Abstract
The investigation into the implementation and widespread adoption of oyster shell recycling methods aimed at restoring coastal ecosystems and enhancing water quality is currently limited. In this study, we investigated the utilization of oyster shell powder (OSP) as a cost-effective and environmentally sustainable method for treating high-fluoride-concentration wastewater, a byproduct of industrial processes. We conducted extensive laboratory testing to determine the optimal conditions for fluoride removal. This involved variations in OSP doses, particle sizes, and initial wastewater pH levels. The results of these tests showed that OSP achieved fluoride removal efficiencies exceeding 98% at an optimal dosage of 5 g/L. In addition, OSP effectively adjusted the wastewater pH from highly acidic (pH 2) to almost neutral (pH 6.87), demonstrating its effectiveness in real-world industrial wastewater treatment. OSP, derived from oyster shell waste, is rich in calcium carbonate and offers a novel approach to wastewater management by leveraging a natural waste product. This study demonstrates the potential of OSP as a waste management strategy and contributor to the circular economy by repurposing industrial byproducts.
1. Introduction
The emergence of the Fourth Industrial Revolution has greatly accelerated the expansion of the semiconductor industry, fueled by an ever-increasing demand for electronic devices [1,2]. Over the past two decades, this sector has witnessed considerable investment and expansion, making it a vital contributor to the technological advancement of human society. This rapid growth is further supported by substantial investments such as the USD 150 billion investment by Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company Limited (TSMC) in advanced semiconductor manufacturing and the USD 20 billion expansion plan announced by Intel in 2021 [3,4]. Invest KOREA, a division of the Korea Trade-Investment Promotion Agency (KOTRA), reported that the revenue of the global semiconductor industry was USD 604 billion in 2022. The United States accounted for 52% of this revenue, followed by Republic of Korea (17.7%), Japan (8.6%), Taiwan (7.5%), and China (3.4%) [5]. Although the semiconductor industry has undoubtedly contributed to economic prosperity, its environmental impacts, particularly those relating to wastewater generation during manufacturing processes, cannot be overlooked [6,7]. A major environmental concern emerges from producing high-fluoride-concentration wastewater during the etching process. This wastewater is characterized by low pH levels and fluoride concentrations ranging from hundreds to thousands of mg/L [8,9].
Chemical precipitation is widely recognized for its feasibility and effectiveness in treating high-fluoride-concentration wastewater [10,11]. The primary chemicals used in this process are CaCl2 and Ca(OH)2, which react with fluoride ions to release precipitating calcium ions [12,13]. However, this method generates a considerable amount of sludge, and pursuing cost-effective and efficient calcium sources is a key research direction.
This study focuses on oyster shells, with an annual production of approximately 300,000 tons in Republic of Korea [14,15]. Only a fraction of these shells is reused, and major environmental impacts arise from the disposal of the remaining shells [16]. Oyster shells, primarily composed of calcium carbonate (CaCO3), hold immense potential as a rich source of calcium. Studies have shown that the calcium carbonate content in oyster shells can be as high as 95%, rendering them a valuable resource for various applications, including environmental and industrial uses [17,18].
The calcium component of oyster shells has been investigated for various environmental applications, including desulfurization materials, soil conditioners, and heavy metal removal. For example, Asaoka et al. reported that oyster shell powder effectively purifies organically rich marine sediments in eutrophic coastal areas by removing hydrogen sulfide from the interstitial water [19]. Hsu initially used oyster shells as an adsorbent to remove heavy metals from wastewater. The experiment did not involve any pretreatment. The results showed that the adsorption of copper was more efficient than that of nickel [20]. In addition, the thermally treated form of oyster shell powder, calcium oxide, readily ionizes into Ca2+ and OH− in water and interacts with eutrophic anions (e.g., PO43− and HPO42−) to serve as a precipitant that controls eutrophication [21,22,23].
Although previous studies have highlighted the environmental benefits of oyster shell recycling, such as their contribution to restoring coastal ecosystems and improving water quality [24,25,26], the practical implementation and widespread adoption of these methods remain limited. This study addressed this gap by applying oyster shell methodologies to real-world wastewater treatment scenarios. By evaluating their applicability and effectiveness, we attempted to move beyond theoretical models and demonstrate concrete and impactful solutions that can be implemented in practice.
The primary objective of this study was to ascertain the feasibility of utilizing oyster shells for fluoride wastewater treatment. We investigated the properties of oyster shell powder prior to and following treatment to acquire a more comprehensive understanding of the mechanism of fluoride removal. This investigation involved various parameters, such as pretreatment procedures, particle size, dosage, initial pH, and fluoride concentration in wastewater. In addition, it focused on examining the impacts of these factors on treatment efficacy. Moreover, our research extended this methodology to real-world wastewater generated by semiconductor and display manufacturing processes to assess its viability in real-world industrial contexts.
This study presents an innovative, eco-friendly, and economically feasible approach for treating fluoride wastewater. It also underscores the versatile environmental applications of oyster shells. This approach not only addresses pressing environmental concerns but also indicates an avenue towards sustainable resource use and recycling.
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of OSP, HF-OSP, and RW-OSP
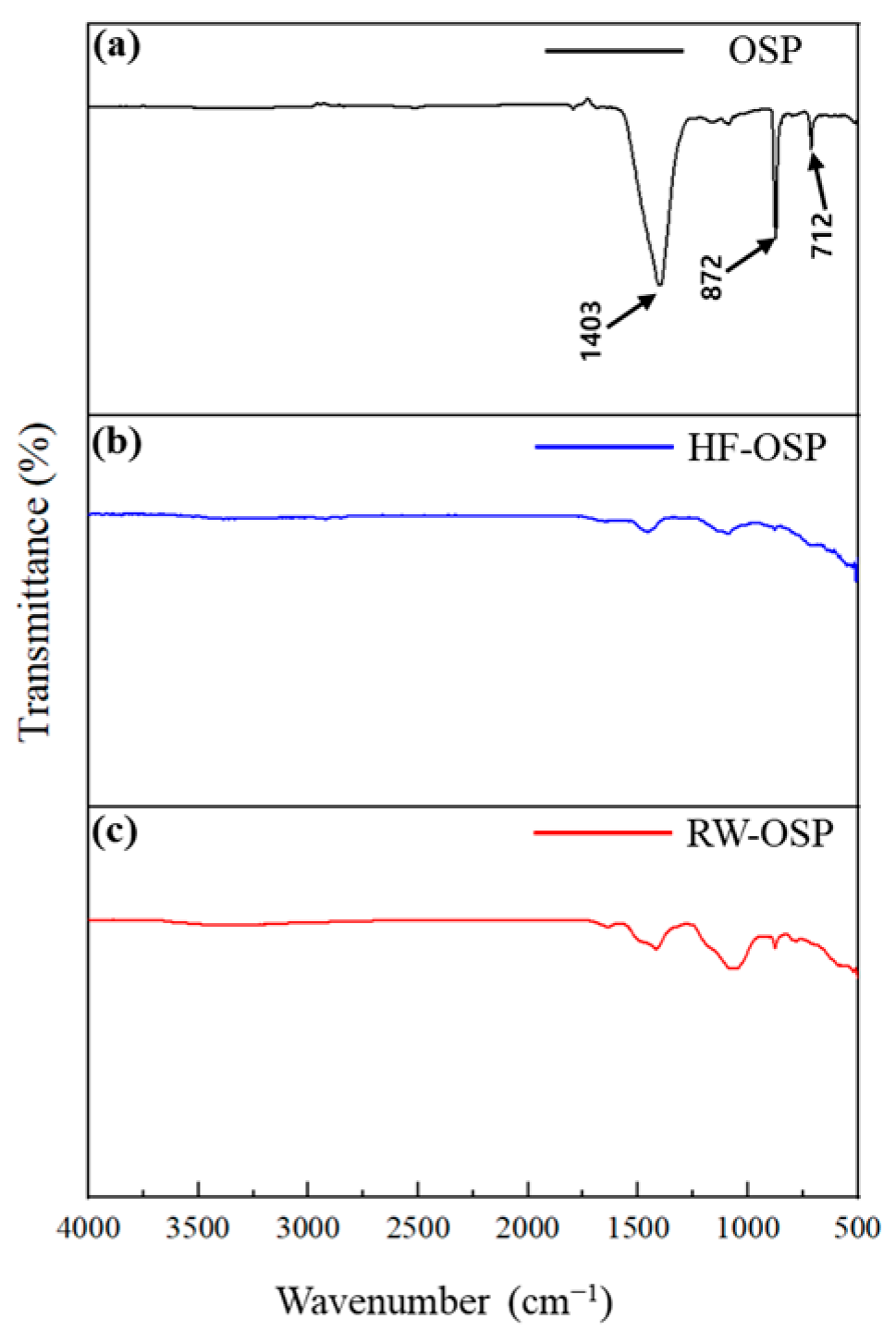
Chemical bond alterations between fluoride and the oyster shell powder (OSP) structure were analyzed using an Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectrometer. Variations in the FTIR spectra of OSP, hydrogen fluoride treated-OSP (HF-OSP), and real wastewater-treated OSP (RW-OSP) are presented in Figure 1. OSP primarily consists of calcium carbonate. Its FT-IR spectrum displays the distinct peaks of calcite at 1403 cm−1 (asymmetric C-O stretching), 872 cm−1 (CO32− bending), and 712 cm−1 (O-C-O bending) [17]. Following the hydrogen fluoride (HF) treatment, the characteristic peaks associated with OSP disappeared, indicating that OSP reacted with HF to form calcium fluoride (CaF2). Similarly, the IR spectrum of the RW-OSP post wastewater treatment showed patterns comparable to those of HF-OSP, suggesting that OSP also reacted with fluoride in wastewater to produce CaF2.
