Effects of Syo-seiryu-to and Its Constituent Crude Drugs on Phorbol Ester-Induced Up-Regulation of IL-33 and Histamine H1 Receptor mRNAs in Swiss 3T3 and HeLa Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Hot Water Extracts from Syo-seiryu-to (SST) and Its Crude Drugs
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Reverse Transcription
2.4. Real-Time Quantitative RT-PCR
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
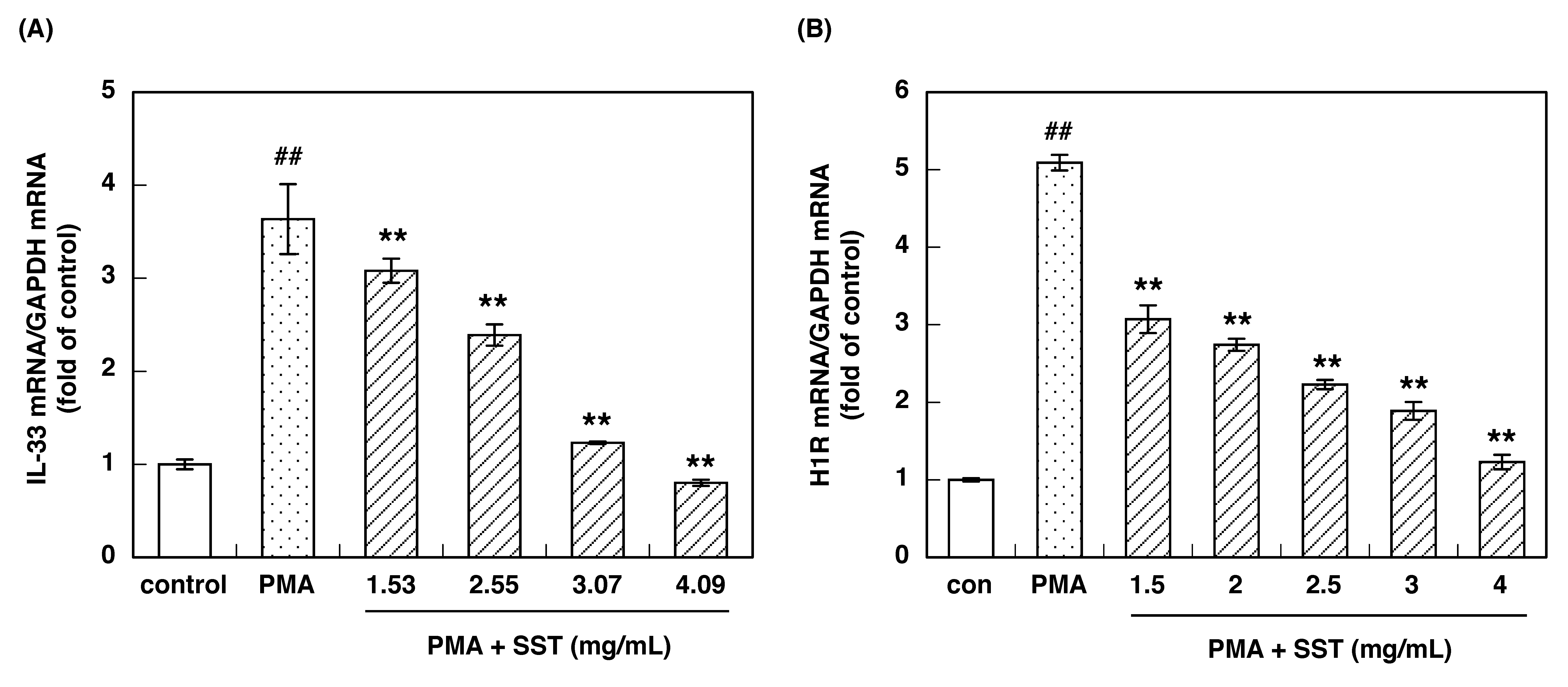
3.1. Effect of SST on PMA-Induced IL-33 and H1R Gene Up-Regulation
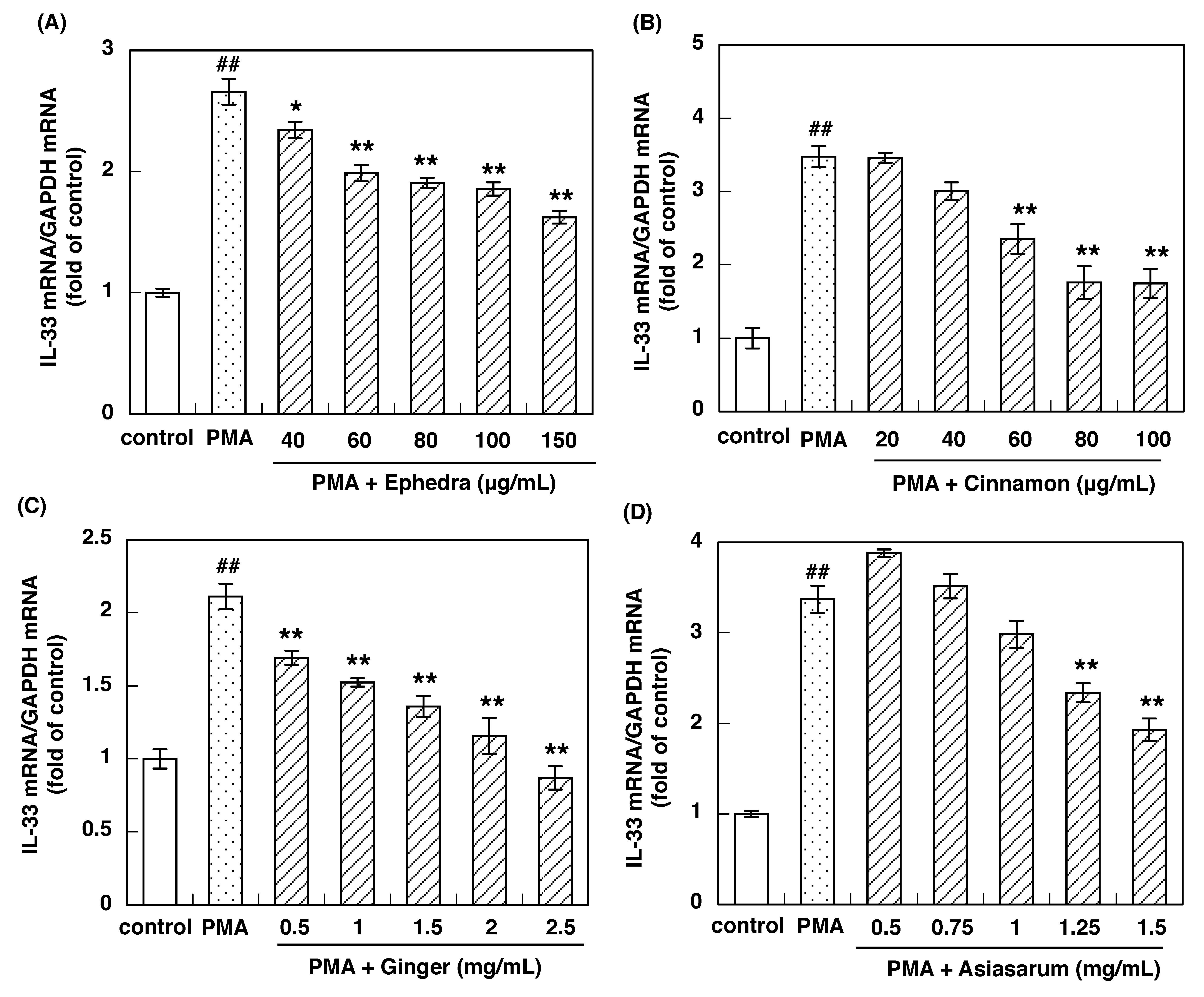
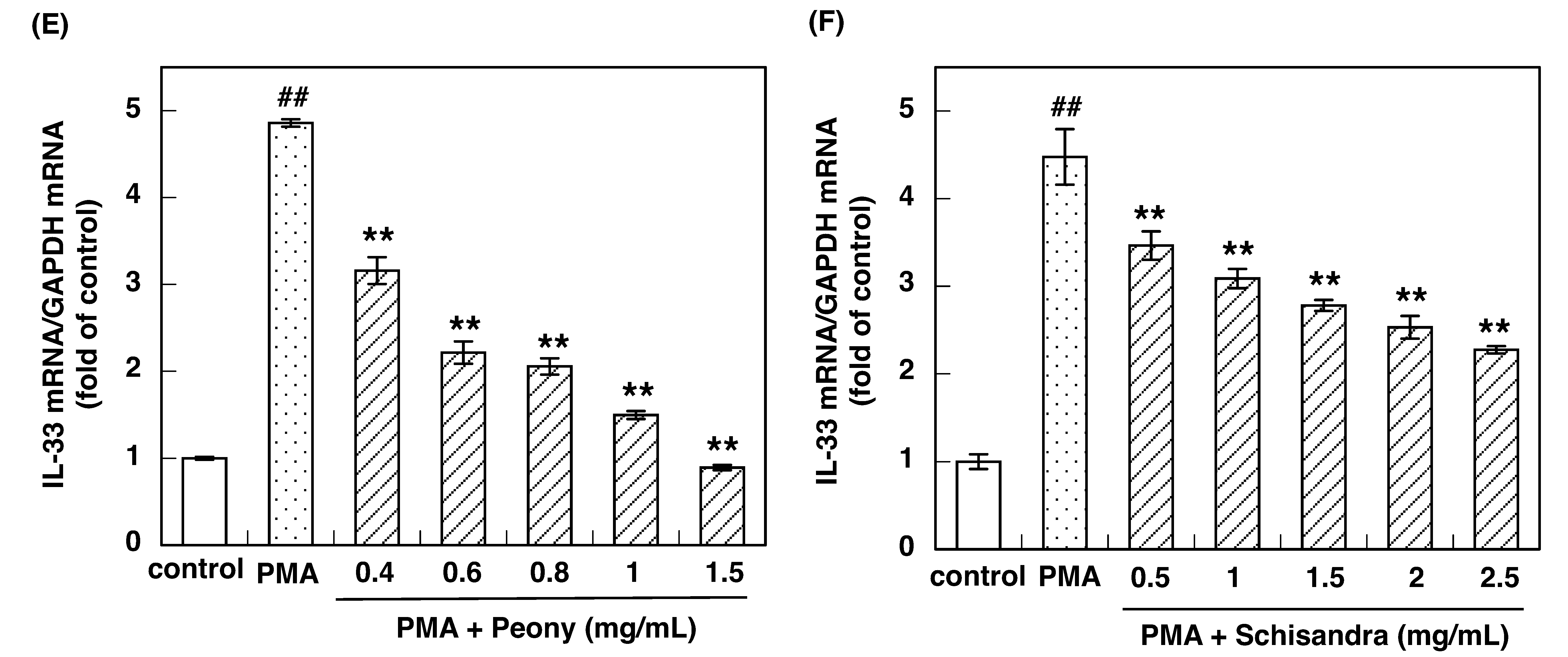
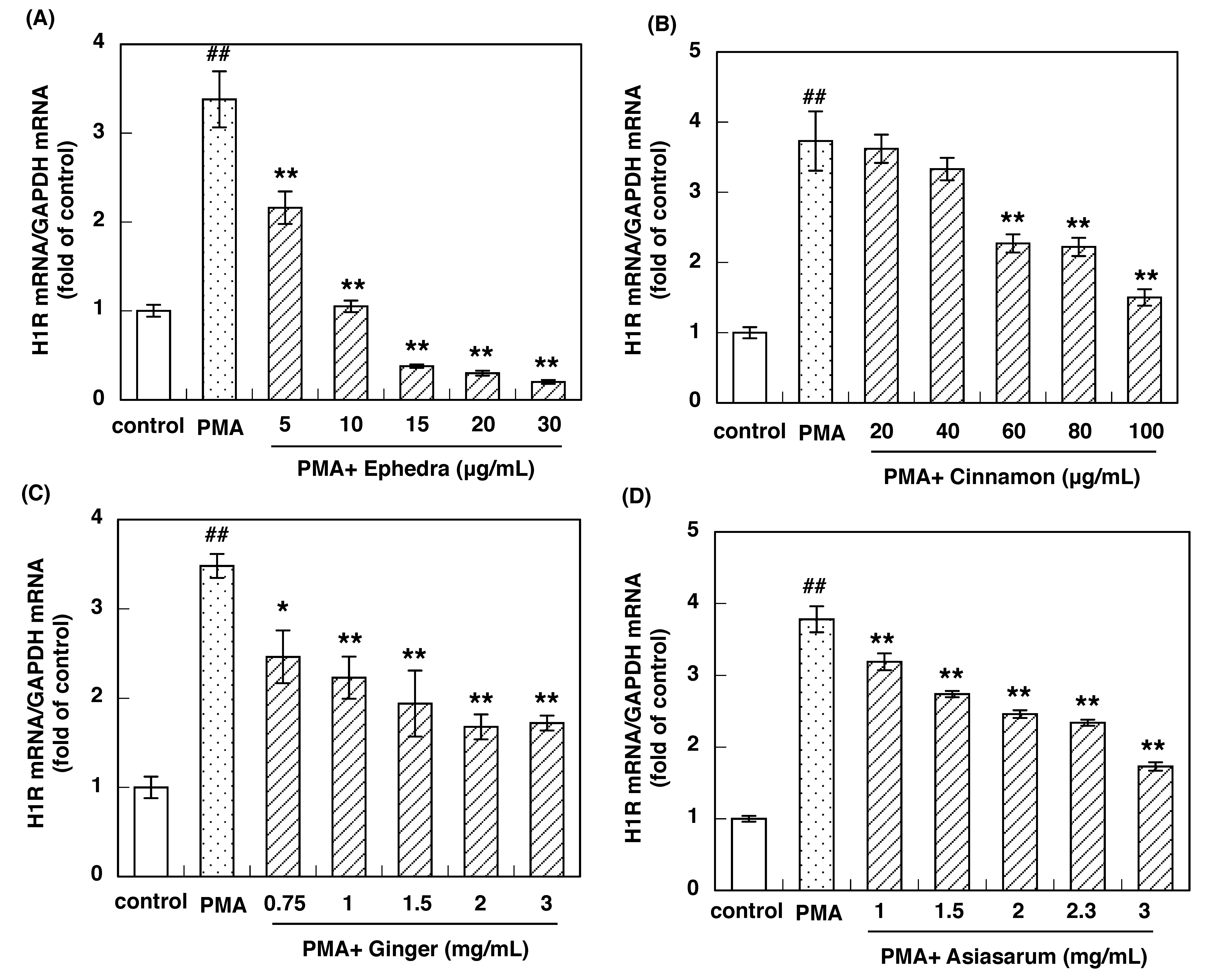
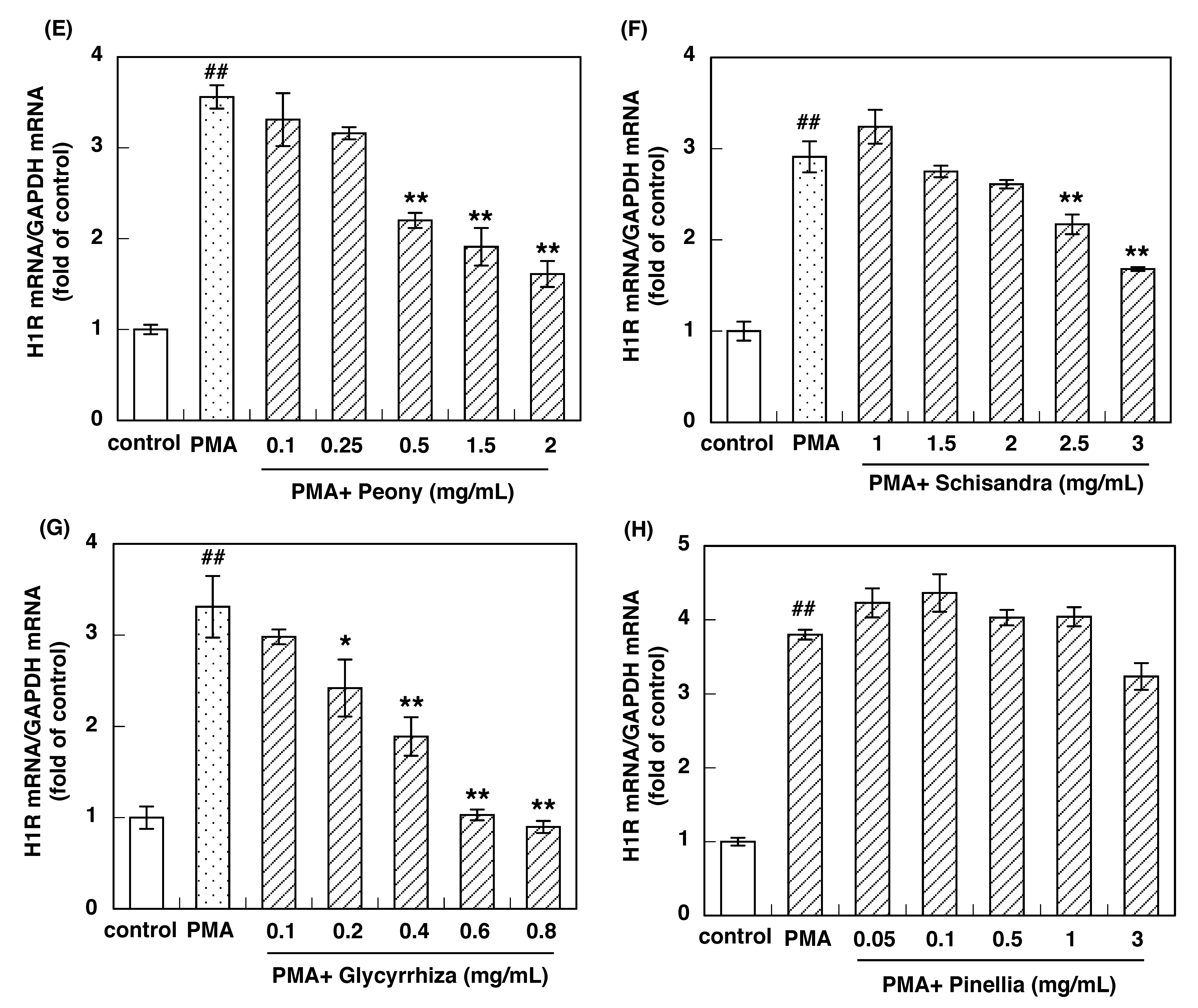
3.2. Effect of Constituent Crude Drugs of SST on PMA-Induced Up-Regulation of IL-33 and H1R Gene Expression
3.3. IC50 of Constituent Crude Drugs of SST to Inhibit PMA-Induced Up-Regulation of IL-33 and H1R Gene Expression
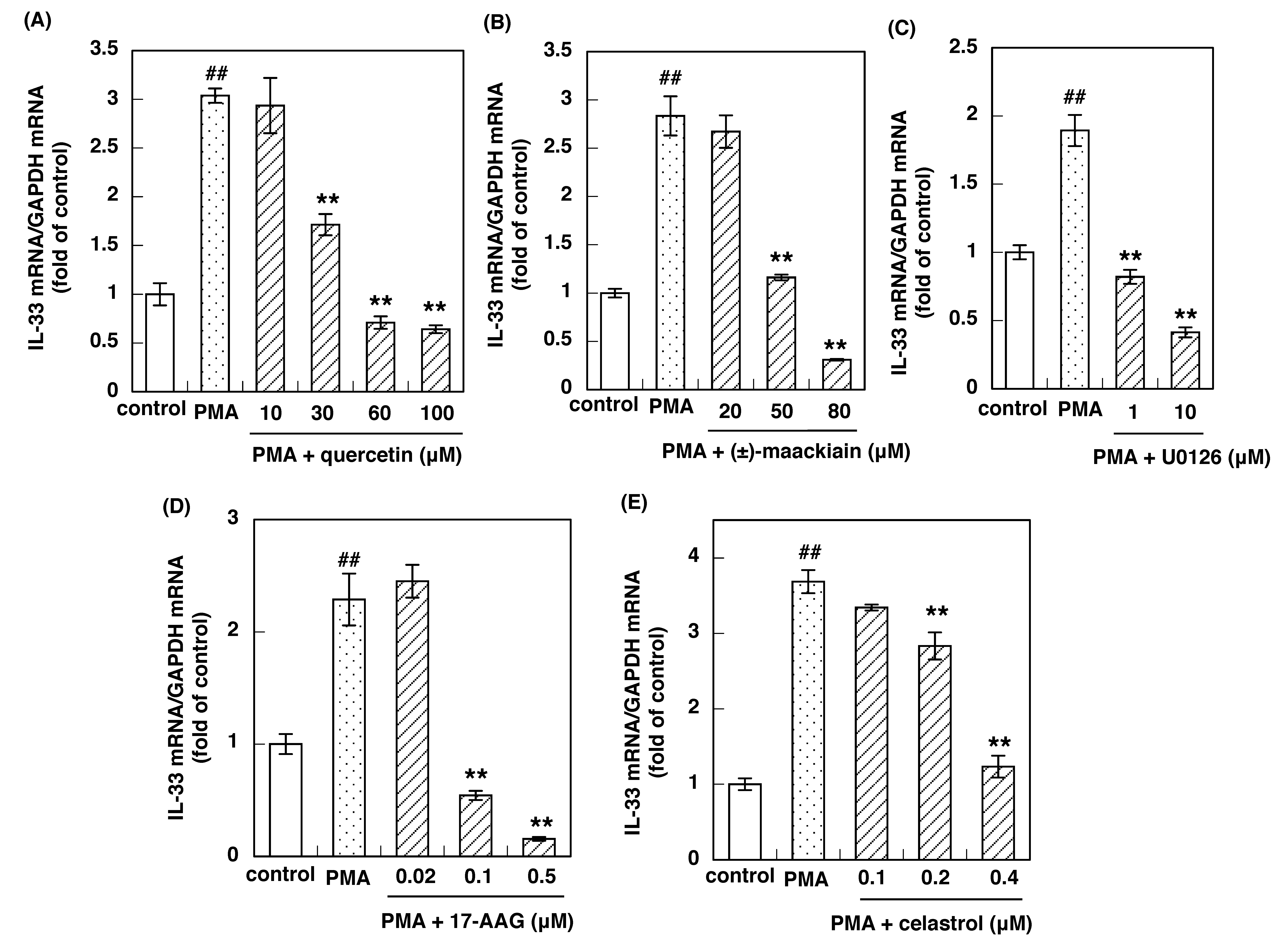
3.4. Effects of Inhibitors of the H1R Gene Expression Signaling Pathway on PMA-Induced IL-33 Gene Up-Regulation
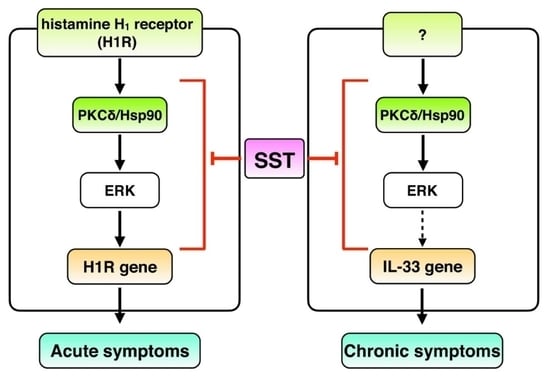
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, M.H.; Hong, S.U.; Kim, H.T.; Seo, H.S.; Kim, K.; Ko, S.G.; Choi, I. A multicenter study on the efficacy and safety of So-Cheong-Ryong-Tang for perennial allergic rhinitis. Complement. Ther. Med. 2019, 45, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakaguchi, M.; Mase, A.; Iizuka, A.; Yuzurihara, M.; Ishige, A.; Amagaya, S.; Komatsu, Y.; Takeda, H.; Matsumiya, T. Further pharmacological study on Sho-seiryu-to as an antiallergic. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 1997, 19, 707–713. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, A.; Ohashi, Y.; Kakinoki, Y.; Washio, Y.; Yamada, K.; Nakai, Y.; Nakano, T.; Nakai, Y.; Ohmoto, Y. The herbal medicine shoseiryu-to inhibits allergen-induced synthesis of tumour necrosis factor alpha by peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with perennial allergic rhinitis. Acta Otolaryngol. Suppl. 