Abstract
In many paper applications the paper is supposed to disintegrate into its constituating fibers after disposal. This happens in water with only very little input of mechanical energy. The aim of this work is to understand the natural aging processes in different pulp types and their impact on the disintegration behavior under low agitation. We first introduce a laboratory testing method to assess the disintegration performance of various paper types in water under low mechanical energy input. Then we investigated the changes in paper disintegration and the corresponding physical properties over a nine-month period of paper storage. We measured wet strength, water retention value WRV, speed of water penetration, and contact angle. Our findings reveal substantial degradation of disintegration over time for unbleached paper. In contrast, for bleached paper the changes are much less pronounced. The best predictor of paper dispersibility turned out to be wet tensile strength. Furthermore, we found a strong relation between deterioration of dispersibility and fiber wetting (contact angle) and fiber swelling (WRV). We hence conclude that the observed decrease of low agitation paper dispersibility over time is related to a deteriorated water uptake into the fibers and fiber-fiber bonds which prevents the breaking of the bonds by the water. As potential aging mechanisms related to water uptake we identified hornification, crosslinking and lignin self-sizing as major factors influencing fiber-water interactions and ultimately the disintegration behavior.
1. Introduction
A key aspect of paper recycling [1] is that it avoids landfilling and incineration, making it the most favorable option for collected waste paper [2]. In the context of paper recycling, the concept of the circular economy is crucial due to its economic, social, and environmental benefits. In the paper industry, this approach helps preserve forests by reducing the demand for fresh wood required to produce virgin pulp [3]. Another important aspect of recycling is the need for environmentally sound management of packaging waste to mitigate potential environmental risks. Recent revisions to European waste legislation set ambitious targets for higher paper recycling rates by 2030 [4]. For 2030, two targets have been established: first, at least 60% of waste should be reused or recycled; second, non-recyclable waste should be reduced by half [5]. To meet these targets, it is essential to reduce waste and enhance the recyclability of paper packaging [4].
In paper recycling the first and most relevant process step is disintegrating the paper into its individual fibers by mixing it with water. The natural aging of paper significantly impacts its dispersibility and, hence, its recyclability. In this context, a desirable property of recyclable paper is to preserve its ability to be easily disintegrated.
Apart from the general relevance for paper recycling there is an entire class of water-dispersible paper products that are specifically designed to disintegrate upon contact with water, thereby eliminating packaging waste. Various such applications are documented in the literature, including coffee cup sleeves [6], wrapping paper for toilet paper rolls [7], seed packets [8], pouches for shampoo and conditioners [9], soap wrappers [10], and germination sheets for gardening [11]. The primary challenge for water-dispersible packaging paper is to achieve a balance between effective disintegration, high dry strength, minimal aging, and low wet strength. These paper products are supposed to disintegrate into their individual fibers under the presence of water and moderate energy input by agitation.
The basic mechanism of paper dispersion in water is that the water reduces the bonding between pulp fibers, causing the paper to disintegrate into the individual fibers [12]. Without any aging paper produced from bleached pulp disintegrates more readily compared to unbleached pulp [13]. Additionally fiber length significantly impacts repulpability, with longer fibers such as those from softwood being less repulpable [13,14] than hardwood pulp fibers. It is also well-established that pulp fiber treatment greatly influences disintegration behavior. Increased refining of the pulp improves fiber-fiber bonding, resulting in increased wet strength, reduced water absorbency [15,16] and also reduced dispersibility [12]. The repulpability, or disintegratability, and subsequent fiber separation of paper in water deteriorate as wet and dry strength increase [17].
The penetration of water into the paper weakens the fiber-fiber bonds, resulting in a loss of paper integrity and strength [17,18,19]. Water uptake hence plays a significant role in the paper’s ability to disintegrate [12].
The addition of papermaking additives, including wet and dry strength agents, sizing agents, and coatings, also influences the repulping process [13]. This study focuses on dry strength agents, such as starch, which enhance fiber bonding strength, reduce water uptake, and consequently degrade the paper’s dispersibility [12].
The fundamental concept behind the disintegration of water-dispersible paper is its interaction with water. This process takes place when water permeates the paper matrix, resulting in the breakdown of the fiber-fiber bonds [20,21]. When examining the aging processes of water-fiber interactions in the context of disintegration, it is crucial to consider the various processes involved and the relevant properties. First, both physical and chemical aging processes influence paper disintegration and other properties over time. The most significant physical process is hornification, an irreversible change in fibers and their water-holding capacity. The hornification status can be determined by calculating the decrease in the water retention value WRV over time using the following equation [22].
The hornification process forms irreversible intra-fiber bonding between cellulose microfibrils, creating crosslinks [23]. The formation of irreversible internal hydrogen bonds increases resistance to swelling forces upon rewetting and it loses the ability to form inter-fiber bonds [24,25]. The aforementioned changes include decreased water retention, reduced fiber flexibility, and increased brittleness [26]. Another noteworthy physical aging process is recrystallization [27], which involves the reorganization of cellulose molecules into a more ordered structure, often induced by changes in temperature and humidity [28].
Conversely, chemical aging processes are also responsible for the degradation of the cellulose in the fibers. First, there is hydrolysis and chain scission. Hydrolysis refers to the process where acidic or alkaline agents together with water, create chain scission [26] and cellulose degradation by the splitting of bonds between glucose units [29]. Another significant process is crosslinking, which involves the oxidative generation of carbonyl groups along neighboring cellulose chains. This leads to the formation of hemiacetal bonds between them, or ester linkages between carboxyl and hydroxyl groups. Crosslinking results in decreased wet elongation, increased wet strength, and restricted swelling due to water sorption [30].
In the context of oxidation, the distinction between the oxidation of lignin and cellulose is significant, as it leads to deterioration and degradation [31]. In cellulose the hydroxyl groups present on the anhydroglucose units are converted into carbonyl and carboxylic groups [29]. In contrast to cellulose, the oxidation of lignin occurs at a significantly faster rate and also results in the formation of carbonyl groups [32].
The aim of this work is to understand how disintegration of paper under low mechanical energy input is changing over storage time. To do this we produced paper handsheets, stored them under defined conditions over a period of nine months, and observed the change in dispersibility of these papers. First, we seek to understand the changes in physical properties over time. Secondly, we investigated the differences between bleached and unbleached paper, as well as the effects of refining and cationic starch addition. Finally, we aimed to interpret and analyze the potential reasons for these changes in relation to physical and chemical aging processes. We investigate wet tensile strength, liquid penetration speed (ultrasonic testing K-Value), water retention value (fiber swelling), and water contact angle. These measurements are studied in the context of aging behavior under different storage conditions to gather information about changes in water uptake and aging behavior, which are crucial for understanding paper disintegration under low agitation and its deterioration over time.
2. Results and Discussion
The results can be categorized into the changes in physical properties over time due to the influence of starch and refining on both unbleached and bleached paper. The potential physical and chemical processes involved in the aging of the papers are discussed. Error bars in the graphs are the 95% confidence limits.
2.1. Physical Properties and Their Changes over Aging Time
First, it can be stated that the storage conditions, whether an office environment with fluctuating temperature and humidity or a climate-controlled environment with constant temperature and humidity, show no discernible effect on the various properties in these trials and can therefore be disregarded in subsequent discussions. As a result, the displayed data originates from the office environment storage, with the disintegration process visualized exclusively from the climate-controlled environment. For a detailed comparison, the visualized test results for storage in the climate-controlled room are provided in Appendix B. The similarity of the results between the types of storage, involuntarily, serves as a repeatability test, demonstrating excellent repeatability of the measurements.
There are numerous differences between unbleached and bleached paper, both generally and specifically in the context of aging. Overall, the properties of both papers exhibit similar behavior and trends. However, the onset and intensity of changes in these properties occur much earlier and are significantly more pronounced in unbleached paper.
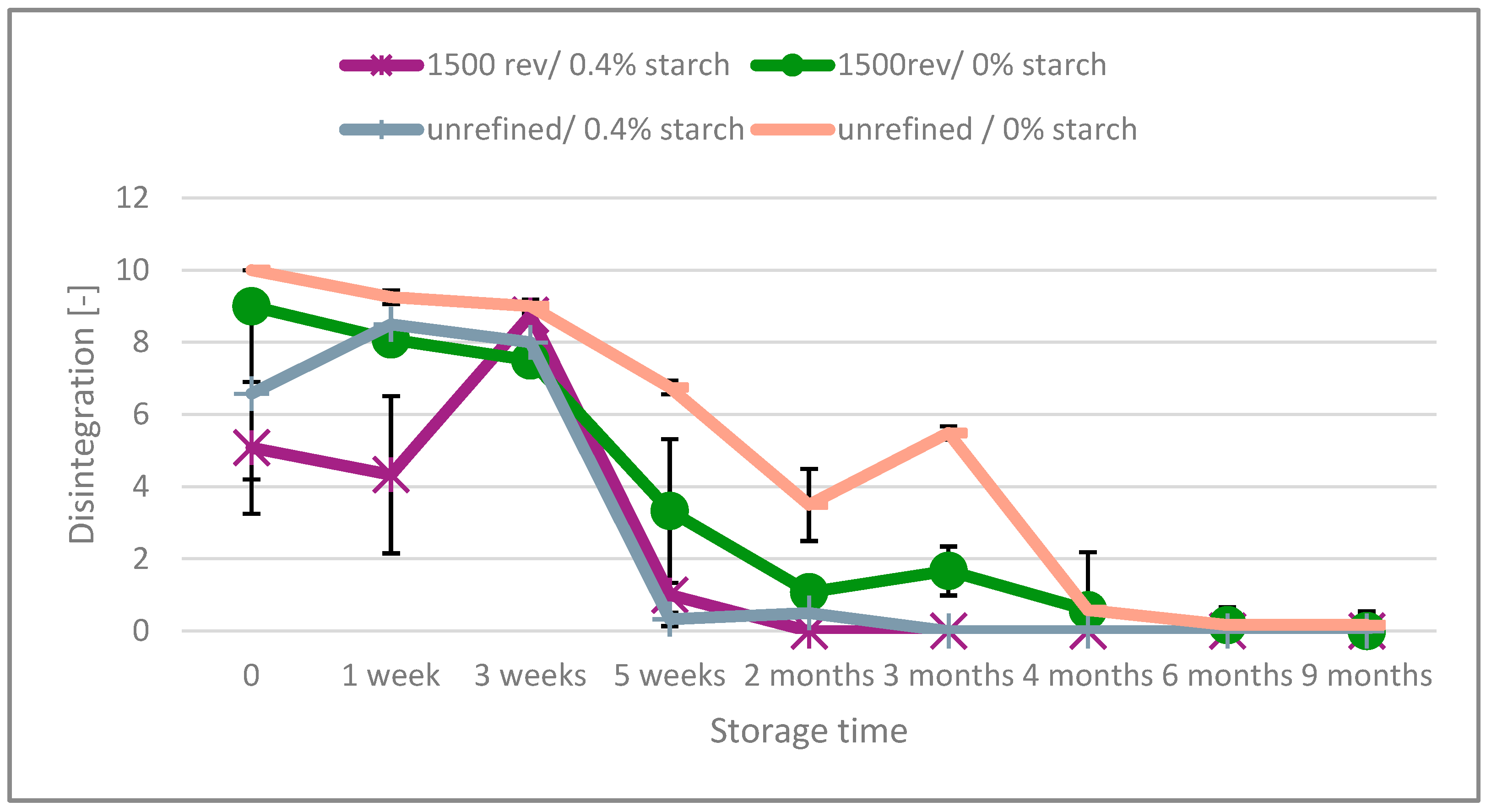
Upon examining the disintegration process, Figure 1 illustrates the impact of starch (expressed as a percentage) and refining intensity (measured in PFI revolutions) on unbleached paper with a surfactant dosage of 0%. It reveals that the disintegration of paper progressively worsens over time, starting more or less immediately after production. The graph also demonstrates that paper without refining and starch addition has the best disintegration behavior over time, and that starch has a more detrimental impact on the aging of unbleached paper compared to refining. After nine months, both non-refined and refined paper, regardless of starch addition, are no longer disintegrable. Notably, paper with starch addition loses its disintegration ability after just five weeks, whereas paper without starch maintains a good disintegration for a longer period.
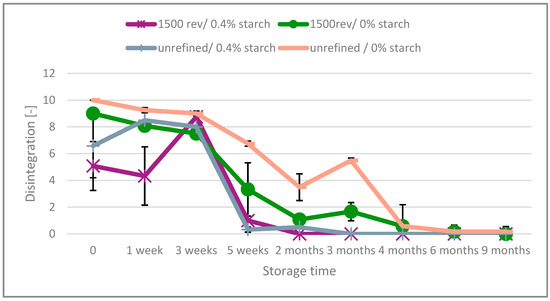
Figure 1.
Disintegration of the unbleached paper over the aging time.
