Estimation of Phenolic and Flavonoid Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Spent Coffee and Black Tea (Processing) Waste for Potential Recovery and Reuse in Sudan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection and Preparation of Coffee and Black Tea Samples
2.2. Preparation of Extracts
2.3. Determination of Total Phenolic Content
2.4. Determination of Total Polyphenols
2.5. Determination of Total Flavonoids Content
2.6. Determination of Antioxidant Activity
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
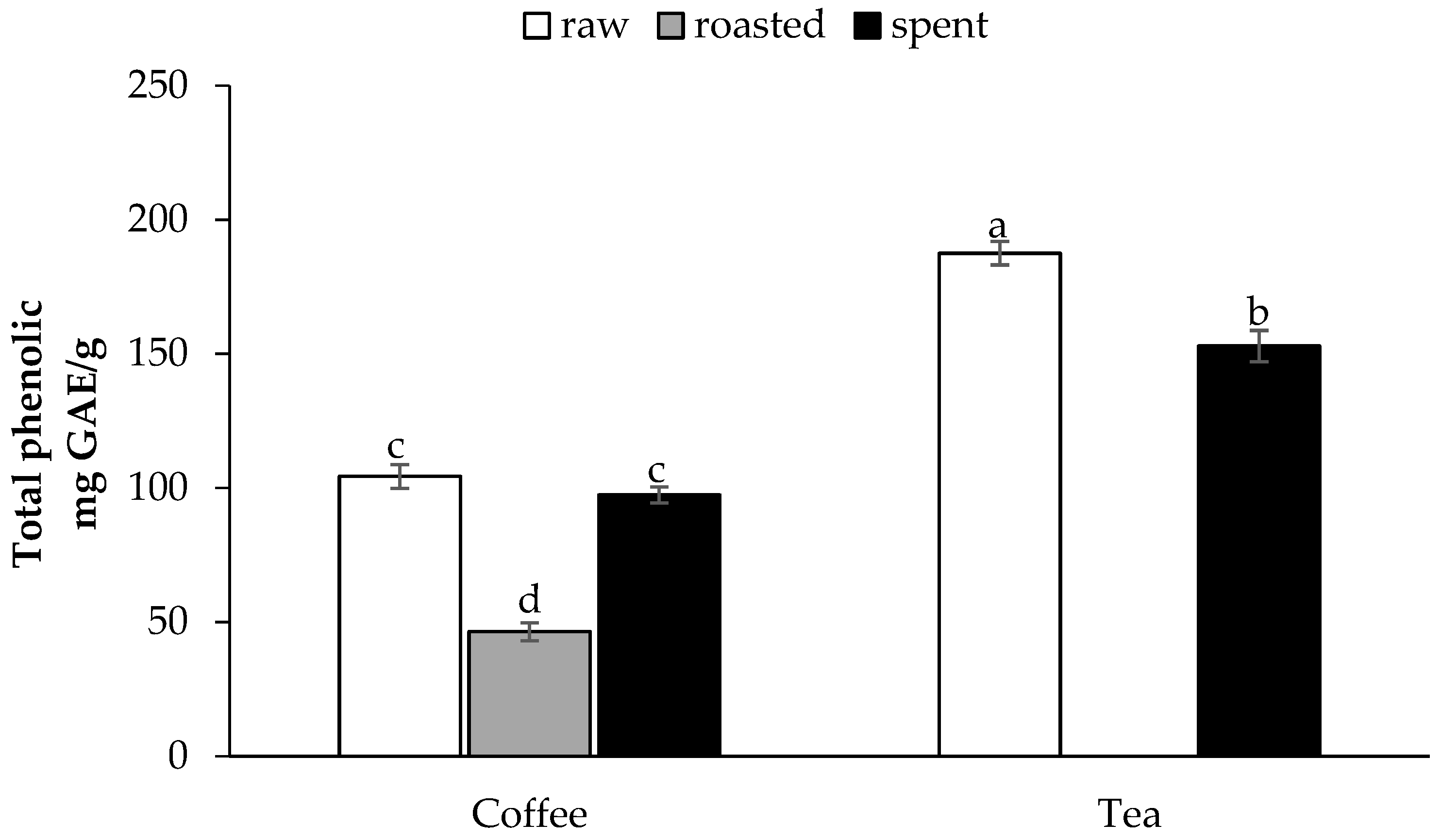
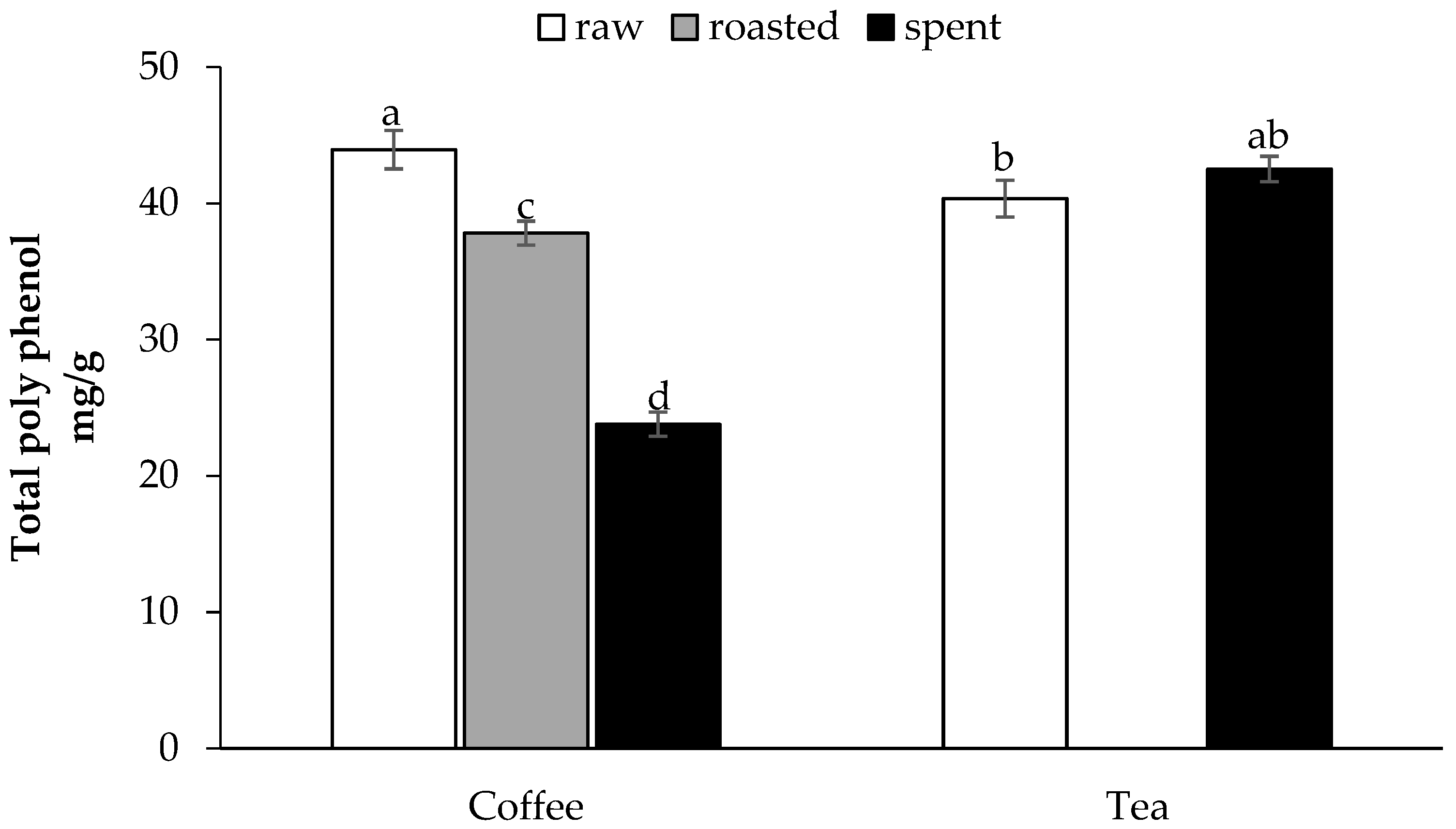
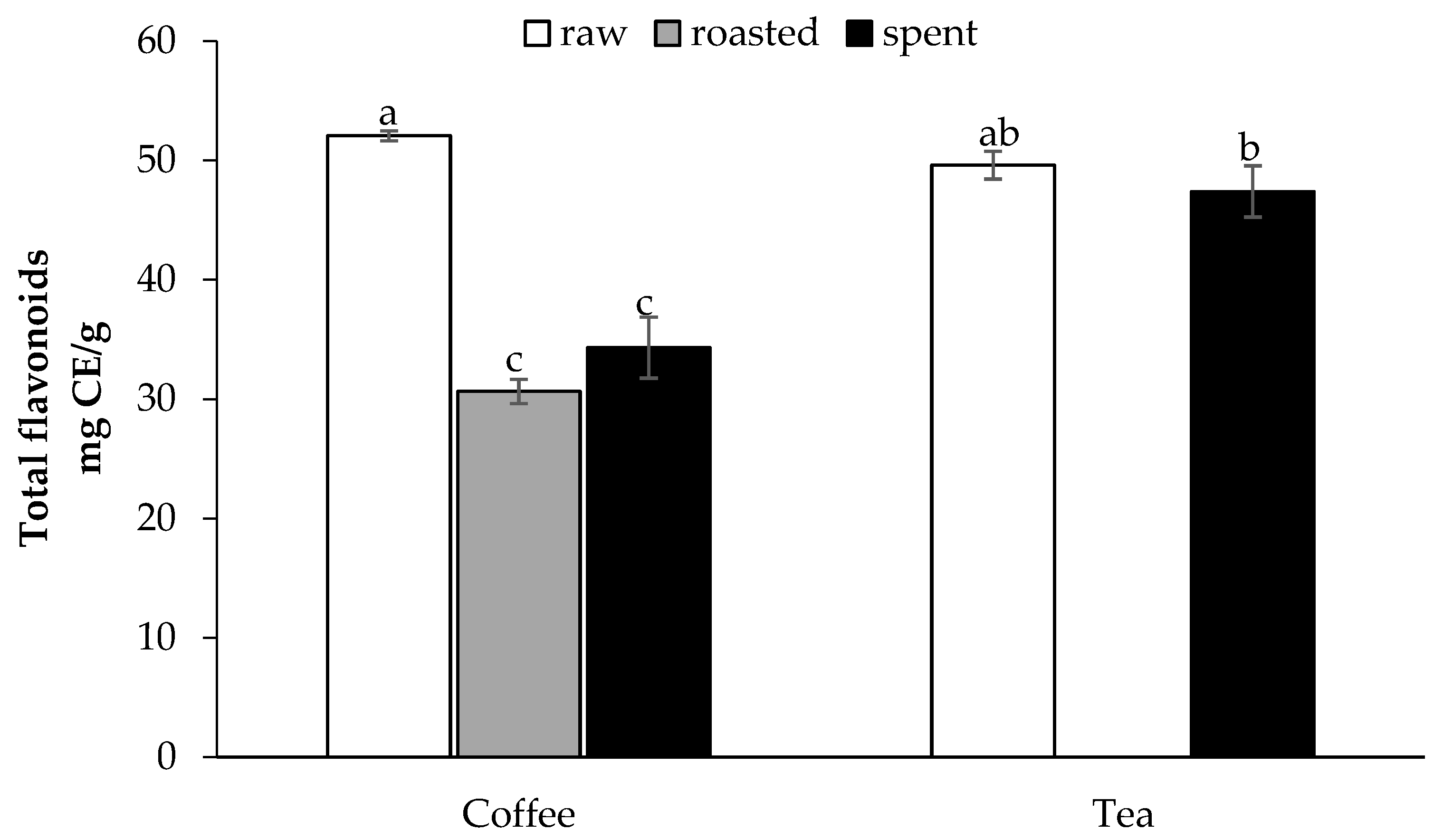
3.1. Phenolic Compounds of Raw and Spent Coffee and Black Tea
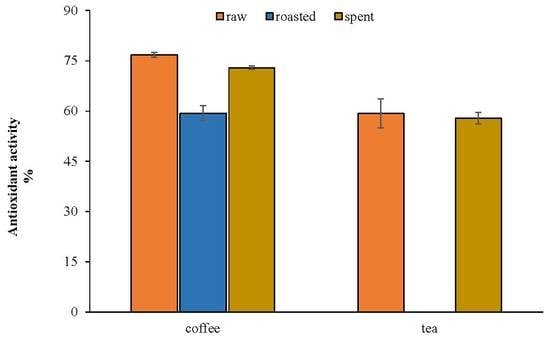
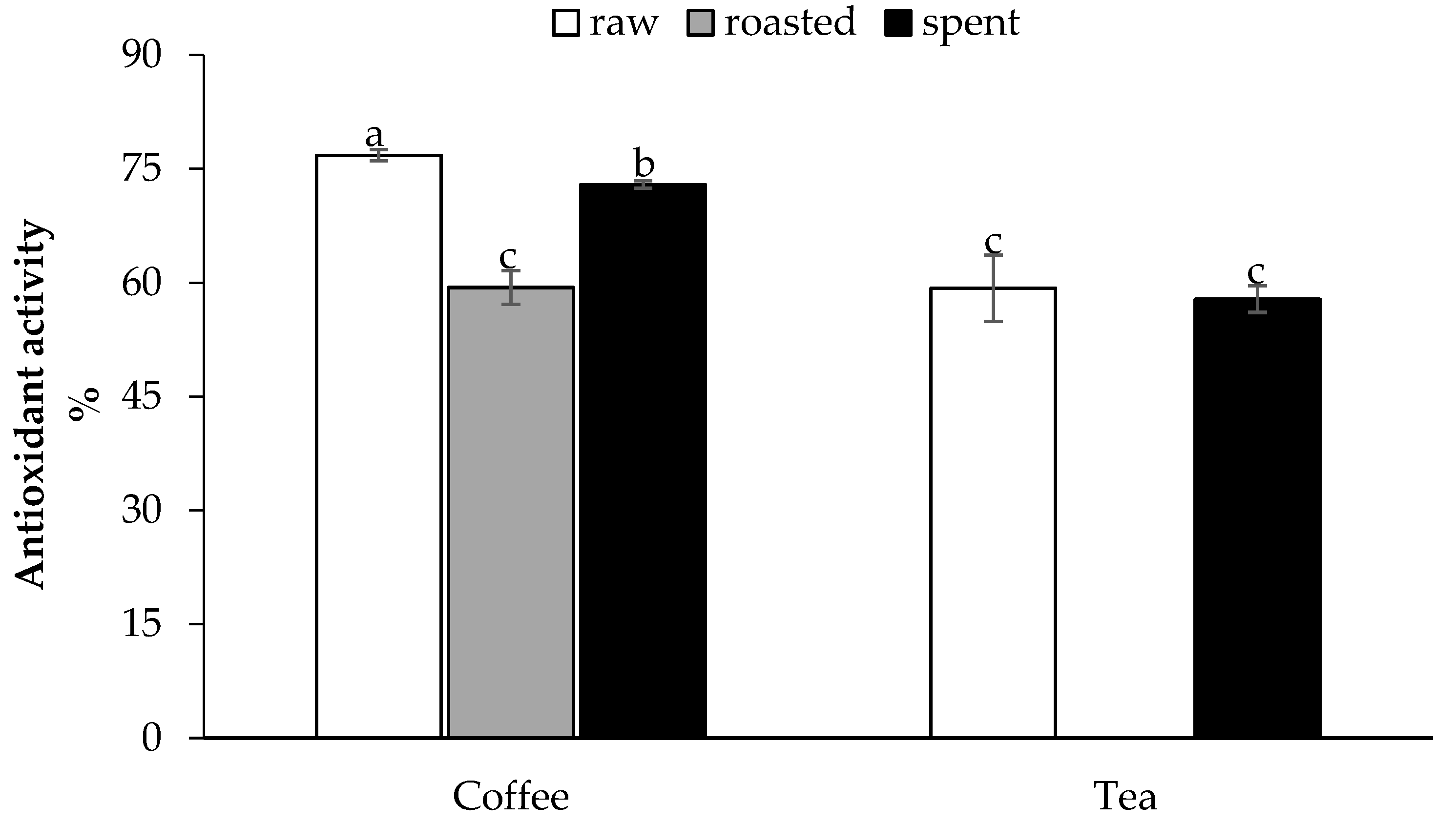
3.2. Antioxidant Activity of Raw and Spent Coffee and Black Tea
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mirabella, N.; Castellani, V.; Sualeh, S. Current options for the valorization of food manufacturing waste: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 65, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiano, A. Recovery of biomolecules from food wastes—A review. Molecules 2014, 19, 14821–14842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajila, C.M.; Naidu, K.A.; Bhat, S.G.; Prasada Rao, U.J.S. Bioactive compounds and antioxidant potential of mango peel extract. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunradi, V.F.G.; da Silva Campelo Borges, G.; Copetti, C.; da Valdemiro Gonzaga, L.; Costa Nunes, E.; Fett, R. Activity and contents of polyphenolic antioxidants in the whole fruit, flesh and peel of three apple cultivars. Arch. Latinoam. Nutr. 2009, 59, 101–106. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez-Carranze, P.; Ávila-Sosa, R.; Guerrero-Beltran, J.A.; Navarro-Cruz, A.R.; Corona-Jimenezi, E.; Ochoa-Velasco, C.E. Optimization of antioxidant compounds extraction from fruit by-products: Apple pomace, orange and banana peel. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2015, 40, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, T.; Inaba, Y.; Takeda, Y. Antioxidant mechanism of carnosic acid: Structural identification of two oxidation products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 5560–5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, S.; Okamoto, Y.; Kawabata, J. Effects of alcoholic solvents on antiradical abilities of protocatechuic acid and its alkyl esters. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2004, 68, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasundram, N.; Sundram, K.; Samman, S. Phenolic compounds in plants and agri-industrial by-products: Antioxidant activity, occurrence, and potential uses. Food Chem. 2006, 99, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moure, A.; Cruz, J.M.; Franco, D.; Domínguez, J.M.; Sineiro, J.; Domínguez, H.; Núñez, M.J.; Parajó, J.C. Natural antioxidants from residual sources. Food Chem. 2001, 72, 145–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieber, A.; Stintzing, F.C.; Carle, R. By-products of plant food processing as a source of functional compounds—Recent developments. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2001, 12, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borguini, R.G.; Torres, E.A.F.S. Tomatoes and tomato products as dietary sources of antioxidants. Food Rev. Int. 2009, 25, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagimoto, K.; Lee, K.G.; Ochi, H.; Shibamoto, T. Anti-oxidative activity of heterocyclic compounds found in coffee volatiles produced by Maillard reaction. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 5480–5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higdon, J.V.; Frei, B. Coffee and health: A review of recent human research. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2006, 46, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokimoto, T.; Kawasaki, N.; Nakamura, T.; Akutagawa, J.; Tanada, S. Removal of lead ions in drinking water by coffee grounds as vegetable biomass. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 281, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterhouse, A.L. Determination of Total Phenolics. In Current Protocols in Food Analytical Chemistry; Wrolstad, R.E., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2001; Units I; pp. I1.1.1–I1.1.8. [Google Scholar]
- Price, M.L.; Butler, L.G. Rapid visual estimation and spectrophotometric determination of tannin content of sorghum grain. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1977, 25, 1268–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.O.; Jeong, S.W.; Lee, C.Y. Antioxidant capacity of phenolic phytochemicals from various cultivars of plums. Food Chem. 2003, 81, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.T.; Wu, J.H.; Wang, S.Y.; Kang, P.L.; Yang, N.S.; Shyur, L.F. Antioxidant activity of extracts from Acacia confuse bark and heart wood. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 3420–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shyur, L.F.; Tsung, J.H.; Chen, J.H.; Chiu, C.Y.; Lo, C.P. Antioxidant properties of extracts from medicinal plants popularly used in Taiwan. Int. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. 2005, 3, 195–202. [Google Scholar]
- Geremu, M.; Tola, Y.B.; Sualeh, A. Extraction and determination of total polyphenols and antioxidant capacity of red coffee (Coffea arabica L.) pulp of wet processing plants. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2016, 3, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuorro, A.; Lavecchia, R. Spent coffee grounds as a valuable source of phenolic compounds and bioenergy. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 34, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanishkieva-Maslarova, N.V. Inhibiting oxidation. In Antioxidants in Food: Practical Applications; Pokorny, J., Yanishlieva, N., Gordon, M.H., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2001; pp. 22–70. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, V.S.Y.; Dou, J.P.; Chen, R.J.Y.; Lin, R.S.; Lee, M.R.; Tzen, J.T.C. Massive accumulation of gallic acid and unique occurrence of myricetin, quercetin, and kaempferol in preparing old oolong black tea. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 7950–7956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadiah, N.I.; Uthumporn, U. Determination of phenolic and antioxidant properties in black tea and spent black tea under various extraction method and determination of catechin, caffeine and gallic acid by HPLC. IJASEIT 2015, 5, 158–164. [Google Scholar]
