Measuring the Prevalence, Treatment, and Associated Treatment Costs of Injury for Older Adults in India: Insights from the National Longitudinal Aging Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Consent to Participate and Ethics Approval
2.2. Data Source
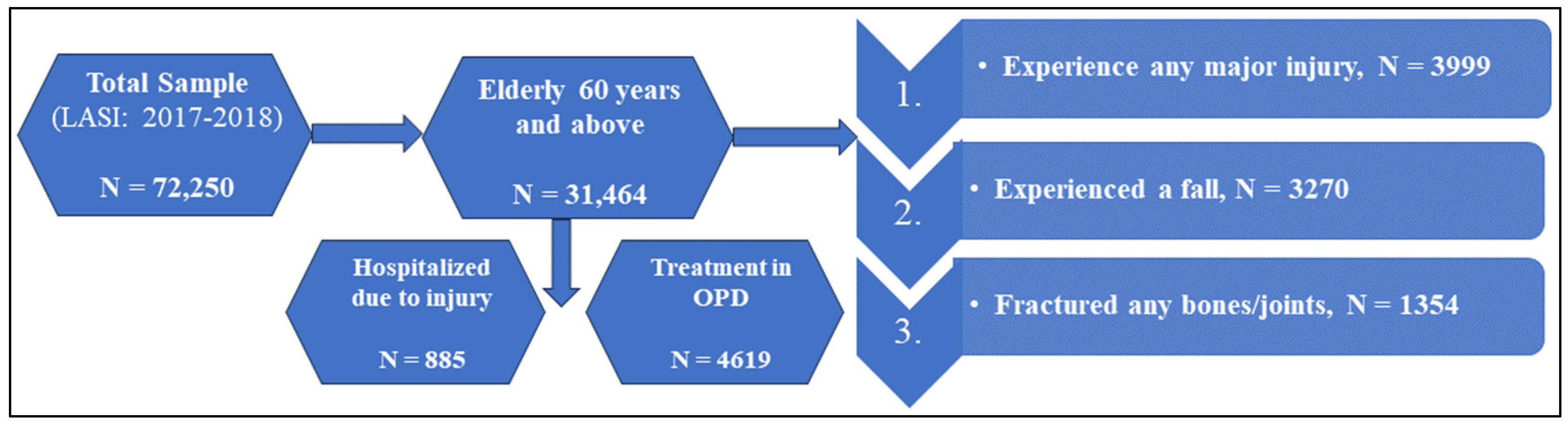
2.3. Study Design and Sample Size
2.4. Defining Injury and Treatment Seeking Behaviour
2.5. Economic Costs Associated with Injury
2.6. Statistical Modeling
3. Results
3.1. Socio-Demographic Characteristics of the Respondents
3.2. Prevalence of Injury by Socio-Demographic Characteristics
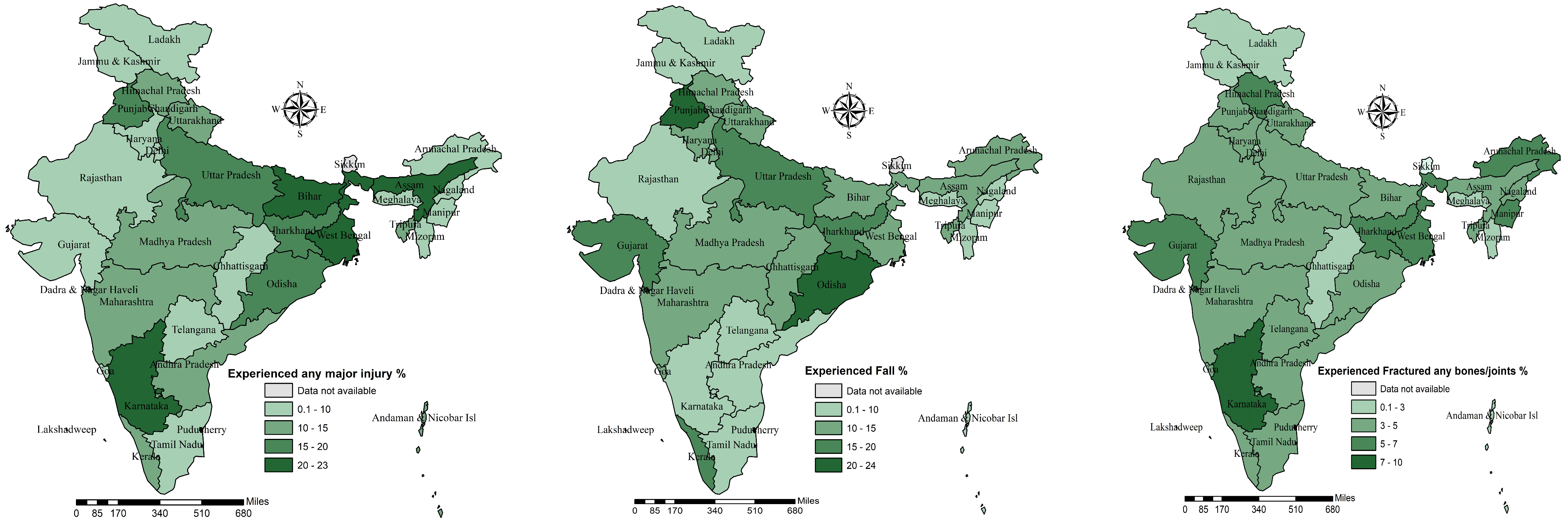
3.3. Prevalence of Types of Injuries by Indian State
3.4. Risk of Injury
3.5. Medical Treatment of Injury by Mechanism
3.6. Treatment for Injury
3.7. Out-of-Pocket Expenditure (OOPE) for Hospitalization
3.8. Out-of-Pocket Expenditure for Outpatient Care
3.9. Factors Affecting Out-of-Pocket Expenditure on Injury
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- James, S.L.; Castle, C.D.; Dingels, Z.V.; Fox, J.T.; Hamilton, E.B.; Liu, Z.; Roberts, N.L.S.; Sylte, D.O.; Henry, N.J.; LeGrand, K.E.; et al. Global injury morbidity and mortality from 1990 to 2017: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Inj. Prev. 2020, 26, i96–i114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, T.; Lim, S.S.; Abbafati, C.; Abbas, K.M.; Abbasi, M.; Abbasifard, M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abbastabar, H.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; et al. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haagsma, J.A.; James, S.L.; Castle, C.D.; Dingels, Z.V.; Fox, J.T.; Hamilton, E.B.; Liu, Z.; Lucchesi, L.R.; Roberts, N.L.S.; Sylte, D.O.; et al. Burden of injury along the development spectrum: Associations between the Socio-demographic Index and disability-adjusted life year estimates from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Inj. Prev. 2020, 26, i12–i26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peden, A.E.; Cullen, P.; Francis, K.L.; Moeller, H.; Peden, M.M.; Ye, P.; Tian, M.; Zou, Z.; Sawyer, S.M.; Aali, A.; et al. Adolescent transport and unintentional injuries: A systematic analysis using the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Public Health 2022, 7, e657–e669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, A.I.; Menon, D.K.; Manley, G.T.; Abrams, M.; Åkerlund, C.; Andelic, N.; Aries, M.; Bashford, T.; Bell, M.J.; Bodien, Y.G. Traumatic brain injury: Progress and challenges in prevention, clinical care, and research. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 1004–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-E.; Kim, J.; Lee, J. Comparison of the characteristics of work-related injuries between older workers and the workers of the conventional working-age in the Republic of Korea, 2010–2014. Inj. Prev. 2021, 27, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemens, T.; Peden, A.E.; Franklin, R.C. Exploring a Hidden Epidemic: Drowning Among Adults Aged 65 Years and Older. J. Aging Health 2021, 33, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, S.L.; Lucchesi, L.R.; Bisignano, C.; Castle, C.D.; Dingels, Z.V.; Fox, J.T.; Hamilton, E.B.; Henry, N.J.; Krohn, K.J.; Liu, Z.; et al. The global burden of falls: Global, regional and national estimates of morbidity and mortality from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Inj. Prev. 2020, 26, i3–i11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Peregrina, S.; Ortiz, C.; Casares-López, M.; Castro-Torres, J.J.; Jimenez del Barco, L.; Anera, R.G. Impact of age-related vision changes on driving. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivari, B.S.; French, M.E.; McGuire, L.C. The public health road map to respond to the growing dementia crisis. Innov. Aging 2020, 4, igz043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlett, S.E.; Rutenberg, A.D.; Rockwood, K. The degree of frailty as a translational measure of health in aging. Nat. Aging 2021, 1, 651–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, A.; Lee, R.; Network, N. Six ways population change will affect the global economy. Popul. Dev. Rev. 2022, 48, 51–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, D.E.; Sekher, T.V.; Lee, J. Longitudinal Aging Study in India (LASI): New data resources for addressing aging in India. Nat. Aging 2021, 1, 1070–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perianayagam, A.; Bloom, D.; Lee, J.; Parasuraman, S.; Sekher, T.; Mohanty, S.K.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Govil, D.; Pedgaonkar, S.; Gupta, S. Cohort profile: The longitudinal ageing study in India (LASI). Int. J. Epidemiol. 2022, 51, e167–e176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dandona, L.; Dandona, R.; Kumar, G.A.; Shukla, D.; Paul, V.K.; Balakrishnan, K.; Prabhakaran, D.; Tandon, N.; Salvi, S.; Dash, A. Nations within a nation: Variations in epidemiological transition across the states of India, 1990–2016 in the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 2017, 390, 2437–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Muhammad, T. Prevalence and risk factors of fall-related injury among older adults in India: Evidence from a cross-sectional observational study. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, A.; Kumar, D.; Bagavandas, M. A review of epidemiology of fall among elderly in India. Indian J. Community Med. Off. Publ. Indian Assoc. Prev. Soc. Med. 2019, 44, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peter, R.M.; Joseph, A.; John, K.; Logaraj, M. A community-based case–control study on the risk of fall among the elderly in rural Kattankulathur block, Tamil Nadu. Indian J. Community Med. Off. Publ. Indian Assoc. Prev. Soc. Med. 2019, 44, 277. [Google Scholar]
- Pitchai, P.; Dedhia, H.B.; Bhandari, N.; Krishnan, D.; D’Souza, N.R.J.; Bellara, J.M. Prevalence, risk factors, circumstances for falls and level of functional independence among geriatric population-A descriptive study. Indian J. Public Health 2019, 63, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmamula, S.; Barrenkala, N.R.; Challa, R.; Kumbham, T.R.; Modepalli, S.B.; Yellapragada, R.; Bhakki, M.; Friedman, D.S.; Khanna, R.C. Falls and visual impairment among elderly residents in ‘homes for the aged’in India. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinja, S.; Jagnoor, J.; Sharma, D.; Aggarwal, S.; Katoch, S.; Lakshmi, P.; Ivers, R. Out-of-pocket expenditure and catastrophic health expenditure for hospitalization due to injuries in public sector hospitals in North India. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ram, B.; Thakur, R. Measuring the burden of accidental injuries in India: A cross-sectional analysis of the National Sample Survey (2017–2018). Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2022, 9, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, J.; Menon, G.; Agarwal, A.; John, D. Burden of injuries and its associated hospitalization expenditure in India. Int. J. Inj. Control Saf. Promot. 2021, 28, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Hershey, D.A. Cross-national differences in goals for retirement: The case of India and the United States. J. Cross-Cult. Gerontol. 2016, 31, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Institute for Population Sciences; National Programme for Health Care of Elderly; Ministry of Health and Family Welfare; Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health; University of Southern California. Longitudinal Ageing Study in India (LASI) Wave 1, 2017–2018, India Report; International Institute for Population Sciences: Mumbai, India, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty, S.K.; Kastor, A. Out-of-pocket expenditure and catastrophic health spending on maternal care in public and private health centres in India: A comparative study of pre and post national health mission period. Health Econ. Rev. 2017, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, J.; Menon, G.R.; John, D. Disease-Specific Out-of-Pocket Payments, Catastrophic Health Expenditure and Impoverishment Effects in India: An Analysis of National Health Survey Data. Appl. Health Econ. Health Policy 2021, 19, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, J.; John, D.; Menon, G. Out of pocket expenditure on tuberculosis in India: Do households face hardship financing? Indian J. Tuberc. 