Two-Step Bio-Dissolution of Metals from Printed Circuit Boards Using Acidophilic Iron- and Sulfur-Oxidizing Mesophiles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
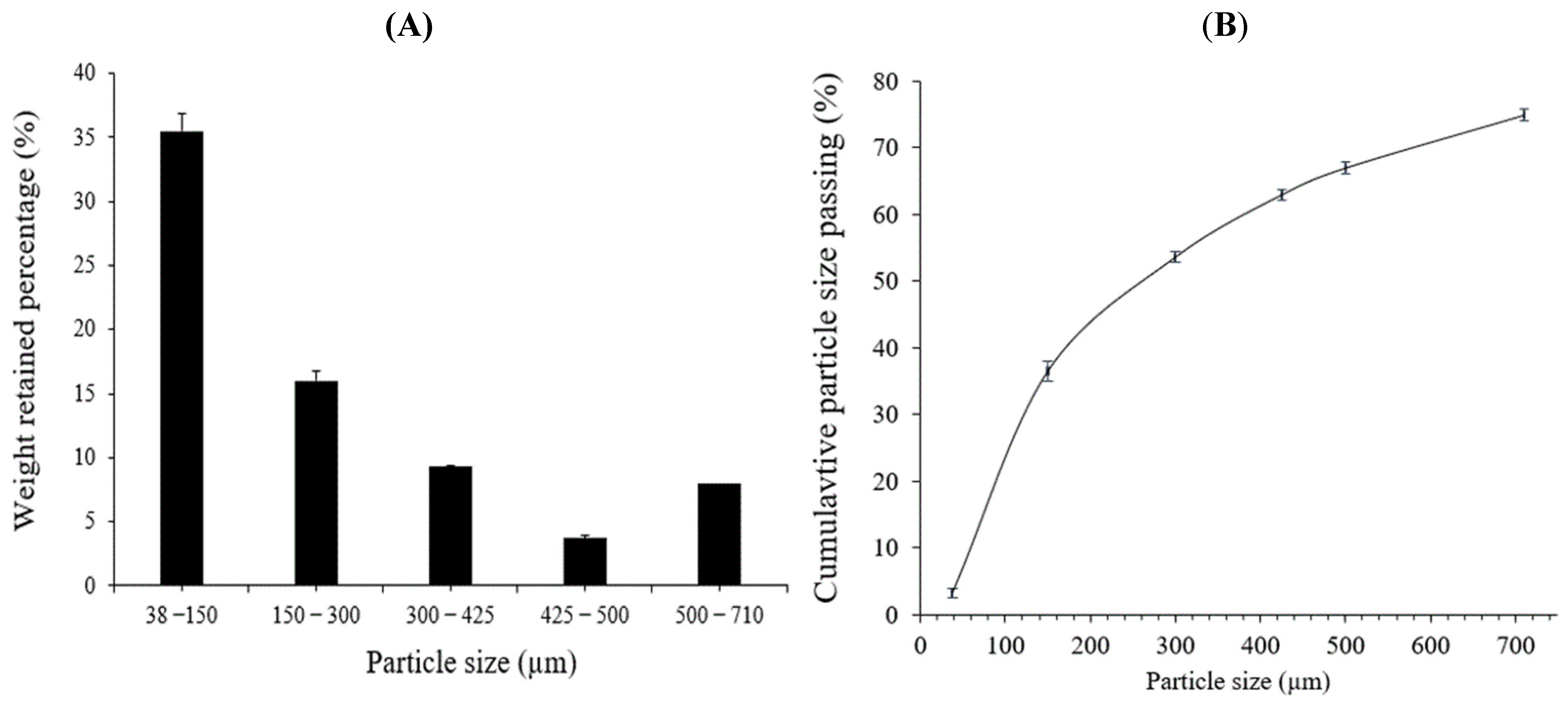
2.1. E-Waste Characterization for Metal Content
Particle Size Distribution (PSD)
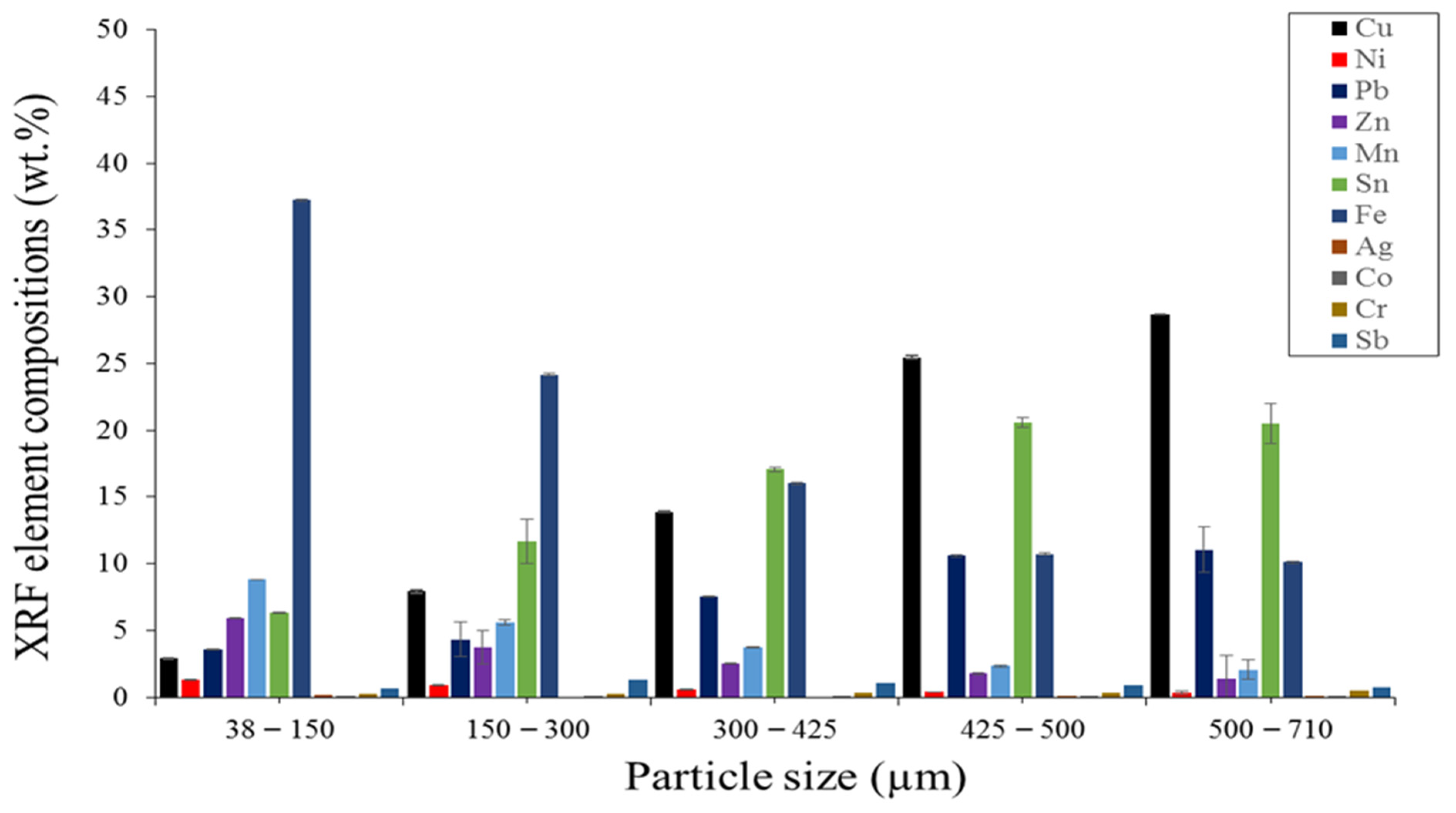
2.2. Printed Circuit Board Element Content Analysis (XRF)
2.3. The Alkalinity Nature of PCB
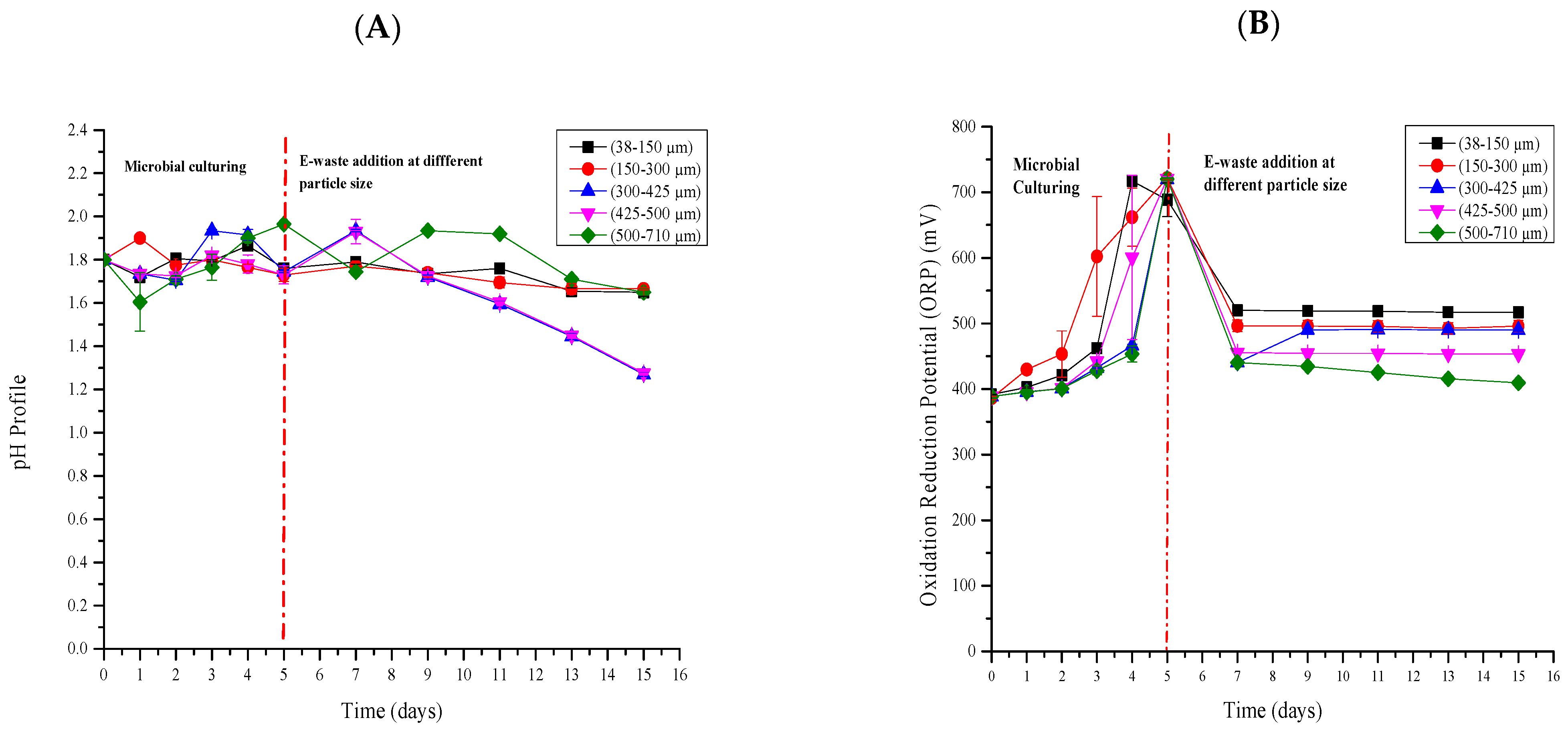
2.4. Culturing of Microorganisms and Element Bioleaching
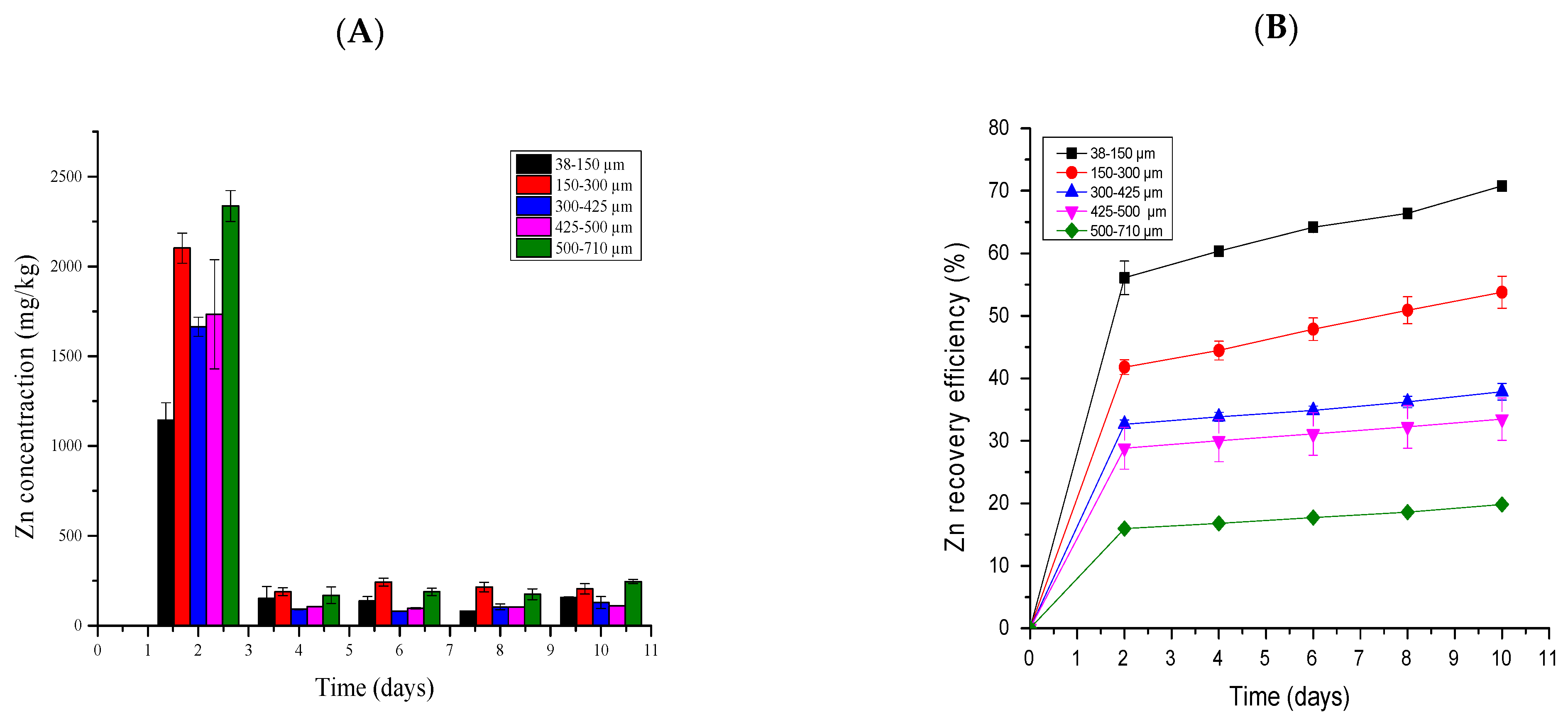
2.5. The Effects of Particle Sizes on Metal Recovery
2.5.1. Zinc Bioleaching
2.5.2. Lead Bioleaching
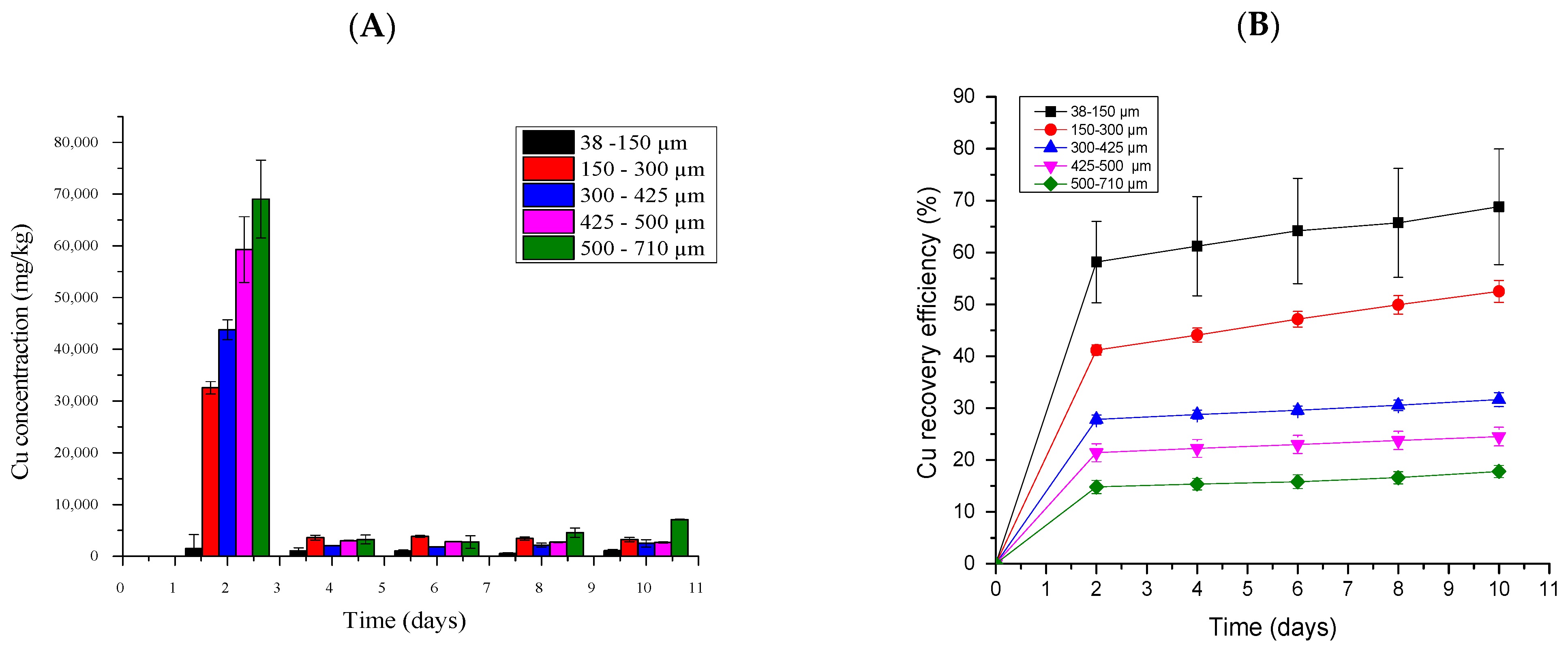
2.5.3. Copper Bioleaching
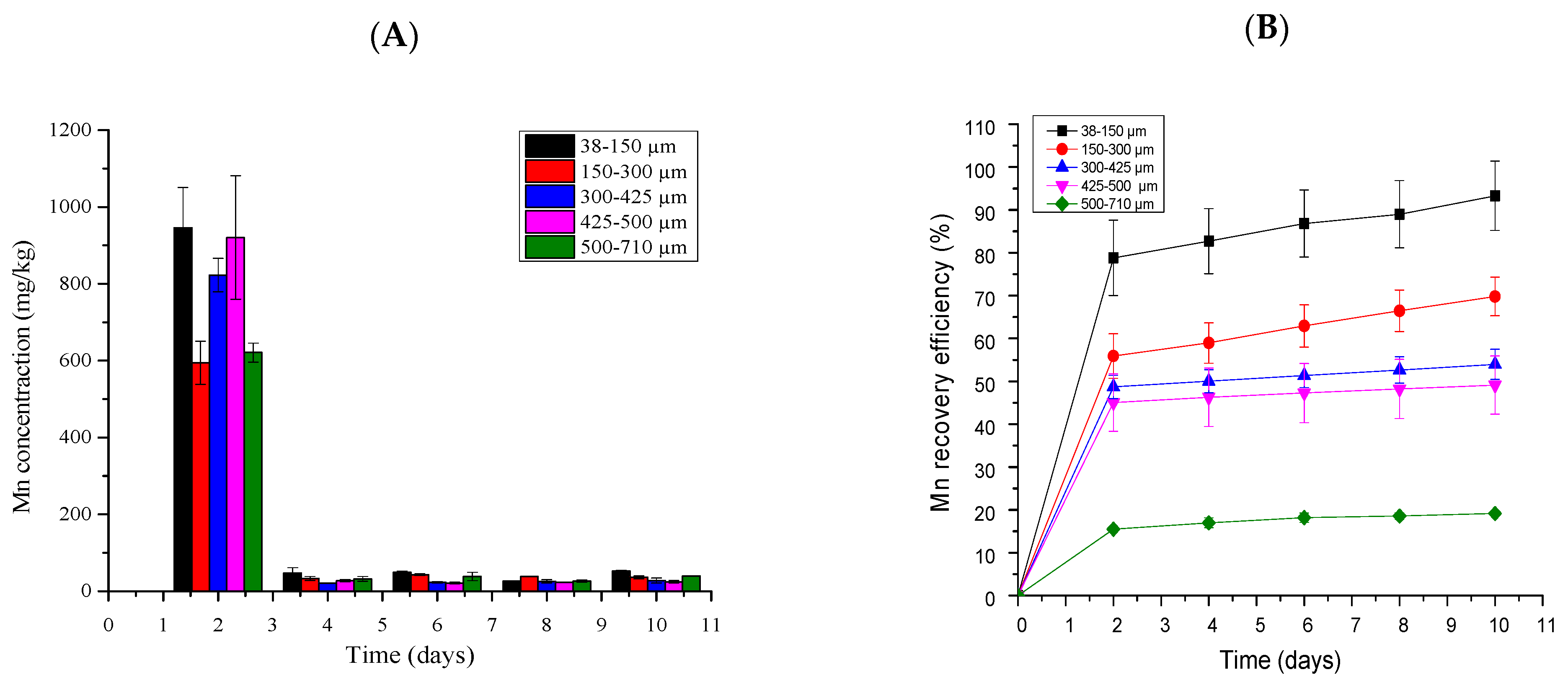
2.5.4. Manganese Bioleaching
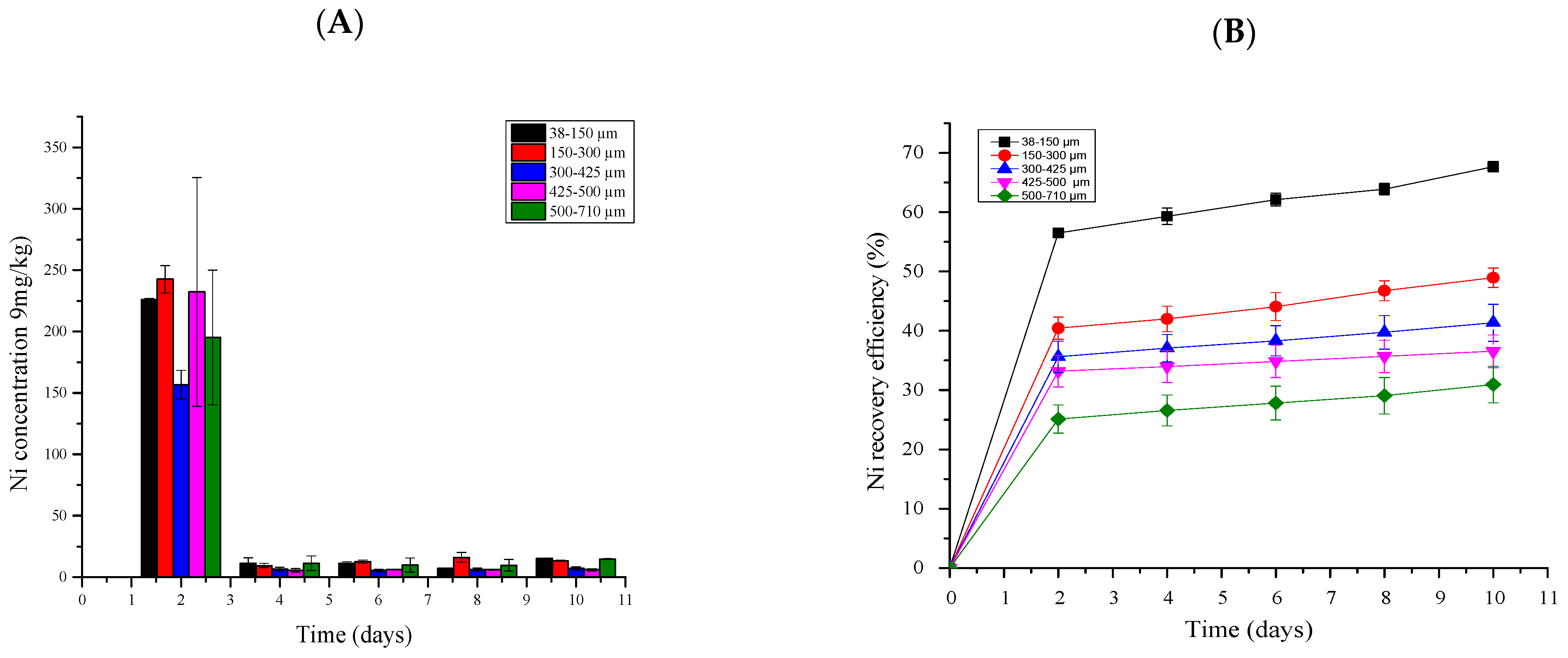
2.5.5. Nickel Bioleaching
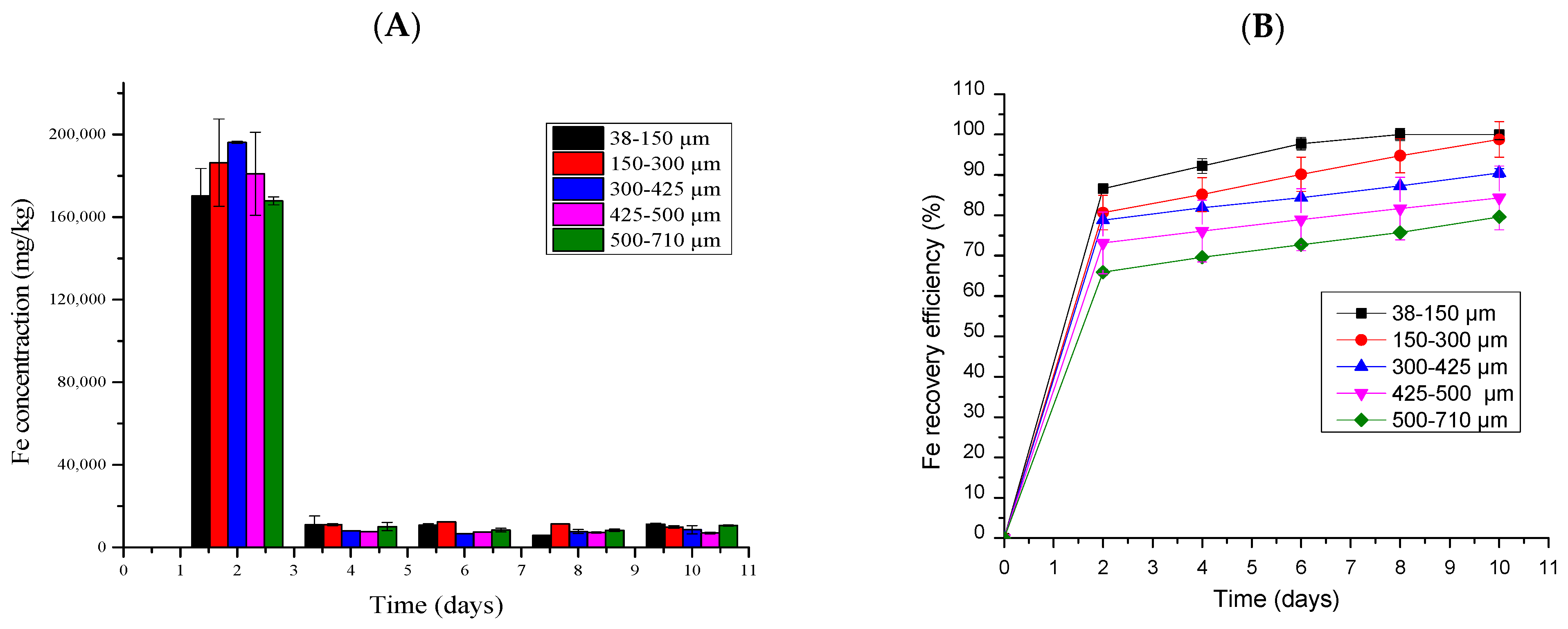
2.5.6. Iron Bioleaching
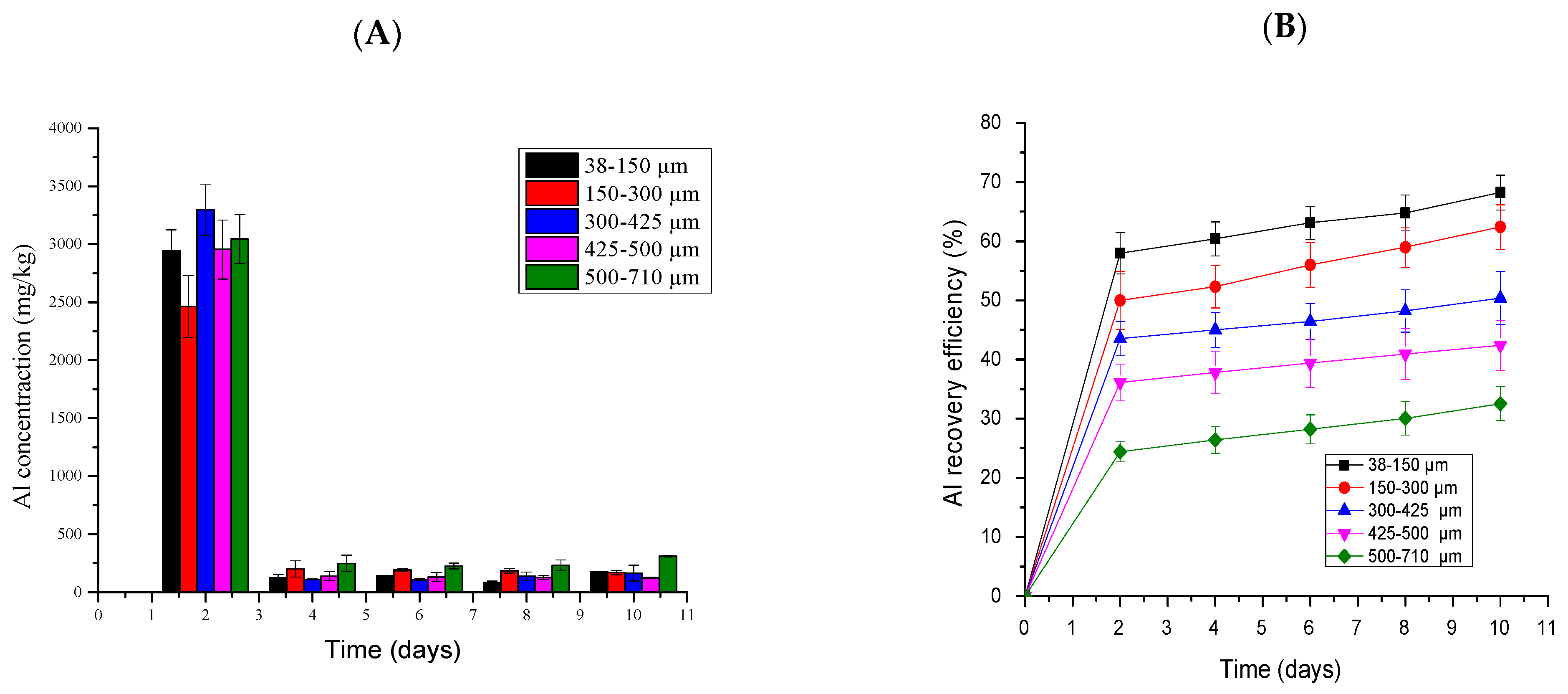
2.5.7. Aluminum Bioleaching
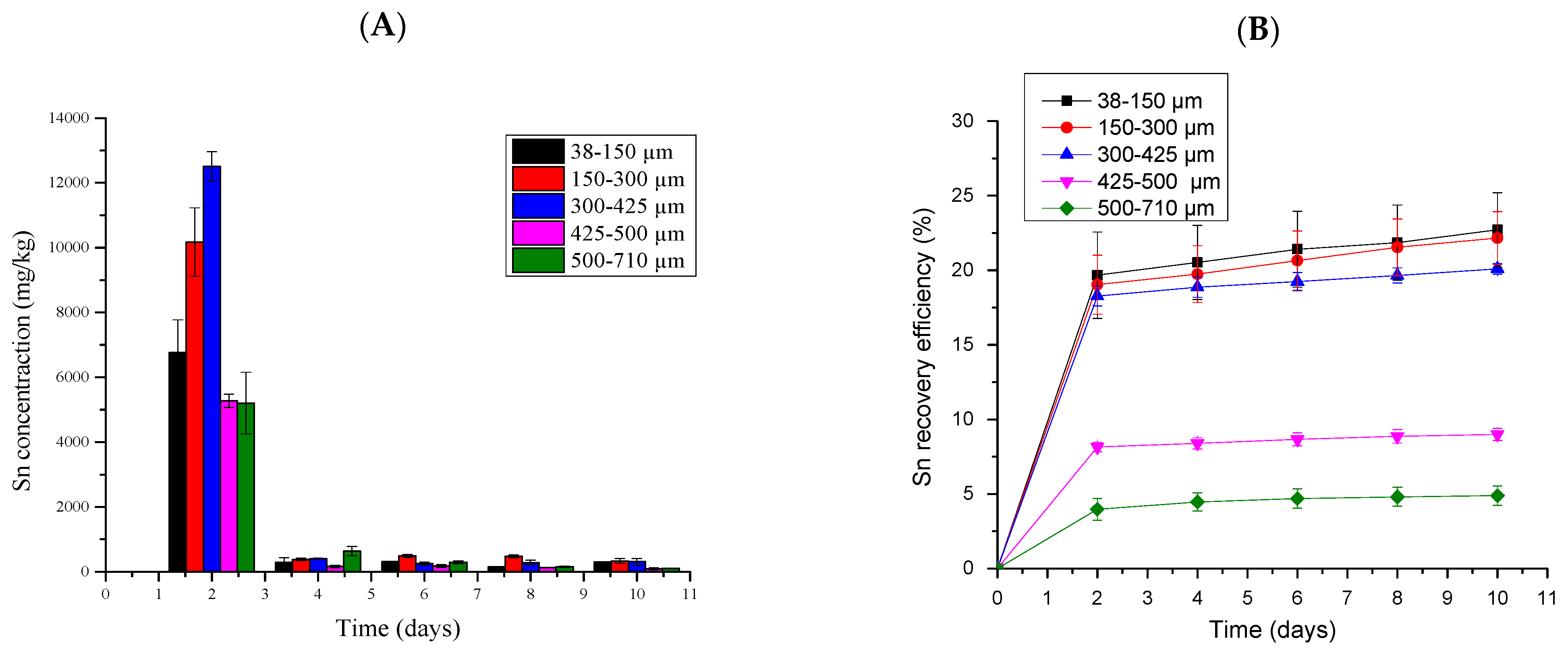
2.5.8. Tin Bioleaching
3. Discussion
3.1. E-Waste Characterization for Metal Content
Particle Size Distribution (PSD)
3.2. Printed Circuit Board Elemental Composition
3.3. The Alkalinity Nature of the PCB
3.4. Physicochemical Conditions during the Bioleaching Process
3.5. The Effects of Particle Sizes on Metal Recovery
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. E-Waste and Microbial Source
