Abstract
Flotation was investigated to treat incineration fly ash with diesel, kerosene, TX-100, or SDS as a collector and methyl isobutyl carbinol (MIBC) or 2-Octyl alcohol as a frother. Fly ash was separated into light and residual materials. Comparison of yield, carbon and sulfur removal showed that kerosene and MIBC showed the best performance. The results revealed that flotation was a method that could simultaneously achieve the removal of organics and S-containing compounds. Specifically, approximately 7.63–9.45% of the total mass was collected as light material, which was enriched with organic carbon. Contents of organic carbon reached 14.35 wt%–14.56 wt% in the light materials from those of 2.74 wt%–3.52 wt% in the original fly ash. Elemental analysis further proved that sulfur was also accumulated in light material. Approximately 78.84–81.69% of the organic carbon and 80.47–82.66% of the sulfur were removed. Decarbonization was primarily achieved through the flotation of organic materials, while desulfurization resulted from both flotation and the dissolution of soluble salts. Furthermore, the contents of the chloride and heavy metals in the residual fly ash also decreased. Particle size analysis showed that flotation was effective in the removal of smaller particles, and those particles were also rich in heavy metals. Overall, by selecting the right collector and frother, flotation was also able to reduce the leaching toxicity of heavy metals. The residual fly ash was safe for further disposal. Organic carbon, sulfur and heavy metals were accumulated in the light materials, which accounted for less than 10% of the original mass. The portion of fly ash needing further treatment was therefore greatly reduced.
1. Introduction
Municipal solid waste (MSW) incineration fly ash is a residual collected from the flue gas purification system [1]. Fly ash accounts for approximately 2–12% of the total quantity of incinerated MSW [2]. Inorganics such as CaO, CaCO3, SiO2, Al2O3 and chloride salts (CaCl2, NaCl, KCl) are the predominant components of fly ash [3]. The compositions were very close to those of auxiliary cementitious materials, such as blast furnace slag. Therefore, fly ash could potentially be reused as construction and geoengineering materials. However, fly ash also contains a large amount of chloride salts, heavy metals and dioxin.
The chlorine content (5–27 wt%) in fly ash is significantly higher than that required for construction materials [4,5]. Washing, heat treatment and electrodialysis are some of the technologies for chlorine removal [6]. Heavy metals and dioxin are highly toxic and susceptible to leaching in the environment. At present, heavy metals are solidified, stabilized or removed via thermal treatment, chemical reagent complexation, washing, bioleaching, etc. [7,8]. Lin et al. [9] categorized heavy metal treatment into two groups: thermal and non-thermal. The former includes melting, sintering, vitrification, and hydrothermal processes, while the latter includes solidification/stabilization, biological/chemical extraction, and mechanochemical processes, among others. The synthesis of dioxins mostly occurred in the tail end of the incinerator and was absorbed by fly ash because of its large surface area [10]. Technologies to degrade dioxin are mostly thermal (plasma technology, hydrothermal treatment, etc.). Photocatalytic and biological degradation are also found to be promising.
Besides biological and chemical methods, physical methods were also employed to separate hazardous components by taking advantage of the difference in particle size or density. Ko et al. [11] used a hydrocyclone to separate fly ash into coarse and fine particles. Since heavy metals such as Pb and Zn tended to accumulate in fine particles, the coarse fraction of fly ash was much less hazardous. Liu et al. [12] investigated column and cell flotation to detoxify medical waste incineration fly ash. Carbonaceous materials (powdered activated carbon) were enriched in the froth. Thus, organics (dioxin) and heavy metals adsorbed on the activated carbon were removed. The removal efficiency of dioxin reached as high as 91% while the leaching of heavy metals in the tailings was greatly reduced.
Flotation is a technology widely used to separate liquid or solid from aqueous in wastewater treatment, mineral processing or particle separation [13]. Flotation was employed to desulfurize iron ores to reduce the emission of SO2 during iron pelletizing in the steel industry [14]. Flotation for fly ash treatment was mainly employed to separate unburned carbon from coal-combustion fly ash. Tokgoz et al. [15] argued that the presence of unburned carbon would reduce the strength of concrete and its resistance to weathering, affecting the water requirement and compactness of the concrete. It is one of the key factors in the determination of the suitability of fly ash as building or ceramic materials [16]. Therefore, the separation of unburned carbon from fly ash is considered essential for maximizing its resource potential.
However, the direct flotation of fly ash was mostly ineffective. Unburned carbon is porous and rich in oxygen-containing surface functional groups after high-temperature combustion in an oxygen-rich environment. Thus, the residual unburned carbon is quite hydrophilic and difficult to separate from water. Therefore, collectors have to be used to enhance flotation by increasing the surface hydrophobicity of carbon. Kerosene, diesel, oleic acid, alkanolamides, and surfactants (e.g., sodium dodecyl sulfate, sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate, Tween-80 and Triton X-100) have all been tested as collectors [17,18,19,20]. In addition, to stabilize the bubbles, the frother (e.g., 2-octanol, methyl isobutyl carbinol) was also added to reduce surface tension [21].
During municipal solid waste incineration, powdered activated carbon is often injected into the flue gas to remove pollutants. The injected activated carbon is later collected in the fly ash. Therefore, incineration fly ash also contains carbon materials that are often rich in both organics and heavy metals. In addition, studies have shown that pollutants such as heavy metals and dioxins tend to be enriched in smaller particles [22]. In this research, air flotation was investigated for its effect on the detoxification of fly ash. A selection of collectors and frothers was tested. The characteristics of fly ash (physical and chemical) before and after flotation were investigated. The changes in organic and inorganic carbon contents, elemental contents (mainly C and S), and heavy metal leaching toxicity were used to select the optimal collector and frother. The ultimate goal was to reveal the feasibility of flotation as a technology for fly ash treatment and provide useful information for its application.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preliminary Experiment
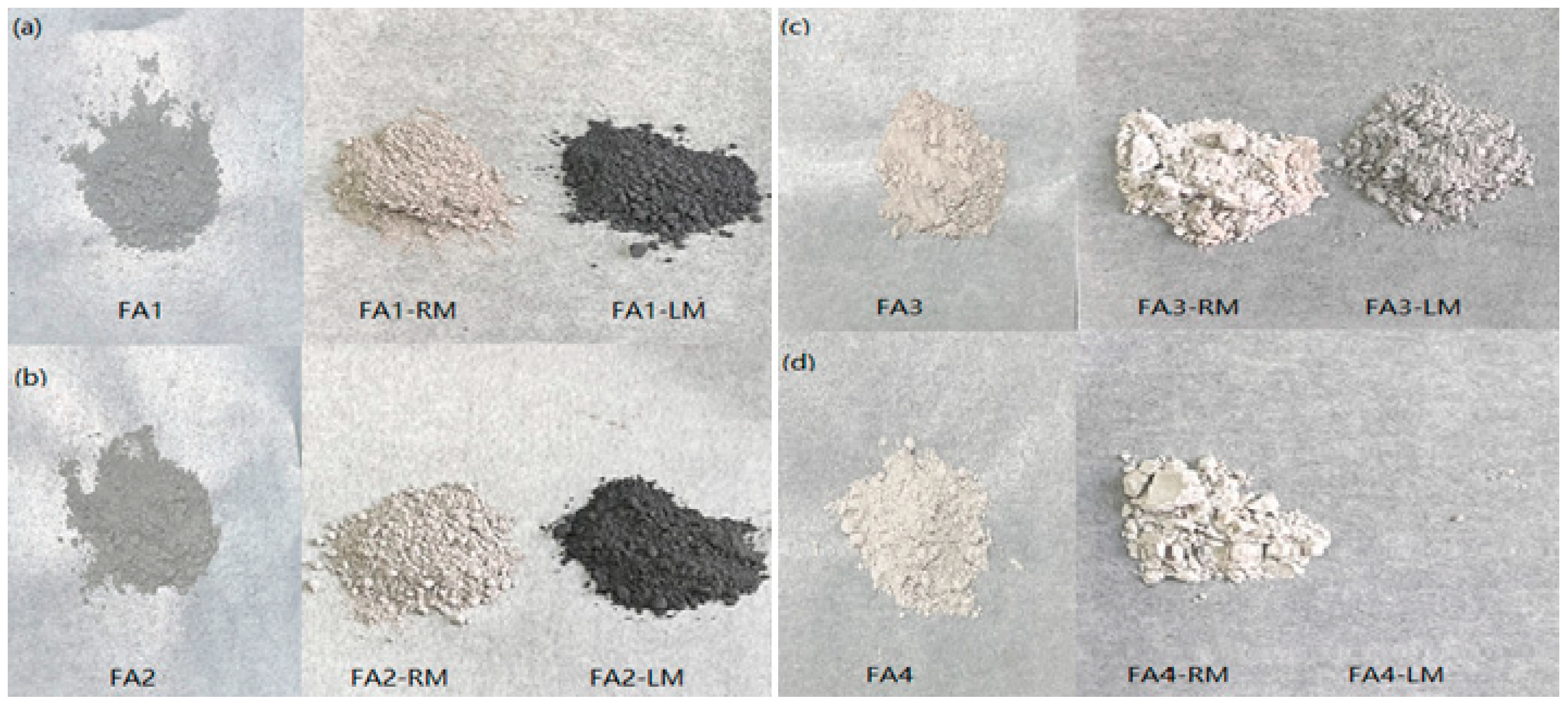
The flotation study started with four fly ashes (named as FA1-FA4) from different cities in China. Preliminary tests on these four fly ashes were conducted with kerosene as a collector and MIBC as a frother. Figure 1 is an image of the original fly ashes together with the light material and residual material collected after flotation. The original fly ashes were different in color. The deeper color could mainly be attributed to the powdered activated carbon added during flue gas treatment. Loss on ignition (LOI) analysis results in Table 1 shows that FA1 and FA2 are much higher in organic carbon (OC) contents. By comparison, the lighter colors of FA3 and FA4 are in agreement with the low OC contents. At the same time, the contents of inorganic carbon (IC) range from 3.16 wt% to 4.67 wt%. The proximate analysis results in Table 1 show that FA3 and FA4 are higher in ash content with little fixed and volatile carbon.

