Agro-Industrial Wastewater Treatment with Acacia dealbata Coagulation/Flocculation and Photo-Fenton-Based Processes
Abstract
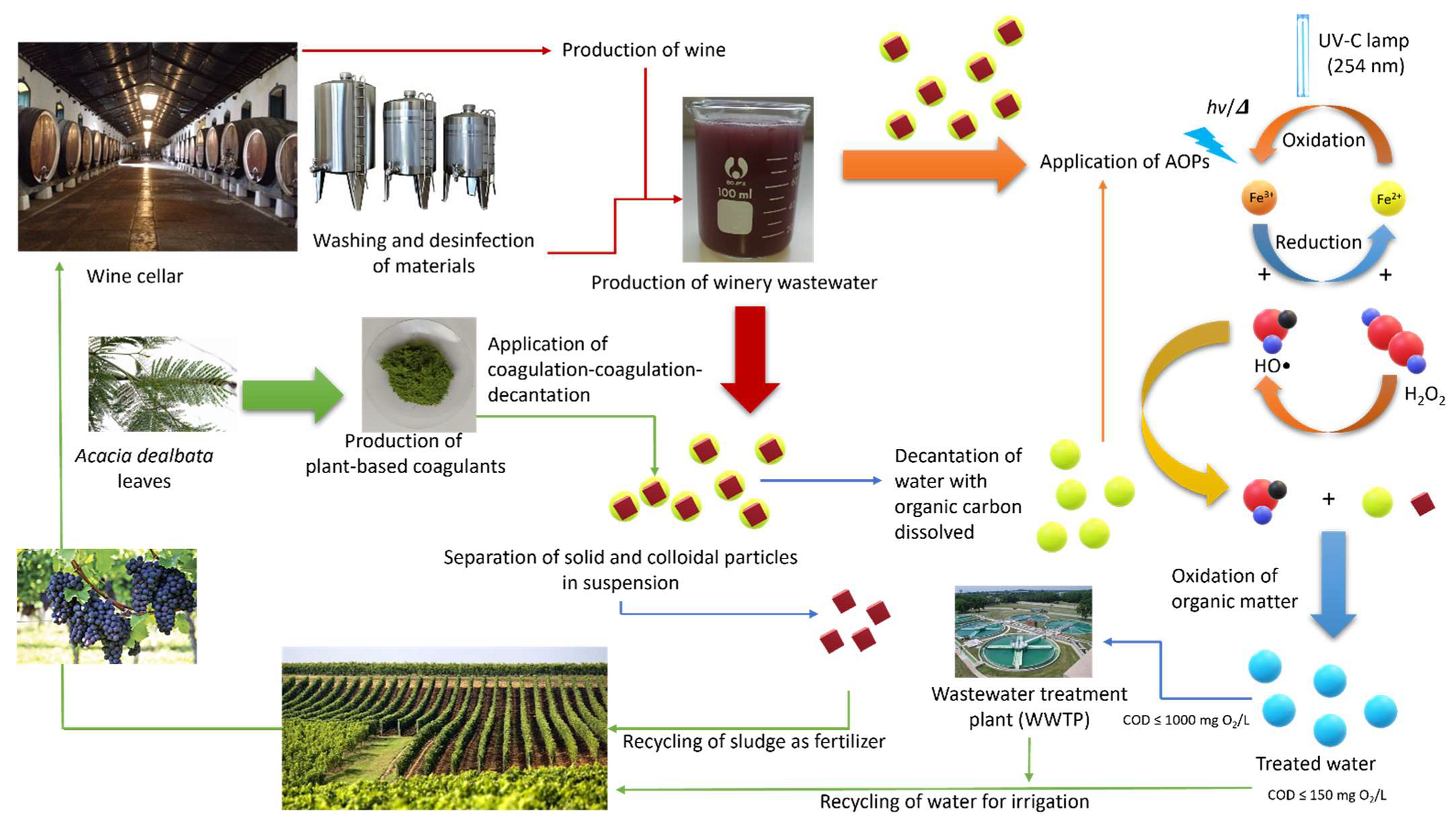
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Winery Wastewater Sampling
2.2. Analytical Determinations
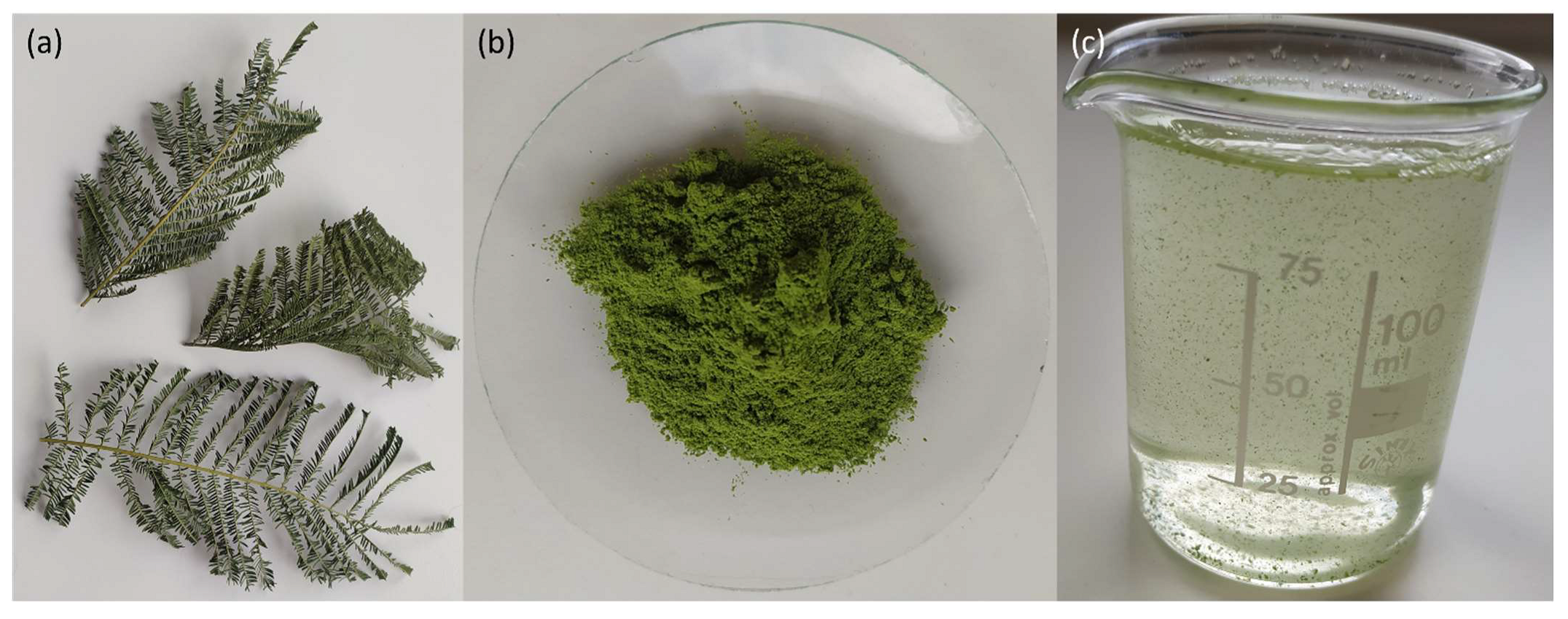
2.3. Leaves Powder Preparation
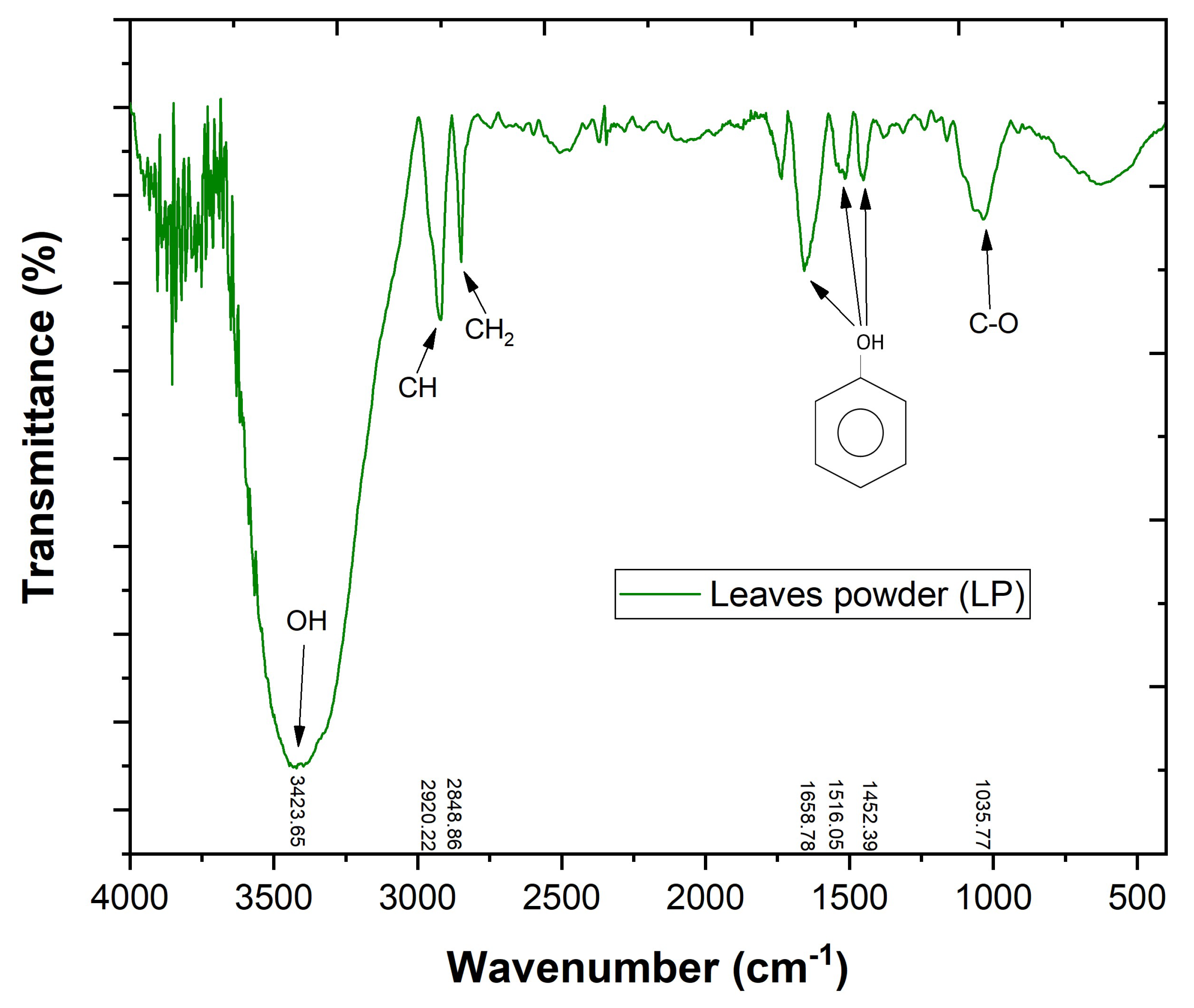
2.4. Leaves Powder Characterization