2019, 66, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keppel, G. Design and Analysis: A Researcher’s Handbook, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, W.; Mayberry, R.; Bae, S.; Singh, K.; He, Q.P.; Lillard, J.W., Jr. A study of effects of multicollinearity in the multivariable analysis. Int. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, O.A.; Wagstaff, A. Analyzing Health Equity Using Household Survey Data: A Guide to Techniques and Their Implementation; World Bank Publications: Herndon, VA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Saikia, N.; Moradhvaj; Bora, J.K. Gender difference in health-care expenditure: Evidence from India human development survey. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- StataCorp. Stata Statistical Software: Release 18; StataCorp LP.: College Station, TX, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Korn, E.L.; Graubard, B.I. Simultaneous Testing of Regression Coefficients with Complex Survey Data: Use of Bonferroni t Statistics. Am. Stat. 1990, 44, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, G. Gender gap in life expectancy in India and role of age groups: A comparison between before and after male–female life expectancy at birth crossover. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keay, L.; Praveen, D.; Salam, A.; Rajasekhar, K.; Tiedemann, A.; Thomas, V.; Jagnoor, J.; Sherrington, C.; Ivers, R.Q. A mixed methods evaluation of yoga as a fall prevention strategy for older people in India. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2018, 4, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadhwaniya, S.; Alonge, O.; Ul Baset, M.K.; Chowdhury, S.; Bhuiyan, A.A.; Hyder, A.A. Epidemiology of fall injury in rural Bangladesh. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagnoor, J.; Keay, L.; Jaswal, N.; Kaur, M.; Ivers, R. A qualitative study on the perceptions of preventing falls as a health priority among older people in Northern India. Inj. Prev. 2014, 20, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leale, I.; Figlioli, F.; Giustino, V.; Brusa, J.; Barcellona, M.; Nocera, V.; Canzone, A.; Patti, A.; Messina, G.; Barbagallo, M.; et al. Telecoaching as a new training method for elderly people: A systematic review. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2024, 36, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.T.; Morton, S.C.; Rubenstein, L.Z.; Mojica, W.A.; Maglione, M.; Suttorp, M.J.; Roth, E.A.; Shekelle, P.G. Interventions for the prevention of falls in older adults: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials. BMJ 2004, 328, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dandona, R.; Kumar, G.A.; Gururaj, G.; James, S.; Chakma, J.K.; Thakur, J.; Srivastava, A.; Kumaresh, G.; Glenn, S.D.; Gupta, G. Mortality due to road injuries in the states of India: The Global Burden of Disease Study 1990–2017. Lancet Public Health 2020, 5, e86–e98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, R.; Ghosh, A.; Kumar, R.; Galwankar, S.; Paul, S.K.; Pal, S.; Sinha, D.; Jaiswal, A.; Moscote-Salazar, L.R.; Agrawal, A. Public health crisis of road traffic accidents in India: Risk factor assessment and recommendations on prevention on the behalf of the Academy of Family Physicians of India. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2019, 8, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaishnav, L.M.; Joshi, S.H.; Joshi, A.U.; Mehendale, A.M. The national programme for health care of the elderly: A review of its achievements and challenges in India. Ann. Geriatr. Med. Res. 2022, 26, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonge, O.; Agrawal, P.; Talab, A.; Rahman, Q.S.; Rahman, A.F.; El Arifeen, S.; Hyder, A.A. Fatal and non-fatal injury outcomes: Results from a purposively sampled census of seven rural subdistricts in Bangladesh. Lancet Glob. Health 2017, 5, e818–e827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Peden, A.E.; Peden, M.; Hyder, A.A.; Jagnoor, J.; Duan, L.; Brown, J.; Passmore, J.; Clapham, K.; Tian, M.; et al. Out of the silos: Embedding injury prevention into the Sustainable Development Goals. Inj. Prev. 2021, 27, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, F.N.; Hossain, J.; Rahman, A.K. Epidemiology of Geriatric Injury in Bangladesh: Findings from a National Survey. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 50, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elango, S.; Ramya, A.; Renita, A.; Ramana, M.; Revathy, S.; Rajajeyakumar, M. An analysis of road traffic injuries in India from 2013 to 2016: A review article. J. Community Med. Health Educ. 2018, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, P.; Underwood, G. Forgetting near-accidents: The roles of severity, culpability and experience in the poor recall of dangerous driving situations. Appl. Cogn. Psychol. Off. J. Soc. Appl. Res. Mem. Cogn. 2000, 14, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulhus, D.L. Two-component models of socially desirable responding. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1984, 46, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.P.; O’Neill, B.; Haddon, W., Jr.; Long, W.B. The injury severity score: A method for describing patients with multiple injuries and evaluating emergency care. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 1974, 14, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sociodemographic Characteristics | Experienced Any. Major Injury | Experienced a Fall | Fractured Any Bones/Joints | Distribution of Total Sample | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n Unweighted | % Weighted | n Unweighted | % Weighted | n Unweighted | % Weighted | n Unweighted | % Weighted | |
| Total | 3999 | 15.1 | 3270 | 12.6 | 1354 | 4.8 | 31,464 | 100 |
| Age | χ2 = 18.514; p < 0.001 | χ2 = 7.001; p = 0.135 | χ2 = 14.995; p = 0.005 | - | ||||
| 60–64 | 1254 | 13.9 | 1.49 | 13.0 | 414 | 4.3 | 10,132 | 29.9 |
| 65–69 | 1114 | 14.3 | 885 | 11.8 | 376 | 4.5 | 8842 | 28.6 |
| 70–74 | 693 | 16.4 | 615 | 13.0 | 232 | 6.4 | 5741 | 18.8 |
| 75–79 | 432 | 14.1 | 346 | 11.7 | 144 | 3.8 | 3360 | 11.5 |
| 80 or above | 506 | 19.3 | 375 | 14.1 | 188 | 5.3 | 3389 | 11.3 |
| Sex | χ2 = 35.526; p < 0.001 | χ2 = 51.313; p < 0.001 | χ2 = 38.158; p < 0.001 | - | ||||
| Male | 1741 | 13.5 | 1407 | 11.7 | 538 | 3.7 | 15,098 | 47.5 |
| Female | 2258 | 16.6 | 1863 | 13.5 | 816 | 5.8 | 16,366 | 52.6 |
| Living Status | χ2 = 25.515; p < 0.001 | χ2 = 22.103; p < 0.001 | χ2 = 10.291; p < 0.05 | - | ||||
| Living alone | 229 | 17.1 | 180 | 14.8 | 66 | 4.4 | 1622 | 5.7 |
| Living with spouse | 729 | 14.6 | 611 | 12.6 | 240 | 4.7 | 6215 | 20.3 |
| Living with spouse and children | 1631 | 13.5 | 1335 | 11.6 | 562 | 4.1 | 13,465 | 40.6 |
| Living with children and other relatives | 1183 | 17.7 | 949 | 13.6 | 412 | 6.2 | 8418 | 27.6 |
| Living with others | 227 | 14.3 | 195 | 13.3 | 74 | 4.2 | 1744 | 5.7 |
| Education status | χ2 = 69.525; p < 0.001 | χ2 = 35.921; p < 0.001 | χ2 = 11.518; p < 0.001 | - | ||||
| No education | 2295 | 15.3 | 1807 | 13.2 | 772 | 4.6 | 16,889 | 56.5 |
| Primary | 1257 | 15.6 | 1066 | 13.1 | 417 | 4.7 | 9798 | 29.3 |
| Secondary | 345 | 14.8 | 280 | 9.8 | 119 | 7.5 | 3322 | 10.2 |
