Abstract
The increasing accumulation of E-waste presents significant environmental challenges, particularly its disposal and resource management. The present study investigates the potential of printed circuit boards (PCBs) as a partial replacement for fine aggregates in cement mortar and concrete. The replacement levels of PCBs ranged from 0 to 35 wt% in cement mortar and from 0 to 30 wt% in concrete, aiming to improve the qualities of both mixes. The specimens were cured for 7 and 28 days, respectively, followed by tests to evaluate the flowability and static mechanical properties. The performance of the developed mortar/concrete was analyzed under aggressive environmental conditions by conducting various durability tests. Properties such as acoustic and thermal conductivity were also evaluated to check the suitability of the developed material for its multifunctionality. Test results revealed that the optimal replacement percentages of fine aggregate by PCBs in mortar and concrete mixes were 25 wt% and 20 wt%, respectively. A decline in mechanical properties was observed after a further increase in replacement level. The results demonstrate the feasibility of E-waste integration in cement and mortar as a sustainable waste management solution.
1. Introduction
Concrete is a universally used construction material and its implementation can be accredited to many positive qualities like low cost, easy deployment, and wide range of applications. Additionally, it can be molded into any shape, becomes strong after curing, and supports enormous and gigantic structures. The tremendous development and progression of electronics-based industries has resulted in the development of numerous electronics products to suit human lifestyles. However, the lifespan of such products is limited and re-fabrication is also not possible for most of the electronic components. Therefore, the non-functioning products are treated as E-waste, which enters dump yards from many sources like households, information technology (IT) companies, sports and gaming sectors, and electronics manufacturing plants, in the form of chips, cables, keyboards, mobile phones, TVs, computers, and other electronic items [1]. In recent times, E-waste has become a serious environmental issue requiring immediate attention and solution. The storage of E-waste materials in dump yards has rapidly increased to approximately five times greater than the population growth rate [2,3,4]. The Global E-waste Monitor by Blade et al. [5] predicts a huge drop in the recycling rate from 22.3% in 2024 to almost 20% in 2030. This decrease in the recycling rate is primarily due to the increase in the consumption of electronic products caused by the upgradation of technology. Also, shorter product life cycles of devices, limited repair options, and design flaws contribute to the staggering growth of E-waste generation [6]. Improper waste management merges all types of trash, causing difficulty in segregating municipal waste, household waste, and industrial waste [7,8,9,10].
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are an important component in the manufacturing of electronic devices. The combination of copper cladding on epoxy base, the presence of soldering alloy, and inserted electronic components like capacitors and transistors makes PCBs a mixed E-waste [11,12,13]. Recent studies have extensively explored the potential of integrating electronic waste into concrete and mortar as a sustainable alternative to natural aggregates. Unlike other E-wastes constituting plastics or glass, PCBs offer added benefits of potentially improving the mechanical properties of concrete. PCB, being a composite material, contains significant amounts of silica, which contribute to the overall enhancement in strength and durability of concrete [14]. Research by Manatkar et al. [15] and Chen et al. [16] demonstrated that partial replacement of fine aggregates with PCBs or other E-waste materials enhanced compressive strength, durability, and chemical resistance, with optimal replacement levels ranging between 15 and 25 wt%. Studies conducted by Sanyal et al. [17] and Wang et al. [18] highlighted additional benefits, including improved thermal insulation, acoustic properties, and reduced leaching of hazardous metals, which mitigate environmental risks. Shah et al. [19] employed machine learning techniques to optimize E-waste aggregate proportions, identifying 20–25% replacement as ideal for balancing mechanical performance and sustainability. Similarly, Ghanem et al. [20] observed significant improvements in flexural strength for E-waste (PCBs)-reinforced concrete beams at these replacement levels, and morphological analyses by Kumar et al. [21] confirmed excellent bonding between E-waste and cement paste at moderate replacement percentages.
Further investigations into durability have revealed improved resistance to environmental stressors like sulfate attacks, and alkali–silica reactions in E-waste-modified concrete mixes [1,22,23,24]. Studies by Wu et al. [25] and Shi et al. [26] emphasized the multi-functional benefits of these materials, including enhanced radiation shielding capabilities and carbonation resistance. Selvaraj et al. [27] demonstrated reductions in carbonation depth through E-waste integration, while Patel et al. [28] highlighted the economic viability of large-scale production due to reduced material costs and landfill expenses.
It is observed that the incorporation of E-waste into construction materials not only addresses waste management challenges but also contributes to eco-friendly practices in construction by maintaining acceptable mechanical properties and durability for structural applications. Several studies have demonstrated the feasibility of using recycled materials as aggregates to enhance the mechanical properties of concrete. For instance, the incorporation of fly ash-based Pozzolana Portland cement (PPC) and an E-waste (PCBs) matrix containing silica and alumina has shown improvements in compressive strength and durability with reduced thermal expansion [29]. Despite these advancements, limited research has been conducted on the impact of E-waste (PCBs) on the mechanical properties and durability of concrete.
This necessitates the need for a comprehensive investigation into the potential of E-waste as a sustainable alternative to natural fine aggregates in both cement mortar and concrete. Several mechanical properties—compression, split tension, flexural, bonding, impact strength, and ultrasonic pulse velocity (UPV)—are analyzed to understand the influence of E-waste aggregate as a replacement for fine aggregate. Durability tests such as water absorption, sulfate resistance, exposure to elevated temperature, and functional tests like acoustic properties and thermal conductivity are also envisaged in this study. By addressing critical challenges such as E-waste accumulation, resource depletion, and construction material shortages, this work is expected to offer a practical and scalable solution for integrating electronic waste into the construction industry, contributing to both waste management and sustainable infrastructure development.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Composition of Pulverized PCB
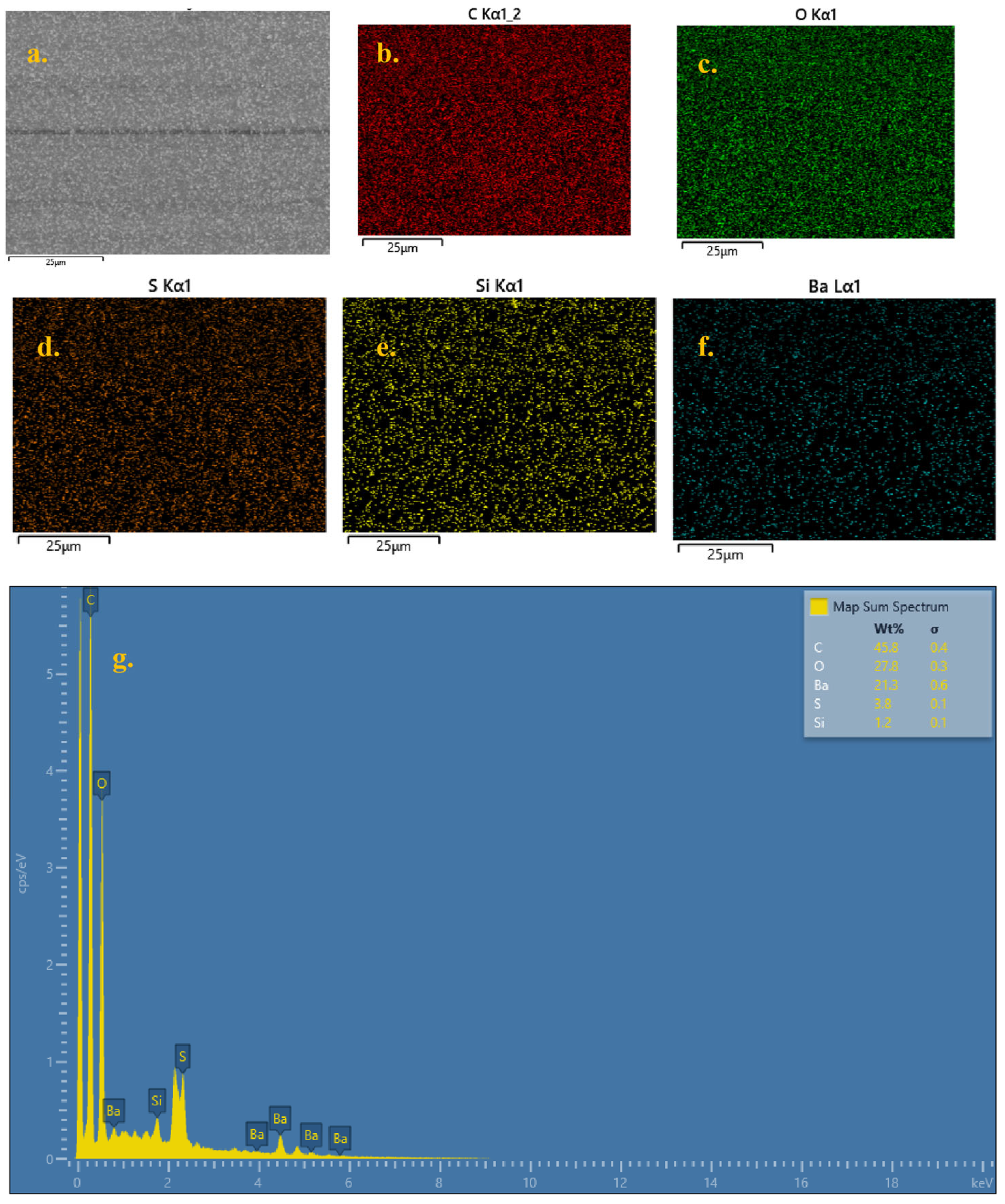
Field-Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FE-SEM) with Energy-Dispersive X-ray (EDX) analysis is a powerful tool for analyzing the surface and chemical composition of the specimens. Figure 1 shows the FE-SEM image and color mapping with EDX plot, confirming the absence of heavy metals such as Tin (Sn) and Lead (Pb). The presence of Barium (Ba) and Sulfur (S) arises from the flame-retardant coating present on the solder mask to enhance the thermal stability of the PCB. These coatings are non-toxic in nature and are generally not soluble in water [30]. The Carbon and Oxygen elements dominate the spectra, indicating the abundant presence of epoxy in PCBs. It can thus be inferred that the waste PCBs are free from any heavy metals or toxic elements.
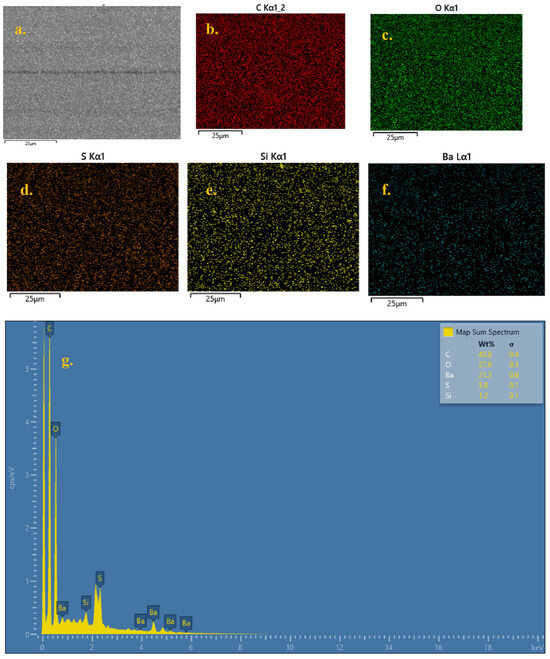
Figure 1.
(a) FE-SEM micrograph, (b–f) elemental color mapping, and (g) EDX spectra of desoldered PCB.
2.2. Fresh Concrete Test (Slump Cone Test)
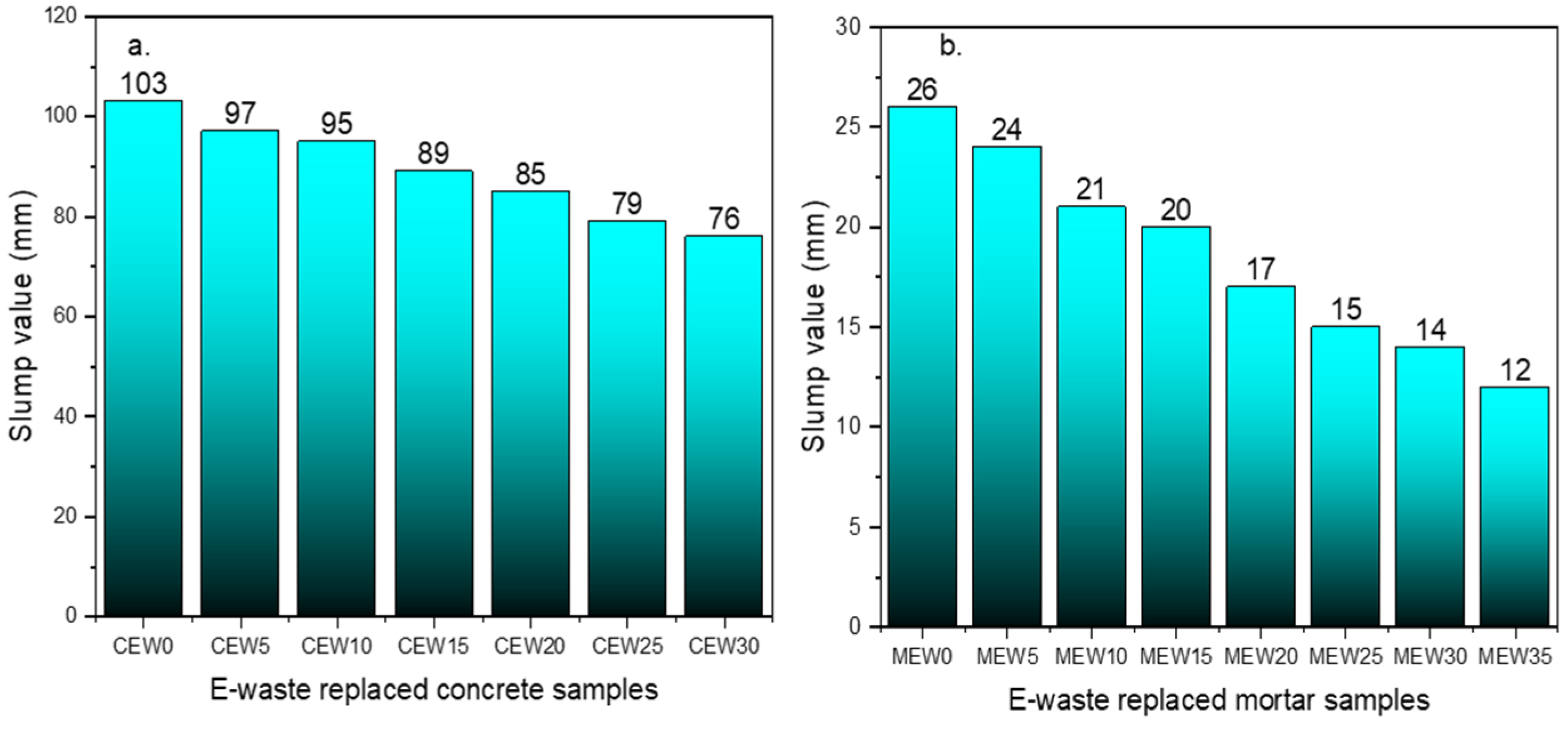
From Figure 2, it can be noted that the slump value of the control sample was recorded as 103 mm, and the CEW30 replacement sample recorded 76 mm. The reduction in slump with increasing replacement percentage of E-waste (PCBs) content is primarily attributed to the irregular and rough surface texture of E-waste particles compared to natural sand. A reduction in internal aggregate friction combined with the smaller particles of PCBs reduces the workability marginally due to the lower density of the waste materials. Similarly, the slump value of the cement mortar mix was recorded as 26 mm for MEW0 and 12 mm for the MEW35 E-waste replacement sample.
