A Siamese Transformer Network for Zero-Shot Ancient Coin Classification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Automatic Ancient Coins Analysis Using Computer Vision and Machine Learning
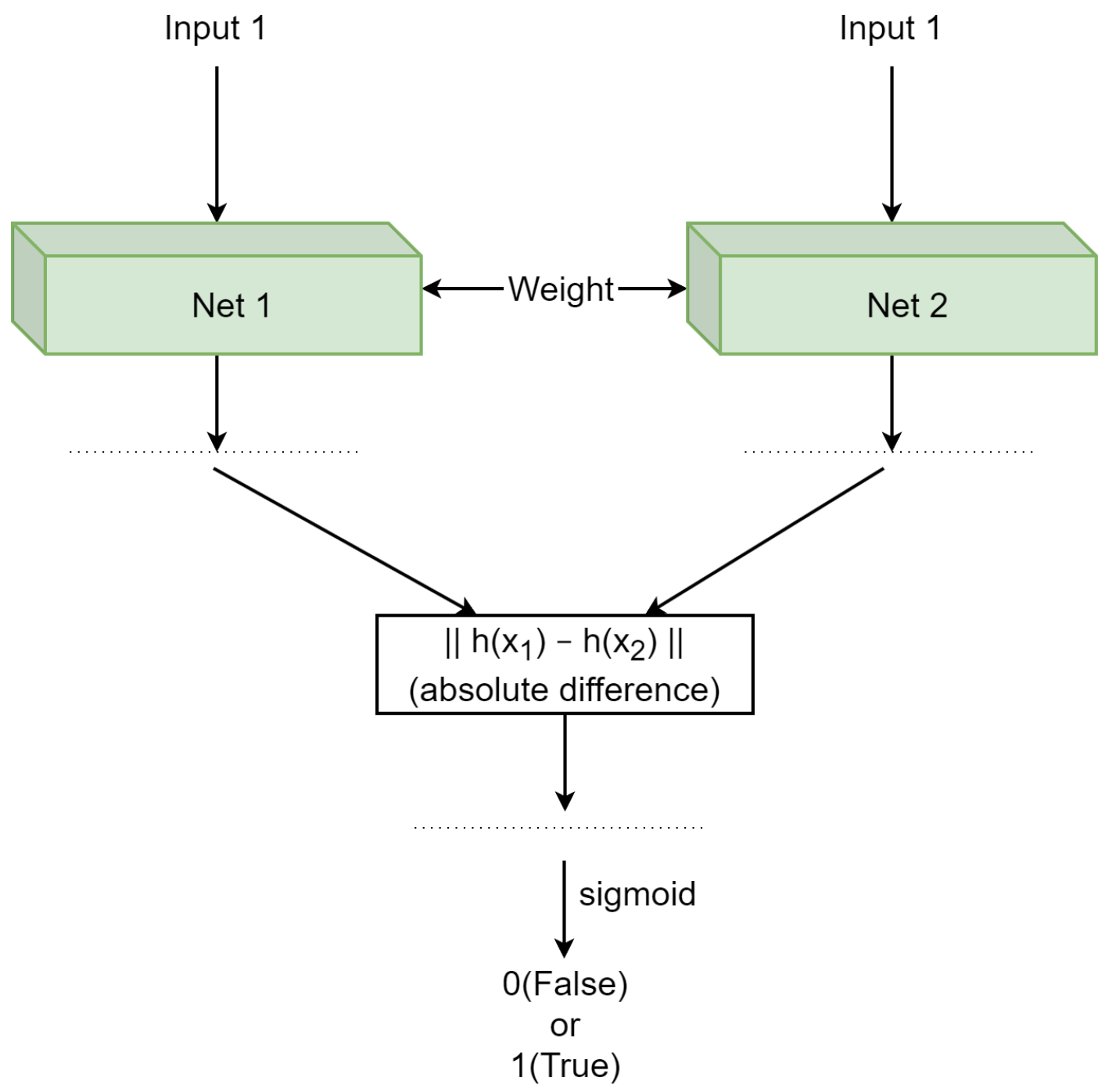
2.2. Siamese Neural Networks
2.3. Transformers
Vision Transformer
3. Proposed Methodology
3.1. Proposed Network Architectures
3.1.1. Single Siamese ViT
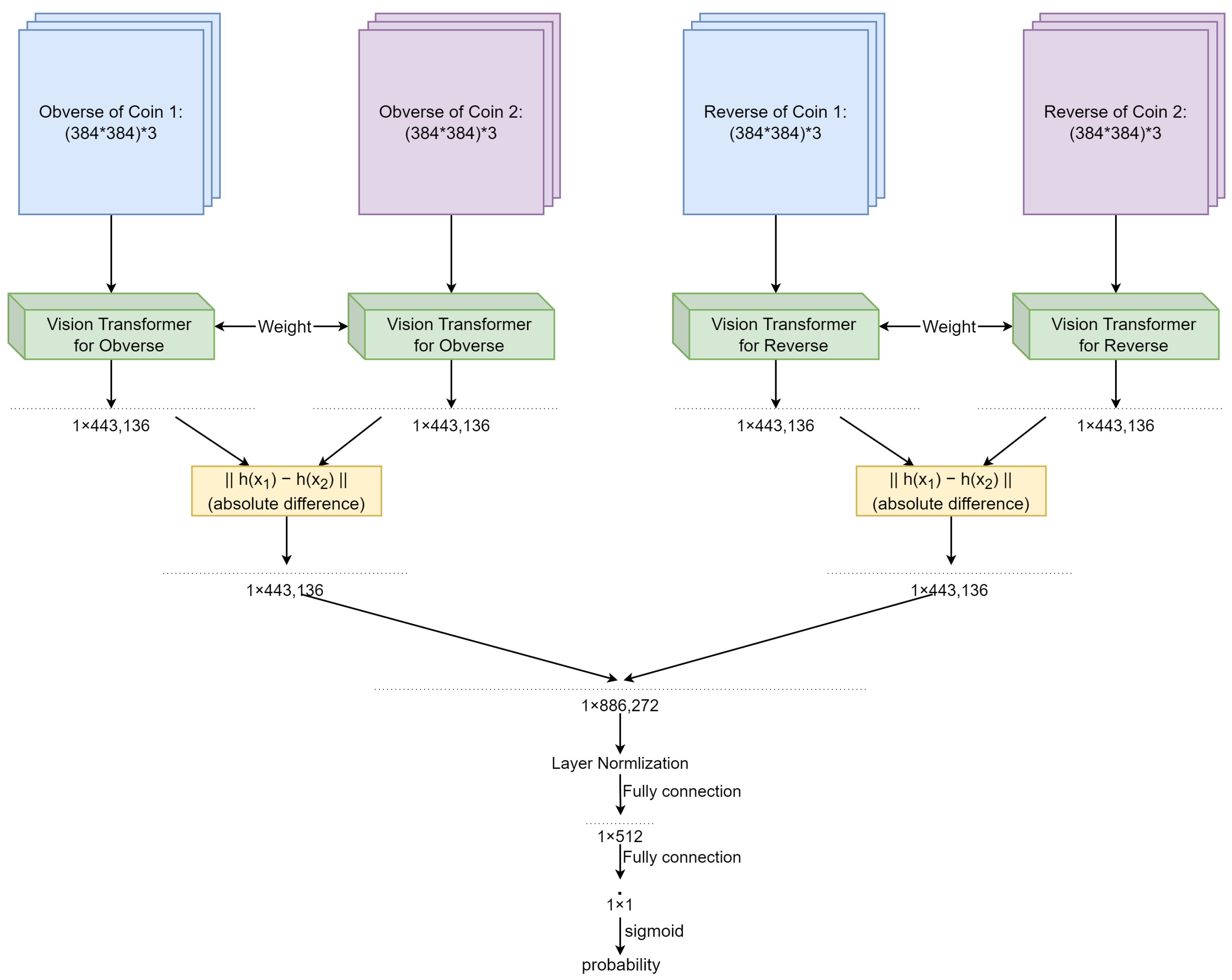
3.1.2. Double Siamese ViT
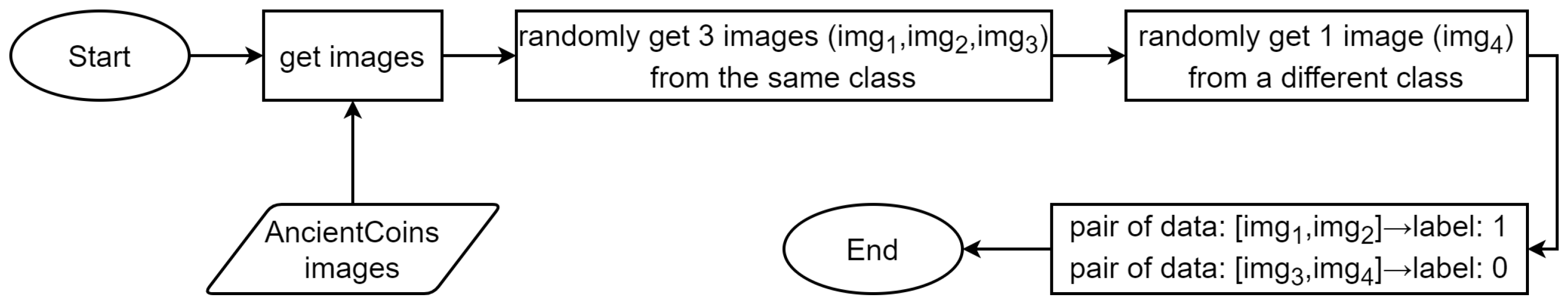
3.2. Training Methodology and the Organization of Training Data
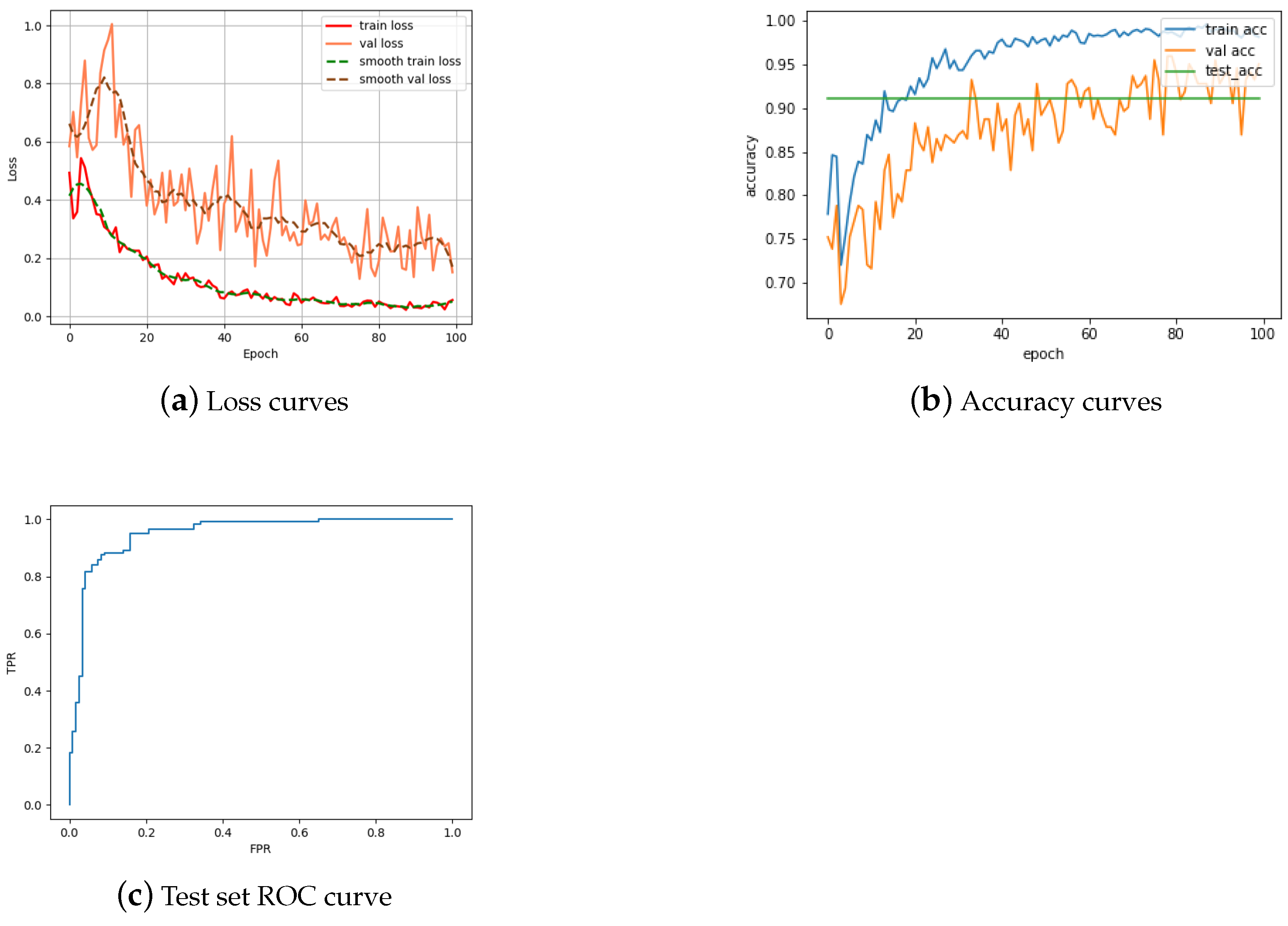
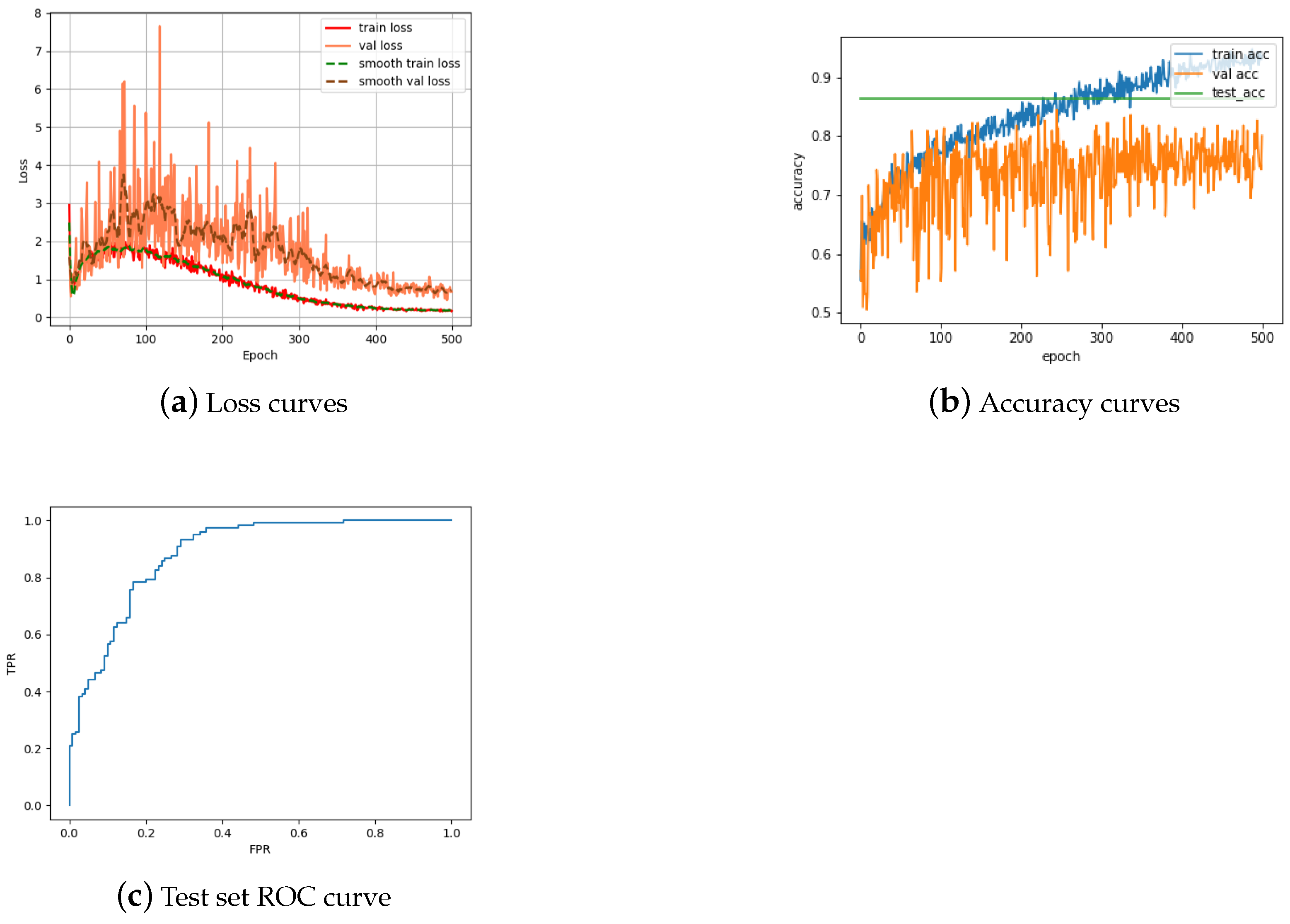
4. Results and Evaluation
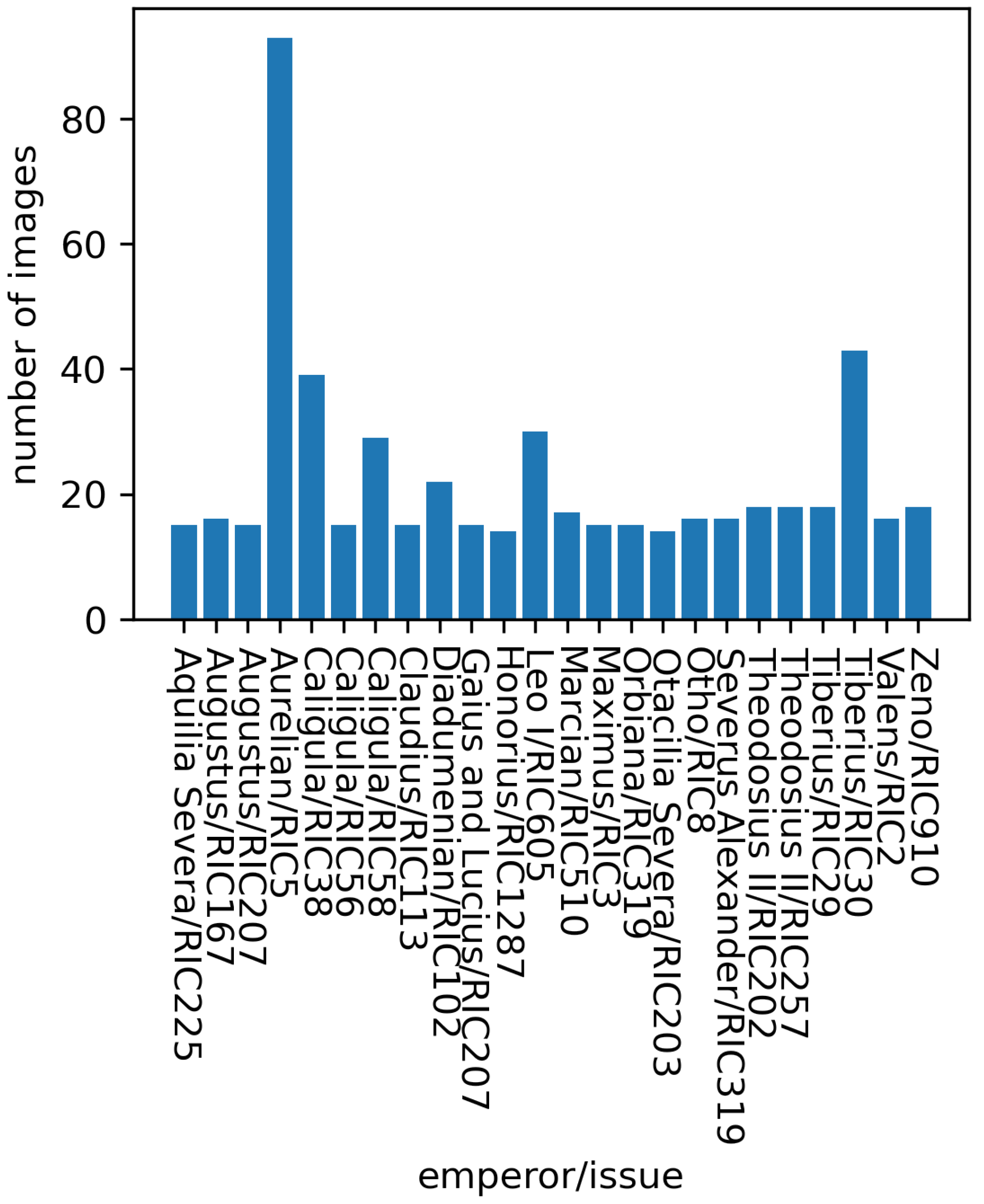
4.1. Data
4.2. Single Siamese ViT
4.2.1. Obverse Matching
4.2.2. Reverse Matching
4.3. Double Siamese ViT
Further Model Probing
4.4. Analysis of Problematic Issuing Authorities
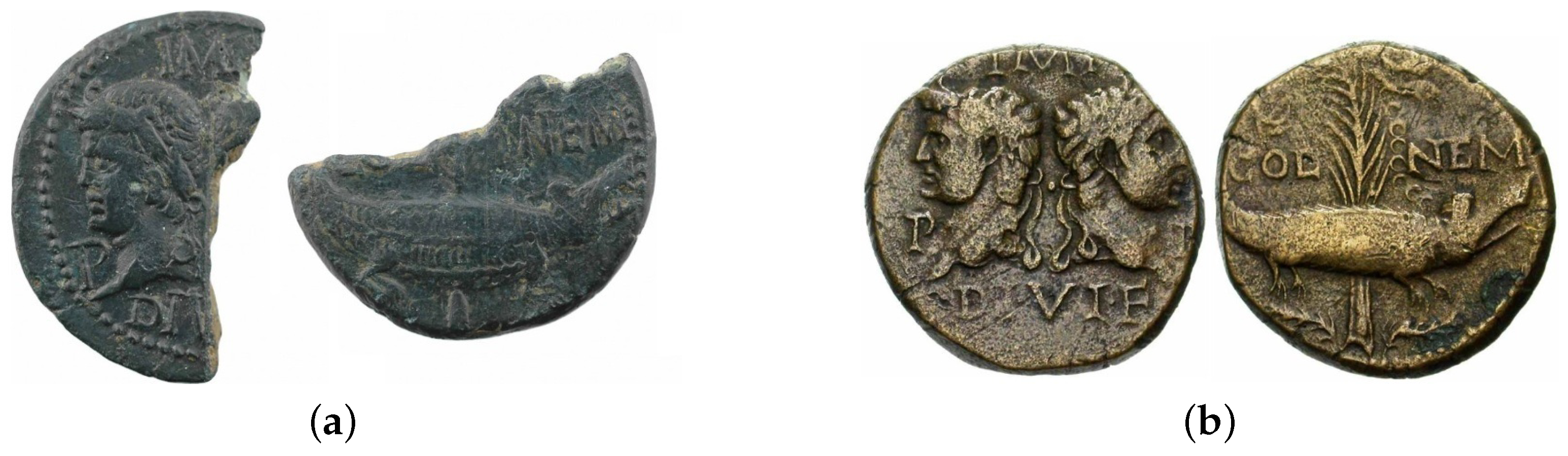
4.4.1. Physically Incomplete Specimens
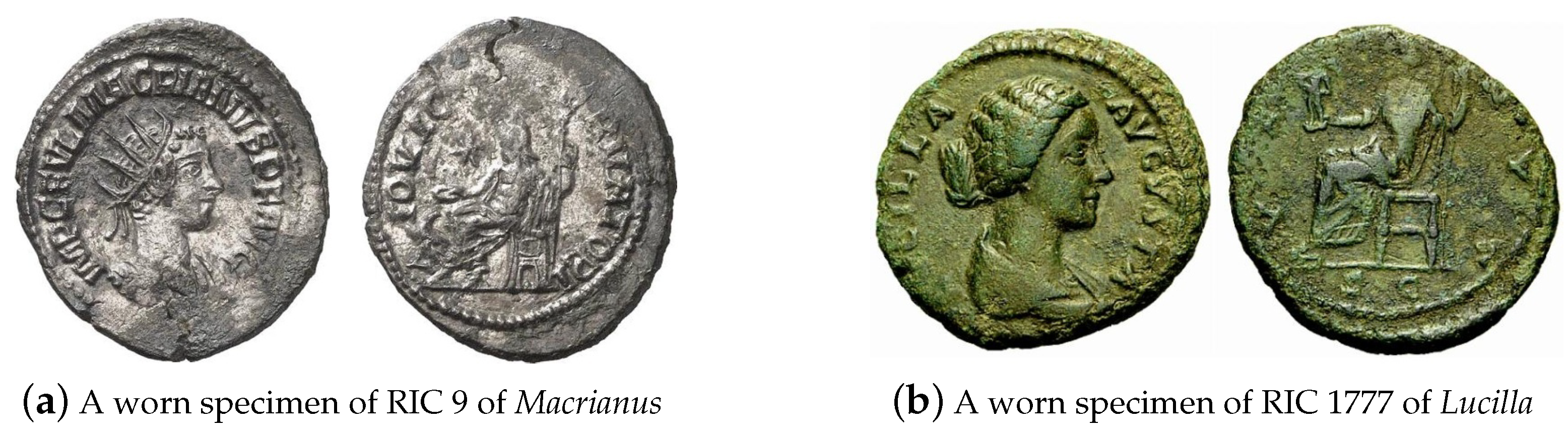
4.4.2. Worn and Environmentally Affected Coins
4.4.3. Data Irregularities
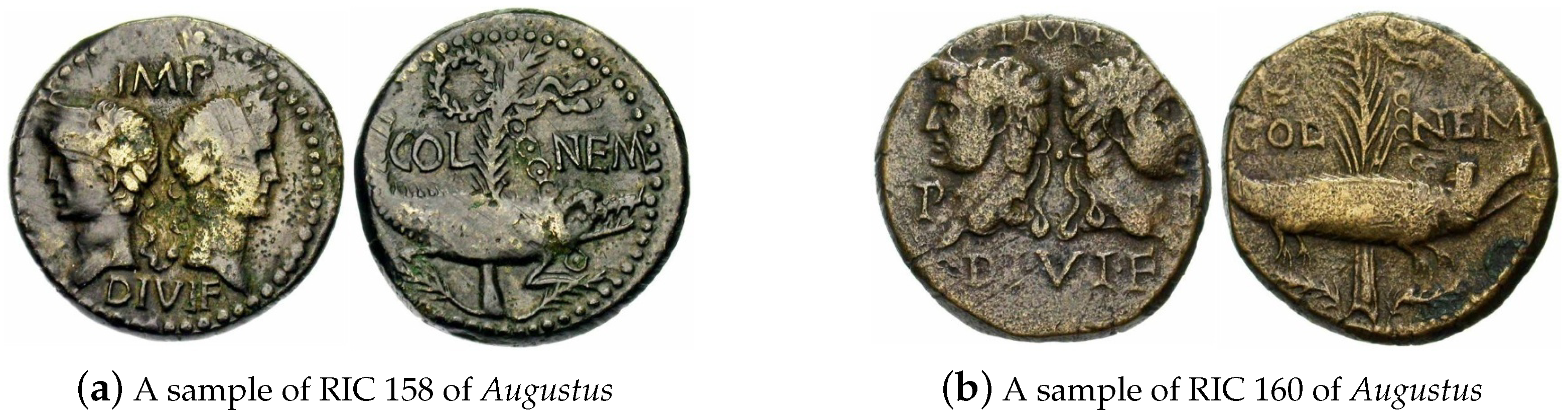
4.4.4. High Similarity between Issues
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Aelia Ariadne | Faustina II | Nero Claudius Drusus |
| Aelia Flacilla | Flavia Titiana | Nerva |
| Aelia Verina | Flavius Victor | Nigrinian |
| Aelius | Florian | Numerian |
| Aemilian | Gaius and Lucius | Octavia |
| Agrippa | Galba | Orbiana |
| Agrippa Postumus | Galeria Valeria | Otacilia Severa |
| Agrippina I | Galerius | Otho |
| Agrippina II | Galerius Antoninus | Pacatian |
| Alexander | Galla Placidia | Paulina |
| Allectus | Gallienus | Pertinax |
| Annia Faustina | Gemellus | Pescennius Niger |
| Annius Verus | Germanicus | Petronius Maximus |
| Anonymous | Geta | Philip I |
| Anthemius | Glycerius | Philip II |
| Antinous | Gordian I | Plautilla |
| Antonia | Gordian II | Plotina |
| Antoninus Pius | Gordian III | Poppaea |
| Aquilia Severa | Gratian | Postumus |
| Arcadius | Hadrian | Priscus Attalus |
| Asinius Gallus | Hanniballianus | Probus |
| Augustus | Helena | Procopius |
| Aurelian | Herennia Etruscilla | Proculus |
| Aureolus | Herennius Etruscus | Pulcheria |
| Avitus | Honoria | Pupienus |
| Balbinus | Honorius | Quietus |
| Basiliscus | Hostilian | Quintillus |
| Bonosus | Johannes | Regalianus |
| Britannicus | Jotapian | Romulus |
| Caesonia | Jovian | Romulus Augustus |
| Caius and Lucius | Jovinus | Sabina |
| Caligula | Julia | Salonina |
| Caracalla | Julia Domna | Saloninus |
| Carausius | Julia Maesa | Sebastianus |
| Carinus | Julia Mamaea | Sejanus |
| Carus | Julia Paula | Septimius Severus |
| City Commemoratives | Julia Soaemias | Severina |
| Civil Wars | Julia Titi | Severus II |
| Claudius | Julian I | Severus III |
| Claudius II (Gothicus) | Julian II | Severus Alexander |
| Clodius Albinus | Julius Marinus | Statilia Messalina |
| Clodius Macer | Julius Nepos | Tacitus |
| Commodus | Laelianus | Tesserae etc. |
| Constans | Leo I | Tetricus I |
| Constantine I | Leo II | Tetricus II |
| Constantine II | Libo | Theodora |
| Constantine III | Licinia Eudoxia | Theodosius I |
| Constantius I | Licinius I | Theodosius II |
| Constantius II | Licinius II | Tiberius |
| Constantius III | Livia | Titus |
| Constantius Gallus | Livilla | Trajan |
| Cornelia Supera | Lucilla | Trajan Decius |
| Crispina | Lucius Verus | Tranquillina |
| Crispus | Macrianus | Trebonianus Gallus |
| Decentius | Macrinus | Uranius Antoninus |
| Delmatius | Magnentius | Vabalathus |
| Diadumenian | Magnia Urbica | Valens |
| Didia Clara | Magnus Maximus | Valentinian I |
| Didius Julianus | Majorian | Valentinian II |
| Diocletian | Manlia Scantilla | Valentinian III |
| Domitia | Marcian | Valeria Messalina |
| Domitia Lucilla | Marciana | Valerian I |