1998, 538, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.H.; Hong, C.Y.; Yu, C.L. Decreased serum IgE level, decreased IFN-gamma and IL-5 but increased IL-10 production, and suppressed cyclooxygenase 2 mRNA expression in patients with perennial allergic rhinitis after treatment with a new mixed formula of Chinese herbs. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2001, 1, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, Y.; Kaneko, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Ishige, A.; Sasaki, H. Possible involvement of suppression of Th2 differentiation in the anti-allergic effect of Sho-seiryu-to in mice. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 90, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, E.; Rho, S.; Lee, E.J.; Seo, Y.H.; Cho, C.; Lee, Y.; Min, B.I.; Shin, M.K.; Hong, M.C.; Bae, H. Traditional Korean medicine (SCRT) modulate Th1 and/or Th2 specific cytokine production in mice CD4+ T cell. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 92, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, E.; Rho, S.; Cho, C.; Choi, H.; Ko, S.; Lee, Y.; Hong, M.C.; Shin, M.K.; Jung, S.G.; Bae, H. So-Cheong-Ryong-Tang, traditional Korean medicine, suppresses Th2 lineage development. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 27, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, T.; Nakao, M.; Shimizu, Y.; Kodera, Y.; Oh-Ishi, M.; Maeda, T.; Yamada, H. Proteomic Analysis of Anti-inflammatory Effects of a Kampo (Japanese Herbal) Medicine “Shoseiryuto (Xiao-Qing-Long-Tang)” on Airway Inflammation in a Mouse Model. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2011, 2011, 604196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, S.T.; Wang, S.D.; Wang, J.Y.; Yu, C.K.; Lei, H.Y. The effect of Chinese herbal medicine, xiao-qing-long tang (XQLT), on allergen-induced bronchial inflammation in mitesensitized mice. Allergy 2000, 55, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.K.; Mizuguchi, H.; Kodama, M.; Dev, S.; Umehara, H.; Kitamura, Y.; Matsushita, C.; Takeda, N.; Fukui, H. Sho-seiryu-to suppresses histamine signaling at the transcriptional level in TDI-sensitized nasal allergy model rats. Allergol. Int. 2009, 58, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudbjartsson, D.F.; Bjornsdottir, U.S.; Halapi, E.; Helgadottir, A.; Sulem, P.; Jonsdottir, G.M.; Thorleifsson, G.; Helgadottir, H.; Steinthorsdottir, V.; Stefansson, H.; et al. Sequence variants affecting eosinophil numbers associate with asthma and myocardinal infarction. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffatt, M.F.; Gut, I.G.; Demenais, F.; Strachan, D.P.; Bouzigon, E.; Heath, S.; von Mutius, E.; Farrall, M.; Lathrop, M.; Cookson, W.O. GABRIEL Consortium. A large-scale, consortium-based genome wide association study of asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, J.; Owyang, A.; Oldham, E.; Song, Y.; Murphy, E.; McClanahan, T.K.; Zurawski, G.; Moshrefi, M.; Qin, J.; Li, X.; et al. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity 2005, 23, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, L.H.; Ohno, T.; Oboki, K.; Kajiwara, N.; Suto, H.; Iikura, M.; Okayama, Y.; Akira, S.; Saito, H.; Galli, S.J.; et al. IL-33 induces IL-13 production by mouse mast cells independently of IgE-FcepsilonRI signals. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 82, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smithgall, M.D.; Comeau, M.R.; Yoon, B.R.; Kaufman, D.; Armitage, R.; Smith, D.E. IL-33 amplifies both Th1- and Th2-type responses through its activity on human basophils, allergen-reactive Th2 cells, iNKT and NK cells. Int. Immunol. 