Figure 1.
Pictures of the original fly ashes, light and residual materials collected after flotation: (a) FA1; (b) FA2; (c) FA3; (d) FA4.

Table 1.
OC and IC contents and proximate analysis results of the original fly ashes.
After flotation, the light materials collected from FA1 and FA2 manifested a much deeper color close to that of activated carbon, as shown in Figure 1. This shows that carbon material with dark color was successfully separated from the light-colored inorganic materials. For FA3 and FA4, the difference in color is less obvious. For FA4, almost no light material was collected, indicating difficulty in material separation via flotation.
In summary, flotation may not be feasible for all fly ashes. Preliminary tests showed that for fly ash that contained enough lighter materials, such as powdered activated carbon, flotation can be effective. Therefore, further studies were conducted on FA1 and FA2 to explore the feasibility of flotation and elucidate the characteristics of separated materials.
2.2. Comparison of Collector
2.2.1. Yields of Light and Residual Materials
The effect of the collector is twofold. First, the addition of a collector could increase the surface hydrophobicity of the target particle. Secondly, it could increase the adhesion of bubbles to particles [23]. Flotation of fly ash was first carried out to compare the effects of collectors. With MIBC as a frother (dosage set at 0.5 g/L), diesel, kerosene, TX-100 and SDS were employed as collectors, with the dosage varied from 5 g/L to 20 g/L.
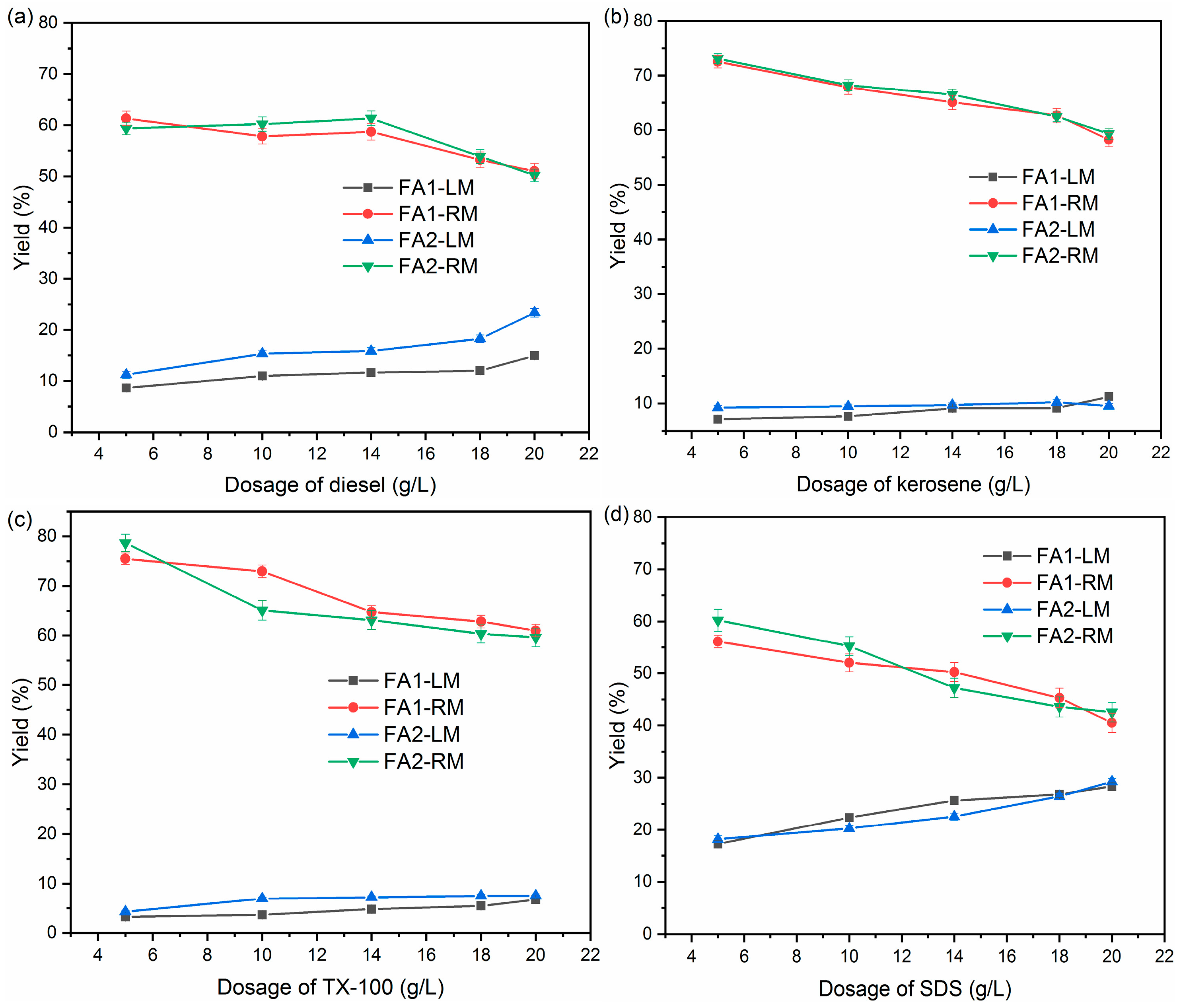
Figure 2 is the yield of light material (LM) and residual material (RM) when a different collector was used.
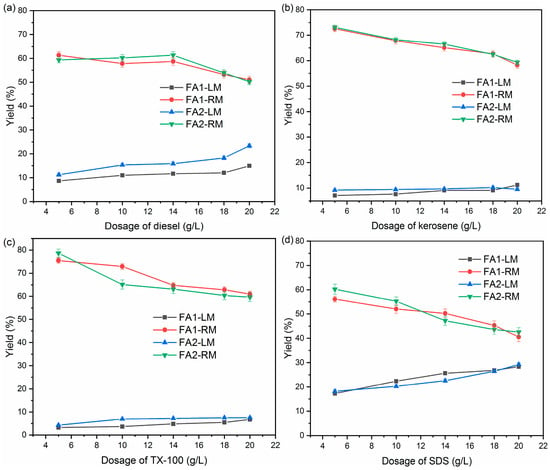
Figure 2.
Yields of light and residual materials by different collectors: (a) diesel; (b) kerosene; (c) TX-100; (d) SDS.
The yields of LM and RM varied with the collector used. For diesel, there is a general trend of increasing LM as the dosage increases. The yield of LM reached as high as 20% when the dosage reached 20 g/L. With kerosene and TX-100 as collectors, LM yields were more stable over the range of dosage. For kerosene, the yields of LM were around 7.1–11.2% while those of TX-100 were approximately 3.2–7.5% for the two ashes. By comparison, the yield of LM increased sharply as the SDS dosage rose. Approximately 30% of fly ash was collected at a dosage of 20 g/L. In general, LM yields followed the order of SDS > diesel > kerosene > TX-100. The pattern of changes under all four collectors is similar for FA1 and FA2, indicating that the characteristics of these two fly ashes did not significantly affect flotation. At the same time, yields of RM decreased correspondingly with the increase of LM for both ashes.
The yield of light material revealed that flotation was able to separate materials in fly ash. Diesel and kerosene have been employed widely as collectors for separating unburned carbon from coal fly ash [24,25]. The adsorption of hydrocarbon oils was found to enhance the hydrophobicity of carbon particles. On the other hand, surfactants were also extensively used as collectors to recover carbon. Surfactant modified the hydrophobicity of the unburned carbon by preferentially adhering to the water–oil–air interface [26]. The addition of surfactant created an interface with higher surface area, lower free energy and surface tension.
Overall, the separation of fly ash varied greatly with the collector. SDS led to the highest amount of fly ash being floated to the surface, while TX-100 was the least effective, with the lowest yield of light material. This is in accordance with the study of Xia et al. [27], which showed that oxygenated aliphatic surfactants have better collecting properties than oxygenated aromatic surfactants. Dey [28] reported that ionic and non-ionic surfactants varied in the formation of mixed films at the liquid/gas interface, which resulted in differences in the reduction of surface tensions. In addition, the yield of LM from SDS is also much higher than that of oils (diesel and kerosene). It is reported that the emulsifying function of surfactant could enhance the floatability of carbon particles by enhancing adhesion between the air bubble and carbon particle [29].
The main purpose of flotation to treat fly ash was to separate light material, such as organic carbon, from the inorganic species. The residual fly ash could then be recycled. Therefore, it is not advisable to have too high a yield of light material, which may mean a high loss of fly ash. At the same time, low yield may mean that the separation is not effective.
Therefore, it is not enough to evaluate the effects of flotation based on yield alone. According to Figure 2, for diesel, kerosene and TX-100, yields of LM stabilized after dosage reached 10 g/L. To better understand the effects of flotation, samples of LM and RM at a dosage of 10 g/L were next analyzed for their organic and inorganic carbon content.