| Graduate and above | 102 | 10.1 | 117 | 8.9 | 46 | 3.1 | 1455 | 4.1 |
| Wealth quintile | χ2 = 16.995; p < 0.005 | χ2 = 10.628; p < 0.05 | χ2 = 20.134; p < 0.001 | - | ||||
| Poorest | 739 | 13.8 | 634 | 11.5 | 245 | 3.8 | 6484 | 21.7 |
| Poorer | 801 | 14.3 | 709 | 13.6 | 261 | 4.2 | 6477 | 21.7 |
| Middle | 835 | 15.7 | 628 | 11.9 | 268 | 4.4 | 6416 | 21.0 |
| Richer | 824 | 15.1 | 679 | 12.7 | 266 | 4.1 | 6170 | 19.2 |
| Richest | 800 | 17.4 | 620 | 13.7 | 314 | 8.2 | 5917 | 16.5 |
| Social Group | χ2 = 139.479; p < 0.001 | χ2 = 75.638; p < 0.001 | χ2 = 32.049; p < 0.001 | - | ||||
| Scheduled tribe | 409 | 12.3 | 388 | 11.5 | 148 | 3.2 | 5173 | 8.3 |
| Scheduled caste | 760 | 16.9 | 600 | 14.0 | 228 | 4.1 | 5140 | 19.4 |
| Other backward caste | 1627 | 15.1 | 1299 | 11.7 | 548 | 5.1 | 11,886 | 46.5 |
| Other caste | 1090 | 15.2 | 871 | 13.4 | 385 | 5.3 | 8218 | 25.8 |
| Religion | χ2 = 108.189; p < 0.001 | χ2 = 25.763; p < 0.001 | χ2 = 15.598; p < 0.001 | - | ||||
| Hindu | 3163 | 15.3 | 2499 | 12.6 | 1045 | 4.9 | 23,037 | 82.2 |
| Muslim | 450 | 15.2 | 329 | 12.3 | 156 | 4.4 | 3731 | 11.3 |
| Other | 386 | 12.9 | 442 | 13.7 | 153 | 4.1 | 4695 | 6.5 |
| Place of residence | χ2 = 59.991; p < 0.001 | χ2 = 59.785; p < 0.001 | χ2 = 0.351; p < 0.05 | - | ||||
| Rural | 2854 | 15.7 | 2337 | 13.6 | 903 | 4.5 | 20,725 | 70.6 |
| Urban | 1145 | 13.8 | 933 | 10.4 | 451 | 5.6 | 10,739 | 29.5 |
| Region | χ2 = 361.681; p < 0.001 | χ2 = 245.233; p < 0.001 | χ2 = 26.269; p < 0.001 | - | ||||
| North | 539 | 11.4 | 489 | 12.9 | 182 | 3.9 | 4734 | 7.7 |
| Central | 787 | 13.5 | 610 | 8.4 | 315 | 5.2 | 7578 | 22.7 |
| East | 1123 | 20.7 | 802 | 15.5 | 282 | 5.0 | 5757 | 23.6 |
| Northeast | 581 | 11.4 | 623 | 13.1 | 268 | 5.0 | 5381 | 22.1 |
| West | 630 | 15.6 | 497 | 13.8 | 189 | 4.5 | 4262 | 21.0 |
| South | 339 | 17.1 | 249 | 9.9 | 118 | 3.4 | 3752 | 3.0 |
| Sociodemographic Characteristics | Odds Ratio | Std. Err. | p-Value | [95% Conf Interval] | Significance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| Age | ||||||
| 60–64 | Ref | |||||
| 65–69 | 1.033 | 0.038 | 0.372 | 0.962 | 1.111 | |
| 70–74 | 1.058 | 0.045 | 0.178 | 0.975 | 1.149 | |
| 75–79 | 1.083 | 0.055 | 0.112 | 0.981 | 1.196 | |
| 80 or above | 1.207 | 0.061 | 0.000 | 1.094 | 1.333 | *** |
| Sex | ||||||
| Male | Ref | |||||
| Female | 1.295 | 0.042 | 0.000 | 1.214 | 1.38 | *** |
| Living Status | ||||||
| Living alone | Ref | |||||
| Living with spouse | 0.854 | 0.059 | 0.023 | 0.745 | 0.979 | ** |
| Living with spouse and children | 0.950 | 0.063 | 0.444 | 0.835 | 1.082 | |
| Living with children and other relatives | 1.034 | 0.068 | 0.610 | 0.909 | 1.177 | |
| Living with others | 0.938 | 0.079 | 0.448 | 0.795 | 1.107 | |
| Education status | ||||||
| No education | Ref | |||||
| Primary | 1.114 | 0.039 | 0.002 | 1.041 | 1.192 | *** |
| Secondary | 0.85 | 0.048 | 0.004 | 0.761 | 0.949 | *** |
| Graduate and above | 0.647 | 0.056 | 0.000 | 0.546 | 0.766 | *** |
| Wealth quintile | ||||||
| Poorest | Ref | |||||
| Poorer | 1.118 | 0.050 | 0.012 | 1.025 | 1.220 | ** |
| Middle | 1.138 | 0.051 | 0.004 | 1.042 | 1.243 | *** |
| Richer | 1.267 | 0.058 | 0.000 | 1.158 | 1.386 | *** |
| Richest | 1.381 | 0.067 | 0.000 | 1.256 | 1.518 | *** |
| Social Group | ||||||
| None of them | Ref | |||||
| Other backward classes | 1.608 | 0.090 | 0.000 | 1.440 | 1.794 | *** |
| Scheduled caste | 1.566 | 0.081 | 0.000 | 1.415 | 1.733 | *** |
| Scheduled tribe | 1.512 | 0.084 | 0.000 | 1.356 | 1.686 | *** |
| Religion | ||||||
| Hindu | Ref | |||||
| Muslim | 0.852 | 0.042 | 0.001 | 0.774 | 0.938 | *** |
| Other | 0.979 | 0.049 | 0.677 | 0.888 | 1.080 | |
| Place of residence | ||||||
| Rural | Ref | |||||
| Urban | 0.804 | 0.027 | 0.000 | 0.752 | 0.859 | *** |
| Region | ||||||
| North | Ref | |||||
| Central | 0.872 | 0.045 | 0.007 | 0.789 | 0.964 | *** |
| East | 1.841 | 0.091 | 0.000 | 1.671 | 2.028 | *** |
| Northeast | 1.150 | 0.060 | 0.007 | 1.038 | 1.274 | *** |