2008, 20, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolarski, B.; Kurowska-Stolarska, M.; Kewin, P.; Xu, D.; Liew, F.Y. IL-33 exacerbates eosinophil-mediated airway inflammation. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 3472–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.E. IL-33: A tissue derived cytokine pathway involved in allergic inflammation and asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2010, 40, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakashita, M.; Yoshimoto, T.; Hirota, T.; Harada, M.; Okubo, K.; Osawa, Y.; Fujieda, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Yasuda, K.; Nakanishi, K.; et al. Association of serum interleukin-33 level and the interleukin-33 genetic variant with Japanese cedar pollinosis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2008, 38, 1875–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haenuki, Y.; Matsushita, K.; Futatsugi-Yumikura, S.; Ishii, K.J.; Kawagoe, T.; Imoto, Y.; Fujieda, S.; Yasuda, M.; Hisa, Y.; Akira, S.; et al. A critical role of IL-33 in experimental allergic rhinitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, H.; Arae, K.; Unno, H.; Miyauchi, K.; Toyama, S.; Nambu, A.; Oboki, K.; Ohno, T.; Motomura, K.; Matsuda, A.; et al. An Interleukin-33-Mast Cell-Interleukin-2 Axis Suppresses Papain-Induced Allergic Inflammation by Promoting Regulatory T Cell Numbers. Immunity 2015, 21, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, H.; Saito, H.; Matsumoto, K.; Nakae, S. Regulatory roles of mast cells in immune responses. Semin. Immunopathol. 