2.5. Coagulation-Flocculation-Decantation Experimental Setup
- (1)
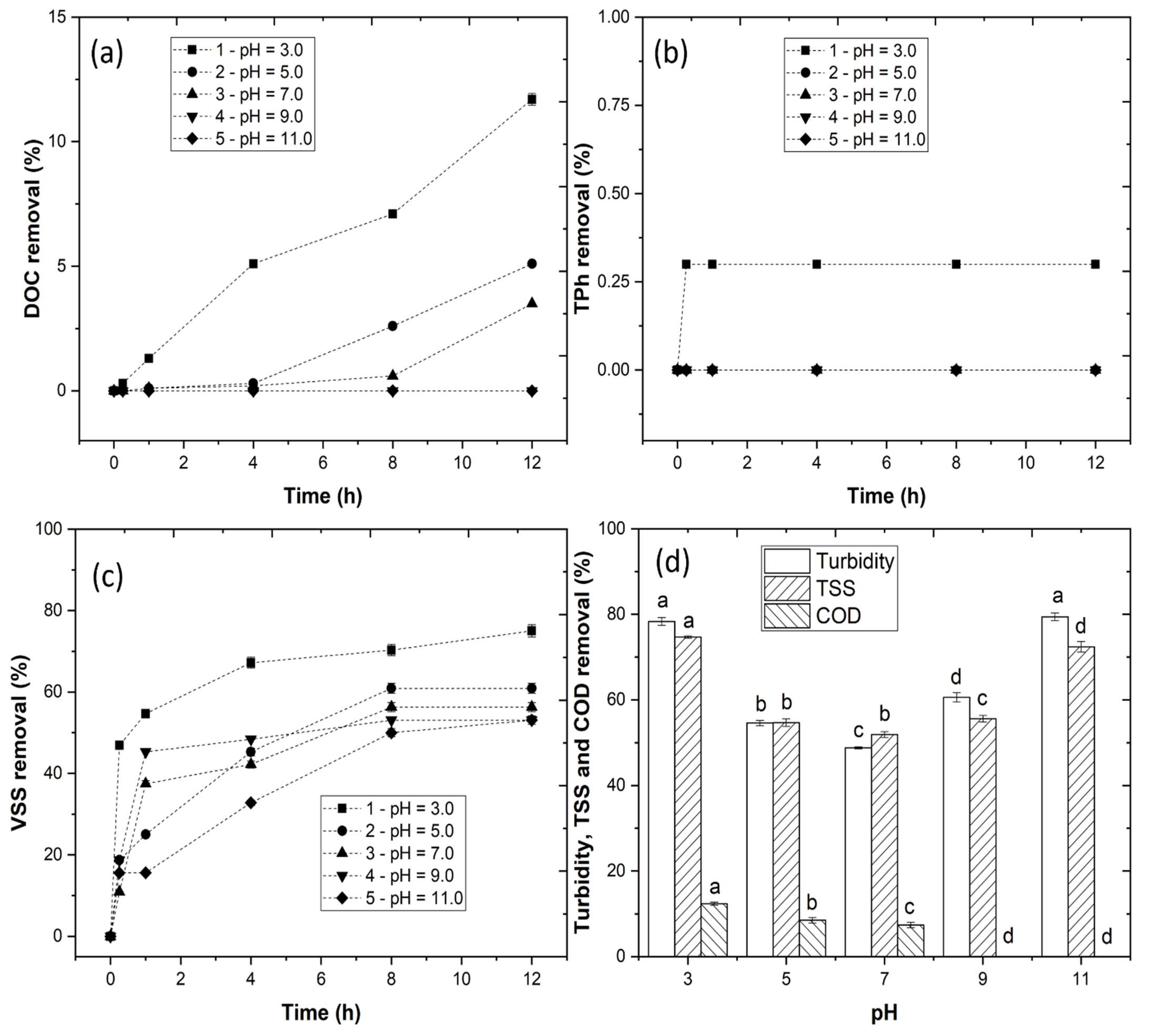
- The pH was varied (3.0, 5.0, 7.0, 9.0, and 11.0) under the following conditions: DOC = 400 mg C/L, [LP]:DOC = 1:1 (w/w);
- (2)
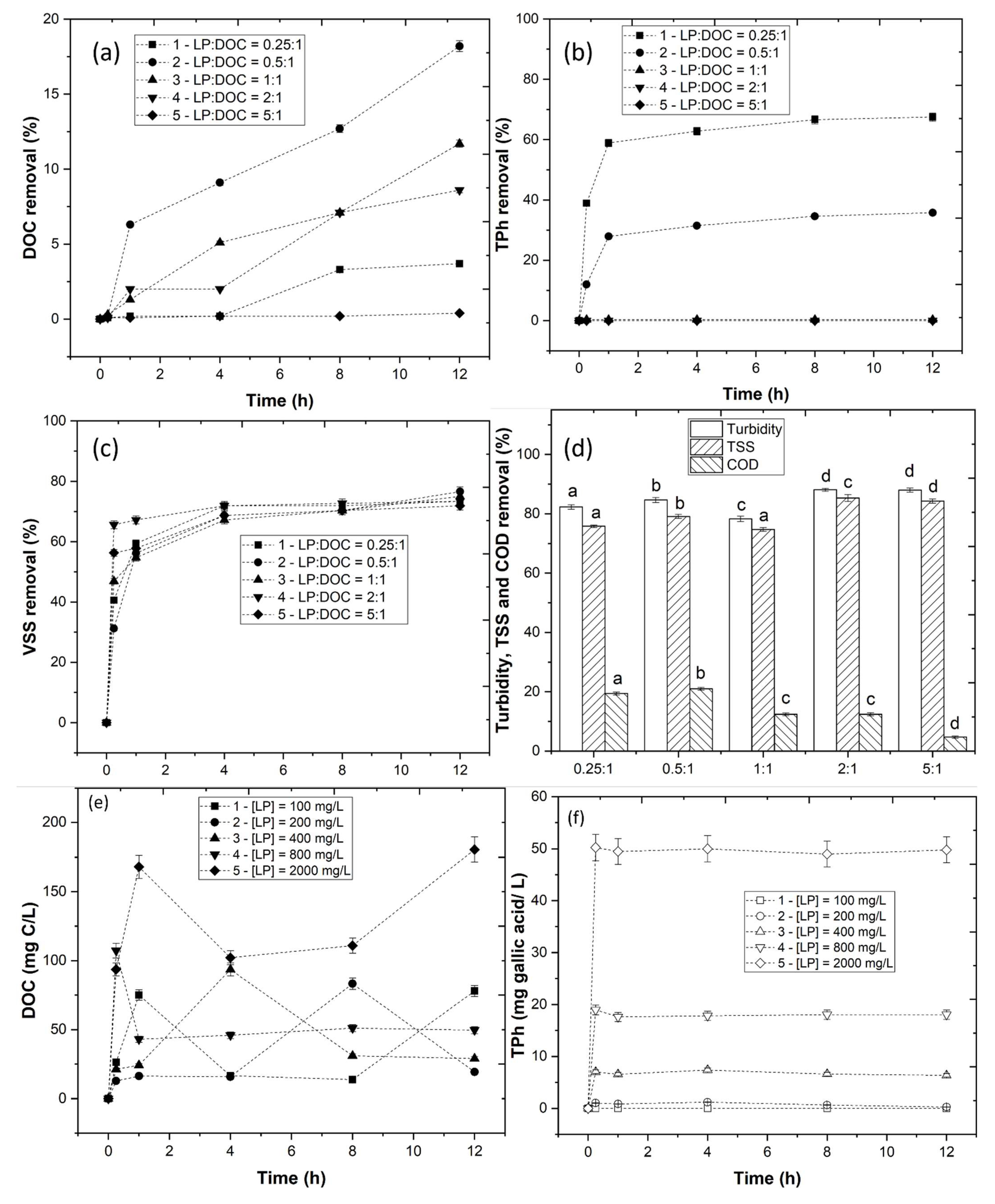
- The ratio LP:DOC was varied (0.25:1, 0.5:1, 1:1, 2:1, and 5:1 w/w) under the following conditions: pH = 3.0, DOC = 400 mg C/L.
