Abstract
Firefighters act within extreme environments, work under threatening conditions and are often exposed to goal conflicts (e.g., self-protection vs. mission objective) during their missions. However, what are the consequences of these safety and task goal conflicts, and what countermeasures could help to reduce their occurrence? In an online survey, 340 firefighters were asked about goal conflicts, risky decision making, debriefings and the frequency of difficulties in teamwork during firefighting. Associations between the survey variables were determined by multivariate regression and mediation analyses. Data show that goal conflicts were associated with risky decision making and unsafe acts. Furthermore, debriefings were associated with fewer goal conflicts, as mediated by less-frequent difficulties with teamwork (communication, leadership and shared mental models). Though limited by the cross-sectional design of our study, the results provide evidence that debriefing is a valuable tool to reduce difficulties experienced with teamwork on missions and therefore reduce the occurrence of conflicting goals. Fewer goal conflicts are associated with a decrease in unsafe decisions and, thus, a safer working environment for firefighters. Accordingly, it is recommended to conduct debriefings, with an increased focus on team aspects.
1. Introduction
In numerous organizations and use cases, the goals of safety and work performance are not always in harmony. This work–safety tension can especially be experienced at work. Imagine that you have to observe a number of safety-related rules at your workplace. For example, certain points on a checklist must be completed before you can start a machine. If you work through each item in detail, it will cost you a lot of time and reduce your productivity. However, violating the rules could endanger your safety. In such a case, discussions with colleagues and superiors, for example, could bring about a decision on how the safety regulations can be better realized. For the fire service, as a so-called high-risk organization, it is not possible to stop work and discuss the procedure in detail as decisions must be made quickly. Even under the most difficult conditions, firefighters have to decide and try to get out of the situation safely for everyone involved.
Unfortunately, this is not always the case, as the following statistics for occupational accidents show. The accident statistics of the firefighters’ accident insurance funds (FUK) in Germany, for example, show that accidents repeatedly occur in the course of fire department activities, especially during firefighting. In the area of responsibility of the FUK for central Germany, as many as 39% of the reportable accidents in 2019 were attributable to firefighting [1]. This is the largest proportion of accidents relating to a single field of activity. The remaining percentages are distributed among activities such as training and instruction or technical assistance.
The Australasian Fire and Emergency Service Authorities Council reported that in the 2019/2020 bushfire season a total of nine firefighters died [2]. Likewise, in the United States, 18 firefighters died from injuries sustained on fire missions in 2019 [3]. Altogether, the likelihood of sustaining an injury during firefighting is higher than in any other fire department activity. In 2019, 39% of all reported accidents in the United States occurred on firefighting missions [4], which is the same proportion as in Germany.
Not only on firefighting missions, but operations in confined spaces also repeatedly lead to fatal accidents. In an Alert from 1986, the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) pointed out that many people are injured or die in such accidents—60% of them are would-be rescuers [5].
Examples from accident reports provide illustrative evidence of the accidents behind the numbers. For example, one report described a mission in the United States in March 2018 during which firefighters suffered burns. Due to a change in the situation with heavy flames and smoke, part of the roof of the two-story apartment building collapsed. Because of the danger, the commander instructed the firefighters to retreat. However, this decision was made too late, causing the firefighters to sustain injuries [6]. During another mission, a firefighter injured his forearm due to a broken windowpane. Despite this injury, the mission continued. Only after approximately 10 min after the accident did the squad member inform the squad leader of his injury, and the mission was immediately stopped. Delayed feedback like this, which leads to delayed decisions, can cause serious problems during missions and endanger the safety of the responders [7].
The numbers and examples show that risky decision-making plays an important role in accidents on firefighting missions and other high-risk situations related to firefighting operations even though there are safety service regulations [8,9] and strategies that are learned in training to behave safely in missions. The term “decision risk” means “the extent to which there is uncertainty about whether potentially significant and/or disappointing outcomes of decisions will be realized” [10] (p. 10). The uncertainty about the outcome of the situation is thereby significantly linked to the perceived risk of the situation [11,12]. Risky decision making refers to risk behavior “that may be characterized by the degree of risk associated with the decisions made” [10] (p. 11). Based on these explanations, Sitkin and Pablo characterize decisions as risky when (a) the expected outcome is uncertain, (b) the goals of the decision are difficult to achieve, and/or (c) the possible outcomes could have extreme consequences [10]. The risk situations, the decisions of firefighters and the behavior they show can be very well classified as such.
The purpose of this study is to analyze conflicting goals during firefighting missions based on a tension between work and safety that leads to risky decision making in firefighting. Furthermore, we are interested in analyzing the effects of possible countermeasures, that is, strategies to reduce goal conflicts during missions. Therefore, we focus on debriefings and analyze their relation to problems experienced with communication, leadership and shared mental models within firefighting teams during missions and how these in turn are related to the emergence of goal conflicts during firefighting.
1.1. Goal Conflicts during Missions
A goal conflict occurs in situations when two or more goals, e.g., acting fast and making no mistakes, are experienced as incompatible and put the acting person in a dilemma [13]. If this takes place at work or on a firefighting mission, an example of a goal conflict is the tension experienced between successfully completing the task and one’s own safety. This means tension can be experienced between completing the task and complying with safety service regulations. How employees then behave individually is often dependent not only on their attitudes or personality traits [10,14,15] but also on the safety culture practiced in the company [16]. If the company’s daily routines reflect the importance of profit and productivity over compliance with safety regulations, employees will behave accordingly and will take greater risks in the workplace [13]. Studies already indicate that aspects of work–safety tension (e.g., time pressure and safety rules) explain a significant portion of the variance in several safety-related driving behaviors while at work, such as traffic violations and unintentional errors [17].
The conflicting goals that firefighters experience during missions cannot simply be explained by the fact that their job is to navigate and make decisions in opaque and complex situations. The often-mentioned gut feeling from which firefighters sometimes make decisions falls under the term naturalistic decision making (NDM) and especially helps experienced firefighters because they are able to compare cues from the current situation to previous situations and to develop adequate goal-oriented strategies. This decision behavior is based on the recognition-primed decision strategy and requires mainly tacit knowledge of the task forces [18,19]. The goal conflicts experienced, on the other hand, tend to be based on different situational demands on the firefighters, resulting in the feeling that they cannot successfully solve the task without at the same time violating the safety service regulations or putting themselves and their colleagues in a dangerous situation. The following brief descriptions of situations, which we extracted from personal interviews with firefighters and accident reports, illustrate the conflicting goals, the work–safety tension experienced and the risky decisions.