| West | 1.279 | 0.070 | 0.000 | 1.15 | 1.423 | *** |
| South | 0.840 | 0.056 | 0.009 | 0.737 | 0.958 | *** |
| Constant | 0.137 | 0.014 | 0.000 | 0.113 | 0.167 | *** |
| Mean dependent var | 0.221 | SD dependent var | 0.415 | |||
| Pseudo r-squared | 0.028 | Number of obs | 30,416 | |||
| Chi-square | 903.655 | Prob > chi2 | 0.000 | |||
| Akaike crit. (AIC) | 31,274.626 | Bayesian crit. (BIC) | 31,507.663 | |||
| Injury Mechanism | Total | 60–64 Years | 65–69 Years | 70–74 Years | 75–79 Years | 80+ Years | Significance | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | ||
| Traffic accident | 463 | 10.8 | 179 | 14.7 | 155 | 11.8 | 66 | 9.6 | 38 | 8.6 | 25 | 4.5 | χ2 = 42.749; p < 0.001 |
| Struck by person or object | 237 | 7.2 | 93 | 8.9 | 85 | 8.2 | 42 | 3.9 | 27 | 7.3 | 26 | 6.7 | χ2 = 4.930; p = 0.294 |
| Fire, flames, burn, electric shock | 22 | 1.2 | 9 | 0.9 | 7 | 0.7 | 2 | 0.1 | 3 | 5.6 | 1 | 0.6 | χ2 = 2.951; p = 0.566 |
| Drowning | 6 | 0.2 | 3 | 0.3 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 2 | 0.6 | 1 | 0.1 | χ2 = 6.289; p = 0.179 |
| Poisoning | 1 | 0.02 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.7 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | χ2 = 2.582; p = 0.630 |
| Animal attack or bite | 197 | 4.8 | 64 | 4.6 | 57 | 6.2 | 30 | 3.2 | 28 | 6.7 | 18 | 3.8 | χ2 = 4.952; p = 0.292 |
| Fall | 3088 | 77.8 | 918 | 77.2 | 824 | 75.6 | 562 | 83.5 | 343 | 74.3 | 441 | 86.6 | χ2 = 54.085; p < 0.001 |
| Others | 29 | 0.8 | 12 | 0.5 | 7 | 0.5 | 4 | 2.3 | 4 | 0.7 | 2 | 0.2 | χ2 = 2.681; p = 0.681 |
| Sociodemographic Characteristics | Receive Medical Treatment for Injury | Any Falls, Seriously Enough to Need Medical Treatment? | Undergone Any Surgery Related to Bones or Joints? | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n Unweighted | % Weighted | n Unweighted | % Weighted | n Unweighted | % Weighted | |
| Total | 3113 | 78.1 | 3355 | 55.5 | 667 | 2.6 |
| Age | χ2 = 2.258; p = 0.262 | χ2 = 2.452; p = 0.653 | χ2 = 13.190; p = 0.010 | |||
| 60–64 | 972 | 77.8 | 1042 | 53.9 | 177 | 1.9 |
| 65–69 | 893 | 88.0 | 910 | 58.2 | 193 | 2.3 |
| 70–74 | 531 | 77.7 | 596 | 53.1 | 132 | 4.4 |
| 75–79 | 329 | 78.4 | 368 | 55.2 | 74 | 2.4 |
| 80 or above | 388 | 75.2 | 439 | 57.5 | 91 | 2.8 |
| Sex | χ2 = 0.009; p = 0.922 | χ2 = 7.413; p < 0.05 | χ2 = 21.179; p < 0.001 | |||
| Male | 1354 | 78.9 | 1323 | 54.4 | 261 | 2.0 |
| Female | 1759 | 77.5 | 2032 | 56.3 | 406 | 3.2 |
| Living Status | χ2 = 20.365; p = 0.669 | χ2 = 3.298; p = 0.50 | χ2 = 1.199; p = 0.878 | |||
| Living alone | 170 | 70.5 | 189 | 47.2 | 37 | 2.0 |
| Living with spouse | 567 | 80.5 | 588 | 54.6 | 127 | 2.7 |
| Living with spouse and children | 1282 | 79.4 | 1328 | 55.8 | 277 | 2.1 |
| Living with children and other relatives | 919 | 76.2 | 1050 | 58.0 | 189 | 3.7 |
| Living with others | 175 | 81.0 | 200 | 53.3 | 37 | 1.9 |
| Education status | χ2 = 4.302; p = 0.231 | χ2 = 5.324; p = 0.15 | χ2 = 0.351; p = 0.439 | |||
| No education | 1773 | 76.8 | 1958 | 54.7 | 364 | 2.2 |
| Primary | 984 | 77.5 | 1048 | 54.6 | 201 | 2.2 |
| Secondary | 281 | 88.0 | 255 | 62.9 | 78 | 6.7 |
| Graduate and above | 75 | 76.3 | 94 | 61.9 | 24 | 2.0 |
| Wealth quintile | χ2 = 18.651; p < 0.001 | χ2 = 17.104; p < 0.05 | χ2 = 26.773; p < 0.001 | |||
| Poorest | 544 | 71.2 | 599 | 49.4 | 104 | 1.8 |
| Poorer | 629 | 77.0 | 686 | 53.3 | 132 | 2.0 |
| Middle | 640 | 79.8 | 682 | 56.8 | 118 | 1.9 |
| Richer | 640 | 75.7 | 692 | 52.7 | 146 | 2.6 |
| Richest | 660 | 86.7 | 696 | 66.6 | 167 | 5.6 |
| Social Group | χ2 = 21.528; p < 0.001 | χ2 = 17.070; p < 0.001 | χ2 = 49.073; p < 0.001 | |||
| Scheduled tribe | 285 | 72.0 | 339 | 48.6 | 48 | 1.0 |
| Scheduled caste | 595 | 78.6 | 654 | 57.8 | 102 | 1.8 |
| Other backward caste | 1265 | 77.3 | 1299 | 54.4 | 281 | 3.2 |
| Other caste | 881 | 80.4 | 947 | 57.1 | 215 | 2.8 |
| Religion | χ2 = 4.097; p = 0.129 | χ2 = 30.432; p < 0.001 | χ2 = 16.686; p < 0.001 | |||