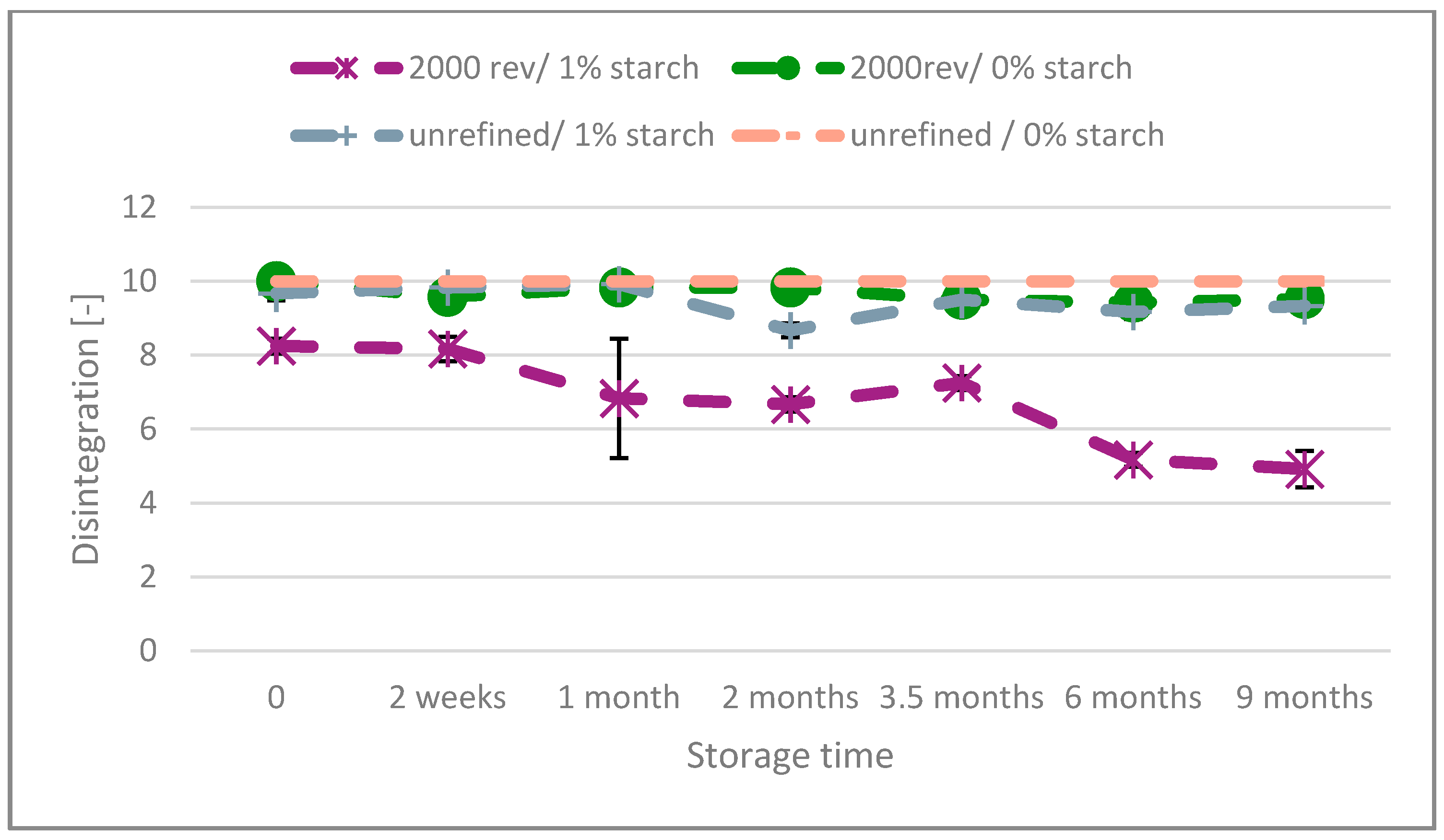
In contrast to unbleached paper, Figure 2 shows that bleached paper with starch (1%) and surfactant (0%) added mostly preserves excellent repulpability over the entire time of the experiment. Only the paper with refining and starch exhibits a decline, all other papers remain stable on very high levels. The refining intensity has a minimal impact on the disintegration behavior in the absence of starch. Bleached paper with starch demonstrates better initial disintegration in non-refined pulp, and this remains relatively stable over time. Conversely, the refined product starts with poorer disintegration and deteriorates further with aging, although it remains somewhat disintegrable after nine months.
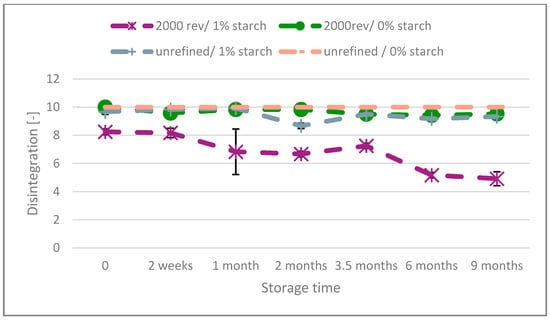
Figure 2.
Disintegration of the bleached paper over the aging time.
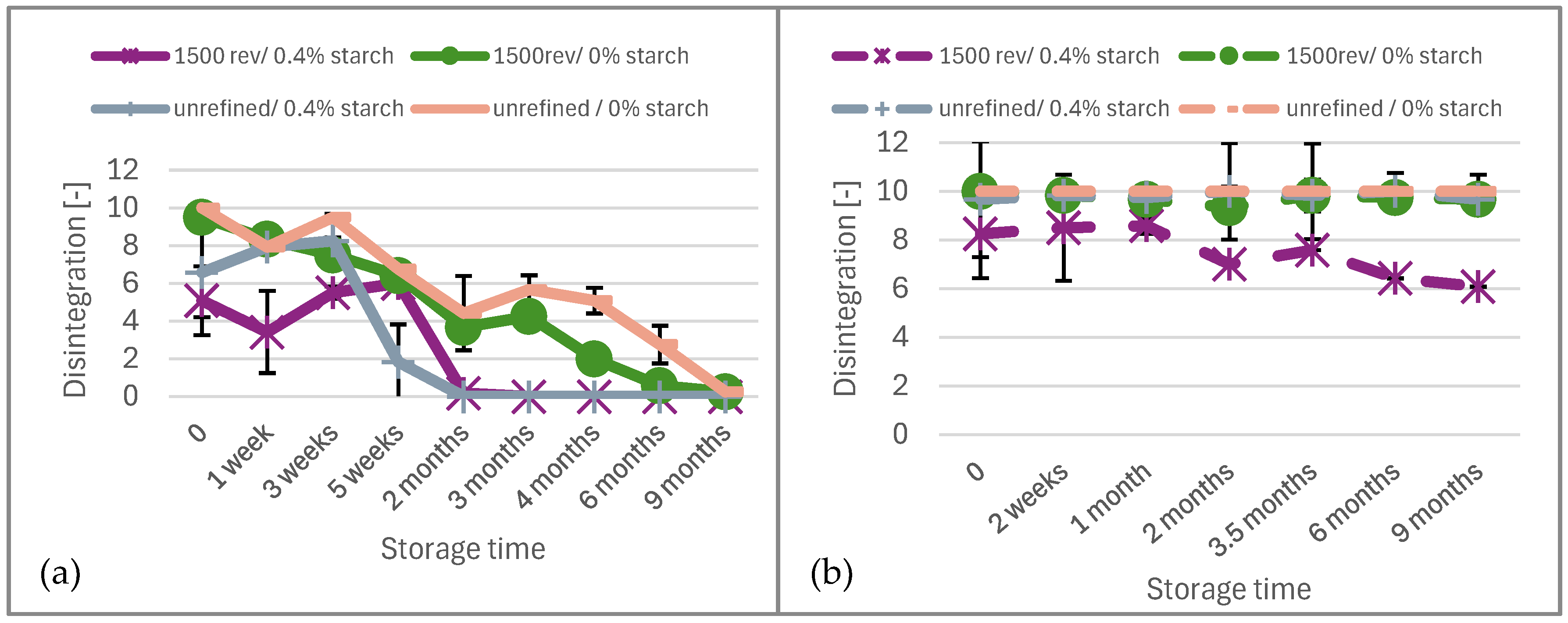
Figure 3 illustrates the disintegration over aging time in a climate-controlled environment. The unbleached paper ages more slowly, similar to paper with added cationic starch, regardless of whether it is refined or not. There is no visible disintegration after 5 weeks in the office environment, and in the climate-controlled environment, disintegration was no longer notified after 2 months. Papers without added cationic starch do not disintegrate after 9 months but age more slowly, showing consistent aging throughout the 9-month period. In the office environment, disintegration was not observed after 6 months. Consequently, it can be concluded that while disintegration is not observed after 9 months in a climate-controlled environment, the paper can be stored slightly longer under constant conditions.
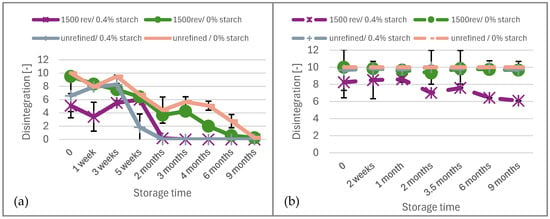
Figure 3.
Disintegration of the (a) unbleached and (b) bleached paper over the aging time in the climate-controlled environment.
In contrast, the bleached paper exhibits results similar to those in Figure 2. Only the refined product shows slightly better results after 9 months, but it still disintegrates after this period.
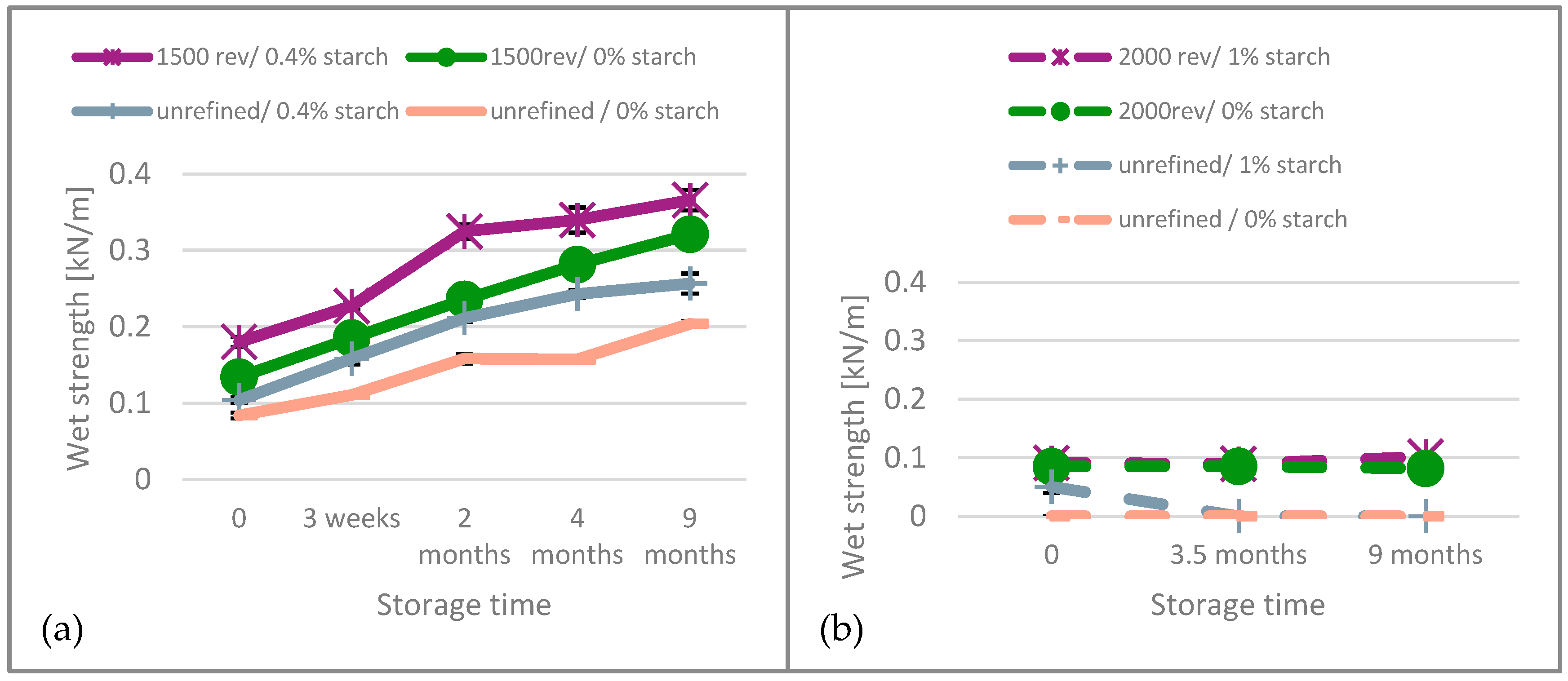
Wet strength has been reported to be an indicator of the disintegration behavior [12,33]. For unbleached paper, Figure 4 (left), it can be observed that wet strength continuously increases over time. For the bleached paper, Figure 4 (left), the wet strength hardly changed during observation.