In an interview, a situation was reported during which essential safety standards were not met. There was no functioning radio communication, no briefing on the situation, no (adequate) safety squad and no functioning breathing apparatus monitoring. The commanding officer nevertheless instructed the responders to proceed as an attack squad into the burning building. The firefighters reported that they felt unsafe in the situation but were over-motivated to complete their task and, also, did not want to contradict the instruction, so they proceeded into the building despite the safety gaps. There was a goal conflict experienced here between achievement of the mission goal and self-protection due to communication problems and problems with the leader. Although a risky decision was made in the squad to favor quick action over safe action, fortunately, in this case no accident occurred, and everything went well.
Another reported situation also shows work–safety tension and the conflict between self-protection and reaching the mission goal, resulting in a risky decision, again, with, fortunately, a good outcome. A firefighter described that he and his team had to work under a vat of molten steel whose mechanics they did not know, so they could not assess when the vat would tip or when the steel would overflow. The firefighter felt unsafe and had an uncomfortable feeling about the job, but, despite this, one team member worked under the vat until the fire was extinguished.
A last example of work–safety tension did not result in a risky decision but left the responders with very negative feelings. A firefighter described how he and the rest of the attack squad had to retreat when the fire area became too hot and the situation too dangerous. He described feelings of powerlessness and stress, as the motivation was great to accomplish the task (firefighting) and the required knowledge was also available, but ultimately the decision was made that their own safety was at risk and therefore the task could not be completed.
As can be seen from the situations described here, the nature of conflicting goals are very industry-specific. It is therefore hardly surprising that theories and empirical findings on conflicting goals at work and work–safety tension have so far been studied in only a few and specific areas, primarily in the fields of production and construction [20,21,22]. As expressed in the aforementioned interviews, goal conflicts and work–safety tension are also relevant for firefighters in firefighting missions. Since there is yet very little empirical evidence, we believe that it is important for safe and successful work in firefighting to investigate tensions between work and safety and to analyze possible goal conflicts and their effects on risky decision making in missions. This is even more important, as in the case of conflicting goals in firefighting, tension between one’s own safety in the mission and the rescue of others seems to be common, so that the pressure on the safety-critical behavior increases. Above all, there might be a tendency to make risky decisions if this unsafe action has been successful in the past (see also outcome history as a predictor for risk behavior [23,24,25]) or if others have been successful with it, since one’s own risk perception seems to be related to personal or even vicarious accident experience [26,27].
1.2. Debriefings after Missions
A debriefing, also called an ‘after-action review’ [28], is a problem-solving process to promote learning after exercises or missions [29]. Such after-action reviews can take place in addition to, for example, the fire department’s regular, more technical mission debriefings. In a post-mission discussion, the team’s strengths and weaknesses are identified and discussed by the team itself with the help of the team leader, and options are explored to solve possible problems. Thus, the focus of the debriefing is not only on the technical details and outcome of the mission, but also on the teamwork aspects, i.e., the teamwork process and nontechnical skills, which is essential for improving team performance for future missions [30,31]. Such a debriefing has the advantage that it can be integrated into the fire department’s regular, more technical mission debriefings [32] and supports informal learning [33].
More successful teams, compared to less successful teams, use debriefings and tend to collectively reflect on their past performance and self-correct after a critical event [34,35]. Emphasizing teamwork aspects results in improved shared mental models, situational awareness of team members and interpositional knowledge within the team [31,36,37]. Debriefings after a mission increase the shared knowledge structures of team members and their leaders [38,39] and improve the accuracy of team members’ mental models as they learn who had what assumptions during the mission, whether or not their own assumptions were correct, what happened in the team at critical moments, what goals did the leader have, and who did what and why [40]. When team members develop and analyze their strategies of action in debriefings, a process of team self-correction occurs. This process leads to the strengthening of shared mental models through explanations and expectations regarding the task and a better understanding of the information needs of the other team members and leaders. This promotes information sharing, communication processes, decision making and coordinated action execution within the team and increases team performance in missions [31,37]. The improvement in team and situational understanding of team members and leaders and the facilitated coordination leading to perfect interaction within the team and with leaders can lead to fewer safety-critical situations in missions, resulting in a decrease in goal conflicts and work–safety tension (during which unsafe behavior or even a violation of rules could occur) [37,41,42].
When a debriefing is guided and emphasizes team self-correction, teams have been shown to have more accurate shared mental models, better performance and a more effective teamwork process than both control groups and teams that received a more traditional, chronologically structured debriefing ([35,37] see also [43]).
1.3. Hypotheses
Studies conducted within other industries [17,20,21,22] demonstrate that goal conflicts at work and during missions lead to a strong experience of work–safety tension and—as a result—to risky decision making and unsafe acts. The occurrence of goal conflicts in firefighting missions was supported by reports within our interviews with fire fighters. We assume that goal conflicts and tensions between work and safety also occur during firefighting missions and that they significantly impact risky decision making during missions.
Hypothesis 1 (H1).
The experience of goal conflicts in firefighting missions correlates significantly positively with risky decision-making strategies.
Research shows that debriefings promote mutual understanding in teams, improve coordination processes and communication structures, support team processes and decision making and help team members more easily understand the perspective of the leaders [31,36,37,38,39,40]. Based on this, we hypothesize that debriefings will also improve teamwork among firefighters, resulting in fewer problems with communication, leadership and shared mental models among teams in firefighting missions. Due to the lower incidence of teamwork problems in the three abovementioned aspects, we further assume that this results in fewer safety-critical situations and thus fewer goal conflicts during missions, which reduces work–safety tension. Accordingly, our second hypothesis is formulated as a mediation hypothesis and divided into three sub-hypotheses. It states that debriefing will lead to fewer conflicting goals in firefighting missions, mediated by fewer teamwork problems during missions. Figure 1 presents an overview of the conceptual model to be tested.
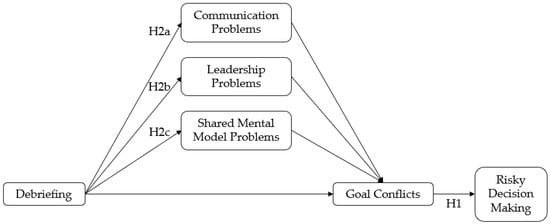
Figure 1.