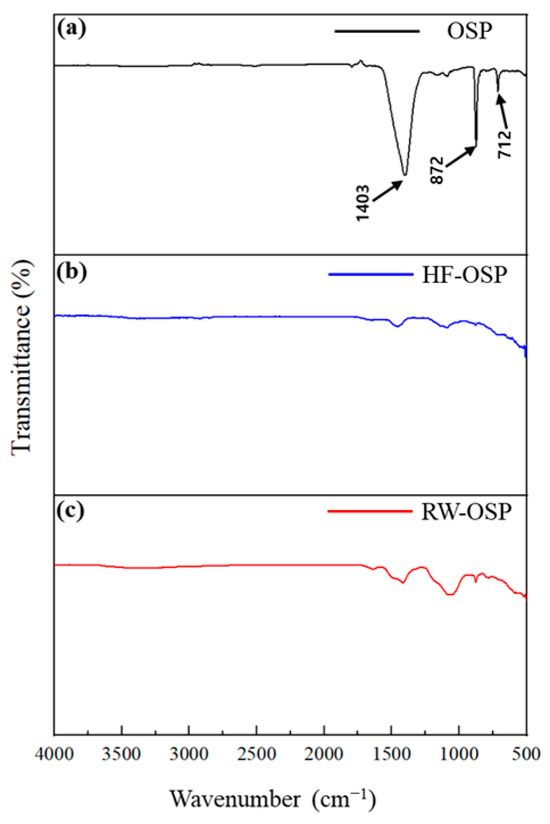
Figure 1.
FT-IR spectra of (a) OSP, (b) HF-OSP, and (c) RW-OSP.
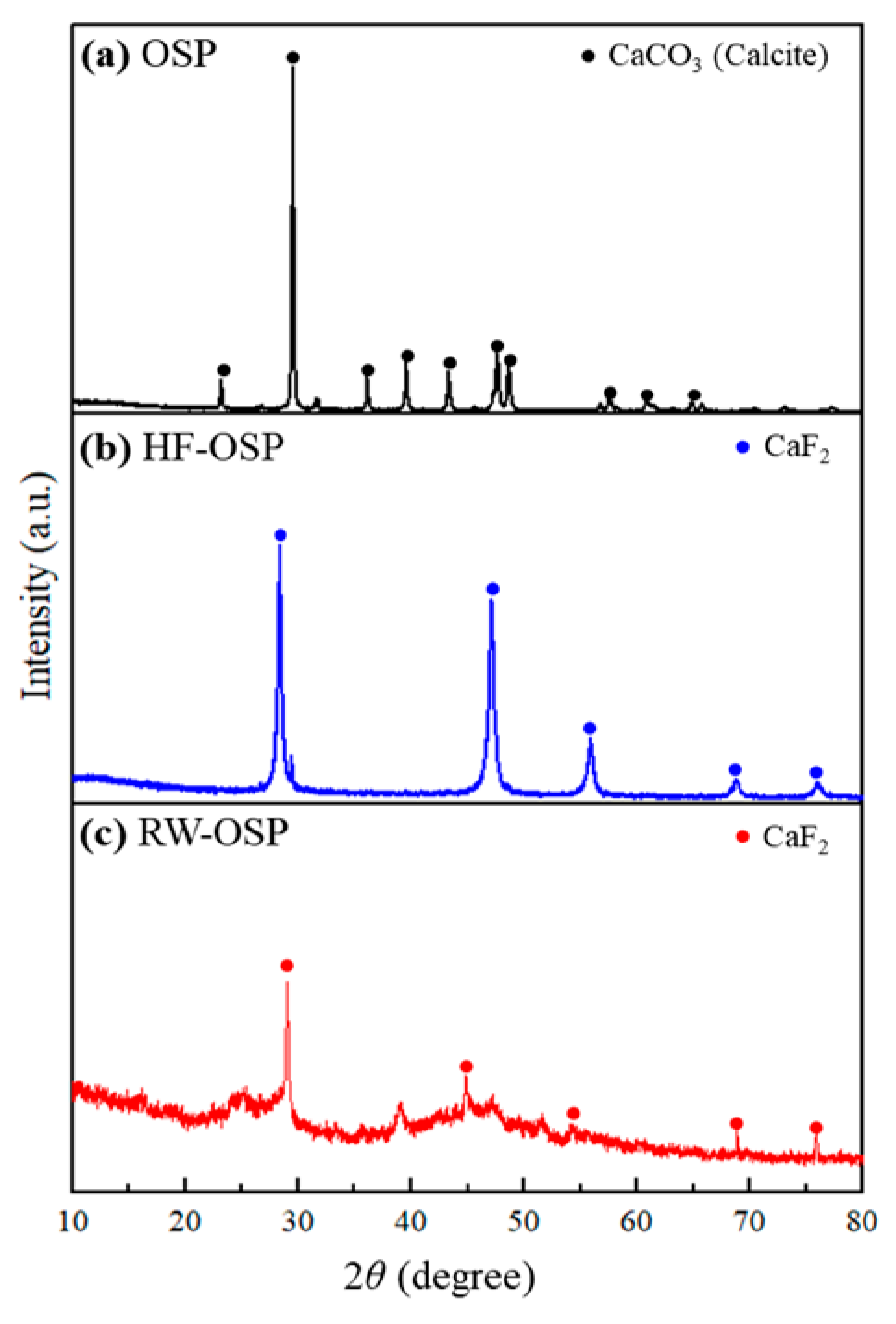
The mineralogical compositions of OSP, HF-OSP, and RW-OSP were determined by X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis (Figure 2). OSP has a highly crystalline structure, and its XRD pattern (Figure 2a) is almost identical to that of calcium carbonate (JCPDS card 47-1743) [27]. As shown in Figure 2b, the XRD pattern of HF-OSP is indexed to the fluorite-type cubic phase of CaF2 with a space group of Fm3m [28]. The pattern matched JCPDS card number 87-0971 [29,30]. This XRD pattern provides evidence of the cubic crystallinity of CaF2, which is formed through the reaction of OSP with HF. This was evidenced by the peaks at 2θ values of 28.35, 47.05, 55.63, 68.84, and 75.85, which corresponded to the characteristic peaks of CaF2 [31]. In an experiment in which OSP was administered to actual semiconductor wastewater, the precipitate was analyzed using XRD (Figure 2c). The analysis revealed peaks similar to those observed for HF-OSP, suggesting that the fluoride present in the wastewater reacted with OSP to form and precipitate CaF2. Additional peaks were also detected, indicating the potential presence of other impurities or different crystalline materials in the wastewater.