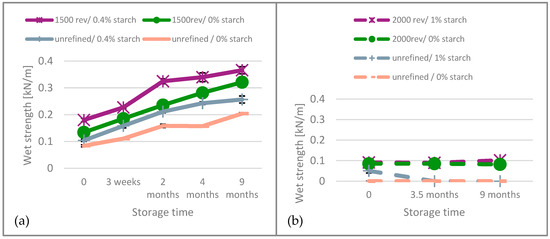
Figure 4.
Wet strength results of (a) unbleached and (b) bleached paper over the aging time.
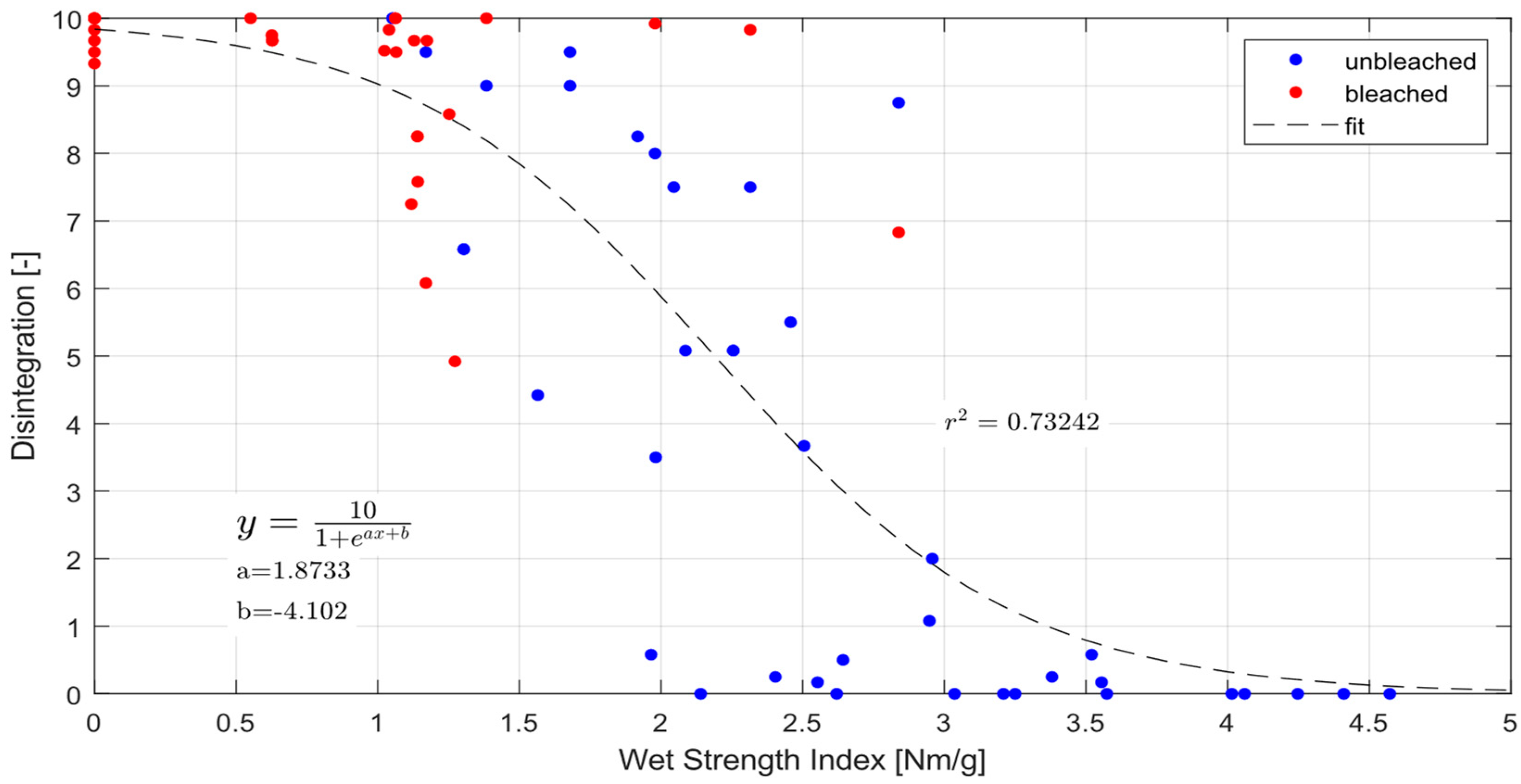
Looking at the bleached and unbleached data together we also find that wet strength is an excellent indicator for the dispersibility changes due to aging, Figure 5. Below a wet strength index of 1 Nm/g the papers are fully dispersible and above 3 Nm/g they do not disperse at all. Fitting a sigmoid type function in the form of we find a correlation coefficient of r2 = 0.73, which is a decent fit, mainly disturbed by some scatter in the transition region between 1 to 3 Nm/g wet strength.
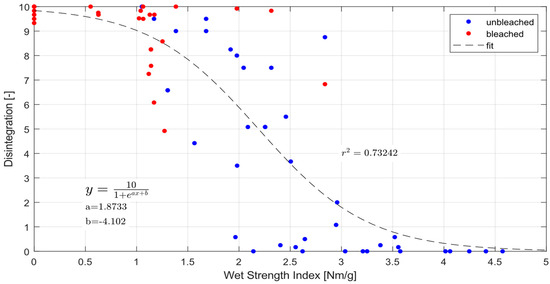
Figure 5.
Disintegration of paper over wet strength.
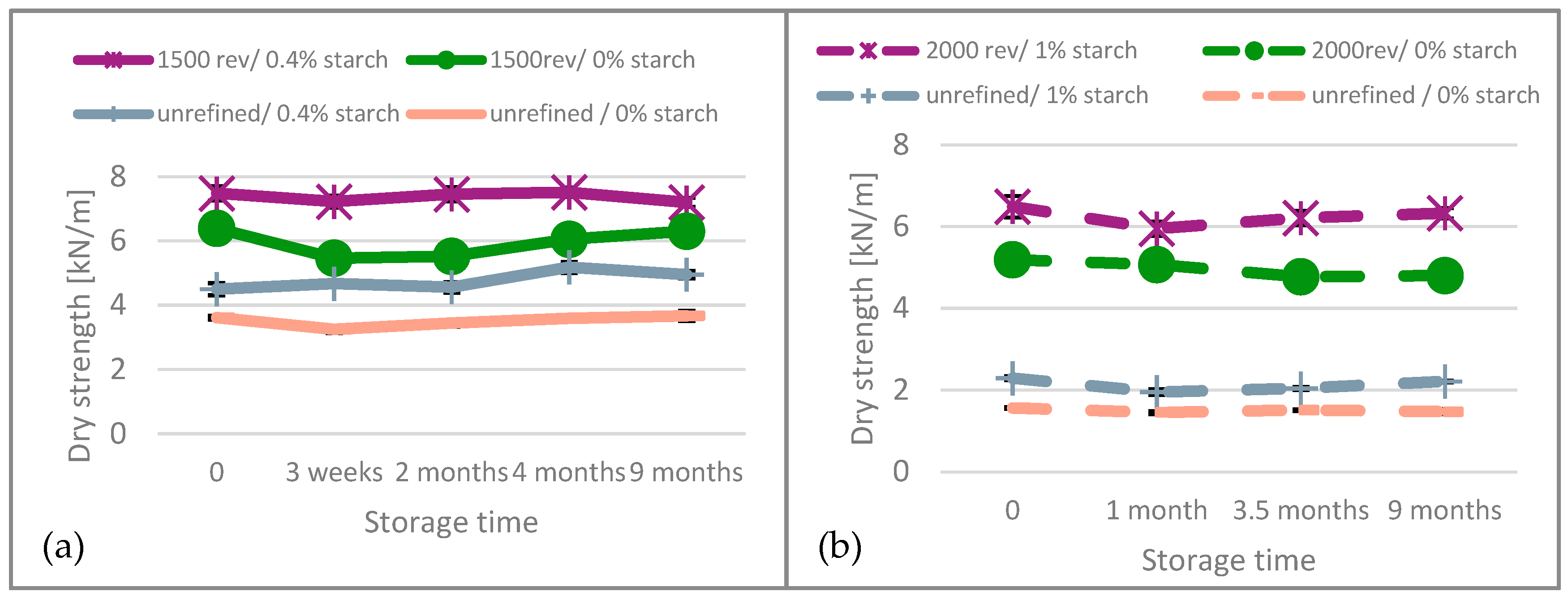
Concerning dry strength, elongation at break, and tensile energy absorption, it can be stated that for both, unbleached and bleached paper, these values remain nearly constant over the aging period, showing no significant changes. We only show tensile strength in Figure 6.
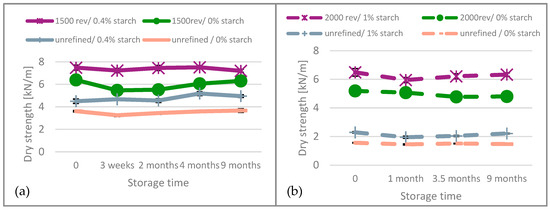
Figure 6.
Dry strength results of (a) unbleached and (b) bleached paper over the aging time.
Water Uptake Properties
Considering that the paper network disintegrates because the water is opening the fiber-fiber bonds it is straightforward to investigate if deterioration of dispersibility is associated with a decrease of water uptake into the fiber network. Sized papers are for example known for preserving their wet strength upon wetting [12,34].
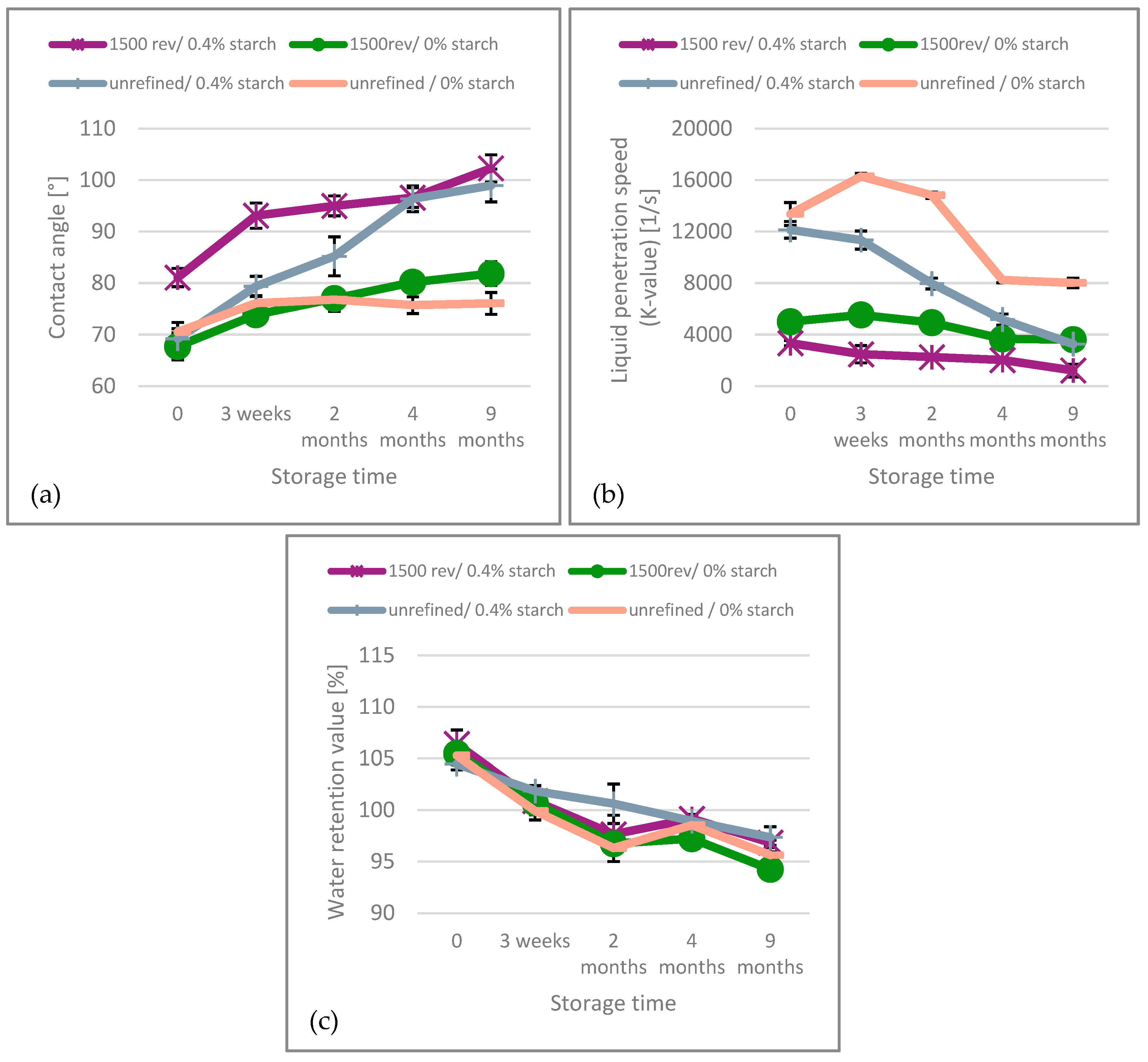
For the unbleached paper the increasing contact angle over time, Figure 7, is coinciding with the decrease in dispersibility and the increase in wet strength. This suggests that the paper’s wettability or hydrophilicity deteriorates with aging, which in turn causes that the penetration into the network pores [12,35] becomes less effective. Furthermore, the contact angle of paper with starch addition exhibits a steeper increase compared to paper without starch, suggesting that starch promotes the paper’s decrease in wettability. The liquid penetration speed of the unbleached papers, represented by the K-value, decreases over time with aging, as also shown in Figure 7. However, the rate of decrease is significantly lower in refined samples compared to unrefined ones, as the initial K-value is much higher in unrefined paper. After 9 months of aging, the penetration speed is similar for samples with cationic starch addition and no refining, and for refined samples without added cationic starch. The lowest penetration speed is observed in refined samples with cationic starch added. Throughout the aging period, the unrefined sample without starch consistently exhibits the fastest penetration speed. Consequently, this indicates that slower aging, in terms of penetration speed, occurs when the sample undergoes less treatment. Over time, the WRV of the unbleached papers also decreases gradually, indicating reduced fiber swelling and diminished water uptake, see also Figure 7. The impact of refining intensity and cationic starch addition on the water retention value (WRV) of the unbleached paper is relatively small. Overall, all three measurements related to water uptake are deteriorating over time: the wetting (contact angle) decreases, the penetration speed (K-value) decreases and also the fiber swelling (WRV) is decreasing. Based on these results none of the mechanisms investigated-wetting, penetration speed or fiber swelling/water uptake–seems to be prevalent with respect to the decrease in dispersibility, but all three are indicating that for unbleached paper the decrease in dispersibility coincides with reduced fiber-water interaction.