Overview of the theorized model.
Hypothesis 2 (H2).
Debriefings lead to fewer goal conflicts in missions, mediated by less frequent difficulties in teamwork (communication (H2a), leadership (H2b) and shared mental models (H2c)).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Procedure and Sample
To test the hypotheses, an online questionnaire was applied in the context of a cross-sectional study. A total of 14 experienced firefighters completed a pretest. During the process, misleading formulations were discovered and corrected. For the main survey, participants were recruited through a professional fire department network, cooperating fire departments, social media, an advertisement in a fire service magazine and the authors’ personal and professional networks. As an incentive, participants could receive personalized feedback on some survey scales, if requested. Informed consent was obtained from each participant. Participants were informed about the purpose of the study and told that they could discontinue participation at any time. The study was approved in advance by the Institutional Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Psychology, Ruhr-University Bochum (No. 482).
The nationwide survey was available online between the 18 January and 25 May 2021. A total of 1135 participants accessed the survey, but only 755 started to answer the study variables. Participants were excluded due to (1) missing values on the study variables (n = 353), (2) not enough experience in firefighting (no firefighting missions or fewer than five firefighting missions combined with less than 2 years of experience) (n = 8), (3) no experience with debriefing (n = 3) or (4) logical mistakes (e.g., evaluation of the intensity of the stressor after having stated to not have experienced it yet; n = 51). The final sample consisted of 340 experienced firefighters (19 females). Their mean age was 40.19 years (SD = 11.09). They had an average of 20.82 years of work experience (SD = 10.81) and worked for volunteer fire departments (64.4%), professional fire departments (31.5%), plant fire departments (3.5%) or other (0.6%).
An a priori power analysis indicated that a sample size of 162 persons was required for mediation with an effect size of f = 0.26 [44]. That sample size was exceeded, indicating that moderate to small effects can also be found.
2.2. Measures
2.2.1. Goal Conflicts
For the assessment of goal conflicts, the authors developed two items which referred to the frequency of goal conflicts experienced in firefighting, meaning tension between (1) self-protection and achievement of the operational objective (“In firefighting missions, I experience conflicts between self-protection and achieving the operational objective.”) and (2) acting fast vs. acting safely (“In firefighting missions, I experience conflicts between acting fast and acting safely.”). The items were rated on a five-point Likert scale (1 = never to 5 = very often or always). The items were combined into a scale that showed good reliability (Spearman–Brown of 0.74).
2.2.2. Risky Decision Making
The measurement of risky decision making (DM) was conducted with the help of five items related to prioritizing and weighing options in firefighting. The items were developed by the authors based on the safety reports studied and the interviews conducted and are: “When deciding between multiple goals in firefighting missions, I make a gut decision on which one to pursue.” (DM1); “Under time pressure, I no longer prioritize goals in firefighting missions, but instead pursue the goals that I believe I can achieve the fastest.” (DM2); “Under time pressure, I work through the objectives in the firefighting mission in the same way as under ‘normal’ operational conditions.” (DM3); “In firefighting missions in which other people are at risk, I take a risk for my own safety in order to achieve my goals.” (DM4); “In firefighting missions in which colleagues are endangered, I take a risk for my own safety in order to achieve the objective.” (DM5). The items were rated on a five-point Likert scale (1 = totally disagree to 5 = totally agree). These items were evaluated separately because each asks about different risky decision-making situations.
2.2.3. Debriefing
Debriefing was measured with the help of three items which examined (1) how often debriefings were conducted after firefighting missions, (2) how adequate they were and (3) how good the opportunities to discuss experiences were. The items were developed by the authors and were rated on a five-point Likert scale (1 = never to 5 = very often or always) for item (1) and (1 = totally disagree to 5 = totally agree) for items (2) and (3). The items were combined into a scale that showed good reliability (Cronbach’s α of 0.81).
2.2.4. Teamwork Problems
The teamwork problems were assessed using the scale “Demands and Resources During Firefighting Missions” (see Appendix A Table A1) [45], which was developed based on 27 interviews with experienced firefighters and an analysis of mission reports.
Communication Problems were measured by six items referring to difficulties with communication experienced during firefighting. One example question is: “Information was not passed on at all or too late and/or there was no coordination. How often did this happen in the firefighting missions you have experienced so far?” The items were rated on a five-point Likert scale (1 = never to 5 = always). The items were combined into a scale that showed good reliability (Cronbach’s α of 0.82).
Leadership Problems were measured by four items referring to difficulties with leadership experienced during firefighting. One example question is: “One or more leaders behaved in a hectic, uncertain and/or uncoordinated manner. This created stress and was transmitted to others. How often did this happen in the firefighting missions you have experienced so far?” The items were rated on a five-point Likert scale (1 = never to 5 = always). The items were combined into a scale that showed good reliability (Cronbach’s α of 0.72).
Shared Mental Model Problems were measured by three items referring to difficulties experienced with shared mental models during firefighting. One example question is: “Firefighters lacked information on the approach and objective of the mission (e.g., work sequence; mission strategy). How often did this happen in the firefighting missions you have experienced so far?” The items were rated on a five-point Likert scale (1 = never to 5 = always). The items were combined into a scale that showed good reliability (Cronbach’s α of 0.65).
2.3. Analysis
As described, goal conflicts are hypothesized to significantly influence decision making (H1). Decision making was assessed with five single items, therefore, for analyzing H1, multivariate regression was used. Further, debriefing was hypothesized to influence goal conflicts that were significantly mediated by teamwork problems (H2a–c). To analyze this relationship, mediation analyses were used. The requirements for the application of mediation were met. Linearity, homoscedasticity and normal distribution were visually checked and met the criteria. Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS statistics package v26.
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Data
Data show that the studied goal conflicts occur during firefighting missions. Thereby, goal conflicts between acting fast and acting safely (M = 3.00, SD = 0.76) are experienced slightly more often than goal conflicts between self-protection and achievement of the operational objective (M = 2.65, SD = 0.80). Table 1 shows the means, standard deviations, skewness, kurtosis and intercorrelations of all study variables.

Table 1.
Intercorrelations between all study variables.