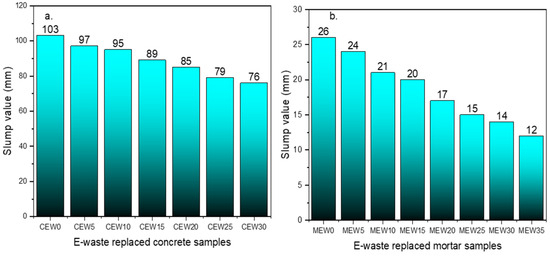
Figure 2.
Comparison of slump value: (a) concrete, (b) cement mortar.
A reduction in slump values stems from changes in the ability of the mix to absorb water as well as the arrangement of particles in the mix. These changes in water absorption and particle arrangement interact differently with the cement paste. River sand generally absorbs water at a rate of 1.2 to 2.0%, whereas E-waste particles (PCBs), when used as a fine aggregate, are non-absorbent and influence both paste–aggregate interactions. This reduction leads to decreased interparticle friction, which results in improved dispersion of the cementitious paste. Few previous studies have examined this pattern of reducing slump values by replacing fine aggregate with E-waste [31,32,33].
2.3. Mechanical Properties
2.3.1. Compressive Strength
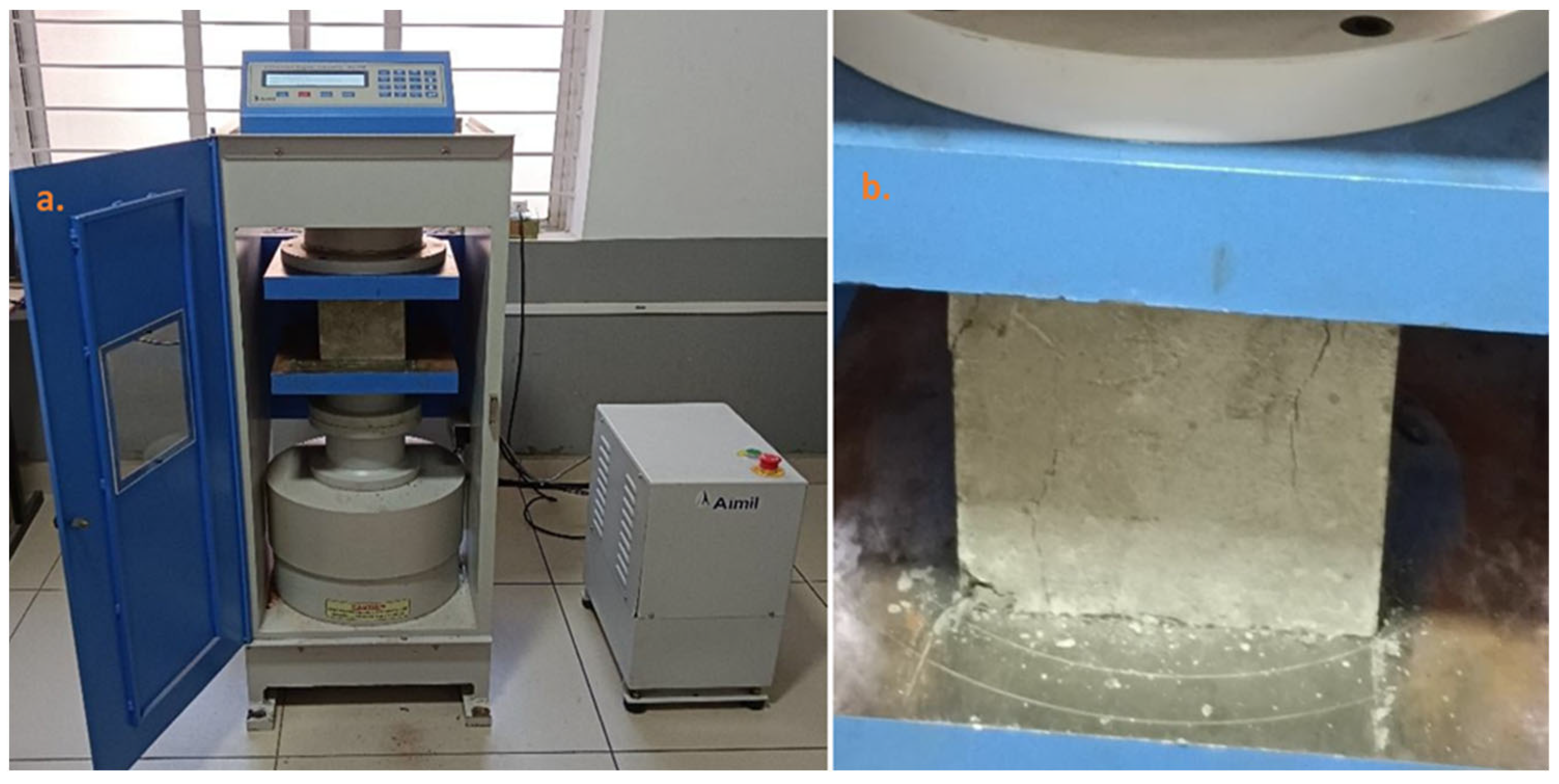
Figure 3 shows the test setup used to conduct axial compression tests with a loading capacity of 3000 kN, maintaining a load rate of 140 MPa/min until the failure of the specimen. The compressive strength of the specimen is calculated using the standard formula.
where Pc = failure load in compression (N) and A = loaded area of the specimen, in mm2 [13,28].
Figure 3.
(a) Compression test setup and (b) test sample under compression.
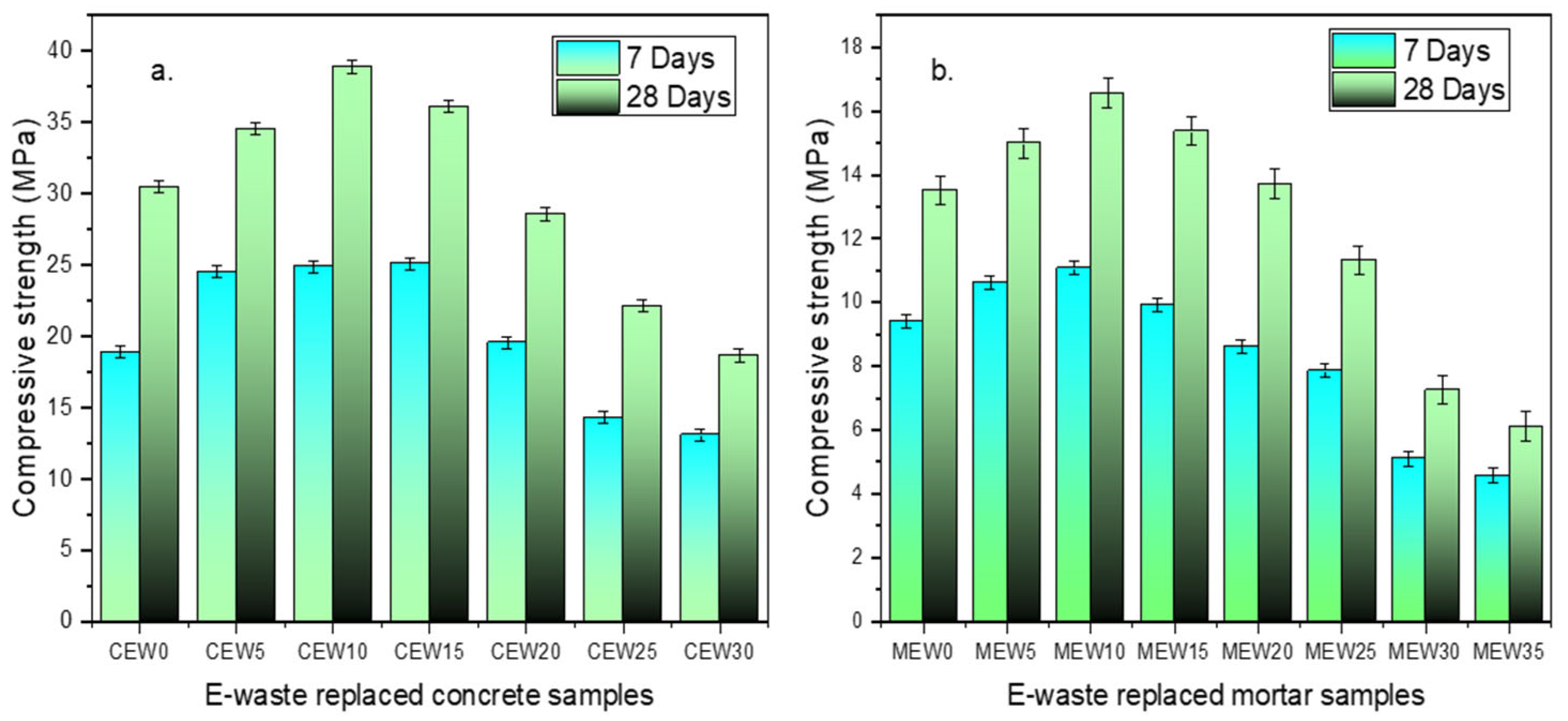
The strength of concrete and mortar was found to be higher than the target strength with the inclusion of E-waste up to an optimal replacement level, beyond which a decline was observed, and the results are illustrated in Figure 4.
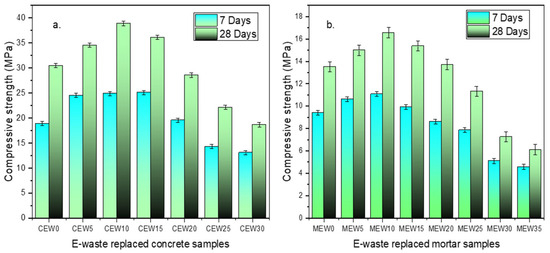
Figure 4.
Compressive strength results of (a) concrete and (b) mortar.
The highest recorded strength for the E-waste-incorporated specimen is 37.2 MPa for concrete and 16.6 MPa for cement mortar. This result indicates that E-waste can effectively contribute to strength enhancement within a certain replacement range. The standard target compressive strength for M25 concrete mix is 25 MPa at 28 days. The control specimen achieved a value of 30 MPa for concrete (CEW0) and 13.8 MPa for the mortar sample (MEW0) after 28 days’ curing. Concrete samples with PCBs up to 20% replacement exhibited improved strength gains with respect to target strength of 25 MPa, followed by a gradual decline beyond this level. At 7 days, the increase in early strength was moderate, suggesting that the pozzolanic reactivity of E-waste particles was limited in the initial hydration phase. By 28 days, the strength increase was more pronounced, indicating a possible densification effect due to fine EW particles filling voids and improving the packing density. The 28-day compressive strength of the optimized mix in this study (37.2 MPa) exceeded that of conventional M25 concrete (31.2 MPa) as reported by Mohan et al. [34]. This improvement is attributed to the synergistic effect of PCB waste.
The standard compressive strength target for 1:3 cement mortar is 7.5 MPa. The E-waste-added cement mortar mix showed an increase in target compressive strength, up to a 25 wt% replacement. Beyond this level, the strength dropped due to excessive replacement affecting the cementitious matrix’s bonding ability. The finer nature of E-waste particles—fiberglass, epoxy resin, and copper/aluminum—contributes to enhanced particle packing, reducing voids and improving the overall density of the concrete/mortar matrix. It is also observed that the presence of E-waste particles seems to improve the bond between aggregate and cement paste, leading to better load transfer and increased strength.
In both cases it is observed that excessive replacement may disturb the compactness of the mix, leading to potential void formation and practical implications. The results indicate that E-waste can be effectively used as a fine aggregate replacement in concrete up to 20 wt% and in mortar up to 25 wt% without compromising compressive strength.
2.3.2. Split Tensile Strength
The split tensile strength tests on mortar/concrete cylindrical specimens were conducted using a universal testing machine. The standard rate of loading was maintained at 1.2 MPa/min to 2.4 MPa/min following ASTM C496/496M.