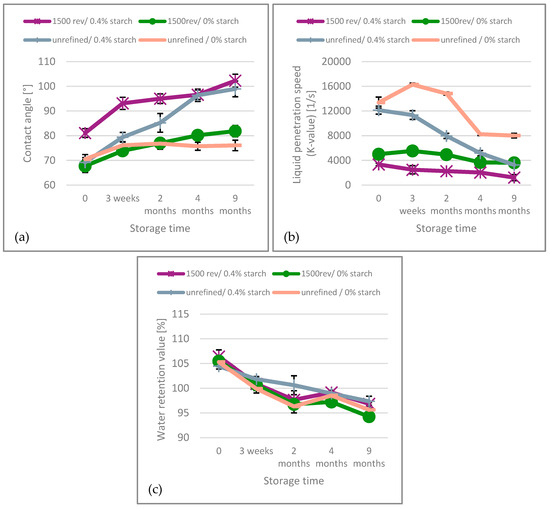
Figure 7.
(a) Contact angle, (b) K-value and (c) Water retention value of the unbleached paper over the aging time.
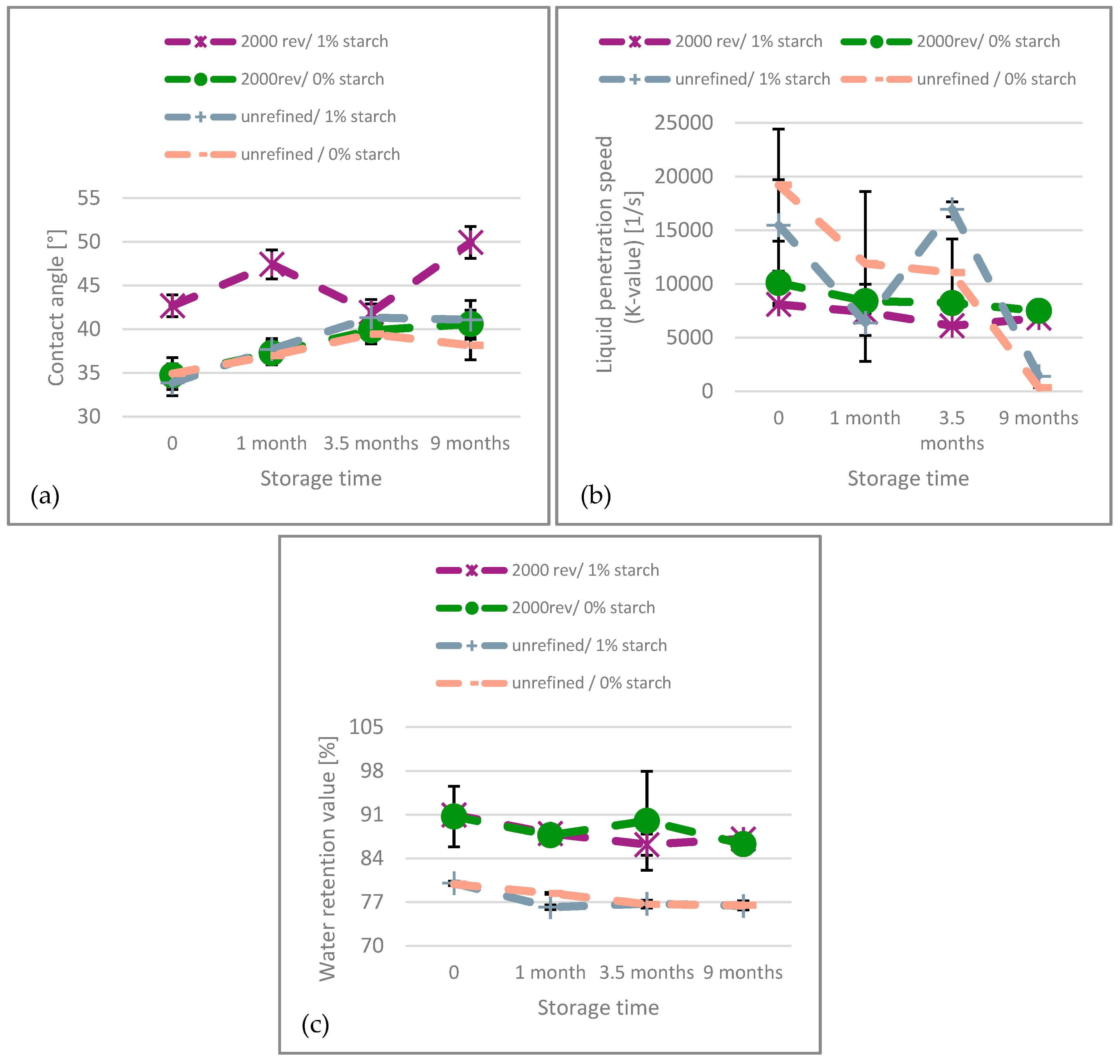
When interpreting the results for bleached paper, Figure 8, the behavior is not as clear as for unbleached paper. The contact angle also increases over time, and the K-value decreases. However, the results show a K-value close to zero in the unrefined paper, indicating that it was not reasonably measurable. The refined paper exhibits an almost constant K-value, suggesting that after nine months, the water penetration speed remains nearly the same as at the beginning. The water retention value is higher for refined paper, which is to be expected due to the inner fibrillation of the fibers and creation of fines during refining. Furthermore, there is a slow but steady decline of WRV over time.
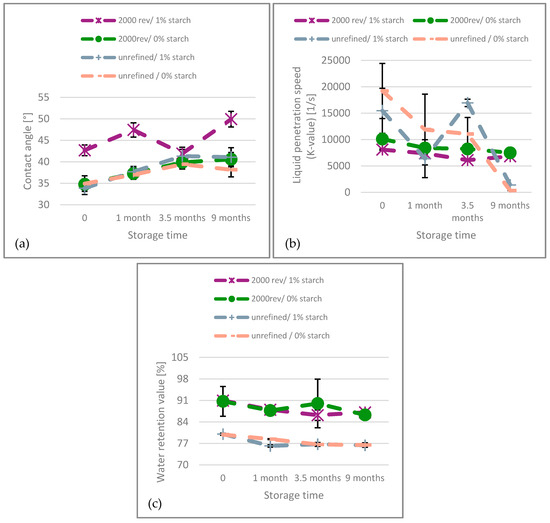
Figure 8.
(a) Contact angle, (b) K-value and (c) Water retention value of the bleached paper over the aging time.
Joint consideration of the results for unbleached (Figure 7) and bleached (Figure 8) paper shows that the K-value results are unstable and do not correlate with the dispersibility behavior, particularly for the bleached paper. In contrast to other sources [20] we do not see a relation between these values. This is plausible, considering the ultrasonic penetration speed measurement (K-value) captures the liquid penetration into the sheet within the first second of contact with water. Dispersing of the sheets is a process that takes several minutes, it is quite likely that other, slower, processes than liquid penetration are playing a more important role here. The other two measurements, fiber swelling (WRV) and fiber wetting (contact angle) are showing a continuous decrease for both, unbleached and bleached papers. Please note that the increase is much stronger for the unbleached paper, which also shows a pronounced decrease in dispersibility. Following these results, it can be concluded that apparently both, a reduction in fiber swelling and surface wetting, are related to the paper aging that reduces its dispersibility.
2.2. Aging Mechanisms Related to Water-Fiber Interaction
Figure 5 illustrates the wet strength and dispersibility of unbleached and bleached paper over time, finding a strong overall relation. Wet strength in this work has been measured after 5 min of immersion in water. It seems that the relation between wet strength and dispersibility, which is well known for wet-strength paper [17], also holds for the natural aging process of paper. Increased wet strength due to paper aging has also been observed by Krause [28]. The increase in wet strength suggests that fiber-fiber bonding in the presence of water is increasing over time [36,37]. The stronger bonds hinder the paper’s ability to break down into individual fibers when immersed in water [12]. It may seem obvious that stronger bonding is the cause for increased dispersibility, however a decrease in dispersibility over time has also been observed for wet cellulose fiber nonwovens (so called wet wipes), who are never dried and hence do not have any fiber-fiber bonding at all [38].
The observed reduction in wetting (contact angle) and fiber swelling (WRV) is justifying the hypothesis that diminished access of the water to the fiber-fiber bonds due to hornification is the driving mechanism. An increased contact angle, as seen in Figure 7 and Figure 8 is known from hornification in paper recycling [39,40]. The irreversible closing of pores by hornification also explains the observed decrease in water retention value (WRV) over aging [41]. This occurs due to the formation of bonds between hydroxyl groups on cellulose surfaces as water is removed [13]. The natural aging of paper also affects the water retention value (WRV) through auto-crosslinking and the hydrolytic breakdown of cellulose chains, both of which are irreversible changes [42]. Another factor contributing to the decline in water retention value (WRV) over time is the densification of the fiber wall structure in the non-crystalline regions, a process known as recrystallization [28].
Considering the much faster dispersibility degradation of unbleached paper, it is well known that lignin plays a crucial role in the degradation of pulp, acting both as an antioxidant and as a catalyst for oxidation [32]. Additionally, the reduction in disintegration may be attributed to lignin self-sizing. During the self-assembly process, lignin molecules can organize in a manner that exposes their hydrophobic regions, thereby increasing the overall hydrophobicity of the paper [43].
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
Beginning with the raw materials, the papers are made from both unbleached (kappa number ~40, brightness ~20) and bleached (kappa number ~11, brightness ~82) industrial softwood Kraft pulp, derived from pine and spruce. Such pulps are typically utilized for brown and white packaging products like bags. 30 g of completely dried pulp is soaked overnight and then refined using a PFI mill as per ISO 5264-2 standard. The refining degree (°SR) of the pulp is assessed following ISO 5267-1. Additives include a non-ionic surfactant from Schärer + Schläpfer (Rothrist, Switzerland) and a cationic potato starch from Südstärke (Schrobenhausen, Germany). A 5% sulfuric acid solution from Merck KGaA (Darmstadt, Germany) is utilized to adjust the pH to 6.8, aligning closely with the conditions used in paper production. The PFI refining process is conducted in accordance with ISO 5264-2. The test papers are handsheets made according to laboratory standard ISO 5269-2, having a basis weight of 80 g/m2 as determined by ISO 536.
Design of Experiments
Two sets of handsheets were produced and investigated: one for paper made from unbleached pulp (5 trial points) and one for paper made from bleached pulp (5 trial points), as illustrated in Table 1. The experimental variables included (1) the concentration of starch, ranging from 0% to 1%, (2) the refining intensity, ranging from 0 to 2000 revolutions (rev) in the PFI mill, and (3) the concentration of the non-ionic surfactant, 0% and 0.2%. To enhance the strength of the paper, ensuring it meets the required standards for packaging materials, starch and refining processes are utilized. However, this approach negatively impacts the dispersibility of the paper. To improve dispersibility a surfactant also utilized as a debonding agent in paper production [33,44,45], is added, which has been reported to also improve the dispersibility of the paper [33].

