Dynamic Failure Risk Assessment of Wastewater Treatment and Reclamation Plant: An Industrial Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bayesian Network
2.2. Dynamic Bayesian Network (DBN)
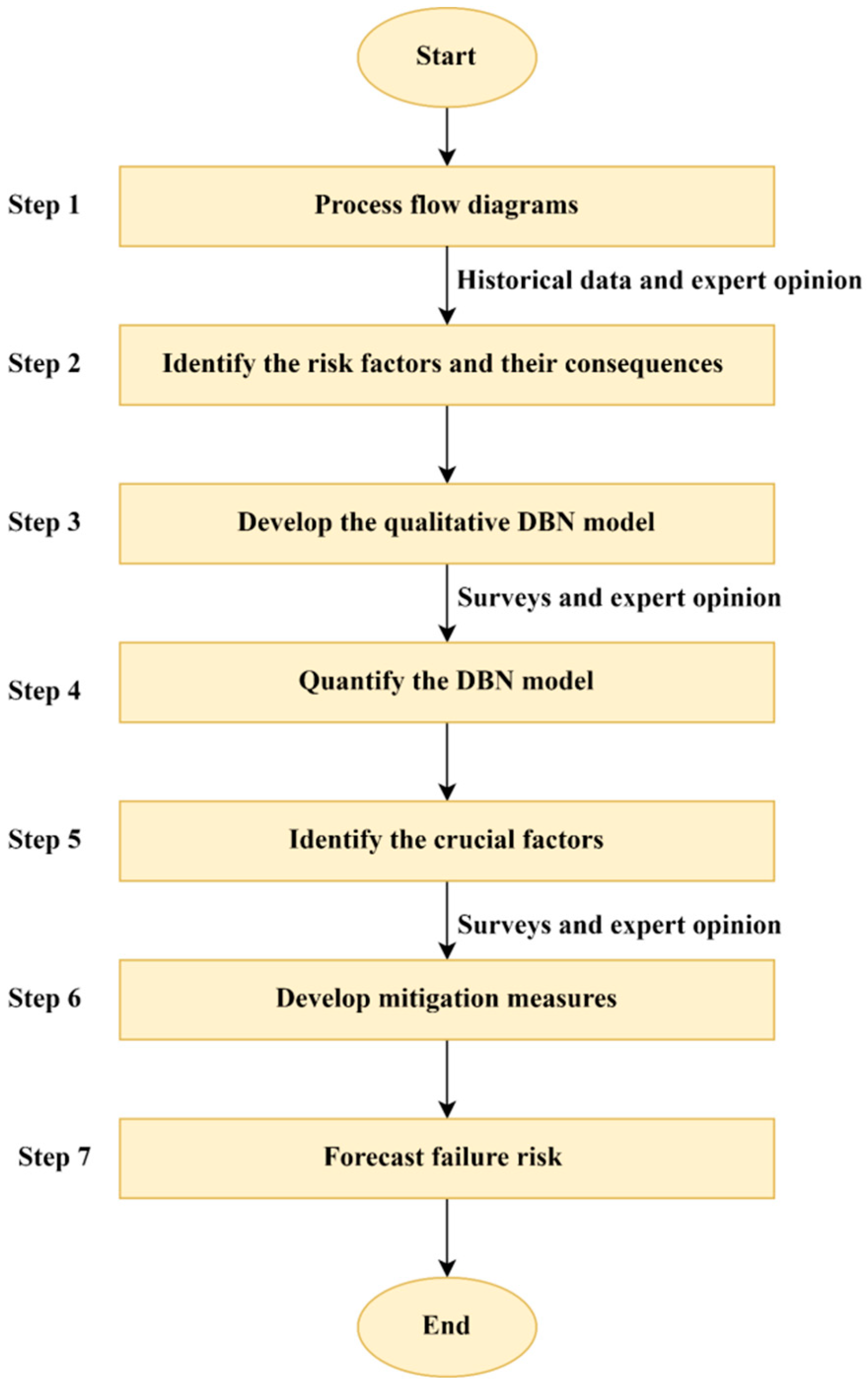
2.3. Proposed DBN-Based Methodology
- Without the fouling, corrosion, scale and biofilm in the facilities of an industry (C1)
- Long-term creation of the fouling, corrosion, scale and biofilm in the industrial facilities (C2)
- Short-term and severe creation the fouling, corrosion, scale and biofilm in the industrial facilities (C3)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Case Study
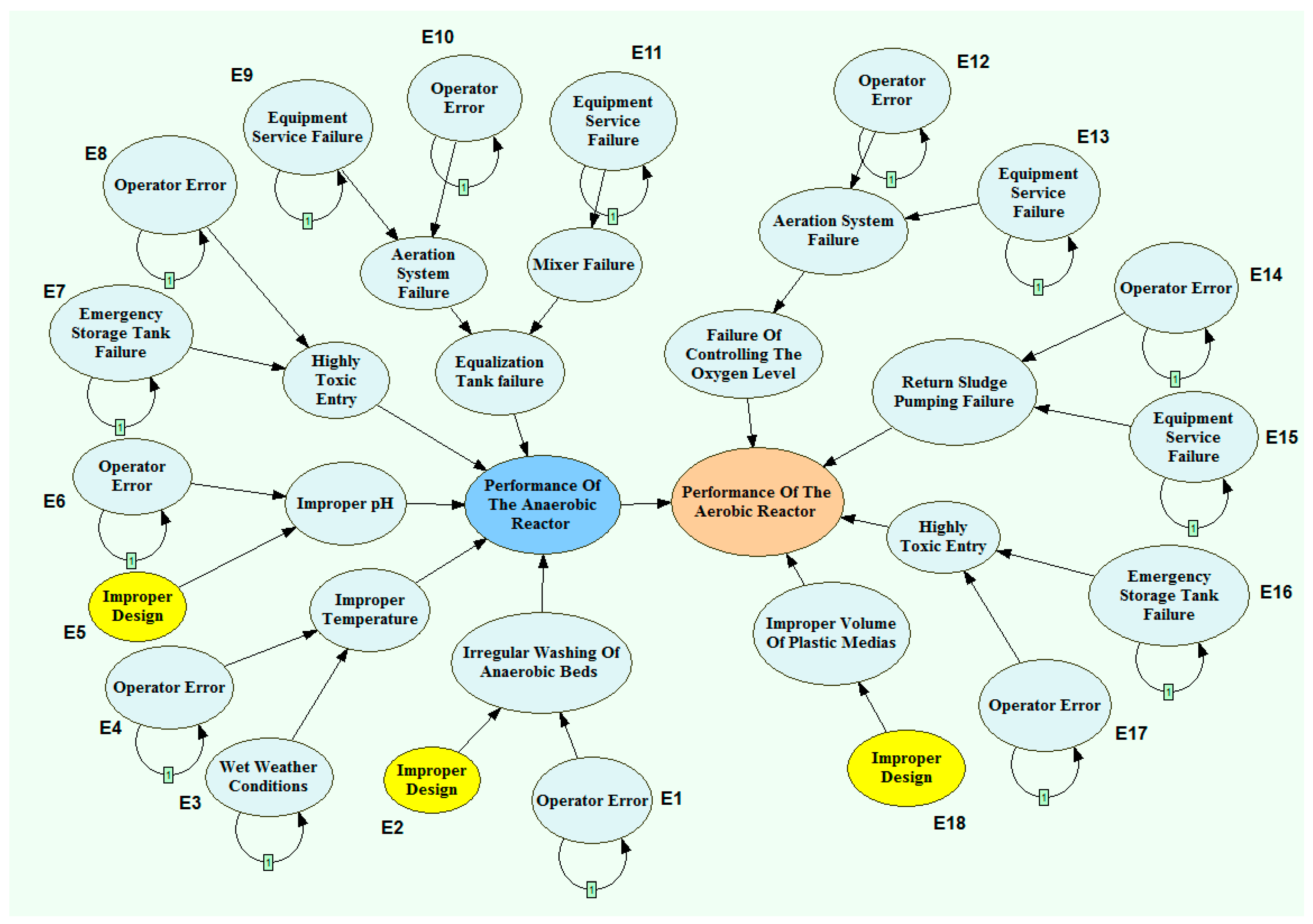
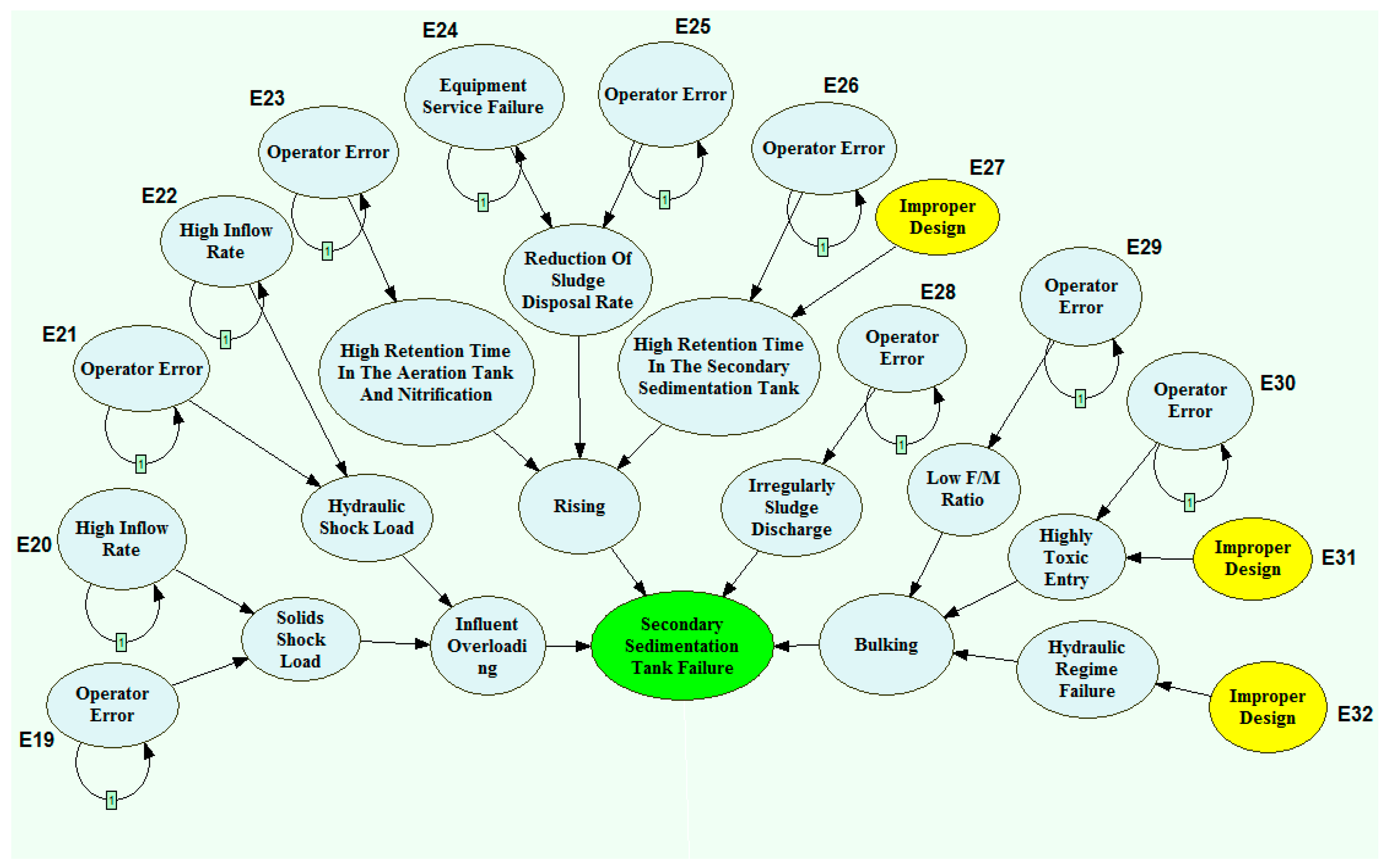
3.2. Qualitative Model Development
3.3. Prior and Conditional Probability Estimation
3.4. Quantitative Analysis of the Model
3.5. The Past Period Risk (2016–2021)
3.6. The Future Period Risk (2022–2030)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Question 1 | How can the performance of emergency storage tank lead to high toxic entry? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (t = 0) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Emergency storage tank | Success | Failure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0.6 | 0.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Question 2 | How can the performance of emergency storage tank lead to high toxic entry with an interval of one year? (t ≥ 1) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Emergency storage tank (t = 0) | Success | Failure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Emergency storage tank (t − 1) | Success | Failure | Success | Failure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 0 | 0.7 | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Question 3 | How can the operator function lead to high toxic entry? (t = 0) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operator function | Success | Failure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0.7 | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Question 4 | How can the operator function lead to high toxic entry with an interval of one year? (t ≥ 1) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operator function (t = 0) | Success | Failure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operator function (t − 1) | Success | Failure | Success | Failure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Question 5 | According to the effects of nodes E16 and E17, determine the percentages of high toxic entry node. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Emergency storage tank | Success | Failure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operator function | Success | Failure | Success | Failure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| High toxic entry | Success | Failure | Success | Failure | Success | Failure | Success | Failure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0.97 | 0.03 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Question 6 | According to the effects of nodes controlling the oxygen level, return sludge pumping, toxic entry, volume of plastic medias, determine the percentages of aerobic reactor performance. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Controlling the oxygen level | Success | Failure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Return sludge pumping | Success | Failure | Success | Failure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxic entry | Success | Failure | Success | Failure | Success | Failure | Success | Failure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Volume of plastic media | S | F | S | F | S | F | S | F | S | F | S | F | S | F | S | F | ||||||||||||||||
| Aerobic reactor performance | S | F | S | F | S | F | S | F | S | F | S | F | S | F | S | F | S | F | S | F | S | F | S | F | S | F | S | F | S | F | S | F |
| Success | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Failure | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 0 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.9 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
References
- Lotfi, K.; Bonakdari, H.; Ebtehaj, I.; Delatolla, R.; Zinatizadeh, A.A.; Gharabaghi, B. A Novel Stochastic Wastewater Quality Modeling Based on Fuzzy Techniques. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2020, 18, 1099–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afrad, M.S.I.; Monir, M.B.; Haque, M.E.; Barau, A.A.; Haque, M.M. Impact of Industrial Effluent on Water, Soil and Rice Production in Bangladesh: A Case of Turag River Bank. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2020, 18, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranade, V.V.; Bhandari, V.M. Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Aslani, H.; Nabizadeh, R.; Alimohammadi, M.; Mesdaghinia, A.; Nadafi, K.; Nemati, R.; Ghani, M. Disinfection of Raw Wastewater and Activated Sludge Effluent Using Fenton like Reagent. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2014, 12, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baghapour, M.A.; Nasseri, S.; Djahed, B. Evaluation of Shiraz Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluent Quality for Agricultural Irrigation by Canadian Water Quality Index (CWQI). Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2013, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganoulis, J. Risk Analysis of Water Pollution; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wezel, A.P.; Van Den Hurk, F.; Sjerps, R.M.A.; Meijers, E.M.; Roex, E.W.M.; Thomas, L. Impact of Industrial Waste Water Treatment Plants on Dutch Surface Waters and Drinking Water Sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchamp, N.; Lence, B.J.; Bouchard, C. Technical Hazard Identification in Water Treatment Using Fault Tree Analysis. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2010, 37, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourouni, K. Availability Assessment of a Reverse Osmosis Plant: Comparison between Reliability Block Diagram and Fault Tree Analysis Methods. Desalination 2013, 313, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheriyoun, M.; Moradinejad, S. Reliability Analysis of a Wastewater Treatment Plant Using Fault Tree Analysis and Monte Carlo Simulation. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piadeh, F.; Ahmadi, M.; Behzadian, K. Reliability Assessment for Hybrid Systems of Advanced Treatment Units of Industrial Wastewater Reuse Using Combined Event Tree and Fuzzy Fault Tree Analyses. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 210, 958–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabesh, M.; Roozbahani, A.; Hadigol, F.; Ghaemi, E. Risk Assessment of Water Treatment Plants Using Fuzzy Fault Tree Analysis and Monte Carlo Simulation. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Civ. Eng. 2022, 46, 643–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, E.; Khakzad, N.; Cozzani, V.; Reniers, G. Safety Analysis of Process Systems Using Fuzzy Bayesian Network (FBN). J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2019, 57, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Analouei, R.; Taheriyoun, M.; Safavi, H.R. Risk Assessment of an Industrial Wastewater Treatment and Reclamation Plant Using the Bow-Tie Method. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tušer, I.; Oulehlová, A. Risk Assessment and Sustainability of Wastewater Treatment Plant Operation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.I.; Amyotte, P.R.; Amin, M.T. Advanced Methods of Risk Assessment and Management: An Overview. In Methods in Chemical Process Safety; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanea, A.M.; Gheorghe, M.; Hanea, R.; Ababei, D. Non-Parametric Bayesian Networks for Parameter Estimation in Reservoir Simulation: A Graphical Take on the Ensemble Kalman Filter (Part I). Comput. Geosci. 2013, 17, 929–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, G.; Demissie, G.; Sadiq, R.; Tesfamariam, S. Integrating Failure Prediction Models for Water Mains: Bayesian Belief Network Based Data Fusion. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2015, 85, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbari, M.J.; Tabesh, M.; Roozbahani, A. Risk Assessment Model to Prioritize Sewer Pipes Inspection in Wastewater Collection Networks. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 190, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, E.; Azadeh, A.; Khakzad, N.; Aliabadi, M.M.; Mohammadfam, I. Dynamic Safety Assessment of Natural Gas Stations Using Bayesian Network. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 36, 1171–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiee Neyestanak, J.; Roozbahani, A. Comprehensive Risk Assessment of Urban Wastewater Reuse in Water Supply Alternatives Using Hybrid Bayesian Network Model. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 5049–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammouh, O.; Gardoni, P.; Cimellaro, G.P. Probabilistic Framework to Evaluate the Resilience of Engineering Systems Using Bayesian and Dynamic Bayesian Networks. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2020, 198, 106813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhong, P.A.; An, R.; Zhu, F.; Xu, B. Risk Analysis for Real-Time Flood Control Operation of a Multi-Reservoir System Using a Dynamic Bayesian Network. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 111, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fam, M.L.; He, X.; Konovessis, D.; Ong, L.S. Using Dynamic Bayesian Belief Network for Analysing Well Decommissioning Failures and Long-Term Monitoring of Decommissioned Wells. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2020, 197, 106855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawsey, W.J.; Minsker, B.S.; Amir, E. Real Time Assessment of Drinking Water Systems Using a Dynamic Bayesian Network. In Restoring Our Natural Habitat-Proceedings of the 2007 World Environmental and Water Resources Congress, Tampa, Florida, 15–19 May 2007; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2007; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, T.; Ge, W.; Wei, D.; Li, H. Risk Analysis of Earth-Rock Dam Breach Based on Dynamic Bayesian Network. Water 2019, 11, 2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Huang, M. Modeling of Wastewater Treatment Processes Using Dynamic Bayesian Networks Based on Fuzzy PLS. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 92129–92140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, C.; Shi, X.; Liu, H. Effluent Quality Prediction in Papermaking Wastewater Treatment Processes Using Dynamic Bayesian Networks. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 282, 125396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yari, M.; Monjezi, M.; Bagherpour, R. A Novel Investigation in Blasting Operation Management Using Decision Making Methods. Rud. Geol. Naft. Zb. 2014, 29, 69–79. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Suntrayuth, S.; Su, J. A Comprehensive Evaluation Method for Industrial Sewage Treatment Projects Based on the Improved Entropy-TOPSIS. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yari, M.; Bagherpour, R.; Khoshouei, M.; Pedram, H. Investigating a Comprehensive Model for Evaluating Occupational and Environmental Risks of Dimensional Stone Mining. Rud. Geol. Naft. Zb. 2020, 35, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekmekcioğlu, Ö.; Koc, K.; Özger, M. Stakeholder Perceptions in Flood Risk Assessment: A Hybrid Fuzzy AHP-TOPSIS Approach for Istanbul, Turkey. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 60, 102327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yari, M.; Bagherpour, R.; Almasi, N. An Approach to the Evaluation and Classification of Dimensional Stone Quarries with an Emphasis on Safety Parameters. Rud. Zb. 2016, 31, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayaty, M.; Tavakoli Mohammadi, M.R.; Rezaei, A.; Shayestehfar, M.R. Risk Assessment and Ranking of Metals Using FDAHP and TOPSIS. Mine Water Environ. 2014, 33, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, K.; Fuller, M.; Stanhope, T.; Stoddart, A. Exploring the Use of a Sanitation Safety Plan Framework to Identify Key Hazards in First Nations Wastewater Systems. Water 2021, 13, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ma, Q.; Cai, B.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, C. Risk Assessment on Deepwater Drilling Well Control Based on Dynamic Bayesian Network. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 149, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsuk, M.E.; Stow, C.A.; Reckhow, K.H. A Bayesian Network of Eutrophication Models for Synthesis, Prediction, and Uncertainty Analysis. Ecol. Modell. 2004, 173, 219–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.A.; Jakeman, A.J.; Barreteau, O.; Borsuk, M.E.; ElSawah, S.; Hamilton, S.H.; Henriksen, H.J.; Kuikka, S.; Maier, H.R.; Rizzoli, A.E.; et al. Selecting among Five Common Modelling Approaches for Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management. Environ. Model. Softw. 2013, 47, 159–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.T.; Khan, F.; Imtiaz, S. Fault Detection and Pathway Analysis Using a Dynamic Bayesian Network. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 195, 777–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, Q.; Liu, Z.; Tian, X. A Dynamic Bayesian Networks Modeling of Human Factors on Offshore Blowouts. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2013, 26, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.T.; Khan, F.; Imtiaz, S. Dynamic Availability Assessment of Safety Critical Systems Using a Dynamic Bayesian Network. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2018, 178, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.P. Dynamic Bayesian Networks: Representation, Inference and Learning. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Berkeley, Berkeley, CA, USA, 2002; pp. 1–281. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, M.T.; Imtiaz, S.; Khan, F. Process System Fault Detection and Diagnosis Using a Hybrid Technique. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2018, 189, 191–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraaijeveld, P.; Druzdzel, M.J. GeNIeRate: An Interactive Generator of Diagnostic Bayesian Network Models. In Proceedings of the 16th International Workshop on Principles of Diagnosis, Monterey, CA, USA, 1–3 June 2005; pp. 175–180. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Z.; Zhao, P. Based on Fuzzy Bayesian Network of Oil Wharf Handling Risk Assessment. Math. Probl. Eng. 2016, 2016, 6532691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.T. An Integrated Methodology for Fault Detection, Root Cause Diagnosis, and Propagation Pathway Analysis in Chemical Process Systems. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2021, 4, 100187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spellman, F.R.; Frank, R. Handbook of Water and Wastewater Treatment Plant Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Judd, S.; Jefferson, B. (Eds.) Membranes for Industrial Wastewater Recovery and Re-Use; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Ji, J.; Khan, F.; Ding, L.; Tong, Q. A Novel Fuzzy Dynamic Bayesian Network for Dynamic Risk Assessment and Uncertainty Propagation Quantification in Uncertainty Environment. Saf. Sci. 2021, 141, 105285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchobanoglous, G.; Burton, F.L.; Stensel, H.D. Wastewater Engineering: Treatment and Reuse; Metcalf & Eddy/Aecom: Dallas, TX, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Spellman, F.R. Handbook of Water and Wastewater Treatment Plant Operations, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeen, S.; Sufaid Khan, M.; Khattak, R.; Zekker, I.; Burlakovs, J.; Rubin, S.S.d.; Ghangrekar, M.M.; Kallistova, A.; Pimenov, N.; Zahoor, M.; et al. Palladium-Supported Zirconia-Based Catalytic Degradation of Rhodamine-b Dye from Wastewater. Water 2021, 13, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, N.U.; Ullah, I.; Alam, S.; Khan, M.S.; Shah, L.A.; Zekker, I.; Burlakovs, J.; Kallistova, A.; Pimenov, N.; Vincevica-Gaile, Z.; et al. Activated Ailanthus Altissima Sawdust as Adsorbent for Removal of Acid Yellow 29 from Wastewater: Kinetics Approach. Water 2021, 13, 2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, A.; Khan, M.S.; Alam, S.; Zekker, I.; Burlakovs, J.; dC Rubin, S.S.; Bhowmick, G.D.; Kallistova, A.; Pimenov, N.; Zahoor, M. Synthesis and Characterization of Pd-Ni Bimetallic Nanoparticles as Efficient Adsorbent for the Removal of Acid Orange 8 Present in Wastewater. Water 2021, 13, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



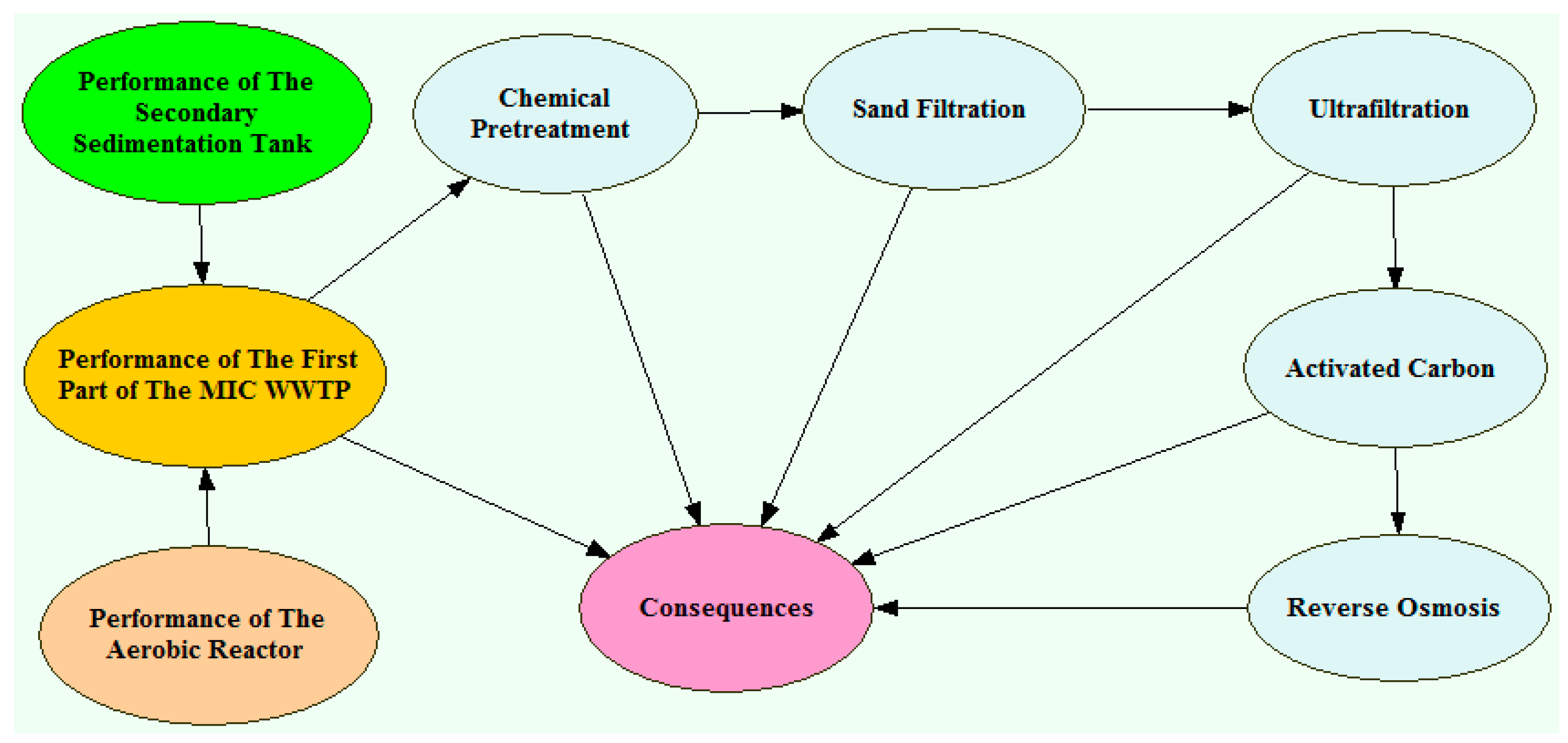
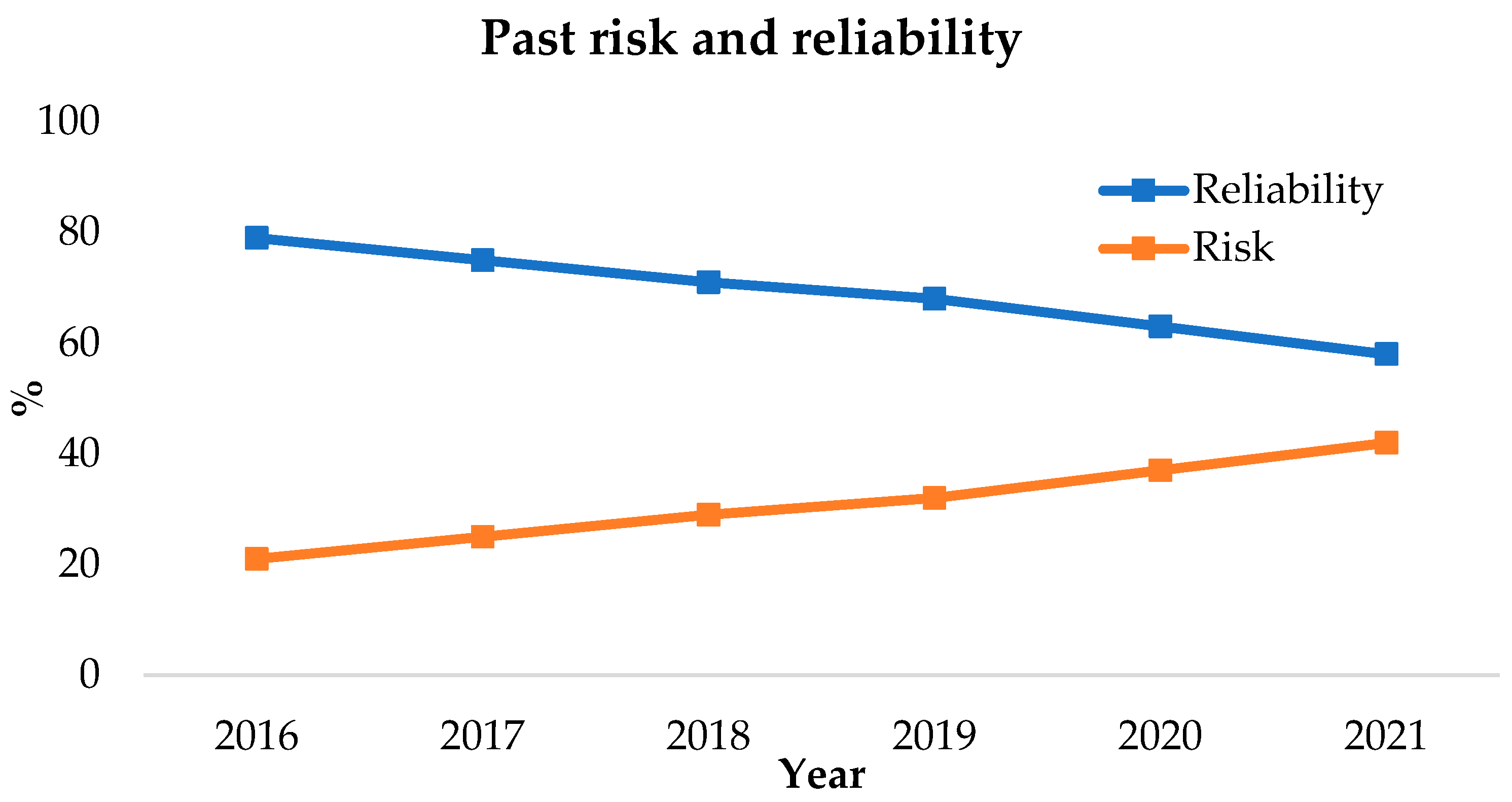

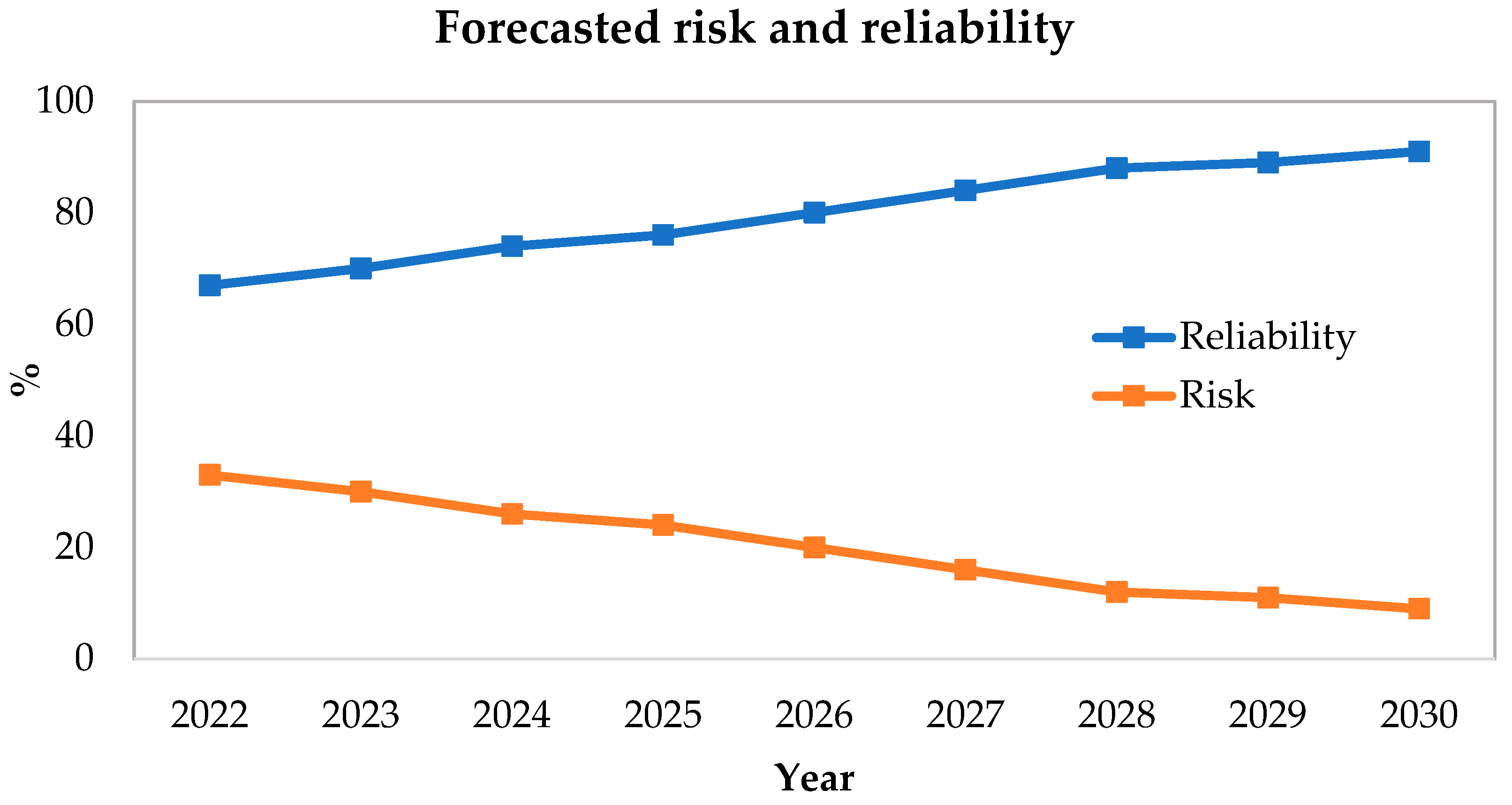
| C | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Success | Failure | ||
| B | Success | Failure | Success | Failure |
| Success | 1 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.1 |
| Failure | 0 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.9 |
| High Toxic Entry Related to the Secondary Sedimentation Tank | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operator Error | Success | Failure | ||
| Improper Design | Success | Failure | Success | Failure |
| Success | 0.99 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0 |