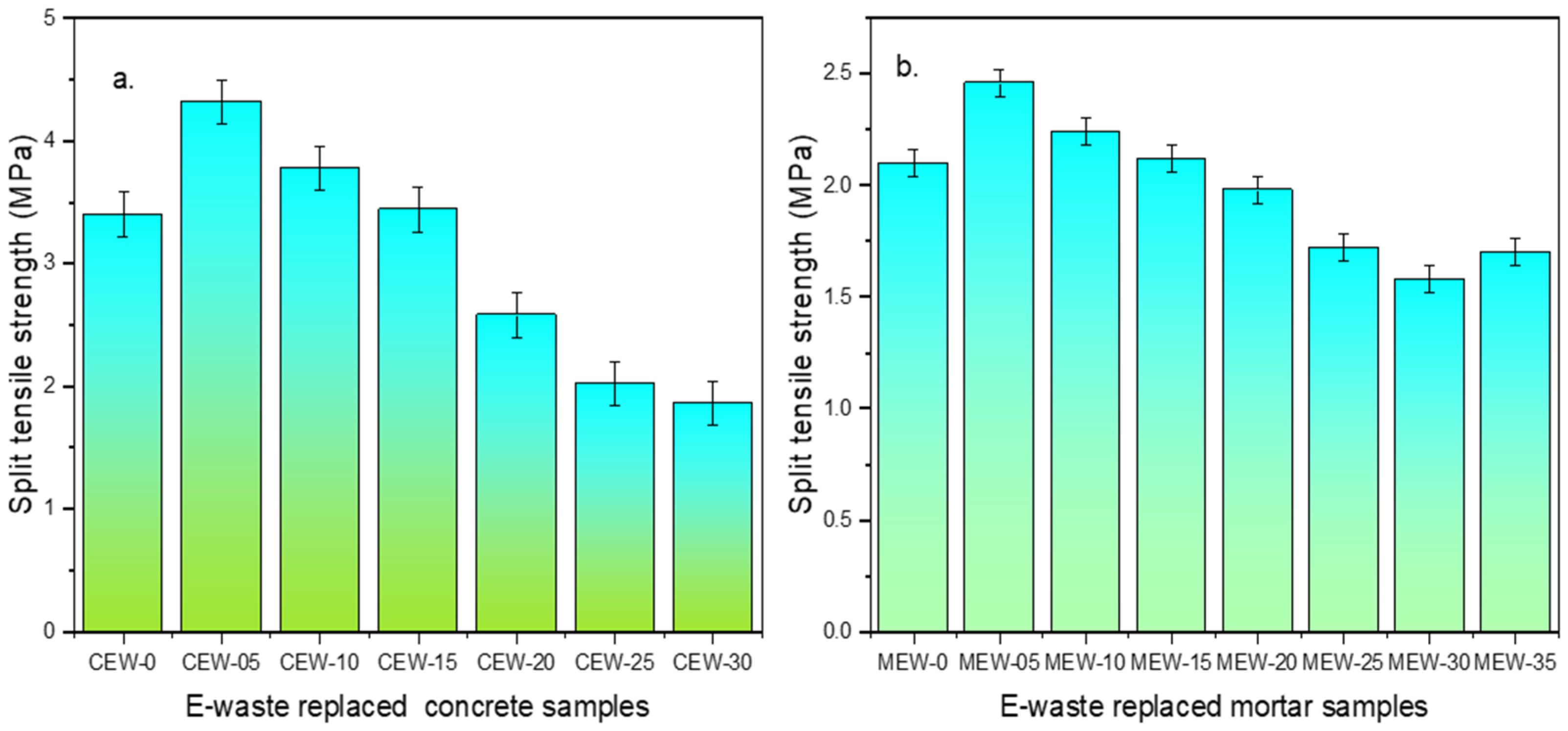
From Figure 5, it can be observed that the split tensile strength of CEW20 concrete samples increased by 31%, while MEW25 mortar samples increased by 24.36% compared to the control samples. The PCB waste particles improve packing, void reduction, and overall density enhancement of the concrete/mortar matrix. They also enhance the bonding between aggregate and cement paste, leading to better load transfer and increased strength. A strength reduction is observed when replacement levels exceed 20 wt% in concrete and 25 wt% in mortar, due to insufficient bonding between the E-waste (PCBs) particles and the cement matrix, leading to weaker interfacial transition zones (ITZ) and reduced cohesiveness. The obtained values are well above the targeted values of 2.8 MPa to 3.5 MPa for concrete and 1.8 MPa to 2.5 MPa for cement mortar. The excessive presence of E-waste can disrupt the compactness of the mix, resulting in potential void formation and increased porosity, creating stress concentration zones that compromise the material’s ability to resist crack propagation. Thus, the findings underscore the fact that E-waste, when used in controlled proportions, can enhance the mechanical properties of concrete and mortar, but excessive replacement negates these benefits due to weak bonding and increased porosity.
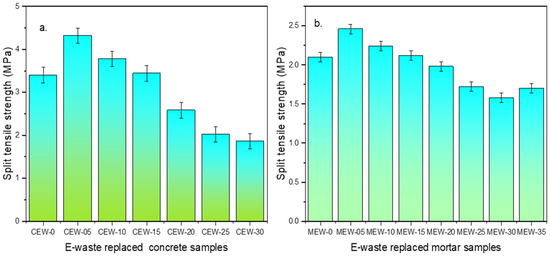
Figure 5.
Split tensile strength results of (a) concrete and (b) mortar.
2.3.3. Flexural Strength
The flexural strength of the mortar/concrete samples are assessed by supporting the specimens on the rollers of the testing machine, which provide a simply supported condition for concrete and mortar beams. The concentrated load is then applied in the three-point bending mode till the failure of the specimen.
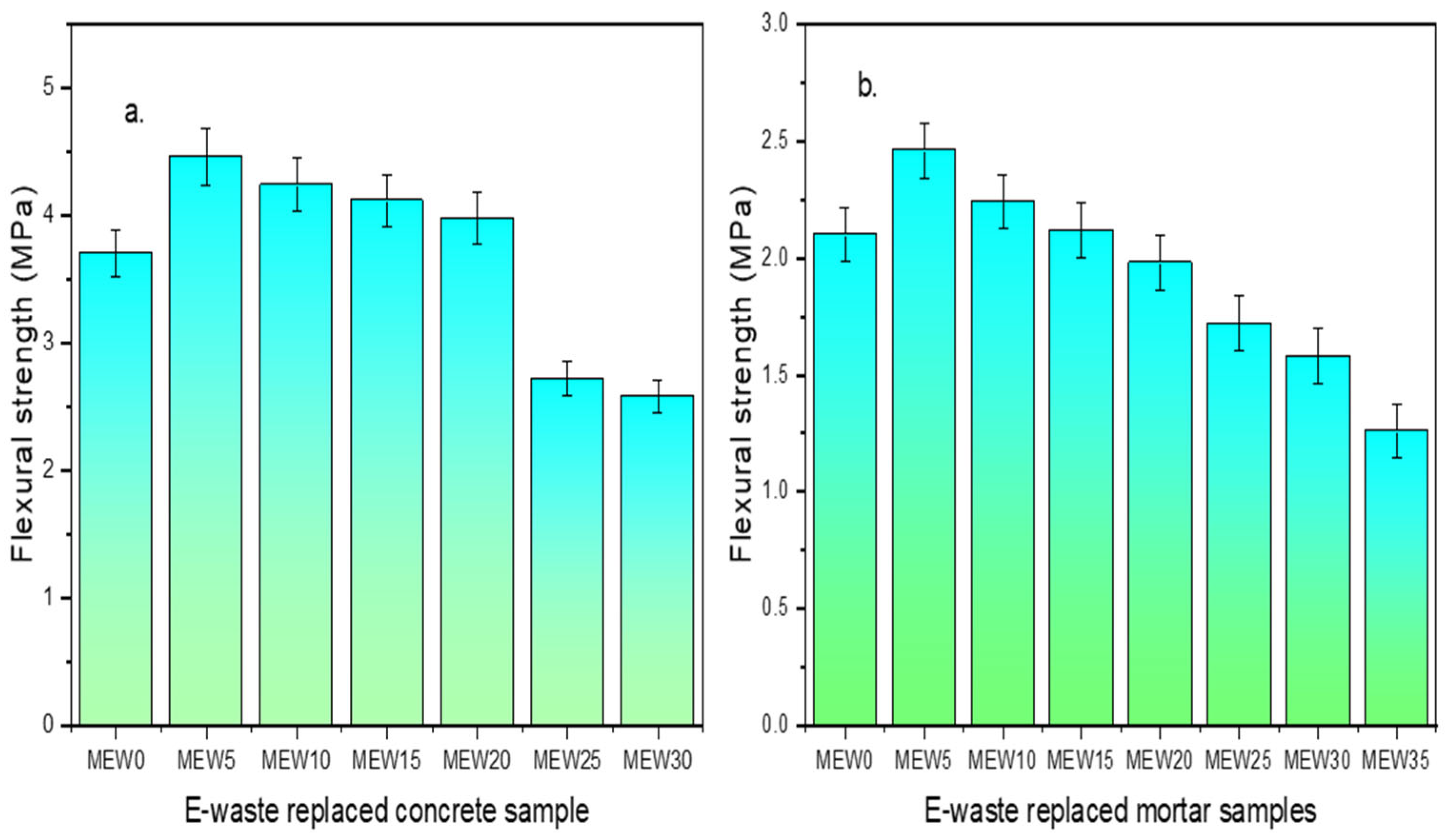
From Figure 6, it can be observed that CEW20 and MEW25 show significant improvements of 7.5% and 12%, respectively, with respect to control samples. The increase in flexural strength is attributed to better stress distribution due to the improved microstructure of the cement matrix, reducing crack propagation, and superior resistance to bending loads. Strength reduction at higher replacement levels beyond 30 wt% in concrete and 35 wt% in mortar is observed. This decline beyond higher levels is a consequence of insufficient bonding and weaker ITZs between the E-waste PCB particles and the cement matrix. For cement mortar mix, potential void formation and variation in mix compactness contribute to the drop in flexural strength. Accordingly, based on the strength results, CEW20 and MEW25 are taken as optimum and further studies are carried out on these combinations and compared with control.
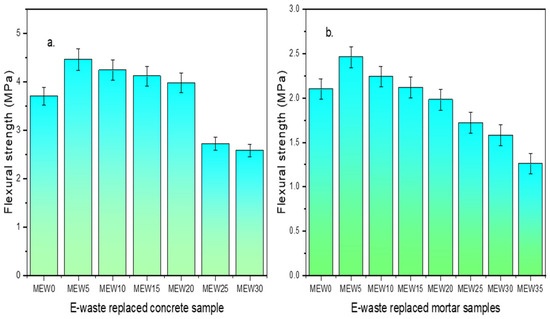
Figure 6.
Flexural strength results of (a) concrete and (b) mortar.
2.3.4. Impact Strength
Impact tests are conducted according to ACI 544.2R-89 by repeatedly dropping a known weight on the test specimens. The weight is dropped from a fixed height until specimen failure. The number of blows required to initiate a visible crack is noted. The impact energy is found using Equation (2)
where N is the number of blows (first crack), m is the mass of the hammer (4.54 kg), g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height of fall, 0.457 m.
Three samples in each category of MEW0, MEW25, CEW0, and CEW20 were tested. Table 1 presents the number of blows of CEW20 and MEW25 and a comparison with control specimens. The mortar/concrete specimen failure resistance improved significantly when the E-waste replacement level reached 20 wt% and 25 wt %.

Table 1.
Impact strength results.
The failure energy of the control sample (CEW0) was in the range of 1161 J, while the sample CEW20 recorded 1609 J, resulting in a 32.35% improvement in energy absorption. The increased failure energy indicates improved ductility as well as better impact loading performance for concrete containing E-waste modifications. The toughness of concrete material increases through an interlocking mechanism enabled by E-waste’s fibrous structure and irregular texture. The combination of better energy dissipation properties and improved crack propagation resistance play a role in increasing the impact strength that moderate E-waste replacement rates deliver to concrete materials. However, a further increase to 25% E-waste replacement (CEW25) resulted in a significant drop in impact resistance, which was 28% lower than the control mix. The E-waste particles may disrupt the matrix continuity and reduce post-crack energy absorption capacity.
These findings align with previous research conducted on the impact resistance of concrete with incorporated E-waste. Similar improvements in impact strength and energy absorption at moderate E-waste replacement levels were observed, with an increase in impact resistance of 39% for concrete with E-waste content, attributed to improved particle interlocking and energy dissipation mechanisms within the modified concrete matrix [35].
2.3.5. Bond Strength (Pull-Out Test)
The bond strength tests evaluate how well concrete adheres to reinforcing steel, which is essential for the overall performance of reinforced concrete structures [36,37]. This provides crucial insights into the structural integrity and load-transfer capabilities of concrete with incorporated E-waste. Three samples were tested, presenting average test results comparing the bond strength of CEW0 and CEW20 samples. Usually, high bond strength is necessary for reinforced concrete structures to ensure that loads are effectively transferred between the concrete and the reinforcement. The bond strength was calculated using Equation (3).
where P is the load, d is the diameter of the rod, and L is the embedment length.
The bond strength of the control specimen, which averages 5.63 MPa, surpasses that of the optimum E-waste (PCBs) replacement specimen, which has an average bond strength of 4.43 MPa. The bonded interface between the cement matrix and E-waste particles experiences a decrease of 5.2% based on changes in interfacial bonding strength. However, according to IS 456:200, clause 26.1.1, 2–51.1, 2 to 5 MPa is the typical bond strength range for M25 concrete with ribbed steel bars.
The non-uniform texture combined with the lower density of E-waste reduces cement paste–aggregate bond strength by creating weaker mechanical interlocking and decreasing stress transmission between reinforcement bars and concrete mass. The hydrophobic properties of E-waste components act as a barrier, which makes hydration more challenging, thus affecting bonding efficiency. This effect is vital at the rebar–concrete interface, where proper hydration is required to create a strong chemical and mechanical bond. The bond strength of the specimen with a 20 wt% E-waste replacement remains suitable for structural requirements, albeit at a reduced margin of safety, despite its decreased values while enabling sustainable EW integration. Xie et al. found that adding recycled aggregates helps maintain the average bond strength [38]. This occurs even when E-waste (PCBs) is present, as it enhances how well the cement paste sticks to and hydrates around the rebar.