Table 1.
Experimental plan.
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Low Agitation Paper Disintegration Test
In the literature repulpability tests for paper recycling (PTS 2012, CEPI 2020) are predominantly performed with a laboratory disintegrator according to ISO 5263-3, and subsequent screening the disintegrated pulp through a Sommerville 0.15 mm slot plate. This test, traditionally used for flakes or shives, is standardized as TAPPI standard T-275. The disintegrator specified ISO 5263-3 has a 90 mm propeller rotating with 3000 rpm, thus creating strong shear forces for disintegration. ISO 12625-17 is specifying tissue disintegration, which is less harsh utilizing a propeller with 50 mm diameter and a rotation speed of 800 rpm. For our purposes we wanted to have an even more sensitive test that is able to better evaluate the gradual decomposition of paper in water under mild disintegration conditions. Hence, our disintegration test aims to demonstrate how commercial papers disintegrate under minimal energy input, with much lower energy applied than in ISO 5263-3, T-275 or ISO 12625-17.
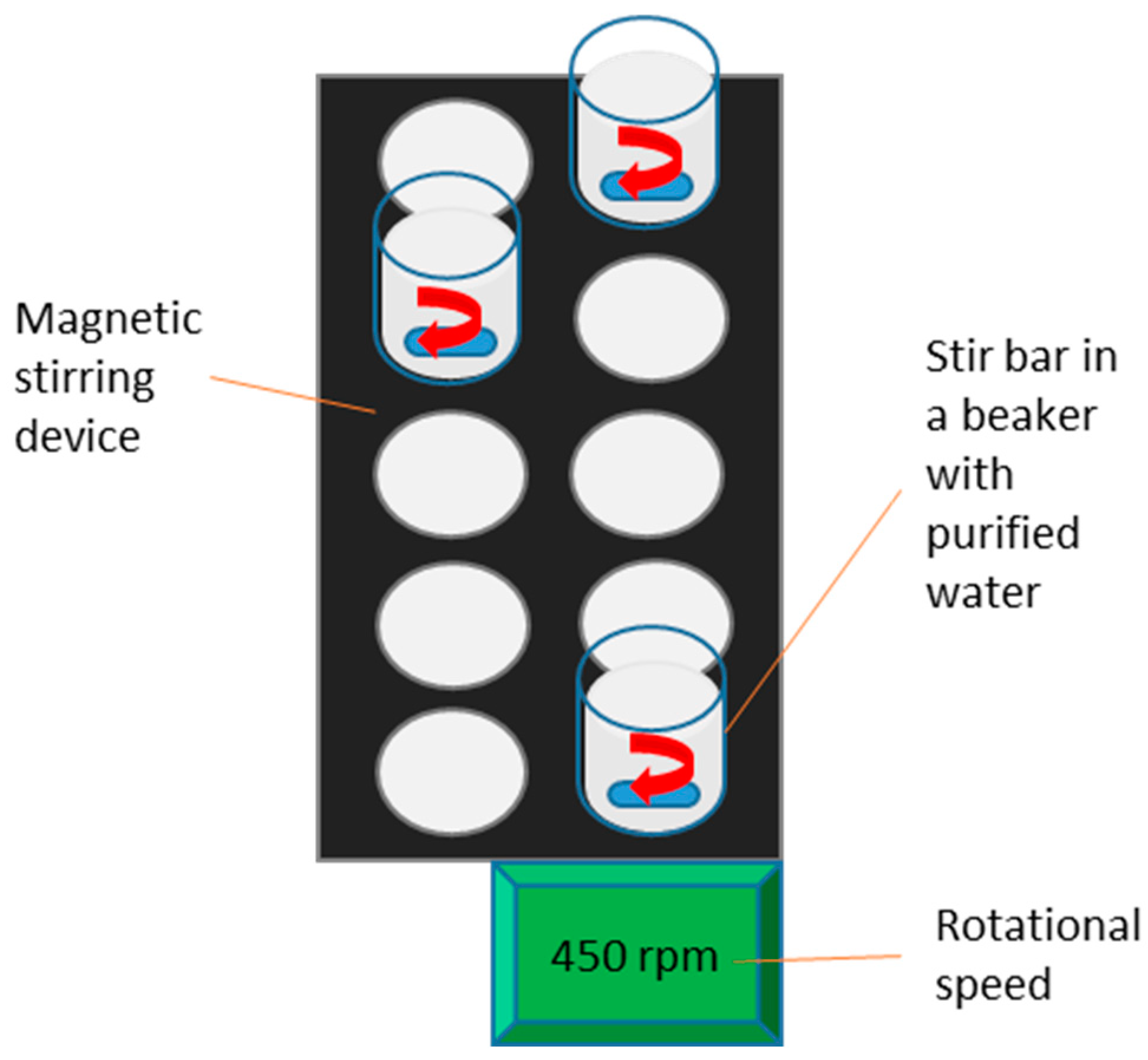
For our disintegration test, two paper strips are placed in 200 mL purified water in a 250 mL beaker. Each paper fragment, measuring 5 × 3 cm, is stirred in a beaker at room temperature using a magnetic stirrer and a stirring rod (3 × 0.5 cm). The size of the paper samples after stirring indicates the degree of disintegration, which is evaluated on a rating scale from 0 to 10.
As shown in Figure 9, the paper fragments, purified water, and magnetic bar are placed in the beaker, which is then set on the stirring device. The used rotation speed is 450 rpm. The test runs for 5 min for bleached papers and 20 min for unbleached papers, as the bleached paper disintegrates more easily. After stirring, the mixture is diluted to 9 L and drained through the forming screen in a Rapid Köthen handsheet former. The paper fragments are then transferred to a support sheet and dried in the sheet former’s vacuum oven for 15 min at 115 °C. Once dried, the paper fragments are photographed.
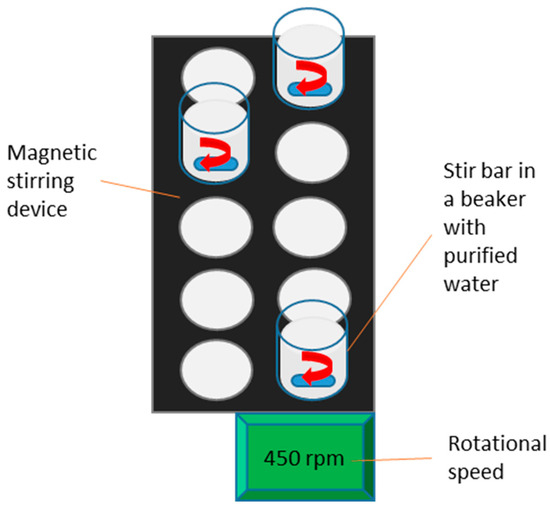
Figure 9.
Paper disintegration test procedure. The disintegration test procedure entails placing two paper fragments, each measuring 5 × 3 cm, into 200 mL purified water with a magnetic stirring rod in a 250 mL beaker. The stirring duration is calibrated to 5 min for bleached papers and 20 min for unbleached papers [12].
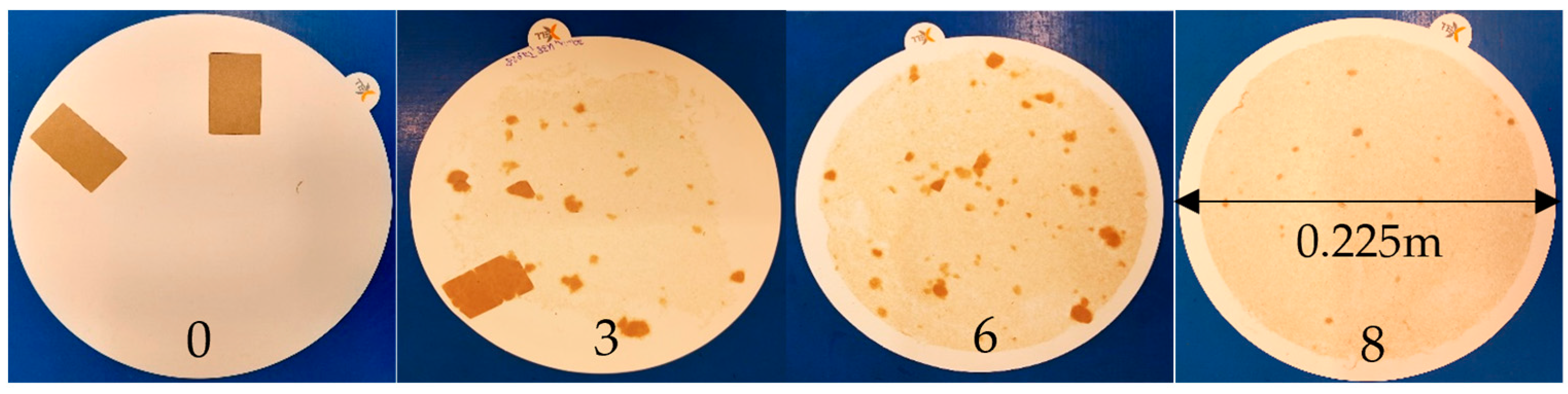
Disintegration is evaluated on a scale from 0 to 10, where 10 indicates complete disintegration and 0 indicates no disintegration. Scores are assigned using a set of 11 reference images, each representing a different level of disintegration. The final score is determined by matching the sample to the closest reference image. Figure 10 illustrates exemplary disintegration results along with their corresponding test scores. The complete set of reference images and corresponding scores is available in Appendix A. For each paper sample, three measurements are conducted.
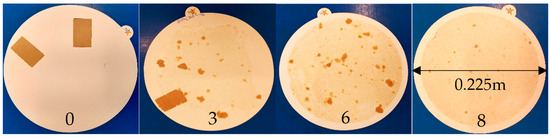
Figure 10.
Exemplary results from the disintegration test: On the left, a sample exhibiting no observable disintegration, resulting in a score of 0. On the right, a paper sample demonstrates effective disintegration, achieving a score of 8. Intermediate samples show varying degrees of disintegration improvement [12].
3.2.2. Tensile Strength (Wet and Dry)
Tensile testing is conducted in accordance with ISO 1924/3 standards. Each paper sample is precisely cut to a width of 15 mm (±1 mm) and a length of 150 mm. For each paper type, 20 strips are evaluated. The tensile strength index (TSI) is determined by dividing the tensile strength by the paper’s grammage. Wet tensile strength measurements were conducted following ISO 3781, the strips are soaked in deionized water for 5 min prior to testing. Tensile energy absorption (TEA) quantifies the energy absorbed during the tensile test, calculated as the area under the stress-strain curve from the initiation of the test until the sample fails.
3.2.3. Water Retention Value
The water-retention-value (WRV) is measured according to ISO 23714:2014. WRV quantifies the ability of fibers to retain water due to fiber swelling. For this procedure, 7–8 g of paper are immersed in a beaker containing distilled water to facilitate water absorption. For our test the residence time in water is 5 min for bleached paper and 20 min for unbleached paper, like for the disintegration test. The suspension is then filtered using a glass frit. Subsequently, 6 g of paper are placed into each tube of a centrifuge, with 4 tubes analyzed per paper sample. The centrifuge is set with a rotor radius of 150 mm, operating at 4000 rpm for 11 min. After centrifugation, the samples are weighed to obtain the wet weight. They are then placed in an oven overnight at 105 °C to determine the dry mass. These weights are subsequently used to calculate the Water Retention Value (WRV) according to Equation (2).
3.2.4. K-Value–Penetration Velocity
The liquid penetration speed into paper (the K-value) is measured with ultrasonic transmission testing. Detailed descriptions of the ultrasonic measurement technique and its interpretation can be found in [46], its correlation to liquid absorption speed has been demonstrated in the literature [35]. The literature also indicates that the K-value relates to the dissolution speed of packaging paper in water, further motivating its inclusion in this study [20]. For our measurements, we utilized a DPM 27 from emco (Leipzig, Germany).