4.2. E-Waste Preparation and Particle Size Distribution
4.3. Characterization of E-Waste (PCB)
4.4. Microorganism Culturing and Medium Preparation
4.5. Bioleaching Tests
4.6. Analytical Methods and Instruments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morkel, F.D. The Effect of Particle Size Distribution on the Extraction of Gold from Printed Circuit Boards Using Ammonium Thiosulphate; Cape Peninsula University of Technology: Cape Town, South Africa, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Marra, A.; Cesaro, A.; Rene, E.R.; Belgiorno, V.; Lens, P.N. Bioleaching of metals from weee shredding dust. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 210, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, B.R.; Sodha, A.B.; Shah, M.B.; Tipre, D.R.; Dave, S.R. Chemical and microbial leaching of base metals from obsolete cell-phone printed circuit boards. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2018, 28, 333–339. [Google Scholar]
- Kucmanová, A.; Sanny, Z.; Gerulová, K.; Pašák, M.; Czére, I. Preliminary bioleaching experiment of e-waste. Ved. Práce Mater. Fak. Slov. Technol. Univ. V Bratislave So Sídlom V Trnave 2021, 29, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubau, A.; Minier, M.; Chagnes, A.; Joulian, C.; Silvente, C.; Guezennec, A.-G. Recovery of metals in a double-stage continuous bioreactor for acidic bioleaching of printed circuit boards (pcbs). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 238, 116481. [Google Scholar]