2.3.6. Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity (UPV) Test
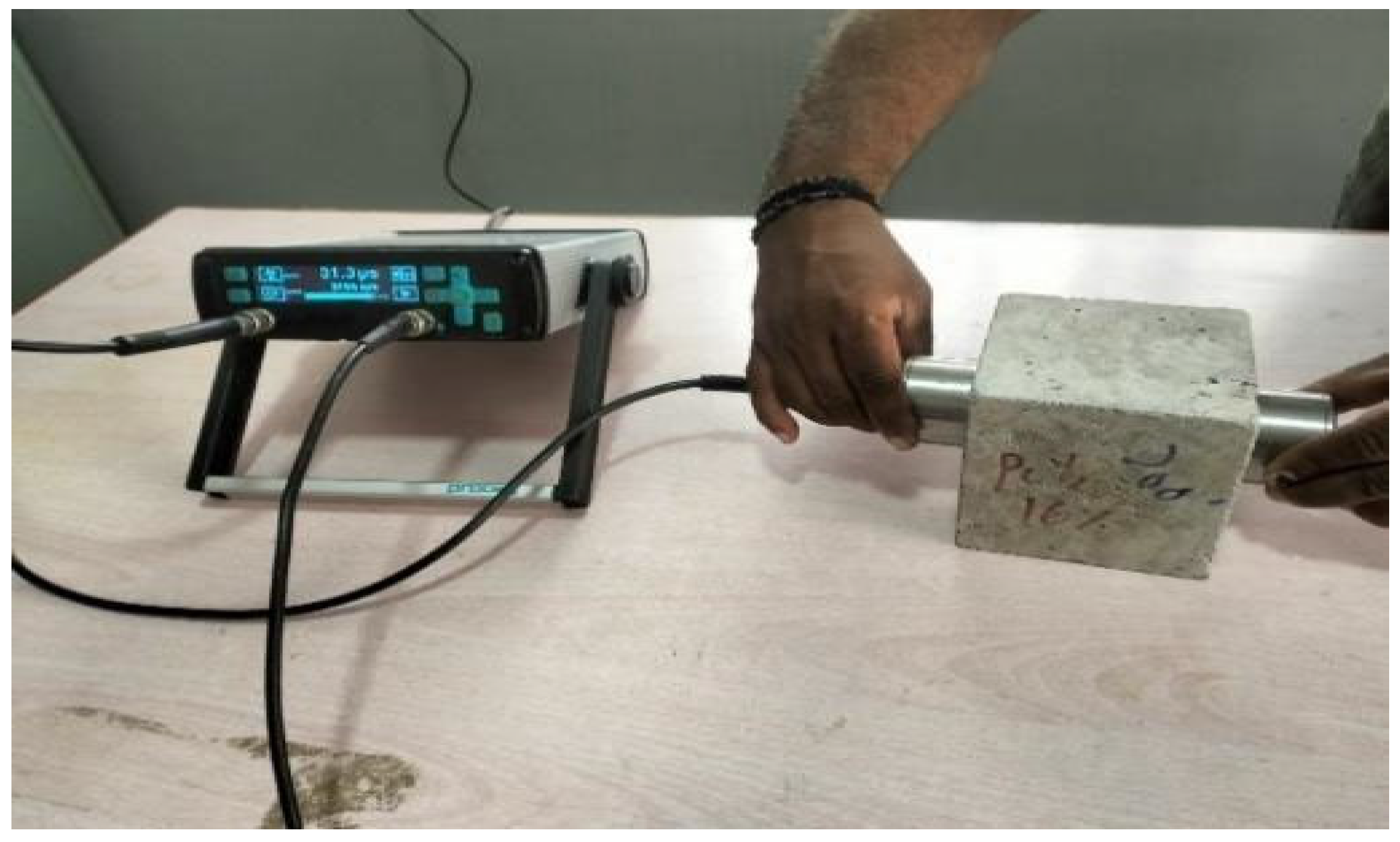
The ultrasonic pulse velocity test is a nondestructive technique adopted to assess the structural integrity of a specimen. Figure 7 shows a test method consisting of a transmitter and a receiver applied to the opposite faces of the concrete sample. The ultrasonic pulses from the transmitter at one end penetrate the specimen, while the receiver at the opposite end receives them.

Figure 7.
Ultrasonic pulse velocity test setup.
The control specimen (CEW0) achieved an average value of 3730 m/s, as the concrete matrix had minimal void spaces, inherent density, and strong particle connections throughout the matrix, classifying it as good quality. The optimum E-waste replacement specimens viz. CEW20 achieved an average value of 3541 m/s. The reduction in velocity indicates that porosity increased and density decreased due to the replacement of fine aggregates with E-waste. The PCB material combines differently with natural fine aggregates to form additional interfacial transition zones (ITZs) in concrete structures, which reduce ultrasonic pulse transmission efficiency marginally. These ITZs, characterized by increased porosity and weaker bonding, hinder the efficient transmission of ultrasonic pulses, resulting in lower UPV values. The UPV values for optimal samples that use 20 wt% E-waste remained inside the good-quality concrete standards, despite the decrease in values. The UPV test showed that pulse velocity decreased by 7.48% in the 20 wt% E-waste replacement specimen. IS 516 (PART 5/SEC 1): 2018 defines the UPV value for M25 concrete as 3.5–4.5 km/s for good quality. The CEW 20 samples maintain the good-quality status as per the mentioned standard. It is concluded that E-waste replacement concurrently affects the concrete’s internal structure, leading to increased porosity and reduced density. Espinosa et al. [39] explored the effects of recycled aggregates on the UPV and mechanical properties of concrete and revealed that the inclusion of a higher percentage of recycled aggregates led to a decrease in UPV values, which they attributed to increased porosity and a heterogeneous microstructure compared to conventional concrete.
2.4. Durability Properties
2.4.1. Sulfate Attack Resistance
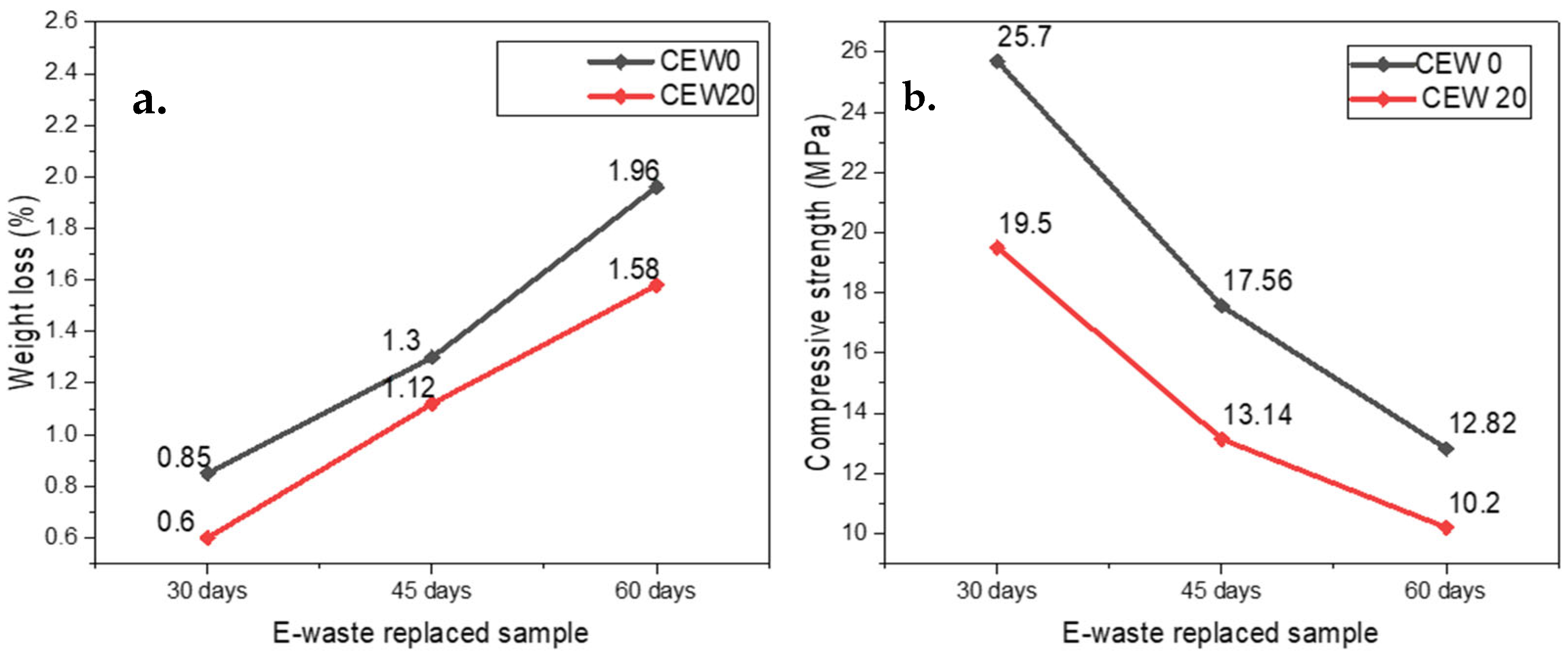
Sulfate attack is a critical durability concern in concrete structures, particularly in high-sulfate-containing environments. The specimens are immersed in 5 wt% concentration of sodium sulfate solution for 60 days, followed by washing with clean water, drying, and weighing. Following this, the samples are subjected to compression test and weight loss assessment, and the obtained results are shown in Figure 8, for CEW0 and CEW20 concrete mixes. The samples were tested at 30, 45, and 60 days and the results are discussed in terms of compressive strength and weight loss and illustrated in Figure 8.
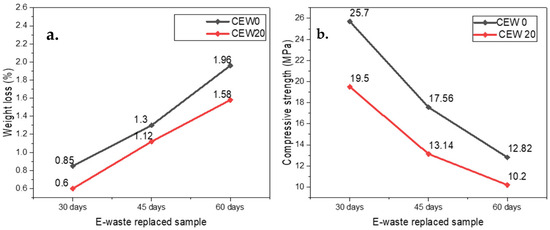
Figure 8.
Effect of sulfate attack: (a) weight loss (%), (b) compressive Strength.
The test results show that the control specimen experiences maximum deterioration with an average weight loss of 1.96% after 60 days of exposure. The CEW20 mix experienced considerably less degradation with an average weight loss of 1.58%. E-waste incorporation within concrete leads to improved sulfate resistance of the matrix by creating a refined pore structure, which restricts aggressive sulfate ions from entering the material. Figure 8 also indicates that the control mix displayed an average compressive strength of 25.70, 17.56, and 12.82 MPa, whereas CEW20 mix shows an average compressive strength of 19.50, 13.14, and 10.20 MPa. The structural integrity of concrete with an optimum dosage of E-waste stays consistent, demonstrating that its compressive strength decreases moderately compared to the control specimen.
Having reduced permeability as one of its properties, E-waste blocks sulfate ions from entering concrete and prevents expansive sulfate reaction materials from forming. Replacement of fine aggregates results in a modest strength reduction when considered across the broad spectrum of properties in the cementitious matrix because it disturbs the ideal packing arrangement and bond formation. The uniqueness lies in its exploration of E-waste as an unconventional material for improving concrete’s sulfate resistance while addressing environmental concerns by repurposing electronic waste. For instance, Ambrose et al. [40] demonstrated that recycled ceramic tiles (RCT) as fine aggregates improved residual compressive strength after sulfate exposure due to their higher initial strength and enhanced aggregate–cement bonding. Similarly, the study highlights that incorporating E-waste refines the pore structure, reducing permeability and mitigating sulfate ion infiltration.
2.4.2. Water Absorption Test
Concrete’s durability is directly linked to its porosity and permeability, which influence its susceptibility to deterioration caused by aggressive substances dissolved in water. By measuring the percentage of water absorbed, the pore structure and density of the concrete matrix can be evaluated, enabling predictions about its long-term performance and suitability for specific applications. The specimens are placed in an oven at 105 °C until they reach a constant weight, dried for 24–48 h post-cooling, and the initial weight (W1) is noted. The samples are then immersed in water at room temperature for 24 h. The specimens are removed from water and gently wiped to remove excess water, and the final weight (W2) is taken, after which the percentage of water absorption is calculated as per IS 1124 (1974) [41].
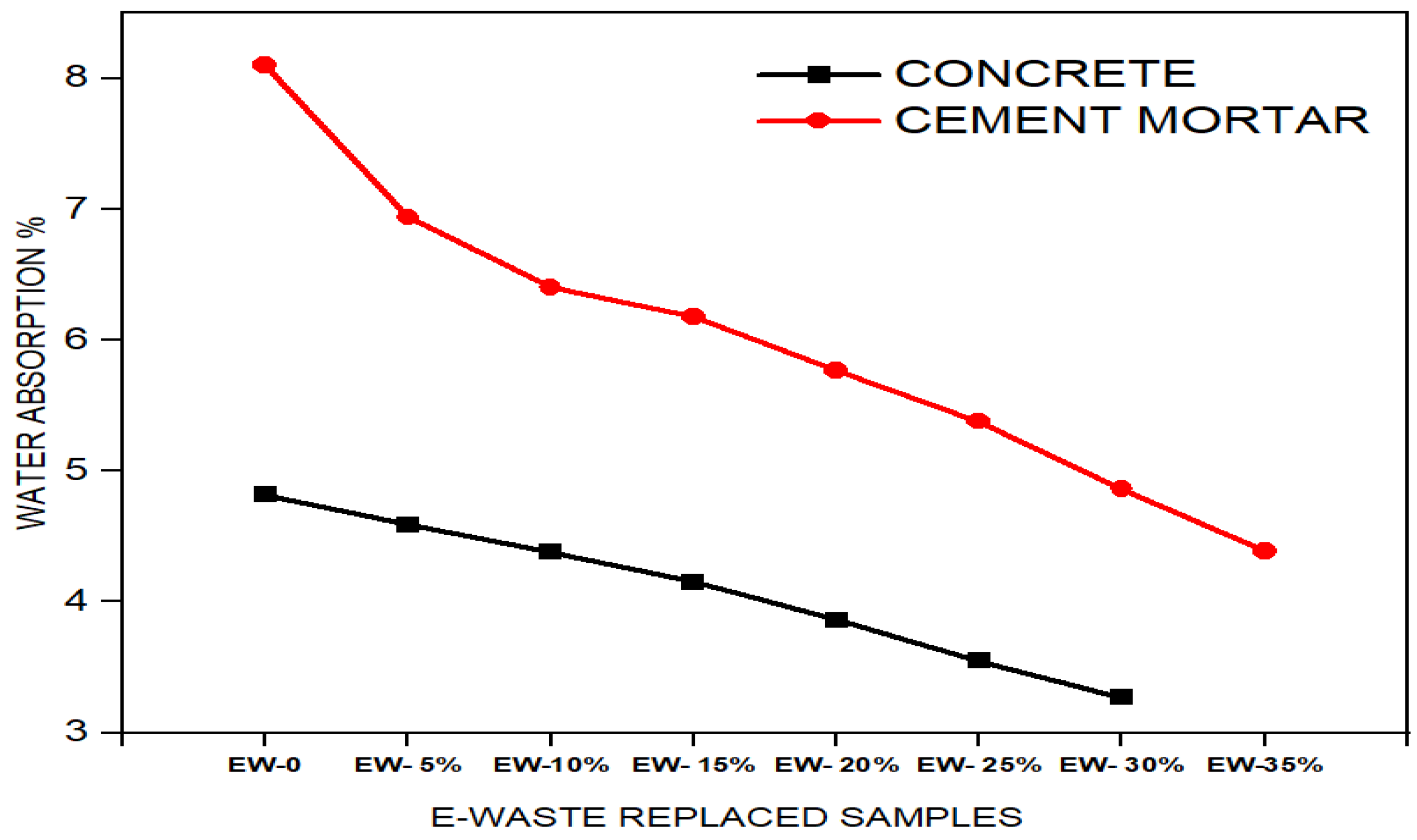
Figure 9 shows that the increase in E-waste replacement levels led to water absorption reduction for both cement mortar and concrete. Cement mortar consistently exhibits higher water absorption than concrete, where the percentage of water absorbed by cement mortar decreased from 8.39% to 4.39% when the material had 35 wt% E-waste.
