Development of Vertical Farming Systems from Waste Polymers Using Additive Manufacturing Techniques
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Developments in FDM for Urban Farming
2.1. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
2.2. Urban Farming with 3D Printing
3. Design Outline
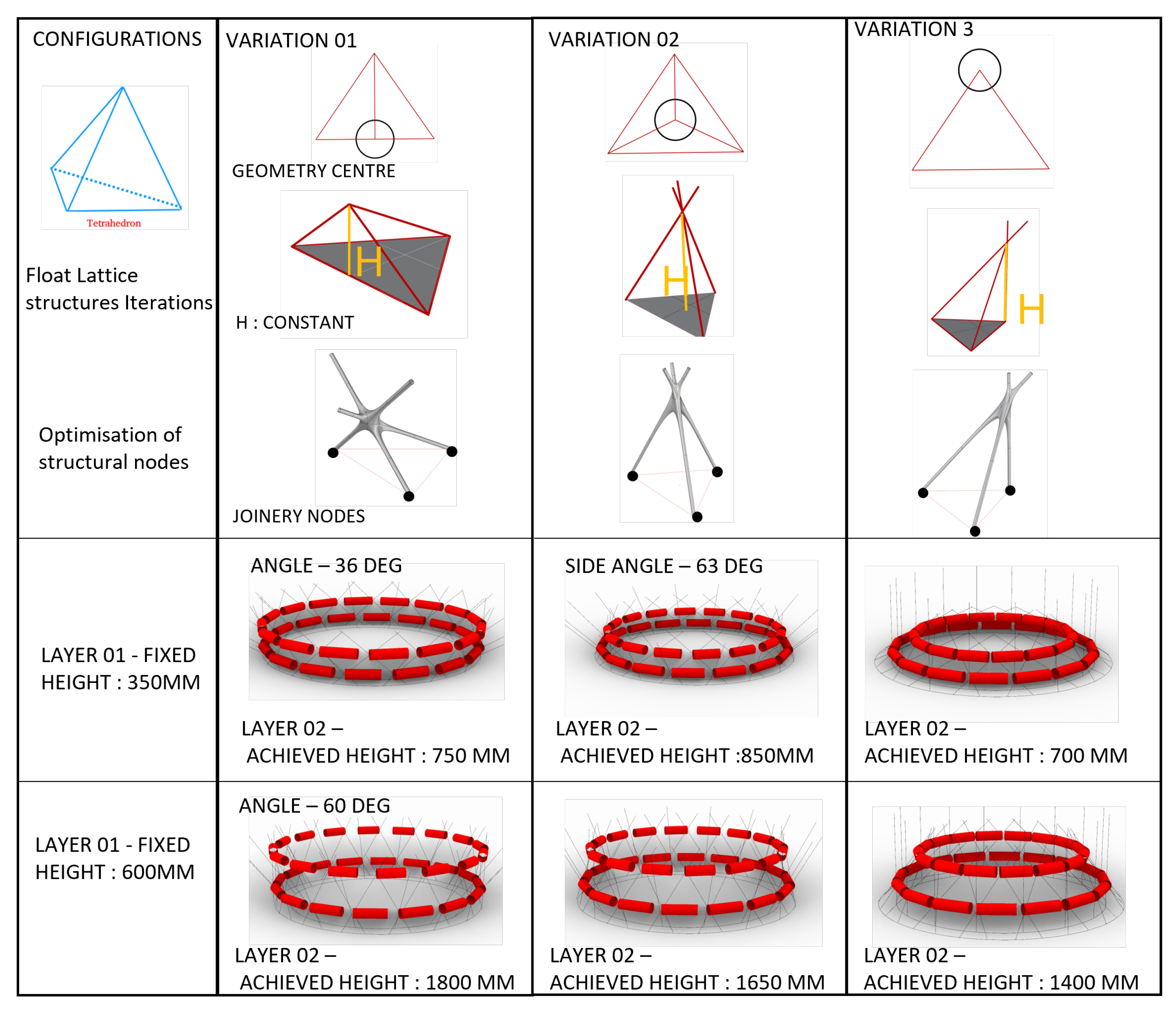
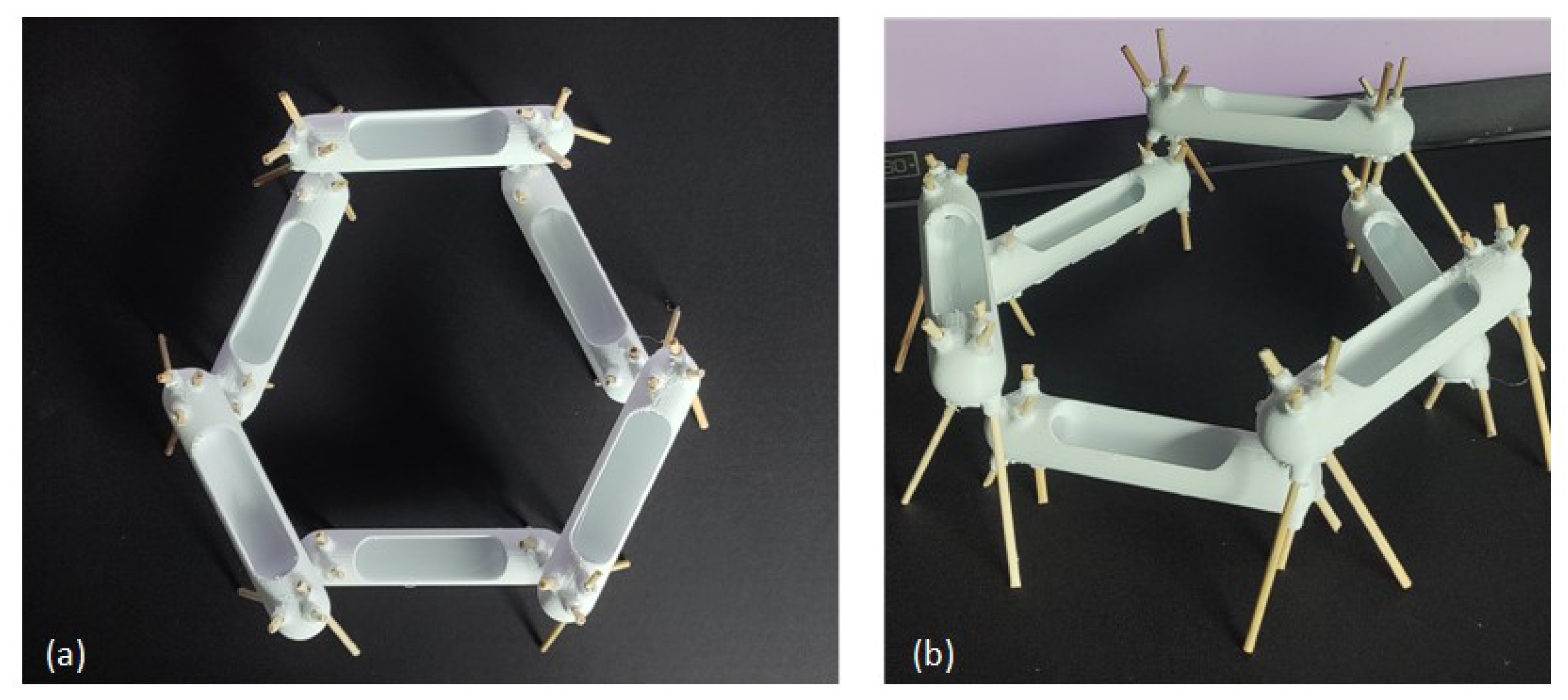
Geometry Definition
4. Design Optimization and Experimentation
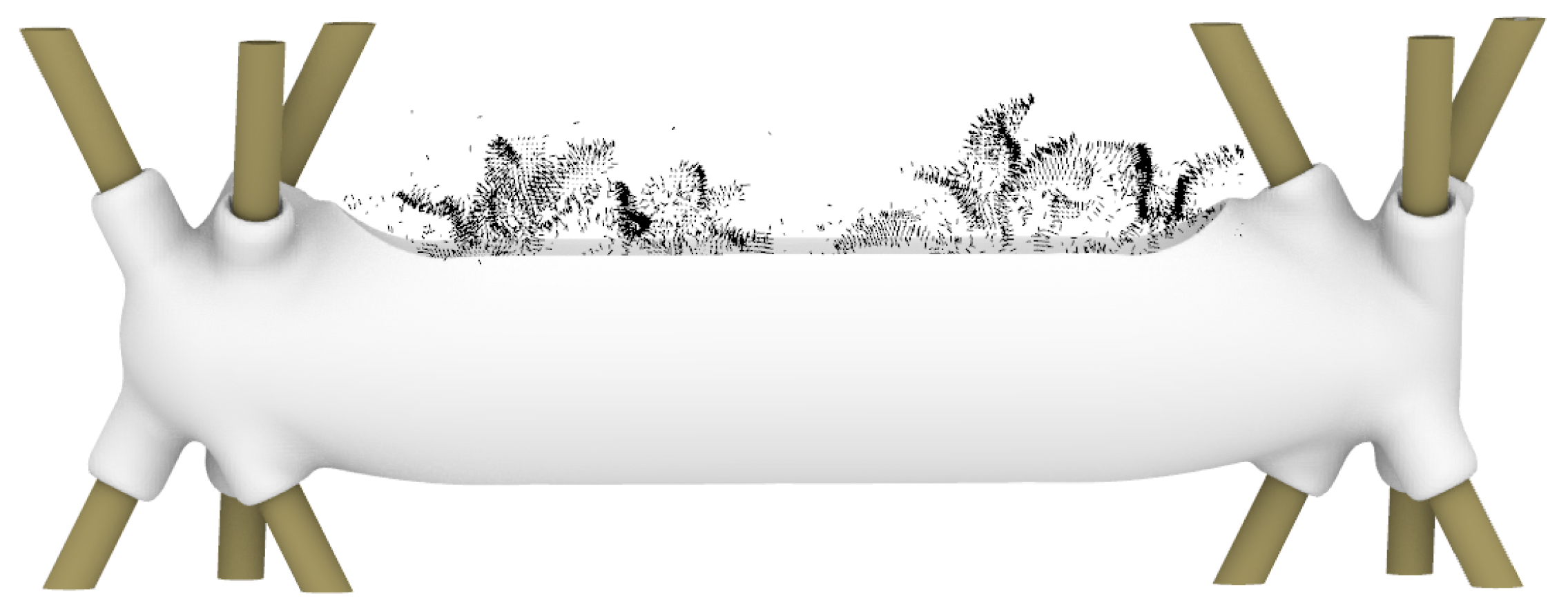
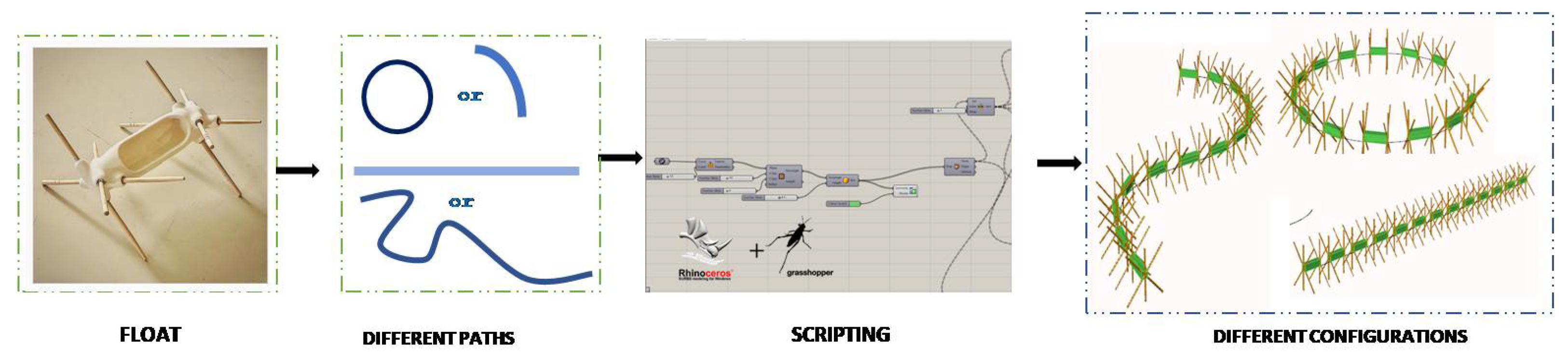
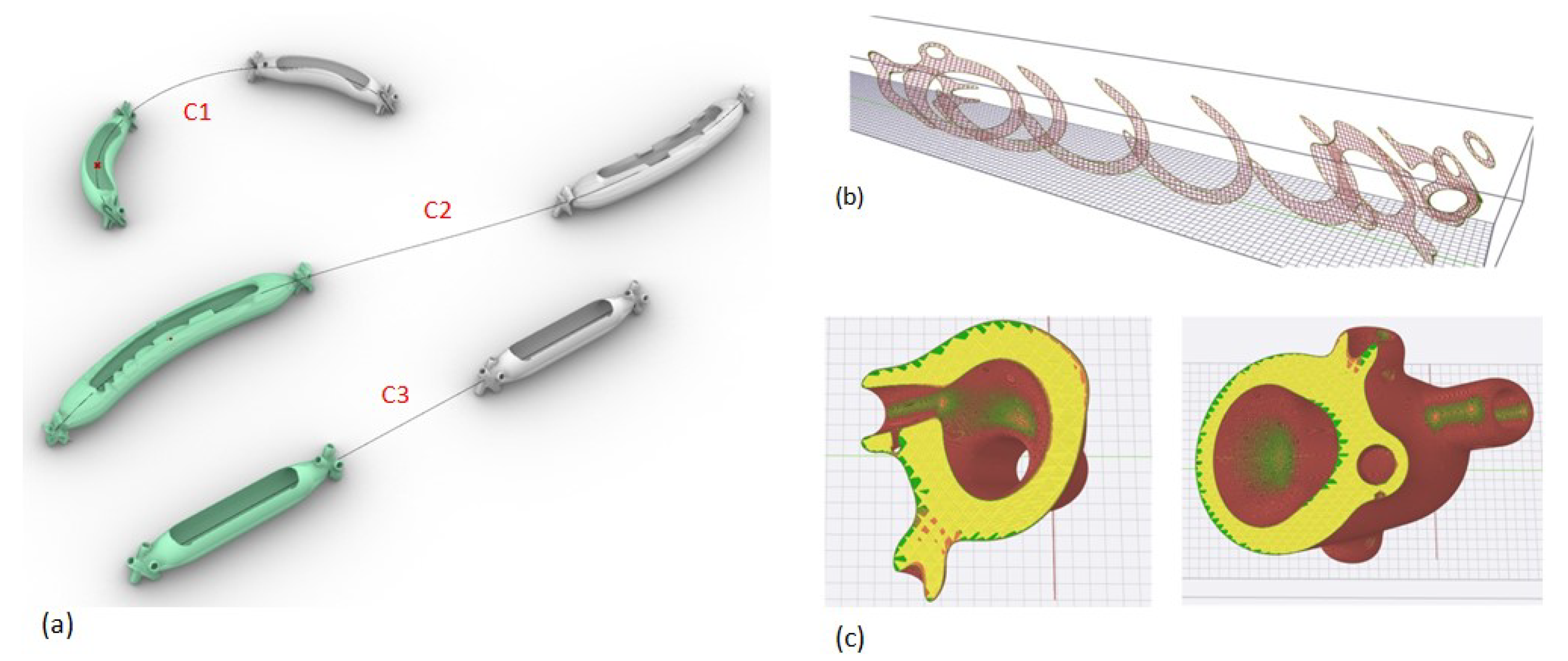
4.1. Design Derivation for AM
4.2. Exploration of Lattice Structures
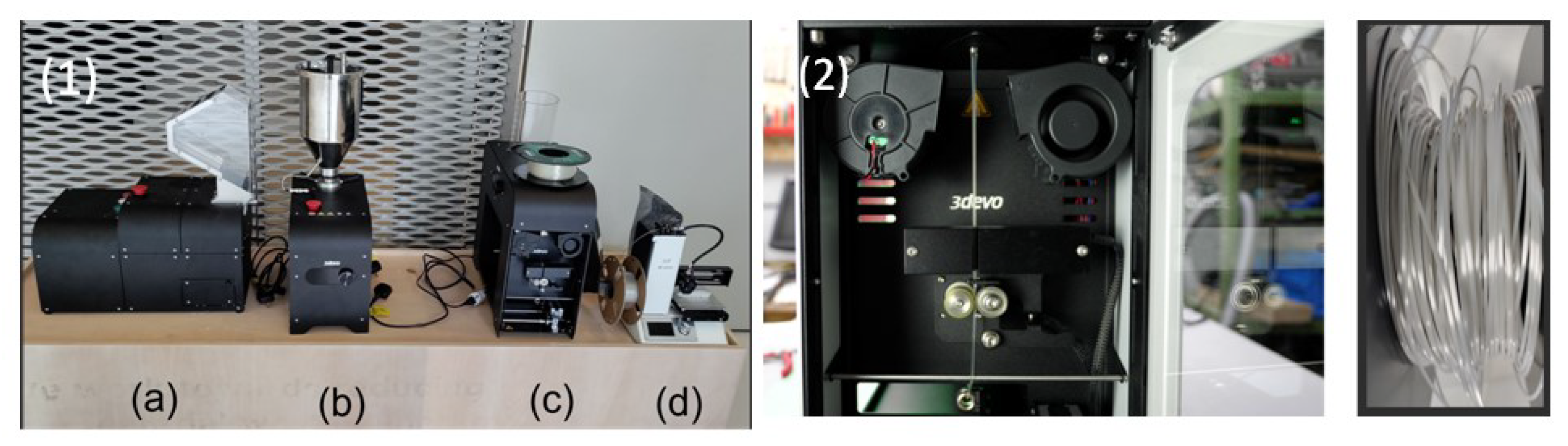
4.3. Materials and Methods
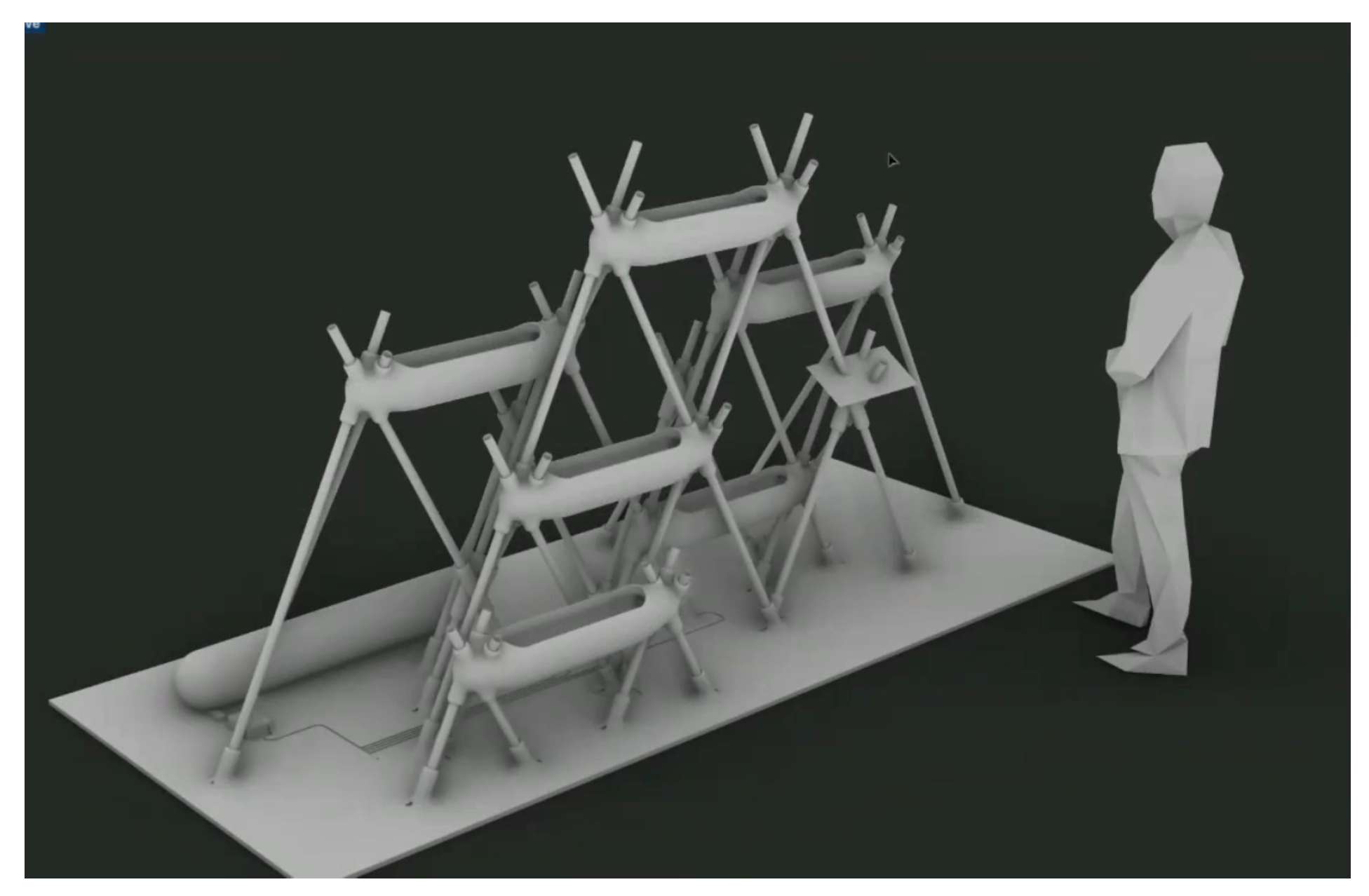
5. Prototyping and Technical Development
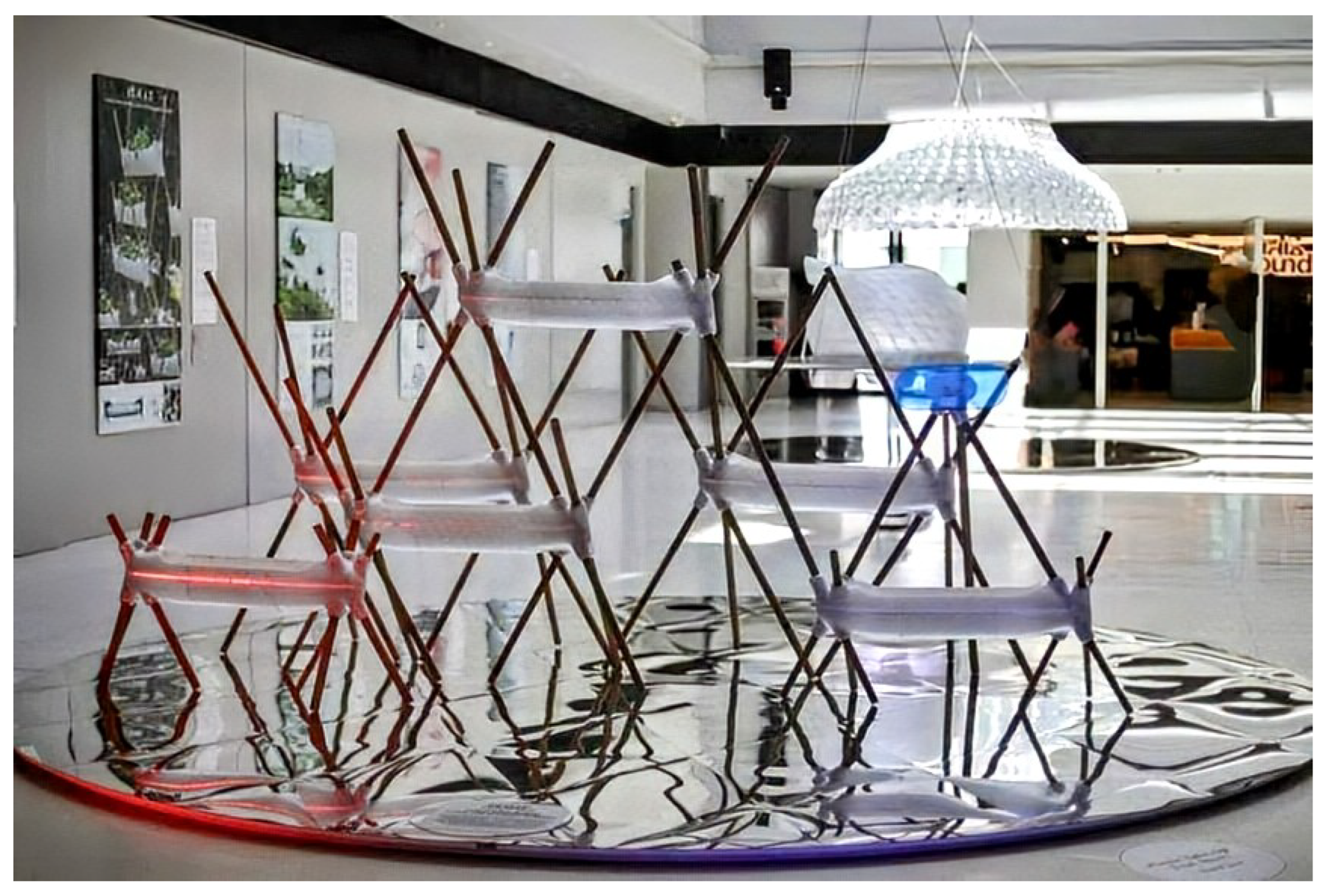
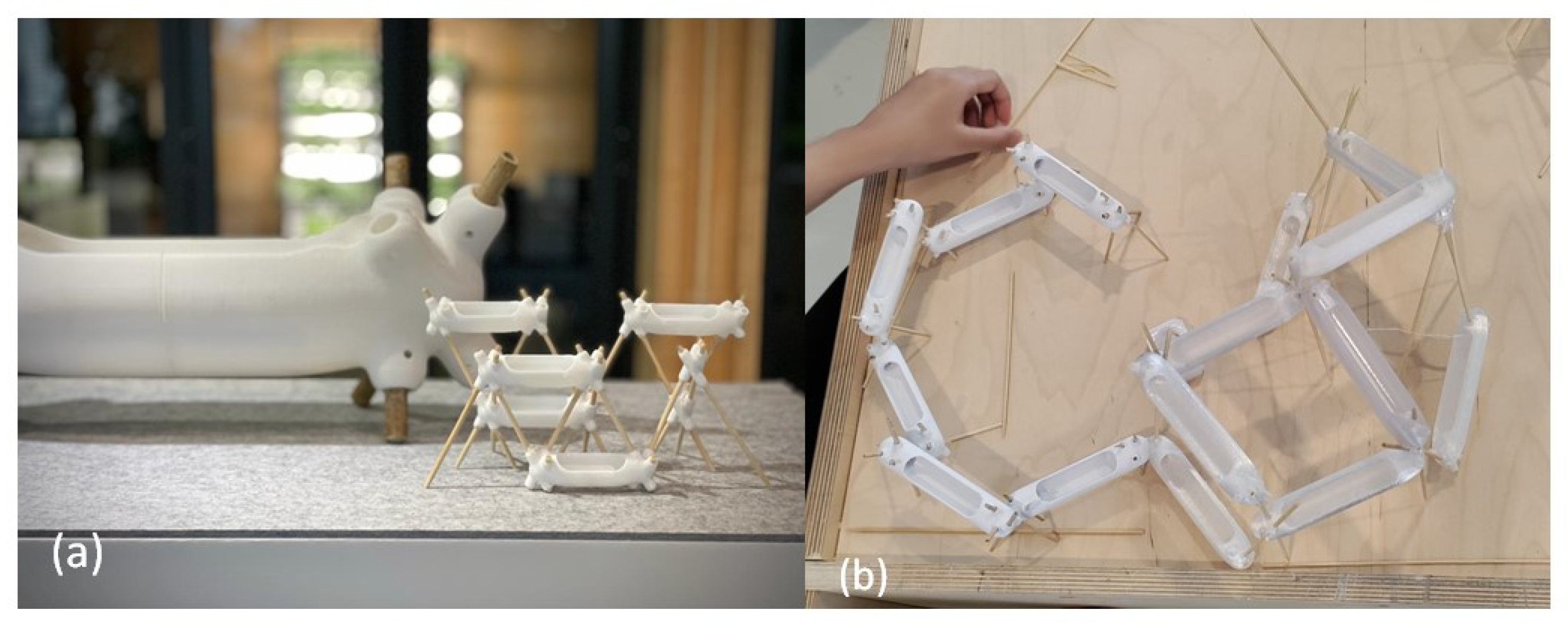
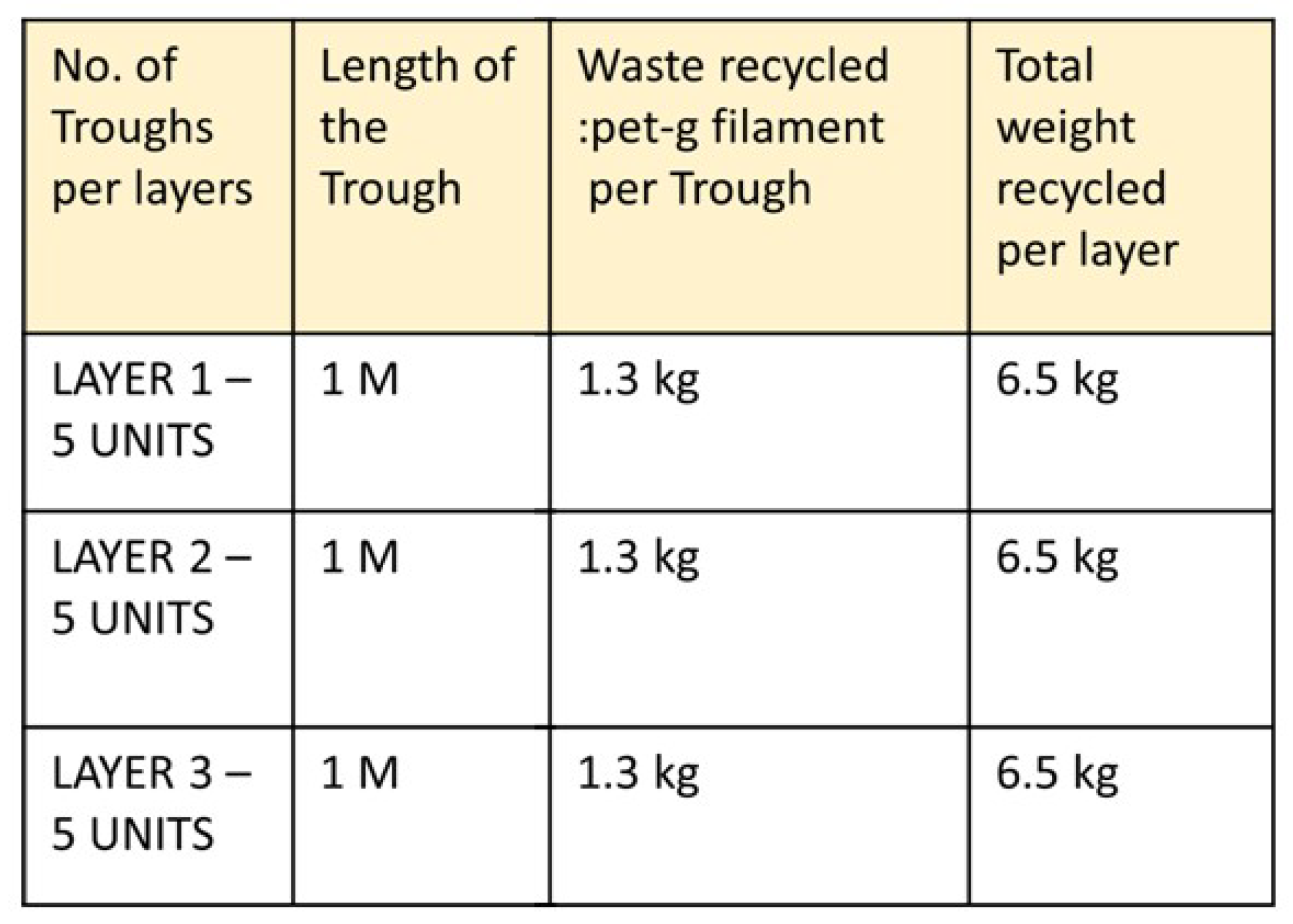
5.1. Technical Development
5.2. Effective Product Demonstration
6. Conclusions and Future Scope
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fróna, D.; Szenderák, J.; Harangi-Rákos, M. The challenge of feeding the world. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, R.; Bellù, L.G. Chapter 2—Global Trends and Challenges to Food and Agriculture into the 21st Century. In Sustainable Food and Agriculture; Campanhola, C., Pandey, S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, K.; Conard, M.; Culligan, P.; Plunz, R.; Sutto, M.P.; Whittinghill, L. Sustainable food systems for future cities: The potential of urban agriculture. Econ. Soc. Rev. 2014, 45, 189–206. [Google Scholar]