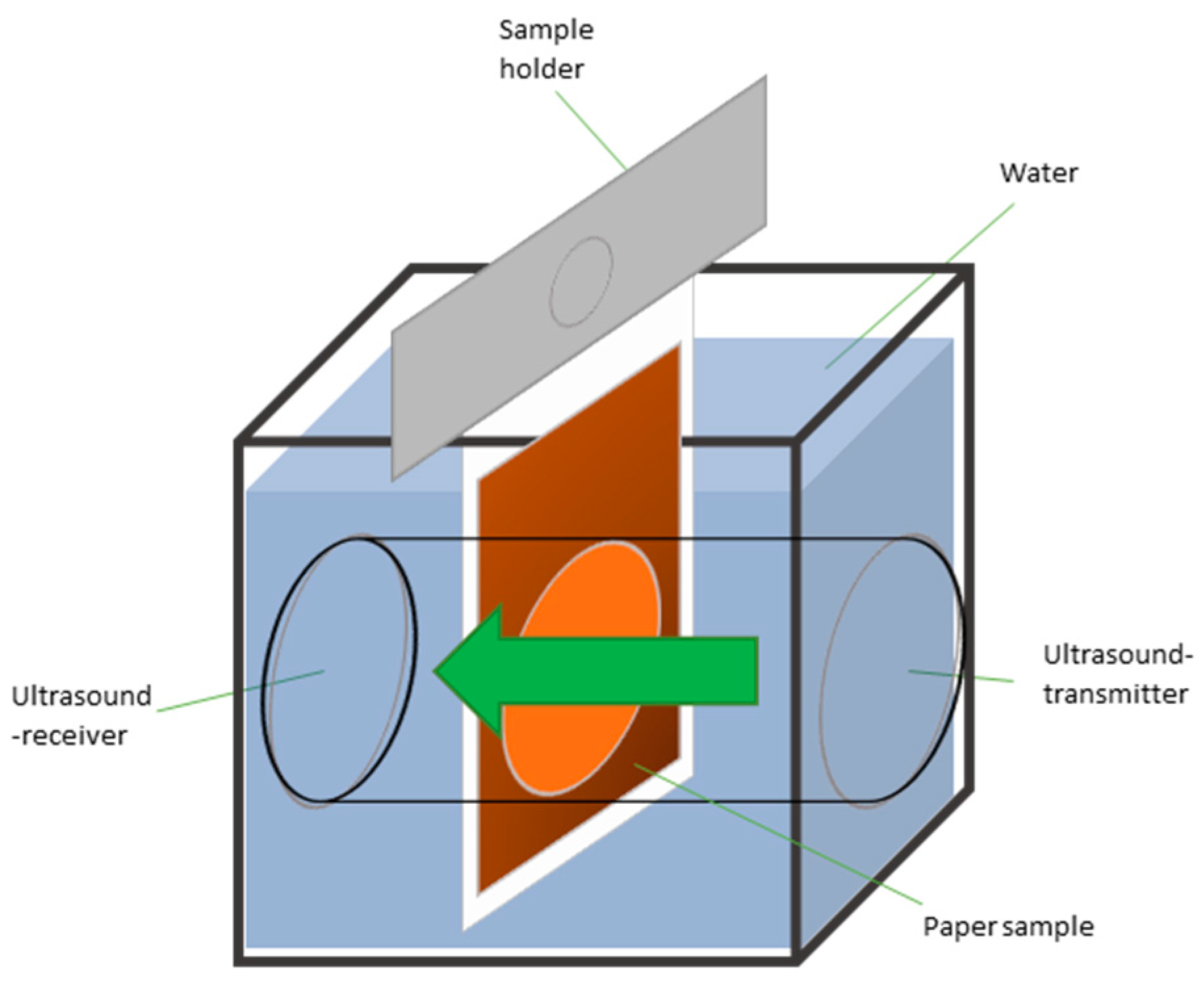
The measurement procedure is illustrated in Figure 11. The sample is secured to a sample holder using double-sided adhesive tape and immersed in a measuring cell filled with distilled water. Upon full submersion, the measurement process commences. Ultrasound waves are transmitted through the sample, and as the liquid penetrates the paper, the intensity of the transmitted ultrasound signal diminishes [46]. The transmission-time diagram shows the penetration dynamics, exemplified in Figure 12. The K-value is calculated using Equation (3).
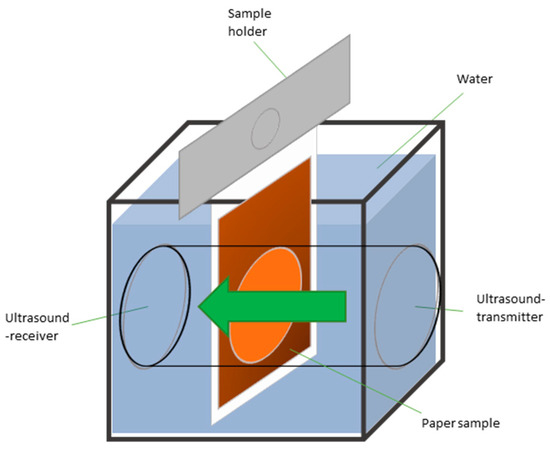
Figure 11.
Principle of ultrasonic liquid penetration measurement: When the sample is immersed, the transmission of ultrasound is monitored as water infiltrates the paper [12].
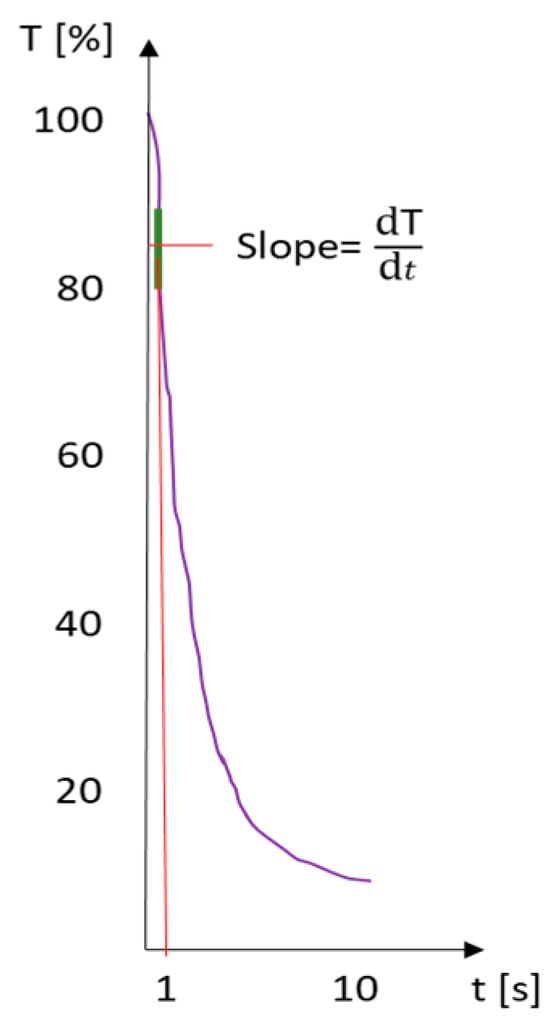
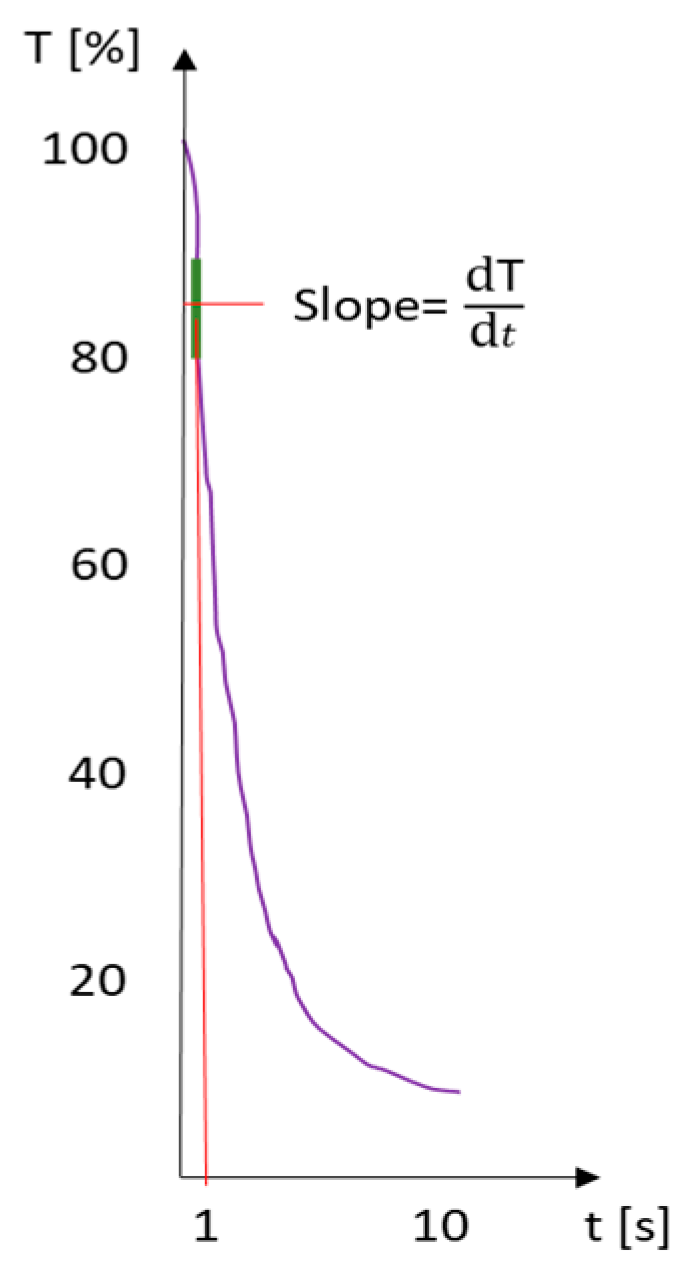
Figure 12.
Ultrasound transmission intensity T over time t: From a measurement of water-dispersible paper, the K-value for water penetration speed is calculated according to the specified Equation (3) [12].
In this context, T (%) signifies the ultrasound intensity, while t represents the elapsed time in seconds. The curve’s slope, denoted as dT/dt, is depicted in Figure 12, with the K-value indicating the point of maximum slope. Although the constant 40.95 may appear arbitrary, it is established by the instrument manufacturer to facilitate the interpretation of the K-value as the peak slope of the declining ultrasound signal. This constant is crucial for ensuring consistent and accurate measurements across different tests.
3.2.5. Contact Angle
The contact angle is assessed using the DataPhysics OCA 35 instrument (Filderstadt, Germany) through the Sessile Drop Method, which captures a quasi-static contact angle. Purified water serves as the test liquid, dispensed in 1.5 µL droplets at a rate of 1 µL/s. The contact angle is measured by capturing the droplet at 100 frames per second and analyzing the image right after the droplet stabilizes. The contact angle is then estimated as the average of the angles on both the left and right sides of the droplet. For each paper sample, 20 droplets are measured, with 10 droplets on each side. It has been determined that for microliter-sized droplets on paper, evaporation and water absorption have a minimal effect on the resulting contact angle [47].
3.2.6. Aging Under Different Storage Conditions
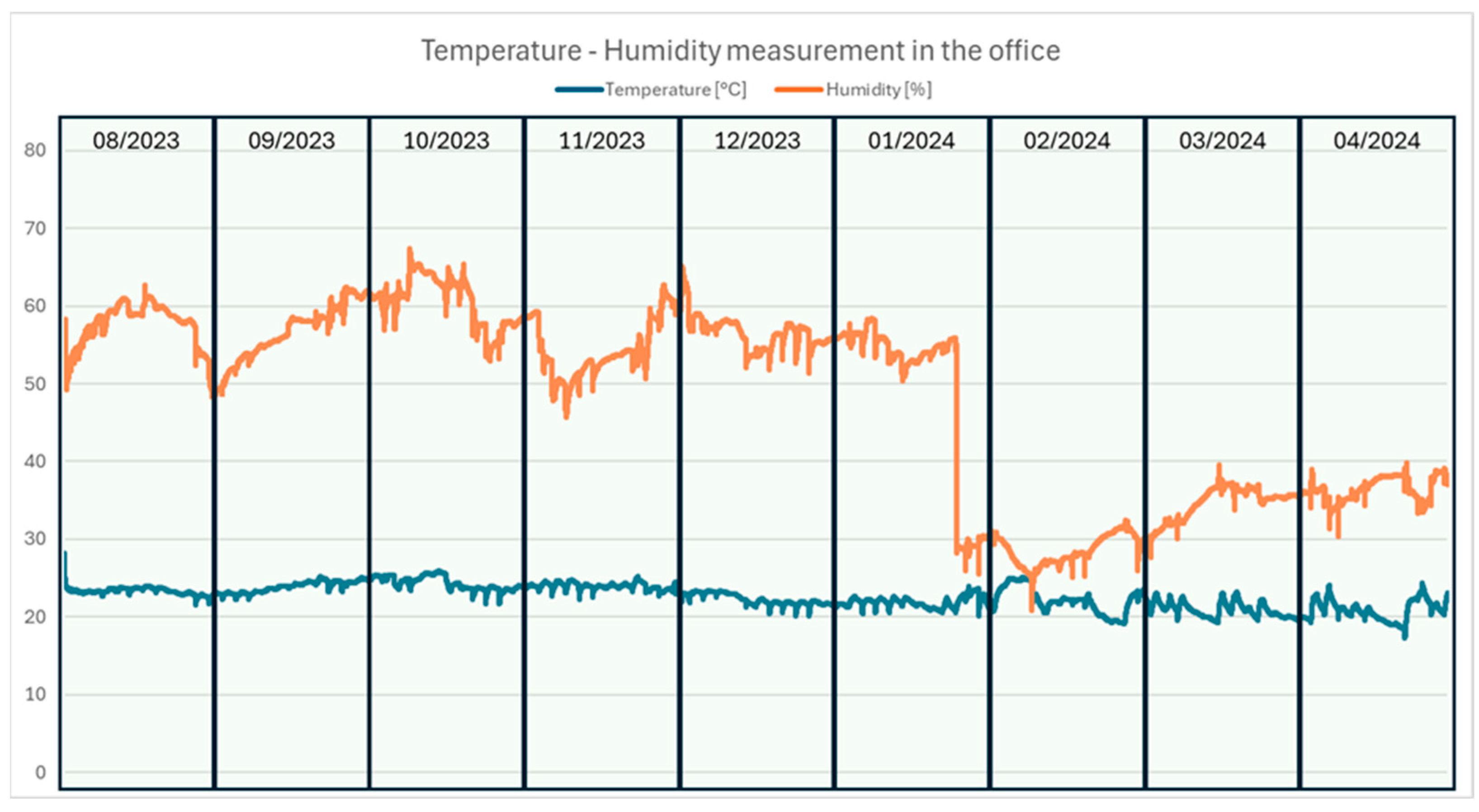
The papers were stored using two different methods: one batch in a climate-controlled room maintaining a constant temperature of 23 ± 1 °C and a constant humidity of 50 ± 2%, and the other batch in a closed box in an office environment where temperature and humidity fluctuated at around 20 °C to 27 °C and 28% and 68%. Two different storage methods have been chosen because it is known that variations in relative humidity are triggering chemical and physical paper aging [27,48], hence an effect of the storage conditions on the paper dispersibility is expected. Temperature and relative humidity in the box during office storage have been recorded, see Figure 13.