3.2. Hypothesis Testing
3.2.1. Hypothesis 1
In line with Hypothesis 1, the multivariate regression with z-standardized variables showed that risky decision making was significantly affected by the experience of goal conflicts (F(5, 334) = 7.60, p < 0.001, η2p = 0.102). Participants who experienced more goal conflicts more often decided what goal they were pursuing (DM1) based on their gut feeling, and they no longer prioritized goals but pursued the goals they believed could be achieved most quickly (DM2). Participants who experienced more goal conflicts could not work off their targets as under normal operating conditions (DM3). Furthermore, they risked their own safety in order to achieve their goals during firefighting missions in which strangers were endangered (DM4), and they took risks for their own safety in order to achieve their goals during firefighting missions in which their own comrades were endangered (DM5). All statistical parameters of the multivariate regression are presented in Table 2. The effect sizes can be interpreted as small to moderate.

Table 2.
Results of the multivariate regression with goal conflicts as predictor and risky decision making as outcome variables.
3.2.2. Hypotheses 2a, 2b and 2c
For all following analyses, the standardized coefficients are reported as well. For indirect effects, the fully standardized effects are reported.
Regarding Hypothesis 2a (debriefings lead to fewer goal conflicts, mediated by fewer communication problems) the a- (β = −0.32, SE = 0.04, t(338) = −6.01, p < 0.001) and b-path (β = 0.39, SE = 0.07, t(337) = 6.78, p < 0.001) of the mediation model with debriefing as the independent variable, communication problems experienced as mediator and goal conflicts as the dependent variable were significant (n = 340). The indirect effect describing the relationship between debriefing and goal conflicts mediated by communication problems was significant (β = −0.12; SE = 0.03, −0.18 < CI < −0.08). The total effect describing the association between debriefing and goal conflicts was significant (β = −0.21, SE = 0.05, t(338) = −3.73, p < 0.001). The direct effect was not significant (β = −0.08, SE = 0.05, t(337) = −1.50, p = 0.136) when controlling for the indirect effect (see Figure 2). These results indicate that the negative relationship between debriefings and goal conflicts is totally mediated by the experience of communication problems, supporting Hypothesis 2a.
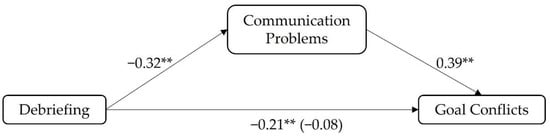
Figure 2.
Results of Hypothesis 2a: ** p < 0.001.
A similar pattern occurred with regard to Hypothesis 2b (debriefings lead to fewer goal conflicts mediated by fewer leadership problems). This time leadership problems were used as the mediator between debriefing and goal conflicts. The a- (β = −0.27, SE = 0.04, t(338) = −4.85 p < 0.001) and b-path (β = 0.33, SE = 0.06, t(337) = 5.86, p < 0.001) of the mediation model were significant. Again, the indirect effect which describes the association between debriefing and goal conflicts mediated by leadership problems was significant (β = −0.09; SE = 0.02, −0.14 < CI < −0.05) as was the total effect describing the association between debriefing and goal conflicts (β = −0.21, SE = 0.05, t(338) = −3.73, p < 0.001). The direct effect remained significant when controlling for the indirect effect (β = −0.12, SE = 0.05, t(337) = −2.10, p = 0.036) (see Figure 3) indicating a partial mediation and supporting Hypothesis 2b.
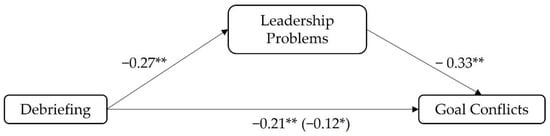
Figure 3.
Results of Hypothesis 2b: * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.001.
The relations could also be confirmed for the third model for testing Hypothesis 2c, in which the problems with shared mental models were included as mediators in the mediation model. Again, the a- (β = −0.31, SE = 0.04, t(338) = −5.41, p < 0.001) and b-path (β = 0.34, SE = 0.06, t(337) = 6.23, p < 0.001) were significant. Likewise, the indirect effect, describing the association between debriefing and goal conflicts mediated by problems with shared mental models (β = −0.10; SE = 0.03, −0.16 < CI < −0.06), and the total effect (β = −0.21, SE = 0.05, t(338) = −3.73, p < 0.001), which describes the association between debriefing and goal conflicts, were significant. The direct effect was not significant (β = −0.10, SE = 0.05, t(337) = −1.83, p = 0.068) when controlling for the indirect effect (see Figure 4), which indicated another total mediation. Thus, results indicate that the negative relationship between debriefings and goal conflicts is totally mediated by the quality of the shared mental models within the teams, supporting Hypothesis 2c.
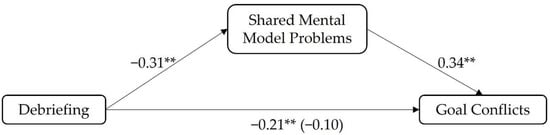
Figure 4.
Results of Hypothesis 2c: ** p < 0.001.
4. Discussion
So far, literature in the context of work–safety tension and goal conflicts lacked research in the area of firefighting. Furthermore, little is known about what causes the conflicting goals or how they can be counteracted. This study aimed to close this research gap and investigate goal conflicts in the context of firefighting missions. We investigated how goal conflicts are related to risky decision making and looked at mechanisms of debriefing as a potential countermeasure.
First of all, our data show that conflicting goals do occur in the field of firefighting: firefighters reported that they sometimes experience conflicts of goals, i.e., conflicts between self-protection and achieving the operational objective as well as conflicts between acting fast and acting safely. This is in line with the initial reports from our interviews and documents as described in the introduction. Moreover, these findings are consistent with results from other industries, such as production and construction [20,21,22]. Similar results could also be shown in the health sector. Health professionals were shown to have goal conflicts between following guidelines on the one hand and acting fast on the other hand; further, they deviate from guidelines during patient interviews when they feel time pressure [46].