2.2.2. Organic Carbon and S Removal
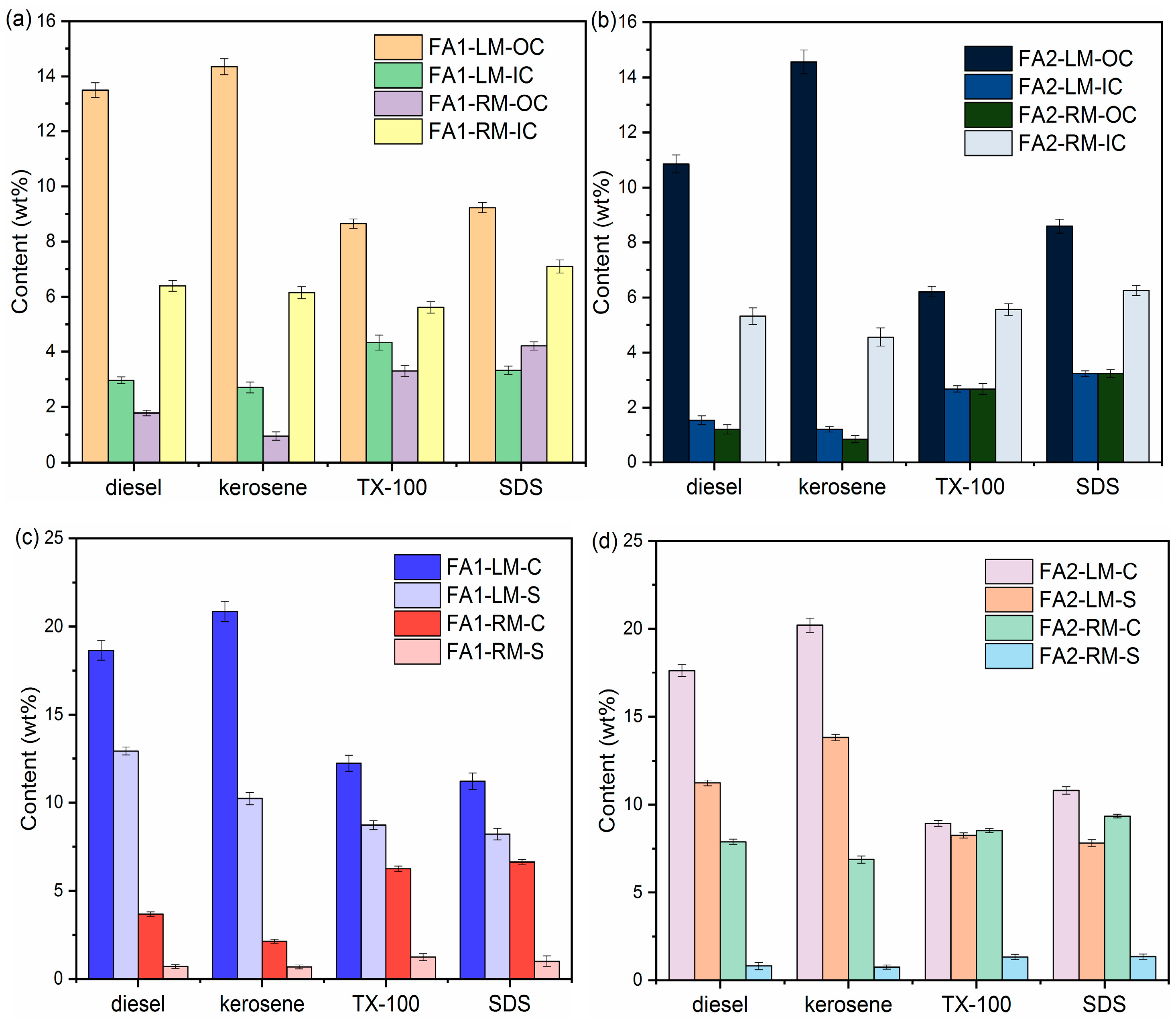
The organic carbon contents in fly ash mostly originated from powdered activated carbon from flue gas treatment. There are also organic compounds due to incomplete combustion during incineration [30]. Sequential loss on ignition (LOI) was employed to measure the organic and inorganic carbon contents. The method is based on differential thermal analysis: organic matter begins to ignite at approximately 200 °C and is completely depleted at approximately 550 °C. Most carbonate minerals are destroyed at higher temperatures (calcite between 800 °C and 850 °C, dolomite between 700 °C and 750 °C). However, volatile salts, structural water and inorganic carbon may also contribute to LOI, thus compromising the accuracy of LOI values. Mu et al. [31] studied the effects of phase transformation of fly ash during the LOI analysis process and recommended 440 °C as the cut-off temperature to calculate LOI for organic carbon. Ca- and Cl-based compounds underwent major phase transformation between 440 °C and 700 °C. Therefore, the LOI at temperatures higher than 440 °C could be attributed to the degradation of carbonate, such as CaCO3. The transformation of salts such as CaClOH and CaCl2 also started around 500 °C and was completed between 700 °C and 900 °C. Therefore, the cut-off temperature for IC also needs adjustment. In this research, LOI440 and LOI700 were used to evaluate the OC and IC contents of the fly ashes accordingly. Figure 3 is the OC and IC results of light and residual materials at the collector dosage of 10 g/L.
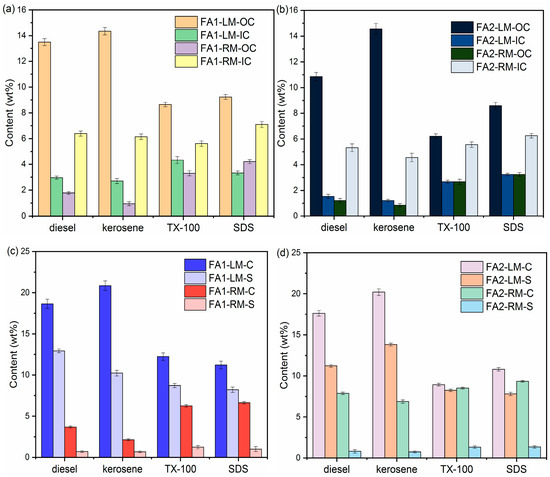
Figure 3.
Contents of OC, IC, C and S of the light materials and residual materials by different collectors: (a,c) FA1; (b,d) FA2.
Kerosene and diesel are the most effective in collecting OC into LM for both types of fly ash. With diesel as collector, the content of OC in FA1-LM reached 13.50 wt% as compared to the original 3.52 wt%. By comparison, with kerosene, the OC in FA1-LM increased to approximately 14.35 wt% while the OC in FA1-RM dropped to 0.95 wt%. OC in FA2-LM increased to 14.56 wt% from the original 2.74 wt% with kerosene. At the same time, IC contents in FA1-RM and FA2-RM increased while those in FA1-LM and FA2-LM decreased as compared with those of the original fly ash. This indicates that IC was mostly retained in the RM.
TX-100 and SDS also showed increases in OC in LM and corresponding drops in OC in RM. The OC values in LM with SDS as collector were 9.23 wt% for FA1 and 8.65 wt% for FA2. SDS as a collector produced a much higher yield of light material than diesel and kerosene. It is possible that part of the inorganic carbon compounds was also collected by SDS, leading to lower OC. This is consistent with the relatively higher IC content in LM with SDS. In addition, the OC values in light materials with TX-100 were also lower. The reason may be different from that of SDS. With TX-100 as the collector, the yield of light material was the lowest, indicating that separation via flotation was not effective enough. That is, part of the organic carbon was not separated.
In summary, OC and IC results showed enrichment of organic carbon in light materials, which results in increases in inorganic carbon in the residual fly ash. The extent of enrichment varied with the collector used.
To further understand the separation of components via flotation, elemental analysis of C, N, H and S contents in LM and RM was carried out to complement the OC/IC analysis via LOI. Tables S1 and S2 in Supplementary Materials list the C, S, H and N contents of light and residual materials after flotation of FA1 and FA2 at a collector dosage of 10 g/L. The changes in N and H were statistically insignificant. Therefore, only changes in C and S are shown in Figure 3c,d. C content via elemental analysis includes both organic and inorganic carbon. C contents in FA1-LM increased to 18.65 wt% (diesel as collector) and 20.85 wt% (kerosene as collector) from the original 8.46 wt%. C contents in LM with SDS and TX-100 were much lower. For FA1, C contents in LM with TX-100 and SDS were 12.23 wt% and 11.21 wt%. Elemental analysis results also revealed significant drops in S contents in the residual fly ash and increases in S in light materials. The S contents of FA1 and FA2 originally were 2.66 wt% and 2.62 wt%, respectively. The S content in the residual materials decreased to between 0.68 wt%–1.35 wt%, while that in the light materials increased to 7.82 wt%–12.92 wt% for FA1 and FA2, as shown in Figure 3c,d. It appears that S-containing compounds were also accumulated in the light material, thus achieving desulfurization of the fly ash.
Since the main purpose of flotation was to remove light carbon material, the organic carbon removal efficiencies were calculated based on Equation (1).
where ηOC: removal efficiency of OC (%); c0: content of OC in the original fly ash(wt%); c1: content of OC in the residual material (wt%); m0: mass of the original fly ash (g); m1: mass of the residual material (g).
At the same time, the efficient removal of C and S based on elemental analysis was calculated based on Equations (2) and (3).
where γc, γs: C, S removal efficiency (%); qc0, qs0: contents of C or S in the original fly ash (wt%); qc1, qs1: contents of C or S in the residual material (wt%).
Table 2 lists the ηOC, γc and γs of both fly ashes via different collectors. ηOC, γc and γs values showed that diesel and kerosene were the most efficient in the removal of OC, with OC removal efficiencies reaching as high as 81.69% for FA1 and 78.84% for FA2 with kerosene. In addition, with diesel or kerosene as collectors, ηOC and γc values were mostly close, indicating that carbon enriched in light material was mainly organic carbon. C content via elemental analysis included both organic and inorganic carbon. Therefore, γc is an index for the removal of both. With TX-100 and SDS, γc values were much higher than those of ηOC. This may mean that the loss of carbon was partly attributed to the removal of IC from fly ash. In addition, more than 80% of the S was removed from fly ash when diesel or kerosene was used. Flotation showcased high desulfurization capability. In light of the ηOC and γs, in general, the effectiveness of flotation followed the order of kerosene > diesel > SDS > TX-100.

Table 2.
OC, C and S removal efficiencies (%) by different collectors.