- Vignoli, J.A.; Bassoli, D.G.; Benassi, M.T. Antioxidant activity, polyphenols, caffeine and melanoidins in soluble coffee: The influence of processing conditions and raw material. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romdhane, M.B.; Krichen, F.; Ghazal, I.; Semia, E.C.; Haddr, A. Effect of extraction methods on chemical composition. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory and antioxidant activity of coffee residue. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2017, 41, 12768–12777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhoosh, R.; Golmovahhed, G.A.; Khodaparast, M.H.H. Antioxidant activity of various extracts of old tea leaves and black tea wastes (Camellia sinensi L.). Food Chem. 2007, 100, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafoor, K.; Al-Juhaimi, F.; Choi, Y.H. Effects of grape (Vitis labrusca B.) peel and seed extracts on phenolics, antioxidants and anthocyanins in grape juice. Pak. J. Bot. 2011, 43, 1581–1586. [Google Scholar]
- Dalar, A.; Türker, M.; Zabaras, D.; Konczak, I. Phenolic composition, antioxidant and enzyme inhibitory activities of (Eryngium bornmuelleri) leaf. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2014, 69, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaroug, M.; Orhan, I.E.; Senol, F.S.; Yagi, S. Comparative antioxidant activity appraisal of traditional Sudanese kisra prepared from two sorghum cultivars. Food Chem. 2014, 156, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sir Elkhatim, K.A.; Elagib, R.A.; Hassan, A.B. Content of phenolic compounds and vitamin C and antioxidant activity in wasted parts of Sudanese citrus fruits. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Raw Coffee | Spent coffee | Raw Tea | Spent Tea | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw coffee | 1 | |||