Confirming Hypothesis 1, our results further showed that conflicting goals are linked to risky decision making: goal conflicts were associated with more gut decisions, less prioritization of goals and more risk-taking to fulfill the mission’s objective. These findings confirm that research from other areas, such as production and construction, can be applied to firefighting [20,21,22]. Furthermore, these results emphasize the importance of research on goal conflicts, particularly in the context of firefighting, as risky decisions in this context are often accompanied by threats to the health and even life of firefighters and other persons. Therefore, every effort should be made to make working conditions for firefighters as safe as possible. In conclusion, the experience of goal conflicts should be reduced as much as possible. One reason why firefighters might be willing to take such a high risk when goal conflicts occur could be due to the situation. On the one hand, there is risk perception [47,48]. This refers to the individual assessment of how risky a situation could be. This involves aspects such as the uncertainty of the situation, how controllable the risk is and how confident one is about this assessment [10]. Due to previous positive experiences during missions, trust in their colleagues and confidence in their training, it could be that the risk of the situation is underestimated, making firefighters willing to take a higher risk [47,49]. Secondly, the framing of the situation or problem could play an important role. If the firefighters are in work–safety tension, the situation is usually already framed negatively, and possible losses are anticipated. In accordance with prospect theory [23], people are then inclined to be more willing to take risks in their behavior. As these findings are supported by further studies [50,51], it can be assumed that the potential threats of the situation also induce firefighters to take higher risks.
We also looked at factors triggering the goal conflicts experienced and a potential countermeasure: debriefing. Confirming Hypothesis 2, we showed that regular, adequate debriefings that give good opportunities to discuss experiences are related to a reduced frequency of experienced goal conflicts. Moreover, as hypothesized, this relationship was mediated by enhanced teamwork, meaning fewer problems related to communication (Hypothesis 2a), leadership (Hypothesis 2b) and shared mental models (Hypothesis 2c). These mechanisms are in line with earlier research, where improved communication, leadership and shared mental models were identified as outcomes of debriefings [31,36,37,38,39,40]. These positive effects of debriefing are particularly interesting to evaluate in the discourse of the literature on risky decision making. The greater the experience of the operational forces, the more likely they are to make decisions based on their abilities and their experience rather than the current conditions of the situation [47]. Accordingly, they underestimate the risk and overestimate their ability to cope with a problem [52,53]. The firefighters thus establish an apparent certainty about the situation [54] and are subject to an illusion with regard to the controllability of the situation [55]. Debriefings can help prevent such moments. They rework the situation in a structured way and facilitate discussion of the processes as well as the perceptions and abilities of everyone in the situation and create a more solid reality base. Their goal is to prevent future goal conflicts and unnecessary risk behavior. Overall, the findings of our study provide evidence that debriefings are an effective tool to influence safe decision making in firefighting missions.
4.1. Strengths and Limitations
As a strength, our study adds to the so-far very scarce knowledge on goal conflicts in the context of firefighting missions. Furthermore, we were able to confirm debriefing as an effective countermeasure, thereby showing that the effects of debriefing on reduced goal conflicts are mediated by reduced difficulties in teamwork, especially with communication, leadership and shared mental models.
A further strength of our study is that we were able to recruit a large sample of 340 firefighters, giving high power to test our hypotheses. Our sample can be seen as fairly representative in terms of gender and age. As in the target population, most of our participants belonged to volunteer fire departments, followed by professional fire departments, plant fire departments and others. In Germany, about 1 million firefighters belong to volunteer fire departments, while about 35,000 total are employed in professional and plant fire departments. Accordingly, the group of professional firefighters is slightly overrepresented in this sample, whereas employees in plant fire departments are underrepresented [56]. Approximately five percent of our participants were female, whereas in volunteer fire brigades throughout Germany approximately ten percent are female and within professional fire brigades approximately two percent. We believe that our findings are, thus, very representative for fire departments in Germany. Although, as a limitation, results should be validated in other countries with potentially different structures and regularities.
Another strength is the design of our online questionnaire, which was used to investigate different aspects of teamwork in firefighting. In order to depict situations and challenges in firefighting missions and their consequences as authentically as possible, the items were created with specific examples. This made it possible to carry out very concrete evaluations. However, this approach led to a processing time of about 40 min, which resulted in a high drop-out rate.
A clear limitation of our study is the cross-sectional design. While our hypotheses contain causal assumptions, the cross-sectional design prevents causal conclusions. Accordingly, the interpretation of our results needs to be seen as first evidence to be validated in future studies using experimental or longitudinal designs.
4.2. Future Perspectives and Practical Implications
With respect to future research, we recommend studies that allow a causal interpretation of results to validate our findings. A promising approach would be to assess goal conflicts in experiments using operational exercises specifically designed to provoke goal conflicts. In such a design, the consequences of goal conflicts could be observed with behavioral markers; further, physiological measurements could capture the acute stress arising from the goal conflicts. In addition, one could use a repeated measures design that systematically varies whether or not debriefing is conducted.
In the field, the effects of debriefing and other potential influencing variables on conflicting goals should be assessed over a longer period of time. Based on these findings, different interventions (e.g., specific debriefing) could be designed and evaluated with respect to their efficacy to reduce goal conflicts and enhance safety behavior.
The most important practical implication of our study is that debriefings are a promising approach to reduce teamwork problems and therefore goal conflicts in firefighting, increasing safety behavior. Accordingly, we recommend the promotion of debriefings that include the systematic discussion of specific teamwork aspects. Debriefings have been shown to help reduce work–safety tension and thus goal conflicts [37,41,42]. It is likely that debriefings that are more focused on teamwork skills can reduce teamwork problems even further, creating a more compatible work environment for firefighting missions. As the literature shows, structured debriefings are especially effective [57,58]; thus, we recommend the use of structured debriefings.
Furthermore, both during firefighter training and later it is essential to conduct regular fire drills in which specific training is targeted, including debriefing. Using training situations that are stressful and can cause goal conflicts create experiences that help the firefighters to master challenging situations during real firefighting missions. With a systematic debriefing, the experience gained during operational exercises can be better processed and stored. In addition, the experiences are shared with the entire team. This means that even team members who have not directly experienced a particular situation can share in the experiences of their comrades and better deal with a similar situation in the future.
Leaders do not necessarily have more practical experience in firefighting missions than the firefighters. It is therefore also important for them to participate in such training in order to gain experience. They, too, need a sense of the stress that goal conflicts can create in firefighting missions in order to be able to avoid this for their forces.
All in all, debriefings are a valuable countermeasure to reduce problems in teamwork and—consequently—reduce the occurrence of goal conflicts. Those who experience fewer conflicting goals and consider debriefings appropriate take fewer risks to their own safety.
