Abstract
Greywater (GW) can be separated in different fractions where the kitchen component might be included. Constructed wetland (CW) systems are commonly used for the onsite treatment of GW, and the fraction treated might impact the performance, operation, and maintenance. These aspects are still poorly explored in the literature and are of importance for a proper design and system sustainability. In this study, a multi-stage household-scale CW system composed of a horizontal flow (HF), followed by a vertical flow (VF) unit, was monitored over 1330 days, focusing on different GW fractions and hydraulic and organic loading rates. The biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) was ~50% lower without the kitchen sink component (GWL) in the system inlet, while no drop was observed in the chemical oxygen demand (COD). Treatment with the GWL component caused a sudden drop in the hydraulic loading rate applied at the HF-CW (~114 to 35 mm per day) and the VF-CW (~230 to 70 mm per day). Even when the HF-CW received ~90 gCOD m−2 per day (GW), the multistage system reached a COD removal of 90%. The lower BOD load when treating GWL avoids clogging and decreases the frequency of maintenance. These variables can be used for the optimal design and operation of a CW, contributing with empirical data to CW guidelines in Brazil, and could additionally be expanded for application in other countries with similar climates.
1. Introduction
Constructed wetlands (CWs), also known as treatment wetlands, are considered to be a highly efficient and low-cost ecotechnology [1,2] that allow for water reuse and create biodiverse ecosystems, ensuring environmentally friendly wastewater treatment [3,4]. CWs, as a nature-based solution, have been widely used to treat various types of wastewater [5,6], such as domestic sewage, agricultural wastewater, industrial effluent, mine drainage, landfill leachate, storm water, polluted river water, and urban runoff.
Publications of this ecotechnology for the greywater (GW) treatment (e.g., wastewater from baths, sinks, washing machines, and kitchen appliances) first occurred in 2000, in particular for decentralized and household applications [7]. Some previous studies presented design parameters and criteria [8,9,10,11,12], while others focused on hydrodynamics and modelling [13,14,15]. Further, pollutant removal studies have also begun to include micro-pollutants [16,17,18], mainly surfactants and personal care products [19,20]. Generally, the performance of CWs is affected by several factors such as climatic and local conditions, native plant species, and substrate materials. In particular, GW exhibits great variability in terms of quali-quantitative characteristics. Depending on the type of appliance contributing to the GW, it might significantly affect parameters such as the organic matter content and flow (for instance, with or without a kitchen and/or laundry component). In this view, long-term studies evaluating real-scale performance, including the characteristic variations and aspects of operation and maintenance (O&M), are important to subsidize proper design criteria.
According to a study by Arden and Ma [21], CWs for GW treatment have been proposed as they are affordable, energy-efficient, and can be used for non-potable reuse of water, although post-treatment may be required to meet the water quality standards required for a given purpose. CWs design equations for biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) removal based on rate constants derived from the North American Treatment Wetland Database (used for domestic sewage and agricultural effluents) may even be conservative while showing little ability to predict performance using hydraulic loading rate (HLR). However, with regard to the hydraulic retention time (HRT), the 3–5 day range allows the effluent to be within the recommended characteristics concerning the physiochemical parameters.
In Europe, many studies have been conducted using multistage CWs systems for GW treatment. These studies have largely focused on local substrates and plant species. Moreover, these were primarily conducted at a constant flow rate, HRT, HLR, and organic loading rate (OLR) [16]. Many of these studies opted to focus on nitrogen removal behavior [10,22], even though GW generally carries a low nitrogen content. Within Europe, Germany, where GW treatment by CWs has been in use for over 20 years [23,24], the local normative was recently revised in the DWA (Deutsche Vereinigung für Wasserwirtschaft, Abwasser und Abfall e. V.) guidelines [25]. Specific points for GW treatment were provided, such as: CWs treating GW require 50% of the specific surface area compared to a conventional system, and the presumed GW generation is 75 L per person (PE−1) per day (d−1). Additionally, regarding the design, the normative suggests reference values for BOD (18–31 g PE−1 d−1) and COD (47–57 g PE−1 d−1) [26].
A recent study by Boano et al. [27] used the Global Wetland and Technology database and presented HLR values of 63–174 mm d−1, with areas of 23–230 m2 (1.7 m2 PE−1), for the horizontal flow (HF) CWs. Generally, it is more common to adopt vertical flow (VF) or intensified CWs for larger scaled projects, with aeration, for example, as the required area for HF is not always available; VF-CW are subject to a HLR which varies between 150 and 300 mm d−1 (0.5–2.8 m2 PE−1). Several studies have shown that the hydraulic and organic loads applied for HF and VF have been below 100 mm d−1 and 200 mm d−1, respectively [28,29,30,31]. Hoffmann et al. [11] suggested values of between 60 and 80 mm d−1 for HF, and ~200 mm d−1 for VF. These values are considered appropriate in hot climate regions, based both on the literature and on projects developed, and are within the values currently applied.
Recent publications have reviewed the design parameters, especially with intensified systems, such as aeration. Both HF- and VF-CWs have demonstrated that HLR and OLR, among other parameters, should be evaluated with operational and technological advances, as well as with the consideration of local conditions [32,33,34]. A recent state-of-the-art CWs study in Brazil [35] stated that only three previous publications have considered GW, while a literature review in Latin America [36] stated only two publications. Although progress has been made in several countries regarding guidelines for CW projects, Brazil is still in the process of establishing its first standards and guidelines. However, CW guidelines in Brazil [37] do not include the treatment of GW, only domestic sewage, with sizing parameters based on the HLR and OLR (BOD).
The aim of this study is to present the performance with both qualitative and quantitative analysis of a multistage constructed wetland for the treatment of GW over a period of 4 years at the household level. The paper also discusses the O&M aspects of the system regarding the presence of the kitchen component (GW) and without it (GWL).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
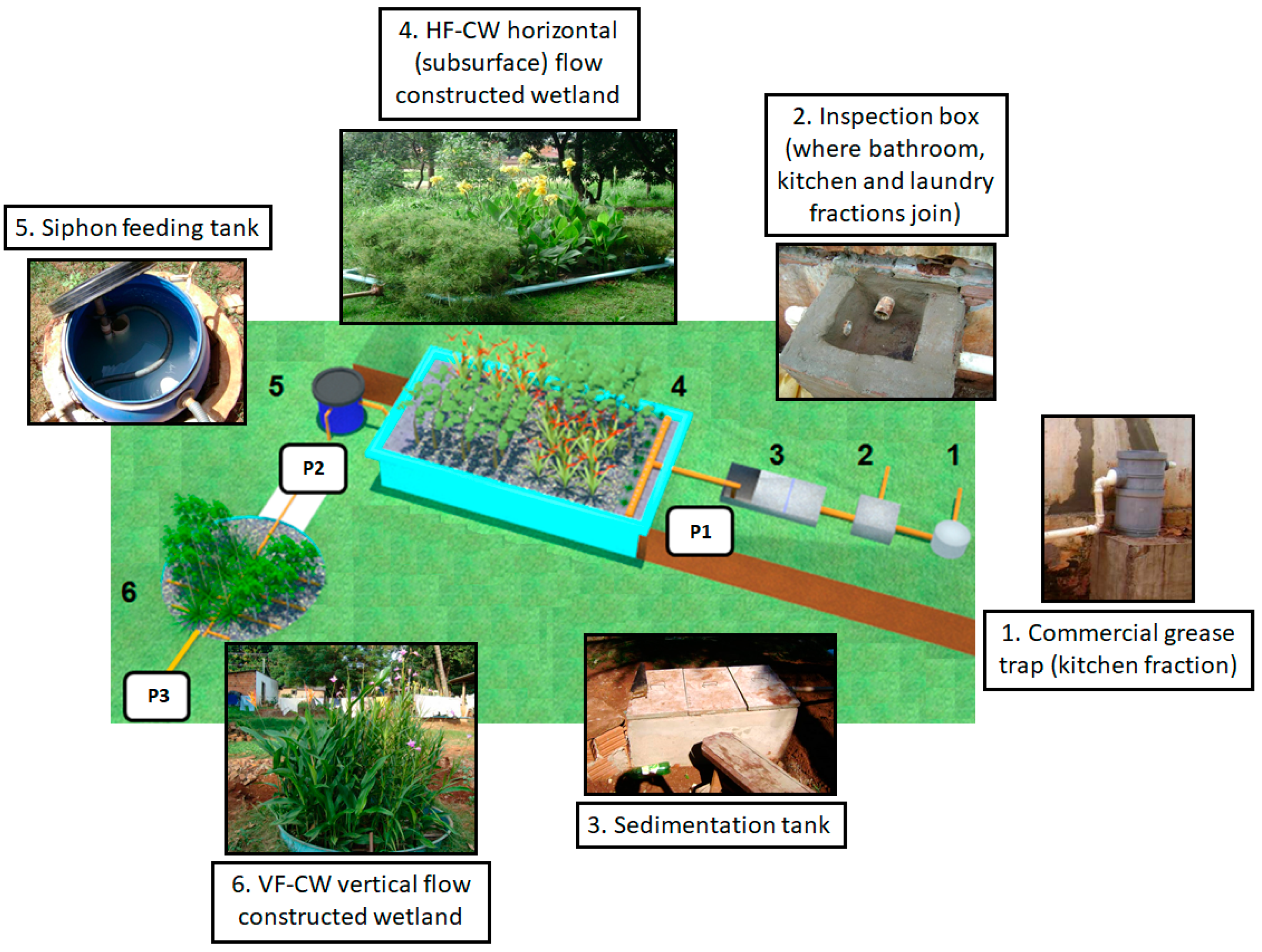
This study was based on the evaluation of a full-scale household level multistage constructed wetland (CW) to study the performance of an HF wetland followed by a VF wetland (Figure 1) in the treatment of GW and light GW (GWL), without the kitchen sink component.