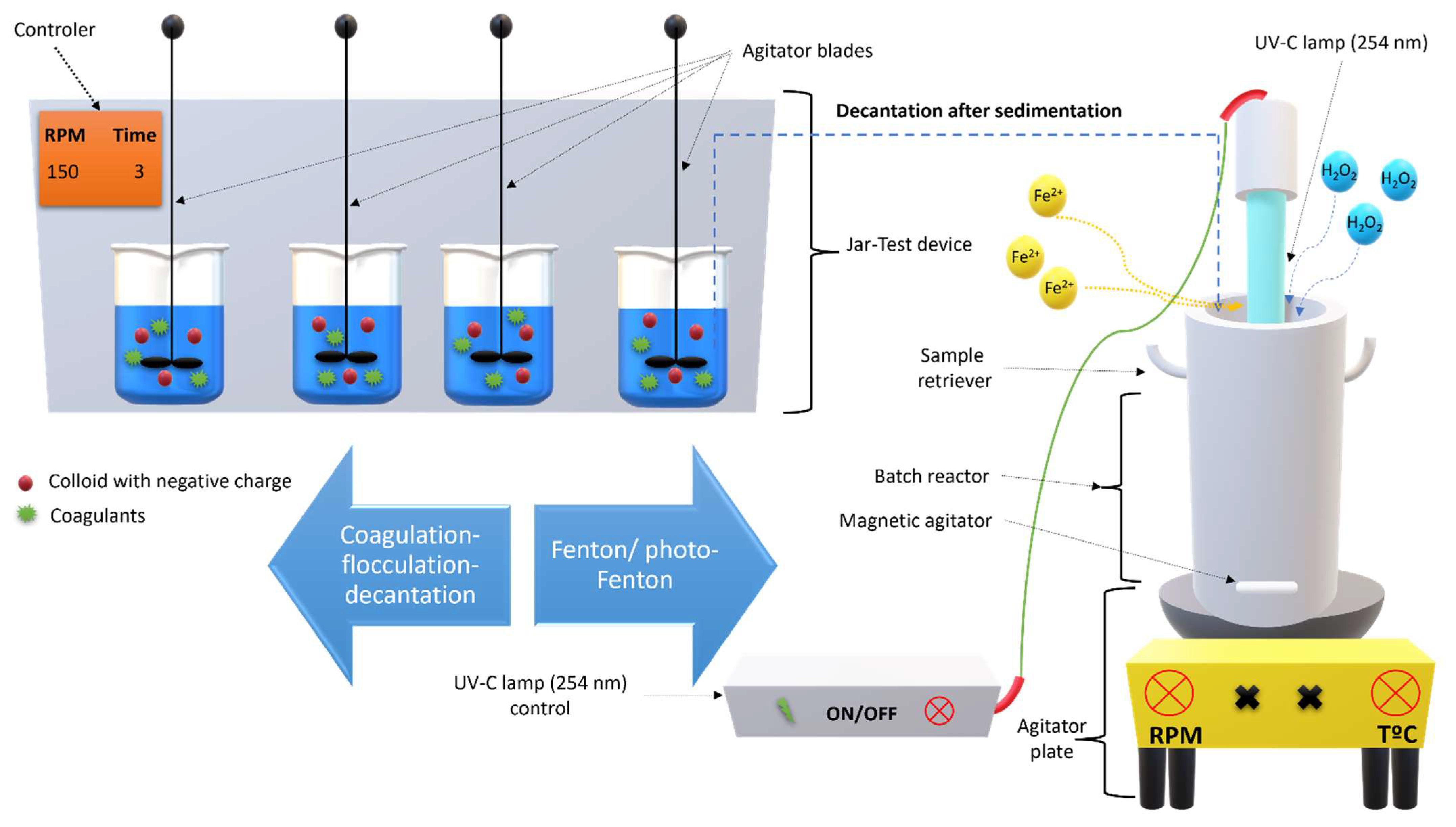
2.6. Fenton Based Experiments Setup
2.7. Phytotoxicity Test
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Leaves Powder Characterization
3.2. Coagulation–Flocculation–Decantation Experiments
3.2.1. Effect of pH Variation
3.2.2. Effect of LP Concentration
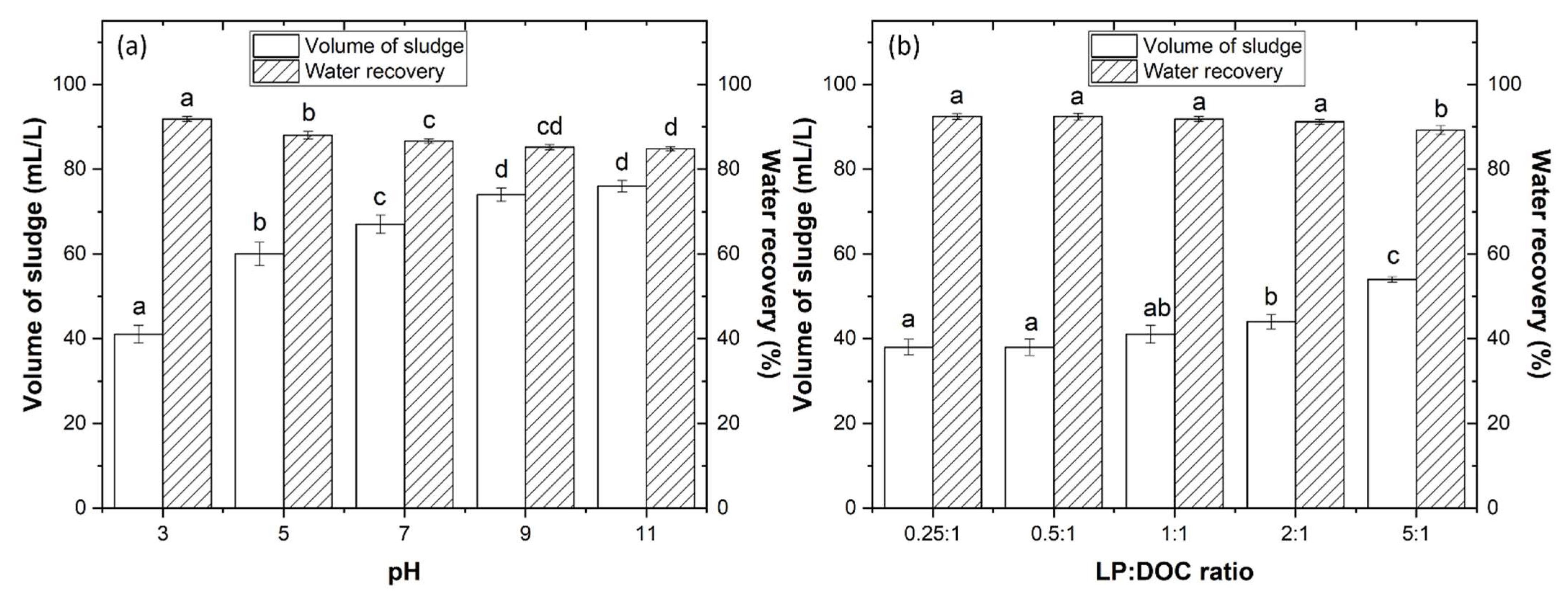
3.2.3. Water and Sludge Recycling
3.3. Fenton-Based Experiments
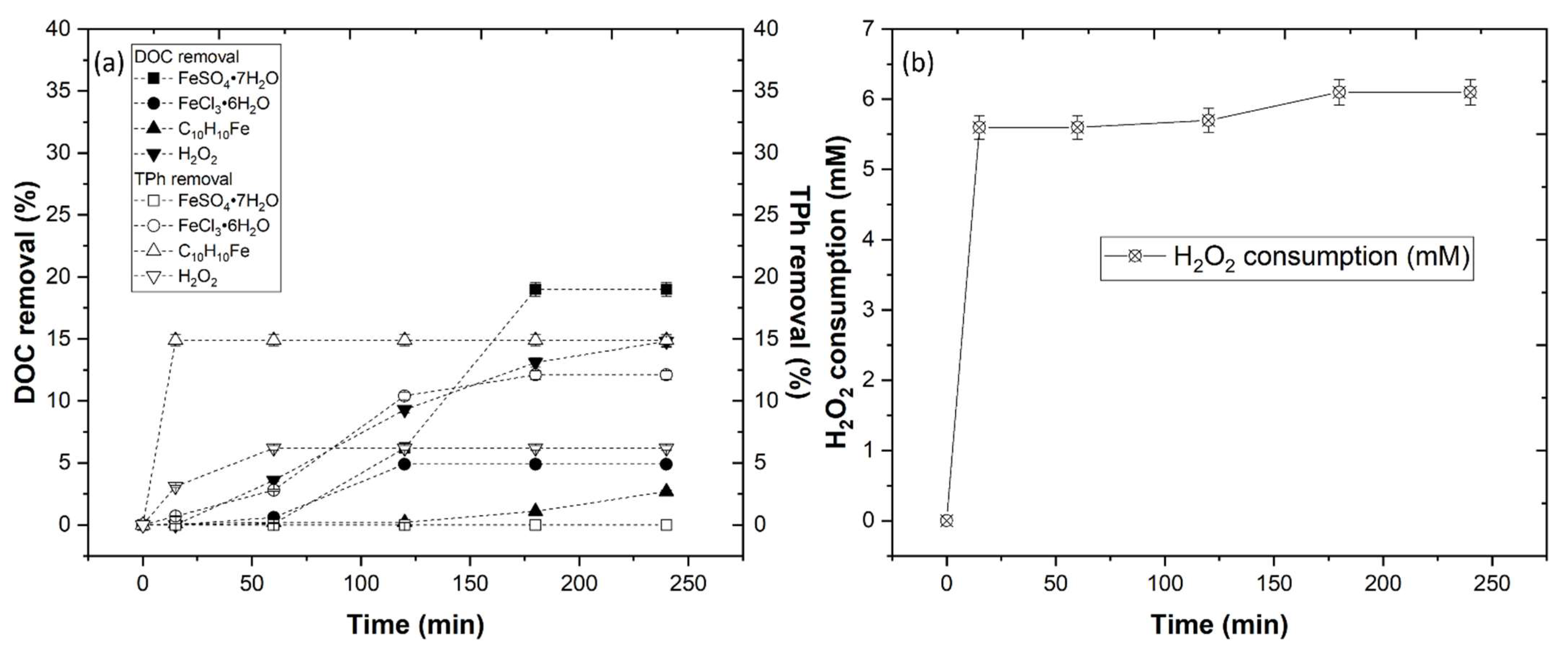
3.3.1. Effect of Iron Compounds and H2O2
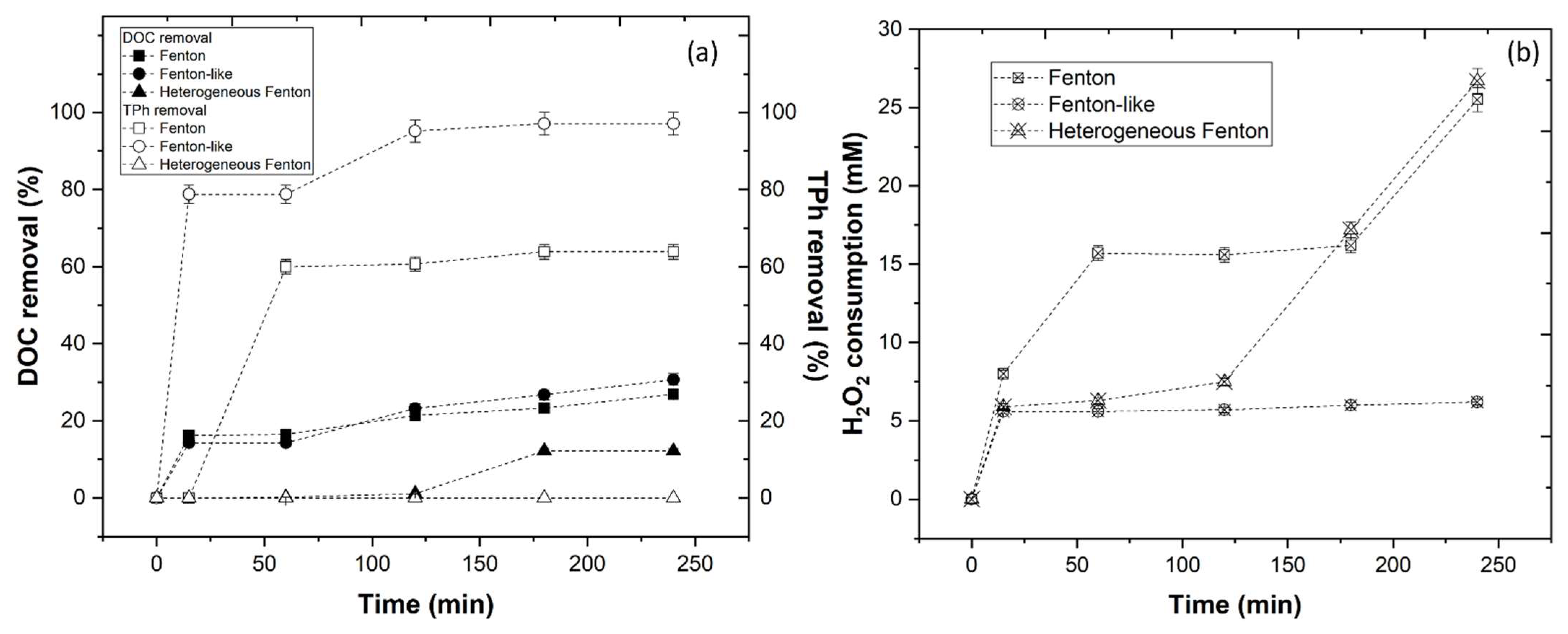
3.3.2. Fenton, Fenton-like, and Heterogeneous Fenton
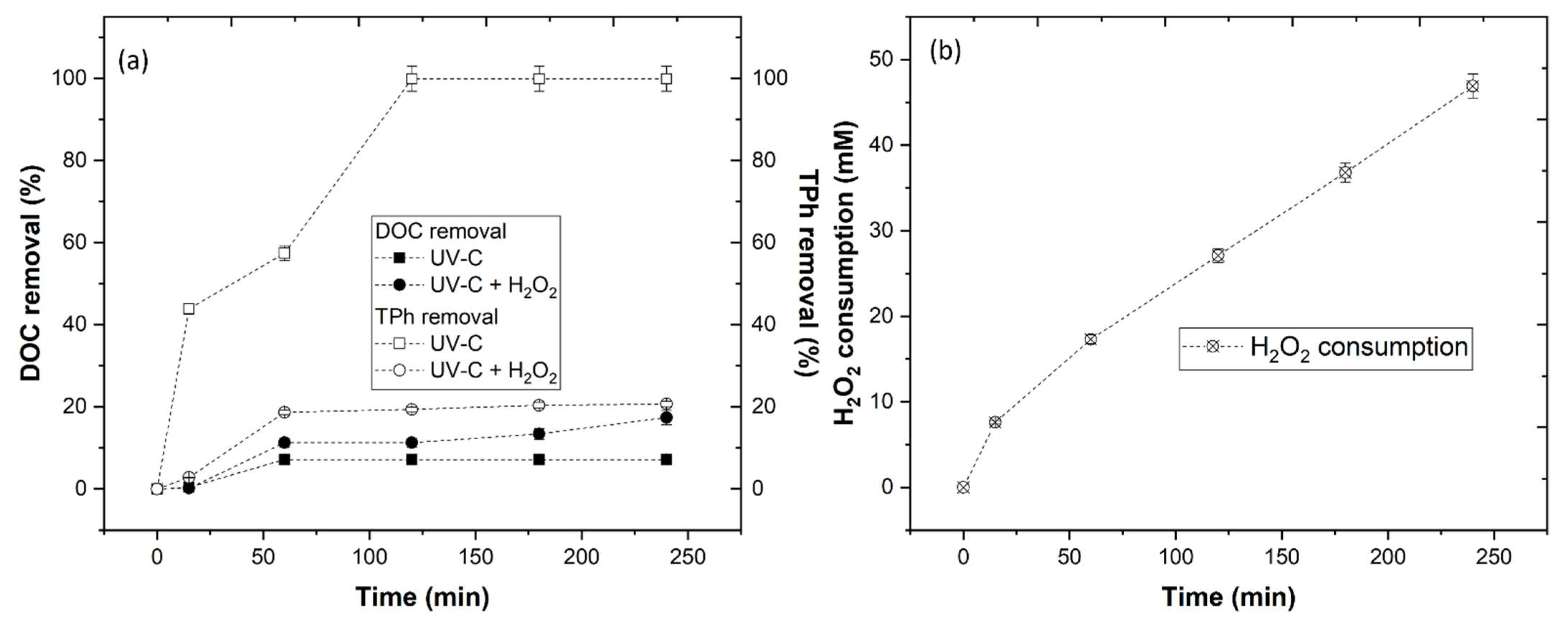
3.3.3. Effect of UV-C and UV-C + H2O2
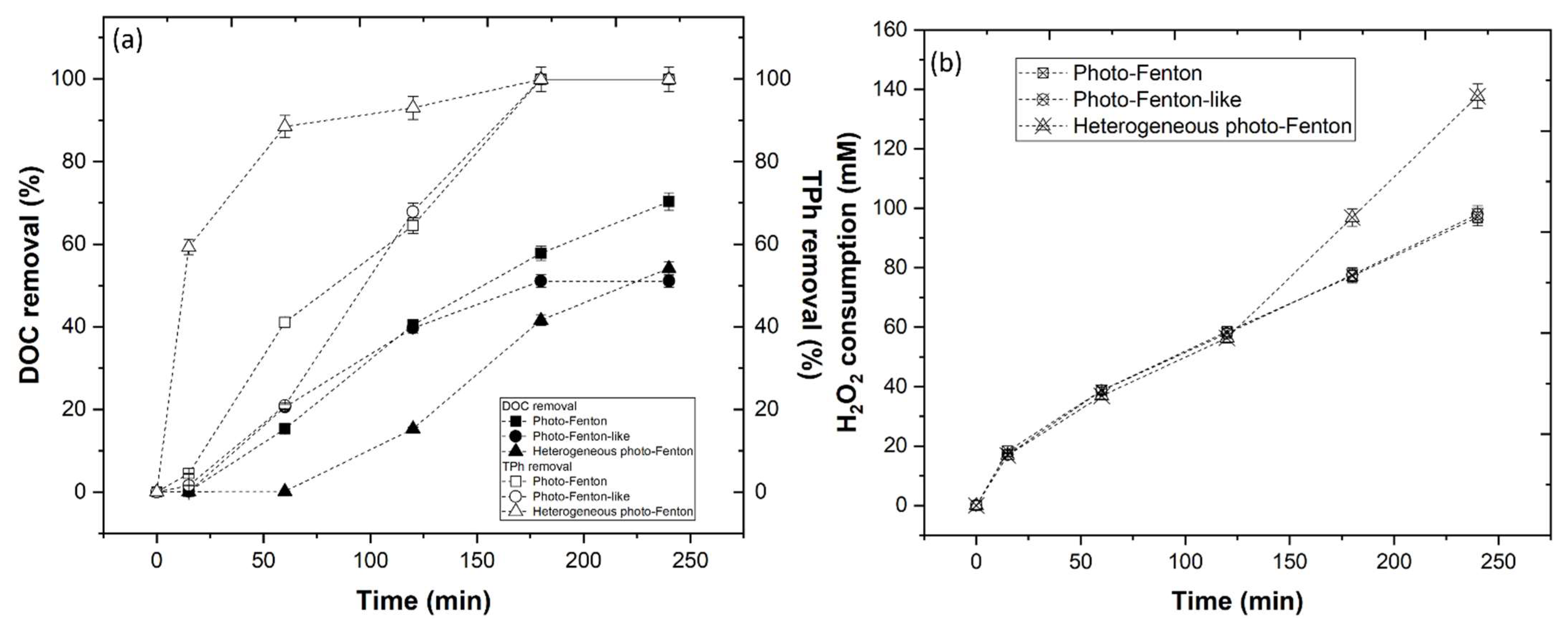
3.3.4. Photo-Fenton-Based Processes
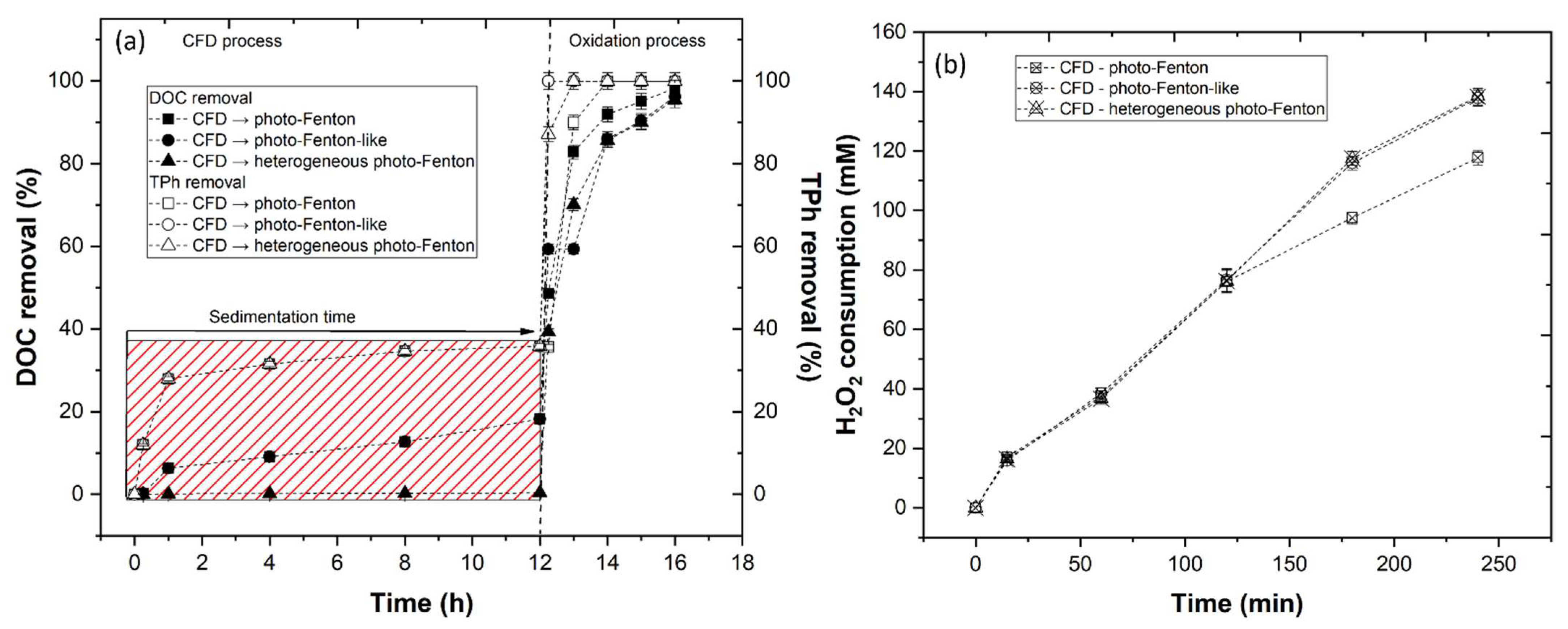
3.3.5. Effect of CFD Combined with AOP
3.4. Kinetic Rate and Operational Costs Assessment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martinez-Burgos, W.J.; Sydney, E.B.; Medeiros, A.B.P.; Magalhães, A.I.; de Carvalho, J.C.; Karp, S.G.; de Vandenberghe, L.P.S.; Letti, L.A.J.; Soccol, V.T.; Soccol, C.R. Agro-Industrial Wastewater in a Circular Economy: Characteristics, Impacts and Applications for Bioenergy and Biochemicals. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 341, 125795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mader, A.E.; Holtman, G.A.; Welz, P.J. Treatment Wetlands and Phyto-Technologies for Remediation of Winery Effluent: Challenges and Opportunities. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, C.M.; Quintanilla, A.; Casas, J.A.; Rodriguez, J.J. Treatment of Real Winery Wastewater by Wet Oxidation at Mild Temperature. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 129, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davididou, K.; Frontistis, Z. Advanced Oxidation Processes for the Treatment of Winery Wastewater: A Review and Future Perspectives. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 96, 2436–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, L.A.; Puma, G.L.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Treatment of Winery Wastewater by Physicochemical, Biological and Advanced Processes: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 286, 343–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Li, H.; Huang, M.; Yang, H.; Li, A. A Review on Chitosan-Based Flocculants and Their Applications in Water Treatment. Water Res. 2016, 95, 59–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, C.S.D.; Neto, A.R.; Duda, R.M.; de Oliveira, R.A.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Madeira, L.M. Combination of Chemical Coagulation, Photo-Fenton Oxidation and Biodegradation for the Treatment of Vinasse from Sugar Cane Ethanol Distillery. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 3634–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heredia, J.B.; Martín, J.S. Removing Heavy Metals from Polluted Surface Water with a Tannin-Based Flocculant Agent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 1215–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorge, N.; Teixeira, A.R.; Marchão, L.; Goufo, P.; Lucas, M.S.; Peres, J.A. Application of NaCl Plant Extracts to Decrease the Costs of Microfiltration for Winery Wastewater Treatment. Chem. Proc. 2022, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renault, F.; Sancey, B.; Charles, J.; Morin-Crini, N.; Badot, P.M.; Winterton, P.; Crini, G. Chitosan Flocculation of Cardboard-Mill Secondary Biological Wastewater Franc. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 155, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, R.B.; Jorge, N.; Lucas, M.S.; Raymundo, A.; Barros, A.I.; Peres, J.A. Food By-Product Valorization by Using Plant-Based Coagulants Combined with AOPs for Agro-Industrial Wastewater Treatment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, H.; Richardson, D.M.; Pauchard, A.; Le Roux, J.J. Genetic Analyses Reveal Complex Introduction Histories for the Invasive Tree Acacia Dealbata Link around the World. Divers. Distrib. 2021, 27, 360–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talhi, M.F.; Cheriti, A.; Belboukhari, N.; Agha, L.; Roussel, C. Biosorption of Copper Ions from Aqueous Solutions Using the Desert Tree Acacia Raddiana. Desalin. Water Treat. 2010, 21, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Martín, J.; Beltrán-Heredia, J.; Dávila-Acedo, M.A. Optimum Coagulant from Acacia Mearnsii de Wild for Wastewater Treatment. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2011, 34, 2069–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulal, P.; Krishnappa, P.B.; Badalamoole, V. Development of Gum Acacia Based Magnetic Nanocomposite Adsorbent for Wastewater Treatment. Polym. Bull. 2021, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.; Roslan, A.; Kamarulzaman, M.F.H.; Erat, M.M. Colloids Removal from Water Resources Using Natural Coagulant: Acacia Auriculiformis. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1885, 020243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, S.; Chen, L.; Liu, Z.; Qin, J. Utilization of Bark Waste of Acacia Mangium: The Preparation of Activated Carbon and Adsorption of Phenolic Wastewater. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2021, 160, 113157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyens, E.; Baeyens, J. A Review of Classic Fenton’s Peroxidation as an Advanced Oxidation Technique. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 98, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, M.M.; Raman, A.A.A.; Asghar, A. A Review on Approaches for Addressing the Limitations of Fenton Oxidation for Recalcitrant Wastewater Treatment. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 126, 119–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alalm, M.G.; Tawfik, A.; Ookawara, S. Comparison of Solar TiO2 Photocatalysis and Solar Photo-Fenton for Treatment of Pesticides Industry Wastewater: Operational Conditions, Kinetics, and Costs. J. Water Process. Eng. 2015, 8, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, B.M.; Rodrigues, C.S.D.; Madeira, L.M. Synthetic Olive Mill Wastewater Treatment by Fenton’s Process in Batch and Continuous Reactors Operation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 34826–34838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, H. Catalytic Ozonation for Water and Wastewater Treatment: Recent Advances and Perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.M.T.; Herney-ramirez, J.; Söylemez, U.; Madeira, L.M. A Lumped Kinetic Model Based on the Fermi’s Equation Applied to the Catalytic Wet Hydrogen Peroxide Oxidation of Acid Orange 7. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 121–122, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tian, S.; Cun, J.; Ning, P. Degradation of Methylene Blue Using a Heterogeneous Fenton Process Catalyzed by Ferrocene. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 28, 5821–5830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tian, S.; Ning, P. Ferrocene-Catalyzed Heterogeneous Fenton-like Degradation of Methylene Blue: Influence of Initial Solution PH. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 6334–6340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez, M.; Santander, I.P.; Contreras, D.R.; Yáñez, J.; Zaror, C.; Salazar, R.A.; Pérez-Moya, M.; Mansilla, H.D. Oxidative Degradation of Sulfathiazole by Fenton and Photo-Fenton Reactions. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2014, 49, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, J.R.; Gonzalez, T.; Cuerda-correa, E.M.; Muñoz-peña, M.J. Combating Paraben Pollution in Surface Waters with a Variety of Photocatalyzed Systems: Looking for the Most Efficient Technology. Open Chem. 2019, 17, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çalık, Ç.; Çifçi, D.İ. Comparison of Kinetics and Costs of Fenton and Photo-Fenton Processes Used for the Treatment of a Textile Industry Wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 304, 114234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.R.; Jorge, N.; Fernandes, J.R.; Lucas, M.S.; Peres, J.A. Textile Dye Removal by Acacia Dealbata Link. Pollen Adsorption Combined with UV-A/NTA/Fenton Process. Top. Catal. 2022, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evgenidou, E.; Konstantinou, I.; Fytianos, K.; Poulios, I. Oxidation of Two Organophosphorous Insecticides by the Photo-Assisted Fenton Reaction. Water Res. 2007, 41, 2015–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Chueca, J.; Amor, C.; Mota, J.; Lucas, M.S.; Peres, J.A. Oxidation of Winery Wastewater by Sulphate Radicals: Catalytic and Solar Photocatalytic Activations. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 22414–22426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.H.; Kang, S.F.; Wu, F.A. Hydroxyl Radical Scavenging Role of Chloride and Bicarbonate Ions in the H2O2/UV Process. Chemosphere 2001, 44, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A. Colorimetry of Total Phenolics with Phosphomolybdic-Phosphotungstic Acid Reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar]
- APHA; AWWA; WEF. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA; Denver, CO, USA; Alexandria, VA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Jorge, N.; Teixeira, A.R.; Matos, C.C.; Lucas, M.S.; Peres, J.A. Combination of Coagulation–Flocculation–Decantation and Ozonation Processes for Winery Wastewater Treatment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, N.; Teixeira, A.R.; Guimarães, V.; Lucas, M.S.; Peres, J.A. Treatment of Winery Wastewater with a Combination of Adsorption and Thermocatalytic Processes. Processes 2022, 10, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals: Terrestrial Plant Test; OECD: Paris, France, 2004; Volume 208. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, D.; Xing, B. Phytotoxicity of Nanoparticles: Inhibition of Seed Germination and Root Growth. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 150, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varnero, M.T.; Rojas, C.; Orellana, R. Índices de Fitotoxicidad En Residuos Orgánicos Durante El Compostaje. Rev. Cienc. Suelo Nutr. Veg. 2007, 7, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiquia, S.M.; Tam, N.F.Y. Elimination of Phytotoxicity during Co-Composting of Spent Pig-Manure Sawdust Litter and Pig Sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 1998, 65, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisperguer, J.; Saravia, Y.; Vergara, E. Structure and Thermal Behavior of Tannins from Acacia Dealbata Bark and Their Reactivity toward Formaldehyde. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2016, 61, 3188–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boulaadjoul, S.; Zemmouri, H.; Bendjama, Z.; Drouiche, N. A Novel Use of Moringa Oleifera Seed Powder in Enhancing the Primary Treatment of Paper Mill Effluent. Chemosphere 2018, 206, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Fu, T.; Liu, J.; Yu, S.; Gao, H.; Eneji, A.E.; Liang, H. Accumulation and Distribution of Calcium and Magnesium in Oat and Correlation Analysis with the Uptake of Sodium, Potassium, and Chloride Elements. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2018, 49, 2765–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S. Physisorption of Gases, with Special Reference to the Evaluation of Surface Area and Pore Size Distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vunain, E.; Mike, P.; Mpeketula, G.; Monjerezi, M.; Etale, A. Evaluation of Coagulating Efficiency and Water Borne Pathogens Reduction Capacity of Moringa Oleifera Seed Powder for Treatment of Domestic Wastewater from Zomba, Malawi. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, K.J.; Hand, D.W.; Crittenden, J.C.; Trussell, R.R.; Tchobanoglous, G. Principles of Water Treatment; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; ISBN 9780470405383. [Google Scholar]
- Agbovi, H.K.; Wilson, L.D. Design of Amphoteric Chitosan Flocculants for Phosphate and Turbidity Removal in Wastewater. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 189, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.Y.; Selvarajoo, A.; Sethu, V.; Koyande, A.K.; Arputhan, A.; Lim, Z.C. Treatment of Palm Oil Mill Effluent (POME) by Coagulation Flocculation Process Using Peanut—Okra and Wheat Germ—Okra. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2018, 20, 1951–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, L.; Lofrano, G.; Belgiorno, V. Olive Mill and Winery Wastewaters Pre-Treatment by Coagulation with Chitosan. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 2447–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Prasad, B.; Mishra, I.M. Pretreatment of Petrochemical Wastewater by Coagulation and Flocculation and the Sludge Characteristics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 178, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amuda, O.S.; Amoo, I.A. Coagulation/Flocculation Process and Sludge Conditioning in Beverage Industrial Wastewater Treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, L.; García, J.; Pena, R.; Garfí, M. Constructed Wetlands for Winery Wastewater Treatment: A Comparative Life Cycle Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilias, M.K.M.; Hossain, M.S.; Ngteni, R.; Al-Gheethi, A.; Ahmad, H.; Omar, F.M.; Naushad, M.; Pandey, S. Environmental Remediation Potential of Ferrous Sulfate Waste as an Eco-Friendly Coagulant for the Removal of NH3-N and COD from the Rubber Processing Effluent. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, A.R.; Hamid, F.S.; Mohamad, S.; Tay, K.S. Stabilized Landfill Leachate Treatment by Coagulation-Flocculation Coupled with UV-Based Sulfate Radical Oxidation Process. Waste Manag. 2018, 76, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimarães, V.; Teixeira, A.R.; Lucas, M.S.; Silva, A.M.T.; Peres, J.A. Pillared Interlayered Natural Clays as Heterogeneous Photocatalysts for H2O2-Assisted Treatment of a Winery Wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 228, 115768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, B.M.; Rodrigues, C.S.D.; Maldonado-hódar, F.J.; Madeira, L.M. Treatment of High-Strength Olive Mill Wastewater by Combined Fenton-like Oxidation and Coagulation/Flocculation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Rosario-muniz, E.; Ma, X. Effects of Inorganic Anions on Fenton Oxidation of Organic Species in Landfill Leachate. Waste Manag. Res. 2012, 30, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhai, Q.; Yin, D.; Sun, Y. The Marriage of Ferrocene and Silicotungstate: An Ingenious Heterogeneous Fenton-like Synergistic Photocatalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 193, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Cho, I.H.; Chang, S.W. Comparison of Fenton and Photo-Fenton Processes for Livestock Wastewater Treatment. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2006, 41, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuerda-Correa, E.M.; Alexandre-Franco, M.F.; Fernández-González, C. Advanced Oxidation Processes for the Removal of Antibiotics from Water. An Overview. Water 2020, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rueda-Márquez, J.J.; Levchuk, I.; Manzano, M.; Sillanpää, M. Toxicity Reduction of Industrial and Municipal Wastewater by Advanced Oxidation Processes (Photo-Fenton, UVC/H2O2, Electro-Fenton and Galvanic Fenton): A Review. Catalysts 2020, 10, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zheng, T.; Zhang, G.; Wang, P. A Review on Fenton-like Processes for Organic Wastewater Treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 762–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Z.; Ma, R.; Li, G. Degradation of Phenol by Nanomaterial TiO2 in Wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2006, 119, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, M.J.; Silva, C.G.; Silva, A.M.T.; Vilar, V.J.P.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Faria, J.L. Photocatalytic Activity of TiO2-Coated Glass Raschig Rings on the Degradation of Phenolic Derivatives under Simulated Solar Light Irradiation. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 224, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor, C.; Lucas, M.S.; Pirra, A.J.; Peres, J.A. Treatment of concentrated fruit juice wastewater by the combination of biological and chemical processes. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2012, 47, 1809–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R. Chemistry, 10th ed.; The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2010; ISBN 978–0–07–351109–2. [Google Scholar]
- Benitez, F.J.; Real, F.J.; Acero, J.L.; Leal, A.I.; Garcia, C. Gallic Acid Degradation in Aqueous Solutions by UV/H2O2 Treatment, Fenton’s Reagent and the Photo-Fenton System. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 126, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan-Alaton, I.; Gurses, F. Photo-Fenton-like and Photo-Fenton-like Oxidation of Procaine Penicillin G Formulation Effluent. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2004, 165, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Hu, C.; Qu, J.; Hu, X. Efficient Photodegradation of Acid Red B by Immobilized Ferrocene in the Presence of UVA and H2O2. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 154, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, N.; Marco, P.; Giménez, J.; Esplugas, S. Photocatalytic Diphenhydramine Degradation under Different Radiation Sources: Kinetic Studies and Energetic Comparison. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 220, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, M.S.; Peres, J.A.; Li, G. Treatment of Winery Wastewater by Ozone-Based Advanced Oxidation Processes (O3, O3/UV and O3/UV/H2O2) in a Pilot-Scale Bubble Column Reactor and Process Economics. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 72, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijpelaar, G.F.; Harmsen, D.J.H.; Beerendonk, E.F.; Van, R.C.; Metz, D.H.; Knol, A.H.; Fulmer, A.; Krijnen, S.; Ijpelaar, G.F.; Harmsen, D.J.H.; et al. Comparison of Low Pressure and Medium Pressure UV Lamps for UV/H2O2 Treatment of Natural Waters Containing Micro Pollutants. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2010, 32, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
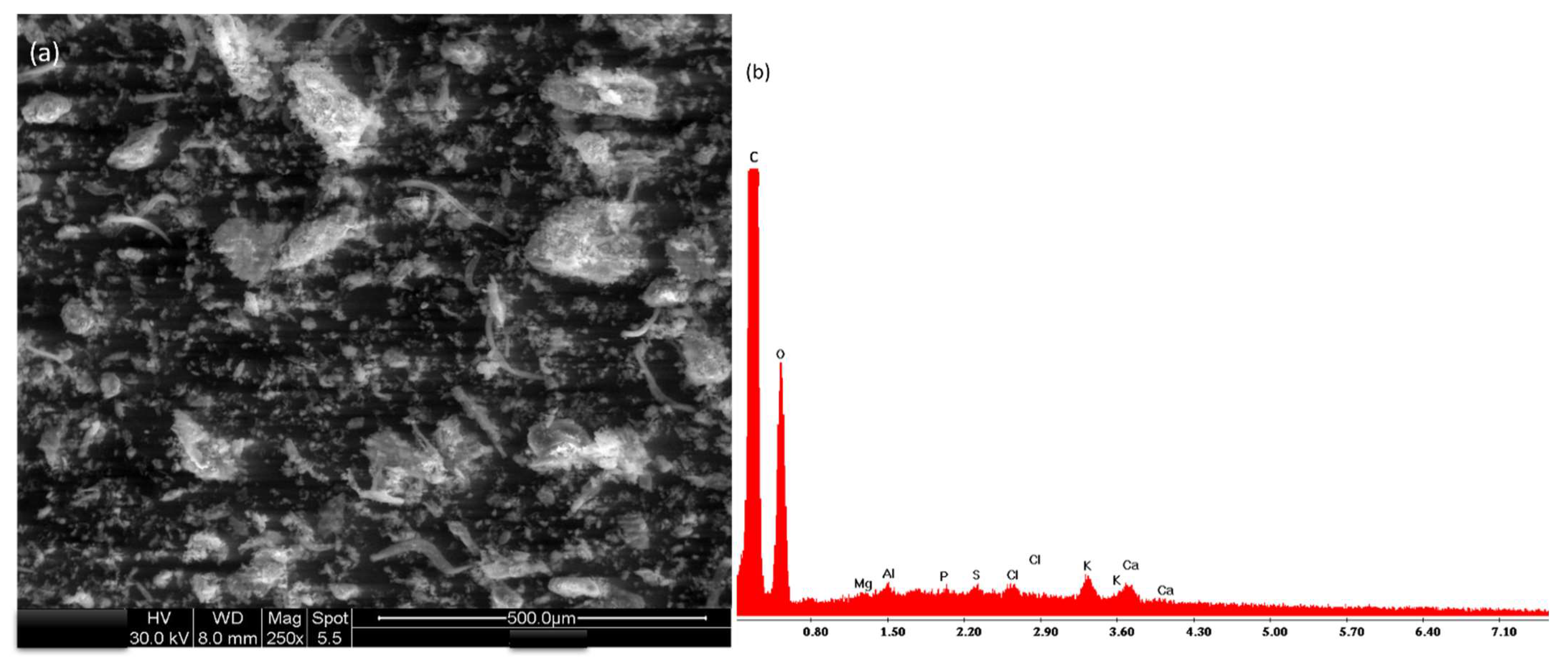


| Parameters | WW |
|---|---|
| pH | 4.0 ± 0.2 |
