A Computational Approach to Hand Pose Recognition in Early Modern Paintings
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The first annotated dataset of painted hands (Painted Hand Pose dataset), introducing a new standard for hand pose annotation in the context of digital art history;
- New hand pose features based on 2D keypoint information produced by HPE methods;
- The introduction of a novel classification task and a proposed solution method based on keypoint feature extraction.
2. Materials and Methods
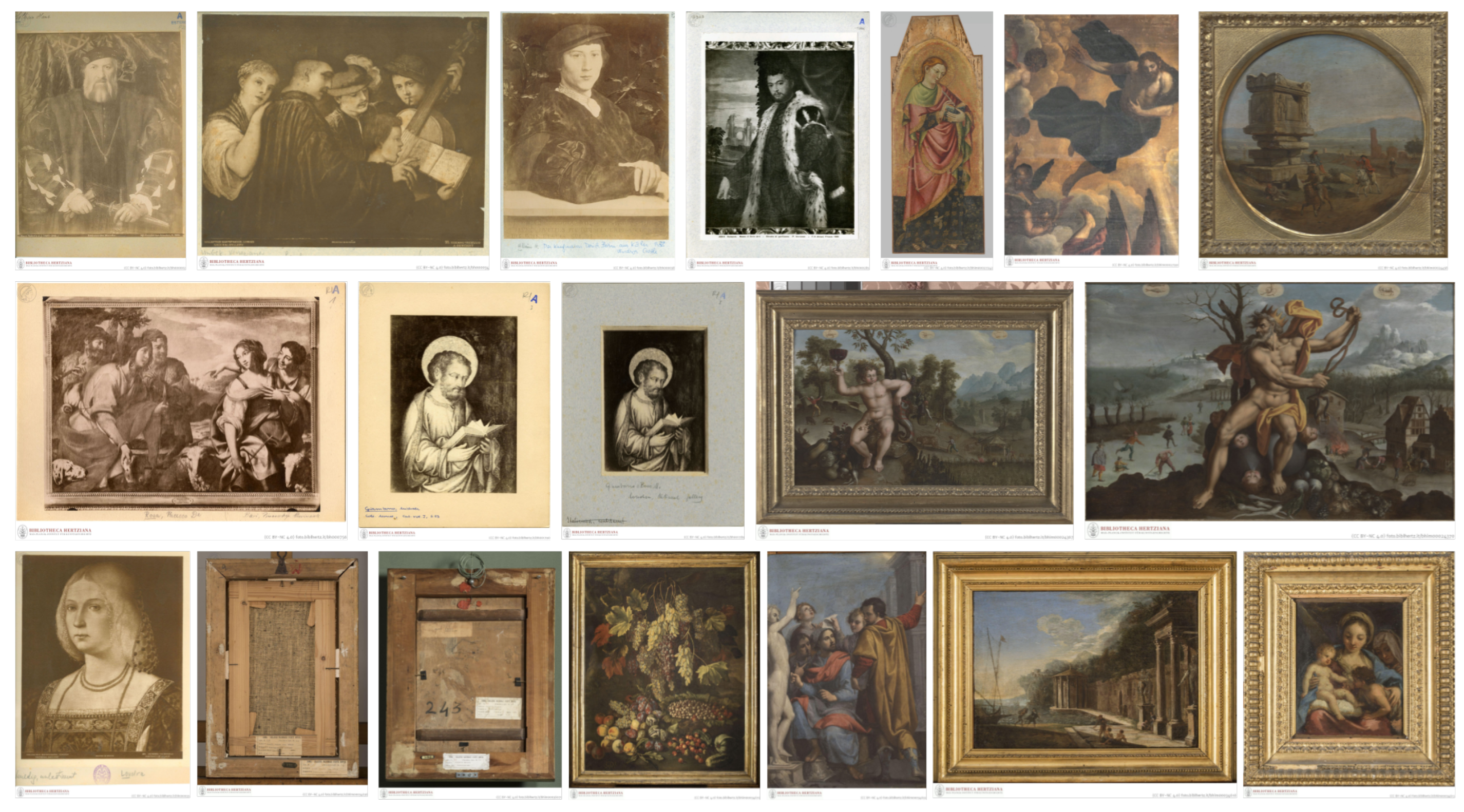
2.1. Dataset
2.1.1. Data Acquisition and Metadata Processing
2.1.2. Hand Extraction
2.1.3. Data Categorization and Annotation
2.2. Feature Descriptors
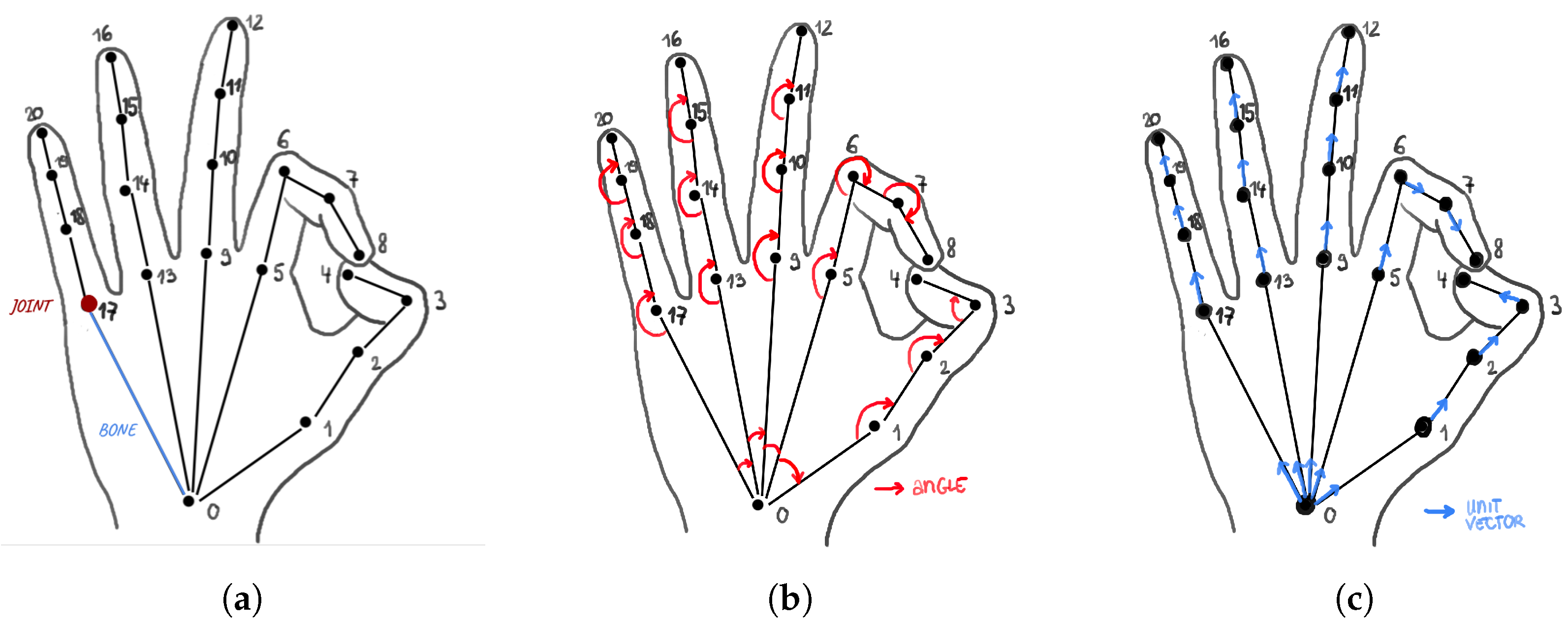
2.2.1. Hand Keypoint Features
2.2.2. Neural-Network-Based Image Features
2.3. Classification Settings
3. Results
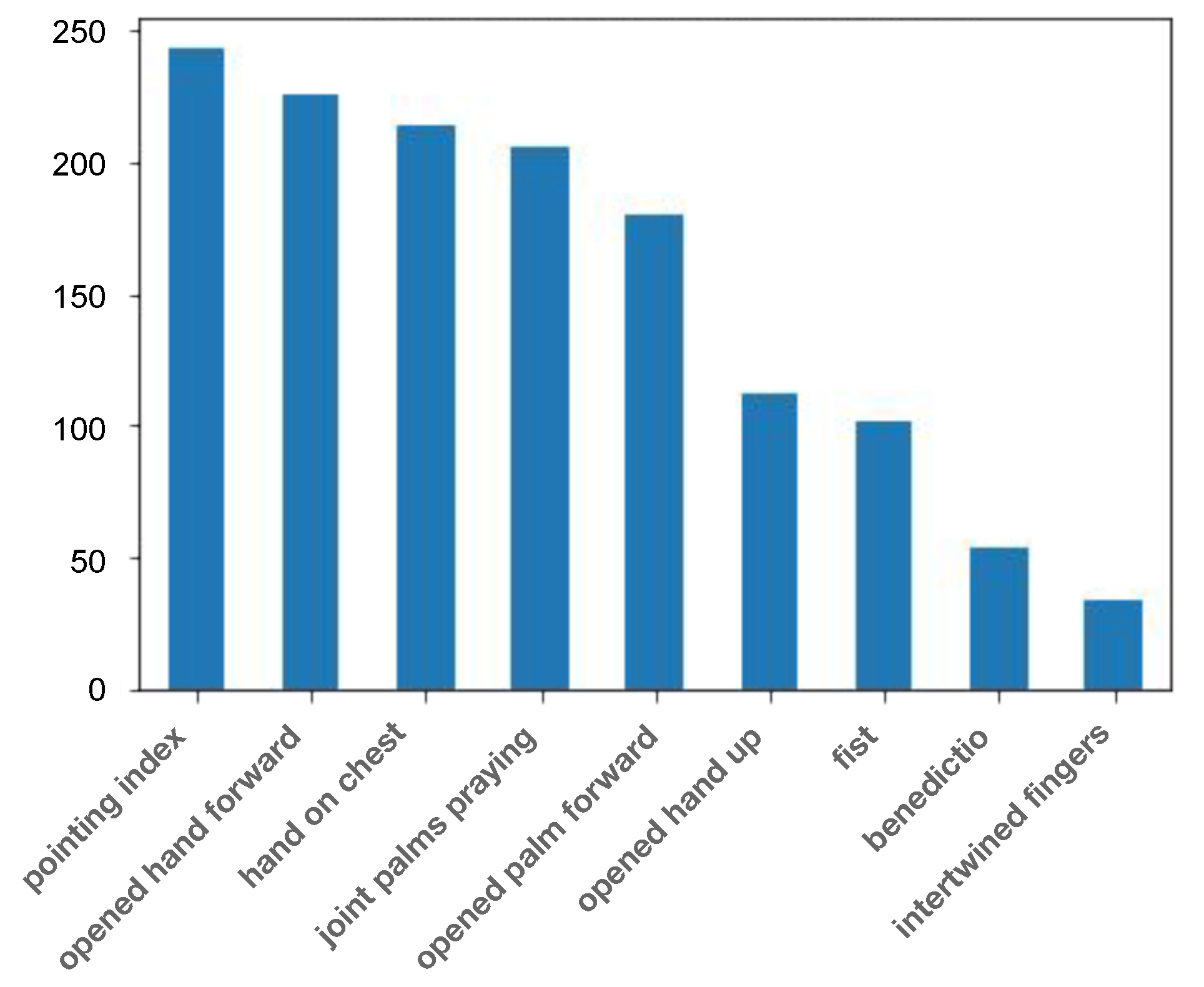
3.1. Exploratory Analysis
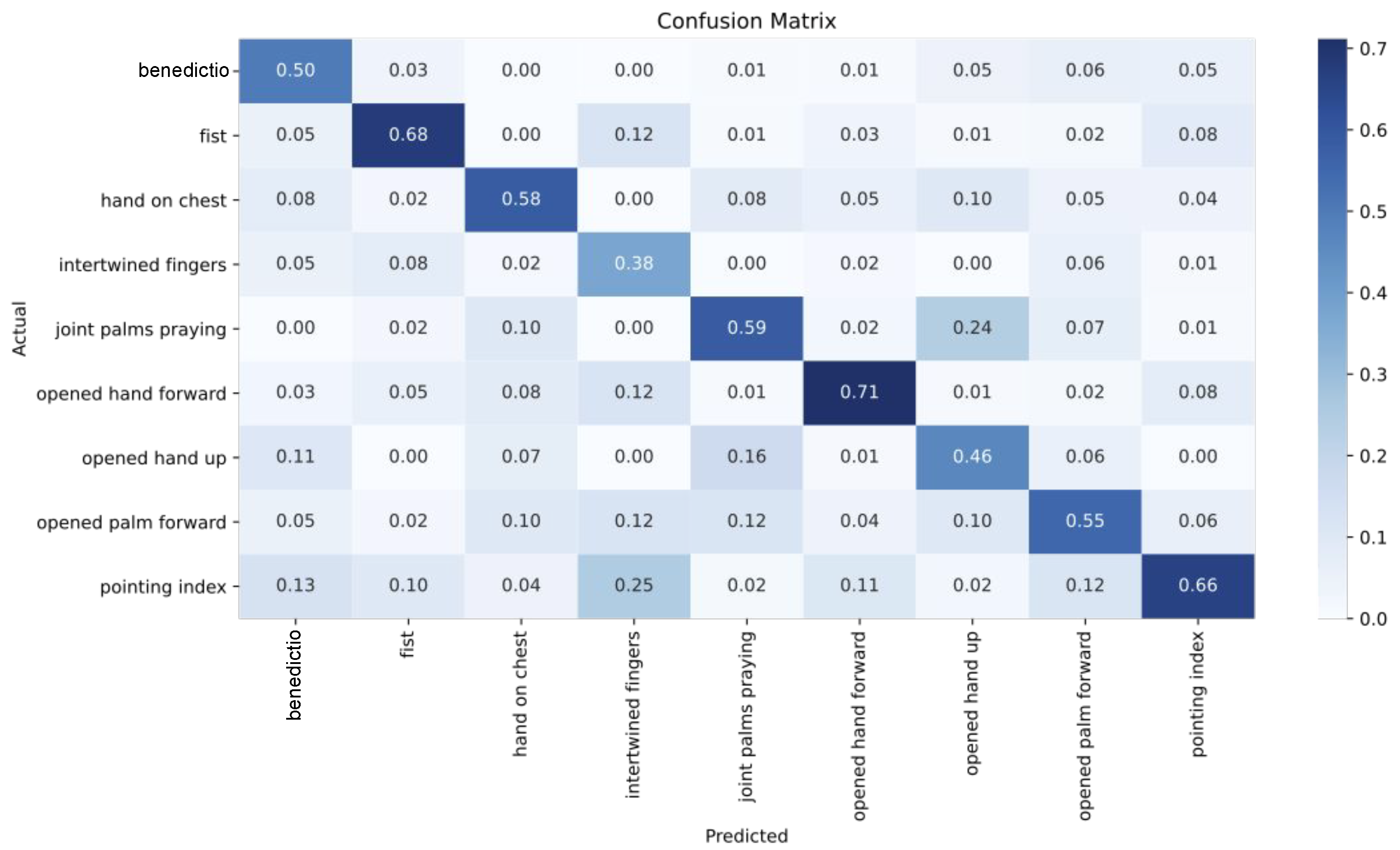
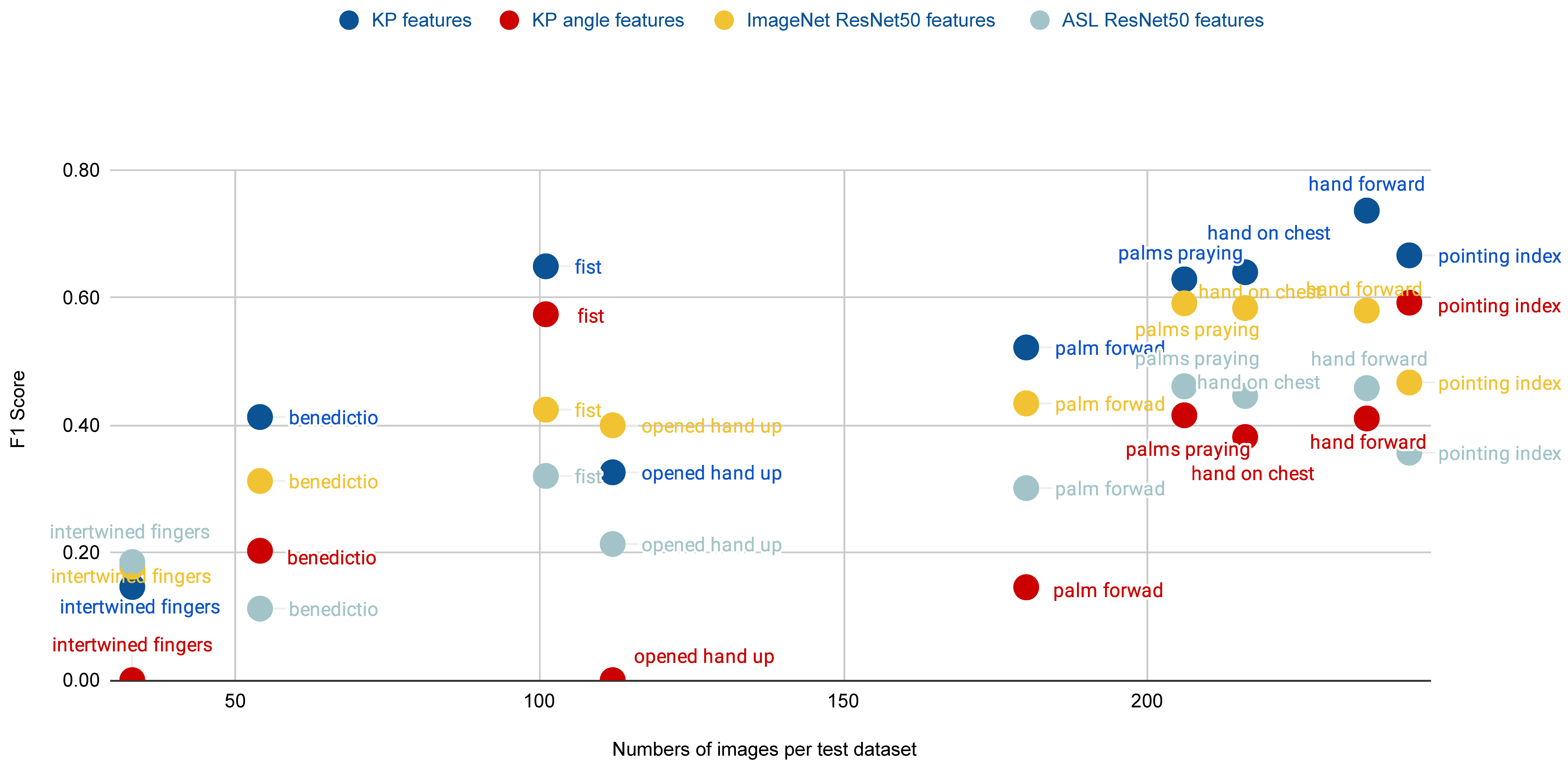
3.2. Classification Results
3.3. Application for Gesture-Based Image Search
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schmitt, J.C. La Raison des Gestes Dans L’Occident Médiéval; Editions Gallimard: Paris, France, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Wittkower, R. La Migration des Symboles; Iconologia; Thames & Hudson: Paris, France, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Dimova, T. Le Langage des Mains Dans L’art: Histoire, Significations et Usages des Chirogrammes Picturaux aux XVIIe et XVIIIe Siecles; Brepols Publishers: Turnhout, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Spicer, J. The Renaissance elbow. In A Cultural History of Gesture. From Antiquity to the Present Day; Bremmer, J., Roodenburg, H., Eds.; Polity Press: Cambridge, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, S.; Karnick, H.; Pant, N.; Patel, U. Genre and Style Based Painting Classification. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 5–9 January 2015; pp. 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, R.S.; Elgammal, A. Towards automated classification of fine-art painting style: A comparative study. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR2012), Tsukuba, Japan, 11–15 November 2012; pp. 3541–3544. [Google Scholar]