2.3. Comparison of Frother
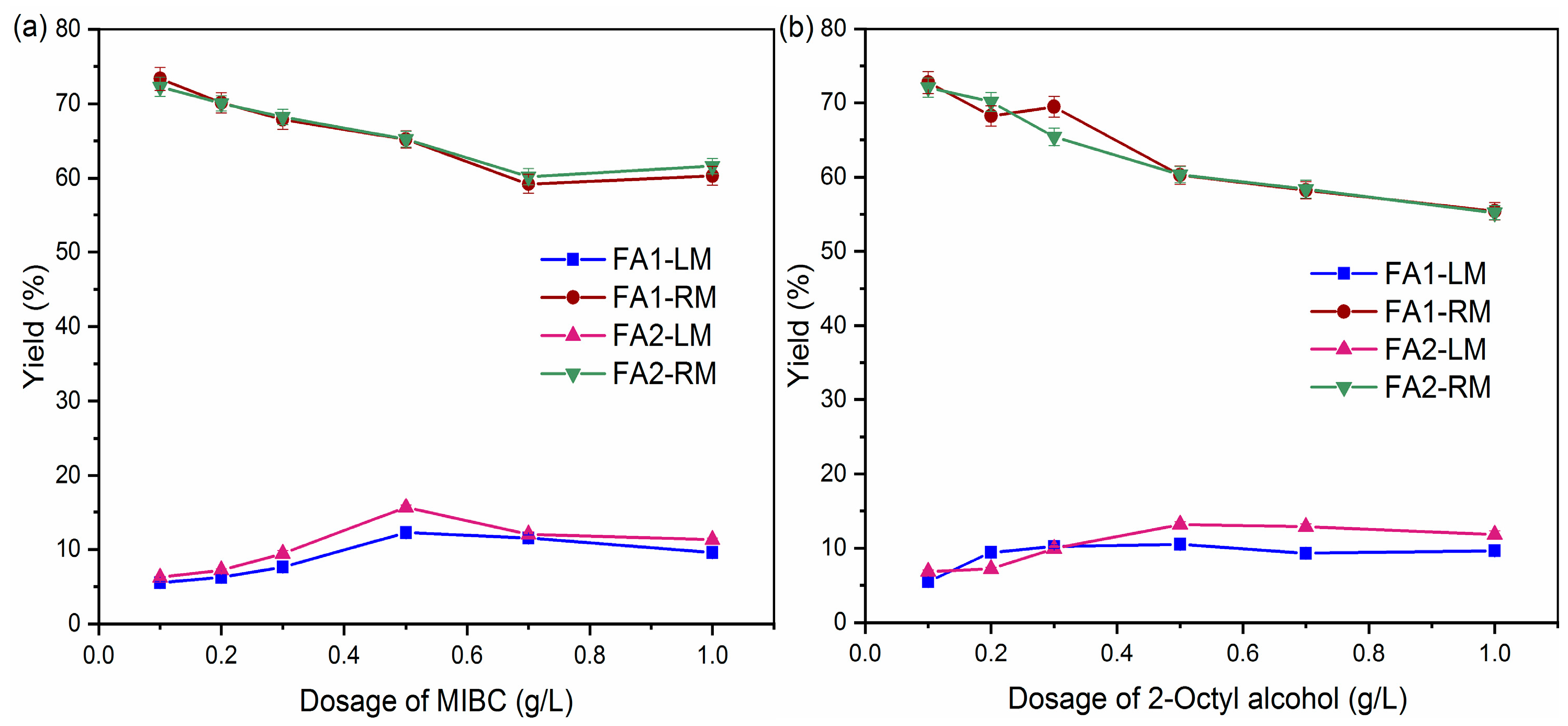
Comparison of collectors showed that kerosene may be a promising candidate with effective separation of organic carbon and S from fly ash. In the comparison of frothers, kerosene was used as a collector by varying the frother (MIBC and 2-Octyl alcohol) and dosage. Figure 4 shows the variation in LM and RM yields with respect to frother dosage. There is a general trend of an increase in the yield of LM from 0.1 g/L to 0.5 g/L. Correspondingly, the yield of RM decreased at this range. Yield of LM decreased slightly or stabilized at a dosage greater than 0.5 g/L. High dosage means more bubbles. They tended to collide with each other more, thus adversely affecting the adhesion between the air bubble and particles [32]. In this research, considering the yield of both LM and RM, a frother dosage of 0.5 g/L seems to be optimal. In addition, the behavior of FA1 and FA2 was similar, indicating that the variation in fly ash did not significantly change the effects of the frother.
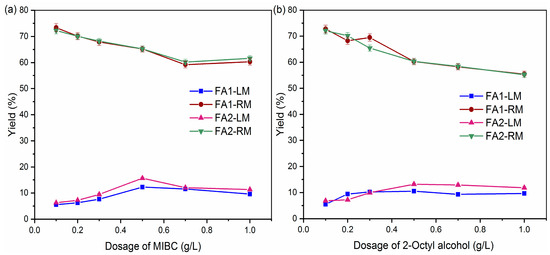
Figure 4.
Yields of light and residual material by different frothers: (a) MIBC; (b) 2-Octyl alcohol.
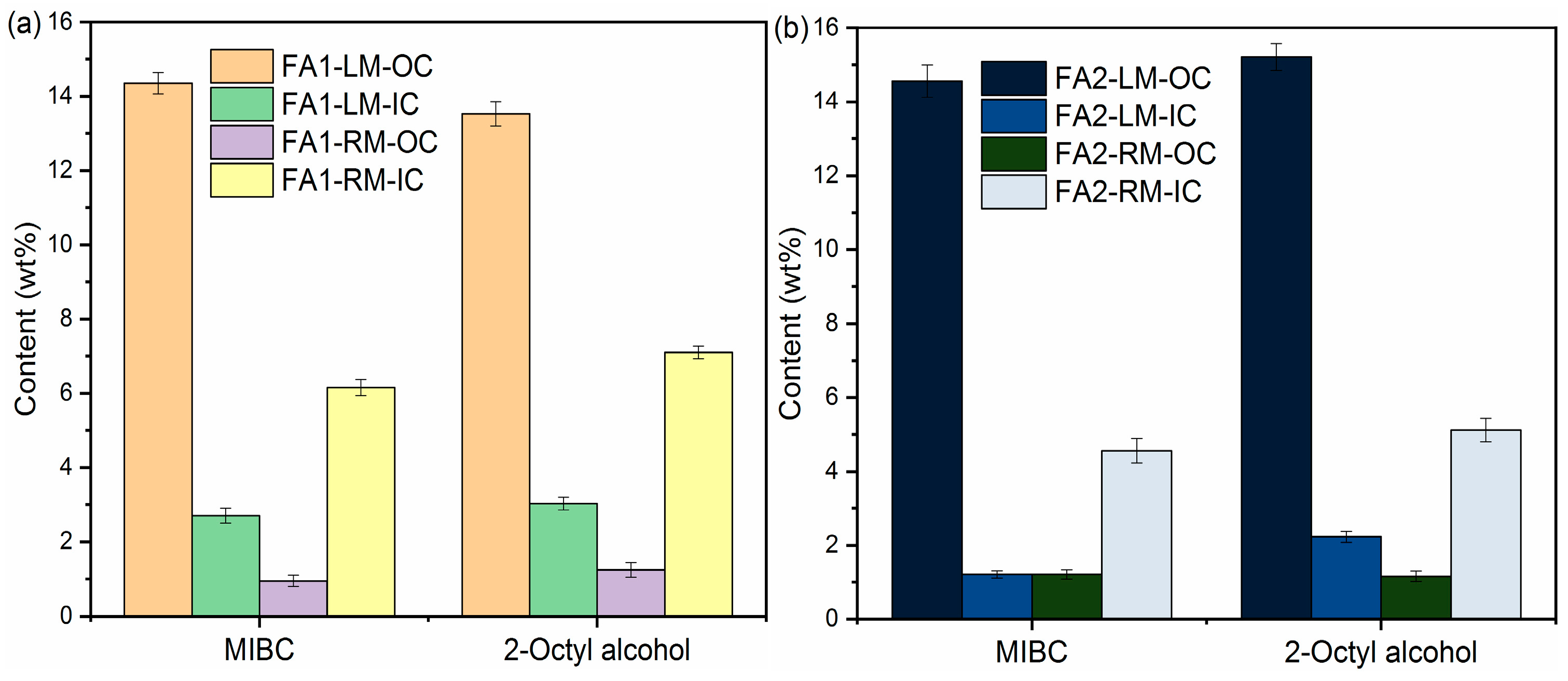
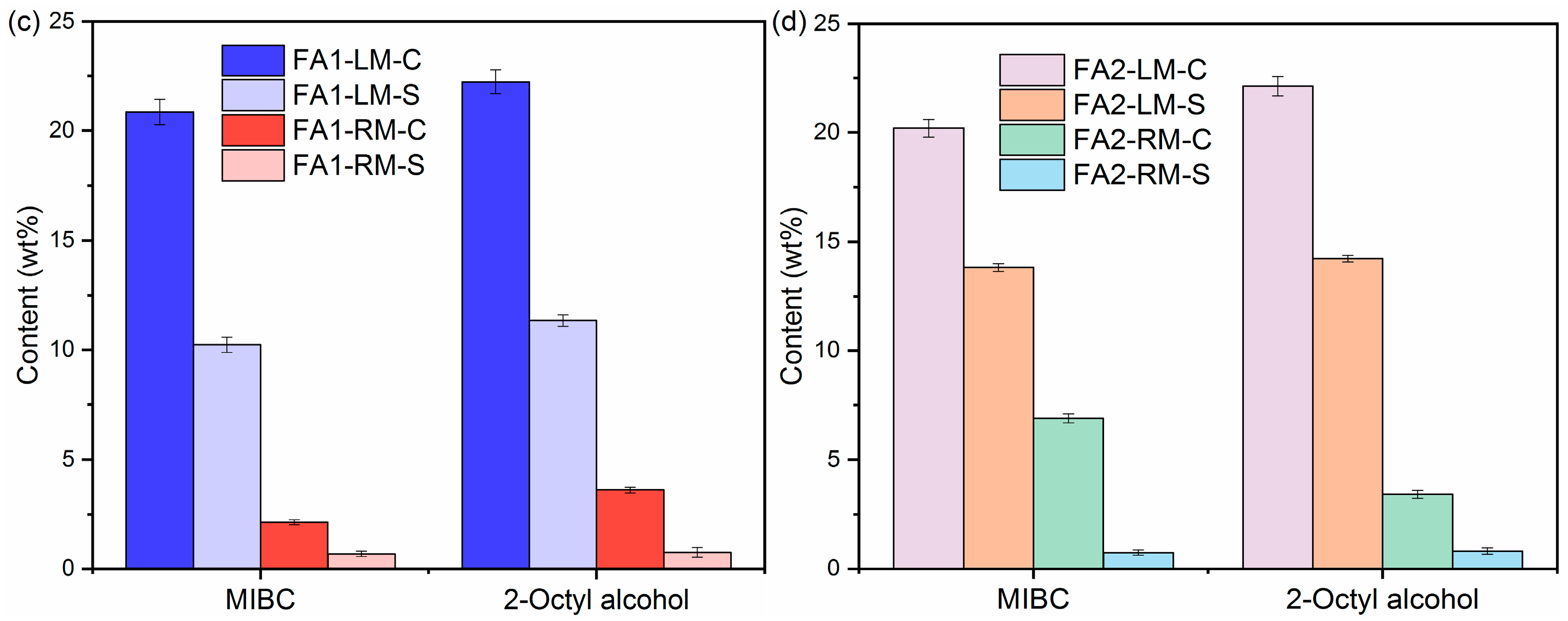
The contents of organic carbon, inorganic carbon, C and S of LM and RM at a frother dosage of 0.5 g/L with kerosene as collector are presented in Figure 5. There are only slight differences in C and S separation from fly ash into light material with MIBC and 2-Octyl alcohol as frothers. For example, the OC values in FA1-LM were 14.35 wt% and 13.53 wt% with MIBC and 2-Octyl alcohol, respectively. The C contents were also similar at 20.85 wt% and 22.23 wt%. OC and C contents in FA2-LM also increased obviously, as shown in Figure 5b,d. Table 3 lists the values of ηOC, γc and γs with different frothers. It appears both are effective in the enrichment of organic carbon in light material. ηOC with MIBC and 2-Octyl alcohol for FA1 were calculated to be 81.69% and 75.34%. In addition, in general, MIBC as a frother performed better than 2-Octyl alcohol in the removal of carbon and S-containing compounds.