| Hindu | 2473 | 78.0 | 2630 | 55.7 | 526 | 2.7 |
| Muslim | 355 | 77.3 | 396 | 57.0 | 78 | 2.9 |
| Other | 285 | 79.9 | 329 | 51.4 | 63 | 1.8 |
| Place of residence | χ2 = 0.132; p = 0.716 | χ2 = 3.535; p < 0.05 | χ2 = 2.419; p = 0.120 | |||
| Rural | 2226 | 78.2 | 2422 | 55.6 | 421 | 2.2 |
| Urban | 887 | 77.6 | 933 | 55.4 | 246 | 3.7 |
| Region | χ2 = 36.547; p < 0.001 | χ2 = 57.485; p < 0.001 | χ2 = 43.029; p < 0.001 | |||
| North | 429 | 79.4 | 449 | 50.6 | 91 | 2.0 |
| Central | 594 | 72.6 | 564 | 48.8 | 140 | 3.5 |
| East | 848 | 77.9 | 939 | 57.8 | 150 | 2.3 |
| Northeast | 483 | 83.7 | 611 | 59.6 | 126 | 2.2 |
| West | 521 | 80.0 | 531 | 55.5 | 121 | 3.2 |
| South | 238 | 69.7 | 261 | 58.8 | 39 | 1.2 |
| Background Characteristics | Hospitalization (Yearly) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public | Private | Average Total | ||||
| INR | USD | INR | USD | INR | USD | |
| Total | 10,727 | 168.56 | 29,747 | 467.44 | 22,316 | 350.67 |
| Age | ||||||
| 60–64 | 5459 | 85.78 | 19,360 | 304.22 | 14,208 | 223.26 |
| 65–69 | 9449 | 148.48 | 33,884 | 532.45 | 22,752 | 357.52 |
| 70–74 | 7036 | 110.56 | 29,052 | 456.52 | 20,792 | 326.72 |
| 75–79 | 12,432 | 195.35 | 46,496 | 730.63 | 32,940 | 517.61 |
| 80 or above | 33,790 | 530.96 | 30,537 | 479.85 | 31,410 | 493.57 |
| Sex | ||||||
| Male | 11,246 | 176.72 | 36,611 | 575.30 | 27,374 | 430.15 |
| Female | 10,351 | 162.65 | 24,028 | 377.57 | 18,358 | 288.47 |
| Living Status | ||||||
| Living alone | 1138 | 17.88 | 19,993 | 314.17 | 15,938 | 250.45 |
| Living with spouse | 8727 | 137.13 | 30,158 | 473.90 | 23,495 | 369.20 |
| Living with spouse and children | 11,216 | 176.25 | 39,260 | 616.92 | 29,044 | 456.39 |
| Living with children and other | 13,510 | 212.29 | 16,998 | 267.10 | 15,296 | 240.36 |
| Living with others | 4930 | 77.47 | 24,791 | 389.56 | 16,129 | 253.45 |
| Education status | ||||||
| No education | 6385 | 100.33 | 21,860 | 343.50 | 15,308 | 240.55 |
| Primary | 14,752 | 231.81 | 28,002 | 440.02 | 23,166 | 364.03 |
| Secondary | 18,383 | 288.87 | 72,232 | 1135.04 | 58,685 | 922.16 |
| Graduate and above | 91,300 | 1434.67 | 31,110 | 488.86 | 41,085 | 645.60 |
| Wealth quintile | ||||||
| Poorest | 4846 | 76.15 | 19,362 | 304.25 | 11,626 | 182.69 |
| Poorer | 3709 | 58.28 | 21,155 | 332.42 | 11,730 | 184.32 |
| Middle | 17,400 | 273.42 | 18,886 | 296.77 | 19,481 | 306.12 |
| Richer | 8841 | 138.93 | 28,432 | 446.77 | 21,648 | 340.17 |
| Richest | 24,021 | 377.46 | 44,860 | 704.92 | 39,756 | 624.72 |
| Social Group | ||||||
| None of them | 3922 | 61.63 | 20,348 | 319.74 | 8909 | 139.99 |
| Other backward classes | 9150 | 143.78 | 15,077 | 236.92 | 12,618 | 198.28 |
| Scheduled caste | 5958 | 93.62 | 29,000 | 455.70 | 22,096 | 347.21 |
| Scheduled tribe | 26,210 | 411.86 | 40,737 | 640.13 | 35,372 | 555.83 |
| Religion | ||||||
| Hindu | 11,064 | 173.86 | 29,326 | 460.82 | 22,653 | 355.96 |
| Muslim | 7674 | 120.59 | 36,532 | 574.06 | 23,024 | 361.79 |
| Other | 12,832 | 201.64 | 23,581 | 370.55 | 17,857 | 280.60 |
| Place of residence | ||||||
| Rural | 11,149 | 175.19 | 23,061 | 362.38 | 18,449 | 289.90 |
| Urban | 9503 | 149.33 | 44,193 | 694.44 | 31,365 | 492.86 |
| Region | ||||||
| North | 32,441 | 509.77 | 18,380 | 288.82 | 24,575 | 386.17 |
| Central | 3476 | 54.62 | 27,421 | 430.89 | 20,571 | 323.25 |
| East | 7852 | 123.38 | 43,554 | 684.40 | 21,755 | 341.85 |
| Northeast | 15,963 | 250.84 | 26,853 | 421.96 | 23,306 | 366.23 |
| West | 6487 | 101.94 | 30,763 | 483.40 | 22,369 | 351.50 |
| South | 22,240 | 349.47 | 36,715 | 576.93 | 26,399 | 414.83 |
| Types of Injury | ||||||
| Major injury | 5021 | 78.90 | 25,632 | 402.78 | 17,343 | 272.52 |
| Falls | 6248 | 98.18 | 27,680 | 434.96 | 19,302 | 303.31 |
| Bones and joints | 24,962 | 392.25 | 38,507 | 605.09 | 33,499 | 526.40 |