5. Conclusions
This study demonstrated that goal conflicts during firefighting missions enhance the probability of risky decision making. As a promising countermeasure, debriefings after missions were found to be related to reduced problems with communication, leadership and shared mental models within teams, which, in turn, reduced the emergence of goal conflicts during firefighting. In order to allow a causal interpretation of the presented findings, it would be interesting for future studies to assess goal conflicts in experimental settings by using mission exercises that are specifically designed to provoke such conflicts. Since this study used cross-sectional methods to show that debriefing effectively reduces goal conflicts during missions, future research should examine the effects of different debriefing interventions in the field over a longer period of time.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.H., C.P., L.H., F.A. and M.H.; methodology, V.H., C.P., L.H., F.A. and M.H.; software, L.H. and F.A..; formal analysis, L.H. and F.A.; investigation, L.H. and F.A..; resources, V.H. and C.P.; data curation, L.H. and F.A.; writing—original draft preparation, V.H., L.H., C.P., F.A. and M.H.; supervision, V.H. and C.P.; project administration, C.P., V.H. and M.H.; funding acquisition, C.P., V.H. and M.H.; writing—review and editing, V.H., C.P., L.H. and F.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the German Social Accident Insurance (DGUV) grant number FP-433.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Psychology, Ruhr-University Bochum (no. 482, approval issued on: 3 August 2018).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Items of the Demands and Resources During Firefighting Missions [45].
Table A1.
Items of the Demands and Resources During Firefighting Missions [45].
| German Item (Used in the Study) | English Item (Translated) |
|---|---|
| Communication Problems | |
| Item 1: Informationen wurden gar nicht oder zu spät weitergegeben und/oder es wurde sich nicht abgesprochen. | Item 1: Information was not passed on at all or too late and/or there was no coordination. |
| Item 2: Informationen wurden gar nicht oder zu spät weitergegeben und/oder es wurde sich nicht abgesprochen. | Item 2: Information was not passed on at all or too late and/or there was no coordination. |
| Item 3: Die weitergegebenen Informationen waren fehlerhaft, ungenau und/oder nicht vollständig. | Item 3: The information passed on was incorrect, inaccurate and/or incomplete. |
| Item 4: Es wurde unnötig viel geredet (z.B. zu viel Diskussion; zu viele Informationen auf einmal). | Item 4: There was an unnecessary amount of talking (e.g., too much discussion; too much information at once). |
| Item 5: Informationen wurden gar nicht oder für die anderen Beteiligten unverständlich weitergegeben (z.B. bahntypische Bezeichnungen; Einbindung der Polizei und weiteren Feuerwehreinheiten/Löschgruppen). | Item 5: Information was not passed on at all or was incomprehensible to the other parties involved (e.g., railroad-typical terms; involvement of police and other fire units/firefighting groups). |
| Item 6: Die durch die Einsatzkraft wahrgenommenen Eindrücke wurden nicht an die anderen Einsatzkräfte weitergegeben, sodass kein gemeinsames Bild der Lage entstand. | Item 6: The impressions perceived by one firefighter were not passed on to the other firefighters, so that no shared picture of the situation emerged. |
| Leadership Problems | |
| Item 1: Die Einsatzkraft befolgte die Anweisungen der Führungskraft, ohne ihre Bedenken bzw. ihre Meinung zu äußern. | Item 1: The firefighter followed the leader’s instructions without voicing his/her concerns or opinion. |
| Item 2: Es gab keine eindeutigen Führungsstrukturen (z.B. es war nicht eindeutig, wer wem welche Befehle geben sollte) und/oder Führungsaufgaben wurden nicht angemessen erfüllt (z.B. keine Befehle; notwendige Entscheidungen wurden nicht getroffen). | Item 2: There were no clear leadership structures (e.g., it was not clear who should give which orders to whom) and/or leadership tasks were not performed adequately (e.g., no orders; necessary decisions were not made). |
| Item 3: Mögliche Gefahren und/oder Einsatzstandards wurden von einer oder mehreren Führungskräften nicht berücksichtigt (z.B. keine funktionierende Atemschutzüberwachung; unzureichende Erkundung der Einsatzstelle). | Item 3: Potential hazards and/or operational standards were not considered by one or more leaders (e.g., no functioning respirator monitoring; inadequate scene reconnaissance). |
| Item 4: Eine oder mehrere Führungskräfte verhielten sich hektisch, unsicher und/oder unkoordiniert. Das erzeugte Stress und übertrug sich auf andere. | Item 4: One or more leaders behaved in a hectic, uncertain and/or uncoordinated manner. This created stress and transferred to others. |
| Shared Mental Models Problems | |
| Item 1: Den Einsatzkräften fehlten Informationen zur Vorgehensweise und zum Ziel des Einsatzes (z.B. Reihenfolge von Arbeitsschritten; Einsatzstrategie). | Item 1: Firefighters lacked information on the course of action and objective of the mission (e.g., sequence of steps; mission strategy). |
| Item 2: Die Einsatzkräfte konnten sich untereinander schlecht bzw. nicht ausreichend einschätzen (z.B. Fähigkeiten; Stärken und Schwächen; Persönlichkeit) und waren deswegen unsicher, ob sie sich aufeinander verlassen konnten. | Item 2: The firefighters knew each other poorly or insufficiently (e.g., skills; strengths and weaknesses; personality) and were therefore unsure whether they could rely on each other. |
| Item 3: Die Einsatzkräfte wussten nicht genug über die anderen Funktionen im Löschzug und deren Aufgaben (z.B. Maschinist hat wenig Wissen über die Funktion des Wassertruppmanns), sodass sie nicht einschätzen konnten, was der andere gerade brauchte (z.B. Informationen) und/oder wie die eigenen Handlungen sich auf die anderen auswirkten. | Item 3: The firefighters did not know enough about the other functions in the firefighting platoon and their duties (e.g., engineer has little knowledge of the water trooper’s function), so they could not assess what the other person needed at the time (e.g., information) and/or how their own actions affected the others. |
References
- Kirstein, G. Unfallzahlen für 2019 liegen vor [Accident figures for 2019 are available]. In Gemeinsame Schrift der Hanseatischen Feuerwehr-Unfallkasse Nord, FeuerwehrUnfallkasse Mitte und der Feuerwehr-Unfallkasse Brandenburg FUK-Dialog–Informationen der Feuerwehr-Unfallkassen [Joint Publication of the Hanseatic Fire Brigade Accident Insurance Fund North, the Central Fire Brigade Accident Insurance Fund and the Brandenburg Fire Brigade Accident Insurance Fund FUK-dialog–Information from the Fire Brigade Accident Insurance Funds]; Heinz, C., Kirstein, G., Ruge, S., Eds.; Schmidt & Klaunig eK: Kiel, Germany, 2020; pp. 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, L.; Brew, N.; Smith, L. 2019–2020 Australian Bushfires-Frequently Asked Questions: A Quick Guide 2020. Available online: https://parlinfo.aph.gov.au/parlInfo/download/library/prspub/7234762/upload_binary/7234762.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- U.S. Fire Administration. Firefighter Fatalities in the United States in 2019. 2020. Available online: https://www.usfa.fema.gov/downloads/pdf/publications/firefighter-fatalities-2019.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- Campbell, R.; Evarts, B. United States Firefighter Injuries in 2019. 2020. Available online: https://www.nfpa.org/-/media/Files/News-and-Research/Fire-statistics-and-reports/Emergency-responders/osffinjuries.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). Preventing Occupational Fatalities in Confined Spaces 1986. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/docs/86-110/default.html (accessed on 9 March 2022).