- Cetinic, E.; Lipic, T.; Grgic, S. Fine-tuning convolutional neural networks for fine art classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 114, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.R.; Chan, C.S.; Aguirre, H.E.; Tanaka, K. Ceci n’est pas une pipe: A deep convolutional network for fine-art paintings classification. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25–28 September 2016; pp. 3703–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguin, B.; Striolo, C.; diLenardo, I.; Kaplan, F. Visual Link Retrieval in a Database of Paintings. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2016 Workshops, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Hua, G., Jégou, H., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 753–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Efros, A.A.; Aubry, M. Discovering Visual Patterns in Art Collections With Spatially-Consistent Feature Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 9270–9279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ufer, N.; Simon, M.; Lang, S.; Ommer, B. Large-scale interactive retrieval in art collections using multi-style feature aggregation. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Champenois, R.; Ginosar, S.; Pastrolin, I.; Rousselot, M.; Bounou, O.; Monnier, T.; Gidaris, S.; Bougard, F.; Raverdy, P.G.; et al. Spatially-consistent Feature Matching and Learning for Heritage Image Analysis. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2022, 130, 1325–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, P.; Schlecht, J.; Ommer, B. Nonverbal Communication in Medieval Illustrations Revisited by Computer Vision and Art History. Vis. Resour. 2013, 29, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.; Kovashka, A. Artistic Object Recognition by Unsupervised Style Adaptation. In Computer Vision—ACCV 2018; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Jawahar, C.V., Li, H., Mori, G., Schindler, K., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 11363, pp. 460–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Monson, E.; Honig, E.; Daubechies, I.; Maggioni, M. Object recognition in art drawings: Transfer of a neural network. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Shanghai, China, 20–25 March 2016; pp. 2299–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smir nov, S.; Eguizabal, A. Deep learning for object detection in fine-art paintings. In Proceedings of the 2018 Metrology for Archaeology and Cultural Heritage (MetroArchaeo), Cassino, Italy, 22–24 October 2018; pp. 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Van Zuijlen, M.; Wijntjes, M.W.A.; Pont, S.C.; Bala, K. Insights from a Large-Scale Database of Material Depictions in Paintings. arXiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impett, L.; Süsstrunk, S. Pose and Pathosformel in Aby Warburg’s Bilderatlas. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2016 Workshops, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–10 October 2016; Hua, G., Jégou, H., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 888–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsocci, V.; Lastilla, L. POSE-ID-on—A Novel Framework for Artwork Pose Clustering. ISPRS Int. J.-Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhu, P.; Villar-Corrales, A.; Kosti, R.; Bendschus, T.; Reinhardt, C.; Bell, P.; Maier, A.; Christlein, V. Enhancing Human Pose Estimation in Ancient Vase Paintings via Perceptually-grounded Style Transfer Learning. J. Comput. Cult. Herit. 2022, 16, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohrt, R.; Ohrt, R. Aby Warburg: Bilderatlas Mnemosyne: The Original; Kulturgeschichte; Hatje Cantz Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Hidalgo, G.; Simon, T.; Wei, S.E.; Sheikh, Y. OpenPose: Realtime Multi-Person 2D Pose Estimation Using Part Affinity Fields. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler, R.A.; Neverova, N.; Kokkinos, I. DensePose: Dense Human Pose Estimation in the Wild. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7297–7306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriluka, M.; Pishchulin, L.; Gehler, P.; Schiele, B. 2D Human Pose Estimation: New Benchmark and State of the Art Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 3686–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, T.; Joo, H.; Matthews, I.; Sheikh, Y. Hand Keypoint Detection in Single Images using Multiview Bootstrapping. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Impett, L.; Bell, P. Ikonographie Und Interaktion. Computergestützte Analyse von Posen in Bildern der Heilsgeschichte. Das Mittelalt. 2019, 24, 31–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impett, L. Analyzing Gesture in Digital Art History. In The Routledge Companion to Digital Humanities and Art History; Routledge: London, UK, 2020; pp. 386–407. [Google Scholar]
- Bernasconi, V. GAB—Gestures for Artworks Browsing. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces, Online, 22–25 March 2022; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2022. IUI ‘22 Companion. pp. 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springstein, M.; Schneider, S.; Althaus, C.; Ewerth, R. Semi-Supervised Human Pose Estimation in Art-Historical Images. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Lisboa, Portugal, 10–14 October 2022; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2022. MM ’22. pp. 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenicek, T.; Chum, O. Linking Art through Human Poses. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition (ICDAR), Sydney, Australia, 20–25 September 2019; pp. 1338–1345. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Akdağ Salah, A.; Salah, A.A. Automatic Analysis of Human Body Representations in Western Art. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2022 Workshops, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Proceedings, Part I. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 282–297. [Google Scholar]