2016, 38, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okubo, K.; Kurono, Y.; Ichimura, K.; Enomoto, T.; Okamoto, Y.; Kawauchi, H.; Suzaki, H.; Fujieda, S.; Masuyama, K. Japanese guidelines for allergic rhinitis 2020. Allergol. Int. 2020, 69, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iriyoshi, N.; Takeuchi, K.; Yuta, A.; Ukai, K.; Sakakura, Y. Increased expression of histamine H1 receptor mRNA in allergic rhinitis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1996, 26, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, Q.T.; Cryer, A.; Dinh, S.; Peiser, C.; Wu, S.; Springer, J.; Hamelmann, E.; Klapp, B.F.; Heppt, W.; Fischer, A. Transcriptional up-regulation of histamine receptor-1 in epithelial, mucus and inflammatory cells in perennial allergic rhinitis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2005, 35, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.K.; Yoshimura, S.; Mishima, R.; Fujimoto, K.; Mizuguchi, H.; Dev, S.; Wakayama, Y.; Kitamura, Y.; Horio, S.; Takeda, N.; et al. Stimulation of histamine H1 receptor up-regulates histamine H1 receptor itself through activation of receptor gene transcription. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2007, 103, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuguchi, H.; Terao, T.; Kitai, M.; Ikeda, M.; Yoshimura, Y.; Das, A.K.; Kitamura, Y.; Takeda, N.; Fukui, H. Involvement of protein kinase Cdelta/extracellular signal-regulated kinase/poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) signaling pathway in histamine-induced up-regulation of histamine H1 receptor gene expression in HeLa cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 30542–30551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuguchi, H.; Kitamura, Y.; Kondo, Y.; Kuroda, W.; Yoshida, H.; Miyamoto, Y.; Hattori, M.; Fukui, H.; Takeda, N. Preseasonal prophylactic treatment with antihistamines suppresses nasal symptoms and expression of histamine H₁ receptor mRNA in the nasal mucosa of patients with pollinosis. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 2010, 32, 745–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, Y.; Mizuguchi, H.; Ogishi, H.; Kuroda, W.; Hattori, M.; Fukui, H.; Takeda, N. Preseasonal prophylactic treatment with antihistamines suppresses IL-5 but not IL-33 mRNA expression in the nasal mucosa of patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis caused by Japanese cedar pollen. Acta Otolaryngol. 2012, 132, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, R.; Mizuguchi, H.; Shaha, A.; Nishida, K.; Yabumoto, M.; Ikeda, H.; Fujino, H.; Kitamura, Y.; Fukui, H.; Takeda, N. Effect of wild grape on the signaling of histamine H1 receptor gene expression responsible for the pathogenesis of allergic rhinitis. J. Med. Investig. 2018, 65, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nariai, Y.; Mizuguchi, H.; Ogasawara, T.; Nagai, H.; Sasaki, Y.; Okamoto, Y.; Yoshimura, Y.; Kitamura, Y.; Nemoto, H.; Takeda, N.; et al. Disruption of Heat Shock Protein 90 (Hsp90)-Protein Kinase Cδ (PKCδ) Interaction by (-)-Maackiain Suppresses Histamine H1 Receptor Gene Transcription in HeLa Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 27393–27402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirasaki, H.; Kanaizumi, E.; Seki, N.; Himi, T. Localization and upregulation of the nasal histamine H1 receptor in perennial allergic rhinitis. Mediator Inflam. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, M.; Ohmori, K.; Hasegawa, K. Histamine H1 receptor-stimulated interleukin 8 and granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor production by bronchial epithelial cells requires extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling via protein kinase C. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2006, 139, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masaki, T.; Kojima, T.; Okabayashi, T.; Ogasawara, N.; Ohkuni, T.; Obata, K.; Takasawa, A.; Murata, M.; Tanaka, S.; Hirakawa, S.; et al. A nuclear factor-kB signaaling pathway via protein kinase Cd regulates replication of respiratory syncytical virus in polarized normal human nasal epithelial cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 2144–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussion, C.; Ortega, N.; Girard, J.P. The IL-1-like cytokine IL-33 is constitutively expressed in the nucleus of endothelial cells and epithelial cells in vivo: A novel ‘alarmin’? PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oboki, K.; Ohno, T.; Kajiwara, N.; Saito, H.; Nakae, S. IL-33 and IL-33 receptors in host defense and diseases. Allergol. Int. 2010, 59, 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, P.; Li, J.; Fu, X.; Yu, Z. Schisandra fruits for the management of drug-induced liver injury in China: A review. Phytomedicine 2019, 59, 152760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, K.; Nagai, F.; Seto, T.; Yamauchi, H. The effects of kampo-formulation and the constituting crude drugs, prescribed for the treatment of peptic ulcer on H,K-ATPase activity. Yakugaku Zasshi 2001, 121, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ok, I.S.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, B.K.; Lee, J.C.; Lee, Y.C. Pinellia ternata, Citrus reticulata, and their combinational prescription inhibit eosinophil infiltration and airway hyperresponsiveness by suppressing CCR3+ and Th2 cytokines production in the ovalbumin-induced asthma model. Mediators Inflamm. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
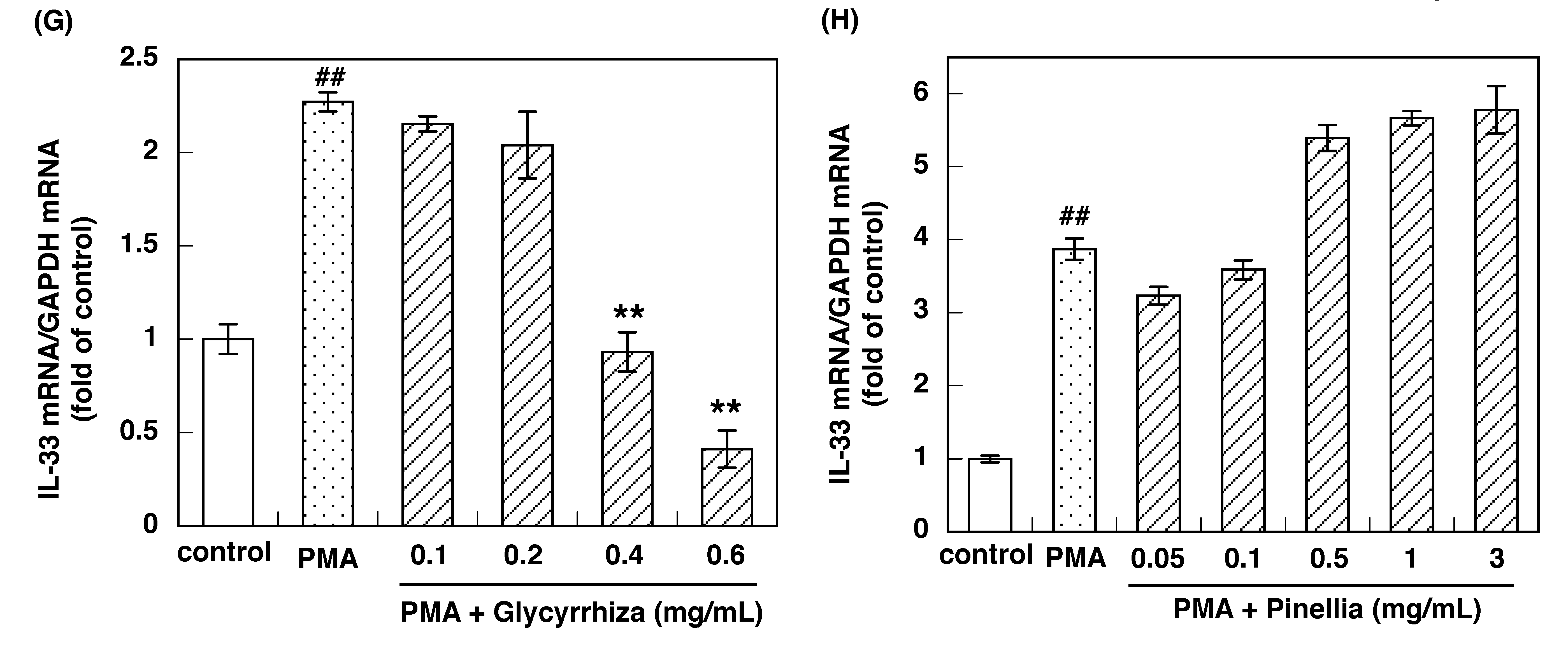
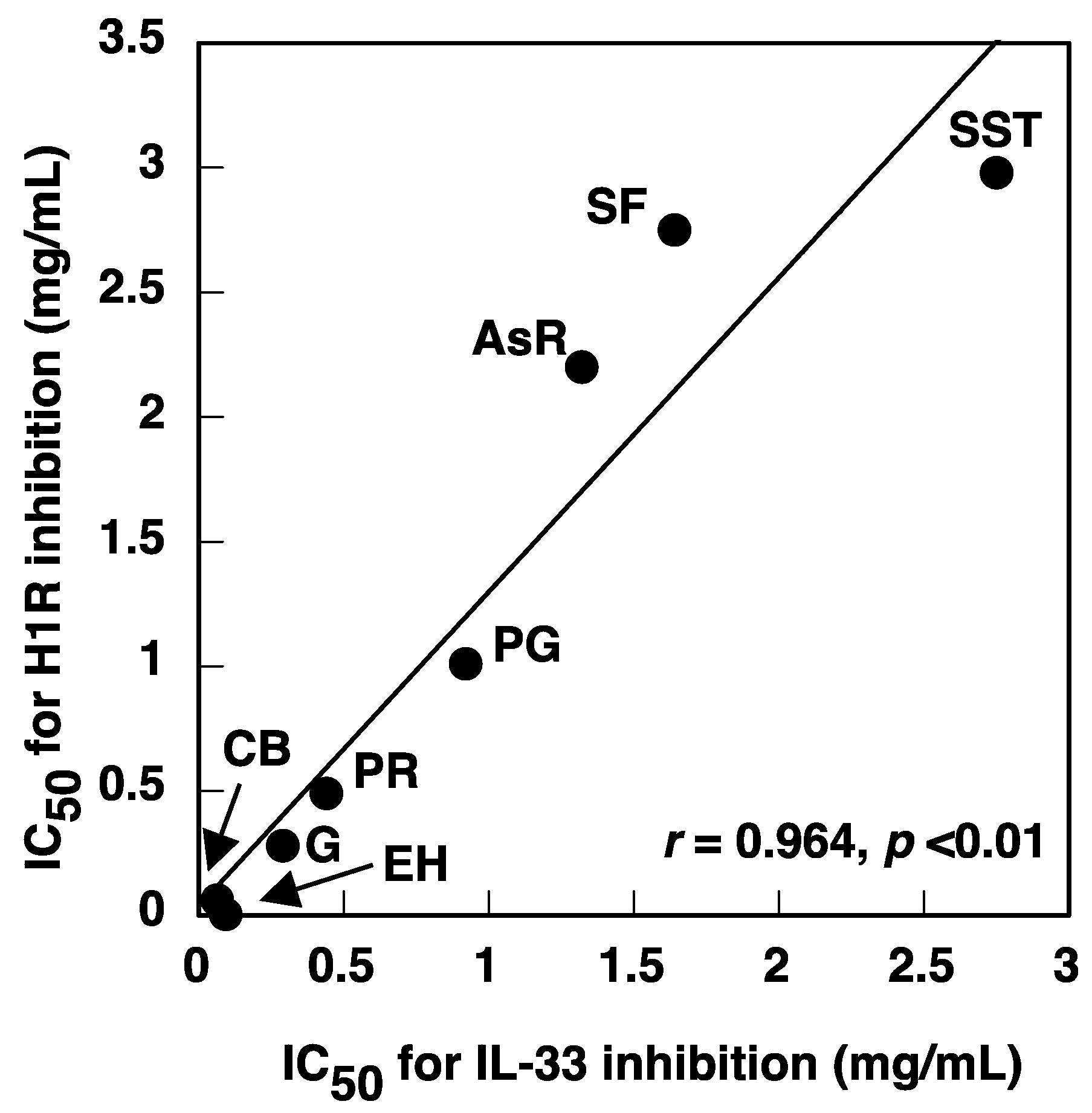
| Crude Drugs | IC50 Values to Inhibit IL-33 Gene Expression (mg/mL) | IC50 Values to Inhibit H1R Gene Expression (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| SST | 2.75 | 2.98 |
| Ephedra herb | 0.093 | 0.0047 |
| Cinnamon bark | 0.064 | 0.062 |
| Processed ginger | 0.92 | 1.01 |