| Domitian | Marcus Aurelius | Valerian II |
| Domitianus | Mariniana | Valerius Valens |
| Domitilla I | Marius | Varbanov |
| Domitilla II | Martinian | Varus |
| Domitius Domitianus | Matidia | Vespasian |
| Drusus | Maxentius | Vespasian II |
| Dryantilla | Maximianus | Vetranio |
| Elagabalus | Maximinus I | Victorinus |
| Eudocia | Maximinus II | Vindix |
| Eudoxia | Maximus | Vitellius |
| Eugenius | Maximus of Spain | Volusian |
| Fabius Maximus | Nepotian | Zeno |
| Fausta | Nero | Zenobia |
| Faustina I | Nero and Drusus Caesars | Zenonis |
| Issuing Authority | Correct | Total | Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aelius | 240 | 413 | 58.1% |
| Aemilian | 31 | 308 | 10.1% |
| Agrippa | 5 | 16 | 31.3% |
| Agrippina II | 5 | 11 | 45.5% |
| Alexander | 44 | 78 | 56.4% |
| Allectus | 22 | 82 | 26.8% |
| Anthemius | 30 | 45 | 66.7% |
| Antoninus Pius | 19,832 | 42,550 | 46.6% |
| Aquilia Severa | 4 | 13 | 30.8% |
| Arcadius | 229 | 416 | 55.0% |
| Augustus | 68,606 | 113,236 | 60.6% |
| Aurelian | 829 | 4778 | 17.4% |
| Balbinus | 24 | 87 | 27.6% |
| Basiliscus | 42 | 57 | 73.7% |
| Britannicus | 126 | 215 | 58.6% |
| Caligula | 585 | 958 | 61.1% |
| Caracalla | 6984 | 17,259 | 40.5% |
| Carausius | 76 | 442 | 17.2% |
| Carinus | 138 | 565 | 24.4% |
| Carus | 31 | 154 | 20.1% |
| Claudius | 6757 | 10,063 | 67.1% |
| Clodius Albinus | 49 | 159 | 30.8% |
| Commodus | 4280 | 9344 | 45.8% |
| Constans | 1521 | 4669 | 32.6% |
| Constantine I | 1340 | 3327 | 40.3% |
| Constantine II | 48 | 106 | 45.3% |
| Constantius Gallus | 59 | 156 | 37.8% |
| Constantius I | 478 | 1338 | 35.7% |
| Constantius II | 2360 | 6581 | 35.9% |
| Constantius III | 3 | 15 | 20.0% |
| Crispina | 87 | 261 | 33.3% |
| Crispus | 347 | 1438 | 24.1% |
| Decentius | 2 | 38 | 5.3% |
| Delmatius | 17 | 57 | 29.8% |
| Diadumenian | 23 | 140 | 16.4% |
| Didius Julianus | 18 | 31 | 58.1% |
| Diocletian | 3226 | 7163 | 45.0% |
| Domitia | 6 | 15 | 40.0% |
| Domitia Lucilla | 33 | 106 | 31.1% |
| Domitian | 7017 | 12,737 | 55.1% |
| Domitianus | 3625 | 6344 | 57.1% |
| Domitius Domitianus | 19 | 92 | 20.7% |
| Elagabalus | 943 | 3096 | 30.5% |
| Eudocia | 4 | 10 | 40.0% |
| Eugenius | 12 | 31 | 38.7% |
| Fausta | 15 | 48 | 31.3% |
| Faustina I | 44 | 233 | 18.9% |
| Faustina II | 13 | 45 | 28.9% |
| Flavius Victor | 6 | 17 | 35.3% |
| Florian | 5 | 79 | 6.3% |
| Gaius and Lucius | 16 | 29 | 55.2% |
| Galba | 1038 | 2424 | 42.8% |
| Galeria Valeria | 20 | 37 | 54.1% |
| Galerius | 490 | 1181 | 41.5% |
| Gallienus | 3239 | 11,205 | 28.9% |
| Germanicus | 5448 | 8804 | 61.9% |
| Geta | 293 | 1292 | 22.7% |
| Gordian I | 2 | 23 | 8.7% |
| Gordian III | 565 | 2095 | 27.0% |
| Gratian | 32 | 144 | 22.2% |
| Hadrian | 25,631 | 53,702 | 47.7% |
| Helena | 25 | 154 | 16.2% |
| Herennia Etruscilla | 57 | 111 | 51.4% |
| Herennius Etruscus | 87 | 239 | 36.4% |
| Honorius | 858 | 1336 | 64.2% |
| Hostilian | 17 | 69 | 24.6% |
| Johannes | 9 | 16 | 56.3% |
| Jovian | 11 | 68 | 16.2% |
| Julia | 256 | 501 | 51.1% |
| Julia Domna | 471 | 1607 | 29.3% |
| Julia Maesa | 22 | 84 | 26.2% |
| Julia Mamaea | 49 | 159 | 30.8% |
| Julia Paula | 11 | 19 | 57.9% |
| Julia Titi | 70 | 123 | 56.9% |
| Julian II | 128 | 672 | 19.0% |
| Julius Nepos | 5 | 10 | 50.0% |
| Leo I | 101 | 155 | 65.2% |
| Licinius I | 417 | 1494 | 27.9% |
| Licinius II | 802 | 2866 | 28.0% |
| Livia | 89 | 126 | 70.6% |
| Lucilla | 91 | 261 | 34.9% |
| Lucius Verus | 1330 | 2793 | 47.6% |
| Macrianus | 3 | 30 | 10.0% |
| Macrinus | 251 | 1240 | 20.2% |
| Magnentius | 216 | 752 | 28.7% |
| Magnia Urbica | 30 | 70 | 42.9% |
| Magnus Maximus | 106 | 283 | 37.5% |
| Manlia Scantilla | 3 | 11 | 27.3% |
| Marcian | 107 | 137 | 78.1% |
| Marciana | 16 | 55 | 29.1% |
| Marcus Aurelius | 57,982 | 112,714 | 51.4% |