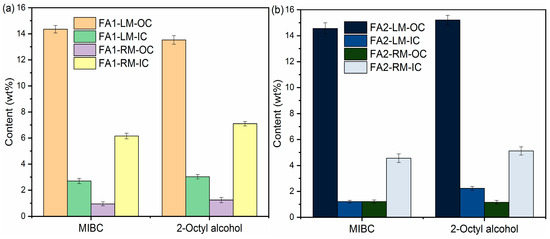
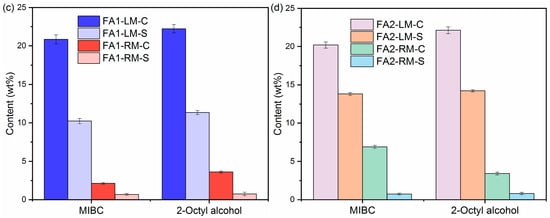
Figure 5.
Contents of OC, IC, C and S of light materials and residual materials by different frothers: (a,c) FA1; (b,d) FA2.

Table 3.
OC, C and S removal efficiencies (%) by different frothers.
Comparison of collector and frother showed that flotation could be used to separate organic carbon from fly ash. Organic carbon was enriched predominantly in the light material together with S-containing compounds, thus achieving both decarbonization and desulfurization. Taking into consideration the efficiency of C and S removal and yields, it appears that kerosene as a collector and MIBC as a frother achieved the best results. And the optimal dosages were 10 g/L and 0.5 g/L, respectively.
The characteristics of light and residual materials under these conditions were next investigated in detail. In addition to C and S, the behavior of heavy metals after flotation was also important to understand the capacity of detoxification via flotation.
2.4. Characterization of Solids After Flotation
2.4.1. Particle Size Distribution
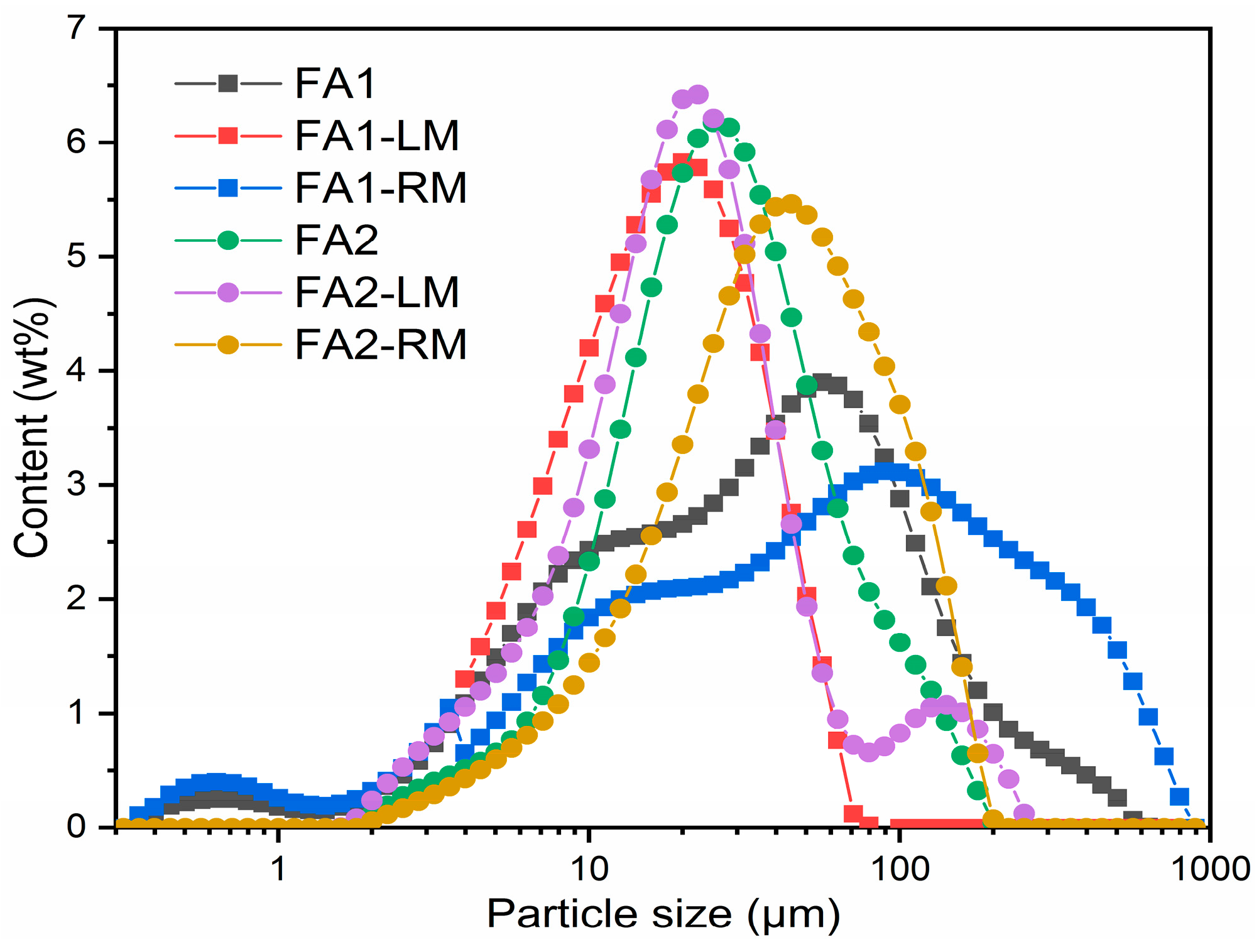
Figure 6 is the particle size distributions of the original FA1, FA2, light and residual materials from flotation. There is an obvious accumulation of smaller particles in the light materials for both fly ashes. Particle sizes of FA1-LM and FA2-LM peaked at 20 μm, while FA1-RM and FA2-RM centered at approximately 40 μm and 100 μm, respectively. The average particle sizes of FA1, FA1-LM and FA1-RM are 35 μm, 16 μm and 80 μm, while those of FA2, FA2-LM and FA2-RM are 30 μm, 20 μm and 76 μm, respectively. The distribution of particles proved that flotation was able to separate smaller particles. The residual fly ashes were larger in size.
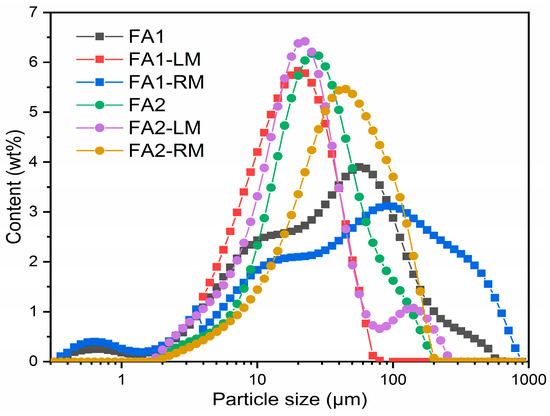
Figure 6.
Particle size distribution of fly ashes before and after flotation.
2.4.2. Chemical Compositions and Crystalline Structures
XRF (X-ray Fluorescence) analysis was also conducted to investigate the effect of flotation on the chemical composition. Results are listed in Table 4. Ca is the most abundant element in the fly ashes. There is a distinct re-distribution of Ca. Most of the original Ca was retained in the residual materials. Ca contents increased from 14.60 wt% and 15.78 wt% to 19.88 wt% and 20.97 wt% for FA1-RM and FA2-RM, respectively. Flotation led to a significant drop in Cl. This could mainly be attributed to the dissolution of chloride salts into the aqueous phase, since Cl in both light materials and residual materials is low at approximately 0.10 wt%. Another element that underwent significant change is S. The S contents via XRF are consistent with results from elemental analysis. The original fly ash had S contents around 2.50 wt%. S contents FA1-LM and FA2-LM increased to 8.43 wt% and 8.89 wt%, proving that flotation was able to separate S-containing compounds into light materials. S contents in the residual materials dropped to around 0.50 wt%. XRF analysis showed the fly ashes were rich in metal elements. Fe, Zn, Pb, Cu and Cr were all detected. A comparison of the composition of metals revealed that these metals tended to be collected in light materials. There is a general trend of drops in heavy metal contents in RM and increases in LM.