- Fire Near Miss–Lessons Learned Become Lessons Applied. Available online: firefighternearmiss.com/reports (accessed on 15 August 2020).
- Atemschutzunfaelle.eu. Available online: atemschutzunfaelle.de/unfaelle/eu/2003/#u20031111-wuppertal (accessed on 15 August 2020).
- Deutsche Gesetzliche Unfallversicherung. DGUV Vorschrift 49–Unfallverhütungsvorschrift–Feuerwehren [DGUV Regulation 49–Accident Prevention Regulation–Fire Brigades] 2018. Available online: https://publikationen.dguv.de/regelwerk/dguv-vorschriften/1507/feuerwehren (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- Federal Emergency Management Agency United States Fire Administration. Developing Effective Standard Operating Procedures for Fire and EMS Departments 1999. Available online: https://www.usfa.fema.gov/downloads/pdf/publications/fa-197-508.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- Sitkin, S.B.; Pablo, A.L. Reconceptualizing the Determinants of Risk Behavior. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1992, 17, 9–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitkin, S.B.; Weingart, L.R. Determinants of Risky Decision-Making Behavior: A Test of the Mediating Role of Risk Perceptions and Propensity. Acad. Manag. J. 1995, 38, 1573–1592. [Google Scholar]
- Libby, R.; Fishburn, P.C. Behavioral models of risk taking in business decision: A survey and evaluation. J. Account. Res. 1977, 15, 272–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, S.L.; McGonagle, A.K.; Dove-Steinkamp, M.L.; Walker, C.T.; Marmet, M.; Barnes-Farrell, J.L. Relationships between psychological safety climate facets and safety behavior in the rail industry: A dominance analysis. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2010, 42, 1460–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henning, J.B.; Stufft, C.J.; Payne, S.C.; Bergman, M.E.; Mannan, M.S.; Keren, N. The influence of individual differences on organizational safety attitudes. Saf. Sci. 2009, 47, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, F.; Mokarami, H.; Cousins, R.; Jahangiri, M. Structural equation modeling of safety performance based on personality traits, job and organizational-related factors. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Ergon. JOSE 2020, 28, 644–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, M.S.; Bradley, J.C.; Wallace, J.C.; Burke, M.J. Workplace safety: A meta-analysis of the roles of person and situation factors. J. Appl. Psychol. 2009, 94, 1103–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, A.; Watson, B.; Biggs, H. Comparing safety climate factors as predictors of work-related driving behavior. J. Saf. Res. 2006, 37, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kahnemann, D.; Klein, G. Conditions for Intuitive Expertise A Failure to Disagree. Am. Psychol. 2009, 64, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klein, G. Naturalistic Decision Making. Hum. Factors 2008, 50, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brandhorst, S.; Kluge, A. The Spectrum of Safety-Related Rule Violations. J. Cogn. Eng. Decis. Mak. 2016, 10, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.L.; Holmes, H. The use of a factor-analytic procedure for assessing the validity of an employee safety climate model. Accid. Anal. Prev. 1986, 18, 455–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedobbeleer, N.; Béland, F. A safety climate measure for construction sites. J. Saf. Res. 1991, 22, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahneman, D.; Tversky, A. Prospect theory: An analysis of decision under risk. Econometrica 1979, 47, 263–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osborn, R.N.; Jackson, D.H. Leaders, riverboat gamblers, or purposeful unintended consequences in the management of complex dangerous technologies. Acad. Manag. J. 1988, 31, 924–947. [Google Scholar]
- Thaler, R.H.; Johnson, E.J. Gambling with the house money and trying to break even: The effects of prior outcomes on risky choice. Manag. Sci. 1990, 36, 643–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morgan, J.; Reidy, J.; Probst, T. Age Group Differences in Household Accident Risk Perceptions and Intentions to Reduce Hazards. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoneda, T.; Itami, K.; Yasuhara, O.; Seki, K.; Kawabata, Y.; Maesako, T.; Zhe, L. Changes in Subjective Understanding of an Accident and Risk Awareness in First-Year Nursing Students Following Medical Accident Simulation-Based Experimental Learning. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference of Educational Innovation through Technology (EITT), Osaka, Japan, 7–9 December 2017; pp. 159–164. [Google Scholar]
- DeGrosky, M.T. Improving After Action Review (AAR) Practice. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Wildland Firefighter Safety Summit: Human Factors–10 Years Later, Missoula, MT, USA, 26–28 April 2005; Butler, B.W., Alexander, M.E., Eds.; The International Association of Wildland Fire: Hot Springs, SD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Mundt, A.S.; Gjeraa, K.; Spanager, L.; Petersen, S.S.; Dieckmann, P.; Østergaard, D. Okay, let’s talk–short debriefings in the operating room. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, C.S.; Wilson, K.A.; Salas, E. Teamwork at 35,000 feet: Enhacing safety through team training. In Contemporary Issues in Human Factors and Aviation Safety; Harris, D., Muir, H.C., Eds.; Aldershot: Ashgate, UK, 2005; pp. 155–180. [Google Scholar]
- Salas, E.; Wilson, K.; Burke, S.; Wightman, D.; Howse, W. Crew Resource Management Training Research, Practice, and Lessons Learned. In Reviews of Human Factors and Ergonomics; Williges, R.C., Ed.; Human Factors and Ergonomics Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; pp. 35–73. [Google Scholar]