| Background Characteristics | Outpatient Care (Monthly) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public | Private | Average Total | ||||
| INR | USD | INR | USD | INR | USD | |
| Total | 1143 | 17.96 | 1743 | 27.39 | 1445 | 22.71 |
| Age | ||||||
| 60–64 | 608 | 9.55 | 1444 | 22.69 | 1115 | 17.52 |
| 65–69 | 710 | 11.16 | 1842 | 28.94 | 1407 | 22.11 |
| 70–74 | 987 | 15.51 | 1900 | 29.86 | 1544 | 24.26 |
| 75–79 | 6423 | 10.09 | 2003 | 31.47 | 2585 | 40.62 |
| 80 or above | 845 | 13.28 | 1745 | 27.42 | 1340 | 21.06 |
| Sex | ||||||
| Male | 1745 | 27.42 | 1833 | 28.80 | 1649 | 25.91 |
| Female | 708 | 11.13 | 1683 | 26.45 | 1307 | 20.54 |
| Living Status | ||||||
| Living alone | 759 | 11.93 | 1097 | 17.24 | 893 | 14.03 |
| Living with spouse | 663 | 10.42 | 1672 | 26.27 | 1331 | 20.92 |
| Living with spouse and children | 2024 | 31.80 | 1628 | 25.58 | 1580 | 24.83 |
| Living with children and other | 627 | 9.85 | 2116 | 33.25 | 1574 | 24.73 |
| Living with others | 496 | 7.79 | 1030 | 16.19 | 769 | 12.08 |
| Education status | ||||||
| No education | 635 | 9.98 | 1490 | 23.41 | 1114 | 17.51 |
| Primary | 948 | 14.90 | 1696 | 26.65 | 1385 | 21.76 |
| Secondary | 436 | 6.85 | 2594 | 40.76 | 2297 | 36.09 |
| Graduate and above | 36,268 | 569.91 | 2450 | 38.50 | 5719 | 89.87 |
| Wealth quintile | ||||||
| Poorest | 533 | 8.38 | 1529 | 24.03 | 1032 | 16.22 |
| Poorer | 729 | 11.46 | 1598 | 25.11 | 1209 | 19.00 |
| Middle | 621 | 9.76 | 1488 | 23.38 | 1110 | 17.44 |
| Richer | 733 | 11.52 | 1649 | 25.91 | 1295 | 20.35 |
| Richest | 3940 | 61.91 | 2172 | 34.13 | 2363 | 37.13 |
| Social Group | ||||||
| None of them | 1274 | 20.02 | 921 | 14.47 | 1007 | 15.82 |
| Other backward classes | 739 | 11.61 | 1755 | 27.58 | 1208 | 18.98 |
| Scheduled caste | 575 | 9.04 | 1795 | 28.21 | 1428 | 22.44 |
| Scheduled tribe | 2489 | 39.11 | 1824 | 28.66 | 1801 | 28.30 |
| Religion | ||||||
| Hindu | 1152 | 18.10 | 1760 | 27.66 | 1462 | 22.97 |
| Muslim | 755 | 11.86 | 1786 | 28.06 | 1359 | 21.36 |
| Other | 1779 | 27.95 | 1529 | 24.03 | 1390 | 21.84 |
| Place of residence | ||||||
| Rural | 1330 | 20.90 | 1582 | 24.86 | 1359 | 21.36 |
| Urban | 527 | 8.28 | 2112 | 33.19 | 1677 | 26.35 |
| Region | ||||||
| North | 4773 | 75.00 | 1199 | 18.84 | 2049 | 32.20 |
| Central | 422 | 6.63 | 2266 | 35.61 | 1857 | 29.18 |
| East | 791 | 12.43 | 1493 | 23.46 | 1123 | 17.65 |
| Northeast | 285 | 4.48 | 1772 | 27.84 | 1442 | 22.66 |
| West | 604 | 9.49 | 1258 | 19.77 | 957 | 15.04 |
| South | 2228 | 35.01 | 3842 | 60.37 | 2656 | 41.74 |
| Types of Injury | ||||||
| Major injury | 811 | 12.74 | 1456 | 22.88 | 1169 | 18.37 |
| Falls | 529 | 8.31 | 1820 | 28.60 | 1311 | 20.60 |
| Bones and joints | 3498 | 54.97 | 2097 | 32.95 | 2223 | 34.93 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yadav, J.; Yadav, P.; Peden, A.E. Measuring the Prevalence, Treatment, and Associated Treatment Costs of Injury for Older Adults in India: Insights from the National Longitudinal Aging Study. Safety 2024, 10, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/safety10030066
Yadav J, Yadav P, Peden AE. Measuring the Prevalence, Treatment, and Associated Treatment Costs of Injury for Older Adults in India: Insights from the National Longitudinal Aging Study. Safety. 2024; 10(3):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/safety10030066
Chicago/Turabian StyleYadav, Jeetendra, Priyanka Yadav, and Amy E. Peden. 2024. "Measuring the Prevalence, Treatment, and Associated Treatment Costs of Injury for Older Adults in India: Insights from the National Longitudinal Aging Study" Safety 10, no. 3: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/safety10030066
APA StyleYadav, J., Yadav, P., & Peden, A. E. (2024). Measuring the Prevalence, Treatment, and Associated Treatment Costs of Injury for Older Adults in India: Insights from the National Longitudinal Aging Study. Safety, 10(3), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/safety10030066






