Elastomeric Composites Containing SBR Industrial Scraps Devulcanized by Microwaves: Raw Material, Not a Trash
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. SBR-r Devulcanization by Microwaves and Gel Content Determination
2.2.2. Preparation of the Composites Containing SBR-r
2.2.3. Vulcanization Characteristics of the Composites
2.2.4. Characterization of the Composites
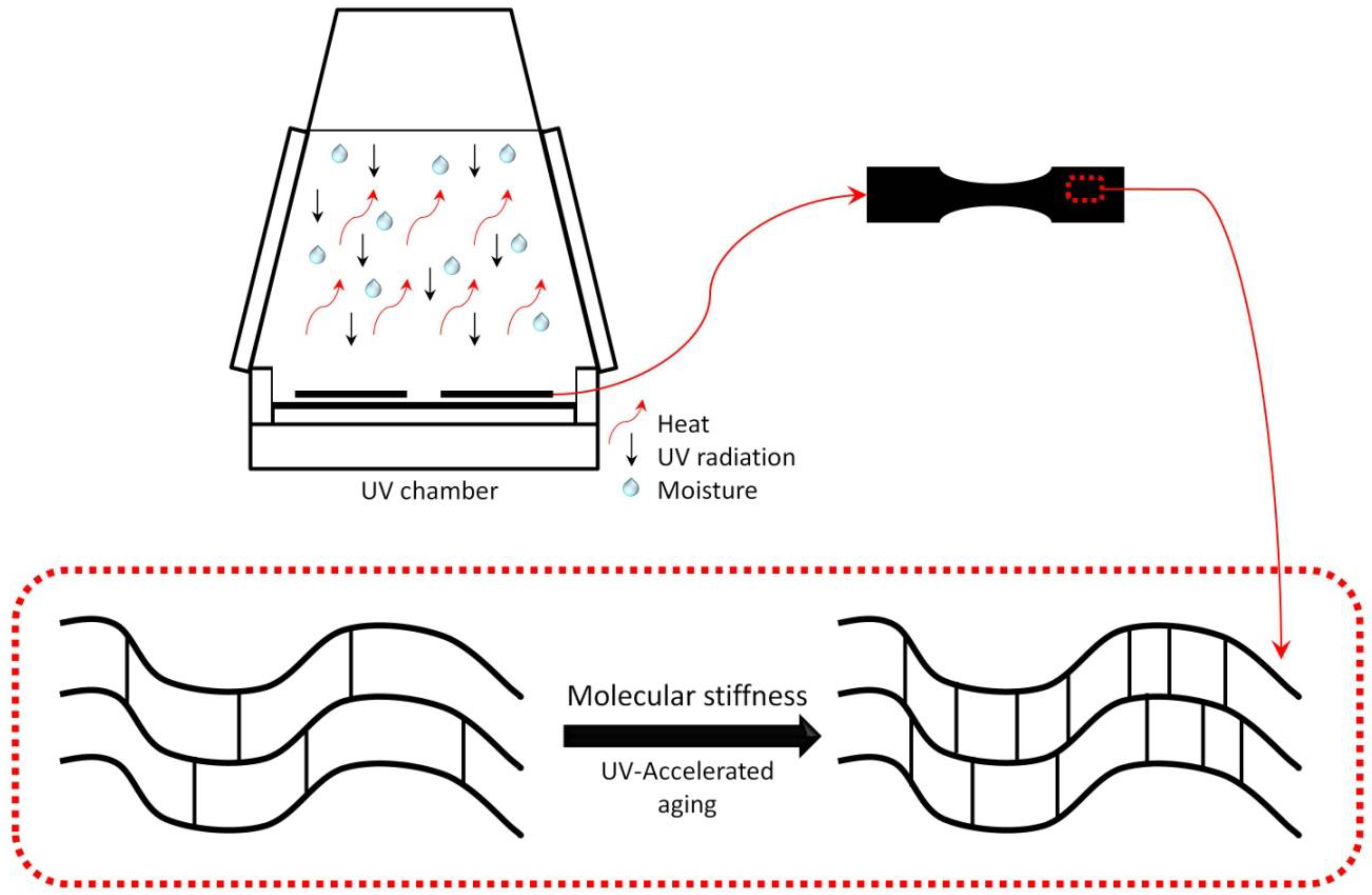
2.2.5. Accelerated Aging Tests
3. Results and Discussion
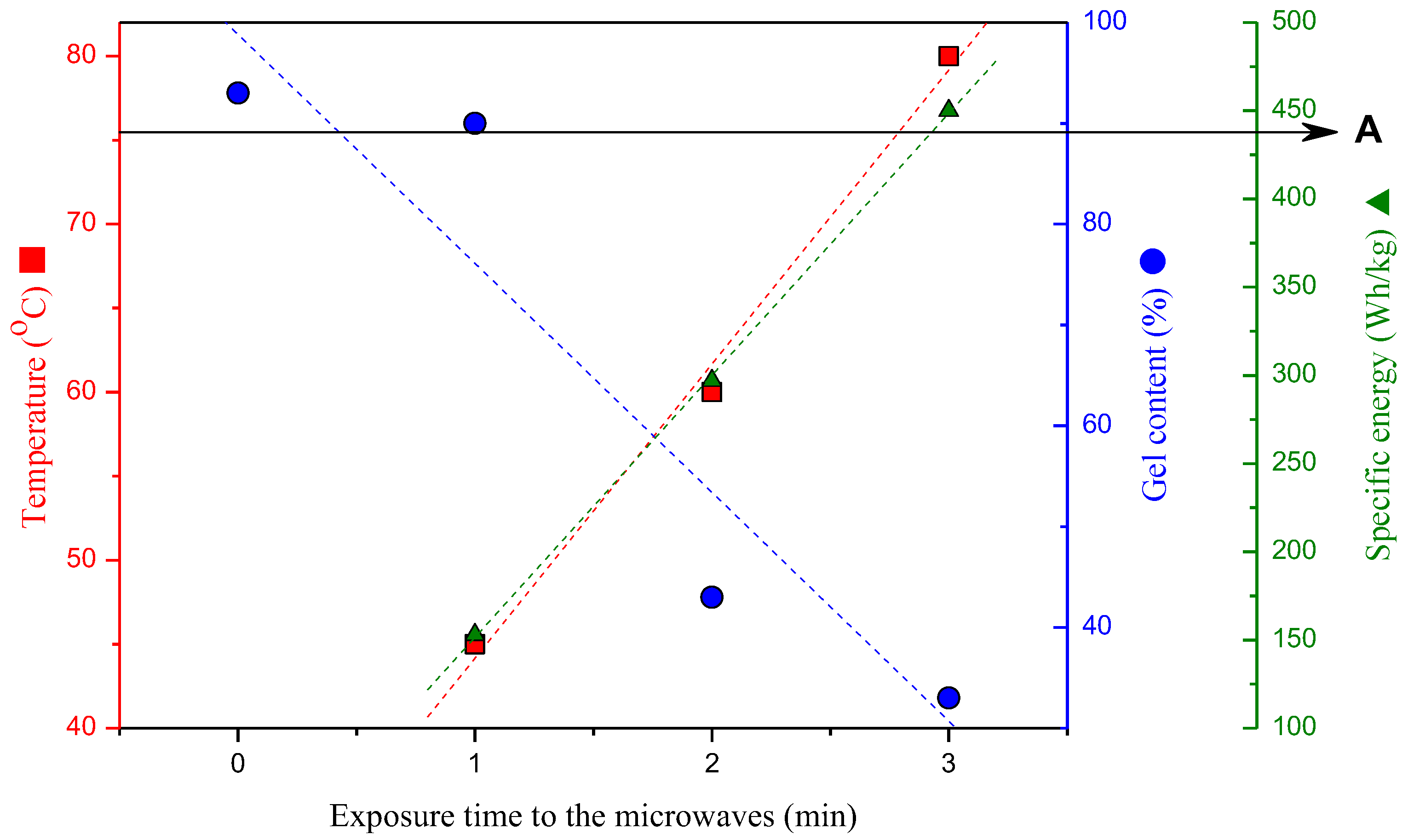
3.1. SBR-r Devulcanization
3.2. Vulcanization Characteristics
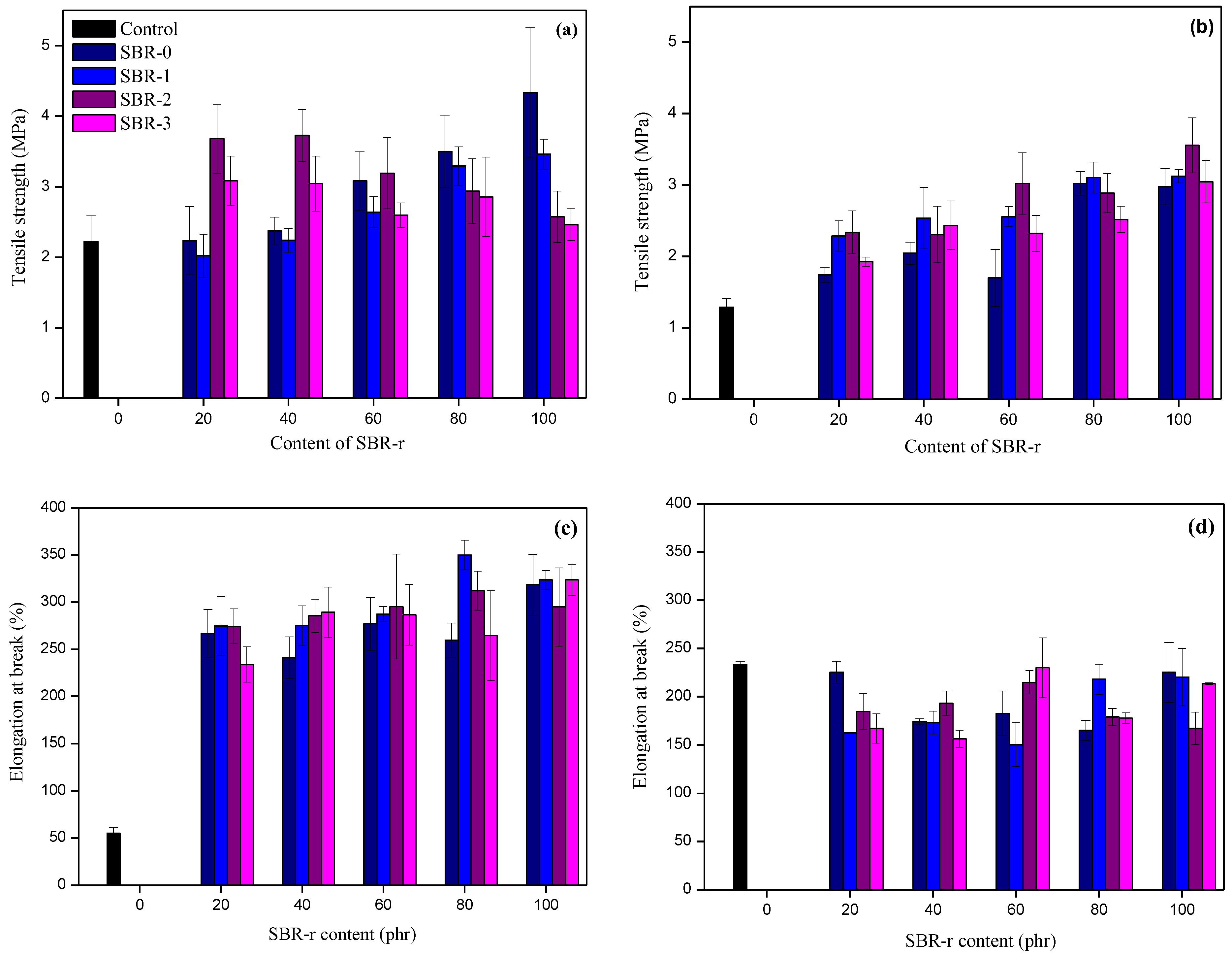
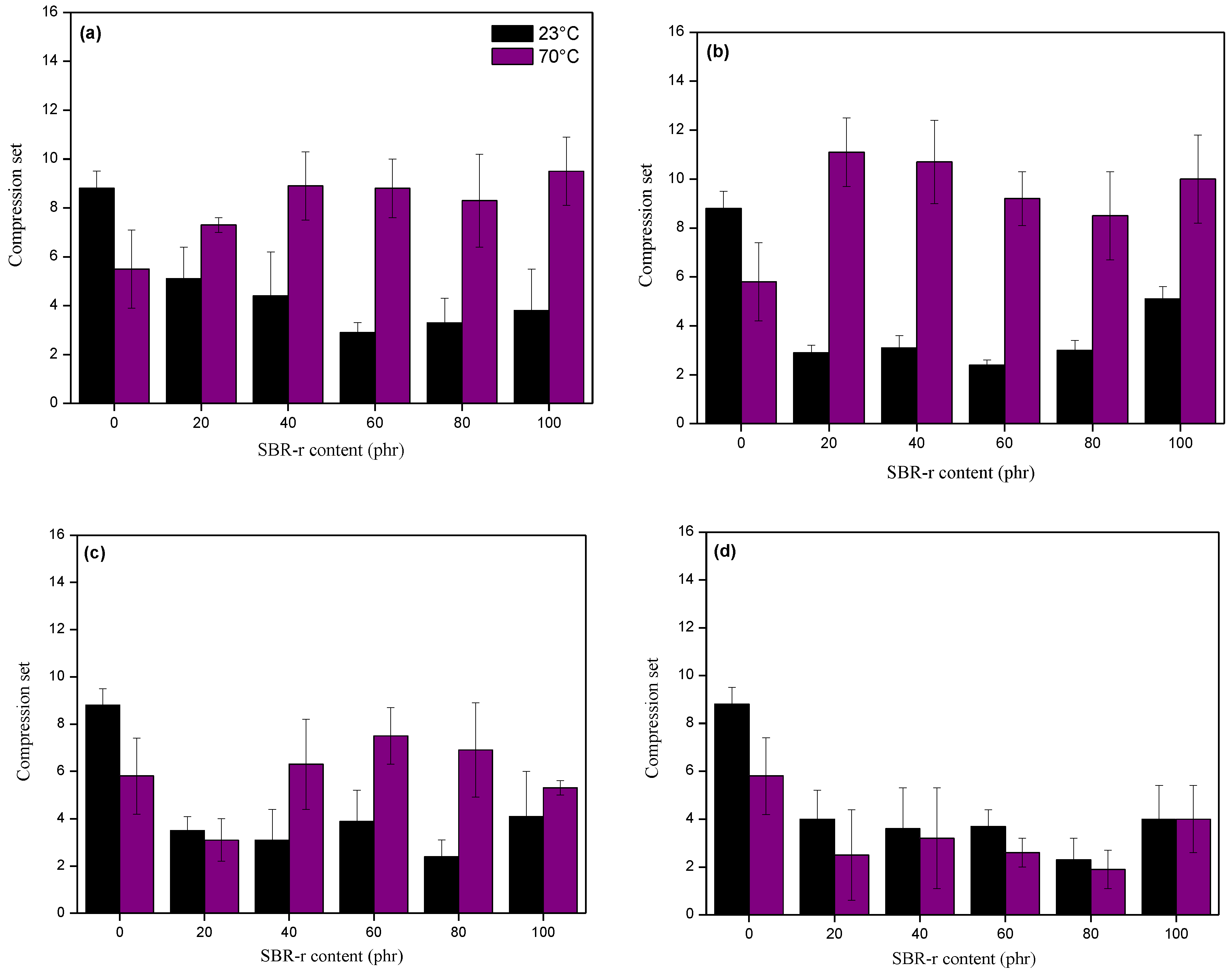
3.3. Characterization of the SBR-r Composites
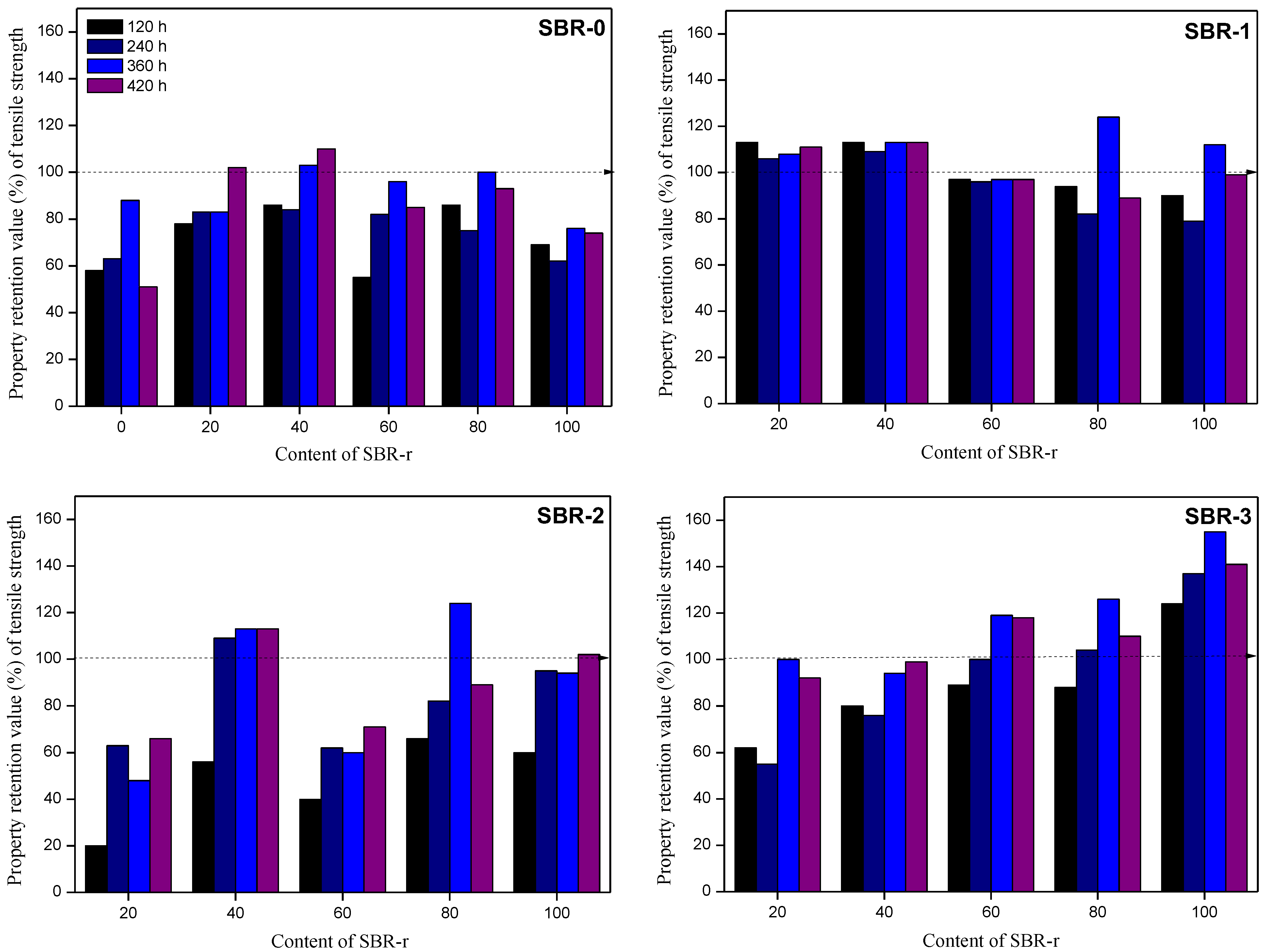
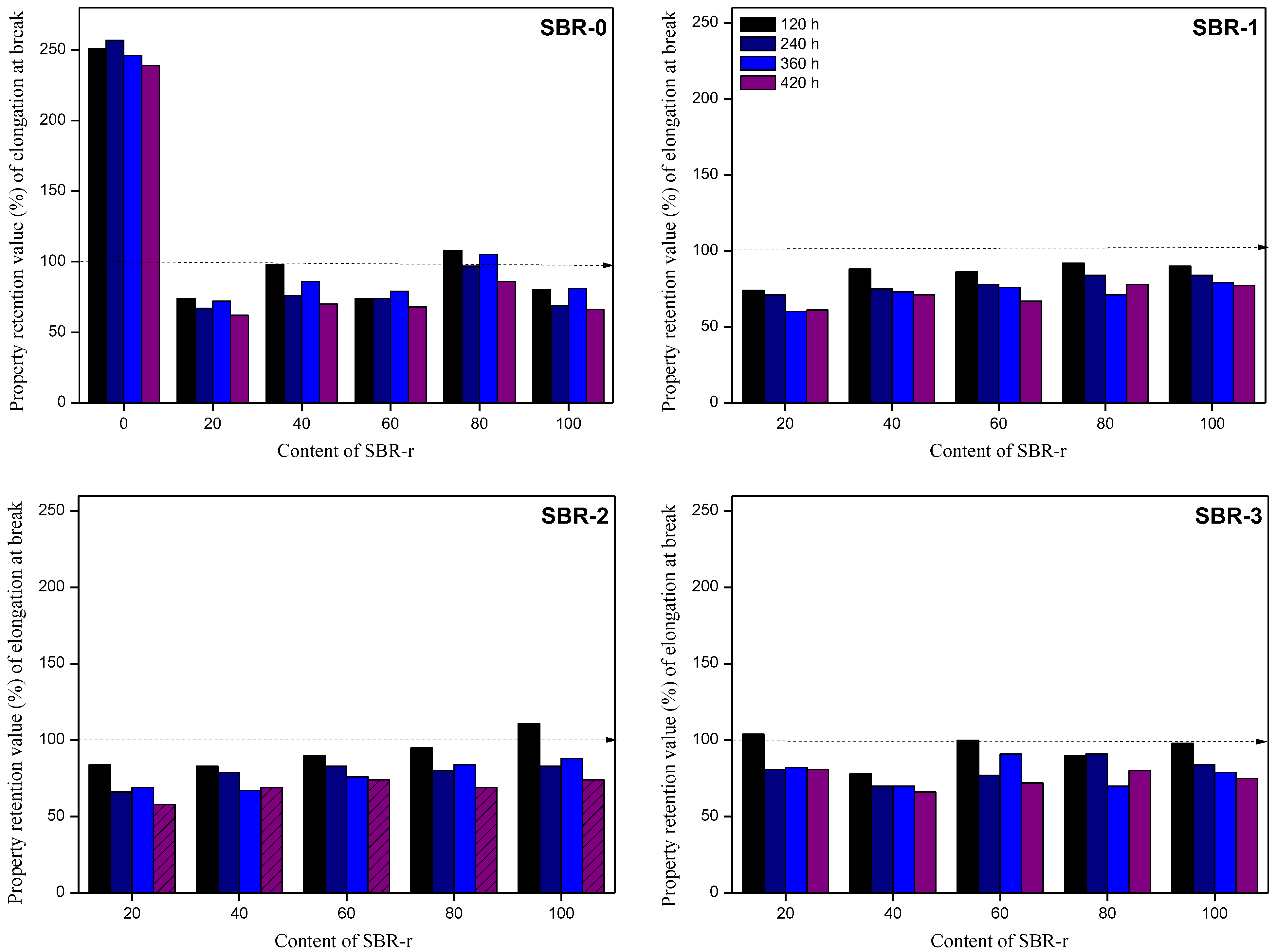
3.4. Accelerated Aging in a UV Chamber
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Sousa, F.D.B. Vulcanization of natural rubber: Past, present and future perspectives. In Natural Rubber: Properties, Behavior and Applications; Hamilton, J.L., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 47–88. ISBN 978-1-63485-454-2. [Google Scholar]
- Adhikari, B.; De, D.; Maiti, S. Reclamation and recycling of waste rubber. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2000, 25, 909–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreeja, T.D.; Kutty, S.K.N. Cure characteristics and mechanical properties of short nylon fiber reinforced natural rubber–reclaimed rubber blends. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2003, 42, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, F.D.B.; Zanchet, A.; Scuracchio, C.H. Influence of reversion in compounds containing recycled natural rubber: In search of sustainable processing. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, D.; Saron, C. Chemical modifications in styrene-butadiene rubber after microwave devulcanization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 3975–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, D.; Scuracchio, C.H.; Saron, C. Microwave devulcanization of SBR containing carbon black. J. Res. Updat. Polym. Sci. 2016, 5, 52–59. [Google Scholar]
- Scuracchio, C.H.; Waki, D.A.; da Silva, M.L.C.P. Thermal analysis of ground tire rubber devulcanized by microwaves. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2007, 87, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibala, D.; Hamed, G.R. Cure and mechanical behavior of rubber compounds containing ground vulcanizates. Part I-Cure behavior. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1994, 67, 636–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formela, K.; Hejna, A.; Zedler, Ł.; Colom, X.; Cañavate, J. Microwave treatment in waste rubber recycling–recent advances and limitations. Express Polym. Lett. 2019, 13, 565–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockstal, L.; Berchem, T.; Schmetz, Q.; Richel, A. Devulcanisation and reclaiming of tires and rubber by physical and chemical processes: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, F.D.B.; Scuracchio, C.H. The role of carbon black on devulcanization of natural rubber by microwaves. Mater. Res. J. Mater. 2015, 18, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, S.K. Re-use of ground rubber waste - A review. Prog. Rubber Plast. Technol. 