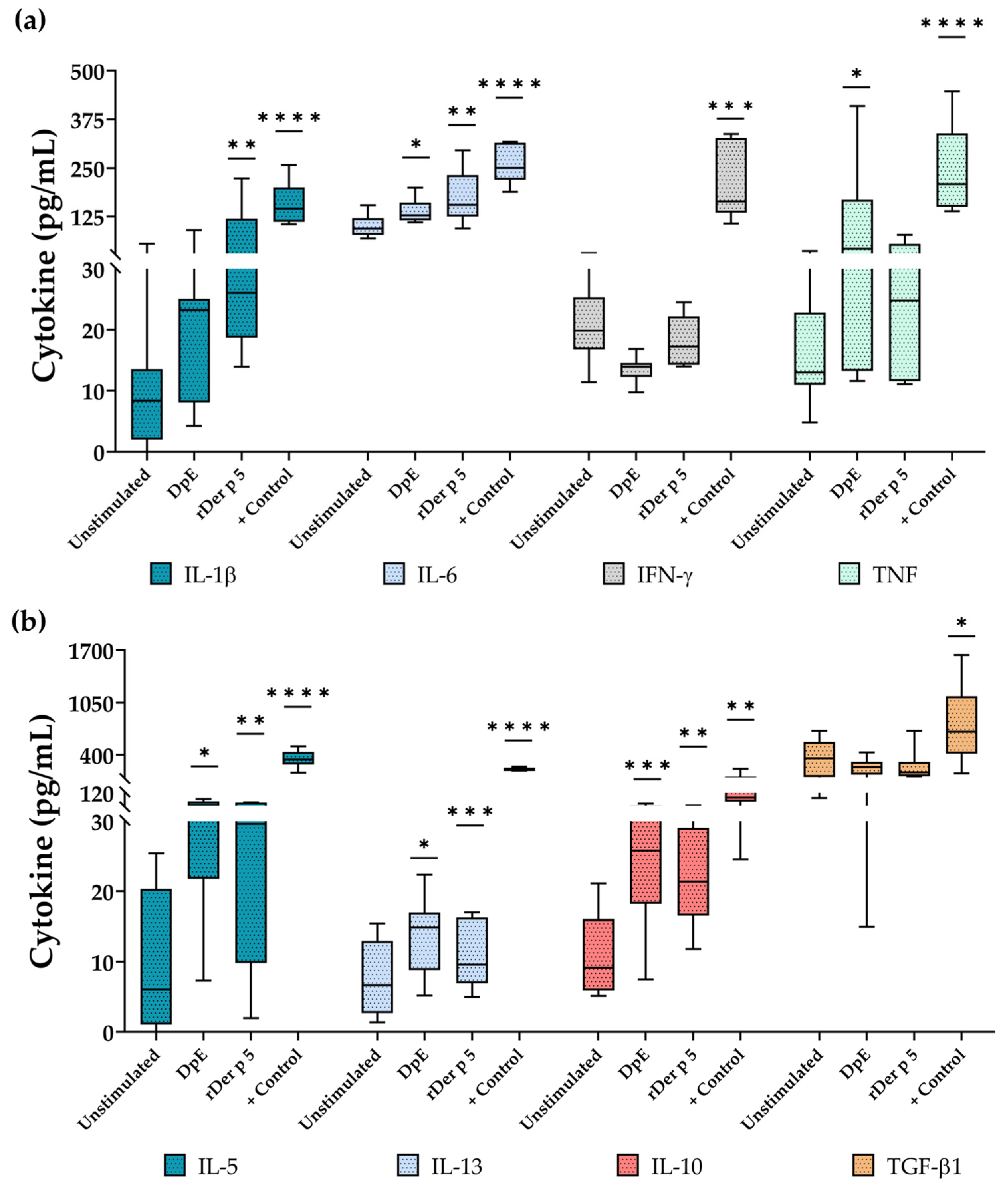
3.6. rDer p 5 Induces the Secretion of Type 2 and Proinflamatory Cytokines
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lundback, B.; Backman, H.; Lotvall, J.; Ronmark, E. Is asthma prevalence still increasing? Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2016, 10, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2019 Chronic Respiratory Diseases Collaborators. Global burden of chronic respiratory diseases and risk factors, 1990–2019: An update from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. EClinicalMedicine 2023, 59, 101936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asher, M.I.; Rutter, C.E.; Bissell, K.; Chiang, C.Y.; El Sony, A.; Ellwood, E.; Ellwood, P.; Garcia-Marcos, L.; Marks, G.B.; Morales, E.; et al. Worldwide trends in the burden of asthma symptoms in school-aged children: Global Asthma Network Phase I cross-sectional study. Lancet 2021, 398, 1569–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkin, M.R.; Strachan, D.P. The hygiene hypothesis for allergy-conception and evolution. Front. Allergy 2022, 3, 1051368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, A.A.; Cooper, P.J.; Figueiredo, C.A.; Alcantara-Neves, N.M.; Rodrigues, L.C.; Barreto, M.L. Global issues in allergy and immunology: Parasitic infections and allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 1217–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderon, M.A.; Linneberg, A.; Kleine-Tebbe, J.; De Blay, F.; Hernandez Fernandez de Rojas, D.; Virchow, J.C.; Demoly, P. Respiratory allergy caused by house dust mites: What do we really know? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acevedo, N.; Zakzuk, J.; Caraballo, L. House Dust Mite Allergy Under Changing Environments. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2019, 11, 450–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogburn, R.N.; Randall, T.A.; Xu, Y.; Roberts, J.H.; Mebrahtu, B.; Karnuta, J.M.; Rider, S.D.; Kissling, G.E.; London, R.E.; Pomes, A.; et al. Are dust mite allergens more abundant and/or more stable than other Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus proteins? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 1030–1032.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraballo, L.; Valenta, R.; Puerta, L.; Pomes, A.; Zakzuk, J.; Fernandez-Caldas, E.; Acevedo, N.; Sanchez-Borges, M.; Ansotegui, I.; Zhang, L.; et al. The allergenic activity and clinical impact of individual IgE-antibody binding molecules from indoor allergen sources. World Allergy Organ. J. 2020, 13, 100118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casset, A.; Mari, A.; Purohit, A.; Resch, Y.; Weghofer, M.; Ferrara, R.; Thomas, W.R.; Alessandri, C.; Chen, K.W.; de Blay, F.; et al. Varying allergen composition and content affects the in vivo allergenic activity of commercial Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus extracts. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2012, 159, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.S.D.; Pinheiro, C.S.; Pacheco, L.G.C.; Alcantara-Neves, N.M. Dermatophagoides spp. hypoallergens design: What has been achieved so far? Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2020, 30, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, G.A.; Randall, T.A.; Glesner, J.; Pedersen, L.C.; Perera, L.; Edwards, L.L.; DeRose, E.F.; Chapman, M.D.; London, R.E.; Pomes, A. Serological, genomic and structural analyses of the major mite allergen Der p 23. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2016, 46, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Zou, X.; Chen, H.; Liao, C.; Hu, H.; Luo, W.; Sun, B. Identifying Potential Co-Sensitization and Cross-Reactivity Patterns Based on Component-Resolved Diagnosis. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 181, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, X.; Xiaoyu, L.; Angel Tsz-Yau, W.; Nat, M.; Xiaojun, X.; Hui, C.; Man-Fung, T.; Judy Kin-Wing, N.; Soo-Kyung, S.; Yang Yie, S.; et al. Genomic Analysis of Blomia tropicalis Identifies Novel Allergens for Component-Resolved Diagnosis of Mite Allergy. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Wan, T.; Malainual, N.; Kwok-Wing Tsui, S. The Genome Analysis of Blomia tropicalis Reveals A Comprehensive Allergen Profile. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, AB82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulsawat, P.; Soongrung, T.; Satitsuksanoa, P.; Le Mignon, M.; Khemili, S.; Gilis, D.; Nony, E.; Kennedy, M.W.; Jacquet, A. The house dust mite allergen Der p 5 binds lipid ligands and stimulates airway epithelial cells through a TLR2-dependent pathway. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2019, 49, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulsawat, P.; Theeraapisakkun, M.; Nony, E.; Le Mignon, M.; Jain, K.; Buaklin, A.; Wongpiyabovorn, J.; Ruxrungtham, K.; Jacquet, A. Characterization of the house dust mite allergen Der p 21 produced in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr. Purif. 2014, 101, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Perez, R.; Poza-Guedes, P.; Pineda, F.; Castillo, M.; Sanchez-Machin, I. Storage Mite Precision Allergy Molecular Diagnosis in the Moderate-to-Severe T2-High Asthma Phenotype. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weghofer, M.; Grote, M.; Dall’Antonia, Y.; Fernandez-Caldas, E.; Krauth, M.T.; van Hage, M.; Horak, F.; Thomas, W.R.; Valent, P.; Keller, W.; et al. Characterization of folded recombinant Der p 5, a potential diagnostic marker allergen for house dust mite allergy. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2008, 147, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shek, L.P.; Chong, A.R.; Soh, S.E.; Cheong, N.; Teo, A.S.; Yi, F.C.; Giam, Y.C.; Chua, K.Y.; Van Bever, H.P. Specific profiles of house dust mite sensitization in children with asthma and in children with eczema. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2010, 21, e718–e722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, E.S.; Aglas, L.; Pinheiro, C.S.; de Andrade Belitardo, E.M.M.; Silveira, E.F.; Huber, S.; Torres, R.T.; Wallner, M.; Briza, P.; Lackner, P.; et al. A hybrid of two major Blomia tropicalis allergens as an allergy vaccine candidate. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2020, 50, 835–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, E.S.; Huber, S.; Alcantara-Neves, N.M.; Asam, C.; Silveira, E.F.; de Andrade Belitardo, E.M.M.; Aglas, L.; Wallner, M.; Gadermaier, G.; Briza, P.; et al. N-terminal peptide deletion influences immunological and structural features of Blo t 5. Allergy 2020, 75, 1503–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos da Silva, E.; Asam, C.; Lackner, P.; Hofer, H.; Wallner, M.; Silva Pinheiro, C.; Alcantara-Neves, N.M.; Ferreira, F. Allergens of Blomia tropicalis: An Overview of Recombinant Molecules. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2017, 172, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrtala, S. Allergens from house dust and storage mites. Allergo J. Int. 2022, 31, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, G.A.; Gosavi, R.A.; Krahn, J.M.; Edwards, L.L.; Cuneo, M.J.; Glesner, J.; Pomes, A.; Chapman, M.D.; London, R.E.; Pedersen, L.C. Der p 5 crystal structure provides insight into the group 5 dust mite allergens. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 25394–25401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiani, S.; Dumez, M.E.; Bitam, I.; Galleni, M. Der p 5 allergen from house dust mite: First epitope mapping of rabbit IgG blocking antibodies. New Microbes New Infect. 2019, 27, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hales, B.J.; Elliot, C.E.; Chai, L.Y.; Pearce, L.J.; Tipayanon, T.; Hazell, L.; Stone, S.; Piboonpocanun, S.; Thomas, W.R.; Smith, W.A. Quantitation of IgE binding to the chitinase and chitinase-like house dust mite allergens Der p 15 and Der p 18 compared to the major and mid-range allergens. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 160, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, C.S.; Silva, E.S.; de Andrade Belitardo, E.M.M.; Pacheco, L.G.C.; Aguiar, E.; Alcantara-Neves, N.M.; Gadermaier, G.; Ferreira, F. En route to personalized medicine: Uncovering distinct IgE reactivity pattern to house dust mite components in Brazilian and Austrian allergic patients. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2021, 11, e12004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Resch, Y.; Chen, K.W.; Swoboda, I.; Focke-Tejkl, M.; Blatt, K.; Novak, N.; Wickman, M.; van Hage, M.; Ferrara, R.; et al. Der p 11 is a major allergen for house dust mite-allergic patients suffering from atopic dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Dominguez, A.; Berings, M.; Rohrbach, A.; Huang, H.J.; Curin, M.; Gevaert, P.; Matricardi, P.M.; Valenta, R.; Vrtala, S. Molecular profiling of allergen-specific antibody responses may enhance success of specific immunotherapy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Hu, H.; Huang, Z.; Liao, C.; Huang, L.; Luo, W.; Jiang, M.; Sun, B. Serum levels of specific immunoglobulin E to Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus allergen components in patients with allergic rhinitis or/and asthma. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2021, 42, e40–e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, S.; Puerta, L.; Mendoza, D.; Chua, K.Y.; Mercado, D.; Caraballo, L. IgE Antibody Responses to Recombinant Allergens of Blomia tropicalis and Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus in a Tropical Environment. All. Clin. Immun. Int. 2007, 19, 233–238. [Google Scholar]
- Posa, D.; Perna, S.; Resch, Y.; Lupinek, C.; Panetta, V.; Hofmaier, S.; Rohrbach, A.; Hatzler, L.; Grabenhenrich, L.; Tsilochristou, O.; et al. Evolution and predictive value of IgE responses toward a comprehensive panel of house dust mite allergens during the first 2 decades of life. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 541–549.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalta, D.; Scala, E.; Asero, R.; Da Re, M.; Conte, M.; Buzzulini, F. Evaluation and predictive value of IgE responses toward a comprehensive panel of house dust mite allergens using a new multiplex assay: A real-life experience on an Italian population. Eur. Ann. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 54, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidon, M.I.; Chiang, W.C.; Liew, W.K.; Ong, T.C.; Tiong, Y.S.; Wong, K.N.; Angus, A.C.; Ong, S.T.; Gao, Y.F.; Reginald, K.; et al. Mite component-specific IgE repertoire and phenotypes of allergic disease in childhood: The tropical perspective. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2011, 22, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Perez, R.; Poza-Guedes, P.; Mederos-Luis, E.; Sanchez-Machin, I. Dupilumab modulates specific IgE mite responses at the molecular level in severe T2-high atopic dermatitis: A real-world experience. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 939598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.M.S.; da Silva, E.S.; Silveira, E.F.; Belitardo, E.; Santiago, L.F.; Silva, R.C.; Dos Santos Alves, V.; Carneiro, D.M.; Ferreira, F.; Jacquet, A.; et al. Recombinant T-cell epitope conjugation: A new approach for Dermatophagoides hypoallergen design. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2023, 53, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khemili, S.; Kwasigroch, J.M.; Hamadouche, T.; Gilis, D. Modelling and bioinformatics analysis of the dimeric structure of house dust mite allergens from families 5 and 21: Der f 5 could dimerize as Der p 5. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2012, 29, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, I.; Seno, F.; Tosatto, S.C.; Trovato, A. PASTA 2.0: An improved server for protein aggregation prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W301–W307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, E.S.; Pacheco, L.G.C.; Fernandes, A.M.S.; Asam, C.; Silveira, E.F.; da Silva Pinheiro, C.; Alcantara-Neves, N.M. Purification and characterisation of the dimeric group 12 allergen from Blomia tropicalis heterologously expressed by Escherichia coli Top10F. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 3405–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques Mello, L.; Viana, K.P.; Moraes Dos Santos, F.; Saturnino, L.T.M.; Kormann, M.L.; Lazaridis, E.; Torreao, C.D.; Soares, C.R.; Abreu, G.A.; Lima, V.B.; et al. Severe asthma and eligibility for biologics in a Brazilian cohort. J. Asthma 2021, 58, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, A.A.; Souza-Machado, A.; Franco, R.; Souza-Machado, C.; Ponte, E.V.; Moura Santos, P.; Barreto, M.L. The impact of a program for control of asthma in a low-income setting. World Allergy Organ. J. 2010, 3, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, K.A.; de Melo-Neto, O.P.; Magalhaes, F.B.; Ponte, J.C.; Felipe, F.A.; dos Santos, M.C.; dos Santos Lima, G.; Cruz, A.A.; Pinheiro, C.S.; Pontes-de-Carvalho, L.C.; et al. Blomia tropicalis Blo t 5 and Blo t 21 recombinant allergens might confer higher specificity to serodiagnostic assays than whole mite extract. BMC Immunol. 2013, 14, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, J.S.; Cardoso, L.S.; Carneiro, N.V.Q.; das Chagas, G.P.P.; Santana, C.V.N.; Atta, A.M.; de Oliveira, I.S.; Carvalho, E.M.; Figueiredo, C.A.; Cruz, A.A. Blood cytokines in atopic and non-atopic eosinophilic moderate to severe asthmatics. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2022, 52, 1452–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curin, M.; Garib, V.; Valenta, R. Single recombinant and purified major allergens and peptides: How they are made and how they change allergy diagnosis and treatment. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017, 119, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasera, R.; Singh, A.B.; Lavasa, S.; Nagendra, K.; Arora, N. Purification and immunobiochemical characterization of a 31 kDa cross-reactive allergen from Phaseolus vulgaris (kidney bean). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Robinson, C. Novel Method for the Purification of House Dust Mite Allergen Der p 1 and Its Use in Structure-Based Chemical Design of Novel Inhibitors. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 2020, 185–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.T.; Lee, J.; Yuk, J.E.; Song, H.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, D.J.; Shin, Y.; Lee, D.C.; Jeong, K.Y.; et al. Novel Sensitive, Two-site ELISA for the Quantification of Der f 1 Using Monoclonal Antibodies. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2021, 13, 665–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenta, R.; Karaulov, A.; Niederberger, V.; Zhernov, Y.; Elisyutina, O.; Campana, R.; Focke-Tejkl, M.; Curin, M.; Namazova-Baranova, L.; Wang, J.Y.; et al. Allergen Extracts for In Vivo Diagnosis and Treatment of Allergy: Is There a Future? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2018, 6, 1845–1855.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, F.C.; Chua, K.Y.; Cheong, N.; Shek, L.P.; Lee, B.W. Immunoglobulin E reactivity of native Blo t 5, a major allergen of Blomia tropicalis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2004, 34, 1762–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadermaier, G.; Hauser, M.; Ferreira, F. Allergens of weed pollen: An overview on recombinant and natural molecules. Methods 2014, 66, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevigne, A.; Campizi, V.; Szpakowska, M.; Bourry, D.; Dumez, M.E.; Martins, J.C.; Matagne, A.; Galleni, M.; Jacquet, A. The Lys-Asp-Tyr Triad within the Mite Allergen Der p 1 Propeptide Is a Critical Structural Element for the pH-Dependent Initiation of the Protease Maturation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhernov, Y.; Curin, M.; Khaitov, M.; Karaulov, A.; Valenta, R. Recombinant allergens for immunotherapy: State of the art. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 19, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaborsky, N.; Brunner, M.; Wallner, M.; Himly, M.; Karl, T.; Schwarzenbacher, R.; Ferreira, F.; Achatz, G. Antigen aggregation decides the fate of the allergic immune response. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, N.; Hofer, G.; Gattinger, P.; Smiljkovic, D.; Blatt, K.; Selb, R.; Stoecklinger, A.; Keller, W.; Valent, P.; Niederberger, V.; et al. Fusion proteins consisting of Bet v 1 and Phl p 5 form IgE-reactive aggregates with reduced allergenic activity. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouvinen, J.; Janis, J.; Laukkanen, M.L.; Jylha, S.; Niemi, M.; Paivinen, T.; Makinen-Kiljunen, S.; Haahtela, T.; Soderlund, H.; Takkinen, K. Transient dimers of allergens. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, D.; Cantillo, J.F.; Herazo, H.; Wortmann, J.; Keller, W.; Caraballo, L.; Puerta, L. Characterization of a hybrid protein designed with segments of allergens from Blomia tropicalis and Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus. Immunol. Lett. 2018, 196, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Yang, W.; Tian, Y.; Peng, H.; Wu, Y. N-terminal truncation contributed to increasing thermal stability of mannanase Man1312 without activity loss. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 1390–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, G.; Ma, Y. Truncation of the unique N-terminal domain improved the thermos-stability and specific activity of alkaline alpha-amylase Amy703. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan-Abad, A.M.; Mohammadi, M.; Mirzaei, H.; Mehrabi, M.; Motedayyen, H.; Arefnezhad, R. Impact of oligomerization on the allergenicity of allergens. Clin. Mol. Allergy 2022, 20, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemi, M.H.; Rytkonen-Nissinen, M.; Miettinen, I.; Janis, J.; Virtanen, T.; Rouvinen, J. Dimerization of lipocalin allergens. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caraballo, L.; Valenta, R.; Acevedo, N.; Zakzuk, J. Are the Terms Major and Minor Allergens Useful for Precision Allergology? Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 651500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smole, U.; Gour, N.; Phelan, J.; Hofer, G.; Kohler, C.; Kratzer, B.; Tauber, P.A.; Xiao, X.; Yao, N.; Dvorak, J.; et al. Serum amyloid A is a soluble pattern recognition receptor that drives type 2 immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soongrung, T.; Mongkorntanyatip, K.; Peepim, T.; Buaklin, A.; Le Mignon, M.; Malainual, N.; Nony, E.; Jacquet, A. The Blomia tropicalis allergen Blo t 7 stimulates innate immune signalling pathways through TLR2. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2018, 48, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Perez, R.; Pineda, F.; Poza-Guedes, P.; Matheu, V.; Sanchez-Machin, I. Minor Allergens in Moderate-Severe Allergic Rhinitis: Group 4 Mite Amylasa (Blo t4) and Geographical Variations. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, AB286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsemann, T.; Bottger, M.; Traidl, S.; Schwager, C.; Gulsen, A.; Freimooser, S.; Roesner, L.M.; Werfel, T.; Jappe, U. Specific IgE against the house dust mite allergens Der p 5, 20 and 21 influences the phenotype and severity of atopic diseases. Allergy 2023, 78, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakzuk, J.; Donado, K.; Mondol, E.; Marrugo, V.; Regino, R.; Lopez, J.F.; Hernandez, K.; Mercado, D.; Dennis, R.; Puerta, L.; et al. IgE sensitization to Blo t 21 and Blo t 5 is associated with asthma in the tropics: A case-control study. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 34, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, P.J.; Ster, I.C.; Chico, M.E.; Vaca, M.; Barreto, M.L.; Strachan, D.P. Patterns of allergic sensitization and factors associated with emergence of sensitization in the rural tropics early in the life course: Findings of an Ecuadorian birth cohort. Front. Allergy 2021, 2, 687073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnelykke, K.; Sparks, R.; Waage, J.; Milner, J.D. Genetics of allergy and allergic sensitization: Common variants, rare mutations. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2015, 36, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo Hernández, D.; Tobón-Borrero, L.; Herrera-Parra, O.; García-Castañeda, C. Seropositividad a Toxocara spp. en estudiantes atópicos de la Universidad de los Llanos. Rev. Cienc. Cuid. 2021, 18, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza da Cunha, S.; Barreto, M.L.; Fiaccone, R.L.; Cooper, P.J.; Alcantara-Neves, N.M.; Simoes Sde, M.; Cruz, A.A.; Rodrigues, L.C. Asthma cases in childhood attributed to atopy in tropical area in Brazil. Rev. Panam. Salud Publica 2010, 28, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Quist, J.C.; Ortego, F.; Lambrecht, B.N.; Castanera, P.; Hernandez-Crespo, P. Effects of domestic chemical stressors on expression of allergen genes in the European house dust mite. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2017, 31, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, N.; Sanchez, J.; Erler, A.; Mercado, D.; Briza, P.; Kennedy, M.; Fernandez, A.; Gutierrez, M.; Chua, K.Y.; Cheong, N.; et al. IgE cross-reactivity between Ascaris and domestic mite allergens: The role of tropomyosin and the nematode polyprotein ABA-1. Allergy 2009, 64, 1635–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, X.; Qi, X.; Yin, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, H.; Yang, L.; Wu, J. Allergens sensitization among children with allergic diseases in Shanghai, China: Age and sex difference. Respir. Res. 2022, 23, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forchert, L.; Potapova, E.; Panetta, V.; Dramburg, S.; Perna, S.; Posa, D.; Resch-Marat, Y.; Lupinek, C.; Rohrbach, A.; Grabenhenrich, L.; et al. Der p 23-specific IgE response throughout childhood and its association with allergic disease: A birth cohort study. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2022, 33, e13829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvey, M. Non-Mammalian Eukaryotic Expression Systems Yeast and Fungi in the Production of Biologics. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Wachter, C.; Van Landuyt, L.; Callewaert, N. Engineering of Yeast Glycoprotein Expression. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2021, 175, 93–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosano, G.L.; Ceccarelli, E.A. Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli: Advances and challenges. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Fukano, C.; Yonemoto, M.; Matsuoka, T.; Masuyama, K.; Ohashi-Doi, K. Comparison of the Allergenic Potency of House Dust Extract and House Dust Mite Allergen Extract for Subcutaneous Allergen Immunotherapy. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 42, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, S.; Gadermaier, G.; Bohle, B.; Ferreira, F.; Briza, P. Proteomic profiling of commercial dust mite skin prick test solutions and allergy vaccines from India. World Allergy Organ. J. 2021, 14, 100516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, N.A.; Pirozzi, G.; Graham, N.M.H. Commonality of the IL-4/IL-13 pathway in atopic diseases. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 13, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaia, C.; Heffler, E.; Crimi, C.; Maglio, A.; Vatrella, A.; Pelaia, G.; Canonica, G.W. Interleukins 4 and 13 in Asthma: Key Pathophysiologic Cytokines and Druggable Molecular Targets. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 851940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takatsu, K. Interleukin-5 and IL-5 receptor in health and diseases. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2011, 87, 463–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelaia, C.; Paoletti, G.; Puggioni, F.; Racca, F.; Pelaia, G.; Canonica, G.W.; Heffler, E. Interleukin-5 in the Pathophysiology of Severe Asthma. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.R.; Wei, S.Z.; Song, X.Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.B.; Ren, C.; Mou, Y.K.; Song, X.C. IL-1beta and Allergy: Focusing on Its Role in Allergic Rhinitis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2023, 2023, 1265449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puel, A.; Casanova, J.L. The nature of human IL-6. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 1969–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubernatorova, E.O.; Gorshkova, E.A.; Namakanova, O.A.; Zvartsev, R.V.; Hidalgo, J.; Drutskaya, M.S.; Tumanov, A.V.; Nedospasov, S.A. Non-redundant Functions of IL-6 Produced by Macrophages and Dendritic Cells in Allergic Airway Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Santamaria, R.; Satitsuksanoa, P. Engineered IL-10: A matter of affinity. Allergy 2022, 77, 1067–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polukort, S.H.; Rovatti, J.; Carlson, L.; Thompson, C.; Ser-Dolansky, J.; Kinney, S.R.; Schneider, S.S.; Mathias, C.B. IL-10 Enhances IgE-Mediated Mast Cell Responses and Is Essential for the Development of Experimental Food Allergy in IL-10-Deficient Mice. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 4865–4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, C.; Horak, F.; Vrtala, S.; Valenta, R.; Niederberger, V. Nasal application of rBet v 1 or non-IgE-reactive T-cell epitope-containing rBet v 1 fragments has different effects on systemic allergen-specific antibody responses. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 1312–1315.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, C.; Lupinek, C.; Ristl, R.; Lemell, P.; Horak, F.; Zieglmayer, P.; Spitzauer, S.; Valenta, R.; Niederberger, V. Effects of nasal corticosteroids on boosts of systemic allergen-specific IgE production induced by nasal allergen exposure. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0114991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
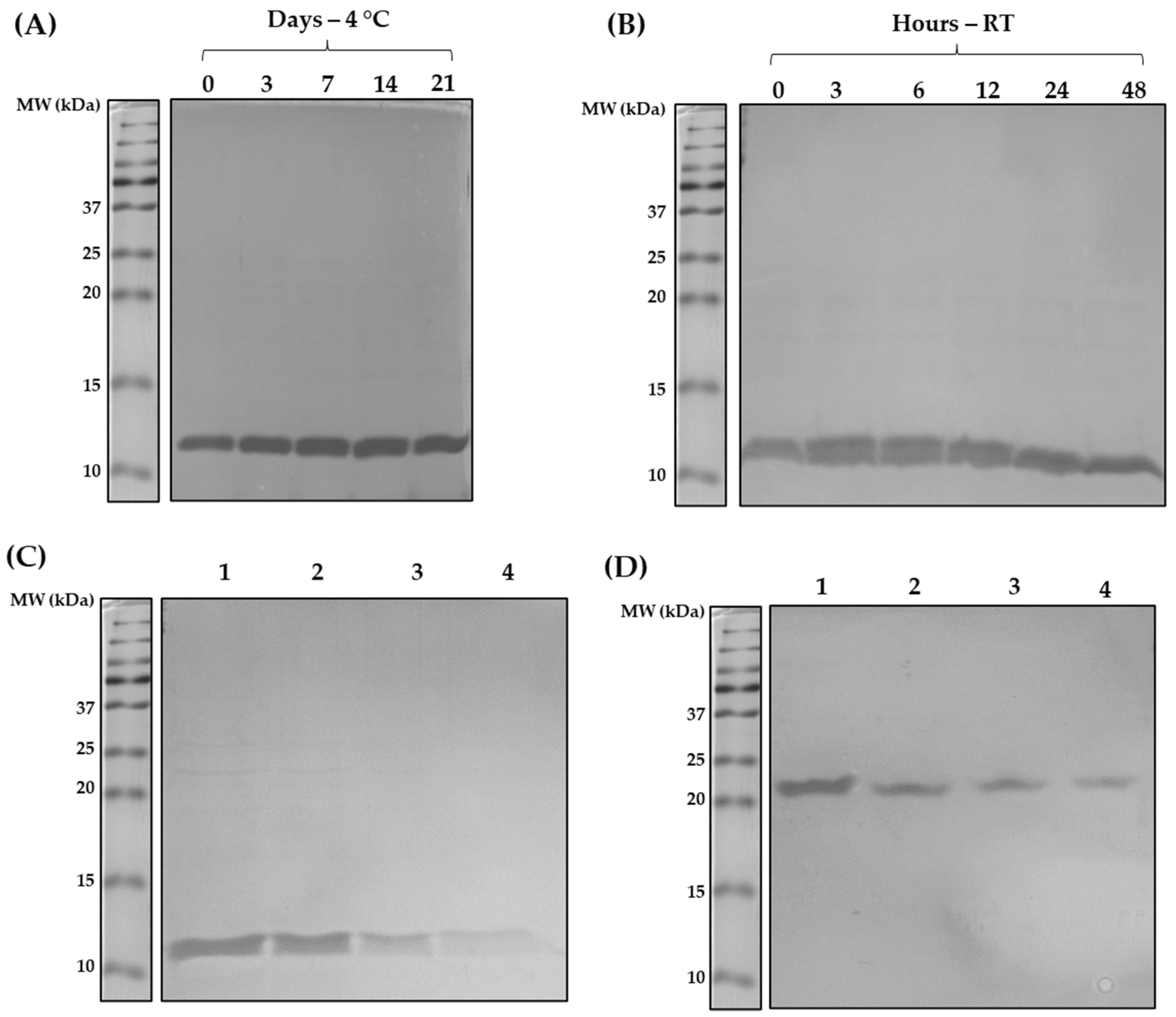

| Temperature (°C) | RH 1 (nm) | |
|---|---|---|
| Pike 01 | Pike 02 | |
| 4 | 1.130 ± 0.841 | 135.832 ± 122.365 |
| 25 | 1.573 ± 1.894 | 15.588 ± 7.640 |
| 37 | 1.490 ± 0.715 | 78.000 ± 67.197 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vieira, C.J.B.; Silva, R.C.; Silveira, E.F.; Fernandes, A.M.S.; Jaramillo-Hernández, D.A.; Garcés, L.F.S.; Fonseca, L.M.S.; Machado, B.A.S.; Fernandes, J.S.; Pinheiro, G.P.; et al. Removal of N-Terminal Peptide Impacts Structural Aspects of an IgE-Reactive Recombinant Der p 5. Allergies 2023, 3, 184-201. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies3030012
Vieira CJB, Silva RC, Silveira EF, Fernandes AMS, Jaramillo-Hernández DA, Garcés LFS, Fonseca LMS, Machado BAS, Fernandes JS, Pinheiro GP, et al. Removal of N-Terminal Peptide Impacts Structural Aspects of an IgE-Reactive Recombinant Der p 5. Allergies. 2023; 3(3):184-201. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies3030012
Chicago/Turabian StyleVieira, Camilo J. B., Raphael C. Silva, Elisânia F. Silveira, Antônio M. S. Fernandes, Dumar A. Jaramillo-Hernández, Luis F. S. Garcés, Larissa M. S. Fonseca, Bruna A. S. Machado, Jamille S. Fernandes, Gabriela P. Pinheiro, and et al. 2023. "Removal of N-Terminal Peptide Impacts Structural Aspects of an IgE-Reactive Recombinant Der p 5" Allergies 3, no. 3: 184-201. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies3030012
APA StyleVieira, C. J. B., Silva, R. C., Silveira, E. F., Fernandes, A. M. S., Jaramillo-Hernández, D. A., Garcés, L. F. S., Fonseca, L. M. S., Machado, B. A. S., Fernandes, J. S., Pinheiro, G. P., Cruz, Á. A., Ferreira, F., Cooper, P., Pacheco, L. G. C., Alcantara-Neves, N. M., Pinheiro, C. S., & da Silva, E. S. (2023). Removal of N-Terminal Peptide Impacts Structural Aspects of an IgE-Reactive Recombinant Der p 5. Allergies, 3(3), 184-201. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies3030012