- Priya, A.; Hait, S. Characterization of particle size-based deportment of metals in various waste printed circuit boards towards metal recovery. Clean. Mater. 2021, 1, 100013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konakcı, R.; Pekcan, M.; Erşan, Y.Ç. Pre-treatment procedure for effective bioleaching of metals from large waste printed circuit board (wpcb) pieces. In Proceedings of the Sixth Edition of EurAsia Waste Management Symposium, İstanbul, Türkiye, 24–26 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Priya, A.; Hait, S. Comparative assessment of metallurgical recovery of metals from electronic waste with special emphasis on bioleaching. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 6989–7008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waghmode, M.; Gunjal, A.; Patil, N. Bioleaching of electronic waste. Pollution 2021, 7, 141–152. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, M.B.; Tipre, D.R.; Dave, S.R. Chemical and biological processes for multi-metal extraction from waste printed circuit boards of computers and mobile phones. Waste Manag. Res. 2014, 32, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adetunji, A.I.; Oberholster, P.J.; Erasmus, M. Bioleaching of metals from e-waste using microorganisms: A review. Minerals 2023, 13, 828. [Google Scholar]
- Sodha, A.B.; Qureshi, S.A.; Khatri, B.R.; Tipre, D.R.; Dave, S.R. Enhancement in iron oxidation and multi-metal extraction from waste television printed circuit boards by iron oxidizing leptospirillum feriphillum isolated from coal sample. Waste Biomass Valorization 2019, 10, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshadi, M.; Mousavi, S. Multi-objective optimization of heavy metals bioleaching from discarded mobile phone pcbs: Simultaneous cu and ni recovery using acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 147, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzal Montes, E. Study and Optimisation of Copper Bioleaching Process for Electronic Waste Valorisation. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Barcelona, Spain, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Benzal, E.; Solé, M.; Lao, C.; Gamisans, X.; Dorado, A. Elemental copper recovery from e-wastes mediated with a two-step bioleaching process. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 5457–5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khashole, M.F. Low Temperature Optimization of Copper Recovery from E-Waste. Master’s Thesis, University of Kwazulu-Natal, Durban, South Africa, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Pradhan, J.K.; Kumar, S. Environmental Impact Assessment and Bioleaching of Metals from Electronic Waste (E-Waste); Jaypee University of Information Technology: Solan, India, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Khaliq, I.; Hof, C.; Prinzinger, R.; Böhning-Gaese, K.; Pfenninger, M. Global variation in thermal tolerances and vulnerability of endotherms to climate change. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 281, 20141097. [Google Scholar]
- Hubau, A.; Chagnes, A.; Minier, M.; Touzé, S.; Chapron, S.; Guezennec, A.-G. Recycling-oriented methodology to sample and characterize the metal composition of waste printed circuit boards. Waste Manag. 2019, 91, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veit, H.M.; de Pereira, C.C.; Bernardes, A.M. Using mechanical processing in recycling printed wiring boards. Jom 2002, 54, 45–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Baez, A.; Pantoja Munoz, L.; Garelick, H.; Purchase, D. Characterisation of rare earth elements in waste printed circuit boards (wpcbs) and their bioleaching potential. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology, Rhodes, Greece, 4–7 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Van Yken, J.; Cheng, K.Y.; Boxall, N.J.; Nikoloski, A.N.; Moheimani, N.; Valix, M.; Sahajwalla, V.; Kaksonen, A.H. Potential of metals leaching from printed circuit boards with biological and chemical lixiviants. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 196, 105433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Bai, J.; Xu, J.; Liang, B. Bioleaching of metals from printed wire boards by acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and their mixture. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 1100–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, A.; Hait, S. Feasibility of bioleaching of selected metals from electronic waste by acidiphilium acidophilum. Waste Biomass Valorization 2018, 9, 871–877. [Google Scholar]
- Işıldar, A.; van de Vossenberg, J.; Rene, E.R.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Lens, P.N. Two-step bioleaching of copper and gold from discarded printed circuit boards (pcb). Waste Manag. 2016, 57, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouchalova, D.; Rouchalova, K.; Janakova, I.; Cablik, V.; Janstova, S. Bioleaching of iron, copper, lead, and zinc from the sludge mining sediment at different particle sizes, ph, and pulp density using acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Minerals 2020, 10, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willner, J.; Fornalczyk, A. Extraction of metals from electronic waste by bacterial leaching. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2013, 39, 197–208. [Google Scholar]
- Sharada, H.M.; Abdel-Halim, S.A.; Hafez, M.A.; Elbarbary, T.A.; Abdel-Fatah, Y.; Ibrahim, I.A. Bioleaching of copper from electronic waste using aspergillus niger. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2021, 12, 8406–8425. [Google Scholar]