- Akintuyi, O.B. Vertical farming in urban environments: A review of architectural integration and food security. Open Access Res. J. Biol. Pharm. 2024, 10, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, K.; Siebert, R.; Hartmann, I.; Freisinger, U.B.; Sawicka, M.; Werner, A.; Thomaier, S.; Henckel, D.; Walk, H.; Dierich, A. Urban agriculture of the future: An overview of sustainability aspects of food production in and on buildings. Agric. Hum. Values 2014, 31, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.; Wong, C.; Paturi, S. Vertical Farming: An Assessment of Singapore City. eTropic Electron. J. Stud. Trop. 2020, 19, 228–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kodmany, K. Digital Agriculture: A Solution for Sustainable Food and Nutritional Security; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 179–197. [Google Scholar]
- Despommier, D. The Vertical Farm: Feeding the World in the 21st Century; Macmillan: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Benke, K.; Tomkins, B. Future food-production systems: Vertical farming and controlled-environment agriculture. Sustain. Sci. Pract. Policy 2017, 13, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okwandu, A.C.; Akande, D.O.; Nwokediegwu, Z.Q.S. Green architecture: Conceptualizing vertical greenery in urban design. Eng. Sci. Technol. J. 2024, 5, 1657–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Guo, G.; Memon, S.A.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, J.H.; Xing, F. Recycling of carbon fibers from carbon fiber reinforced polymer using electrochemical method. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 78, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladapo, B.I.; Zahedi, S.A.; Balogun, V.A.; Ismail, S.O.; Samad, Y.A. Overview of Additive Manufacturing Biopolymer Composites. In Encyclopedia of Materials: Composites; Brabazon, D., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2021; pp. 915–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucknall, D.G. Plastics as a materials system in a circular economy. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2020, 378, 20190268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Hui, D.; Singh, R.; Ahuja, I.; Feo, L.; Fraternali, F. Recycling of plastic solid waste: A state of art review and future applications. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 115, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, R.; Martinho, A.; Oliveira, J. Evaluating the potential use of recycled glass fibers for the development of gypsum-based composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 321, 126320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, R.; Martinho, A.; Oliveira, J.P. Recycling of reinforced glass fibers waste: Current status. Materials 2022, 15, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Despeisse, M.; Ford, S. The role of additive manufacturing in improving resource efficiency and sustainability. In Advances in Production Management Systems: Innovative Production Management Towards Sustainable Growth: IFIP WG 5.7, Proceedings of the International Conference, APMS 2015, Tokyo, Japan, 7–9 September 2015; Proceedings, Part II; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 129–136. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Miller, J.; Vezza, J.; Mayster, M.; Raffay, M.; Justice, Q.; Al Tamimi, Z.; Hansotte, G.; Sunkara, L.D.; Bernat, J. Additive Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Review. Sensors 2024, 24, 2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prashar, G.; Vasudev, H.; Bhuddhi, D. Additive manufacturing: Expanding 3D printing horizon in industry 4.0. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. 2022, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisneros-López, E.; Pal, A.; Rodriguez, A.; Wu, F.; Misra, M.; Mielewski, D.; Kiziltas, A.; Mohanty, A. Recycled poly (lactic acid)–based 3D printed sustainable biocomposites: A comparative study with injection molding. Mater. Today Sustain. 2020, 7, 100027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Kellens, K.; Tang, R.; Chen, C.; Chen, G. Sustainability of additive manufacturing: An overview on its energy demand and environmental impact. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 21, 694–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Song, J.; Cheng, K.; Liu, Z.; Yang, F. Migration and remediation of typical contaminants in soil and groundwater: A state of art review. Land Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 2700–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladapo, B.I.; Zahedi, S.A.; Omigbodun, F.T. A systematic review of polymer composite in biomedical engineering. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 154, 110534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Rao, C.; Gu, F.; Sharmin, N.; Fu, J. Close-looped recycling of polylactic acid used in 3D printing: An experimental investigation and life cycle assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 197, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Ma, Y. Path planning strategies to optimize accuracy, quality, build time and material use in additive manufacturing: A review. Micromachines 2020, 11, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakkanen, J.; Manfredi, D.; Minetola, P.; Iuliano, L. About the use of recycled or biodegradable filaments for sustainability of 3D printing: State of the art and research opportunities. In Sustainable Design and Manufacturing 2017: Selected papers on Sustainable Design and Manufacturing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 776–785. [Google Scholar]
- Ford, S.; Despeisse, M. Additive manufacturing and sustainability: An exploratory study of the advantages and challenges. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 137, 1573–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Kumar, R. Additive Manufacturing for Plastic Recycling: Efforts in Boosting a Circular Economy; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary, K.; Sangwan, K.S.; Goyal, D. Environment and economic impacts assessment of PET waste recycling with conventional and renewable sources of energy. Procedia CIRP 2019, 80, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, A.; Rognoli, V.; Levi, M. Design, materials, and extrusion-based additive manufacturing in circular economy contexts: From waste to new products. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zander, N.E.; Gillan, M.; Burckhard, Z.; Gardea, F. Recycled polypropylene blends as novel 3D printing materials. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 25, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, C.; Sweet, K.; Ok, J. Closing the Loop—Recycling Waste Plastic. In Proceedings of the Anthropocene. Design in the Age of Humans—25th International Conference of the Association for Computer-Aided Architectural Design Research in Asia (CAADRIA), Bangkok, Thailand, 8 May–8 June 2020; pp. 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Nováková, K.; Prokop, Š.; Vele, J.; Achten, H. Crowd-printing recycled polyethylene tereftalate. Comput. Better Tomorrow 2018, 53. [Google Scholar]
- BANYAN Eco Wall—The World’s First Fully 3D Printed, Irrigated Green Wall—BigRep Industrial 3D Printers—bigrep.com. Available online: http://bigrep.com/posts/banyan-eco-wall/ (accessed on 21 June 2024).
- Schiavarelli, N.; WASP—3dwasp.com. WASP Hortus Sistema di Coltivazione Verticale Idroponica|Stampanti 3D. Available online: https://www.3dwasp.com/wasp-hortus-sistema-di-coltivazione-verticale-idroponica/ (accessed on 21 June 2024).
- Pasquero, C.; Poletto, M. Bio-digital aesthetics as value system of post-Anthropocene architecture. Int. J. Archit. Comput. 2020, 18, 120–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisostomo, J.L.B.; Dizon, J.R.C. 3D printing applications in agriculture, food processing, and environmental protection and monitoring. Adv. Sustain. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2021, 3, 372312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraveas, C.; Bayer, I.S.; Bartzanas, T. 4D printing: Perspectives for the production of sustainable plastics for agriculture. Biotechnol. Adv. 2022, 54, 