| Spent coffee | 0.9922 | 1 | ||
| Raw tea | 0.9078 | 0.8491 | 1 | |
| Spent tea | 0.9141 | 0.857 | 0.997 | 1 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdeltaif, S.A.; SirElkhatim, K.A.; Hassan, A.B. Estimation of Phenolic and Flavonoid Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Spent Coffee and Black Tea (Processing) Waste for Potential Recovery and Reuse in Sudan. Recycling 2018, 3, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling3020027
Abdeltaif SA, SirElkhatim KA, Hassan AB. Estimation of Phenolic and Flavonoid Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Spent Coffee and Black Tea (Processing) Waste for Potential Recovery and Reuse in Sudan. Recycling. 2018; 3(2):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling3020027
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdeltaif, Samar A., Khitma A. SirElkhatim, and Amro B. Hassan. 2018. "Estimation of Phenolic and Flavonoid Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Spent Coffee and Black Tea (Processing) Waste for Potential Recovery and Reuse in Sudan" Recycling 3, no. 2: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling3020027
APA StyleAbdeltaif, S. A., SirElkhatim, K. A., & Hassan, A. B. (2018). Estimation of Phenolic and Flavonoid Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Spent Coffee and Black Tea (Processing) Waste for Potential Recovery and Reuse in Sudan. Recycling, 3(2), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling3020027