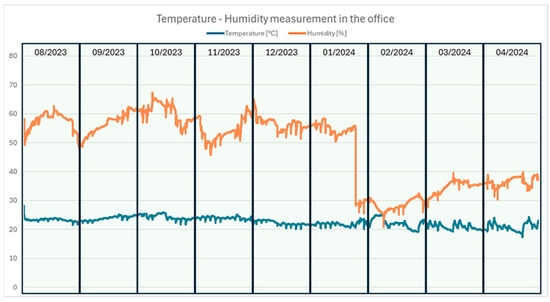
Figure 13.
Temperature and humidity measurement in the office over the aging time.
The testing intervals were adjusted based on changes observed in the measured paper properties. When significant changes were detected between measurements, the interval between steps were reduced. Conversely, if no changes were observed, the interval between steps were increased. Nine months comprises a normal life time for a paper packaging before disposal. Hence we have chosen 9 months as a representative maximal storage time. The final time schedule for the measurements performed is shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Paper testing schedule for different storage times.
4. Conclusions
In the present work we have investigated dispersibility of paper under low agitation, as it is required for paper products which are supposed to disintegrate in water after usage. For measurement of paper dispersibility we applied a custom developed test with mild disintegration conditions, i.e., very low mechanical energy input.
Our findings indicate a significant difference in the aging behavior between bleached and unbleached paper. The unbleached paper exhibits a strong decrease in disintegration over time. With starch addition disintegration is gone after just 5 weeks, without cationic starch and refining, after 9 months. In contrast, the bleached paper maintains good dispersibility even after 9 months, with only a slight decrease observed in samples with refining and cationic starch added.
Wet strength has been found to be a very good indicator for dispersibility, Figure 10. First this is valuable as wet strength apparently provides an easy lab-test for monitoring dispersibility and its degradation over time. Second it corroborates that the diminishing of paper dispersibility over time is related to prolonged fiber-fiber bonding in the presence of water.
The observed higher resistance of the fiber-fiber bonds can be related to a continuous reduction in fiber swelling (WRV) and fiber wetting (contact angle) over time. Water penetration speed (measured with ultrasound) was not well correlated to the changes in paper dispersibility. We hence conclude that the aging of the paper over time leads to a deteriorated liquid uptake, which protects the fiber-fiber bonds from being penetrated and broken by the water.
To mitigate the aging of paper and the decrease in disintegration, it hence seems to be crucial to explore methods to delay aging, e.g., by avoiding utilization of refining and starch (if possible as both are highly relevant for paper strength). Reducing swings in relative humidity is also known to delay paper aging [27,48]. We could however, somewhat unexpectedly, not find a significant difference in dispersibility between a 9-month storage in constant climate compared to storage in an office, with variable climate conditions. Also maintaining low wet strength in general should lead to better disintegration results and potentially slower aging.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, U.H. and A.C.P.; methodology, U.H. and A.C.P.; software, U.H.; validation, A.C.P.; formal analysis, U.H. and A.C.P.; investigation, A.C.P.; resources, A.C.P.; data curation, A.C.P.; writing—original draft preparation, U.H. and A.C.P.; writing—review and editing, U.H. and A.C.P.; visualization, U.H. and A.C.P.; supervision, U.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Austrian Research Promotion Agency FFG, grant number 892416.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data can be obtained on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the COMET program Wood, project number 892416, of the Austrian Research Promotion Agency FFG managed by Wood K plus—Competence Center for Wood Composites & Wood Chemistry, Linz, Austria, Area Wood & Paper Surface Technologies. Open Access Funding by the Graz University of Technology.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A
Dispersibility Scores:
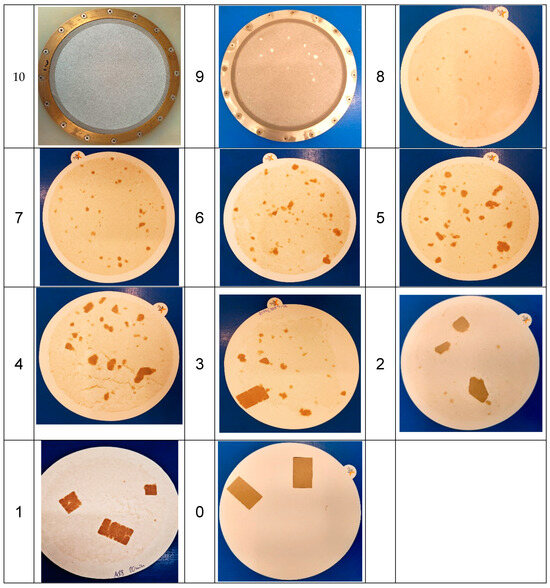
Figure A1.
Chart with sample images and according dispersibility scores, as it is used for assignment of dispersibility scores by the lab technician.
Figure A1.
Chart with sample images and according dispersibility scores, as it is used for assignment of dispersibility scores by the lab technician.
Appendix B
Climate-controlled environment stored paper:
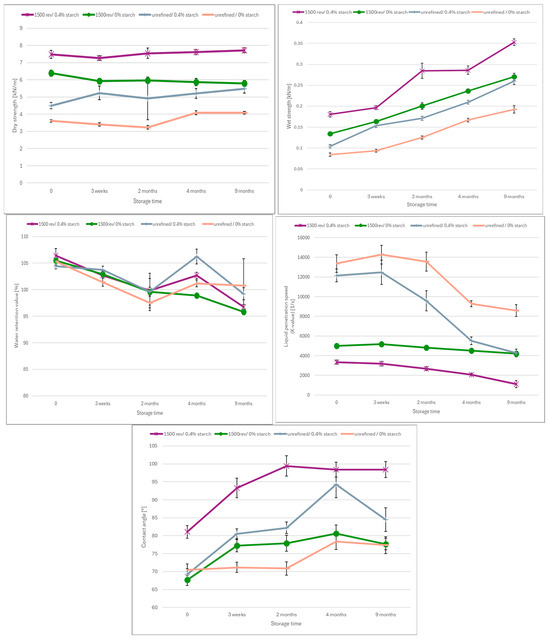
Figure A2.
Unbleached paper.
Figure A2.
Unbleached paper.
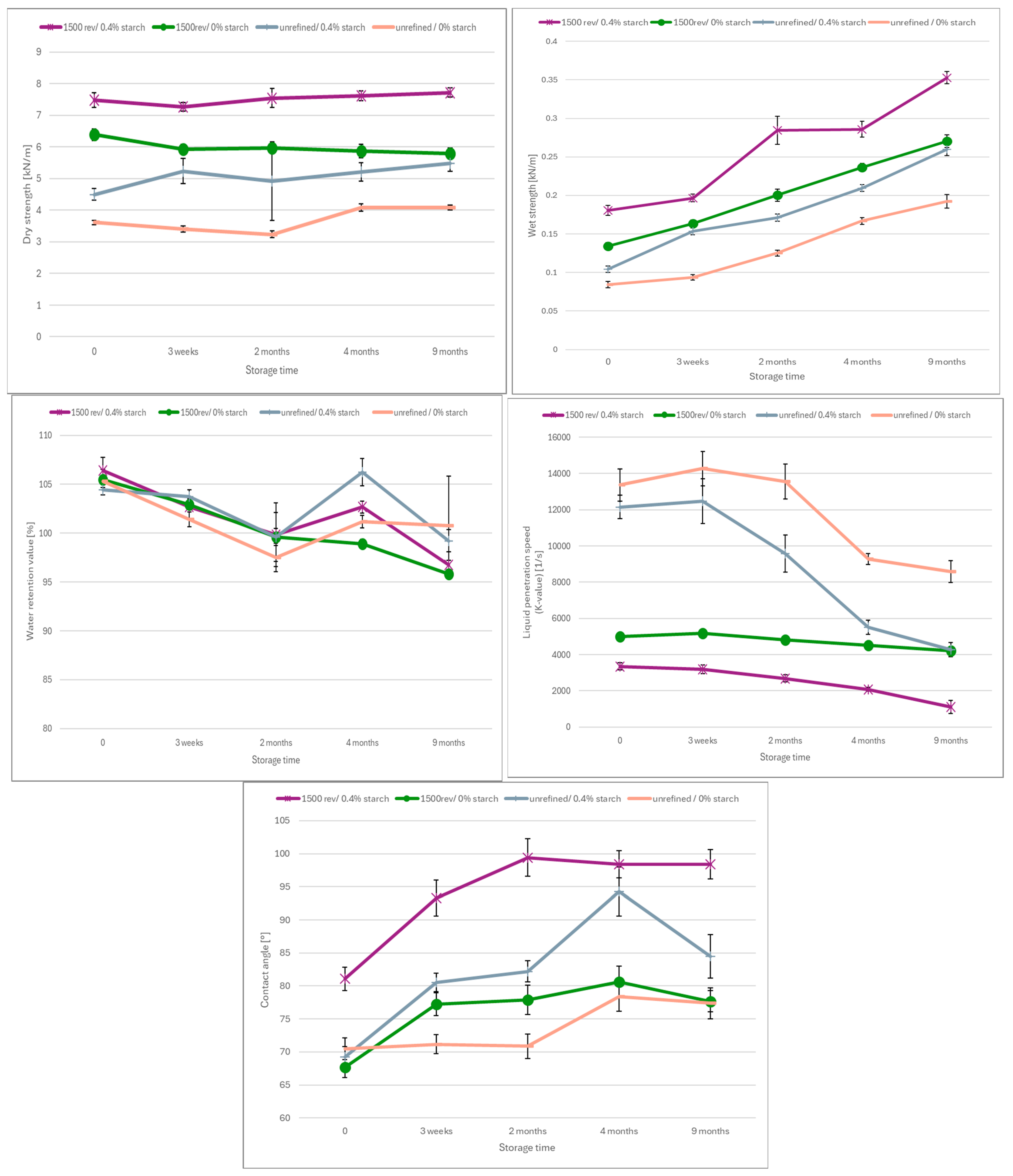
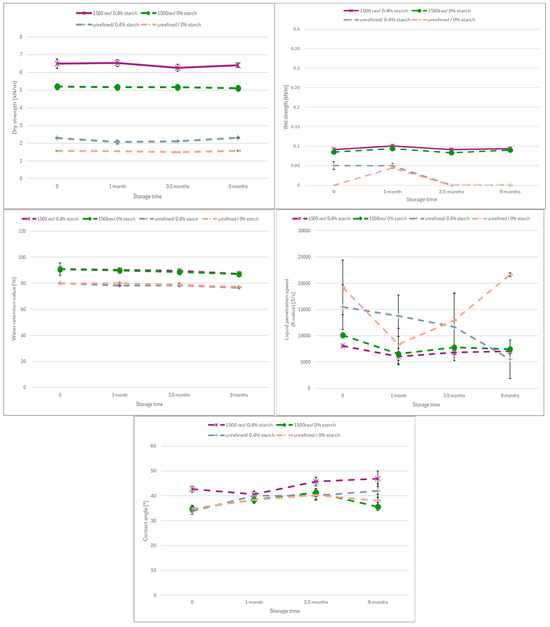
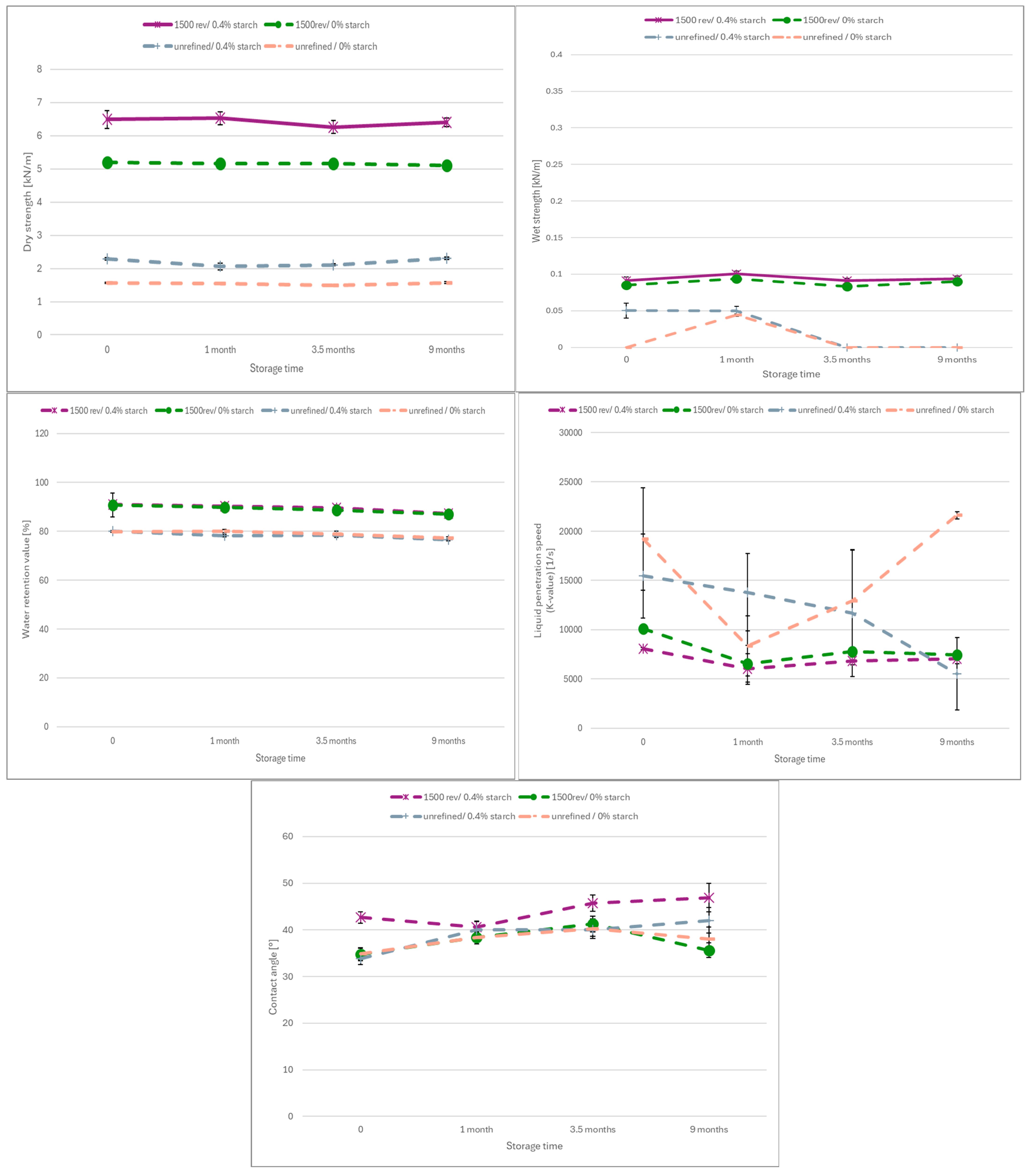
Figure A3.