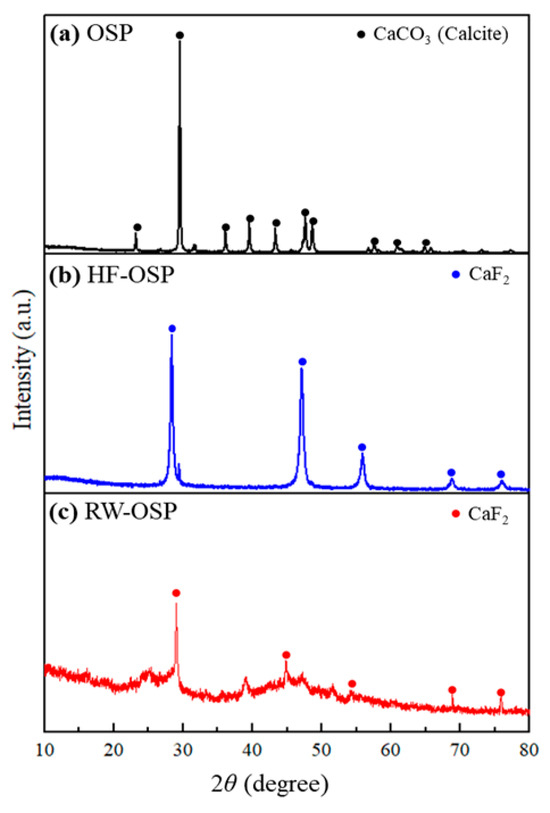
Figure 2.
X-ray diffraction patterns demonstrating phase transitions in OSP: (a) native OSP (calcite), (b) HF-OSP (CaF2 formation), and (c) RW-OSP (CaF2 confirmation).
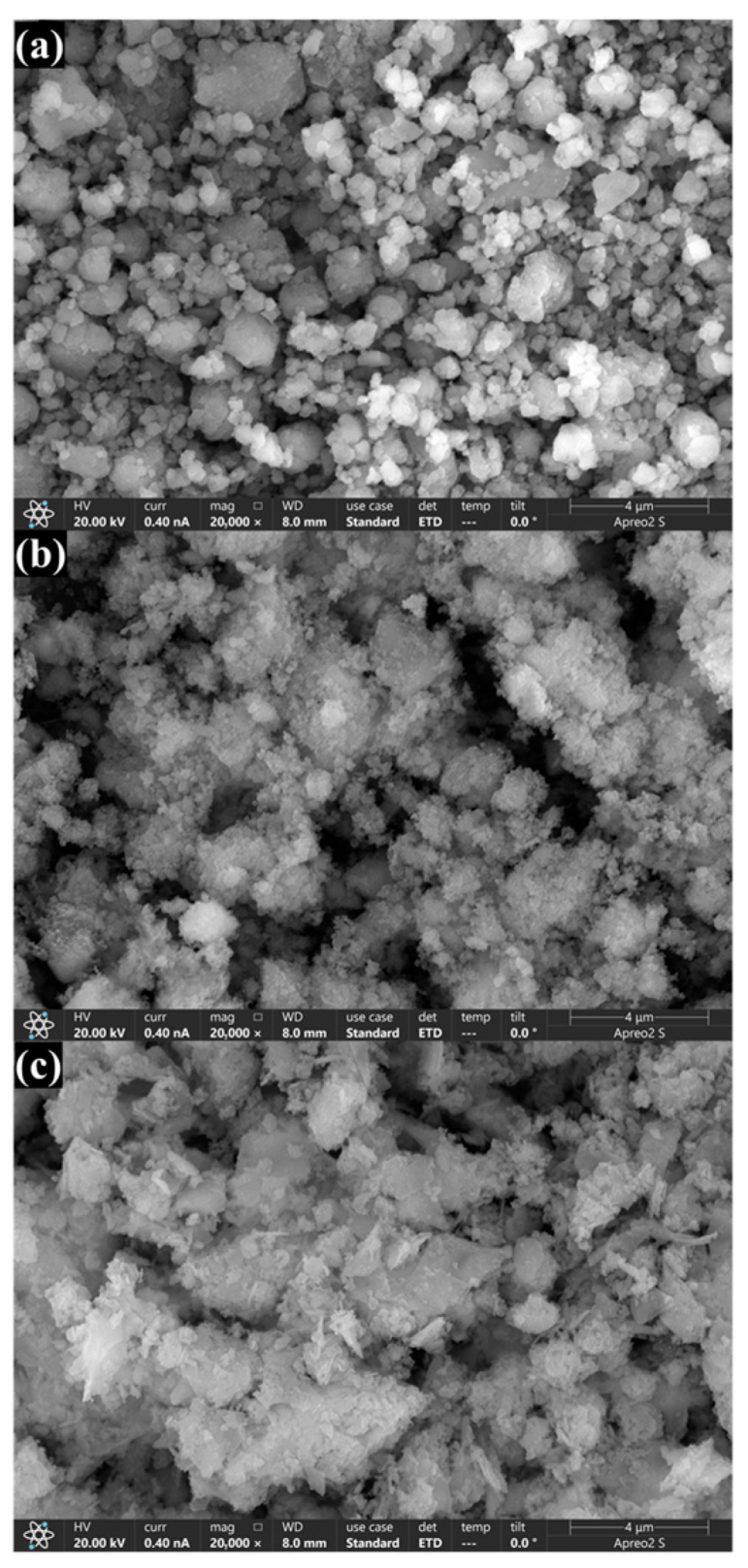
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis was used to examine the surface morphology of the OSP before and after treatment with HF and real wastewater. Figure 3 displays the distinct morphological changes between the samples. OSP (Figure 3a) exhibited an irregular and densely packed particle structure with a rough surface. HF-OSP (Figure 3b) exhibited significant changes in surface texture, increasing roughness. The particles were more agglomerated due to the reaction between the calcium ions of OSP and the fluoride ions of HF, which signified the formation of a new compound, CaF2. Similarly, RW-OSP showed a trend similar to that of HF-OSP. The particles displayed a cauliflower-like structure, resulting from the complex components in the real wastewater reacting with OSP. Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) spectra of HF-OSP and RW-OSP confirmed the presence of 11.91–57.74 wt% fluorine, which was uniformly distributed on the surface (Figure S1, Figure S2 and Figure S3).