2001, 17, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, A.M.; Madhusoodanan, K.N.; Alex, R.; George, B. Incorporation of devulcanised rubber in fresh rubber compounds: Impact of filler correction on vulcanisate properties. Prog. Rubber Plast. Recycl. Technol. 2017, 33, 281–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanchet, A.; Bandeira Dotta, A.; de Sousa, F.D.B. Relationship among vulcanization, mechanical properties and morphology of blends containing recycled EPDM. Recycling 2017, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanchet, A.; Dal’Acqua, N.; Weber, T.; Crespo, J.S.; Brandalise, R.N.; Nunes, R.C.R. Propriedades reométricas e mecânicas e morfologia de compósitos desenvolvidos com resíduos elastoméricos vulcanizados. Polim. E Tecnol. 2007, 17, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanchet, A.; Masiero, A.; de Sousa, F.D.B.; Brandalise, R.N. The influence of UV-accelerated aging process on industrial waste containing EPDM. Recycling 2019, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, F.D.B.; Scuracchio, C.H.; Hu, G.H.; Hoppe, S. Effects of processing parameters on the properties of microwave-devulcanized ground tire rubber/polyethylene dynamically revulcanized blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, F.D.B.; Gouveia, J.R.; De Camargo Filho, P.M.F.; Vidotti, S.E.; Scuracchio, C.H.; Amurin, L.G.; Valera, T.S. Blends of ground tire rubber devulcanized by microwaves/HDPE—Part A: Influence of devulcanization process. Polim. E Tecnol. 