- Hagemann, V.; Kluge, A. The Effects of a Scientifically Based Team Resource Management Intervention for Fire Service Teams. Int. J. Hum. Factors Ergon. 2013, 2, 196–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannenbaum, S.I.; Beard, R.L.; McNall, L.A.; Salas, E. Informal learning and development in organizations. In Learning, Training, and Development in Organizations; Kozlowski, S.W.J., Salas, E., Eds.; Routledge Taylor & Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 303–331. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, S.; Mendel, M.; Nir, M. Learning from Successful and Failed Experience: The Moderating Role of Kind of After-Event-review. J. Appl. Psychol. 2006, 91, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith-Jentsch, K.; Zeisig, R.L.; Acton, B.; McPherson, J.A. Team Dimensional Training: A Strategy for Guided Team Self-Correction. In Making Decisions Under Stress; Cannon-Bowers, J.A., Salas, E., Eds.; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1998; pp. 271–298. [Google Scholar]
- Rasker, P.C.; Post, W.M.; Schraagen, J.M. Effects of two types of intra-team feedback on developing a shared mental model in Command & Control teams. Ergonomics 2000, 43, 1167–1189. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smith-Jentsch, K.; Cannon-Bowers, J.A.; Tannenbaum, S.I.; Salas, E. Guided Team Self-Correction. Small Group Res. 2008, 39, 303–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolbe, M.; Weiss, M.; Grote, G.; Knauth, A.; Dambach, M.; Spahn, D.R.; Grande, B. TeamGAINS: A tool for structured debriefings for simulation-based team trainings. BMJ Qual. Saf. 2013, 22, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas, E.; Klein, C.; King, H.; Salisbury, M.; Augenstein, J.S.; Birnbach, D.J.; Robinson, D.W.; Upshaw, C. Debriefing Medical Teams: 12 Evidence-Based Best Practices and Tips. Jt. Comm. J. Qual. Patient Saf. 2008, 34, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon-Bowers, J.A.; Salas, E.; Converse, S. Shared Mental Models in Expert Team Decision Making. In Individual and Group Decision Making; Castellan, N.J., Ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1993; pp. 221–246. [Google Scholar]
- Flin, R.; O’Connor, P.; Chrichton, M. Safety at the Sharp End. A Guide to Non-Technical Skills; Aldershot: Ashgate, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wahl, A.M.; Kongsvik, T. Crew resource management training in the maritime industry: A literature review. WMU J. Marit. Aff. 2018, 17, 377–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uitdewilligen, S.; Waller, M.J.; Zijlstra, F.R.H. Team Cognition and Adaptability in Dynamic Settings: A Review of Pertinent Work. Hodgkinson/Int. Rev. Ind. Organ. Psychol. 2010, 25, 293–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, M.S.; MacKinnon, D.P. Required Sample Size to Detect the Mediated Effect. Psychol. Sci. 2007, 18, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heinemann, L.; Aust, F.; Holtz, M.; Peifer, C.; Hagemann, V. Entwicklung Eines Fragebogens zur Erfassung von Stressoren und Ressourcen der Teamarbeit in Brandschutzeinsätzen–ein Qualitativer Ansatz [Development of a Questionnaire to Assess Stressors and Resources of Teamwork in Firefighting Missions—A Qualitative Approach]. Symposiumsvortrag bei der 12. Tagung der Fachgruppe Arbeits-, Organisations- und Wirtschaftspsychologie (AOW) der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Psychologie (DGPs) [Symposium presentation at the 12th Conference of the Division of Industrial, Organizational and Business Psychology (AOW) of the German Psychological Society (DGPs)], Chemnitz, Germany. 2021. Available online: https://osf.io/ykmhv/ (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- Presseau, J.; Francis, J.J.; Campbell, N.C.; Sniehotta, F.F. Goal conflict, goal facilitation, and health professionals’ provision of physical activity advice in primary care: An exploratory prospective study. Implement. Sci. 2011, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baird, I.S.; Thomas, H. Toward a contingency model of strategic risk taking. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1985, 10, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bettman, J.R. Perceived risk and its components: A model and empirical test. J. Mark. Res. 1973, 10, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roll, R. The hubris hypothesis of corporate takeovers. J. Bus. 1986, 59, 197–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neale, M.A.; Bazerman, M.H.; Northcraft, G.B.; Alperson, C. “Choice shift” effects in group decisions: A decision bias perspective. Int. J. Small Group Res. 1986, 2, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, J. Performance, slack, and risk taking in organizational decision making. Acad. Manag. J. 1986, 29, 562–585. [Google Scholar]
- Jemison, D.B.; Sitkin, S.B. Corporate acquisitions: A process perspective. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1986, 11, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- March, J.G.; Shapira, Z. Managerial perspectives on risk and risk taking. Manag. Sci. 1987, 33, 1404–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slovic, P.; Fischhoff, B.; Lichtenstein, S. Facts Versus Fears: Understanding Perceived Risk. In Judgment under Uncertainty: Heuristics and Biases; Kahneman, D., Slovic, P., Tversky, A., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1980; pp. 463–489. [Google Scholar]
- Langer, E.J. The illusion of control. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1975, 32, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutscher Feuerwehrverband e.V. (DFV) (n.d.) [German Fire Brigades Association]. Aktuellste Statistische Daten [Most Recent Statistical Data]. Available online: https://www.feuerwehrverband.de/presse/statistik/ (accessed on 9 March 2022).
- Ahmed, M.; Sevdalis, N.; Paige, J.T.; Paragi-Gururaja, R.; Nestel, D.; Arora, S. Identifying best practice guidelines for debriefing in surgery: A tri-continental study. Am. J. Surg. 2012, 203, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolbe, M.; Grande, B.; Spahn, D.R. Briefing and debriefing during simulation-based training and beyond: Content, structure, attitude and setting. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2015, 29, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).