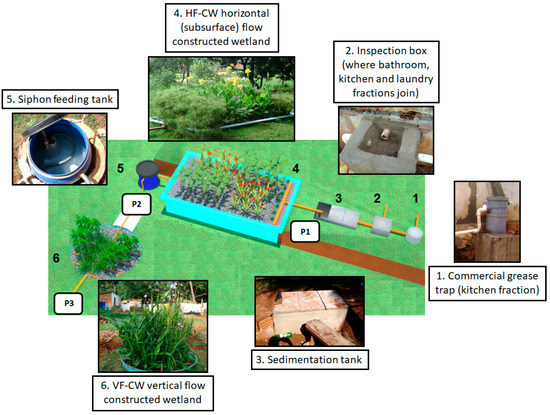
Figure 1.
Set up of the constructed wetland (CW) system representing the pre-treatment and multistage system.
2.2. Set up and Design
The HF-CW was designed based on the required surface area [38] for a 70% BOD removal and 20% nitrogen removal. The VF-CW was designed based on the O2 balance required to remove the remaining BOD and nitrogen present in the HF-CW effluent [39], with five effluent applications (batch) per day on the VF-CW.
The treatment system was composed of a commercial grease trap for the kitchen GW component, an inspection box, where all GW merged, a sedimentation tank (250 L), the HF-CW, a siphon-feeding tank, and the VF-CW. The HF-CW was a fiberglass structure 1.6 m × 2.9 m × 0.4 m in size (4.64 m2) filled with fine gravel (diameter up to 4.8 mm; Ks = 6.0 · 10−3 m s−1; and porosity = 0.44), while the inlet and outlet zones were filled with coarse gravel (D60 = 7.5 mm; Cu = D60/D10 = 1.5; Ks = 3.6 · 10−3 m s−1; and porosity = 0.44).
2.3. Plants
The plants selected for the HF-CW were Heliconia psittacorum (popularly known as Heliconia or Andromeda), Cyperus isocladus (dwarf type), and Canna sp. (popularly known as Beri). For the VF-CW, the chosen plants were Arundina bambusifolia (a terrestrial multi-perennial orchid, known as bamboo orchid) and Alpinia purpurata (red ginger).
2.4. Mode of Operation
The operational conditions are presented in Table 1. There was no control in the inlet flow to evaluate the system performance under real conditions and eventual OLR and HLR peaks. Influent flow was registered by means of three water meters (multijet, Actaris®, Campo Grande, Brazil) installed in the kitchen, bathroom, and laundry room, which measured the water consumed in each.

Table 1.
Operational parameters and quantitative characteristics for the greywater for Phase 1 (290 days), Phase 2 (240 days), and Phase 3 (800 days—only light greywater).
Flow regulation was not applied in order to assess the performance under regular conditions of load and hydraulic peaks. Instead, we calculated quantitative parameters such as peak-flow, OLR, and HLR, according to the methods presented by von Sperling et al. [40].
2.5. Monitoring and Analytical Methods
The monitoring period was divided into three phases that were conducted in different days/years (only one multistage CW system): the first phase of 290 days (March to December, year 1), the second phase of 240 days (from March to September, year 2), and a third phase of 800 days (October to August, year 3, 4, and 5) which was GWL only, i.e., no kitchen sink component. In phase 1, the samples (Figure 1) were collected at three points (P1: inlet HF; P2: outlet HF and inlet VF; and P3: outlet VF). In phase 2 (until September) and 3 (until December), the samples were only collected from P1 and P3.
Physico-chemical and bacteriological analyses were performed biweekly according to the standard method for the examination of water and wastewater from the American Public Health Association [41]. The parameters analyzed were: COD, BOD, total phosphorus (TP), ammonia (NH4+), temperature, pH, turbidity, and E. coli.
2.6. Operation and Maintenance
The operation and maintenance were performed by the project participants. Pruning, sedimentation tank desludging, scum formation and accumulation, cleaning around the system and siphon system cleaning were the monitored aspects. The frequency and observations were recorded in a worksheet for comparison before and after diverting the flow of the kitchen component.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
The Shapiro–Wilk test was performed for the conventional wastewater quality parameters to determine whether the data were normally distributed. Given that the data followed a normal distribution, and considering its paired structure, both an ANOVA and a Tukey’s test were performed to compare the concentrations. The multistage system performance was statistically evaluated by comparing the means of effluent concentrations of various parameters under different operating conditions, using a paired sample ‘t’ test at a 95% confidence level (p < 0.05).
The Pearson correlation coefficient was selected for correlation analysis, according to de Oliveira et al. [17]. To classify the data in the system into categories, the cluster analysis results were selected to show homogeneity or heterogeneity between the data in the formed clusters, according to the study by de Souza Pereira et al. [42]. The multivariate principal component analysis (PCA) technique was used, which allows for the quantification of the significance of the variables to aid the explanation of the clusters. In this technique, orthogonal variables are created, which are explained by a small set of uncorrelated data called principal components (PCs). The PCA interpretation was carried out by observing the angular measurement formed between the data, with a smaller angle indicating a higher correlation, a larger angle indicating a lower correlation, and with opposite variables being inversely correlated according Atalla et al. [43].
3. Results
3.1. GW Qualitative Characteristics
Regarding the evaluated parameters (Table 2), only the BOD obtained a statistical difference when phase 1 and 2 (GW) were compared with phase 3 (GWL), i.e., with (~425 mgBOD L−1) and without (~149 mgBOD L−1) the kitchen sink component. Therefore, the use of different BOD values would be suggested for the design of CW treating different fractions of GW.

Table 2.
Qualitative characteristics for the units (P1: inlet horizontal flow—HF; P2: outlet HF and inlet vertical flow—VF; and P3: outlet VF).