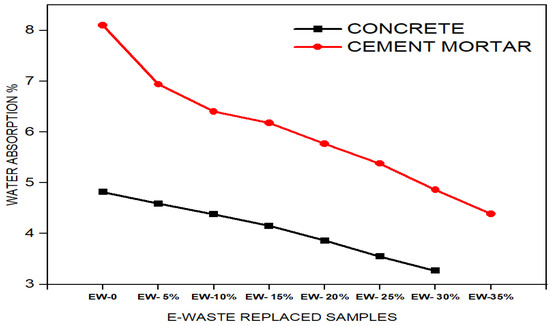
Figure 9.
Variation of water absorption with E-waste replacement of fine aggregates in concrete and mortar.
Concrete demonstrates lower water absorption values, starting from 4.82% during the initial phase, which reduced to 3.27% by increasing E-waste content up to 30 wt%. The water absorption rates decline due to the densification of the structure, credited to the inclusion of E-waste particles, while overall internal porosity decreases. The non-absorbent nature of E-waste (PCBs) materials reduces water permeability, resulting in reduced water retention.
2.5. Functional Properties
2.5.1. Acoustic Properties
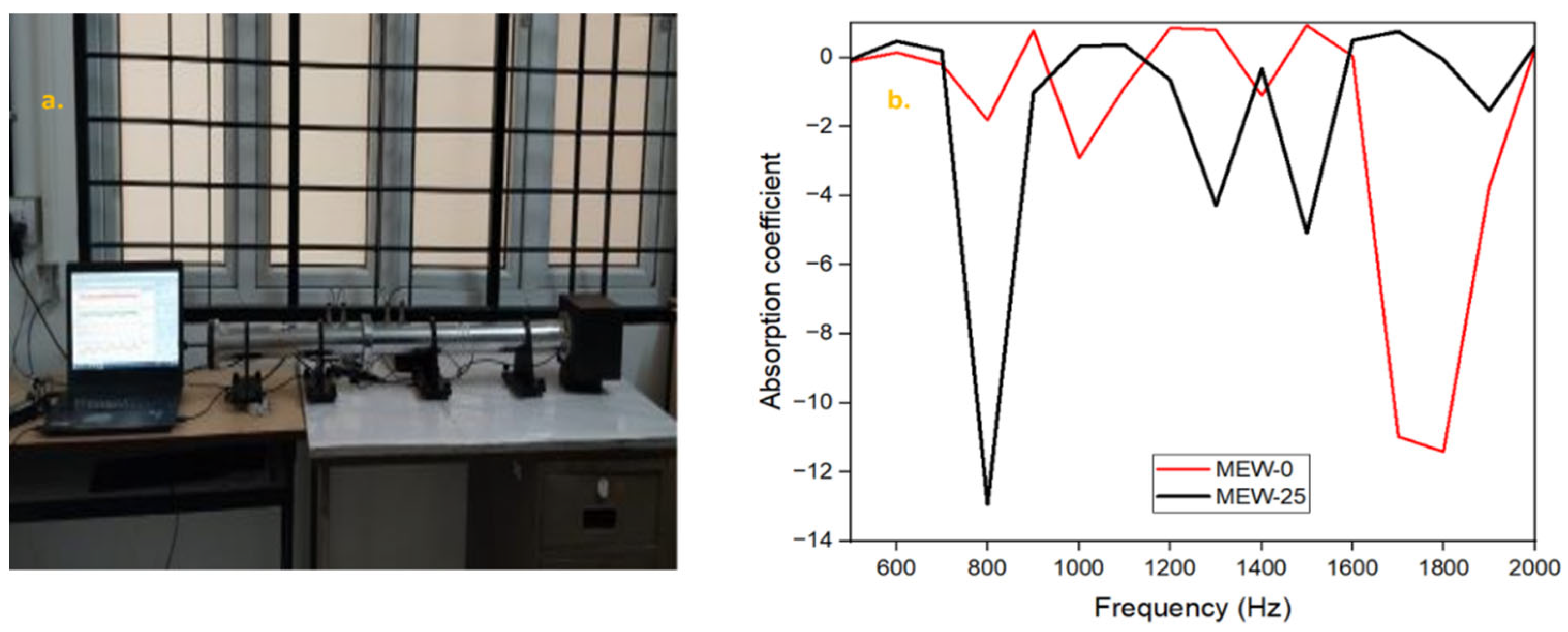
Functional properties refer to the characteristics of a material and how well it performs its intended purpose in construction. Because the in situ sound absorption instrument can have measurement errors below 200 Hz, the frequency range chosen for this study is from 500 to 2500 Hz [42]. The sound absorption tests were conducted using a suitable setup as shown in Figure 10a, and Figure 10b presents the acoustic test results for the mortar samples.
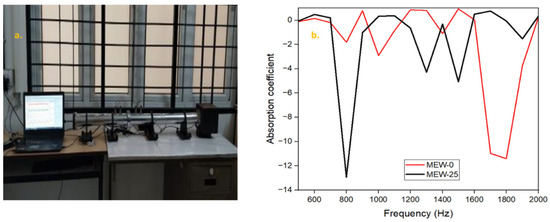
Figure 10.
(a) Sound absorption test setup; (b) variation of sound absorption coefficient with frequency.
The conventional mortar mix MEW0 produces noticeable absorption coefficient dips at two resonant frequency points of 800 Hz and 1800 Hz, credited to the sound wave reflection occurring in the material due to high density and homogeneity. The MEW25 mortar mix displayed a more consistent and uniform sound absorption response within the 1000–1600 Hz frequency range. This enhancement can be attributed to the sound wave dissipation in the cementitious composite material due to non-porous and irregularly shaped E-waste particles that create additional air voids, thereby disrupting matrix continuity and resulting in enhanced scattering effects and frictional losses in the structure. A modified transition zone between the cement mortar matrix and E-waste particles influences acoustic impedance values, thus leading to superior sound energy control and decreased wave formation patterns inside the structure.
The polymer component in PCBs, together with metallic elements, produces acoustic impedance discrepancies that lead to improved sound energy dissipation relative to standard cement mortar. The MEW25 mix shows promising results with balanced sound absorption across the mid-to-high frequency range, even though its low-frequency absorption is constrained by cementitious matrix stiffness properties. The aforementioned behavior indicates the potential for using it as a construction solution for sound-dampening applications.
The Noise Reduction Coefficient (NRC) for standard cement mortar samples used in acoustic applications is generally required to be higher than 0.035 [43]. The mortar samples with partial replacement of cement by PCB demonstrated an appreciable enhancement in NRC, with values ranging from 0.09 to 0.12. This improvement is assigned to the porous structure of the PCB particles, which improves sound absorption by increasing internal damping and scattering of sound waves.
2.5.2. Thermal Conductivity
Materials with low thermal conductivity display high resistance to heat flow, which limits heat transfer into buildings, and improves thermal comfort. Thermal conductivity of insulating materials usually ranges from 0.1 W/m⋅K to 0.7 W/m⋅K. The test specimens were placed between hot and cold plates, each of 45 × 30 × 1.8 cm in size. The test conditions were adjusted in such a way that the heat flow took place only in the vertical direction [44]. The temperature of the plates was observed until they reached a steady state. The thermal conductivity of the panel was calculated using Equation (4).
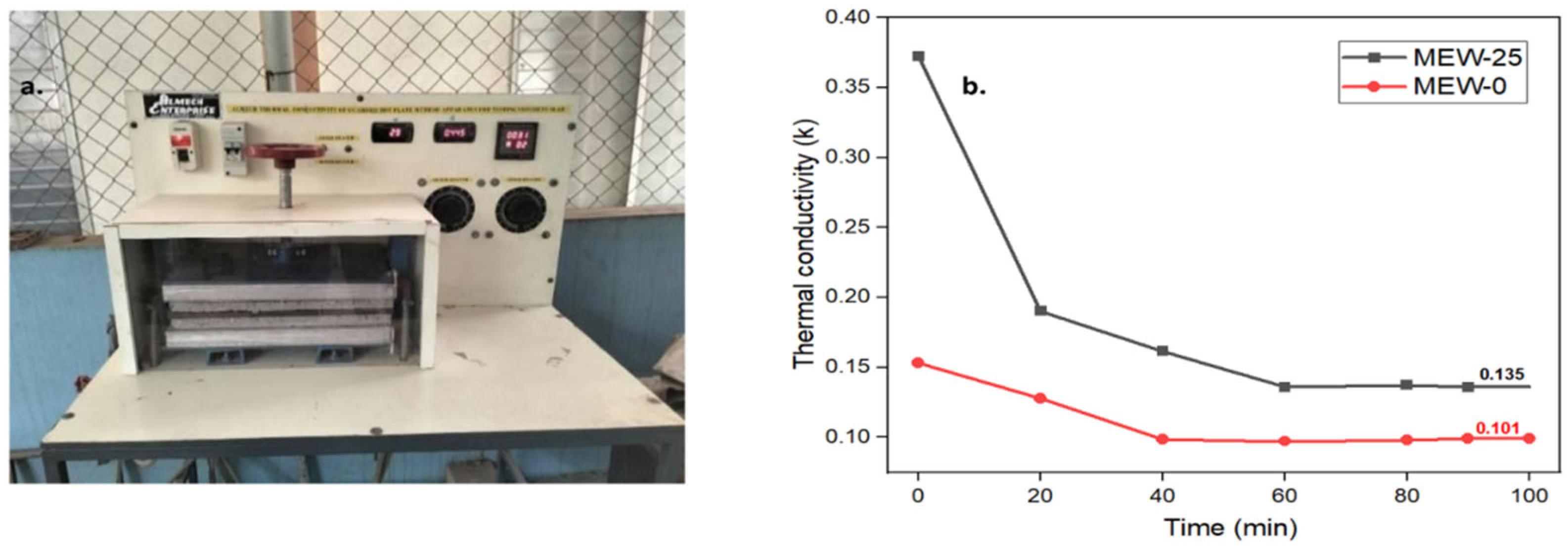
Figure 11a shows the test setup and Figure 11b presents the thermal conductivity test results for the (MEW0) control specimen and MEW25. The control specimen displayed lower and steady thermal conductivity, measuring 0.10 W/m·K, whereas the E-waste-incorporated specimen showed elevated conductivity before decreasing to 0.13 W/m·K. The high initial thermal conductivity of the E-waste-modified sample stems from the metallic components in the E-waste contents, which differ thermally from typical cementitious substances. The E-waste-modified mix develops thermal barriers through its expanding air voids, which slow down the overall heat transfer over time. Observed outcomes indicate that E-waste product integration modifies thermal resistance characteristics in mortar, improving the mix’s degradation resistance. The marginal increase in the thermal conductivity of E-waste-filled samples will not affect the thermal insulation capabilities of those materials.
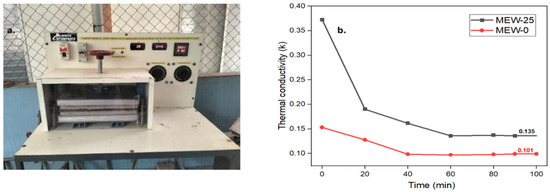
Figure 11.
(a) Thermal conductivity test setup; (b) variation of thermal conductivity with time.
The thermal conductivity for conventional concrete typically ranges from 1.4 to 2.5 W/mK [45]. The PCB-replaced cement mortar sample (MEW-25) exhibited thermal conductivity of 1.05 W/mK, lower than conventional mortar, suggesting improved thermal insulation.