2015, 25, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, F.D.B.; Gouveia, J.R.; de Camargo Filho, P.M.F.; Vidotti, S.E.; Scuracchio, C.H.; Amurin, L.G.; Valera, T.S. Blends of ground tire rubber devulcanized by microwaves/HDPE-Part B: Influence of clay addition. Polim. E Tecnol. 2015, 25, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanchet, A.; Carli, L.N.; Giovanela, M.; Brandalise, R.N.; Crespo, J.S. Use of styrene butadiene rubber industrial waste devulcanized by microwave in rubber composites for automotive application. Mater. Des. 2012, 39, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scuracchio, C.H.; Bretas, R.E.S.; Isayev, A.I. Blends of PS with SBR devulcanized by ultrasound: Rheology and morphology. J. Elastomers Plast. 2004, 36, 45–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, D.Á.; Pirityi, D.; Tamás-Bényei, P.; Bárány, T. Microwave devulcanization of ground tire rubber and applicability in SBR compounds. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, F.D.B.; Zanchet, A.; Marczynski, E.S.; Pistor, V.; Fiorio, R.; Crespo, J.S. Devulcanized EPDM without paraffinic oil in the production of blends as a potential application of the residues from automobile industry. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2019, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, T.; Zanchet, A.; Crespo, J.S.; Oliveira, M.G.; Suarez, J.C.M.; Nunes, R.C.R. Caracterização de artefatos elastoméricos obtidos por revulcanização de resíduo industrial de SBR(copolímero de butadieno e estireno). Polim. E Tecnol. 2011, 21, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carli, L.N.; Boniatti, R.; Teixeira, C.E.; Nunes, R.C.R.; Crespo, J.S. Development and characterization of composites with ground elastomeric vulcanized scraps as filler. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seghar, S.; Ait Hocine, N.; Mittal, V.; Azem, S.; Al-Zohbi, F.; Schmaltz, B.; Poirot, N. Devulcanization of styrene butadiene rubber by microwave energy: Effect of the presence of ionic liquid. Express Polym. Lett. 2015, 9, 1076–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, F.D.B.; Scuracchio, C.H. Vulcanization behavior of NBR with organically modified clay. J. Elastomers Plast. 2012, 44, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, F.D.B.; Scuracchio, C.H.; Hu, G.H.; Hoppe, S. Devulcanization of waste tire rubber by microwaves. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 138, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanchet, A.; Carli, L.N.; Giovanela, M.; Crespo, J.S.; Scuracchio, C.H.; Nunes, R.C.R. Characterization of microwave-devulcanized composites of ground SBR scraps. J. Elastomers Plast. 2009, 41, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carli, L.N.; Bianchi, O.; Mauler, R.S.; Crespo, J.S. Crosslinking kinetics of SBR composites containing vulcanized ground scraps as filler. Polym. Bull. 2011, 67, 1621–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, P.A.; Kutty, S.K.N. Cure characteristics and mechanical properties of butadiene rubber/whole tyre reclaimed rubber blends. Prog. Rubber Plast. Recycl. Technol. 2002, 18, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, F.D.B.; Zanchet, A.; Scuracchio, C.H. From devulcanization to revulcanization: Challenges in getting recycled tire rubber for technical applications. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 8755–8765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, F.D.B.; Zanchet, A.; Ornaghi Júnior, H.L.; Ornaghi, F.G. Revulcanization kinetics of waste tire rubber devulcanized by microwaves: Challenges in getting recycled tire rubber for technical application. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 15413–15426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.S.; Isayev, A.I. Continuous ultrasonic devulcanization of unfilled butadiene rubber. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 93, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.S.; Ghose, S.; Isayev, A.I. Effects of ultrasonic treatment on unfilled butadiene rubber. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2003, 41, 2959–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, H.; Ishak, S.; Hamid, Z.A.A. Effect of blend ratio on cure characteristics, tensile properties, thermal and swelling properties of mica-filled (ethylene-propylene-diene monomer)/(recycled ethylene-propylene-diene monomer) (EPDM/r-EPDM) blends. J. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 2015, 21, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, G.R.; Zhao, J. Tensile behavior after oxidative aging of gum and black-filled vulcanizates of SBR and NR. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1999, 72, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-S.; Han, D.-H. Comparison of recovery behaviors of thermally aged SBR composite from compressed and circular deformations. Thermochim. Acta 2009, 490, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Gao, J. Aging of ethylene–propylene–diene monomer (EPDM) in artificial weathering environment. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2007, 92, 1841–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, T.M.; Kumaran, M.G.; Unnikrishnan, G.; Kunchandy, S. Ageing studies of ethylene propylene diene monomer rubber/styrene butadiene rubber blends: Effects of heat, ozone, gamma radiation, and water. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 107, 2923–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compound | Sample | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | 20 SBR-r | 40 SBR-r | 60 SBR-r | 80 SBR-r | 100 SBR-r | |
| SBR-1502 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| SBR-r | - | 20 | 40 | 60 | 80 | 100 |
| ZnO | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 |
| Stearic acid | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| TBBS | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Sulfur | 1.75 | 1.75 | 1.75 | 1.75 | 1.75 | 1.75 |
| Sample | MH (dN.m) | ML (dN.m) | ∆M (dN.m) | ts1 (min) | t90 (min) | CRI (min−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | 24.6 | 4.9 | 19.7 | 12.4 | 22.5 | 0.10 |
| 20 SBR-0 | 23.9 | 5.9 | 18.0 | 6.9 | 13.0 | 0.16 |
| 40 SBR-0 | 17.7 | 5.4 | 12.3 | 5.7 | 10.0 | 0.23 |
| 60 SBR-0 | 23.0 | 7.2 | 15.8 | 4.6 | 9.5 | 0.20 |
| 80 SBR-0 | 19.6 | 6.4 | 13.2 | 5.7 | 7.0 | 0.77 |
| 100 SBR-0 | 11.2 | 5.8 | 5.4 | 4.3 | 6.3 | 0.50 |
| 20 SBR-1 | 24.5 | 5.3 | 19.2 | 4.9 | 6.5 | 0.63 |
| 40 SBR-1 | 26.4 | 5.8 | 20.6 | 5.4 | 9.1 | 0.27 |
| 60 SBR-1 | 22.8 | 6.3 | 16.5 | 3.4 | 8.4 | 0.20 |
| 80 SBR-1 | 22.0 | 6.8 | 15.2 | 3.9 | 7.3 | 0.29 |