| Electrical conductivity (μS/cm) | 62.5 ± 3.1 |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 296 ± 5.9 |
| Total suspended solids—TSS (mg/L) | 750 ± 15 |
| Volatile suspended solids—VSS (mg/L) | 640 ± 12.8 |
| Chemical Oxygen Demand—COD (mg O2/L) | 2145 ± 21.5 |
| Biochemical Oxygen Demand—BOD5 (mg O2/L) | 550 ± 5.5 |
| Dissolved Organic Carbon—DOC (mg C/L) | 400 ± 8.0 |
| Total Nitrogen—TN (mg N/L) | 9.07 ± 0.5 |
| Total polyphenols—TPh (mg gallic acid/L) | 22.6 ± 1.1 |
| Biodegradability index—BOD5/COD | 0.26 ± 0.03 |
| Aluminum (mg/L) | 0.01 ± 0.001 |
| Calcium (mg/L) | 1.07 ± 0.1 |
| Cobalt (mg/L) | 0.01 ± 0.001 |
| Copper (mg/L) | 0.014 ± 0.001 |
| Iron (mg/L) | 0.05 ± 0.001 |
| Magnesium (mg/L) | 0.51 ± 0.01 |
| Manganese (mg/L) | 0.016 ± 0.002 |
| Potassium (mg/L) | 20.5 ± 1.0 |
| Sodium (mg/L) | 0.19 ± 0.04 |
| Zinc (mg/L) | 10.53 ± 0.2 |
| Processes | k × 10−3 (min−1) | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fenton | 1.31 ± 5.3 × 10−5 a | 529 ± 5.9 a | 0.920 |
| Fenton-like | 1.49 ± 2.6 × 10−5 b | 465 ± 5.3 b | 0.939 |
| Heterogeneous Fenton | 0.64 ± 3.8 × 10−6 c | 1081 ± 5.9 c | 0.920 |
| Photo-Fenton | 5.21 ± 4.3 × 10−5 d | 133 ± 4.6 d | 0.989 |
| Photo-Fenton-like | 3.38 ± 2.6 × 10−5 e | 205 ± 5.6 e | 0.941 |
| Heterogeneous photo-Fenton | 3.36 ± 7.3 × 10−5 e | 206 ± 1.7 e | 0.915 |
| CFD + photo-Fenton | 15.0 ± 4.5 × 10−5 f | 46 ± 2.9 f | 0.970 |
| CFD + photo-Fenton-like | 12.7 ± 9.9 × 10−5 g | 55 ± 2.9 g | 0.985 |
| CFD + heterogeneous photo-Fenton | 11.5 ± 8.7 × 10−5 h | 60 ± 3.4 g | 0.983 |
| Processes | Energy Efficiency (E) (mg/L DOC/kWh) | Energy Cost (€/g/L DOC) | Reagent Cost (€/g/L DOC) | Total Cost (€/g/L DOC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fenton | n.q. | n.q. | 0.33 ± 8.7 × 10−5 a | 0.33 ± 8.7 × 10−5 a |
| Fenton-like | n.q. | n.q. | 0.08 ± 1.0 × 10−4 b | 0.08 ± 1.0 × 10−4 b |
| Heterogeneous Fenton | n.q. | n.q. | 0.34 ± 1.4 × 10−4 c | 0.34 ± 1.5 × 10−4 c |
| Photo-Fenton | 2201 ± 5.7 a | 3.63 × 10−2 ± 5.2 × 10−5 a | 1.25 ± 3.4 × 10−4 d | 1.29 ± 5.8 × 10−4 d |
| Photo-Fenton-like | 1598 ± 11.3 b | 5.01 × 10−2 ± 3.7 × 10−5 b | 1.26 ± 1.8 × 10−4 e | 1.31 ± 5.4 × 10−4 e |
| Heterogeneous photo-Fenton | 1692 ± 14.2 c | 4.73 × 10−2 ± 3.3 × 10−5 c | 1.77 ± 3.2 × 10−4 f | 1.82 ± 9.6 × 10−5 f |
| CFD + photo-Fenton | 2515 ± 9.4 d | 3.18 × 10−2 ± 9.1 × 10−5 d | 1.52 ± 1.4 × 10−3 g | 1.55 ± 1.9 × 10−4 g |
| CFD + photo-Fenton-like | 2452 ± 6.7 e | 3.26 × 10−2 ± 1.3 × 10−4 e | 1.78 ± 2.7 × 10−4 f | 1.81 ± 1.6 × 10−4 h |
| CFD + heterogeneous photo-Fenton | 2428 ± 8.1 f | 3.29 × 10−2 ± 5.7 × 10−5 f | 1.78 ± 5.3 × 10−4 h | 1.81 ± 1.8 × 10−4 i |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jorge, N.; Teixeira, A.R.; Lucas, M.S.; Peres, J.A. Agro-Industrial Wastewater Treatment with Acacia dealbata Coagulation/Flocculation and Photo-Fenton-Based Processes. Recycling 2022, 7, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling7040054
Jorge N, Teixeira AR, Lucas MS, Peres JA. Agro-Industrial Wastewater Treatment with Acacia dealbata Coagulation/Flocculation and Photo-Fenton-Based Processes. Recycling. 2022; 7(4):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling7040054
Chicago/Turabian StyleJorge, Nuno, Ana R. Teixeira, Marco S. Lucas, and José A. Peres. 2022. "Agro-Industrial Wastewater Treatment with Acacia dealbata Coagulation/Flocculation and Photo-Fenton-Based Processes" Recycling 7, no. 4: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling7040054
APA StyleJorge, N., Teixeira, A. R., Lucas, M. S., & Peres, J. A. (2022). Agro-Industrial Wastewater Treatment with Acacia dealbata Coagulation/Flocculation and Photo-Fenton-Based Processes. Recycling, 7(4), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling7040054