- Do, M.H.; Nguyen, G.T.; Thach, U.D.; Lee, Y.; Bui, T.H. Advances in hydrometallurgical approaches for gold recovery from e-waste: A comprehensive review and perspectives. Miner. Eng. 2023, 191, 107977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Balboa, C.; Martínez-Alesón García, P.; López-Rodas, V.; Costas, E.; Baselga-Cervera, B. Microbial biominers: Sequential bioleaching and biouptake of metals from electronic scraps. MicrobiologyOpen 2022, 11, e1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagannath, A.; Shetty, V.; Saidutta, M. Bioleaching of copper from electronic waste using acinetobacter sp. Cr b2 in a pulsed plate column operated in batch and sequential batch mode. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1599–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghassa, S.; Farzanegan, A.; Gharabaghi, M.; Abdollahi, H. Novel bioleaching of waste lithium ion batteries by mixed moderate thermophilic microorganisms, using iron scrap as energy source and reducing agent. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 197, 105465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafavi, M.; Mirazimi, S.; Rashchi, F.; Faraji, F.; Mostoufi, N. Bioleaching and kinetic investigation of wpcbs by a. Ferrooxidans, a. Thiooxidans and their mixtures. J. Chem. Pet. Eng. 2018, 52, 81–91. [Google Scholar]