Table 4.
Chemical composition (wt%) via XRF.
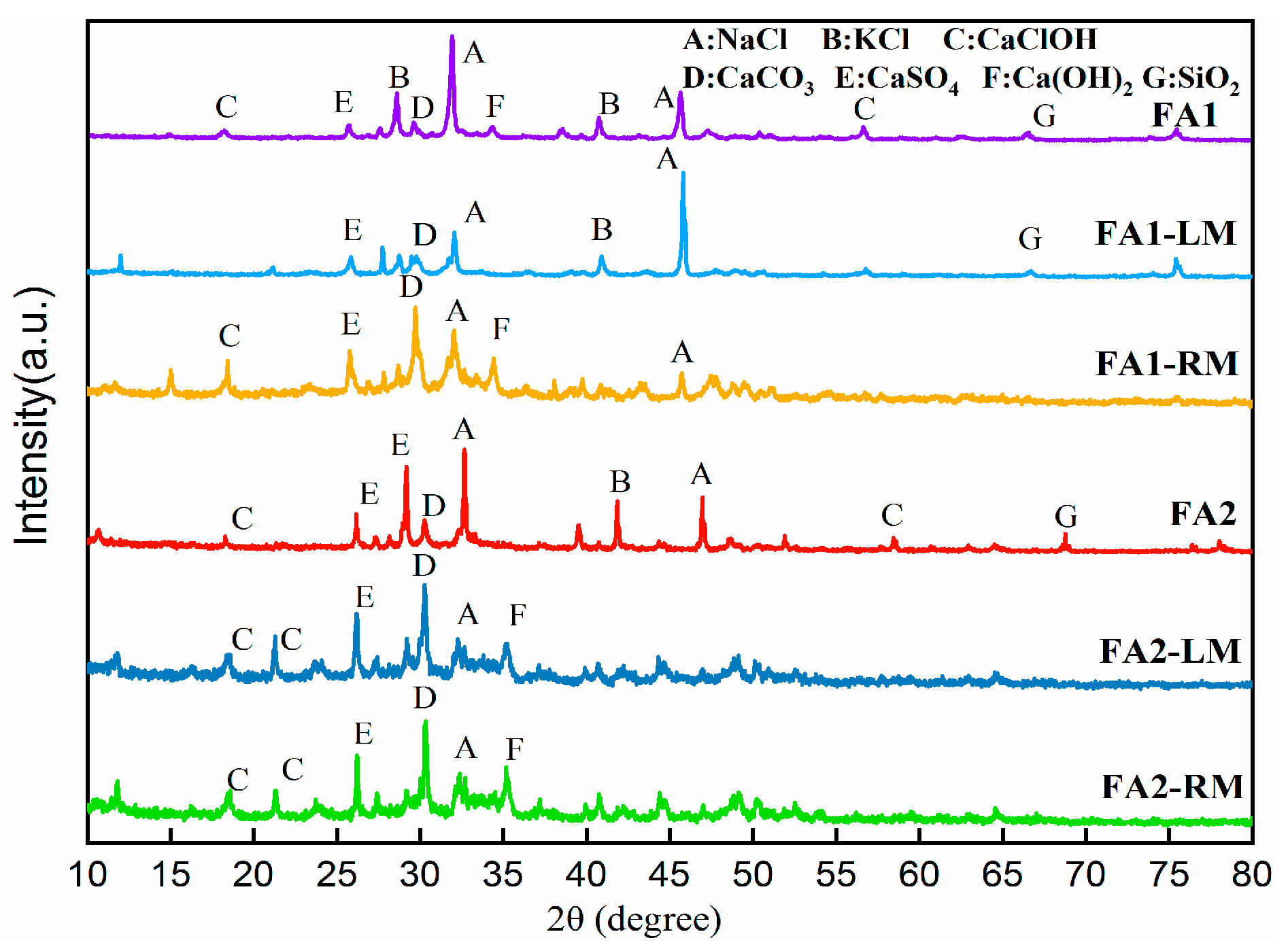
To further understand the changes in compounds via flotation. Figure 7 illustrates the XRD (X-ray Diffraction) crystalline structure results of the solids. XRD showed the lowering of peaks of NaCl and KCl after flotation. This could be due to the fact that the crystallinity of these salts was partially lost due to dissolution. Other compounds, such as CaClOH, CaCO3 or CaSO4, were all found in flotation products, although the sharpness of peaks in light materials and residual materials lessened. No heavy metals were detected by XRD. This did not mean that heavy metals were non-existent. It could be that the contents of heavy metals were lower, or they were not in a crystalline structure [33].
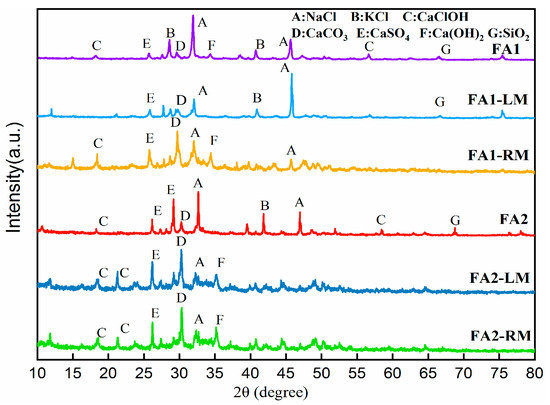
Figure 7.
XRD patterns of fly ashes before and after flotation.
2.4.3. Heavy Metals Contents and Leaching Toxicities
For the effects of flotation on the separation of heavy metals, the digestion method was used to analyze heavy metals in fly ash, light and residual materials. Results are shown in Table 5. Six heavy metals (Zn, Pb, Cd, Cu, Cr and Ni) were detected in the original fly ashes. Others, such as Sr and Sn, were found in very trace amounts. Among them, Zn had the highest content in both ashes, followed by Pb and Cd. Flotation showed enrichment of heavy metals in light materials. Figure S1 in the Supplementary Materials is the distribution of heavy metals in particles of different size ranges. It showed that more than 80% of almost all heavy metals were found in particles of less than 100 μm. In particular, Pb, Cd, Ni and Cu were predominantly found in particles sized between 1 μm and 10 μm, while 30–40% of Zn was found in these particles. Therefore, the removal of smaller particles was effective in removing heavy metals, thus detoxifying fly ash. As shown in Table 5, the contents of Pb decreased to 0.45 g/kg and 0.22 g/kg for FA1-RM and FA2-RM, respectively. Other heavy metals also witnessed drops, although to different degrees.

Table 5.
Contents (g/kg) of heavy metals.
Table 6 is the leaching toxicity of heavy metals of fly ashes. The last column is the standard limitations of leaching toxicity of heavy metals for landfills in China [34]. The Concentration of leaching of Pb and Cd of the original fly ashes was above the limitations required. After flotation, the leaching toxicity of all heavy metals in the residual materials met the requirement, while those in light materials were still high. However, with kerosene as a collector and MIBC as a frother, the yield of light materials from FA1 and FA2 accounted for only 7.63% and 9.45% of the original mass. That is, instead of the large volume of fly ash, flotation reduced the mass that needs to be detoxified to approximately less than 10%. It seems that flotation is a great volume-reduction tool and can be used as pre-treatment. The residual materials were then safe to be used, with leaching toxicity greatly reduced.

Table 6.
Leaching toxicity (mg/L) of heavy metals.
2.5. Quality of Wastewater
In addition to the light and residual materials, flotation also produced approximately 0.3 L of wastewater (WW) for every 100 g of fly ash. Based on the yield as shown in Figure 2 and Figure 4, at the optimal conditions, 67.89% and 68.22% of the original fly ash remained as residual materials for FA1 and FA2. 7.63% and 9.45% were light materials. That is, 24.48% and 22.33% of the masses were lost mostly due to the dissolution of salts.