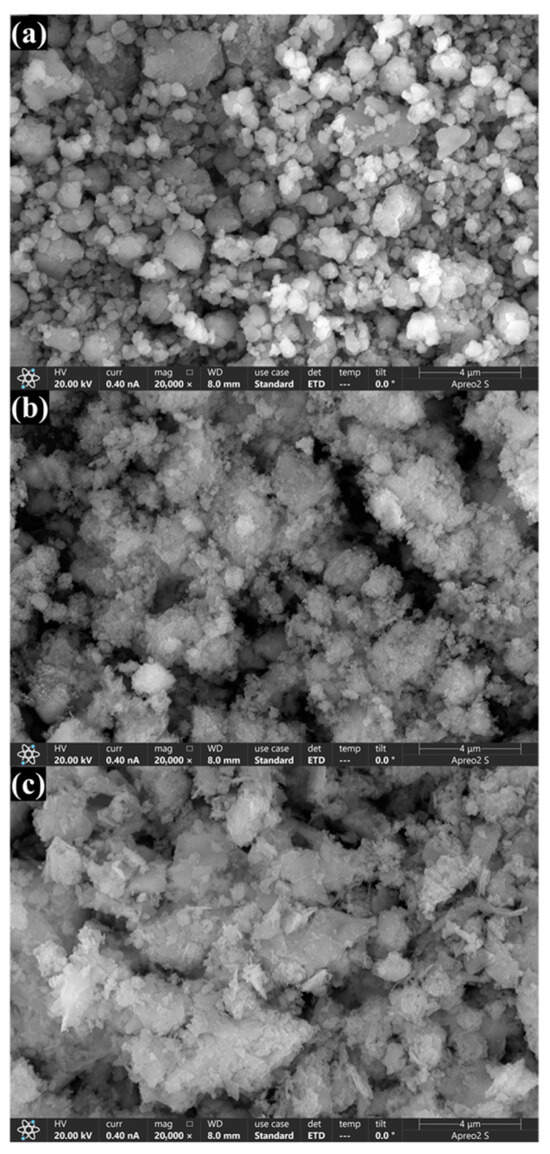
Figure 3.
SEM analysis of OSP morphological changes: (a) native OSP, (b) post hydrofluoric acid treatment, and (c) post real wastewater treatment.
2.2. Effect of OSP Dosage on Fluoride Removal
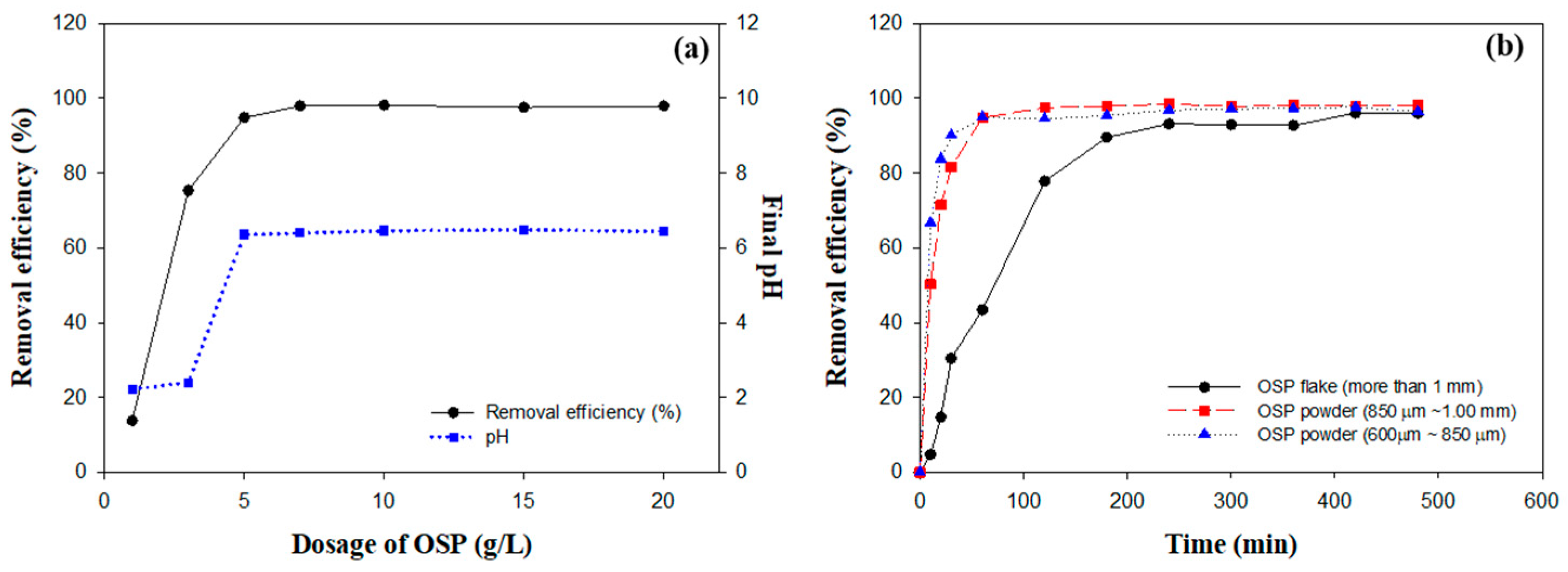
This study investigated the effects of different doses of OSP on the fluoride removal efficiency and the associated pH changes in aqueous solutions. The experiments were performed utilizing a fluoride solution with a concentration of 309 mg/L and an initial pH of 2, which corresponds to the typical conditions encountered in semiconductor processing wastewater [32]. Figure 4a illustrates a considerable increase in fluoride removal efficiency with increasing OSP dosage. Removal efficiencies exceeding 90% were achieved at doses greater than 5 g/L, with the maximum efficiency plateauing at 98.13% at a dosage of 10 g/L. No further improvements were observed beyond this point, indicating that the reactive capacity was saturated under the specific experimental conditions.
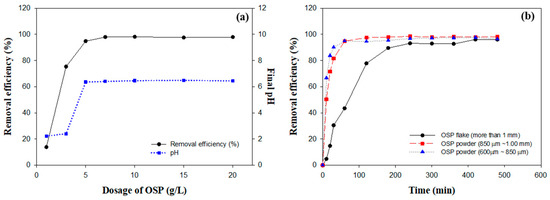
Figure 4.
Comprehensive analysis of OSP performance in fluoride removal: (a) dose–response relationship of OSP, (b) effect of particle size on removal efficiency.
Concurrent increases in OSP dosage also corresponded to increases in solution pH. At doses of 5 g/L and above, the pH values ranged between 6.36 and 6.49, approaching a nearly neutral level. The primary component of OSP, calcium carbonate (CaCO3), reacts with HF to generate these high fluoride removal efficiencies and pH changes [33]. The following reaction represents this process:
The carbonic acid (H2CO3) produced in this reaction dissociates in water, forming bicarbonate ions (HCO3⁻). These bicarbonate ions further decompose into carbonate ions (CO32⁻) and water. This decomposition releases hydroxide ions (OH⁻), which contribute significantly to the observed pH increase [34]. As the OSP dosage increases, a greater amount of calcium carbonate dissolves and actively participates in the reaction, thereby amplifying the pH increase. These results provide important data for the design and optimization of wastewater treatment systems utilizing OSP, particularly for treating fluoride-rich industrial wastewater. The capacity of OSP to efficiently eliminate fluoride while simultaneously adjusting the pH to neutral offers major advantages in line with environmental management and sustainability goals.
2.3. Influence of OSP Particle Size on Fluoride Removal Efficiency
Figure 4b shows the analysis results of the impact of various OSP particle sizes on fluoride removal efficiency. Particles within the 600–850 μm range achieved an impressive 90% removal efficiency within the first 60 min, eventually stabilizing at 96.40% after 480 min. This efficiency was largely attributed to their high surface-area-to-volume ratio (SA) [35]. The increased SA enhanced the solubility and accelerated the reaction kinetics of OSP by providing a greater number of active sites available for chemical interactions [35,36]. This interaction promoted faster dissolution and more efficient reaction processes because larger surface areas enabled more fluoride ions to contact and react with OSP.