The concentration of BOD effluent from the HF-CW (~13 mgBOD L−1) in phase 3, without a kitchen sink, was similar to that from the VF-CW (~7 mgBOD L−1) in phase 1 with a kitchen sink. There was also no difference in phase 3, without a kitchen sink, with the VF constructed effluent (~8 mgBOD L−1), indicating that, to achieve the same effluent quality, multistage system is required when the kitchen component is present, while the HF-CW would suffice for GWL.
3.2. GW Quantitative Parameters and CW Treatment Performance
Table 3 shows that when there was only GWL, i.e., no kitchen component, the production of GW was ~60 L PE−1 d−1 and that of phase 3 was ~39 L PE−1 d−1. However, it should be noted that there was less variation in GW generation compared to that in GWL, according to the standard deviation (~40 L PE−1 d−1) and peak-flow (4.0), which were higher in phase 3. Burnat and Mahmoud [44] also obtained a peak-flow value of 2.4, with the kitchen component, which corresponds to the phase 2 value in this study, and is similar to that stated by Silva et al. [12] in Brazil.

Table 3.
Qualitative and quantitative characteristics of greywater for the present work and related literature.
The HLR applied (Table 4) in phases 1 and 2, including the kitchen component, were ~111–114 mm d−1 and 228–233 mm d−1 for the HF-CW and the VF-CW, respectively. In phase 3, without the kitchen component (GWL), HLR dropped to ~35 mm d−1 and 72 mm d−1 for the HF-CW and VF-CW, respectively.

Table 4.
Operational parameters for constructed wetland (CW) treating greywater for the present work and the related literature.
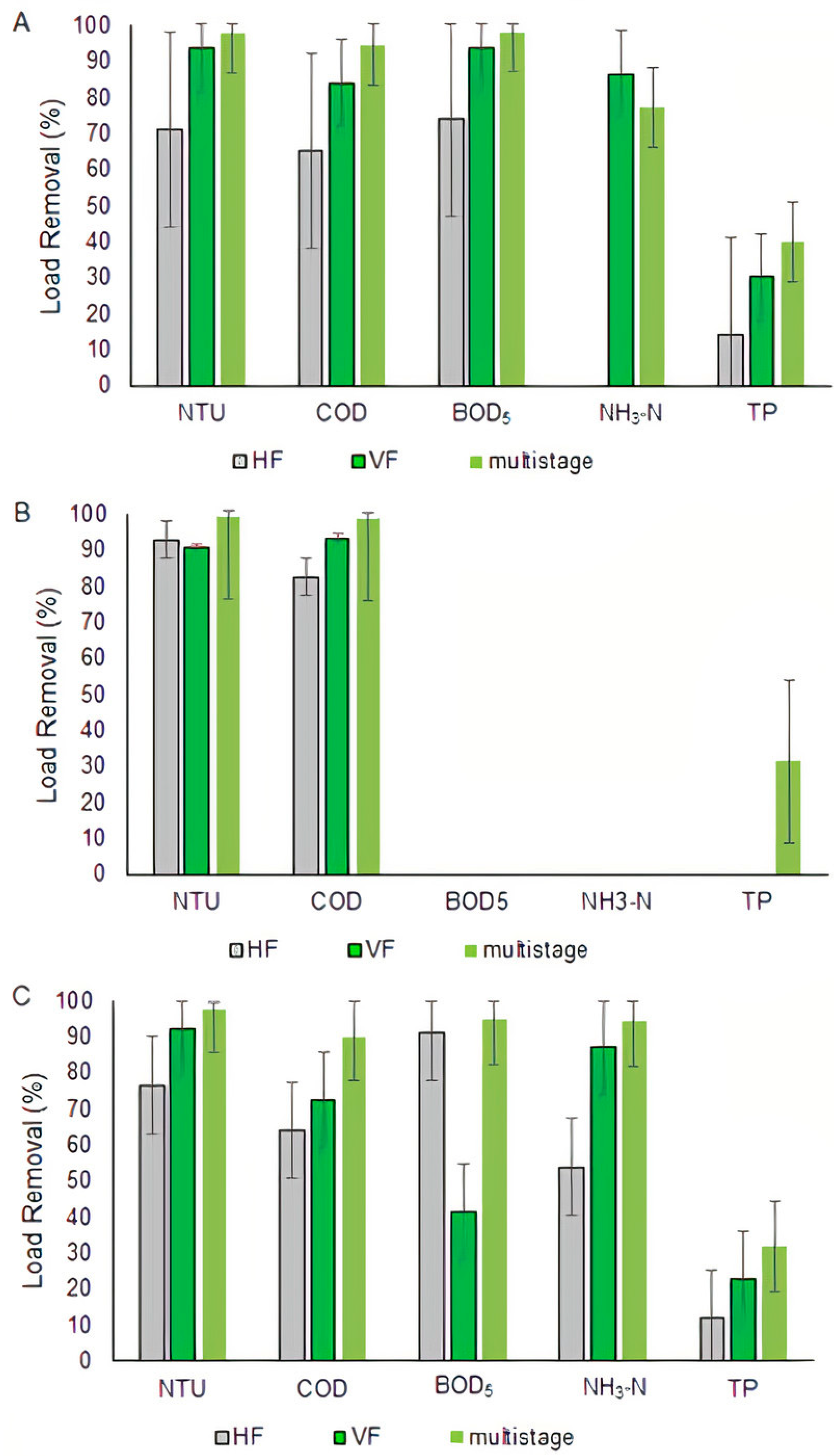
The applied OLR also showed a significant decrease from phases 1 and 2 to phase 3 (only GWL). The HF-CW received OLRs of 79 and 97 gCOD m−2 d−1 in phases 1 and 2, respectively, which reduced to 12 gCOD m−2 d−1 in phase 3. Higher loads in phase 2 compared to phase 1 promoted higher COD removals, 82% compared to 65%, respectively (Figure 2), resulting in lower loads applied to the VF-CW. We hypothesize that biofilm formation and full plants development played a role in the better performance during phase 2 as compared to phase 1.
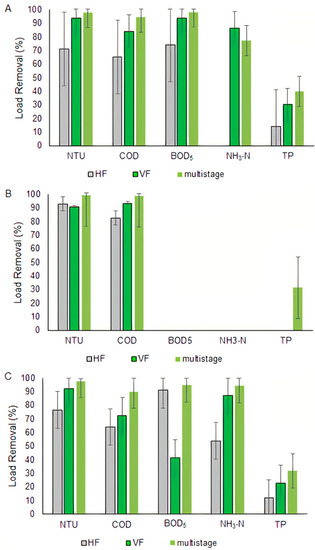
Figure 2.
Organic loading rate removal (%) for horizontal flow treatment wetland (HF-CW), vertical flow treatment wetland (VF-CW), and CW system at phase 1 (A), 2 (B), and 3 (C). NTU (turbidity); COD (chemical oxygen demand); BOD (biochemical oxygen demand); NH4+ (ammonia); and TP (total phosphorous).