107785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, K.; Siebert, R.; Thomaier, S. Perception and acceptance of agricultural production in and on urban buildings (ZFarming): A qualitative study from Berlin, Germany. Agric. Hum. Values 2016, 33, 753–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, J.; Baeza, E.; Heuvelink, E.; Rieradevall, J.; Muñoz, P.; Ercilla, M.; Stanghellini, C. Productivity of a building-integrated roof top greenhouse in a Mediterranean climate. Agric. Syst. 2017, 158, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Chalabi, M. Vertical farming: Skyscraper sustainability? Sustain. Cities Soc. 2015, 18, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bañón, C.; Raspall, F. 3D printing floating modular farms from Plastic Waste. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 70, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bañón, C.; Raspall, F. 3D Printing Architecture: Workflows, Applications, and Trends; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Garwacki, M.; Cudnik, I.; Dziadowiec, D.; Szymczak, P.; Andrzejewski, J. The Development of Sustainable Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol-Based (PETG) Blends for Additive Manufacturing Processing—The Use of Multilayered Foil Waste as the Blend Component. Materials 2024, 17, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepahi, M.; Abusalma, H.; Jovanovic, V.; Eisazadeh, H. Mechanical Properties of 3D-Printed Parts Made of Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 6851–6861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidakis, N.; Petousis, M.; Tzounis, L.; Grammatikos, S.; Porfyrakis, E.; Maniadi, A.; Mountakis, N. Sustainable