Conversely, particles within the 850–1000 μm range exhibited comparatively slower initial reaction rates; however, their efficiency increased over time, peaking at 98.19% by the end of the experiment. Particles with sizes exceeding 1000 μm exhibited the slowest initial reaction, with an efficiency of only 4.71% in the first 10 min; however, they eventually achieved efficiencies comparable to those of smaller particles, reaching 96.05% after 480 min. This indicates that extended reaction times can offset the initially low reaction rates of larger particles.
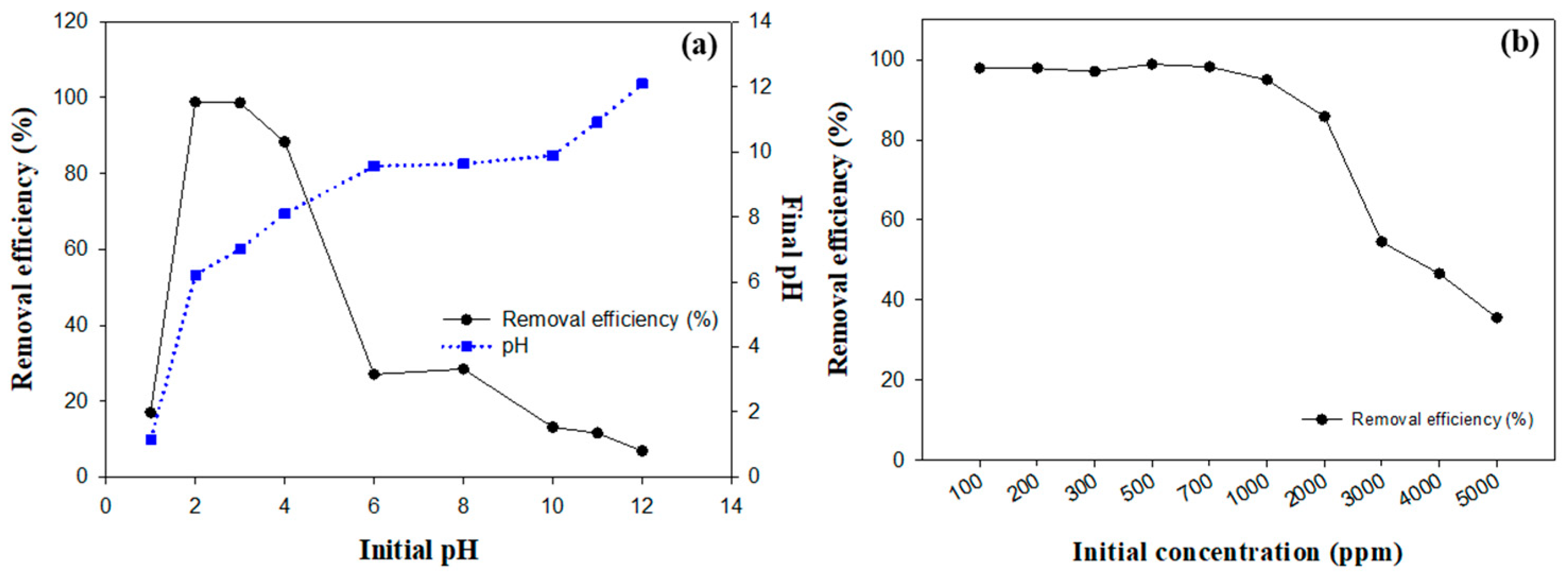
2.4. Impact of Initial pH on Fluoride Removal Efficiency
Figure 5a presents the experimental results demonstrating the impact of the initial pH on fluoride removal. At a pH of 1, the abundance of hydrogen ions inhibited the reaction between calcium and fluoride ions, preventing the formation of calcium fluoride. As a result, the fluoride removal efficiency was relatively low, at 16.96%. At a pH of 2, the competition from hydrogen ions decreased, and the utilization of calcium ions increased, resulting in a significant increase in the fluoride removal efficiency to 98.80%. This is because the optimized reaction conditions between calcium and fluoride ions facilitated the effective formation of calcium fluoride precipitates. The solubility product constant (Ksp) for CaF2 is given by the following equation:
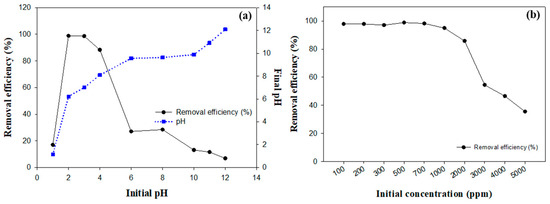
Figure 5.
Comprehensive investigation of the dynamics of OSP in fluoride mitigation: (a) influence of initial pH on removal efficiency and pH changes, (b) impact of initial fluoride concentration on removal efficiency.
A high removal efficiency of 98.60% was maintained at a pH of 3. This pH level provided optimal conditions by balancing the availability of calcium ions with a lower concentration of hydrogen ions, thereby promoting the formation of CaF2 by exceeding its Ksp [34,37]. As the pH continued to increase, the fluoride removal efficiency decreased to 27.06% at a pH of 6. This reduction was due to the decreased solubility of calcium carbonate under less acidic conditions, which limited the availability of free calcium ions required for the reaction [7].
2.5. Influence of Initial Fluoride Concentration on Removal Efficiency
The removal efficiencies at different initial fluoride concentrations are shown in Figure 5b. At lower concentrations of up to 1000 mg/L, the fluoride removal efficiency remained consistently high, above 94%. The peak efficiency of 98.84% was observed at 500 mg/L. This optimal performance can be attributed to the sufficient reactive capacity of OSP at these concentrations. However, as the fluoride concentration exceeded 1000 mg/L, a noticeable decline in the removal efficiency was observed. The efficiency decreased to 85.78% at 2000 mg/L and further decreased to 35.52% at 5000 mg/L.
Quantitative calculations based on the chemical reaction between CaCO3 and HF, as demonstrated in Equation (1), provide insight into this trend. If 95% of OSP is composed of calcium carbonate, the mass of calcium carbonate would be approximately 0.1425 g, corresponding to 1.425 × 10⁻3 M CaCO3, considering its molar mass of 100 g/mol. Based on stoichiometry, a 1:2 molar ratio is required between calcium carbonate and HF, resulting in a total of 2.85 × 10⁻3 M HF. For a 30 mL solution at a concentration of 2000 mg/L, the required HF mass is 0.06 g, which slightly exceeds the stoichiometric amount (0.057 g). This suggests that at 2000 mg/L, OSP can effectively react with the available HF, achieving high removal efficiency. However, at higher concentrations, such as 3000 mg/L and beyond, the quantity of HF surpasses the reactive capacity of OSP. Consequently, the removal efficiency decreases significantly due to the limited availability of CaCO3.
2.6. Verification of the Effectiveness of OSP in Actual Semiconductor Wastewater
The ability of OSP to reduce fluoride concentration and neutralize pH was confirmed by evaluating its efficiency in treating actual semiconductor wastewater. Semiconductor wastewater, which can be broadly classified into organic, nitrogenous, hydrofluoric acid, and acid/alkaline types, is predominantly composed of hydrofluoric acid wastewater with a pH of 2–3, accounting for 60–70% of the total wastewater. The fluoride concentration in semiconductor wastewater typically ranges from 200 to 300 mg/L, depending on the manufacturing process [38].