3.3. Correlation Analysis, Principal Component Analysis (PCA), and Cluster Analysis
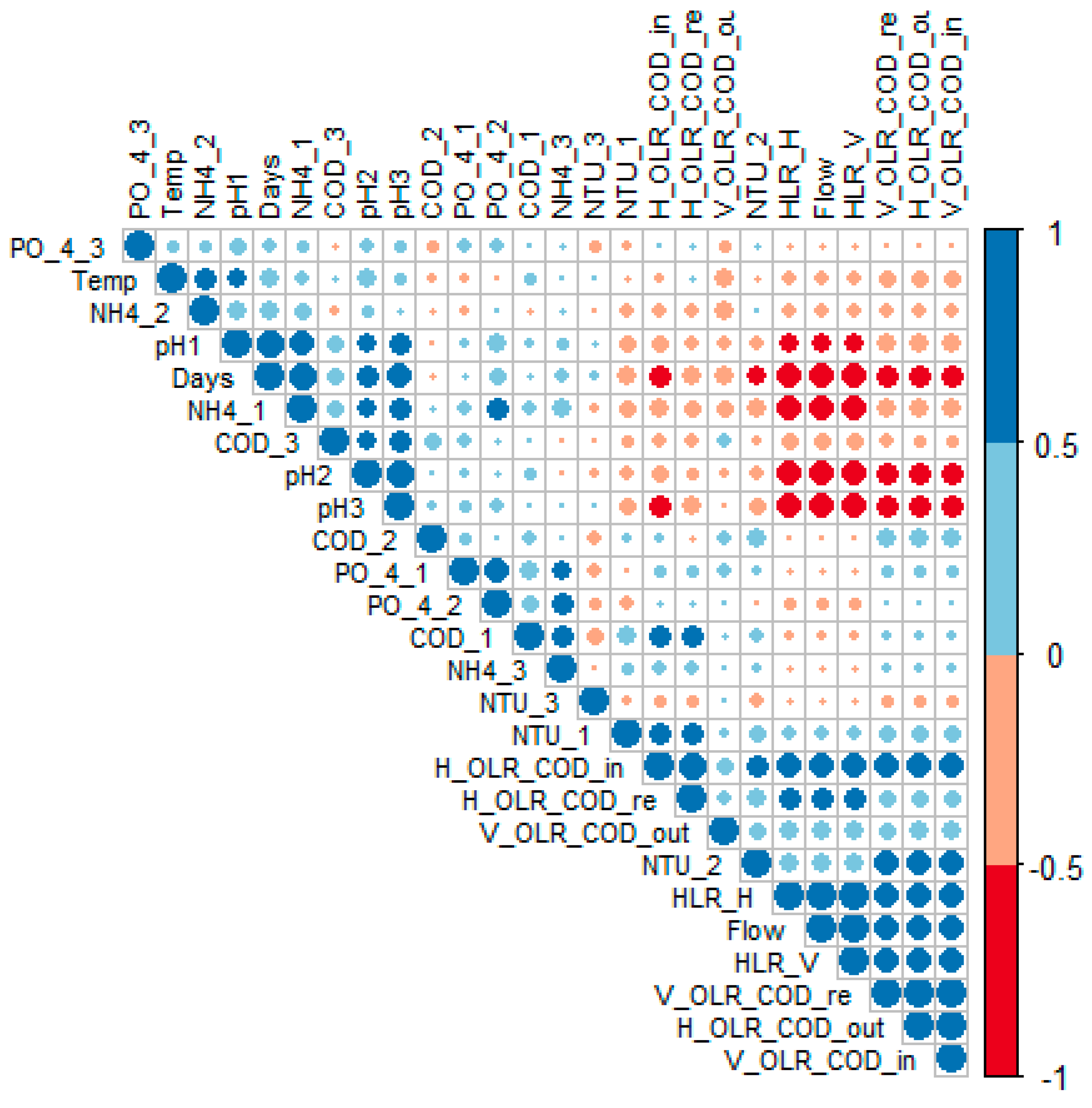
The correlation analysis (Figure 3) demonstrated that, along the 3 phases, the hydraulic parameters decreased.
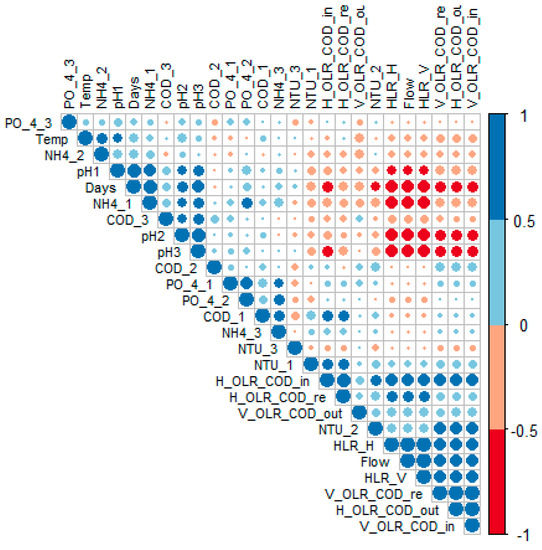
Figure 3.
Correlation matrix between different quali-quantitative parameters of the multistage system treating greywater. The red and blue dots correspond to negative and positive correlations, respectively. Small dots with light colors represent lower intensity correlations, and larger dots with darker colors correspond to higher intensity correlations.
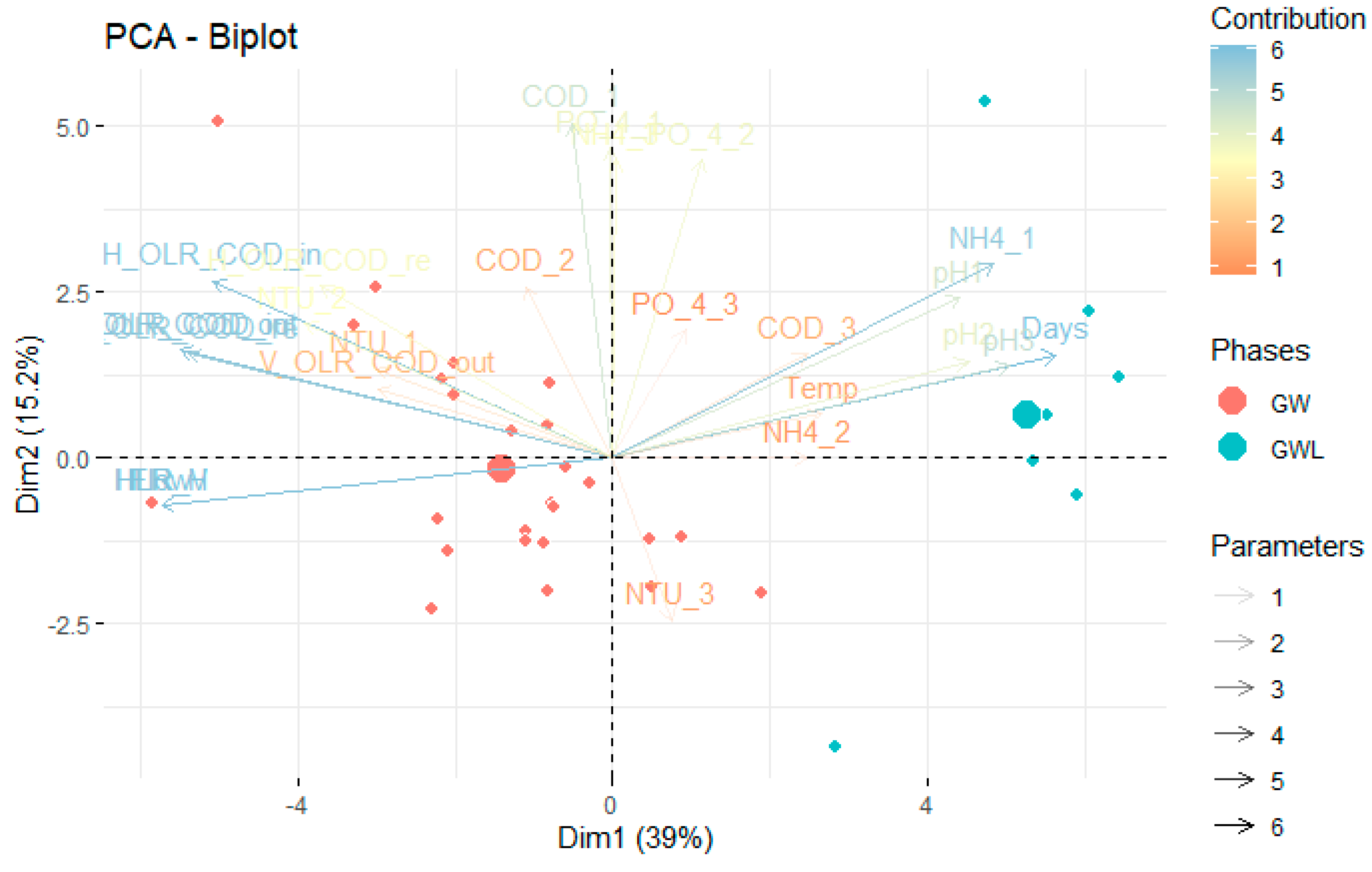
With regard to the quality parameters, as the flow decreased, the concentration of ammonia (NH4+) increased and the pH value became more basic. PCA (Figure 4) revealed that the hydraulic and quantitative parameters, specifically the HLR and OLR (COD), as well as the monitoring time in days (days), and the ammonia (NH4+) concentration, were the most representative parameters in terms of the performance of the system.