2.5.3. Elevated Temperature Response
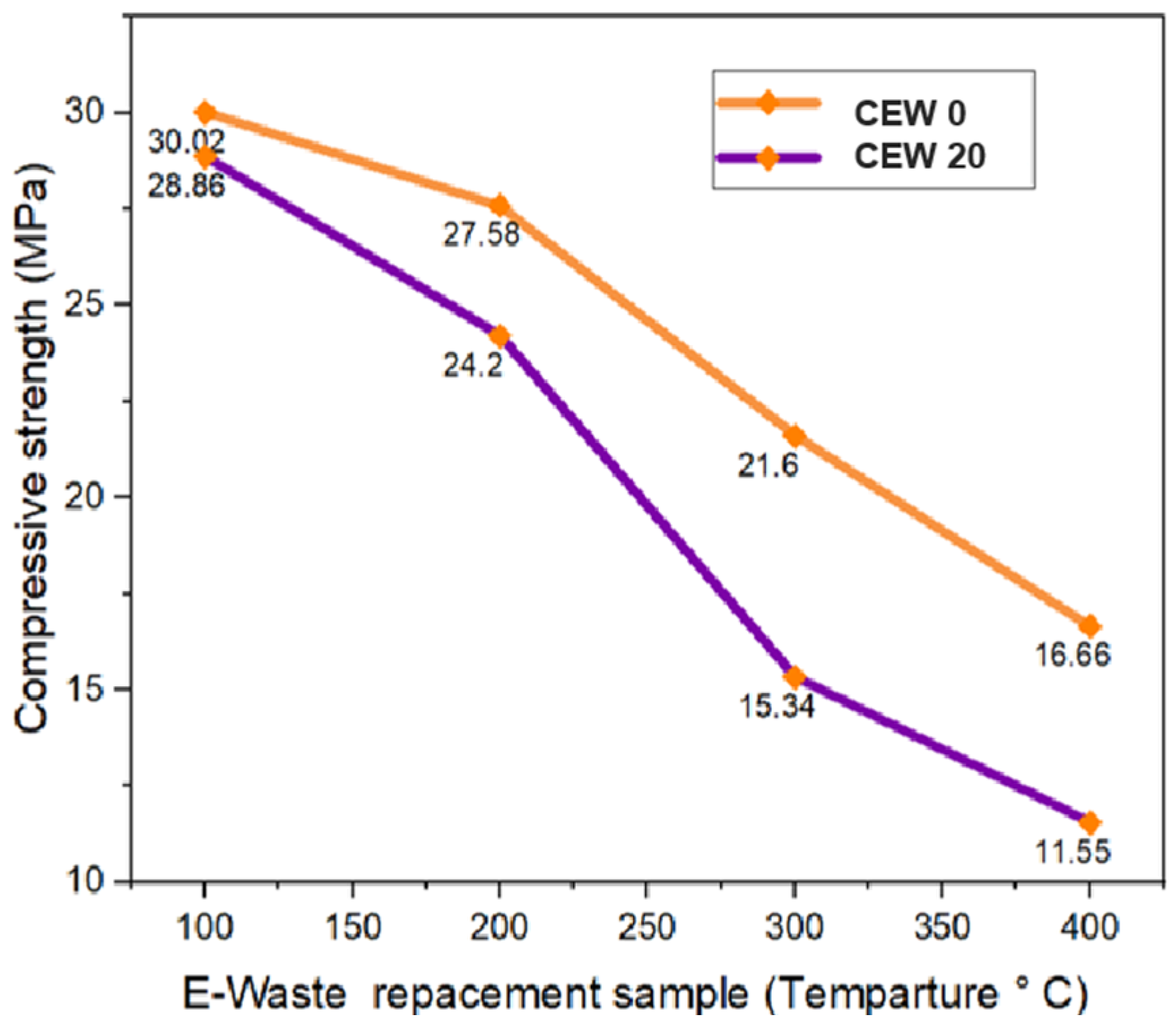
Figure 12 shows the compressive strength variation of various samples after exposure to elevated temperature. Three specimens were heated to 100 °C, 200 °C, 300 °C, and 400 °C, and then maintained at those respective temperatures for one hour, according to previous reports [46,47]. After cooling to room temperature, the specimens were subjected to compression strength evaluation. The results indicated a reduction in compressive strength for specimens exposed to higher temperatures, highlighting the adverse effects of thermal exposure on concrete.
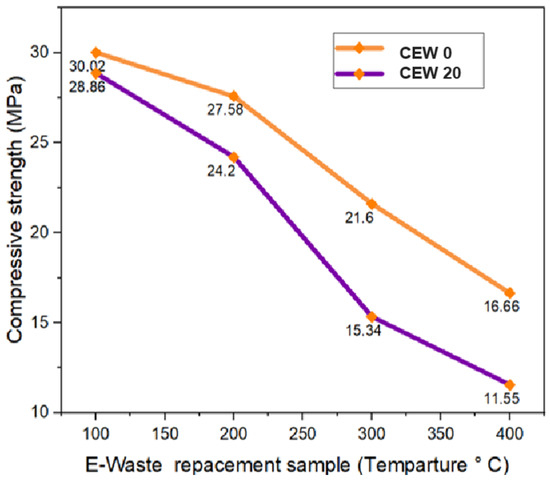
Figure 12.
Variation in compressive strength with temperature.
Figure 12 indicates a significant decrease in compressive strength for both the specimens after exposure to elevated temperature. The control specimen exhibited a 44.5% reduction in compressive strength, while the 20 wt% E-waste replacement specimens showed a 60.2% reduction. However, the rate of strength loss is more pronounced in the E-waste replacement specimens, indicating reduced thermal resistance. The E-waste typically contains thermoset resins, fiberglass, and some plastic materials. These components have lower thermal resistance than natural fine aggregates. Elevating the temperature in the sample containing E-waste material causes decay and creates micro voids and the heating of organic resin increases the internal porosity and debilitates the cementitious mix. The relative compressive strength of the control specimen was slightly higher than the E-waste replacement sample. Kavitha et al. [48] found a similar trend of strength loss after thermal exposure. When concrete was subjected to high temperatures, it tended to reduce its compressive strength. The strength retention of the control and E-waste samples in this study was lower than what they found, which suggests that the mix can be used only at a moderately elevated temperature.
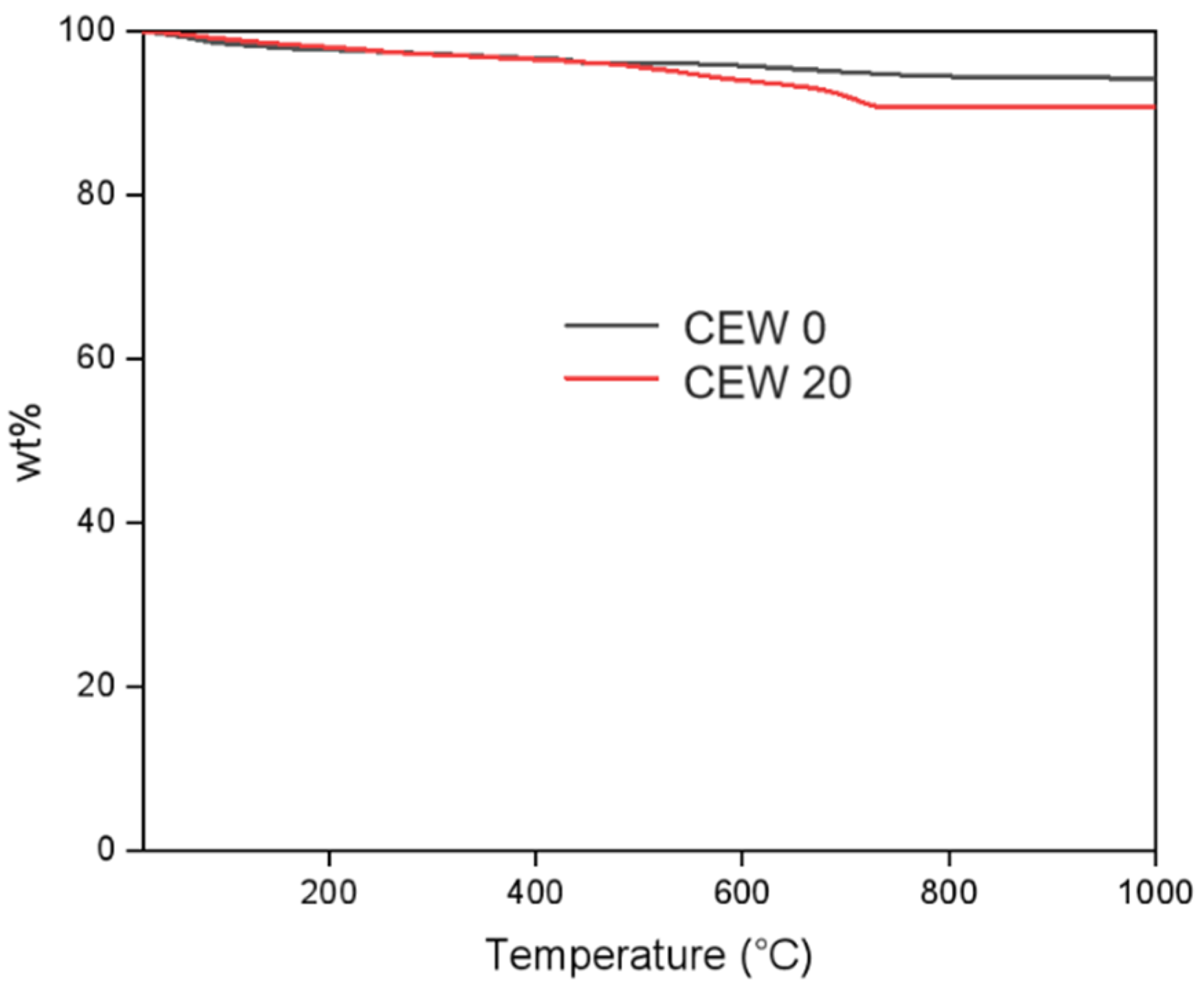
Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) was employed to observe the weight loss behavior of concrete samples with increasing temperature. The thermogram presented in Figure 13 shows that the weight loss in both the control sample and that incorporating 20% PCB (CEW 20) was nearly identical up to 450 °C. Beyond this temperature, the CEW 20 sample exhibited a slightly higher weight loss, approximately 4% more than the control. The marginal difference suggests that CEW 20 can be considered as a viable substitute for the control sample in applications ranging up to 400 °C.
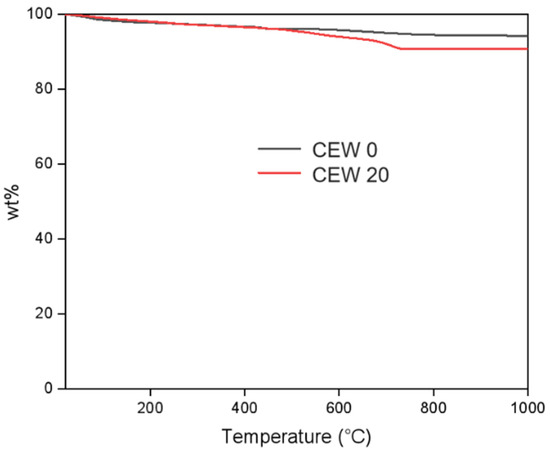
Figure 13.
TGA thermograms for CEW0 and CEW20 partially replaced samples.
2.6. Microstructural Studies
Microstructural studies in concrete focus on understanding the internal structure and composition of the material at a microscopic level. These studies reveal details about the hydration products, the distribution of pores and cracks, and the interfaces between different phases (such as the cement paste and aggregates). Microstructural analysis helps to explain the material’s mechanical properties, durability, and failure mechanisms.
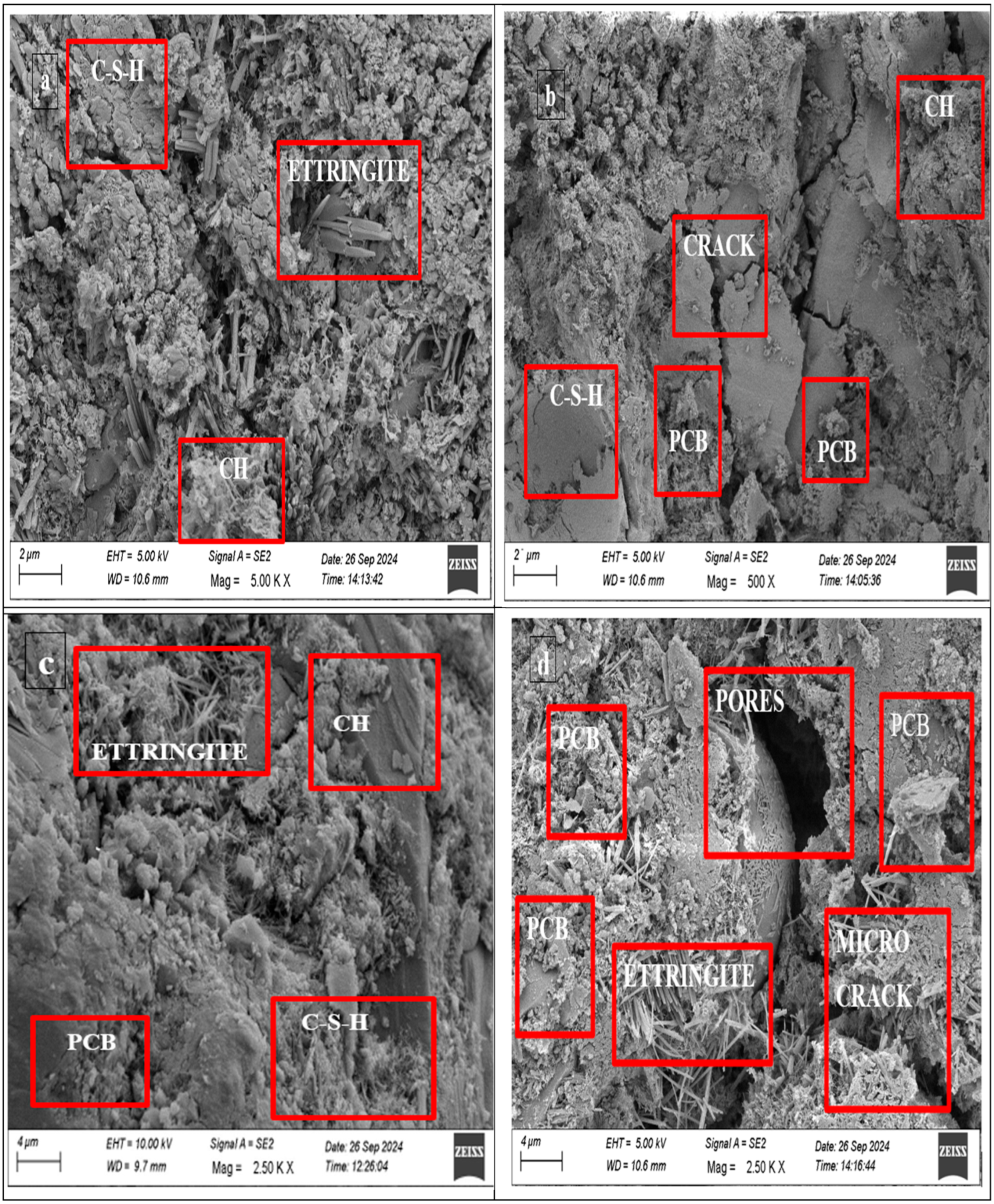
The SEM images shown in Figure 14 reveal marked differences in the surface appearance, cementitious bonds, and particle distribution. A dense and well-hydrated cementitious phase structure stands out in the control mix. The well-structured calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H) gel formed during the hydration process develops a homogeneous matrix structure that contains few voids. Several needle-shaped ettringite crystals can act as indicators for early hydration reactions, resulting in the strengthening of the material structure. The strong mechanical properties developed from the interconnected hydration phases present in the smooth matrix are indicators of enhanced cohesion. Meanwhile, the CEW30 E-waste replacement sample displayed an irregular and porous microstructural pattern and developed microcracks. The introduction of E-waste particles destroys the continuous cementitious phase, enabling greater void generation and deteriorating matrix densification. Porosity, along with micro-cracking, negatively impacts both durability and strength, which in turn affects the long-term durability and service life of the material. The modified properties lead to superior acoustic and thermal insulation performance through enhanced porosity based on previously documented findings regarding such changes. Additional mix proportion adjustments and additive tests will help minimize E-waste (PCBs)-related negative influence while enabling the valuable properties of this material to support sustainable concrete applications.