| Mariniana | 8 | 25 | 32.0% |
| Marius | 5 | 23 | 21.7% |
| Maxentius | 131 | 441 | 29.7% |
| Maximianus | 1209 | 3677 | 32.9% |
| Maximinus I | 128 | 420 | 30.5% |
| Maximinus II | 52 | 107 | 48.6% |
| Maximus | 79 | 124 | 63.7% |
| Nero | 7476 | 14,409 | 51.9% |
| Nero Claudius Drusus | 57 | 95 | 60.0% |
| Nerva | 723 | 1672 | 43.2% |
| Numerian | 63 | 192 | 32.8% |
| Octavia | 205 | 502 | 40.8% |
| Otacilia Severa | 55 | 264 | 20.8% |
| Otho | 32 | 72 | 44.4% |
| Pacatian | 9 | 28 | 32.1% |
| Pertinax | 119 | 261 | 45.6% |
| Pescennius Niger | 95 | 281 | 33.8% |
| Philip I | 337 | 1188 | 28.4% |
| Philip II | 35 | 143 | 24.5% |
| Plautilla | 138 | 307 | 45.0% |
| Plotina | 6 | 12 | 50.0% |
| Postumus | 591 | 2639 | 22.4% |
| Probus | 2013 | 10,033 | 20.1% |
| Procopius | 34 | 110 | 30.9% |
| Pupienus | 42 | 101 | 41.6% |
| Quietus | 2 | 23 | 8.7% |
| Quintillus | 92 | 235 | 39.1% |
| Romulus | 259 | 570 | 45.4% |
| Sabina | 75 | 157 | 47.8% |
| Salonina | 37 | 190 | 19.5% |
| Saloninus | 8 | 31 | 25.8% |
| Septimius Severus | 11,676 | 25,252 | 46.2% |
| Severina | 17 | 127 | 13.4% |
| Severus Alexander | 6477 | 12,931 | 50.1% |
| Severus II | 114 | 213 | 53.5% |
| Severus III | 6 | 10 | 60.0% |
| Tacitus | 131 | 537 | 24.4% |
| Tetricus I | 1 | 21 | 4.8% |
| Theodosius I | 197 | 637 | 30.9% |
| Theodosius II | 865 | 1442 | 60.0% |
| Tiberius | 1687 | 2307 | 73.1% |
| Titus | 3494 | 6124 | 57.1% |
| Trajan | 11,177 | 25,257 | 44.3% |
| Trajan Decius | 127 | 356 | 35.7% |
| Tranquillina | 22 | 57 | 38.6% |
| Trebonianus Gallus | 466 | 1193 | 39.1% |
| Vabalathus | 3 | 22 | 13.6% |
| Valens | 53 | 309 | 17.2% |
| Valentinian I | 28 | 144 | 19.4% |
| Valentinian II | 26 | 139 | 18.7% |
| Valentinian III | 145 | 382 | 38.0% |
| Valerian I | 74 | 328 | 22.6% |
| Vespasian | 17,935 | 31,933 | 56.2% |
| Vetranio | 65 | 384 | 16.9% |
| Victorinus | 68 | 236 | 28.8% |
| Vitellius | 3089 | 5070 | 60.9% |
| Volusian | 175 | 675 | 25.9% |
| Zeno | 107 | 156 | 68.6% |
| 30,2974 | 613,087 | 49.4% |
| Issuing Authority | Correct | Total | Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aelius | 293 | 413 | 70.9% |
| Aemilian | 133 | 309 | 43.0% |
| Agrippa | 12 | 17 | 70.6% |
| Agrippina II | 6 | 10 | 60.0% |
| Alexander | 39 | 78 | 50.0% |
| Allectus | 54 | 80 | 67.5% |
| Anthemius | 26 | 46 | 56.5% |
| Antoninus Pius | 29,641 | 42,549 | 69.7% |
| Aquilia Severa | 10 | 12 | 83.3% |
| Arcadius | 310 | 418 | 74.2% |
| Augustus | 79,227 | 113,253 | 70.0% |
| Aurelian | 2695 | 4772 | 56.5% |
| Balbinus | 56 | 85 | 65.9% |
| Basiliscus | 32 | 57 | 56.1% |
| Britannicus | 75 | 212 | 35.4% |
| Caligula | 711 | 961 | 74.0% |
| Caracalla | 10,728 | 17,264 | 62.1% |
| Carausius | 332 | 439 | 75.6% |
| Carinus | 339 | 565 | 60.0% |
| Carus | 71 | 154 | 46.1% |
| Claudius | 7598 | 10,066 | 75.5% |
| Clodius Albinus | 75 | 160 | 46.9% |
| Commodus | 6720 | 9338 | 72.0% |
| Constans | 2193 | 4669 | 47.0% |
| Constantine I | 2271 | 3328 | 68.2% |
| Constantine II | 74 | 105 | 70.5% |
| Constantius Gallus | 103 | 153 | 67.3% |
| Constantius I | 749 | 1339 | 55.9% |
| Constantius II | 4472 | 6577 | 68.0% |
| Constantius III | 12 | 15 | 80.0% |
| Crispina | 168 | 259 | 64.9% |
| Crispus | 943 | 1437 | 65.6% |
| Decentius | 22 | 38 | 57.9% |
| Delmatius | 23 | 58 | 39.7% |
| Diadumenian | 89 | 143 | 62.2% |
| Didius Julianus | 18 | 31 | 58.1% |
| Diocletian | 4950 | 7168 | 69.1% |
| Domitia | 10 | 15 | 66.7% |
| Domitia Lucilla | 26 | 107 | 24.3% |
| Domitian | 8803 | 12,739 | 69.1% |
| Domitianus | 4419 | 6342 | 69.7% |
| Domitius Domitianus | 52 | 92 | 56.5% |
| Elagabalus | 1705 | 3099 | 55.0% |
| Eudocia | 4 | 11 | 36.4% |
| Eugenius | 16 | 31 | 51.6% |
| Fausta | 20 | 48 | 41.7% |
| Faustina I | 156 | 232 | 67.2% |
| Faustina II | 33 | 45 | 73.3% |
| Flavius Victor | 8 | 17 | 47.1% |