Table 1 shows the characteristics of the wastewater before and after treatment with OSP, conducted at a dosage of 5 g/L and a particle size range of 180–600 µm. After treatment, the pH of the wastewater significantly increased from 2.15 to 6.87, reaching nearly neutral levels. The fluoride concentration decreased considerably from 344.1 mg/L to 3.02 mg/L, demonstrating the effectiveness of OSP in reducing fluoride levels in real wastewater. However, the impact on other anions such as chloride, sulfate, and phosphate was minimal. The concentration of total nitrogen (TN) slightly increased from 57.92 mg/L before treatment to 78.79 mg/L after treatment, indicating that OSP does not directly affect nitrogen removal. The concentration of total phosphorus (TP) decreased from 2.9 mg/L to 1.6 mg/L, suggesting some calcium in OSP combined with phosphate ions to form insoluble calcium phosphate, thereby contributing to partial phosphorus removal.

Table 1.
Characteristics of real wastewater and treated real wastewater.
3. Discussion
The similarity between the IR spectra of HF-OSP and RW-OSP and the typical IR signature of CaF2 supports this conclusion [39]. These findings imply that OSP was successfully precipitated as CaF2 when it reacted with HF solution and real wastewater. The XRD analysis further corroborates the formation of CaF2, as evidenced by the matching peaks with known fluorite structures. This demonstrated the successful precipitation of CaF2 in its fluorite form following the treatment of OSP with HF. Additionally, the XRD results for RW-OSP indicate that OSP effectively reacted with fluoride in real wastewater to form CaF2, although the presence of other peaks suggests impurities or other crystalline structures may also form during the reaction process. SEM analysis reveals that the surface morphology of OSP undergoes significant changes following treatment with HF and wastewater. The transition from a rough, irregular structure to a more agglomerated, cauliflower-like appearance highlights the impact of these treatments on the physical characteristics of OSP. The EDS data confirm the uniform distribution of fluorine on the surface of HF-OSP and RW-OSP, further supporting the formation of CaF2. These observations suggest that both HF and wastewater treatment not only alter the chemical composition but also significantly affect the surface characteristics of OSP, which may influence its potential applications in environmental remediation.
The carbonic acid (H2CO3) produced in the reaction between calcium carbonate and HF dissociates in water, forming bicarbonate ions (HCO3⁻). These bicarbonate ions further decompose into carbonate ions (CO32⁻) and water, releasing hydroxide ions (OH⁻) that contribute to the observed pH increase [34]. As the OSP dosage increases, more calcium carbonate dissolves and actively participates in the reaction, amplifying the pH increase. This relationship between OSP dosage and pH regulation is critical, as it highlights the dual functionality of OSP in both removing fluoride and adjusting the pH of the solution. These results offer valuable insights for the design and optimization of wastewater treatment systems utilizing OSP, particularly for industrial wastewater that contains high levels of fluoride. The ability of OSP to efficiently eliminate fluoride while simultaneously increasing the pH to near-neutral levels presents significant advantages for environmental management and sustainability objectives. This dual functionality of OSP makes it an effective and environmentally friendly solution for treating fluoride-rich industrial wastewater.
Optimizing OSP particle size is also essential to enhance the performance of wastewater treatment systems. The high fluoride removal efficiency observed for smaller particle sizes can be attributed to their high surface-area-to-volume ratio, which accelerates reaction kinetics and promotes faster fluoride removal. In contrast, larger particles, despite their slower initial rates, ultimately reach comparable efficiencies with sufficient reaction time. This suggests that both particle size and reaction time must be carefully considered to maximize the effectiveness of OSP in fluoride removal applications. In addition, the influence of OSP dosage and particle size on the pH of the solution must be carefully evaluated, as pH changes can significantly impact the overall fluoride removal efficiency. OSP serves as an environmentally friendly alternative that can effectively reduce fluoride concentrations while also balancing pH to a neutral state [33]. The ability to tailor OSP particle sizes to specific treatment requirements provides flexibility in industrial wastewater treatment applications. These properties underscore the potential of OSPs in sustainable environmental management, particularly for industrial processes that generate fluoride-rich wastewater. By optimizing OSP particle size, dosing, and pH control, it is possible to achieve high removal efficiencies and maintain environmentally favorable conditions in wastewater treatment systems.
Furthermore, understanding the relationship between the solubility product of CaF2 and pH is crucial for optimizing fluoride removal efficiency. At lower pH levels, particularly around 2–3, the decreased competition from hydrogen ions allows for more efficient use of calcium ions, facilitating the formation of CaF2 precipitates. This is crucial for achieving high fluoride removal rates because the formation of CaF2 is favored under these conditions, as indicated by the low solubility product constant (Ksp). As the pH increases, the solubility of calcium carbonate decreases, which limits the availability of free calcium ions, thus reducing the overall fluoride removal efficiency. This illustrates the delicate balance required to maintain optimal pH conditions for effective fluoride removal using OSPs. By maintaining favorable conditions for forming insoluble CaF2 and adjusting the pH accordingly, OSPs can achieve efficient treatment of fluoride ions from hydrofluoric acid wastewater. This knowledge is essential for designing and optimizing industrial wastewater treatment systems, providing a sustainable and effective solution for enhancing fluoride removal efficiency through precise pH control [40].
These findings also indicate that while OSP is highly effective at lower fluoride concentrations, its removal capacity is constrained by the stoichiometric availability of calcium carbonate at higher fluoride concentrations. The sharp decline in removal efficiency at concentrations exceeding 1000 mg/L is due to the limited reactive capacity of CaCO3, as the available HF surpasses the stoichiometric ratio required for effective reaction. This underscores the necessity for the meticulous optimization of OSP dosage relative to the fluoride concentration in wastewater treatment applications. To achieve the most effective removal efficiency, it is crucial to balance the dosage of OSP with the initial fluoride concentration. This study provides critical data for designing OSP-based water treatment systems, particularly for industrial wastewater containing high fluoride concentrations. Furthermore, optimizing fluoride removal by selecting appropriate OSP particle sizes and adjusting initial conditions can enhance the efficiency of treatment processes. These adjustments can present a viable alternative for effectively treating industrial wastewater with high fluoride concentrations, aligning with sustainable environmental management goals.
Finally, the significant reduction in fluoride concentration and the near-neutralization of pH primarily resulted from the interaction between the calcium ions in the OSP and the fluoride ions in the wastewater. The substantial electronegativity difference between calcium (EN: 1.0) and fluoride (EN: 4.0) leads to the formation of stable CaF2 through strong ionic bonding. This compound, being highly insoluble in water, effectively removes fluoride from the wastewater. In contrast, anions such as sulfate (EN: 2.58) and phosphate (EN: 2.1), which have relatively smaller electronegativity differences with calcium, do not form stable precipitates as effectively as fluoride does. The slight increase in TN concentration post treatment indicates the need for additional treatment steps for nitrogen removal, as OSP does not target nitrogenous compounds. The observed decrease in T-P suggests that while OSP primarily targets fluoride, it also has a secondary effect on phosphorus removal, possibly through the formation of calcium phosphate precipitates. These experimental results highlight the high potential of OSP as a primary treatment agent for fluoride removal in hydrofluoric acid wastewater. However, to comprehensively treat such wastewater, a secondary treatment step is necessary to address other anionic substances and to further reduce TN and TP levels. Integrating OSP treatment with a reverse osmosis (RO) system could be a viable strategy. The neutralization of wastewater by OSP treatment would reduce its corrosivity and alleviate the burden on RO membranes, thereby extending the membrane replacement cycle. This approach aligns with sustainable wastewater management strategies that prioritize efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Moreover, in line with the principles of a circular economy, the precipitated CaF2 can be repurposed in several valuable ways [41]. It can be used as a raw material for the production of hydrofluoric acid or in the manufacture of aluminum and glass, where CaF2 acts as a flux. Additionally, it can be utilized in the production of optical components and ceramics. Exploring these reuse options not only helps in reducing waste but also contributes to resource efficiency and sustainability.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
Hydrofluoric acid (purity: 49–51%) was purchased from Duksan Co., Ltd. (Seoul, Republic of Korea). Oyster shell (OS) waste was collected from a local market in Tongyeong, Republic of Korea. Alfusone was acquired from Dojindo Laboratories Co., Ltd. (Kumamoto, Japan). Acetone (99.8%, Guaranteed) was obtained from Dajung Chemical & Metals Co., Ltd. (Siheung, Republic of Korea). Semiconductor wastewater was procured from an industrial company located in the Gumi Industrial Complex. (Gumi, Republic of Korea). The TN and TP LR sets for TN and TP analyses, respectively, were purchased from C-MAC Co., Ltd. (Daejeon, Republic of Korea). The reagents for PO43− and NH4+ analyses, along with other reagents such as NaOH and HCl used in this study, were all of analytical grade.