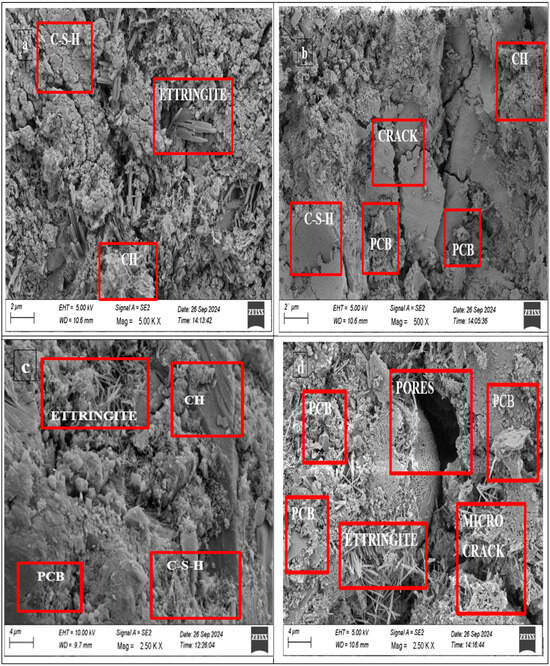
Figure 14.
SEM analysis of concrete specimens: (a) CEW0, (b) CEW20, (c) CEW10, (d) CEW30.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
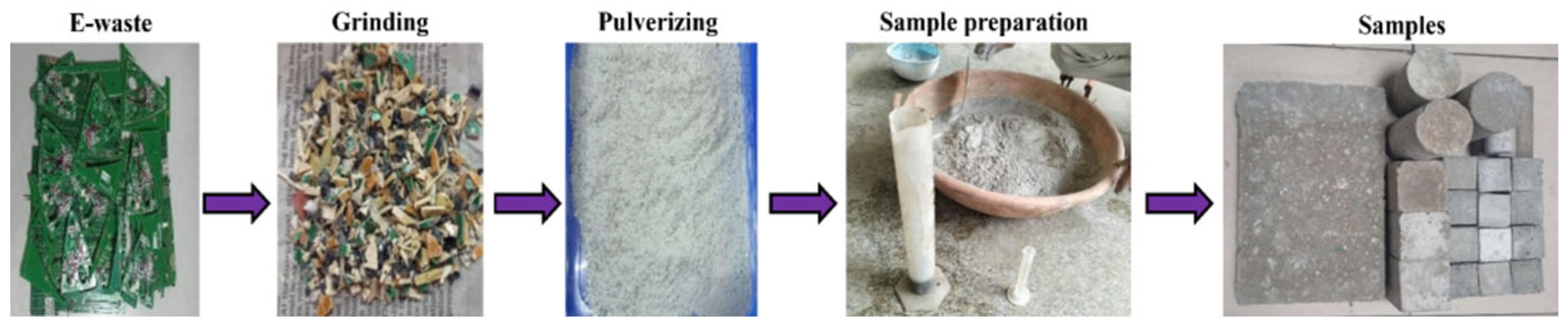
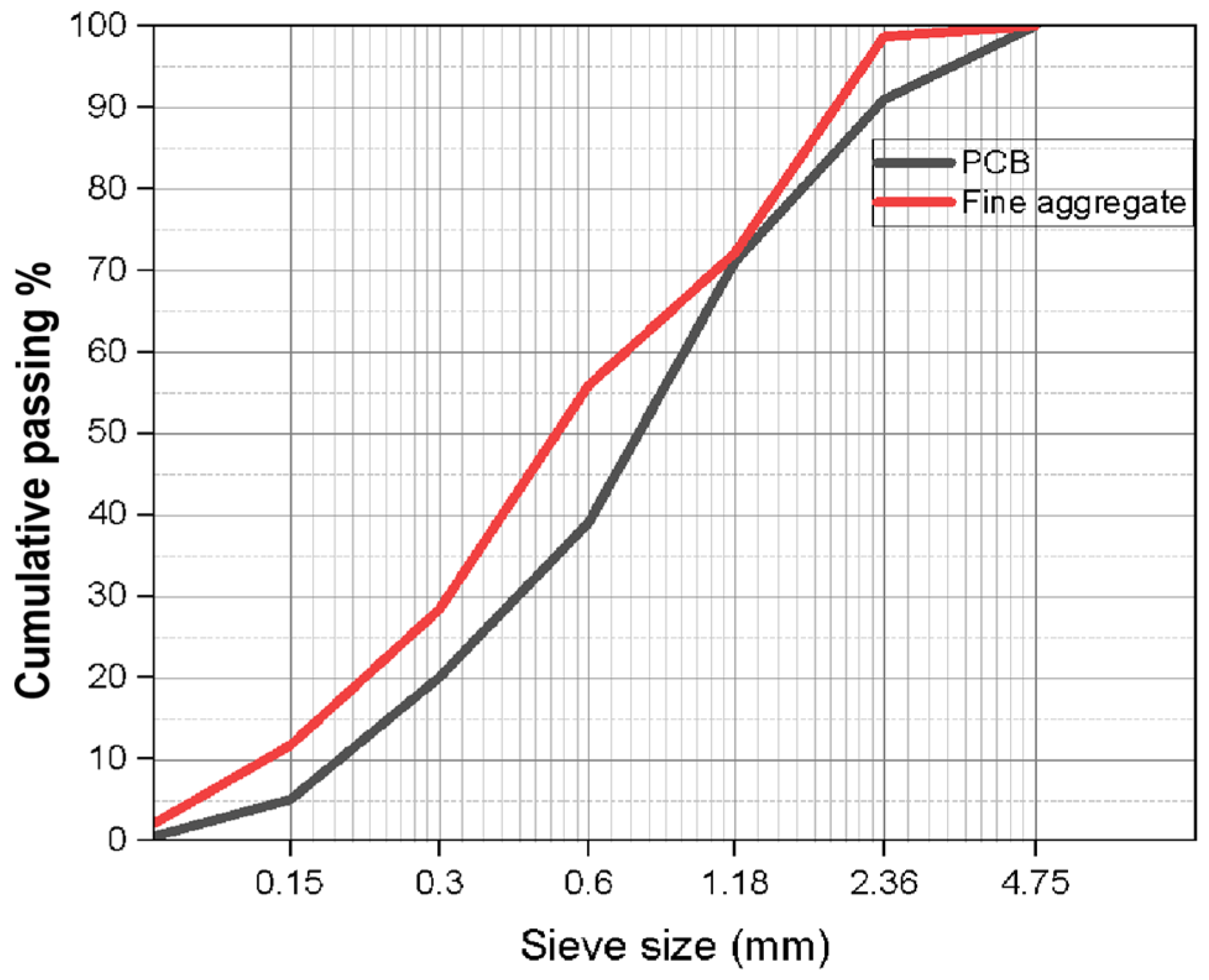
The experimental work was carried out using locally available Pozzolana Portland Cement (PPC) procured from the Associated Cement Companies (ACC) conforming to the Indian Standard IS-1489 (Part-1):2015 [49]. According to IS 383–2016, the locally available coarse aggregates passing through a 20 mm sieve and retained on a 12.5 mm sieve, as well as fine aggregates passing through a 4.75 mm sieve with a fineness modulus of 2.58 and in line with grading zone II of IS:383-1970 [50], were selected. The discarded printed circuit boards were obtained from a leading manufacturing company (FIEM Industries Limited), Hosur, Tamilnadu, India. The electronic components mounted on the PCBs were removed by the supplier. Further, they were subjected to desoldering to remove any traces of heavy elements like Tin (Sn). The size reduction of the PCBs thus obtained was achieved using a scrap grinder and pulverizer as illustrated in Figure 15, which presents the E-waste particle size reduction process and sample preparation. The pulverized E-waste particles were screened by passing through a size 4.75 mm sieve to obtain the finer particles. The particle size gradation curve of fine aggregate and E-waste is presented in Figure 16. The properties of the materials used are listed in Table 2.

Figure 15.
E-waste (PCBs) particle size reduction process and sample preparation.
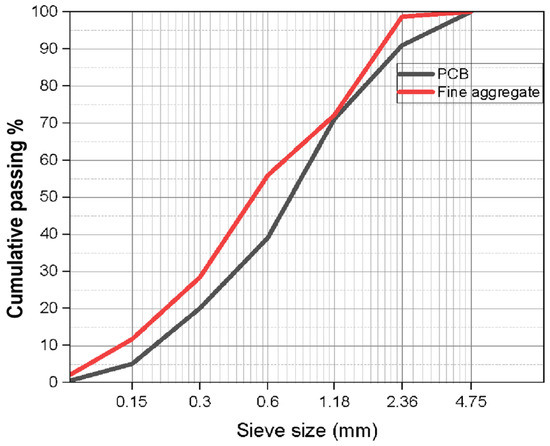
Figure 16.
Particle size distribution curve of fine aggregate and E-waste.

Table 2.
Properties of materials used.
3.2. Methods
Cement mortar with a mix ratio of 1:3 was prepared as per IS 2250:1981, and M25-grade concrete mix was prepared conforming to IS 10262:2019 [51,52], and the quantities are listed in Table 3. The fine aggregate in the concrete and mortar were replaced by ground E-waste at varied levels between 5% and 30% (maintaining an interval of 5%) in concrete, and addition of up to 35% in mortar. The mix proportions of E-waste incorporated into cement mortar and concrete are presented in Table 4 and Table 5, respectively, along with the nomenclature used. For cement mortar samples, the notation used is MEW, where M represents mortar and EW the E-waste. In the case of concrete samples, it is CEW, where C corresponds to concrete and EW to E-waste. The number after EW gives the percentage replacement of fine aggregate.

Table 3.
Mix proportion used for cement mortar and concrete.

Table 4.
Mix proportion of E-waste-incorporated cement mortar.

Table 5.
M25 concrete mix proportion.
After casting, the specimens were demolded after 24 h of exposure at ambient temperature and subsequently water cured for 28 days for hydration and strength gain. Table 6 presents the details of test specimens used for various property assessments.

Table 6.
Details of test specimens.
The slump cone test for concrete was conducted as per IS 1199 (Part 2) 2018, and mini slump flow was measured for cement mortar following ASTM C1437. Various tests were conducted to examine the mechanical, functional, and durability characteristics of the prepared specimens. All tests were conducted on three specimens for each mix proportion and the average values with standard deviation are reported. The variation of compressive strength with E-waste replacement in fine aggregate for cement mortar and concrete samples was evaluated at curing ages of 7 and 28 days. The compressive strength test of concrete and cement mortar cubes was performed as per IS 516 (Part 1/Sec 1):2021 and IS 4031 (Part 6):1988 [53]. The loading rate for compressive strength was maintained at 140 MPa/min as per the IS 516 (Part 1/Sec 1):2021 [54]. The specimen was tested using a computerized control digital compression testing machine with a capacity of 3000 kN, and the load was applied until failure. The split tensile strength and flexural strength tests were carried out conforming to IS 516 (Part 2/Sec 1): 2021, respectively. The impact strength tests for cement mortar and concrete were conducted conforming to ACI 544.2R-89, using cylindrical samples measuring 100 × 50 mm. An ultrasonic pulse velocity (UPV) test using Proceq Pundit Lab manufactured by PROCEQ SA, Switzerland was employed to assess the quality and integrity of concrete by measuring the speed of sound waves traveling through the specimen. The test was performed as per IS 516 (Part 5/SEC 1):2018 [55]. Durability studies, involving sulfate attack on concrete cylinders immersed in Na2SO4 solution, were conducted following ASTM C1012 [56]. The fire resistance of the developed samples was investigated by exposing the samples to elevated temperatures, where the cube specimens were heated in a furnace at 100 °C, 200 °C, 300 °C, and 400 °C and subsequently tested to find the residual strength [57]. The sound absorption coefficient of concrete was tested using an impedance tube at a frequency range of 500–2500 Hz, according to ISO 10534-2. Thermal conductivity tests were conducted using the hot guarded plate method conforming to ASTM C 177-97 standards. Thermal degradation studies were conducted using a NETZSCH, STA 2500 TGA, manufactured by NETSCH Analysis and Testing, Germany at 10 °C/min, from room temperature to 1100 °C. Microstructural studies were carried out using a Field-Emission Scanning Electron Microscope (FE-SEM), model ZEISS GEMINI SEM 300, manufactured by Carl Zeiss, Germany to understand the changes in hydration products, pore distribution, and interfacial bonding, along with determination of the chemical composition with color mapping.