Bleached paper.
Figure A3.
Bleached paper.
References
- Senarathna, W.G.C.; Sulaksha, L.G.; Weerarathn, D.; Jayathma, W.M.V.; Gamage, D.G.M.; Thennakoon, T.M.T.; Hewage, H.T.; Panagoda, L.P.S.; Sandunika, D.M.; Perera, M.D. Paper Recycling for a Sustainable Future: Global Trends. J. Res. Technol. Eng. 2023, 4, 169–186. [Google Scholar]
- Villanueva, A.; Wenzel, H. Paper Waste—Recycling, Incineration or Landfilling? A Review of Existing Life Cycle Assessments. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirković, I.B.; Bolanča, Z.; Medek, G. Impact of Aging and Recycling on Optical Properties of Cardboard for Circular Economy. Recycling 2024, 9, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Foggia, G.; Beccarello, M. An Overview of Packaging Waste Models in Some European Countries. Recycling 2022, 7, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environment Agency. Reaching 2030’s Residual Municipal Waste Target: Why Recycling Is Not Enough; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2022; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Naithani, V.; Lucia, L.; Banerjee, S. High-Bulk Water Dispersible Paper-Based Composites. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 11334–11338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K. Water-Dispersible Wrapping Paper and Wrapping Paper. Patent No. JP3472494B2, 2 December 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Caspar, T.; Gaspareto, D.; Gaultney, L.D.; Ross, G.; Hallahan, B.; Hallahan, D.; Johnson, B.D.; Jones, B.H.; Kratz, K.; Lakshmanan, P.; et al. Plant Artificial Seeds and Methods for the Production Thereof. Australian Patent AU2012358929B2, 27 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Green, B. Water-Dispersible and Biodegradable Films for the Packaging of Liquids and Moisture-Sensitive Materials. Patent No. US20210032002A1, 4 February 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Banks, M.S. Water Disintegratable Soap Package. Patent No. US2539395A, 6 November 1946. [Google Scholar]
- Koyama, M.; Kishimoto, M.; Ishino, Y. Water-Dispersible Paper. Patent No. US 9,388,532 B2, 12 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pfennich, A.C.; Schoeffmann, E.A.; Lammer, H.; Hirn, U. Water-Soluble Paper for Packaging Applications—Balancing Material Strength and Dispersibility. Nord. Pulp. Pap. Res. J. 2023, 8, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blechschmidt, J.; Dobschall, E.; Blechschmidt, J.; Heinemann, S.; Fischer, K.; Bäurich, C.; Naujock, V.P.H.; Gliese, T.; Kleemann, S.; Naujock, H.; et al. Taschenbuch Der Papiertechnik; Hanser: München, Germany, 2021; 7 (167–195) and 9 (252–294); ISBN 9783446438026. [Google Scholar]
- Tervahartiala, T.; Hildebrandt, N.C.; Piltonen, P.; Schabel, S.; Valkama, J.P. Potential of All-Cellulose Composites in Corrugated Board Applications: Comparison of Chemical Pulp Raw Materials. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2018, 31, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigac, J.; Fišerová, M. Influence of Pulp Refining on Tissue Paper Properties. Tappi J. 2008, 7, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Luettgen, C. Repulping of Wet Strength Paper Towel with Potassium Monopersulfate. Tappi J. 2020, 19, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Mosse, W.K.J.; Sharman, S.; Batchelor, W.; Garnier, G. Paper Strength Development and Recyclability with Polyamideamine-Epichlorohydrin (PAE). BioResources 2012, 7, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adel, A.M.; Dupont, A.L.; Abou-Yousef, H.; El-Gendy, A.; Paris, S.; El-Shinnawy, N. A Study of Wet and Dry Strength Properties of Unaged and Hygrothermally Aged Paper Sheets Reinforced with Biopolymer Composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 9212–9224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, N.K.; Rajan, V. Wet Strength Paper Repulping: Effect of Process Variables. Appita J. 2004, 57, 305–310. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, B.U.; Ryu, J.Y.; Song, B.K. Factors Influencing Deflaking Kinetics in Repulping to Produce Molded Pulp. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2009, 15, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirn, U.; Schennach, R. Comprehensive Analysis of Individual Pulp Fiber Bonds Quantifies the Mechanisms of Fiber Bonding in Paper. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayme, G. Micro-Swelling Measurement in Cellulosic Pulp. Wochenbl. Pap. 1944, 6, 187–194. [Google Scholar]
- Lindström, T. The Porous Lamellar Structure of the Cell Wall; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1986; pp. 99–109. [Google Scholar]
- Salmén, L.; Stevanic, J.S. Effect of Drying Conditions on Cellulose Microfibril Aggregation and “Hornification”. Cellulose 2018, 25, 6333–6344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scallan, A.M.; Laivins, G.V. The Mechanism of Hornification of Wood Pulps. In Products of Papermaking; FRC: Manchester, UK, 2018; pp. 1235–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, K.L.; Cameron, R.E. A Review of the Relationship between Thermally-Accelerated Ageing of Paper and Hornification. Cellulose 1999, 6, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Małachowska, E.; Pawcenis, D.; Dańczak, J.; Paczkowska, J.; Przybysz, K. Paper Ageing: The Effect of Paper Chemical Composition on Hydrolysis and Oxidation. Polymers 2021, 13, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koura, A.; Krause, T. Warum Altert Papier? In Die Alterung von Papier, Teil II. der Einfluß der Mahlung auf die Alterung ligninfreier Faserstoffe; Papier: Camden, UK, 1978; pp. 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, H.A. The Chemistry of Paper Preservation: Part 1. The Aging of Paper and Conservation Techniques. J. Chem. Educ. 1996, 73, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zervos, S. Natural and Accelerated Ageing of Cellulose and Paper: A Literature Review. In Cellulose: Structure and Properties, Derivatives and Industrial Uses; Nova Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 155–203. [Google Scholar]
- Area, M.C.; Cheradame, H. Paper Aging and Degradation: Recent Findings and Research Methods. BioResources 2011, 6, 5307–5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Małachowska, E.; Dubowik, M.; Boruszewski, P.; Łojewska, J.; Przybysz, P. Influence of Lignin Content in Cellulose Pulp on Paper Durability. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlak, J.; Frazier, R. Review: The Softness of Hygiene Tissue. BioResources 2022, 17, 3509–3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahti, J.; Kouko, J.; Hirn, U. Time-Dependent Mechanical Response of Paper during Web-Fed High-Speed Inkjet Printing. Nord. Pulp. Pap. Res. J. 2019, 34, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldner, C.; Mayrhofer, A.; Hirn, U. Measuring Liquid Penetration in Thin, Porous Sheets with Ultrasound and Drop Absorption—Scope and Limitations. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 650, 129551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, C.T.J. A Survey of Paper Mechanics in Fundamental Terms. In The Fundamental Properties of Paper Related to Its Uses; FRC: Manchester, UK, 1973; pp. 202–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellers, C.; Iversen, T.; Lindstrom, T.; Nilsson, T.; Rigdahl, M. Ageing/Degradation of Paper, a Literature Survey. FoU-Proj. Papperskonservering 1989, 139, 47–48. [Google Scholar]
- Harter, T.; Bernt, I.; Winkler, S.; Hirn, U. Reduced Dispersibility of Flushable Wet Wipes after Wet Storage. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geffert, A.; Geffertova, J.; Stevulova, N.; Seman, B. The Change of Swelling of Pulp Fibres under Recycling. Solid State Phenom. 2016, 244, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okayama, T. The Effects of Recycling on Pulp and Paper Properties. Kami Pa Gikyoshi/Jpn. Tappi J. 2002, 56, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cildir, H.; Howarth, P. The Effect of Re-Use on Paper Strength. Pap. Technol. 13 1972, 10, 333. Available online: https://cir.nii.ac.jp/crid/1570572700078753152 (accessed on 20 march 2025).
- Gratton, M.F. The Recycling Potential of Calendared Newsprint Fibers. In Proceedings of the 1991 CPPA Recycling Forum, Montreal, QC, Canda, 29–31 October 1991; CPPA Press: Sacramento, CA, USA, 1991; p. 65. [Google Scholar]
- Trovagunta, R.; Marquez, R.; Tolosa, L.; Barrios, N.; Zambrano, F.; Suarez, A.; Pal, L.; Gonzalez, R.; Hubbe, M.A. Lignin Self-Assembly Phenomena and Valorization Strategies for Pulping, Biorefining, and Materials Development: Part 1. The Physical Chemistry of Lignin Self-Assembly. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 332, 103247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.K.; Biswas, O.; Pandey, P. To Improve the Disintegration Potential of Toilet Grade Tissue Paper. Nord. Pulp. Pap. Res. J. 2022, 37, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sealey, I.J.E.; Us, S.C.; Miller, B.T.; Us, S.C. SOFT, Low Lint, Through Air Dried Tissue and Method of Forming the Same. Patent No.: US 10,941,525 B2, 26 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Waldner, C.; Hirn, U. Ultrasonic Liquid Penetration Measurement in Thin Sheets—Physical Mechanisms and Interpretation. Materials 2020, 13, 2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krainer, S.; Hirn, U. Contact Angle Measurement on Porous Substrates: Effect of Liquid Absorption and Drop Size. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 619, 126503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Małachowska, E.; Dubowik, M.; Boruszewski, P.; Przybysz, P. Accelerated Ageing of Paper: Effect of Lignin Content and Humidity on Tensile Properties. Herit. Sci. 2021, 9, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).