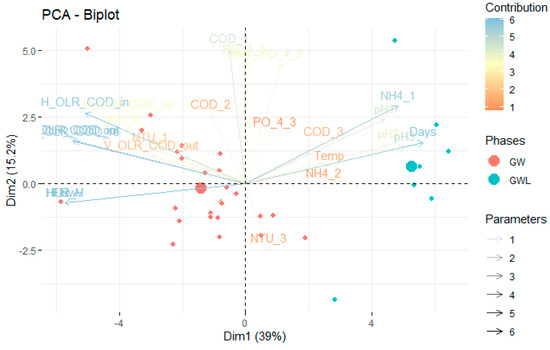
Figure 4.
Principal component analysis (PCA) in greywater with (GW) and without kitchen sink component (GWL) treated by constructed wetlands (multistage system). Contributions of quali-quantitative parameters by PCA with cluster (GW and GWL).
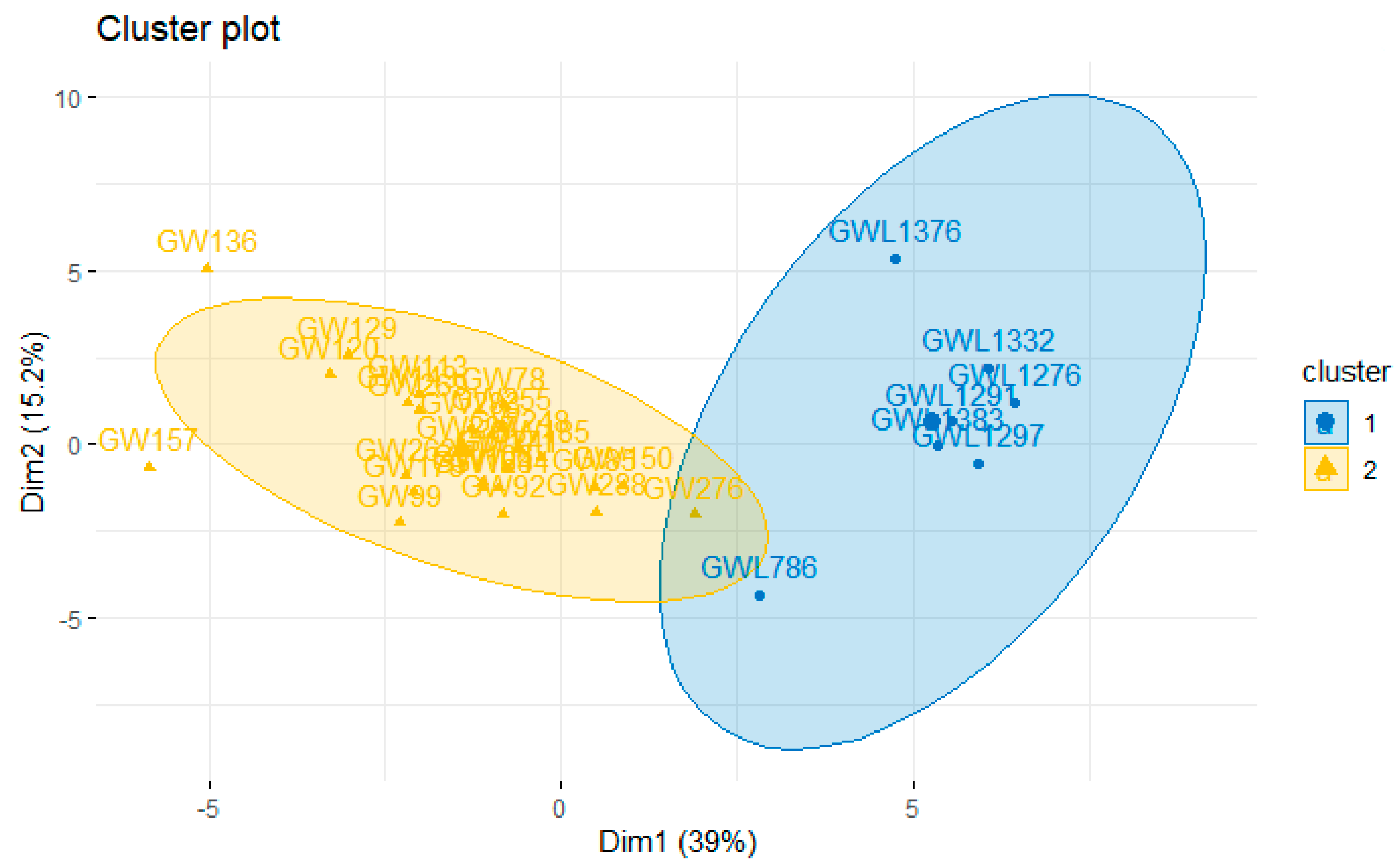
The cluster analysis results are shown in Figure 5, indicating that the optimal number of clusters is two, grouping GW with kitchen sink (yellow) and GW without kitchen sink (blue).
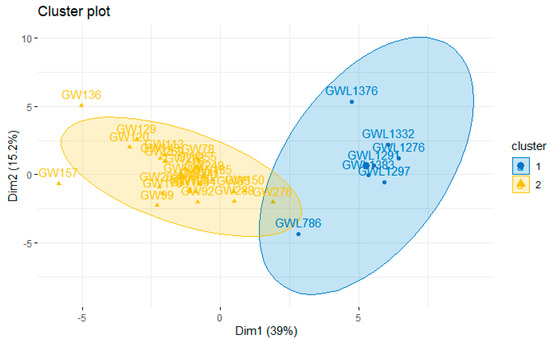
Figure 5.
Cluster analysis in greywater with and without kitchen sink component treated by constructed wetlands (multistage system).
3.4. Operation and Maintenance (O&M) Aspects
There was no change in the pruning routine of the plants or cleaning of the site around the system, such as weeding and sweeping during phase 3, when the system was only operated with GWL (Table 5). However, there was a significant difference in the maintenance routine with regard to cleaning the sedimentation tank and the siphon system, from a fortnightly pattern to every 18 months.

Table 5.
Operation and maintenance aspects and frequency before/after diverting the flow of the kitchen sink component (operation with light greywater only).
4. Discussion
4.1. BOD
BOD was the only parameter that showed a significant inlet reduction without the component of the kitchen sink. Using BOD as a design parameter allowed for ~50% reduction in the required area of constructed wetlands, in line with the German guidelines proposed in the DWA [25], when comparing domestic sewage and GW. Notably, without the component of the kitchen sink, the BOD and cross-sectional OLR (HF) were below 110 mg L−1 and 250 gBOD m−2 d−1, respectively, values recommended to avoid clogging in VF- and HF-CWs [37,54]. Therefore, BOD values of the present study are recommended to design constructed wetlands when the kitchen sink component is absent.