4. Conclusions
This comprehensive study demonstrates that E-waste (PCBs) can be effectively utilized as a partial replacement for fine aggregate in mortar at a 25 wt% replacement level, and 20 wt% replacement in concrete without compromising the fundamental properties. The materials like copper, aluminum, and iron present in PCBS react with lime released during cement hydration to form additional C-S-H gel, which helps to increase the concrete’s strength over time. The particles from crushed E-waste can fill voids within the concrete mix, leading to better packing and a uniform distribution of ingredients. The use of E-waste (PCBs) materials can reduce the overall porosity and permeability of concrete.
- ➢
- Mechanical properties showed a noticeable improvement with increasing E-waste content up to 25 wt% for cement mortar and 20 wt% for concrete. When 25 wt% of PCB was used as replacement for fine aggregate, the mortar’s compressive and tensile strengths improved by 5.8%, while the strength of concrete samples increased by 3.1% for 20 wt% replacement, compared to the control mix. These enhancements are attributed to better matrix densification and the pozzolanic-like behavior of E-waste particles.
- ➢
- The durability properties were improved, especially the water absorption behavior. Compared to the control mixes, the modified mixes showed a 1.7% decrease in water absorption. This meant they were less likely to let water in and were able to endure in moisture-prone conditions.
- ➢
- However, excessive replacement beyond the optimal level led to inferior performance due to inadequate cement hydration. The dehydrated cement and broken C-S-H gel structures indicated this observation. These mixes exhibited higher permeability and lower strength characteristics due to the presence of a large number of pores and tiny cracks.
- ➢
- Functional properties such as acoustic and thermal insulation also showed improvements in the modified mixes. The improvement is primarily due to the low conductivity of PCB materials, as well as the increased porosity and heterogeneous internal structure introduced by the E-waste. These small pores in the material structure reduce the conduction of heat and sound vibrations, thereby elevating thermal and sound insulation. The thermal stability of PCB-incorporated concrete was found to match that of the control samples up to 400 °C, as ascertained from TGA.
Overall, this study aligns well with the theme of sustainable construction, demonstrating a feasible solution for environmentally responsible infrastructure development. The utilization of waste PCBs in concrete mixtures can be achieved at a lower cost, offering economic advantages without compromising structural or functional performance.
Further research will aim to explore long-term performance under diverse environmental conditions, investigate dynamic load responses, decipher the flow behavior of the developed mix through rheological characterization, and conduct leaching studies to confirm the absence of heavy metal traces. Moreover, a comprehensive Life Cycle Analysis (LCA) will be undertaken to evaluate the environmental impacts and validate the material’s viability from a circular economy perspective.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.K.; methodology, S.K., J.K., and M.K.M.; validation, J.K. and M.K.M.; formal analysis, S.K.; investigation, S.K.; data curation, S.K. and S.G.K.B.; writing—original draft preparation, S.K. and S.G.K.B.; writing—review and editing, J.K. and M.K.M.; supervision, J.K. and M.K.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data will be made available by the authors upon request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Department of Civil Engineering, Amrita Viswa Vidyapeetham, Coimbatore, for providing testing and sample preparation facilities. Additionally, the authors gratefully acknowledge the support received from Center of Excellence—Advance Materials and Green Technologies (COE-AMGT) for their assistance in material characterization. All individuals acknowledged have provided their consent to be included.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Danish, A.; Mosaberpanah, M.A.; Ozbakkaloglu, T.; Salim, M.U.; Khurshid, K.; Bayram, M.; Amran, M.; Fediuk, R.; Qader, D.N. A compendious review on the influence of e-waste aggregates on the properties of concrete. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 18, e01740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needhidasan, S.; Sai, P. Demonstration on the limited substitution of coarse aggregate with the E-waste plastics in high strength concrete. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 22, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjunath, T.A. Partial Replacement of E-plastic Waste as Coarse-Aggregate in Concrete. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2016, 35, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borthakur, A.; Govind, M. Public understandings of E-waste and its disposal in urban India: From a review towards a conceptual framework. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 1053–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldé, C.P.; Kuehr, R.; Yamamoto, T.; McDonald, R.; Althaf, S.; Bel, G.; Deubzer, O.; Fernandez-Cubillo, E.; Forti, V.; Gray, V.; et al. Global E-Waste Monitor 2024; International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and United Nations Institute for Training and Research (UNITAR): Geneva, Switzerland; Bonn, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Dixit, S.; Arora, R.; Kumar, K.; Bansal, S.; Vatin, N.; Araszkiewicz, K.; Epifantsev, K. Replacing E-waste with coarse aggregate in architectural engineering and construction industry. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 56, 2353–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalpana, M.; Vijayan, D.S.; Benin, S.R. Performance study about ductility behavior in electronic waste concrete. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 33, 1015–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothinathan, S.K.M.; Kumar, P.; Arunachelam, N.; Gnanaraj, S.C. Effect of PCB as partial replacement of fine aggregate and coarse aggregate in concrete. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 49, 2369–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuqin, L.; Minyan, T.; Hongwei, T.; Xiaoyu, L.; Jian, G. Assessing sustainability on Chinese university campuses: Development of a campus sustainability evaluation system and its application with a case study. J. Build. Eng. 2019, 24, 100747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, R.; Ganesh, V.N.; Mahesh, S.R.; Vishnuvardhan, K. Performance evaluation of E-waste and Jute Fibre reinforced concrete through partial replacement of Coarse Aggregates. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 45, 6242–6246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janani, S.; Preethi, K.; Gowtham, S.; Kulanthaivel, P. A sustainable reuse of e waste as a partial replacement material for aggregate. Mater. Today Proc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.; Panigrahi, S.K. Production of sustainable GGBFS-based self-compacting geopolymer concrete containing e-waste aggregates under ambient temperature curing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 440, 137373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, Z.; Qureshi, M.I.; Ahmad, A.; Khan, S.U.; Javaid, M.F. An experimental study on the mechanical and durability properties assessment of E-waste concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 38, 102177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sua-iam, G.; Chatveera, B. Effect of printed circuit board dust on the workability and mechanical properties of self-compacting concrete: A preliminary study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 53, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manatkar, P.A.; Deshmukh, G.P. Use of non-metallic e-waste as a coarse aggregate in concrete. Int. J. Res. Eng. Technol. 2015, 4, 242–246. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.; Li, J. Enhancement of Compressive Strength and Durability of Sulfate-Attacked Concrete. Buildings 2024, 14, 2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, A.P.; Mohanty, S.; Sarkar, A. Application of Recycled Aggregates Generated from Waste Materials towards Improvement in Acoustical and Thermal Conductivity of Concrete. Mater. Today Proc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, G. Leaching behavior of heavy metals from PCB-embedded concrete matrices. Waste Manag. 2020, 118, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Houda, M.; Khan, S.; Althoey, F.; Abuhussain, M.; Abuhussain, M.A.; Javed, M.F. Mechanical behavior of E-waste aggregate concrete using a novel machine learning algorithm: Multi-expression programming (MEP). J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 5720–5740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanem, H.; Chahal, S.; Khatib, J.; Elkordi, A. Flexural behavior of concrete beams reinforced with recycled plastic mesh. Buildings 2022, 12, 2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Bansal, T.; Haq, M.; Sharma, U.; Kumar, A.; Jha, P.; Sharma, D.; Kamyab, H.; Valencia, E.A.V. Utilizing E-Waste as a Sustainable Aggregate in Concrete Production: A Review. Buildings 2024, 14, 2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Balachandran, V. E-waste problems: An analysis. Int. J. Adv. Res. Manag. Soc. Sci. 2015, 4, 60–71. [Google Scholar]
- Sabrin, R.; Shahjalal, M.; Bachu, H.A.E.; Habib, M.M.L.; Jerin, T.; Billah, A.M. Recycling of different industrial wastes as a supplement of cement for sustainable production of mortar. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 86, 108765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.; Pradhan, M.; Panigrahi, S.K. Sustainable Self-Compacting Conventional Concrete Development with Optimal Content of Ladle Furnace Slag Concerning Mechanical and Durability Characteristics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 471, 140761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.Y. Data-driven Approaches for Predicting Hazardous Substances in the Building Stock. Doctoral Thesis, Department of Building and Environmental Technology, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, D.; Xia, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, F.; Ma, X.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, M.; Yu, K. Recycling E-waste CRT glass in Sustainable Geopolymer Concrete for Radiation Shielding Applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, T.; Kaliyavaradhan, S.K.; Kakria, K.; Malladi, R.C. Use of e-waste in metakaolin-blended cement concrete for sustainable construction. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muchhadiya, P.D.; Pitroda, J.R.; Gujar, R.; Soni, J. Multiple Regression Models for Compressive and Flexural Strength of Recycled Printed Circuit Board Concrete. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 62, 6992–6997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyan, M.V.; Ravella, D.P.; Alaneme, G.U. Transforming electronic waste into sustainable building materials for a cleaner environment: A review. Discov. Mater. 2024, 4, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzie, C.A.; Southworth, B.; Stephenson, G.; Feisthauer, N. The Importance of Understanding the Chemical Form of a Metal in the Environment: The Case of Barium Sulfate (Barite). Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2008, 14, 974–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeshal, I.; Tayeh, B.A.; Alyousef, R.; Alabduljabbar, H.; Mohamed, A.M.; Alaskar, A. Use of Recycled Plastic as Fine Aggregate in Cementitious Composites: A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 253, 119146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osei, D.Y. Experimental Investigation on Recycled Plastics as Aggregate in Concrete. Int J Struct Civ Eng Res 2014, 3, 168–174. [Google Scholar]
- Akinyele, J.O.; Ajede, A. The Use of Granulated Plastic Waste in Structural Concrete. Afr. J. Sci. Technol. Innov. Dev. 2018, 10, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, H.T.; Jayanarayanan, K.; Mini, K.M. A Sustainable Approach for the Utilization of PPE Biomedical Waste in the Construction Sector. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2022, 32, 101060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafsirojjaman, T.; Dogar, A.U.R.; Liu, Y.; Manalo, A.; Thambiratnam, D.P. Performance and Design of Steel Structures Reinforced with FRP Composites: A State-of-the-Art Review. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 138, 106371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C1709-18; Standard Guide for Evaluation of Alternative Supplementary Cementitious Materials (ASCM) for Use in Concrete. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.K.; Kumaran, A.S.; Kandasamy, A.; Mohamed, M.J.S. Strength Characteristics of Concrete Using Electronic Plastic Waste and Coconut Shell as Natural Aggregates. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 56, 2353–2358. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.; Li, J.; Lu, Z.; Li, Z.; Fang, C.; Huang, L.; Li, L. Combination Effects of Rubber and Silica Fume on the Fracture Behaviour of Steel-Fibre Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 203, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, A.B.; Revilla-Cuesta, V.; Skaf, M.; Faleschini, F.; Ortega-López, V. Utility of Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity for Estimating the Overall Mechanical Behavior of Recycled Aggregate Self-Compacting Concrete. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrose, E.; Ogirigbo, O.R.; Ekop, I.E. Compressive Strength and Resistance to Sodium Sulphate Attack of Concrete Incorporated with Fine Aggregate Recycled Ceramic Tiles. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2023, 27, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IS 1124; Method of Test for Determination of Water Absorption, Apparent Specific Gravity and Porosity of Natural Building Stones. BIS: New Delhi, India, 1974.
- Palomar, I.; Barluenga, G.; Puentes, J. Lime–cement mortars for coating with improved thermal and acoustic performance. Build. Environ. 2012, 48, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Pyo, S. Experimental Study on the Sound Absorption Performance of Surface-Perforated Mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 307, 124824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Homoud, M.S. Performance characteristics and practical applications of common building thermal insulation materials. Build. Environ. 2005, 40, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardhira, P.J.; Ardra, R.; Harika, M.; Sathyan, D. Study on Fibre Reinforced Foam Concrete-a Review. Mater. Today Proc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, C.-S.; Azhar, S.; Anson, M.; Wong, Y.-L. Comparison of the Strength and Durability Performance of Normal-and High-Strength Pozzolanic Concretes at Elevated Temperatures. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodur, V.K.R. Performance-based fire resistance design of concrete structures. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2007, 237, 1999–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, S.S.; Madhavan, M.K.; Jayanarayanan, K.; Sarker, P.K. Axial Compressive Behavior of CFRP and MWCNT Incorporated GFRP Confined Concrete Cylinders After Exposure to Various Aggressive Environments. J. Compos. Sci. 2024, 8, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IS 1489-1 (1991); Specification for Portland Pozzolana Cement, Part 1: Flyash Based. Bureau of Indian Standards: New Delhi, India, 1991.
- IS 383:1970; Specification for Coarse and Fine Aggregates from Natural Sources for Concrete. Bureau of Indian Standards: New Delhi, India, 1970.
- IS 2250:1981; Code of Practice for Preparation and Use of Masonry Mortars. Bureau of Indian Standards: New Delhi, India, 1981.
- IS 10262:2019; Code of Practice for Concrete Mix Proportioning. Bureau of Indian Standards: New Delhi, India, 2019.
- IS: 4031 (6); Methods of Physical Tests for Hydraulic Cement. Part 6: Determination of Compressive Strength of Hydraulic Cement Other than Masonry Cement. Bureau of Indian Standards: New Delhi, India, 1989.
- IS 516 (Part 1/Sec 1); 2021 Method of Tests for Strength of Concrete. Indian Standard: New Delhi, India, 2002.
- IS 516 (Part 5/Sec 1); 2018—Hardened Concrete—Methods of Test—Part 5 Non-Destructive Testing of Concrete—Section 1 Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity. Bureau of Indian Standards: New Delhi, India, 2018.
- ASTM C1012; Standard Test Method for Length Change of Hydraulic-Cement Mortars Exposed to a Sulfate Solution. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024.
- ASTM C177-19; Standard Test Method for Steady-State Heat Flux Measurements and Thermal Transmission Properties by Means of the Guarded-Hot-Plate. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).