| Florian | 33 | 80 | 41.3% |
| Gaius and Lucius | 19 | 29 | 65.5% |
| Galba | 1565 | 2428 | 64.5% |
| Galeria Valeria | 12 | 37 | 32.4% |
| Galerius | 828 | 1181 | 70.1% |
| Gallienus | 7238 | 11,199 | 64.6% |
| Germanicus | 4576 | 8811 | 51.9% |
| Geta | 688 | 1289 | 53.4% |
| Gordian I | 15 | 22 | 68.2% |
| Gordian III | 1176 | 2094 | 56.2% |
| Gratian | 84 | 144 | 58.3% |
| Hadrian | 37,712 | 53,704 | 70.2% |
| Helena | 60 | 156 | 38.5% |
| Herennia Etruscilla | 82 | 110 | 74.5% |
| Herennius Etruscus | 165 | 236 | 69.9% |
| Honorius | 942 | 1337 | 70.5% |
| Hostilian | 37 | 68 | 54.4% |
| Johannes | 8 | 16 | 50.0% |
| Jovian | 47 | 69 | 68.1% |
| Julia | 370 | 503 | 73.6% |
| Julia Domna | 975 | 1606 | 60.7% |
| Julia Maesa | 58 | 84 | 69.0% |
| Julia Mamaea | 118 | 159 | 74.2% |
| Julia Paula | 15 | 18 | 83.3% |
| Julia Titi | 102 | 124 | 82.3% |
| Julian II | 412 | 675 | 61.0% |
| Julius Nepos | 7 | 10 | 70.0% |
| Leo I | 102 | 156 | 65.4% |
| Licinius I | 916 | 1494 | 61.3% |
| Licinius II | 1227 | 2869 | 42.8% |
| Livia | 92 | 126 | 73.0% |
| Lucilla | 182 | 263 | 69.2% |
| Lucius Verus | 2082 | 2793 | 74.5% |
| Macrianus | 22 | 31 | 71.0% |
| Macrinus | 660 | 1242 | 53.1% |
| Magnentius | 539 | 747 | 72.2% |
| Magnia Urbica | 36 | 68 | 52.9% |
| Magnus Maximus | 176 | 282 | 62.4% |
| Manlia Scantilla | 2 | 11 | 18.2% |
| Marcian | 105 | 139 | 75.5% |
| Marciana | 38 | 55 | 69.1% |
| Marcus Aurelius | 79,759 | 112,717 | 70.8% |
| Mariniana | 17 | 25 | 68.0% |
| Marius | 10 | 25 | 40.0% |
| Maxentius | 175 | 439 | 39.9% |
| Maximianus | 2509 | 3675 | 68.3% |
| Maximinus I | 278 | 419 | 66.3% |
| Maximinus II | 62 | 109 | 56.9% |
| Maximus | 94 | 124 | 75.8% |
| Nero | 10,227 | 14,412 | 71.0% |
| Nero Claudius Drusus | 66 | 94 | 70.2% |
| Nerva | 1143 | 1673 | 68.3% |
| Numerian | 92 | 192 | 47.9% |
| Octavia | 280 | 505 | 55.4% |
| Otacilia Severa | 185 | 262 | 70.6% |
| Otho | 37 | 73 | 50.7% |
| Pacatian | 22 | 28 | 78.6% |
| Pertinax | 152 | 260 | 58.5% |
| Pescennius Niger | 162 | 278 | 58.3% |
| Philip I | 785 | 1186 | 66.2% |
| Philip II | 97 | 141 | 68.8% |
| Plautilla | 163 | 309 | 52.8% |
| Plotina | 10 | 12 | 83.3% |
| Postumus | 1776 | 2645 | 67.1% |
| Probus | 5866 | 10,030 | 58.5% |
| Procopius | 60 | 109 | 55.0% |
| Pupienus | 68 | 98 | 69.4% |
| Quietus | 7 | 23 | 30.4% |
| Quintillus | 128 | 234 | 54.7% |
| Romulus | 324 | 567 | 57.1% |
| Sabina | 94 | 157 | 59.9% |
| Salonina | 97 | 192 | 50.5% |
| Saloninus | 13 | 30 | 43.3% |
| Septimius Severus | 17,822 | 25,252 | 70.6% |
| Severina | 80 | 129 | 62.0% |
| Severus Alexander | 8472 | 12,933 | 65.5% |
| Severus II | 139 | 211 | 65.9% |
| Severus III | 7 | 10 | 70.0% |
| Tacitus | 325 | 535 | 60.7% |
| Tetricus I | 15 | 22 | 68.2% |
| Theodosius I | 436 | 636 | 68.6% |
| Theodosius II | 731 | 1444 | 50.6% |
| Tiberius | 1848 | 2304 | 80.2% |
| Titus | 4348 | 6126 | 71.0% |
| Trajan | 18,421 | 25,258 | 72.9% |
| Trajan Decius | 268 | 360 | 74.4% |
| Tranquillina | 46 | 57 | 80.7% |
| Trebonianus Gallus | 832 | 1189 | 70.0% |
| Vabalathus | 15 | 22 | 68.2% |
| Valens | 237 | 310 | 76.5% |
| Valentinian I | 99 | 141 | 70.2% |
| Valentinian II | 105 | 139 | 75.5% |
| Valentinian III | 236 | 382 | 61.8% |
| Valerian I | 176 | 328 | 53.7% |
| Vespasian | 23,508 | 31,934 | 73.6% |
| Vetranio | 199 | 386 | 51.6% |
| Victorinus | 165 | 237 | 69.6% |
| Vitellius | 3804 | 5070 | 75.0% |
| Volusian | 460 | 677 | 67.9% |
| Zeno | 89 | 155 | 57.4% |
| 421,686 | 613,111 | 68.8% |
| Issuing Authority | Correct | Total | Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aelius | 350 | 411 | 85.2% |
| Aemilian | 245 | 308 | 79.5% |
| Agrippa | 10 | 17 | 58.8% |
| Agrippina II | 7 | 11 | 63.6% |
| Alexander | 71 | 78 | 91.0% |
| Allectus | 60 | 80 | 75.0% |
| Anthemius | 34 | 46 | 73.9% |