- Arshadi, M.; Yaghmaei, S. Bioleaching of basic metals from electronic waste pcb’s. J. Min. Mech. Eng. 2020, 1, 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Priya, A.; Hait, S. Biometallurgical recovery of metals from waste printed circuit boards using pure and mixed strains of acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and acidiphilium acidophilum. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 143, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Magoda, K.; Nomngongo, P.N.; Mekuto, L. Two-Step Bio-Dissolution of Metals from Printed Circuit Boards Using Acidophilic Iron- and Sulfur-Oxidizing Mesophiles. Recycling 2024, 9, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling9010006
Magoda K, Nomngongo PN, Mekuto L. Two-Step Bio-Dissolution of Metals from Printed Circuit Boards Using Acidophilic Iron- and Sulfur-Oxidizing Mesophiles. Recycling. 2024; 9(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling9010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleMagoda, Kundani, Philiswa N. Nomngongo, and Lukhanyo Mekuto. 2024. "Two-Step Bio-Dissolution of Metals from Printed Circuit Boards Using Acidophilic Iron- and Sulfur-Oxidizing Mesophiles" Recycling 9, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling9010006
APA StyleMagoda, K., Nomngongo, P. N., & Mekuto, L. (2024). Two-Step Bio-Dissolution of Metals from Printed Circuit Boards Using Acidophilic Iron- and Sulfur-Oxidizing Mesophiles. Recycling, 9(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling9010006