For the BOD, the input concentrations in HF-CW ranged between 425 (phase 1) and 542 mg L−1 (phase 2), followed by a significant drop in phase 3 (only GWL) to 150 mg L−1. These values are within the range of Busser [49] in Vietnam, Shrestha et al. [30] in Nepal, Martin [51] in Malaysia, and Dallas and Ho [52] in Costa Rica. Li and Otterpohl [55] observed that GW obtained from the washing machine or the laundry tank has BOD values of 48–472 mg L−1. However, when analyzing the kitchen component, the values increased to 536–1460 mg L−1, which is similar to the findings of studies by Alderlieste and Langeveld [45] in Mali, Burnat and Mahmoud [44] in Palestine, Faruqui and Al-Jayyousi [47] and Al-Jayyousi [48] in Jordan, and Friedler [50] in Israel.
4.2. COD
The COD:BOD ratio was close to 2 in phase 1 and 2, and increased to around 7 during phase 3, when kitchen GW was absent. Therefore, the biological treatment capacity dropped. Although the mean COD concentration was higher in phases 1 (708 mg L−1) and 2 (808 mg L−1), with the kitchen component, there was no statistical difference for phase 3 (GWL), with a mean value of 675 mg L−1, which is in agreement with those found by Magalhães Filho et al. [14] in GWL (minimum of 589 mg L−1 and a mean value of 771 mg L−1) and are also within the range stated by Shrestha et al. [30], Friedler [50], and Gross [56], from 411 to 984 mg L−1. These results confirm that the higher organic/biodegradable load is present in kitchen GW while the other fractions present more chemical substances due to personal and house care products.
The stable influent COD concentration without the kitchen fraction might lead to an oversized system if COD is used as design parameter instead of BOD. In this case, it is of upmost importance to observe the flow reduction, which in our case was quite representative, being around 50% of the total flow.
4.3. pH, E. coli, and Turbidity
The pH and temperature for phases 1, 2, and 3 did not show any significant variation throughout the monitoring period. The microbiological parameter representing E. coli had a 3-log reduction from P1 (106) to P3 (103), which allows for reuse considering the WHO guidelines, mainly with the effluent turbidity achieved in phase 2 and 3, i.e., below 3 NTU, allowing the application of solar disinfection (SODIS) process [57,58].
4.4. GW Production
A comparison between the L PE−1 d−1 of GWL and GW in this study with the values in the literature shows that, in general, the values close to 20 and 50 L PE−1 d−1 do not include all GW components. The values from 60 to those exceeding 100 L PE−1 d−1 include the effluent from the kitchen sink and laundry. Therefore, if the project focuses on GWL, the value considered must be lower than what is recommended in the German guidelines (75 L PE−1 d−1).
The mean value of 39 L PE−1 d−1 (GWL) is similar to those from studies in Mali [45], South Africa [46], Palestine [44], and Jordan [47,48] which ranged between 20 and 50 L PE−1 d−1. The mean value of 60 L PE−1 d−1 (GW) is similar to those from studies in Vietnam [49], Israel [50], Nepal [30], Malaysia [51], and Costa Rica [52], which ranged from 72 to 225 L PE−1 d−1. However, the values determined by Hernandez Leal et al. [53] in the Netherlands ranged from 60 to 100 L PE−1 d−1, which were within the range of this study. These differing results are due to consumption habits. For example, in homes with solar heating, the shower runs until the water is heated [59]. Although the climatic condition is a factor that affects the performance of a CW, the GW production also depends on other factors, such as habits and social and economic issues.
In Brazil, Silva et al. [12] obtained similar values in a house with three residents; 60 and 35 L PE−1 d−1, with and without the kitchen component, respectively. Thus, for projects treating GW in CW, values of ~60 and ~35 L PE−1 d−1 for GW with and without the kitchen component, respectively, seem to be adequate and, therefore, is suggested for the design of CWs when data on water flows are not available.
4.5. Hydraulic and Organic Loadings
For the effective design and delivery of more compact and efficient treatment systems, the quantification of per capita generation is of upmost importance considering its direct influence on HLRs. A comparison between the operational parameters from the different phases in this study and those in the literature (Table 4) indicates that applying HLR up to 114–120 mm d−1 (for horizontal flow) and up to 200–233 and mm d−1 (for vertical flow); and OLR up to 97 gCOD m−2 d−1 (for horizontal flow, using fine gravel) and up to 60 gCOD m−2 d−1 (for vertical flow, using coarse sand) result in a better performance for the removal of COD, BOD, NTU, and NH4+ (Figure 2). These operational parameters can be used to scale CW, according to the Brazilian guidelines [37].
Several studies recommend that for HF-CW, the HLR for GW should be 60–80 mm d−1 [8,28,29]. An improved performance for the HF-CW was achieved with an HLR of ~100 mm d−1. It can therefore be suggested that, for CW projects with GW, HF-CW can receive 100 mm d−1 or 0.8–1.0 m2 PE−1 [29,52,60,61,62,63], while VF-CW can receive 200 mm d−1 or 0.4–0.6 m2 PE−1 [29,54,63]. For VF-CWs in warm climates, Hoffmann et al. [11] reported that an HLR of up to 200 mm d−1 in the pre-treated effluent could be applied without any negative impacts, with a short-term HLR of up to 500 mm d−1 applied during precipitation events. Shrestha et al. [30] and Jenssen [31] used an HLR of ~80 mm d−1, similar to phase 3 of this study, without the kitchen component.
Hoffman et al. [11] suggested an OLR of 16 gCOD m−2 d−1 for HF-CW in cold climates. In phases 1 and 2, the HF-CW operated with loads four to six times higher than those in an average temperature of ~20 °C. In warm climates, Ramprasad et al. [16] used 25 gCOD m−2 d−1, while Silva et al. [12] used 5–9 gCOD m−2 d−1 (only GWL), both with a HF-CW and a removal efficiency of ~80%. Therefore, we suggest that long term experiments should be conducted by applying an OLR of 70–90 gCOD m−2 d−1 to assess the process of clogging. In phase 1 and 2, the cross-sectional OLR was above 250 gBOD m−2 d−1, which is the maximum value recommended by Dotro et al. [2]. However, Paulo et al. [10] highlighted that using fine gravel instead of coarse sand with GW in warm climates prevents clogging problems, if pre-treatment is provided.
The organic loading rate for the VF-CW decreased from 60 gCOD m−2 d−1 (phase 1), to 16 gCOD m−2 d−1 (phase 2), to 9 gCOD m−2 d−1 (phase 3). In [11] a value of 60–70 gCOD m−2 d−1 is suggested for VF-CW in warm climates. In our study, the VF-CW obtained a COD removal of 90% and 85% with an OLR of 16 gCOD m−2 d−1 and 60 gCOD m−2 d−1, respectively. Therefore, an OLR up to 60–70 gCOD m−2 d−1 can be recommended, mainly for VF-CW as post-treatment of HF-CW in a multistage system.
4.6. Multivariate Analysis
The results obtained by multivariate analysis, including correlation analysis, PCA, and cluster analysis, supported the observations of basic and descriptive statistics.
The values of the hydraulic parameters decreased as the component of the kitchen sink was removed (phase 3) and the number of people in the house decreased (from phase 1 to phase 2). The removal of COD based on the applied OLR followed this drop, demonstrating the capacity of the multistage system to cope with high loads. Evaluating the effect of removing the component from the kitchen sink (GWL) over time indicates that HLR, OLR (COD), and the ammonia concentration, were the most representative for the performance of the studied system.
Although the only parameter that showed a difference between GW with and without the kitchen sink component in the ANOVA and Tukey’s test was the BOD, there was a significant difference between GW with (GW) or without (GWL) the kitchen sink components in the cluster analysis, when all the grouped characteristics were evaluated, indicating that there is a significant difference in quali-quantitative characteristics among them. Therefore, it is appropriate to consider these aspects in the design and O&M of future projects to improve the technological performance and to increase the chance of acceptance by the user.