| Antoninus Pius | 35,169 | 42,553 | 82.6% |
| Aquilia Severa | 12 | 13 | 92.3% |
| Arcadius | 376 | 417 | 90.2% |
| Augustus | 90,666 | 113,236 | 80.1% |
| Aurelian | 3666 | 4773 | 76.8% |
| Balbinus | 65 | 86 | 75.6% |
| Basiliscus | 39 | 57 | 68.4% |
| Britannicus | 139 | 215 | 64.7% |
| Caligula | 772 | 962 | 80.2% |
| Caracalla | 14,570 | 17,263 | 84.4% |
| Carausius | 323 | 439 | 73.6% |
| Carinus | 454 | 566 | 80.2% |
| Carus | 142 | 155 | 91.6% |
| Claudius | 8074 | 10,067 | 80.2% |
| Clodius Albinus | 119 | 160 | 74.4% |
| Commodus | 7681 | 9343 | 82.2% |
| Constans | 3283 | 4667 | 70.3% |
| Constantine I | 2827 | 3328 | 84.9% |
| Constantine II | 89 | 106 | 84.0% |
| Constantius Gallus | 124 | 157 | 79.0% |
| Constantius I | 1221 | 1339 | 91.2% |
| Constantius II | 5616 | 6579 | 85.4% |
| Constantius III | 15 | 15 | 100.0% |
| Crispina | 221 | 262 | 84.4% |
| Crispus | 1120 | 1438 | 77.9% |
| Decentius | 32 | 39 | 82.1% |
| Delmatius | 48 | 57 | 84.2% |
| Diadumenian | 114 | 143 | 79.7% |
| Didius Julianus | 25 | 32 | 78.1% |
| Diocletian | 5787 | 7162 | 80.8% |
| Domitia | 6 | 15 | 40.0% |
| Domitia Lucilla | 89 | 106 | 84.0% |
| Domitian | 10,417 | 12,739 | 81.8% |
| Domitianus | 5269 | 6344 | 83.1% |
| Domitius Domitianus | 78 | 92 | 84.8% |
| Elagabalus | 2598 | 3101 | 83.8% |
| Eudocia | 9 | 12 | 75.0% |
| Eugenius | 27 | 31 | 87.1% |
| Fausta | 27 | 47 | 57.4% |
| Faustina I | 215 | 232 | 92.7% |
| Faustina II | 36 | 45 | 80.0% |
| Flavius Victor | 14 | 17 | 82.4% |
| Florian | 74 | 80 | 92.5% |
| Gaius and Lucius | 21 | 28 | 75.0% |
| Galba | 1774 | 2428 | 73.1% |
| Galeria Valeria | 36 | 38 | 94.7% |
| Galerius | 1037 | 1183 | 87.7% |
| Gallienus | 9496 | 11,200 | 84.8% |
| Germanicus | 6819 | 8815 | 77.4% |
| Geta | 1044 | 1291 | 80.9% |
| Gordian I | 17 | 23 | 73.9% |
| Gordian III | 1739 | 2097 | 82.9% |
| Gratian | 123 | 144 | 85.4% |
| Hadrian | 44,306 | 53,709 | 82.5% |
| Helena | 132 | 157 | 84.1% |
| Herennia Etruscilla | 79 | 109 | 72.5% |
| Herennius Etruscus | 171 | 235 | 72.8% |
| Honorius | 1154 | 1335 | 86.4% |
| Hostilian | 54 | 69 | 78.3% |
| Johannes | 15 | 15 | 100.0% |
| Jovian | 61 | 69 | 88.4% |
| Julia | 420 | 503 | 83.5% |
| Julia Domna | 1259 | 1607 | 78.3% |
| Julia Maesa | 58 | 83 | 69.9% |
| Julia Mamaea | 132 | 160 | 82.5% |
| Julia Paula | 12 | 18 | 66.7% |
| Julia Titi | 115 | 122 | 94.3% |
| Julian II | 512 | 670 | 76.4% |
| Julius Nepos | 7 | 10 | 70.0% |
| Leo I | 126 | 156 | 80.8% |
| Licinius I | 1123 | 1494 | 75.2% |
| Licinius II | 2102 | 2868 | 73.3% |
| Livia | 110 | 126 | 87.3% |
| Lucilla | 164 | 261 | 62.8% |
| Lucius Verus | 2252 | 2792 | 80.7% |
| Macrianus | 18 | 32 | 56.3% |
| Macrinus | 1044 | 1240 | 84.2% |
| Magnentius | 600 | 748 | 80.2% |
| Magnia Urbica | 47 | 68 | 69.1% |
| Magnus Maximus | 222 | 284 | 78.2% |
| Manlia Scantilla | 10 | 12 | 83.3% |
| Marcian | 123 | 138 | 89.1% |
| Marciana | 47 | 56 | 83.9% |
| Marcus Aurelius | 91,099 | 112,704 | 80.8% |
| Mariniana | 13 | 23 | 56.5% |
| Marius | 19 | 26 | 73.1% |
| Maxentius | 379 | 439 | 86.3% |
| Maximianus | 3111 | 3669 | 84.8% |
| Maximinus I | 321 | 422 | 76.1% |
| Maximinus II | 90 | 109 | 82.6% |
| Maximus | 107 | 123 | 87.0% |
| Nero | 11,095 | 14,408 | 77.0% |
| Nero Claudius Drusus | 74 | 94 | 78.7% |
| Nerva | 1343 | 1674 | 80.2% |
| Numerian | 160 | 193 | 82.9% |
| Octavia | 348 | 503 | 69.2% |
| Otacilia Severa | 210 | 261 | 80.5% |
| Otho | 64 | 71 | 90.1% |
| Pacatian | 23 | 29 | 79.3% |
| Pertinax | 202 | 262 | 77.1% |
| Pescennius Niger | 222 | 279 | 79.6% |
| Philip I | 1013 | 1188 | 85.3% |
| Philip II | 124 | 142 | 87.3% |
| Plautilla | 234 | 311 | 75.2% |
| Plotina | 9 | 10 | 90.0% |
| Postumus | 2022 | 2641 | 76.6% |
| Probus | 8366 | 10,039 | 83.3% |
| Procopius | 84 | 109 | 77.1% |