Additive Manufacturing: Mechanical Response of Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol over Multiple Recycling Processes. Materials 2021, 14, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinter, E.; Welle, F.; Mayrhofer, E.; Pechhacker, A.; Motloch, L.; Lahme, V.; Grant, A.; Tacker, M. Circularity study on PET bottle-to-bottle recycling. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, S.M.; Singh, D. Experimental Investigation on Filament Extrusion Using Recycled Materials. Master’s Thesis, Halmstad University, Halmstad, Sweden, 2020. [Google Scholar]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ezhilarasu, S.; Bañón, C.; Silva, A. Development of Vertical Farming Systems from Waste Polymers Using Additive Manufacturing Techniques. Recycling 2024, 9, 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling9050090
Ezhilarasu S, Bañón C, Silva A. Development of Vertical Farming Systems from Waste Polymers Using Additive Manufacturing Techniques. Recycling. 2024; 9(5):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling9050090
Chicago/Turabian StyleEzhilarasu, Sunilkarthik, Carlos Bañón, and Arlindo Silva. 2024. "Development of Vertical Farming Systems from Waste Polymers Using Additive Manufacturing Techniques" Recycling 9, no. 5: 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling9050090
APA StyleEzhilarasu, S., Bañón, C., & Silva, A. (2024). Development of Vertical Farming Systems from Waste Polymers Using Additive Manufacturing Techniques. Recycling, 9(5), 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling9050090