4.2. Pre-Treatment of Oyster Shells
OS waste derived from Crassostrea gigas was subjected to various pre-treatment steps to evaluate its suitability as an eco-friendly material. The initial cleaning process entailed utilizing high-pressure water jets to remove sediment and extraneous debris effectively. The shells were then immersed in a 1% NaClO solution for 24 h to ensure complete eradication of organic matter. Following immersion, the shells were thoroughly rinsed and subjected to a drying process at 60 °C for 24 h. This procedure was designed to eliminate organic contaminants while simultaneously preserving the inherent chemical composition of the shells. After drying, the shells were processed using a ball mill (Pulverisette 7, FRITSCH, Idar-Oberstein, Germany). The milling parameters were precisely controlled: 20 g of oyster shell material was milled using 5 μm diameter balls at a rotational speed of 800 rpm for a total duration of 30 min. This protocol was meticulously developed to produce a homogenous particle size, which allows for a more accurate assessment of physical properties in subsequent analyses. OSP was then segregated using sieves with mesh sizes of 600 μm, 850 μm, and 1 mm, yielding three distinct particle size fractions for analysis.
4.3. Characterization
FT-IR spectroscopy was conducted to analyze the OSP, HF-OSP, RW-OSP. Spectra were recorded from 4000 to 500 cm−1 using an ALPHA II FT-IR spectrometer (Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA). XRD was employed to determine the crystal structures of OSP, HF-OSP, and RW-OSP. XRD was conducted using a D8 Advance A25 system (Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA) with Cu Kα radiation (λ = 1.54 Å) across a 2θ range of 10–80°. The surface morphologies and elemental compositions were examined by field-emission scanning electron microscopy combined with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (FE-SEM/EDS) using an Apreo S instrument (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA).
4.4. Batch Experiments
HF removal experiments were conducted to assess the effectiveness of OSP in removing fluoride ions from aqueous solutions under various conditions. HF solutions (30 mL) were subjected to OSP treatment in various experiments designed to assess the effects of particle size, dosage, solution pH, and initial HF concentration.
In the first experiment, OSPs with a particle size ranging from 600 μm to over 1 mm were introduced into HF solutions (289 mg/L, pH 2) at a concentration of 5 g/L. The mixtures were agitated at 160 rpm at 25 °C, and fluoride ion concentrations were monitored over periods extending from 10 to 480 min. Subsequently, various doses of OSP, ranging from 1 to 20 g/L with a particle size of 180–600 μm, were tested against a 30 mL HF solution (309 mg/L, pH 2) for a period of 12 h to determine the optimal OSP concentration for maximum fluoride removal.
The third part of this study involved adjusting the pH of a 30 mL HF solution (309 mg/L) treated with OSP (0.15 g, 5 g/L, 180–600 μm). The mixture was maintained at 25 °C and agitated at 160 rpm over 12 h to investigate the influence of pH on fluoride removal efficiency. Lastly, the effect of initial fluoride concentration was examined by adding OSP (0.15 g, 5 g/L, 180–600 μm) to HF solutions with concentrations ranging from 100 to 5000 mg/L. The solutions were agitated for 12 h at the same temperature and speed.
4.5. Analytical Methods and Calculations
Fluoride–UV/visible spectrometry was employed for measuring the fluoride concentrations before and after treatment of the HF solution (Supplementary Information). This method followed the water pollution standard method (ES 04351.1b by KMOE, 2014), which is the standard method established by the Korean Ministry of Environment. The details of the analytical procedure are described extensively in APHA method 4500-F [42]. HF removal efficiency was calculated using Equation (3).
where the initial and final HF concentrations are expressed by Ci and Cf (mg/L), respectively.
The characteristics of real wastewater were analyzed by measuring TN and TP using a DR 6000 spectrophotometer (HACH, Loveland, Colorado, USA) at wavelengths of 410 nm for TN and 880 nm for TP. The concentrations of PO43− and NH4+ were determined using a QuAAtro39 continuous segmented flow analyzer (Seal Analytical Ltd., Norderstedt, Germany). Fluoride (F−), chloride (Cl−), sulfate (SO42−), and bromide (Br−) were analyzed via ion chromatography (IC) using a Dionex Aquion IC system (Thermo Fisher, USA). All the measurements were performed according to the protocols specified for each analytical instrument.
5. Conclusions
The findings of this study confirm the high efficacy of OSP in eliminating fluoride from industrial wastewater, establishing it as a viable solution for environmental management. When OSP was applied at a concentration of 5 g/L, it effectively decreased fluoride levels in wastewater from 344.1 mg/L to a remarkable 3.02 mg/L (99.12% removal efficiency). In addition, it substantially contributed to neutralizing the pH, which improved the potential for safer discharge or subsequent biological treatment. This study highlights the dual benefits of OSP in treating fluoride-rich wastewater and promoting environmental sustainability by repurposing waste materials. Further research is recommended to determine the scalability of OSP treatment and its potential for application to other industrial effluents. This will expand the influence of this cost-effective and eco-friendly wastewater treatment technology. In addition, future research needs to concentrate on performing a lifecycle assessment of OSP usage to understand the environmental impacts and benefits associated with its use.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/recycling9050086/s1, Figure S1: EDS spectrum and microscopic analysis of OSP; Figure S2: EDS spectrum and microscopic analysis of HF-OSP; Figure S3: EDS spectrum and microscopic analysis of RW-OSP.
Author Contributions
S.B.K.: Conceptualization, Investigation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Data curation, Writing—original draft. G.-I.K.: Formal analysis, Methodology. B.-C.M.: Methodology. S.M.K.: Methodology. Z.W.: Formal analysis, Writing—review and editing. S.W.W.: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program (S3366606), funded by the Ministry of SMEs and Startups (MSS), Republic of Korea.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We thank Joung-Min Bae at the FITI Testing & Research Institute for her assistance with the IC analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kamakura, N. From globalising to regionalising to reshoring value chains? The case of Japan’s semiconductor industry. Camb. J. Reg. Econ. Soc. 2022, 15, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.T.; Chen, C.H. Formulation of research and development strategy by analysing patent portfolios of key players the semiconductor industry according to patent strength and technical function. World Pat. Inf. 2022, 70, 102125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TSMC. TSMC 2021 Business Overview. 2021. Available online: https://investor.tsmc.com/sites/ir/annual-report/2021/2021_Business_Overview_E.pdf (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- Intel Corporation. Intel Announces Next US Site with Landmark Investment in Ohio. 2021. Available online: https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/newsroom/news/intel-announces-next-us-site-landmark-investment-ohio.html#gs.b12lx4 (accessed on 21 January 2022).