| Pupienus | 72 | 99 | 72.7% |
| Quietus | 17 | 23 | 73.9% |
| Quintillus | 185 | 233 | 79.4% |
| Romulus | 487 | 565 | 86.2% |
| Sabina | 113 | 156 | 72.4% |
| Salonina | 158 | 191 | 82.7% |
| Saloninus | 13 | 28 | 46.4% |
| Septimius Severus | 20,869 | 25,254 | 82.6% |
| Severina | 99 | 129 | 76.7% |
| Severus Alexander | 10,081 | 12,929 | 78.0% |
| Severus II | 187 | 210 | 89.0% |
| Severus III | 9 | 10 | 90.0% |
| Tacitus | 415 | 535 | 77.6% |
| Tetricus I | 21 | 22 | 95.5% |
| Theodosius I | 548 | 639 | 85.8% |
| Theodosius II | 1048 | 1446 | 72.5% |
| Tiberius | 1912 | 2304 | 83.0% |
| Titus | 4950 | 6117 | 80.9% |
| Trajan | 20,731 | 25,259 | 82.1% |
| Trajan Decius | 312 | 356 | 87.6% |
| Tranquillina | 45 | 56 | 80.4% |
| Trebonianus Gallus | 996 | 1196 | 83.3% |
| Vabalathus | 15 | 23 | 65.2% |
| Valens | 256 | 312 | 82.1% |
| Valentinian I | 120 | 141 | 85.1% |
| Valentinian II | 113 | 139 | 81.3% |
| Valentinian III | 263 | 381 | 69.0% |
| Valerian I | 236 | 328 | 72.0% |
| Vespasian | 25,734 | 31,933 | 80.6% |
| Vetranio | 302 | 388 | 77.8% |
| Victorinus | 181 | 236 | 76.7% |
| Vitellius | 3945 | 5077 | 77.7% |
| Volusian | 580 | 676 | 85.8% |
| Zeno | 131 | 156 | 84.0% |
| 496,882 | 613,110 | 81.0% |
References
- Arandjelović, O.; Zachariou, M. Images of Roman imperial denarii: A curated data set for the evaluation of computer vision algorithms applied to ancient numismatics, and an overview of challenges in the field. Sci 2020, 2, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber-Mörk, R.; Nölle, M.; Rubik, M.; Hödlmoser, M.; Kampel, M.; Zambanini, S. Automatic coin classification and identification. In Advances in Object Recognition Systems; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; Volume 127. [Google Scholar]
- Kiourt, C.; Evangelidis, V. AnCoins: Image-Based Automated Identification of Ancient Coins Through Transfer Learning Approaches. In Pattern Recognition, Proceedings of the ICPR International Workshops and Challenges, Virtual Event, 10–15 January 2021; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 54–67. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, K.; He, B.; Wang, F.; Zhang, T.; Ding, Q. A novel method for classification of ancient coins based on image textures. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Digital Media and Its Application in Museum & Heritages, Chongqing, China, 10–12 December 2007; pp. 63–66. [Google Scholar]
- Zaharieva, M.; Kampel, M.; Zambanini, S. Image based recognition of ancient coins. In Computer Analysis of Images and Patterns, Proceedings of the 12th International Conference, CAIP 2007, Vienna, Austria, 27–29 August 2007; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 547–554. [Google Scholar]
- Arandjelović, O. Reading ancient coins: Automatically identifying denarii using obverse legend seeded retrieval. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2012, Proceedings of the 12th European Conference on Computer Vision, Florence, Italy, 7–13 October 2012; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 317–330. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, J.; Arandjelović, O. Understanding ancient coin images. In Recent Advances in Big Data and Deep Learning, Proceedings of the INNS Big Data and Deep Learning Conference INNSBDDL2019, held at Sestri Levante, Genova, Italy 16–18 April 2019; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 330–340. [Google Scholar]
- Schlag, I.; Arandjelovic, O. Ancient Roman coin recognition in the wild using deep learning based recognition of artistically depicted face profiles. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2898–2906. [Google Scholar]