| 100 SBR-1 | 21.9 | 7.4 | 14.5 | 2.7 | 7.2 | 0.22 |
| 20 SBR-2 | 22.7 | 5.1 | 17.6 | 6.7 | 14.4 | 0.13 |
| 40 SBR-2 | 23.0 | 5.3 | 17.7 | 4.6 | 10.2 | 0.18 |
| 60 SBR-2 | 23.4 | 5.6 | 17.8 | 3.6 | 7.3 | 0.27 |
| 80 SBR-2 | 22.9 | 6.6 | 16.3 | 3.0 | 6.5 | 0.29 |
| 100 SBR-2 | 21.7 | 7.2 | 14.5 | 2.6 | 6.0 | 0.29 |
| 20 SBR-3 | 21.5 | 5.2 | 16.3 | 6.7 | 13.3 | 0.15 |
| 40 SBR-3 | 17.0 | 4.5 | 12.5 | 5.1 | 9.0 | 0.26 |
| 60 SBR-3 | 18.8 | 4.9 | 13.9 | 4.5 | 8.5 | 0.25 |
| 80 SBR-3 | 19.1 | 5.7 | 13.4 | 3.4 | 6.5 | 0.32 |
| 100 SBR-3 | 21.0 | 6.6 | 14.4 | 2.8 | 6.1 | 0.30 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zanchet, A.; de Sousa, F.D.B. Elastomeric Composites Containing SBR Industrial Scraps Devulcanized by Microwaves: Raw Material, Not a Trash. Recycling 2020, 5, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling5010003
Zanchet A, de Sousa FDB. Elastomeric Composites Containing SBR Industrial Scraps Devulcanized by Microwaves: Raw Material, Not a Trash. Recycling. 2020; 5(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling5010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleZanchet, Aline, and Fabiula Danielli Bastos de Sousa. 2020. "Elastomeric Composites Containing SBR Industrial Scraps Devulcanized by Microwaves: Raw Material, Not a Trash" Recycling 5, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling5010003
APA StyleZanchet, A., & de Sousa, F. D. B. (2020). Elastomeric Composites Containing SBR Industrial Scraps Devulcanized by Microwaves: Raw Material, Not a Trash. Recycling, 5(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling5010003