4.7. O&M Considerations
Avoiding the kitchen GW component can be advantageous, as this decreases O&M, making the process more manageable by the householders. Few studies have detailed the aspects of O&M in warm climates. In a study by Alderlieste and Langeveld [45], the grease trap needed to be cleaned frequently and, thus, adaptations were required. Although Werner et al. [63] treated only bath GW, it was necessary to ensure periodic maintenance as they used a grease trap instead of a sedimentation tank, and opted for a VF-CW before a HF-CW system. This kind of information is essential for designing and operating constructed wetlands treating GW, being essential to be presented in the studies when available. The German CW standard [25], which also covers GW and small systems, suggests that it is necessary to self-manage operational requirements such as malfunctions (hydraulic, mechanical, and electrical), which must be indicated acoustically and/or visually with an alarm system and be independent of the power network. Maintenance checks must also be conducted regularly (monthly) to ensure proper functioning of the pre-treatment, pump shaft, influent structure, air pumps, and effluent structure. Measurements of the sludge level in the pre-treatment and sufficient re-aeration of the filter should be carried out to prevent clogging. Moreover, measurement or records of the flow should be obtained, the water on/in the filter should be evenly distributed, and invasive plant species and weeds should be removed. At the household level, where the user is usually an operator, it is beneficial to separate the fraction of the kitchen sink such that less maintenance is required.
For the successful implementation of a full-scale project, it is important to ensure that users take the responsibility of periodic (ideally monthly) maintenance of the grease trap and sedimentation tank on the household scale to avoid clogging, especially if the kitchen component is included. Otherwise, the use of a CW is not feasible at this scale [64].
5. Conclusions
In this study, a real scale multistage constructed wetland system was applied for the household treatment of greywater. The four years monitoring period showed relevant difference when treating all fractions of greywater (GW) as compared to light greywater, when excluding the kitchen fraction (GWL). There is a significant difference in characteristics (quali-quantitative) when there is no kitchen sink (GWL) component. The only advantage observed with GW was that the COD:BOD ratio is more adequate to biological treatment, showing a better performance regarding organic loading removal. Nevertheless, it requires the multistage system (both horizontal and vertical flow units) to achieve the same quality the horizontal flow unit achieve alone when treating GWL. Further advantages for separating the kitchen fraction are the requirement of smaller area and substantial reduction in maintenance that can improve the likelihood of system acceptance by the householders.
Our findings suggest that, to achieve better performance, an HF-CW can be loaded up to 114 mm per day (0.8 m2 per person) and the VF-CW up to 233 mm per day (0.5 m2 per person). When the kitchen sink component is included, these values increase by up to 4-fold at certain times of the day and week (peak-flow).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.J.C.M.F. and P.L.P.; methodology, F.J.C.M.F., J.C.M.d.S.F., and P.L.P.; formal analysis, F.J.C.M.F. and P.L.P.; investigation, F.J.C.M.F., J.C.M.d.S.F., and P.L.P.; resources, P.L.P.; data curation, F.J.C.M.F., J.C.M.d.S.F., and P.L.P.; writing—original draft preparation, F.J.C.M.F. and P.L.P.; writing—review and editing, F.J.C.M.F. and P.L.P.; supervision, P.L.P.; project administration, P.L.P.; funding acquisition, P.L.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by International Foundation for Science (IFS, Sweden), grant number W/4130-1, Brazilian National Council of Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), Brazilian National Council for the Improvement of Higher Education (CAPES)—Brazil—Finance Code 001 and The APC was funded by Fundação Universidade Federal de Mato Grosso do Sul—UFMS/MEC—Brazil.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Masi, F.; El Hamouri, B.; Abdel Shafi, H.; Baban, A.; Ghrabi, A.; Regelsberger, M. Treatment of segregated black/grey domestic wastewater using constructed wetlands in the Mediterranean basin: The zero-m experience. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dotro, G.; Langergraber, G.; Molle, P.; Nivala, J.; Puigagut, J.; Stein, O.; von Sperling, M. Treatment Wetlands; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2017; Volume 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Randerson, P.F. Constructed wetlands and vegetation filters: An ecological approach to wastewater treatment. Environ. Biotechnol. 2006, 2, 78–89. [Google Scholar]
- Vymazal, J. Constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: Five decades of experience. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadlec, R.H.; Wallace, S.D. Treatment Wetlands, 2nd ed.; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Vymazal, J. Constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment. Water 2010, 2, 530–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otterpohl, R. Black, brown, yellow, grey-the new colors of sanitation. Water 2001, 21, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Morel, A.; Diener, S. Greywater Management in Low and Middle-Income Countries, Review of Different Treatment Systems for Households or Neighbourhoods; Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag): Dübendorf, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Paulo, P.L.; Boncz, M.A.; Asmus, A.; Jonsson, H.; Ide, C.N. Greywater Treatment in Constructed Wetland at Household Level. Gewasserschutz Wasser Abwasser 2007, 206, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Paulo, P.L.; Begosso, L.; Pansonato, N.; Shrestha, R.R.; Boncz, M.A. Design and configuration criteria for wetland systems treating greywater. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 2001–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, H.C.; Platzer, M.; Winker, E.; von Muench, E. Technology Review of Constructed Wetlands; Deutsche Gesellschaft fur Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH: Eschborn, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, J.B.; Oliveira, P.J.A.; Boncz, M.A.; Paulo, P.L. A modified constructed wetland system for greywater treatment. Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 91, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rengers, E.E.; Silva, J.B.; Paulo, P.L.; Janzen, J.G. Hydraulic performance of a modified constructed wetland system through a CFD-based approach. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2016, 12, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães Filho, F.J.C.M.; Sobrinho, T.A.; Steffen, J.L.; Arias, C.A.; Paulo, P.L. Hydraulic and hydrological aspects of an evapotranspiration-constructed wetland combined system for household greywater treatment. J. Environ. Sci. Heal. Part A 2018, 53, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raude, J.M.; Mutua, B.M.; Kamau, D.N. Simulation of the Hydraulics and Treatment Performance of Horizontal Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetland Treating Greywater. Int. J. Ecotoxicol. Ecobiol. 2018, 3, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramprasad, C.; Smith, C.S.; Memon, F.A.; Philip, L. Removal of chemical and microbial contaminants from greywater using a novel constructed wetland: GROW. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 106, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Oliveira, M.; Atalla, A.A.; Frihling, B.E.F.; Cavalheri, P.S.; Migliolo, L.; Magalhães Filho, F.J.C. Ibuprofen and caffeine removal in vertical flow and free-floating macrophyte constructed wetlands with Heliconia rostrata and Eichornia crassipes. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 373, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lv, T.; Carvalho, P.N.; Zhang, L.; Arias, C.A.; Chen, Z.; Brix, H. Ibuprofen and iohexol removal in saturated constructed wetland mesocosms. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 98, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramprasad, C.; Philip, L. Surfactants and personal care products removal in pilot scale horizontal and vertical flow constructed wetlands while treating greywater. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, F.; Ehrampoush, M.H.; Eslami, H.; Ghaneian, M.T.; Fallahzadeh, H.; Talebi, P.; Fard, R.F.; Ebrahimi, A.A. Removal of linear alkylbenzene sulfonate and turbidity from greywater by a hybrid multi-layer slow sand filter microfiltration ultrafiltration system. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 211, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arden, S.; Ma, X. Constructed wetlands for greywater recycle and reuse: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comino, E.; Riggio, V.; Rosso, M. Grey water treated by an hybrid constructed wetland pilot plant under several stress conditions. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 53, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolde, E. Greywater reuse systems for toilet flushing in multi-storey buildings—Over ten years experience in Berlin. Urban Water 1999, 1, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolde, E. Greywater recycling systems in Germany-results, experiences and guidelines. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 51, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DWA. Standard DWA-A 262E: Principles for Dimensioning, Construction and Operation of Wastewater Treatment Plants with Planted and Unplanted Filters for Treatment of Domestic and Municipal Wastewater; German Association for Water, Wastewater and Waste (DWA): Hennef, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nivala, J.; van Afferden, M.; Hasselbach, R.; Langergraber, G.; Molle, P.; Rustige, H.; Nowak, J. The new German standard on constructed wetland systems for treatment of domestic and municipal wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 2414–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boano, F.; Caruso, A.; Costamagna, E.; Ridolfi, L.; Fiore, S.; Demichelis, F.; Galvão, N.; Pisoeiro, J.; Rizzo, A.; Masi, F. A review of nature-based solutions for greywater treatment: Applications, hydraulic design, and environmental benefits. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 2019, 134731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, A. Constructed wetlands in water pollution control: Fundamentals to their understanding. Water Sci. Technol. 1995, 32, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridderstolpe, P. Introduction to Greywater Management; Report. 2004-4; Stockholm Environment Institute: Stockholm, Sweden, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, R.R.; Haberl, R.; Laber, J.; Manandhar, R.; Mader, J. Application of constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment in Nepal. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 44, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenssen, P.D. An Urban Ecological Sanitation Pilot Study in Humid Tropical Climate; Report No. UEMS_TEC_02_47; Natural Resources and Environmental Board Sarawak: Sarawak, Malaysia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Ding, A.; Zheng, L.; Anderson, B.C.; Kong, L.; Wu, A.; Xing, L. Relationship between design parameters and removal efficiency for constructed wetlands in China. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 123, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, W.H.; Jung, Y.; Park, J.W.; Lee, S.; Maeng, S.K. Effects of hydraulic loading rate and organic load on the performance of a pilot-scale hybrid VF-HF constructed wetland in treating secondary effluent. Chemosphere 2019, 218, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nivala, J.; Boog, J.; Headley, T.; Aubron, T.; Wallace, S.; Brix, H.; Mothes, S.; van Afferden, M.; Müller, R.A. Side-by-side comparison of 15 pilot-scale conventional and intensified subsurface flow wetlands for treatment of domestic wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 1500–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, A.I.; Beretta, M.; Fragoso, R.; Duarte, E. Overview of the state of the art of constructed wetlands for decentralized wastewater management in Brazil. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 187, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Dominguez, M.A.; Konnerup, D.; Brix, H.; Arias, C.A. Constructed Wetlands in Latin America and the Caribbean: A Review of Experiences during the Last Decade. Water 2020, 12, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Sperling, M.; Sezerino, P.H. Dimensionamento de Wetlands Construídos No Brasil. Boletim Wetlands Brasil, Edição Especial, dezembro/2018. p. 65, ISSN 2359-0548. Available online: https://gesad.ufsc.br/boletins/ (accessed on 7 July 2021).
- Rousseau, D.P.L.; Vanrolleghem, P.A.; de Pauw, N. Model-based design of horizontal subsurface flow constructed treatment wetlands: A review. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1484–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platzer, C.; Hoffmann, H.; Cardia, W. O wetland como componente de ecosan—Experiências com o uso e dimensionamento no clima subtropical. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Sustainable Sanitation: Food and Water Security for Latin America, Fortaleza, Brazil, 26–28 November 2007. [Google Scholar]
- von Sperling, M.; Verbyla, M.E.; Oliveira, S.M.A.C. Assessment of Treatment Plant Performance and Water Quality Data: A Guide for Students, Researchers and Practitioners; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA; AWWA; WPCF. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; p. 953. [Google Scholar]
- de Souza Pereira, M.A.; Cavalheri, P.S.; de Oliveira, M.Â.C.; Filho, F.J.C.M. A multivariate statistical approach to the integration of different land-uses, seasons, and water quality as water resources management tool. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atalla, A.; Pelissari, C.; de Oliveira, M.; de Souza Pereira, M.A.; Cavalheri, P.S.; Sezerino, P.H.; Filho, F.J.C.M. Influence of earthworm presence and hydraulic loading rate on the performance of vertical flow constructed wetlands. Environ. Technol. 2019, 2019, 1710572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnat, J.M.Y.; Mahmoud, N. Evaluation of On-Site Gray Wastewater Treatment Plants Performance in Bilien and Biet-Diko Villages/Palestine; Environment Protection Committee (EPC): Tripoli, Lebanon, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Alderlieste, M.C.; Langeveld, J.G. Wastewater planning in Djenné, Mali. A pilot project for the local infiltration of domestic wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 51, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adendorff, J.; Stimie, C. Food from used water—Making the previously impossible happen. In The Water Whell; South African Water Research Commission (WRC): Gezina, South Africa, 2005; Volume 3, pp. 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Faruqui, N.; Al-Jayyousi, O. Greywater reuse in urban agriculture for poverty alleviation—A case study in Jordan. Water Int. 2002, 27, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jayyousi, O.R. Greywater reuse: Towards sustainable water management. Desalination 2003, 156, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busser, S. Studies on Domestic Wastewater Flows in Urban and Peri-Urban Hanoi. Semester Work Thesis, ETH Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Friedler, E. Quality of individual domestic greywater streams and its implication for onsite treatment and reuse possibilities. Environ. Technol. 2004, 25, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C. Ecological Sanitation Greywater Demonstration Project at Hui Sing Garden, Kuching, Sarawak, Malaysia; Urban Environmental Management System (UEMS) Project Natural Resources and Environment Board (NREB): Sarawak, Malaysia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Dallas, S.; Ho, G. Subsurface flow reedbeds using alternative media for the treatment of domestic greywater in Monteverde, Costa Rica, Central America. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 52, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez Leal, L.; Zeeman, G.; Temmink, H.; Buisman, C. Characterisation and biological treatment of greywater. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 56, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harindra Corea, E.J. Appropriate Disposal of Sewage in Urban and Suburban Sri Lanka. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Leeds, Leeds, UK, 2001; p. 270. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.W.K.; Otterpohl, R. Review of the technological approaches for grey water treatment and reuses. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3439–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, A.; Shmueli, O.; Ronen, Z.; Raveh, E. Recycled vertical flow constructed wetland (RVFCW)-a novel method of recycling greywater for irrigation in small communities and households. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Health Guidelines for the Use of Wastewater in Agriculture and Aquaculture; Report of a WHO Scientific Group; WHO Technical Report Series, No. 778; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- EAWAG/SANDEC. Solar Water Disinfection: A Guide for the Application of Sodis; SANDEC: Dübendorf, Switzerland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves, R.F.; Keller, R.P.; Franci, T.K. Comparative analysis of greywater reuse practices in German and Brazilian urban buildings. Rev. DAE 2019, 217, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crites, R.; Tchobanoglous, G. Small and decentralized wastewater management systems. In Water Resources and Environmental Engineering, 1st ed.; WCB/McGraw-Hill: Boston, MA, USA, 1998; p. 1084. [Google Scholar]
- Kadlec, R.H.; Knight, R.L. Treatment Wetlands; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996; p. 893. [Google Scholar]
- Sasse, L. DEWATS—Decentralised Wastewater Treatment in Developing Countries; BORDA: Bremen, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, C.; Klingel, F.; Bracken, P.; Schlick, J.; Freese, T.; Rong, W. Kurzbericht ecosan Projekt—Koulikoro, Mali; Deutsche Gesellschaft für Technische Zusam-Menarbeit (GTZ): Eschborn, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Paulo, P.L.; Azevedo, C.; Begosso, L.; Galbiati, A.F.; Boncz, M.A. Natural systems treating greywater and blackwater on-site: Integrating treatment, reuse and landscaping. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 50, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).