- Aslan, S.; Vascon, S.; Pelillo, M. Two sides of the same coin: Improved ancient coin classification using Graph Transduction Games. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 131, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.; Arandjelović, O. Learning to Describe: A New Approach to Computer Vision Based Ancient Coin Analysis. Sci 2020, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampel, M.; Zaharieva, M. Recognizing ancient coins based on local features. In Advances in Visual Computing, Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium, ISVC 2008, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 1–3 December 2008; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kampel, M.; Huber-Mörk, R.; Zaharieva, M. Image-based retrieval and identification of ancient coins. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2009, 24, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambanini, S.; Kampel, M. Robust Automatic Segmentation of Ancient Coins. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications, Lisboa, Portugal, 5–8 February 2009; pp. 273–276. [Google Scholar]
- Huber-Mörk, R.; Zambanini, S.; Zaharieva, M.; Kampel, M. Identification of ancient coins based on fusion of shape and local features. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2011, 22, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, H.; Zambanini, S.; Kampel, M. Supporting ancient coin classification by image-based reverse side symbol recognition. In Computer Analysis of Images and Patterns, Proceedings of the 15th International Conference, CAIP 2013, York, UK, 27–29 August 2013; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Zachariou, M.; Dimitriou, N.; Arandjelović, O. Visual reconstruction of ancient coins using cycle-consistent generative adversarial networks. Sci 2020, 2, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, H.; Zambanini, S.; Kampel, M.; Vondrovec, K. Ancient coin classification using reverse motif recognition: Image-based classification of roman republican coins. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2015, 32, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, B.; Arandjelović, O. Towards computer vision based ancient coin recognition in the wild—Automatic reliable image preprocessing and normalization. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Anchorage, AK, USA, 14–19 May 2017; pp. 1457–1464. [Google Scholar]
- Arandjelović, O. Automatic attribution of ancient Roman imperial coins. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 1728–1734. [Google Scholar]
- Zaharieva, M.; Huber-Mörk, R.; Nölle, M.; Kampel, M. On ancient coin classification. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Virtual Reality, Archaeology and Intelligent Cultural Heritage, Brighton, UK, 26–30 November 2007; pp. 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, H.; Zambanini, S.; Kampel, M. Encoding spatial arrangements of visual words for rotation-invariant image classification. In Pattern Recognition, Proceedings of the 36th German Conference, GCPR 2014, Münster, Germany, 2–5 September 2014; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 443–452. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Arandjelović, O. Classification of ancient roman coins by denomination using colour, a forgotten feature in automatic ancient coin analysis. Sci 2020, 2, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fare, C.; Arandjelović, O. Ancient roman coin retrieval: A systematic examination of the effects of coin grade. In Advances in Information Retrieval, Proceedings of the 39th European Conference on IR Research, ECIR 2017, Aberdeen, UK, 8–13April 2017; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 410–423. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Pavlovic, V. Discovering characteristic landmarks on ancient coins using convolutional networks. J. Electron. Imaging 2017, 26, 011018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromley, J.; Guyon, I.; LeCun, Y.; Säckinger, E.; Shah, R. Signature verification using a “Siamese” time delay neural network. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 1993, 6, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Transformer: Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 6000–6010. [Google Scholar]