- Park, D.Y. Report of Investment Opportunities-Industries-Semiconductor. Invest Korea. 2023. Available online: https://www.investkorea.org/ik-en/cntnts/i-312/web.do (accessed on 7 September 2023).
- Eng, C.Y.; Yan, D.; Withanage, N.; Liang, Q.; Zhou, Y. Wastewater treatment and recycle from a semiconductor industry: A demo-plant study. Water Pract. Technol. 2019, 14, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, J.; Lee, J.; Rho, H.; Park, K.D.; Choi, Y.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.; Woo, Y.C. A review of semiconductor wastewater treatment processes: Current status, challenges, and future trends. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 429, 139570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.F.; Liu, J.C. Precipitation removal of fluoride from semiconductor wastewater. J. Environ. Eng. 2007, 133, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wald, P.H.; Jones, J.R. Semiconductor manufacturing: An introduction to processes and hazards. Am. J. Ind. Med. 1987, 11, 203–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, D.; Gao, F. Investigation on the simultaneous removal of fluoride, ammonia nitrogen and phosphate from semiconductor wastewater using chemical precipitation. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 307, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.C.; Liu, J.C. Coupled precipitation-ultrafiltration for treatment of high fluoride-content wastewater. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 58, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.H.; Kim, E.I.; Park, J.Y. Fluoride removal capacity of cement paste. Desalination 2007, 202, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacson, C.F.Z.; Lu, M.C.; Huang, Y.H. Chemical precipitation at extreme fluoride concentration and potential recovery of CaF2 particles by fluidized-bed homogenous crystallization process. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 415, 128917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.H.; Lee, J.H.; Yoo, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Bae, J.S.; Park, C.Y. Toward transformation of bivalve shell wastes into high value-added and sustainable products in South Korea: A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2024, 129, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Maritime Institute (KMI). A Study on Resources Circulation for Marine Debris of Aquaculture Farm; Office for Government Policy Coordination of Korea: Sejong-si, Republic of Korea, 2018; ISBN 979-1-18-922679-4. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, H.; Mesquita-Guimarães, J.; Henriques, B.; Silva, F.S.; Fredel, M.C. The potential use of oyster shell waste in new value-added by-product. Resources 2019, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.B.; Wang, Z.; Won, S.W. Polyethylenimine-crosslinked calcium silicate hydrate derived from oyster shell waste for removal of Reactive Yellow 2. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2023, 40, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seesanong, S.; Seangarun, C.; Boonchom, B.; Laohavisuti, N.; Thompho, S.; Boonmee, W.; Mongkol, S.; Rungrojchaipon, P. Bio-green synthesis of calcium acetate from oyster shell waste at low cost and reducing the emission of greenhouse gases. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2023, 33, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaoka, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Kondo, S.; Hayakawa, S. Removal of hydrogen sulfide using crushed oyster shell from pore water to remediate organically enriched coastal marine sediments. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 4127–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, T.C. Experimental assessment of adsorption of Cu2+ and Ni2+ from aqueous solution by oyster shell powder. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 995–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Islam, S.M.A.; Hong, S.J.; Cho, K.M.; Math, R.K.; Heo, J.Y.; Kim, H.; Yun, H.D. Composted oyster shell as lime fertilizer is more effective than fresh oyster shell. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2010, 74, 1517–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namasivayam, C.; Sakoda, A.; Suzuki, M. Removal of phosphate by adsorption onto oyster shell powder—Kinetic studies. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2005, 80, 356–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.H.; Polprasert, C. Roles of oyster shells in an integrated constructed wetland system designed for P removal. Ecol. Eng. 2008, 34, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, E.Y. Oyster shell recycling and marine ecosystems: A comparative analysis in the Republic of Korea and Japan. J. Coast. Res. 2021, 114, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howie, A.H.; Bishop, M.J. Contemporary oyster reef restoration: Responding to a changing world. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 689915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perricone, V.; Mutalipassi, M.; Mele, A.; Buono, M.; Vicinanza, D.; Contestabile, P. Nature-based and bioinspired solutions for coastal protection: An overview among key ecosystems and a promising pathway for new functional and sustainable designs. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2023, 80, 1218–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.B.; Wang, Z.; Won, S.W. Recovery of palladium from acidic solution using polyethylenimine-crosslinked calcium silicate hydrate derived from oyster shell waste: Adsorption and mechanisms. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2023, 2023, 6473526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerward, L.; Olsen, J.S.; Steenstrup, S.; Malinowski, M.; Åsbrink, S.; Waskowska, A. X-ray diffraction investigations of CaF2 at high pressure. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1992, 25, 578–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.C.; Kawano, K. Luminescence studies of the rare earth ions-doped CaF2 and MgF2 films for wavelength conversion. J. Alloys Compd. 2006, 408–412, 838–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandurangappa, C.; Lakshminarasappa, B.N.; Nagabhushana, B.M. Synthesis and characterization of CaF2 nanocrystals. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 489, 592–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chingo Aimacaña, C.M.; Pila, K.O.; Quinchiguango Perez, D.A.; Debut, A.; Attia, M.F.; Santos-Oliveira, R.; Whitehead, D.C.; Reinoso, C.; Alexis, F.; Dahoumane, S.A. Bimodal ultrasound and X-ray bioimaging properties of particulate calcium fluoride biomaterial. Molecules 2021, 26, 5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J. A Study on the Treatment of Hydrofluoric acid Wastewater from Semiconductor Manufacturing Process and the Possibility of Reuse. Master’s Thesis, Department of Environmental Engineering Graduate School, University of Seoul, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sinharoy, A.; Lee, G.Y.; Chung, C.M. Optimization of calcium fluoride crystallization process for treatment of high-concentration fluoride-containing semiconductor industry wastewater. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinharoy, A.; Lee, G.Y.; Chung, C.M. Process intensification for enhanced fluoride removal and recovery as calcium fluoride using a fluidized bed reactor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, N.; Li, Z.; Lin, X.; Zhu, W.; Lu, C.; Ding, W.; Zou, J. Nanostructuring of Mg-based hydrogen storage materials: Recent advances for promoting key applications. NanoMicro Lett. 2023, 15, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.; Wang, M.; Kuang, W.; Ouyang, J.; Han, D.; Gao, Z.; Gong, J. Advances of combinative nanocrystal preparation technology for improving the insoluble drug solubility and bioavailability. Crystals 2022, 12, 1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devasthali, O.S.; Shah, A.J.; Jadhav, S.V. Fluoride removal from water using filtration and chemical precipitation. In Advanced Treatment Technologies for Fluoride Removal in Water: Water Purification; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Park, Y.S.; Jung, G.I.; Kim, J.W.; Jo, Y.M. Removal of fluoride ions from electronic industrial wastewater using lime stone slurry. Appl. Chem. Eng. 2018, 29, 258–263. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, G.; Sun, Y.; Wu, S.; Li, W.; Hu, C.; Zhuang, J.; Zhang, X.; Lei, B.; Liu, Y. Assembly of shell/core CDs@ CaF2 nanocomposites to endow polymers with multifunctional properties. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 155601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Huang, T.; Sun, X. Impact of acid-base conditions on defluoridation by induced crystallization. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 83, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.F.; Wu, J.L.; Chang, K.L.; Lee, W.J.; Chang, C.P.; Lin, Y.C.; Chen, P.H. Recycle of synthetic calcium fluoride and waste sulfuric acid to produce electronic grade hydrofluoric acid. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 40633–40639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA (American Public Health Association); AWWA (American Water Works Association); WEF (Water Environment Federation). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; APHA/AWWA/WEF: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).