- Milani, F.; Fraternali, P. A Dataset and a Convolutional Model for Iconography Classification in Paintings. J. Comput. Cult. Herit. 2021, 14, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetinic, E. Towards Generating and Evaluating Iconographic Image Captions of Artworks. J. Imaging 2021, 7, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carfì, A.; Mastrogiovanni, F. Gesture-Based Human–Machine Interaction: Taxonomy, Problem Definition, and Analysis. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2023, 53, 497–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisharady, P.K.; Saerbeck, M. Recent methods and databases in vision-based hand gesture recognition: A review. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2015, 141, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, B.K.; Sarma, D.; Bhuyan, M.; MacDorman, K.F. Review of constraints on vision-based gesture recognition for human–computer interaction. IET Computer Vision 2018, 12, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudah, M.; Al-Naji, A.; Chahl, J. Hand Gesture Recognition Based on Computer Vision: A Review of Techniques. J. Imaging 2020, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Kallu, K.D.; Ahmed, S.; Cho, S.H. Hand Gestures Recognition Using Radar Sensors for Human-Computer-Interaction: A Review. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Bazarevsky, V.; Vaku nov, A.; Tkachenka, A.; Sung, G.; Chang, C.L.; Grundmann, M. MediaPipe Hands: On-device Real-time Hand Tracking. arXiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M, S.; Rakesh, S.; Gupta, S.; Biswas, S.; Das, P.P. Real-time hands-free immersive image navigation system using Microsoft Kinect 2.0 and Leap Motion Controller. In Proceedings of the 2015 Fifth National Conference on Computer Vision, Pattern Recognition, Image Processing and Graphics (NCVPRIPG), Patna, Bihar, 16–19 December 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Yuan, J.; Meng, J.; Zhang, Z. Robust Part-Based Hand Gesture Recognition Using Kinect Sensor. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2013, 15, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, G.; Dominio, F.; Zanuttigh, P. Hand gesture recognition with leap motion and kinect devices. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Paris, France, 27–30 October 2014; pp. 1565–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, J.C.; Cabido, R.; Pantrigo, J.J.; Montemayor, A.S.; Vélez, J.F. Convolutional Neural Networks and Long Short-Term Memory for skeleton-based human activity and hand gesture recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 76, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köpüklü, O.; Gunduz, A.; Kose, N.; Rigoll, G. Real-time Hand Gesture Detection and Classification Using Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 14th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2019), Lille, France, 14–18 May 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, G.; Sokal, K.; Uboweja, E.; Bazarevsky, V.; Baccash, J.; Bazavan, E.G.; Chang, C.L.; Grundmann, M. On-device Real-time Hand Gesture Recognition. arXiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastgoo, R.; Kiani, K.; Escalera, S. Sign Language Recognition: A Deep Survey. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 164, 113794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheok, M.J.; Omar, Z.; Jaward, M.H. A review of hand gesture and sign language recognition techniques. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2019, 10, 131–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Gupta, P.; Jha, R.K.; Bhatia, A.; Jha, K.; Shah, B.K. Sign Language Alphabet Recognition Using Convolution Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2021 5th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS), Madurai, India, 6–8 May 2021; pp. 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Matsuoka, A.; Hasan, M.A.M.; Srizon, A.Y. American Sign Language Alphabet Recognition by Extracting Feature from Hand Pose Estimation. Sensors 2021, 21, 5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, H.; Tan, J.; Xu, H.; Yang, C.; Peng, G.; Wang, L.; Liu, J. Hand Image Understanding via Deep Multi-Task Learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 11281–11292. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraj, A. ASL Alphabet. 2018. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/grassknoted/asl-alphabet (accessed on 21 February 2023).