- Chicco, D. Siamese neural networks: An overview. In Artificial Neural Networks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, W.; Ma, H.; Fu, H. Siamese neural network based gait recognition for human identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Shanghai, China, 20–25 March 2016; pp. 2832–2836. [Google Scholar]
- Long, T. Research on application of athlete gesture tracking algorithms based on deep learning. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2020, 11, 3649–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichida, A.Y.; Meneguzzi, F.; Ruiz, D.D. Measuring semantic similarity between sentences using a Siamese neural network. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 8–13 July 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ostertag, C.; Beurton-Aimar, M. Matching ostraca fragments using a Siamese neural network. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 131, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlemont, S.; Lefebvre, G.; Duffner, S.; Garcia, C. Siamese neural network based similarity metric for inertial gesture classification and rejection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 4–8 May 2015; Volume 1, pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Alletto, S.; Rigazio, L. Similarity mapping with enhanced Siamese network for multi-object tracking. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.09156. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.D.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language models are few-shot learners. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 1877–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Xu, Z.; Taylor, G.; Studer, C.; Goldstein, T. Visualizing the loss landscape of neural nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2018, 31, 6391–6401. [Google Scholar]
- Ba, J.L.; Kiros, J.R.; Hinton, G.E. Layer normalization. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1607.06450. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Arandjelović, O. Reimagining the central challenge of face recognition: Turning a problem into an advantage. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 83, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arandjelovic, O. Learnt quasi-transitive similarity for retrieval from large collections of faces. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4883–4892. [Google Scholar]









Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Z.; Arandjelović, O.; Reid, D.; Lei, Y.; Büttner, J. A Siamese Transformer Network for Zero-Shot Ancient Coin Classification. J. Imaging 2023, 9, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9060107
Guo Z, Arandjelović O, Reid D, Lei Y, Büttner J. A Siamese Transformer Network for Zero-Shot Ancient Coin Classification. Journal of Imaging. 2023; 9(6):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9060107
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Zhongliang, Ognjen Arandjelović, David Reid, Yaxiong Lei, and Jochen Büttner. 2023. "A Siamese Transformer Network for Zero-Shot Ancient Coin Classification" Journal of Imaging 9, no. 6: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9060107
APA StyleGuo, Z., Arandjelović, O., Reid, D., Lei, Y., & Büttner, J. (2023). A Siamese Transformer Network for Zero-Shot Ancient Coin Classification. Journal of Imaging, 9(6), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9060107