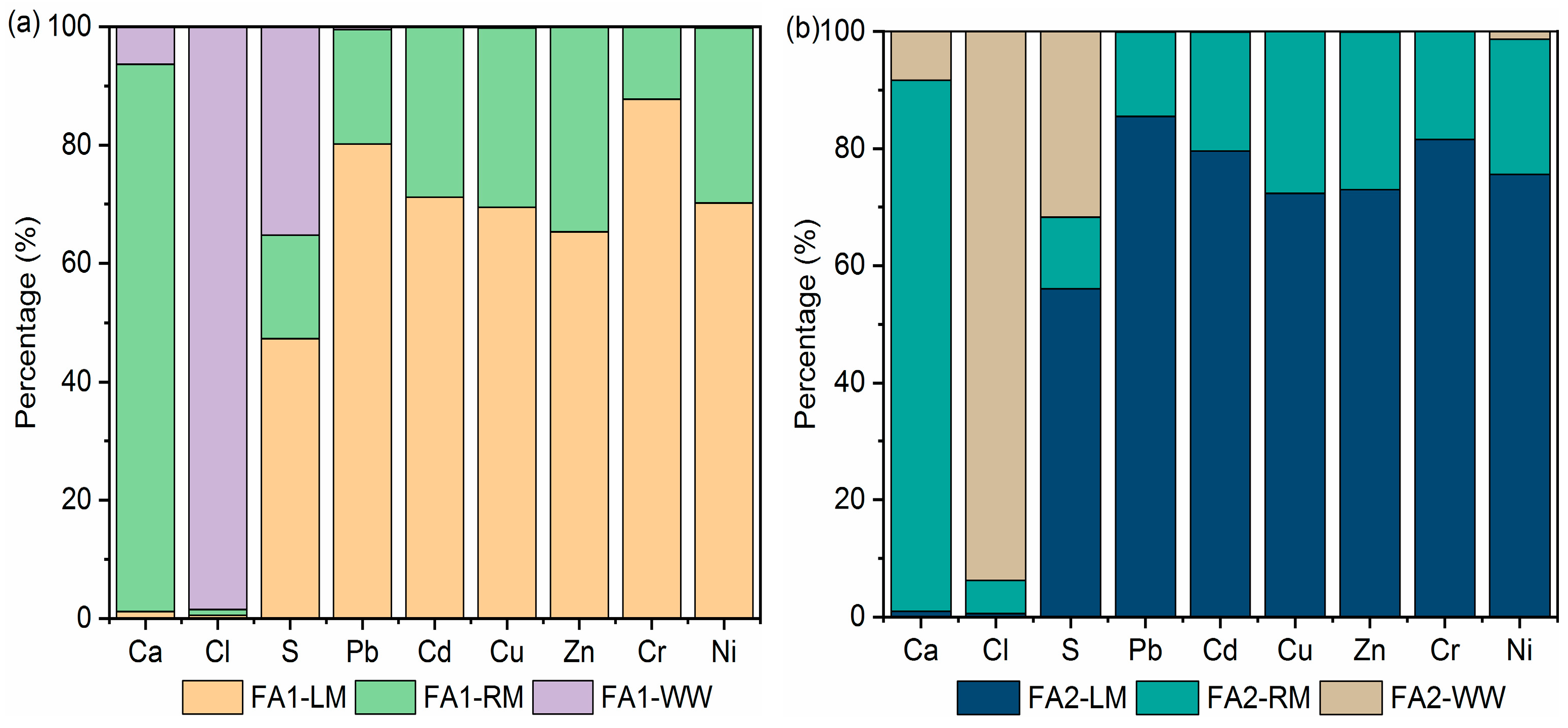
Table S3 in the Supplementary Materials shows the concentrations of the main components, including heavy metals, in the aqueous phase. The distribution of Ca, Cl and S elements in light, residual materials and flotation wastewater was then calculated based on the XRF results (Table 4) and concentrations in the aqueous phase. The distribution of heavy metals was calculated based on the heavy metal contents in Table 5. Results are shown in Figure 8. Most of the Ca was retained in the residual material. In contrast, the loss of chloride could be attributed to dissolution since more than 90% of the chloride was found in wastewater. The desulfurization effects are twofold. Part of it was due to dissolution, as approximately 24.88–35.27% of the S was found in the aqueous phase, while approximately 47.31–56.03% was floated to light materials. Only a small percentage remained in the residual fly ash. The dissolution of heavy metals was limited. Concentrations of Zn and Pb were the highest. Zn in wastewater ranged from 6.61 mg/L to 7.29 mg/L for FA1 and FA2, while those of Pb were 14.82 mg/L and 15.19 mg/L. Most of the heavy metals were found in light material, while a very small amount of heavy metal was dissolved. Mass balance calculation manifested that 75–85% of the Pb was collected in light materials. Although heavy metals such as Pb and Zn were detected in the wastewater, the percentage of mass was low, as shown in Figure 8. This is in accordance with the fly ash washing results. Washing with just water or surfactant solution did not result in significant loss of heavy metals. This is because some of the metals were present as non-soluble oxides or salts [35]. To remove heavy metals by washing, an alkaline or acidic solution was often needed [36]. Overall, the wastewater was high in calcium, chloride and sulfate salts, but the concentrations of heavy metals were relatively low. In our research group, CO2 carbonation was used to treat fly ash washing wastewater to recover Ca. During carbonation, Pb and Zn co-precipitated and were removed [37]. It is possible that the flotation wastewater could also be treated by carbonation since it contained a high concentration of Ca, while at the same time removing heavy metals.
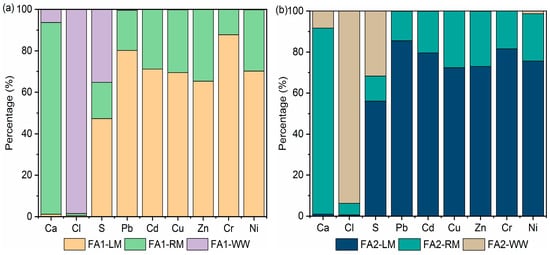
Figure 8.
Distribution of main elements and heavy metals after flotation: (a) FA1; (b) FA2.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
Four fly ashes from Zhejiang, Guangdong, Jiangsu and Jilin Provinces across China were selected for flotation tests and named as FA1–FA4. Other reagents, including diesel, kerosene, methyl isobutyl carbinol (MIBC), Triton X-100 (TX-100) and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) were all obtained from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China.
3.2. Flotation Experiment
Flotation was carried out via a flotation equipment (LC-XFD, Lichen Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). Diesel, kerosene, non-ionic surfactant TX-100 and anionic surfactant SDS were compared as flotation collectors while 2-Octyl alcohol and MIBC were used as frothers. During flotation tests, 100 g of fly ash was added to 500 mL of deionized water and mixed by stirring (200 rpm) for 3 min. The collector was next added to the slurry and stirred for 3 min before the addition of the frother. The fly ash, collector and frother mixture was stirred for another 3 min before the air pump was turned on to start the flotation. The air flow was 0.2 m3/h, and the flotation time was set at 5 min. Dosages of collector and frother were set at 5 g/L–20 g/L and 0.1 g/L–1.0 g/L based on preliminary tests and relevant studies [38,39]. All flotation experiments were conducted at room temperature (25 °C) and in triplicate. Averages and standard deviations were calculated.
Froth and concentrate were collected after flotation. Solids in the froth and concentrate were separated from liquid via centrifugation, then washed thoroughly with deionized water, dried and weighed. Solids collected from froth and concentrate were named as light material (LM) and residual material (RM), respectively. Liquids were filtered through 0.45 μm syringe filters, and the filtrate was stored for future analysis.
The yield of LM and RM was determined by Equations (4) and (5).
where YLM and YRM are the yield of light and residual material; mYM is the mass of the dried light material (g); mRM is the mass of dried residual material; m0 is the original mass of fly ash.
3.3. Analysis of Solids
Loss on ignition analysis were employed to determine the organic carbon and inorganic carbon contents of the original fly ash and flotation products (LM and RM) based on a standard method of China (GB/T 34231-2017) [40] and modified according to the study of Mu et al. [31]. Specifically, 10 g of fly ash was heated to 105 °C for 2 h in a muffle furnace, then cooled to room temperature and weighed. The mass in grams was designated as DW105. Solid remained after 105 °C was next heated to 440 °C and remained at this temperature for 2 h, then cooled and weighed to obtain DW440. The remaining mass was further heated at 700 °C for another 2 h, and the mass remaining was recorded as DW700. All analyses were carried out in triplicate. Averages and standard deviations were calculated. Loss on ignition, contents of organic carbon (OC) and inorganic carbon (IC) were calculated as in Equations (6)–(10) [23].
where WS is the original mass of fly ash; DW105, DW440 and DW700 are mass of solids after 105 °C, 440 °C and 700 °C treatment; LOI105, LOI440 and LOI700 are the loss on ignition at 105 °C, 440 °C and 700 °C (wt%); OC and IC are the organic and inorganic content (wt%).
Elemental analysis was conducted by an Element Analyzer (vario MACRO cube, Elementar Trading Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). Chemical compositions were determined by X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (XRF-1800, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) and the crystalline phases were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD, Rigaku UItima IV, Osaka, Japan) with 2θ ranging from 5° to 90°. In addition, a Laser Particle Size Analyzer (Mastersizer2000, Malvern, UK) was used to determine the particle size distribution.
The heavy metal content of the solids was determined by digesting the ash with a solution of HNO3 and HCl first. Digested liquid was analyzed for heavy metals. The acetic acid buffer solution method (HJ/T 300-2007, China) [41] was employed to investigate the fly ash’s heavy metal leaching toxicity. Heavy metals in liquids from all the above-mentioned analyses were measured by Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES, Optima8000, PerkinElmer, Shelton, CT, USA).
3.4. Analysis of Liquid
Liquid collected after flotation was analyzed for concentrations of heavy metals, Na+, K+, Ca2+, Cl− and SO42−. Heavy metals, Na+ and K+ were measured by ICP-OES. Ca2+ was measured by a standard method of China (GB 7476-1987) using EDTA titration [42]. Cl− and SO42− were analyzed via a Dionex ICS 6000 Ion Chromatography system (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
4. Conclusions
Four municipal solid waste incineration fly ashes were investigated for treatment via flotation to separate light materials such as activated carbon or residual organic carbon. Results showed that organic carbon contents could be a good indicator for the suitability of using flotation. Flotation was effective for fly ashes that contained more than 2.70 wt% of organic carbon. Flotation with kerosene as a collector and MIBC as a frother was able to achieve decarbonization and desulfurization with efficiencies reaching as high as 78.84–81.69% and 80.47–82.66% respectively. Organic contents in the residual fly ash reduced from the original 2.74 wt%–3.52 wt% to 0.85 wt%–0.95 wt%. This indicates that flotation was able to separate organic carbon from inorganic carbon. Flotation also led to the accumulation of S-containing compounds in the light material. The S content in the residual fly ash dropped to approximately 0.67 wt% from the original approximately 2.60 wt% according to elemental analysis results. Mass balance of the S content in light and residual materials and wastewater further revealed that dissolution of the S compound also played a significant role, with approximately 24.88–35.27% of the desulfurization being the result of dissolution.