| Asiasarum root | 1.32 | 2.20 |
| Peony root | 0.44 | 0.49 |
| Schisandra fruit | 1.64 | 2.75 |
| Glycyrrhiza | 0.29 | 0.28 |
| Pinellia tuber | NO * | NO * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakano, S.; Yamamoto, S.; Esu, T.; Naniwa, S.; Konishi, Y.; Wakugawa, T.; Kitamura, Y.; Fujii, T.; Kamimura, S.; Fukui, H.; et al. Effects of Syo-seiryu-to and Its Constituent Crude Drugs on Phorbol Ester-Induced Up-Regulation of IL-33 and Histamine H1 Receptor mRNAs in Swiss 3T3 and HeLa Cells. Allergies 2021, 1, 163-175. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies1030015
Nakano S, Yamamoto S, Esu T, Naniwa S, Konishi Y, Wakugawa T, Kitamura Y, Fujii T, Kamimura S, Fukui H, et al. Effects of Syo-seiryu-to and Its Constituent Crude Drugs on Phorbol Ester-Induced Up-Regulation of IL-33 and Histamine H1 Receptor mRNAs in Swiss 3T3 and HeLa Cells. Allergies. 2021; 1(3):163-175. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies1030015
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakano, Seiichi, Sayaka Yamamoto, Takako Esu, Shiho Naniwa, Yuki Konishi, Tomoharu Wakugawa, Yoshiaki Kitamura, Tatsuya Fujii, Seiichiro Kamimura, Hiroyuki Fukui, and et al. 2021. "Effects of Syo-seiryu-to and Its Constituent Crude Drugs on Phorbol Ester-Induced Up-Regulation of IL-33 and Histamine H1 Receptor mRNAs in Swiss 3T3 and HeLa Cells" Allergies 1, no. 3: 163-175. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies1030015
APA StyleNakano, S., Yamamoto, S., Esu, T., Naniwa, S., Konishi, Y., Wakugawa, T., Kitamura, Y., Fujii, T., Kamimura, S., Fukui, H., Takeda, N., & Mizuguchi, H. (2021). Effects of Syo-seiryu-to and Its Constituent Crude Drugs on Phorbol Ester-Induced Up-Regulation of IL-33 and Histamine H1 Receptor mRNAs in Swiss 3T3 and HeLa Cells. Allergies, 1(3), 163-175. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies1030015