- Lucafò, C.; Marzoli, D.; Zdybek, P.; Malatesta, G.; Smerilli, F.; Ferrara, C.; Tommasi, L. The Bias toward the Right Side of Others Is Stronger for Hands than for Feet. Symmetry 2021, 13, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzoli, D.; Lucafò, C.; Pagliara, A.; Cappuccio, R.; Brancucci, A.; Tommasi, L. Both right- and left-handers show a bias to attend others’ right arm. Exp. Brain Res. 2015, 233, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertz, R. La prééminence de la main droite: Étude sur la polarité religieuse. Revue Philosophique de la France et de L’Étranger 1909, 68, 553–580. [Google Scholar]
- Barasch, M. Giotto and the Language of Gesture; Cambridge studies in the history of art; University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Bernasconi, V. La main baladeuse. Jeu de Paume en ligne 2022. as part of the online exhibition Contagions visuelles. Available online: https://jdp.visualcontagions.net/nautilus (accessed on 7 June 2022).
- Hughes, A. Why AI-generated hands are the stuff of nightmares, explained by a scientist. BBC Science Focus Magazine, 4 February 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chayka, K. The Uncanny Failure of A.I.-Generated Hands. The New Yorker, 10 March 2023. [Google Scholar]





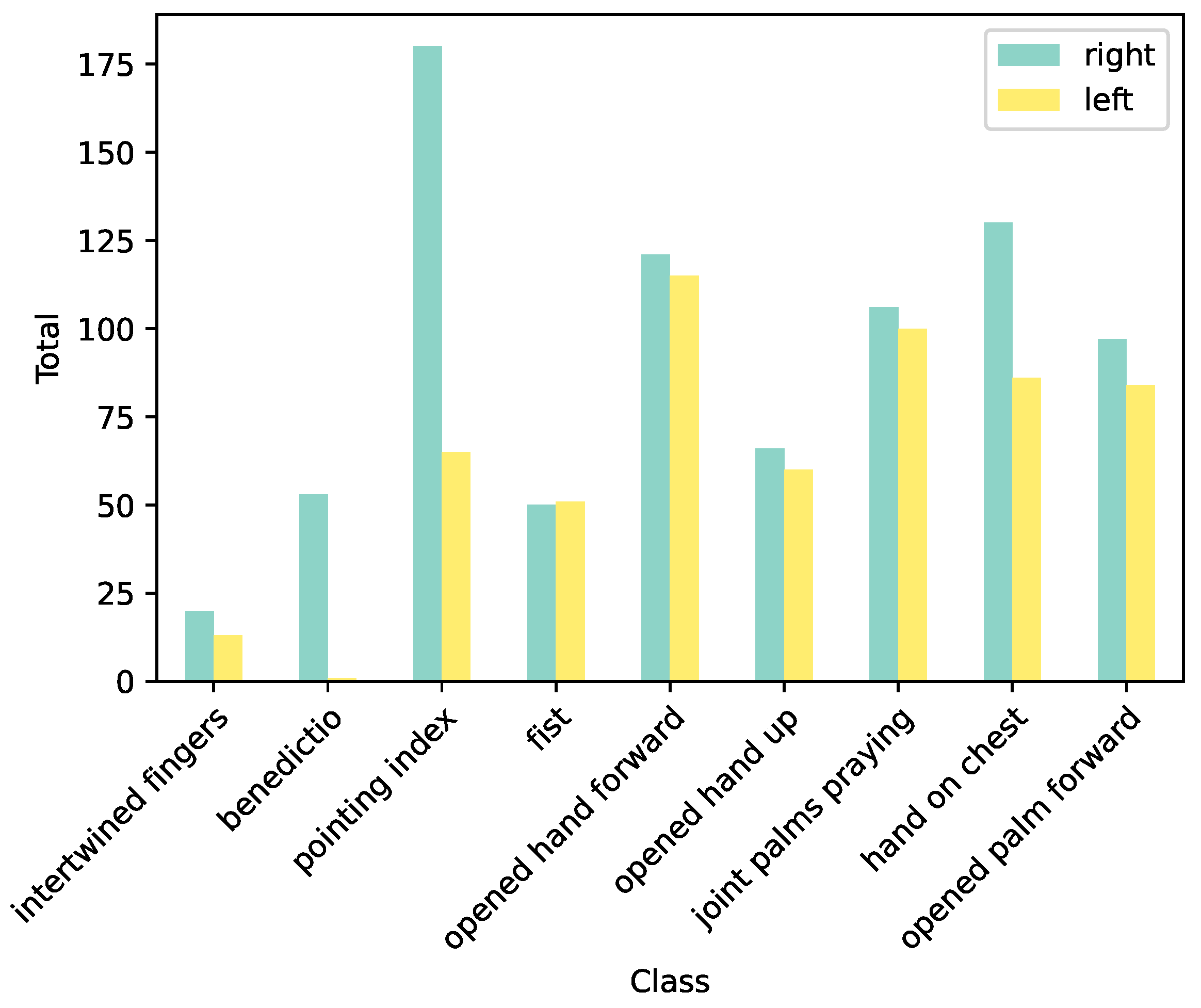
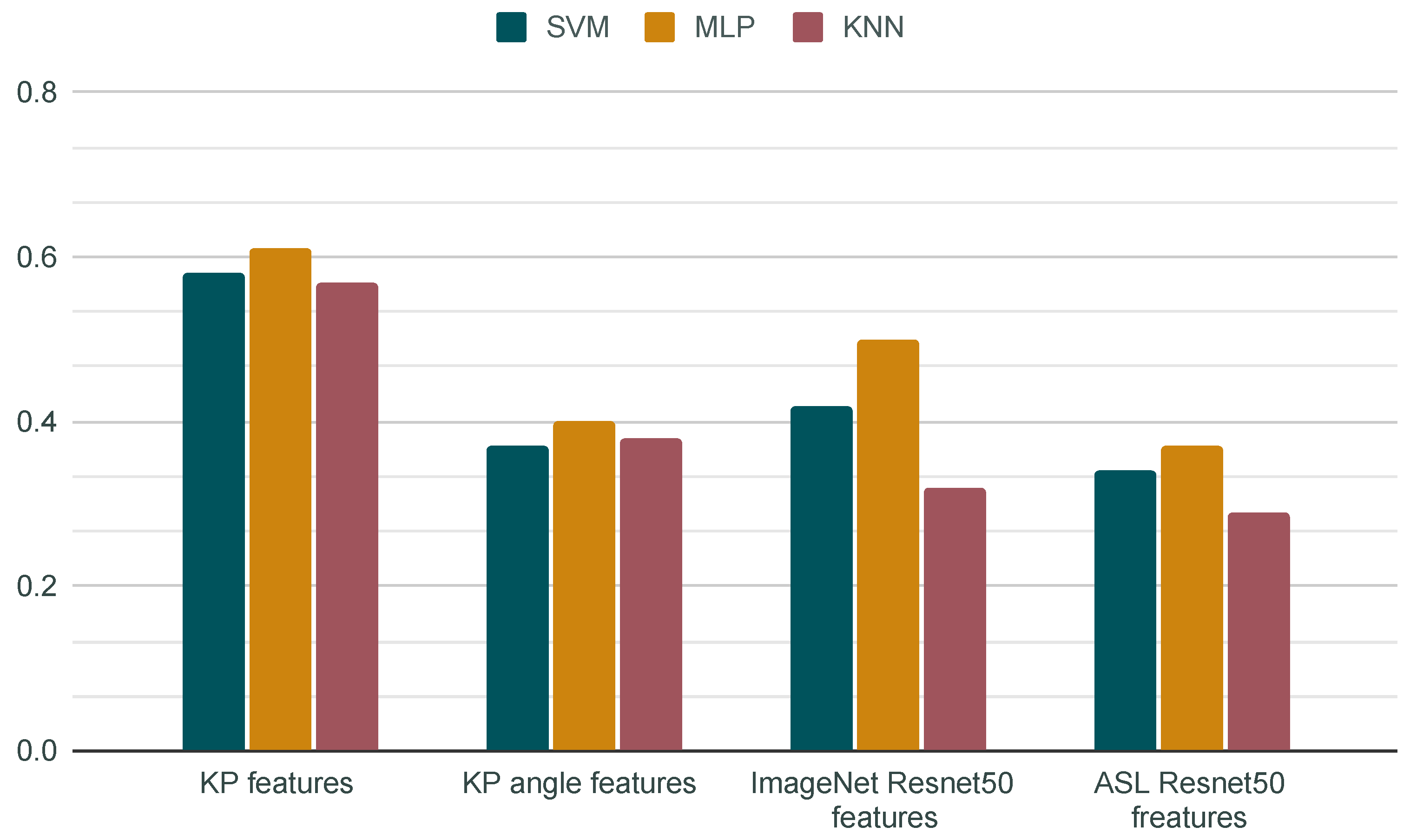



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bernasconi, V.; Cetinić, E.; Impett, L. A Computational Approach to Hand Pose Recognition in Early Modern Paintings. J. Imaging 2023, 9, 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9060120
Bernasconi V, Cetinić E, Impett L. A Computational Approach to Hand Pose Recognition in Early Modern Paintings. Journal of Imaging. 2023; 9(6):120. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9060120
Chicago/Turabian StyleBernasconi, Valentine, Eva Cetinić, and Leonardo Impett. 2023. "A Computational Approach to Hand Pose Recognition in Early Modern Paintings" Journal of Imaging 9, no. 6: 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9060120
APA StyleBernasconi, V., Cetinić, E., & Impett, L. (2023). A Computational Approach to Hand Pose Recognition in Early Modern Paintings. Journal of Imaging, 9(6), 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9060120