| Failure | 0.01 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 1 |
| E1 (t = 0) | E1 (t = 1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Success | Failure | ||
| Success | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.10 |
| Failure | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.90 |
| Parameter | Total Samples | Minimum (mg/L) | Maximum (mg/L) | Average (mg/L) | Standard Deviation (mg/L) | Standard Effluent Limit (mg/L) | Removal Rate (mg/L) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 2021 | 2016 | 2021 | 2016 | 2021 | 2016 | 2021 | 2016 | 2021 | 2016 | 2021 | ||
| CODIN | 350 | 382 | 345 | 402 | 1560 | 1680 | 455 | 534 | 53 | 49 | 60 | 91 | 79 |
| CODOUT | 15 | 30 | 337 | 440 | 40 | 110 | 22 | 27 | |||||
| BODIN | 280 | 220 | 234 | 210 | 850 | 780 | 310 | 256 | 48 | 38 | 30 | 92 | 67 |
| BODOUT | 10 | 18 | 80 | 120 | 25 | 83 | 18 | 26 | |||||
| TSSIN | 293 | 320 | 234 | 334 | 806 | 850 | 348 | 402 | 44 | 53 | 40 | 89 | 75 |
| TSSOUT | 13 | 22 | 300 | 402 | 38 | 99 | 26 | 36 | |||||
| Risk Factors | Proposed Risk-Mitigation Measures |
|---|---|
| Operator errors |
|
| Improper design |
|
| Equipment service failure |
|
| Wet weather conditions |
|
| Time | Success (%) | Failure (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2022 | 63 | 37 |
| 2023 | 63 | 37 |
| 2024 | 65 | 35 |
| 2025 | 72 | 28 |
| 2026 | 75 | 35 |
| 2027 | 80 | 20 |
| 2028 | 90 | 10 |
| 2029 | 95 | 5 |
| 2030 | 95 | 5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Analouei, R.; Taheriyoun, M.; Amin, M.T. Dynamic Failure Risk Assessment of Wastewater Treatment and Reclamation Plant: An Industrial Case Study. Safety 2022, 8, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/safety8040079
Analouei R, Taheriyoun M, Amin MT. Dynamic Failure Risk Assessment of Wastewater Treatment and Reclamation Plant: An Industrial Case Study. Safety. 2022; 8(4):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/safety8040079
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnalouei, Razieh, Masoud Taheriyoun, and Md Tanjin Amin. 2022. "Dynamic Failure Risk Assessment of Wastewater Treatment and Reclamation Plant: An Industrial Case Study" Safety 8, no. 4: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/safety8040079
APA StyleAnalouei, R., Taheriyoun, M., & Amin, M. T. (2022). Dynamic Failure Risk Assessment of Wastewater Treatment and Reclamation Plant: An Industrial Case Study. Safety, 8(4), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/safety8040079