In addition, flotation was able to remove mainly smaller particles, which are rich in heavy metals. The leaching toxicity of heavy metals of the residual fly ash decreased to a safe level. The detoxification of heavy metals could be mainly attributed to flotation, since a very small portion of them was dissolved into the aqueous phase. In summary, the results showed that flotation is effective in the separation of different chemical compounds from fly ash. The behavior of compounds varied depending on their floatability and solubility. In the end, flotation produced a light material rich in heavy metals, while the residual materials are safer and coarser than those of the original fly ash. The mass of the light material amounts to less than 10% of the original, which means flotation could greatly reduce the volume of toxic materials and could be used as a pre-treatment for the incineration of fly ash.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/recycling10040135/s1, Figure S1: Distribution of heavy metals in different particle size range; Table S1: Elemental analysis results (wt%) of FA1 and its flotation products; Table S2: Elemental analysis results (wt%) of FA2 and its flotation products; Table S3: Quality of flotation wastewater (unit: mg/L).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.C.; methodology, P.L.; validation, P.L. and S.Z.; investigation, P.L. and S.Z.; data curation, S.Z. and Y.C.; writing—original draft preparation, S.Z. and P.L.; writing—review and editing, W.C.; visualization, Y.C.; supervision, W.C.; project administration, W.C.; funding acquisition, W.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Baowu Huanke Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China (project number PFFP2411001).
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Qianqian Zhao and Yingping Lu from Baowu Huanke Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China, for providing the fly ash samples in this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| FA | Fly ash |
| MIBC | Methyl isobutyl carbinol |
| TX-100 | Triton X-100 |
| SDS | Sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| LM | Light material |
| RM | Residual material |
| LOI | Loss of ignition |
| OC | Organic carbon |
| IC | Inorganic carbon |
| WW | Wastewater |
References
- Cai, Z.; Yang, Q.; Han, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, P.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Pan, W.P. Synergistic removal of Hg0, HCl, and SO2 from flue gas in municipal solid waste incineration by mechanically modified fly ash. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Dai, S.; Li, J.; Lin, L.; Qin, W.; Gao, Y.; Hu, E.; Jiang, J. Towards circular economy: Sustainable valorization of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash for recovery of high-purity chlorides and calcium, and separation of heavy metals. Environ. Res. 2025, 277, 121536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leba-Kamanya, C.; Lei, H.; Niu, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, K. The Effect of chlorine and glass additives on heavy metal volatilization during vitrification of simulated municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. Mater. Lett. 2024, 377, 137381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Xu, Q.; Kong, L.; Li, K.; Wu, C.; Bai, J. Immobilization of heavy metals with chlorine and liquid phase formation during thermal treatment of MSWI fly ash. Fuel 2024, 378, 122949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, B.; Zhu, F.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, T.; Wang, Y. Study on the reduction of chlorine and heavy metals in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash by organic acid and microwave treatment and the variation of environmental risk of heavy metals. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 870, 161929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Pan, Y.; Fan, W.; Guo, H.; Zhang, H. Fly ash-CaO sorbents prepared via hydration for CO2 capture in municipal solid waste incineration. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; He, T.; Da, Y.; Xu, Y.; Luo, R.; Yang, R. Improve toxicity leaching, physicochemical properties of incineration fly ash and performance as admixture by water washing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 386, 131568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Liu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Liu, R.; Wang, D.; Wang, B.; You, Y. Simultaneous realization of heavy metal Cd solidification and chloride separation in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash: Mechanism and DFT analysis. Chemosphere 2024, 348, 140741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, J. Disposal technology and new progress for dioxins and heavy metals in fly ash from municipal solid waste incineration: A critical review. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 311, 119878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B. Degradation technologies and mechanisms of dioxins in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 250, 119507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, M.S.; Chen, Y.L.; Wei, P.S. Recycling of municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash by using hydrocyclone separation. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wei, G.X.; Zhang, R.; Liu, G.S.; Zhou, J.H.; Zeng, T.T. Detoxification of medical waste incinerator fly ash through successive flotation. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Chen, P.; Liu, T.; Li, Y. Research and application of fluidized flotation units: A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2023, 126, 50–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehati, R.; Yazdi, M.R.S.; Omran, A.H. Assessment of the effect of iron magnetic concentrate desulfurization by flotation method on the quality of green and cooked pellets: A laboratory and pilot-scale study. Miner. Eng. 2023, 202, 108269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokgoz, D.D.G.; Ozerkan, N.G.; Antony, S.J. Untreated municipal solid waste incineration ashes for cement replacement. J. Eng. Res. 2023, 11, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, C.; Wang, J.; He, Q.; Qi, X.; Xue, P.; Zhu, X. Environmentally-friendly emulsion-like collector prepared from waste oil: Application in flotation recovery of unburned carbon in coal fly ash. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 379, 134561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Yan, C.; Wang, H.; Zhou, S.; Liang, H. The result of surfactants on froth flotation of unburned carbon from coal fly ash. Fuel 2017, 190, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hower, J.C.; Groppo, J.G.; Graham, U.M.; Ward, C.R.; Kostova, I.J.; Maroto-Valer, M.M.; Dai, S. Coal-derived unburned carbons in fly ash: A review. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2017, 179, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.; Jiao, F.; Chen, Z.; Dong, B.; Fang, C.; Zhang, C.; Deng, X. Separation of unburned carbon from coal fly ash: Pre-classification in liquid-solid fluidized beds and subsequent flotation. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 165, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, Z.; Xia, W.; Shao, H.; Zheng, K.; Liang, L.; Peng, Y.; Xie, G. Application of compound reagent H511 in the flotation removal of unburned carbon from fly ash. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 595, 124699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H. Investigation on mechanism of intensifying coal fly ash froth flotation by pre-treatment of non-ionic surfactant. Fuel 2019, 254, 115601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, F.; Wang, Z.; Ren, K.; Liu, S.; Ding, H. Analysis of composition characteristics and treatment techniques of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 357, 120783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santisteban, J.I.; Mediavilla, R.; Lo pez-Pamo, E.; Dabrio, C.J.; Zapata, M.B.R.; Garcia, M.J.G.; Castano, S.; Martinez-Alfaro, P.E. Loss on ignition: A qualitative or quantitative method for organic matter and carbonate mineral content in sediments? J. Paleolimnol. 2004, 32, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, T.; Wheelock, T.D. Process conditions for the separation of carbon from fly ash by froth flotation. Int. J. Coal Prep. Util. 2008, 28, 133–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, L. Used engine oil as flotation collector for the removal of unburned carbon from coal fly ash. Int. J. Coal Prep. Util. 2022, 42, 3794–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helbig, C.; Baldauf, H.; Mahnke, J.K.; Stöckelhuber, W.; Schulze, H.J. Investigation of Langmuir monofilms and flotation experiments with anionic/cationic collector mixtures. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1998, 53, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Zhang, R.; Xing, Y.; Gui, X. Improving the adsorption of oily collector on the surface of low-rank coal during flotation using a cationic surfactant: An experimental and molecular dynamics simulation study. Fuel 2019, 235, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S. Enhancement in hydrophobicity of low rank coal by surfactants—A critical overview. Fuel Process. Technol. 2012, 94, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.J.; An, P.; Wu, F.; Xie, G.Y.; Xia, W. Enhancing flotation removal of unburned carbon from fly ash by coal tar-based collector: Experiment and simulation. Fuel 2023, 332, 126023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; He, H.; He, C.; Li, B.; Luo, W.; Ren, P. Low-carbon blended cement containing wet carbonated municipal solid waste incineration fly ash and mechanically activated coal fly ash. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 21, e03671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Saffarzadeh, A.; Shimaoka, T. Influence of ignition process on mineral phase transformation in municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash: Implications for estimating loss-on-ignition (LOI). Waste Manag. 2017, 59, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, L.A.; Prates, L.M.; Pereira, A.M.; Correia, J.C.G.; Marques, M.L.S.; Filippova, I.V.; Filippov, L.O. Unconventional collector-frother surfactant mixtures for goethitic iron ore slimes reverse flotation: Experimental and molecular study. J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 427, 127433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Záleská, M.; Pavlík, Z.; Pavlíková, M.; Pivák, A.; Reiterman, P.; Lauermannová, A.M.; Jiříčková, A.; Průša, F.; Jankovský, O. Towards immobilization of heavy metals in low-carbon composites based on magnesium potassium phosphate cement, diatomite, and fly ash from municipal solid waste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 470, 14062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, M.; Sun, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, W.; Yin, J.; Long, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, H. Stabilized MSW incineration fly ash co-landfilled with organic waste: Leaching pattern of heavy metals and related influencing factors. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 165, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.F.; Wang, Y.G.; Sun, Y.M.; Fang, G.L.; Li, Y.L. Release of soluble ions and heavy metal during fly ash washing by deionized water and sodium carbonate solution. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yi, Y. Water washing and acid washing of gasification fly ash from municipal solid waste: Heavy metal behavior and characterization of residues. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 320, 121043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.F.; Chen, Y.F.; Wang, Y.G.; Zhao, N. Combing activated carbon adsorption and CO2 carbonation of to treat fly ash washing wastewater and recover high quality CaCO3. Water 2024, 16, 2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Huang, H.; Liu, J.; Dong, L.; Bilal, M.; Shao, H.; Tao, D. Effects of carrier particles on flotation removal of unburned carbon particles from fly ash. Powder Technol. 2024, 434, 119247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Takasu, K.; Gao, W. Carbon removal performance and economic analysis of waste fried oil for coal fly ash flotation. Powder Technol. 2025, 454, 120658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 34231-2017; Determination of Loss on Ignition for Coal Combustion Residues. National Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017. Available online: https://openstd.samr.gov.cn/bzgk/std/newGbInfo?hcno=8104BFC39AB3DF5CF6BA753C5C5D5C9D (accessed on 17 September 2017).
- HJ/T 300-2007; Solid Waste-Extraction Procedure for Leaching Toxicity-Acetic Acid Buffer Solution Method. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2007. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/jcffbz/200704/t20070418_102860.shtml (accessed on 1 May 2007).
- GB 7476-1987; Water Quality-Determination of Calcium-EDTA Titrimetrlc Method. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1987. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/jcffbz/198708/t19870801_66849.shtml (accessed on 1 August 1987).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).