The Influence of Compatibilizer Addition and Gamma Irradiation on Mechanical and Rheological Properties of a Recycled WEEE Plastics Blend
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
| Compatibilizers Used | Description | Amounts of Compatibilizer |
|---|---|---|
| Kraton® G1652 E | SEBS (30 wt% styrene) | 0.83, 1.25, 2.5, 5, 10, 20 wt% |
| Kraton® FG1901 E | SEBS-g-MAH | 2.5, 5, 10 wt% |
| Royaltuf® 372P20 | SAN modified with EPDM | 5, 10, 20 wt% |
| Fusabond® P353 | PP-g-MAH | 0.83, 2.5, 5, 10 wt% |
2.2. Processing Equipment
| Material | Amount of Kraton® G1652 E (wt %) |
|---|---|
| WEEEBR reference | 0 |
| WEEEBR | 2.5 |
| WEEEBR | 5 |
| WEEEBR | 10 |
| WEEEBR (gamma-irradiated granulate) | 0 |
| WEEEBR (gamma-irradiated granulate) | 2.5 |
| WEEEBR (gamma-irradiated granulate) | 5 |
| WEEEBR (gamma-irradiated dog bones) | 0 |
2.3. Material Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Tensile Properties
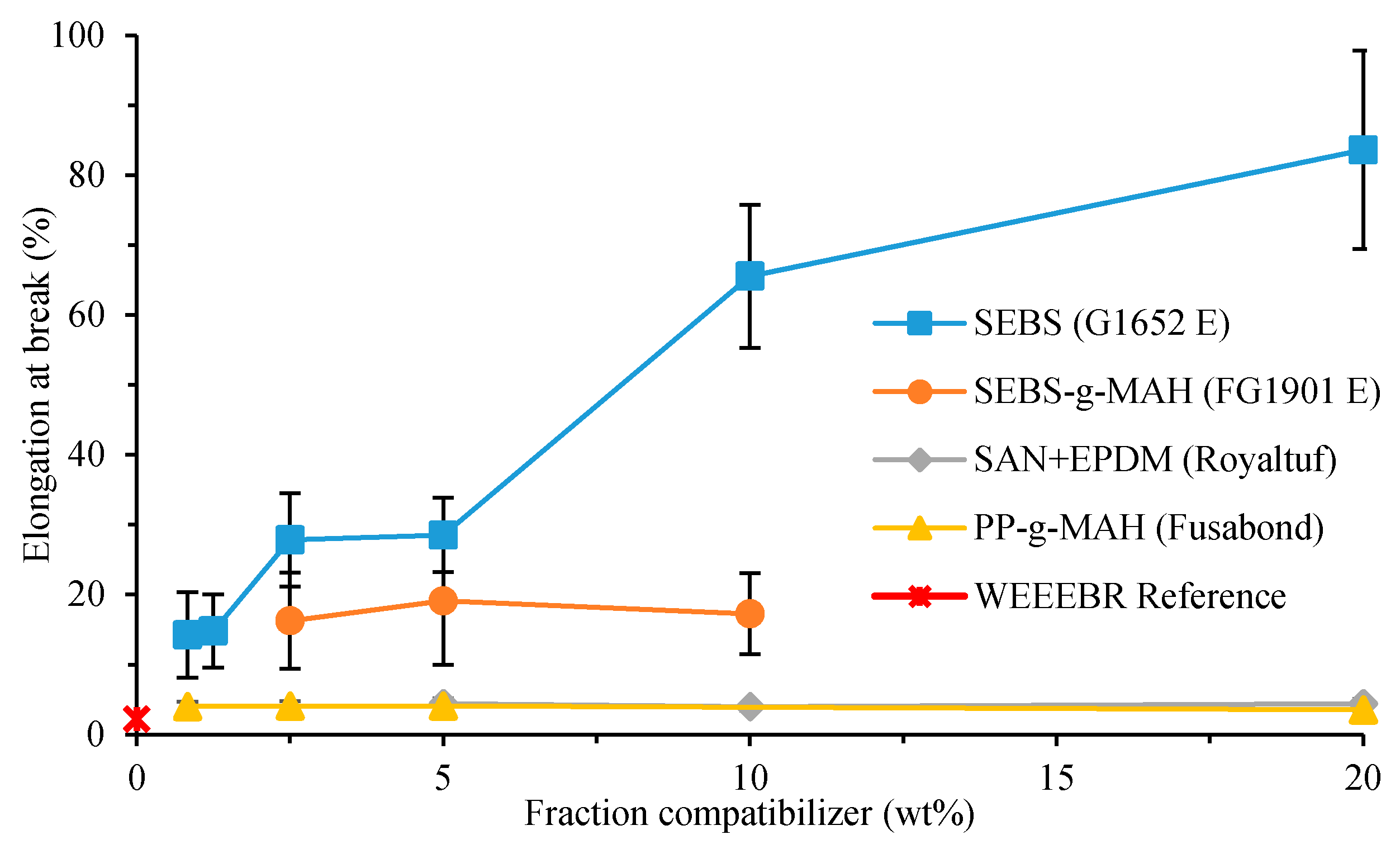
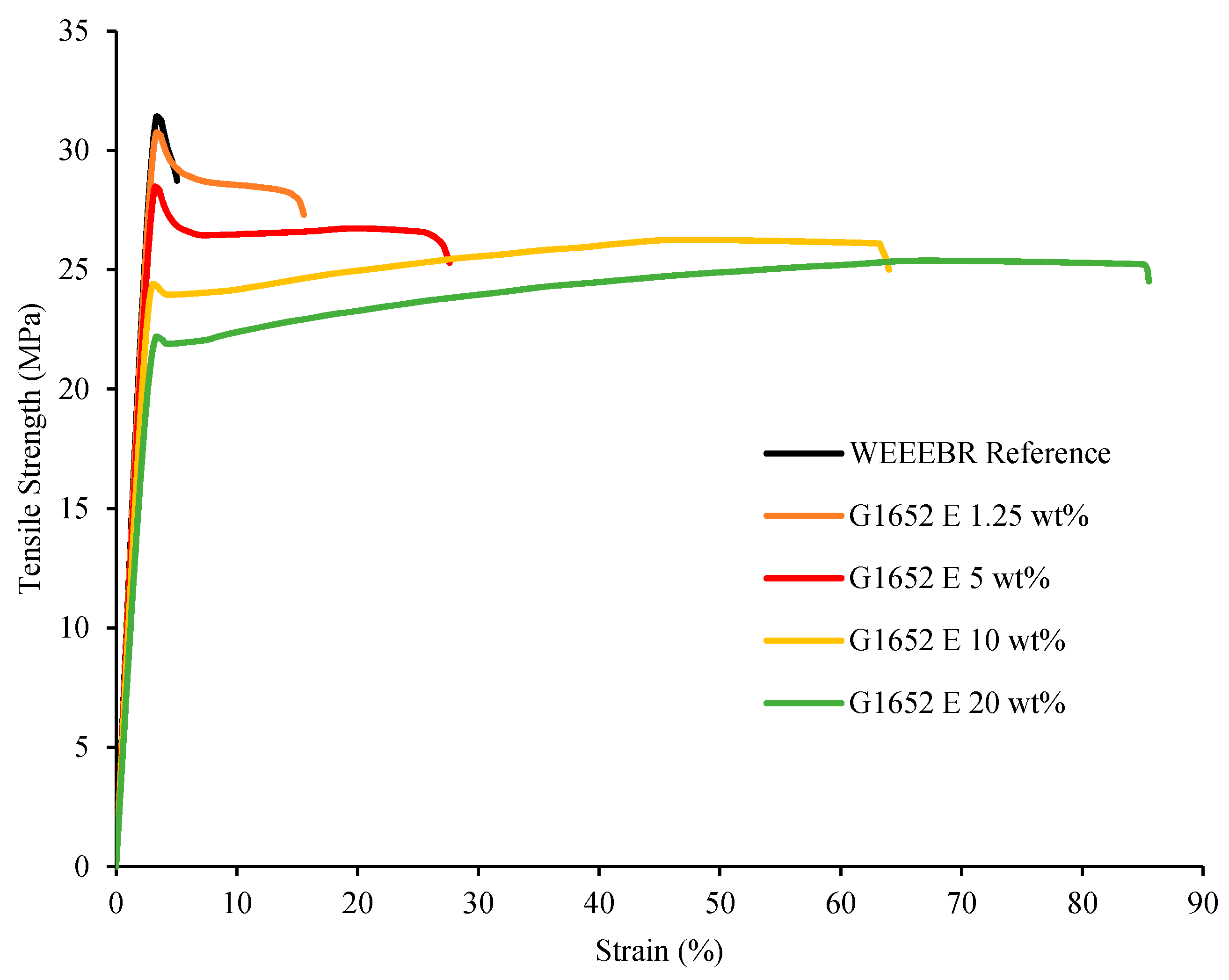

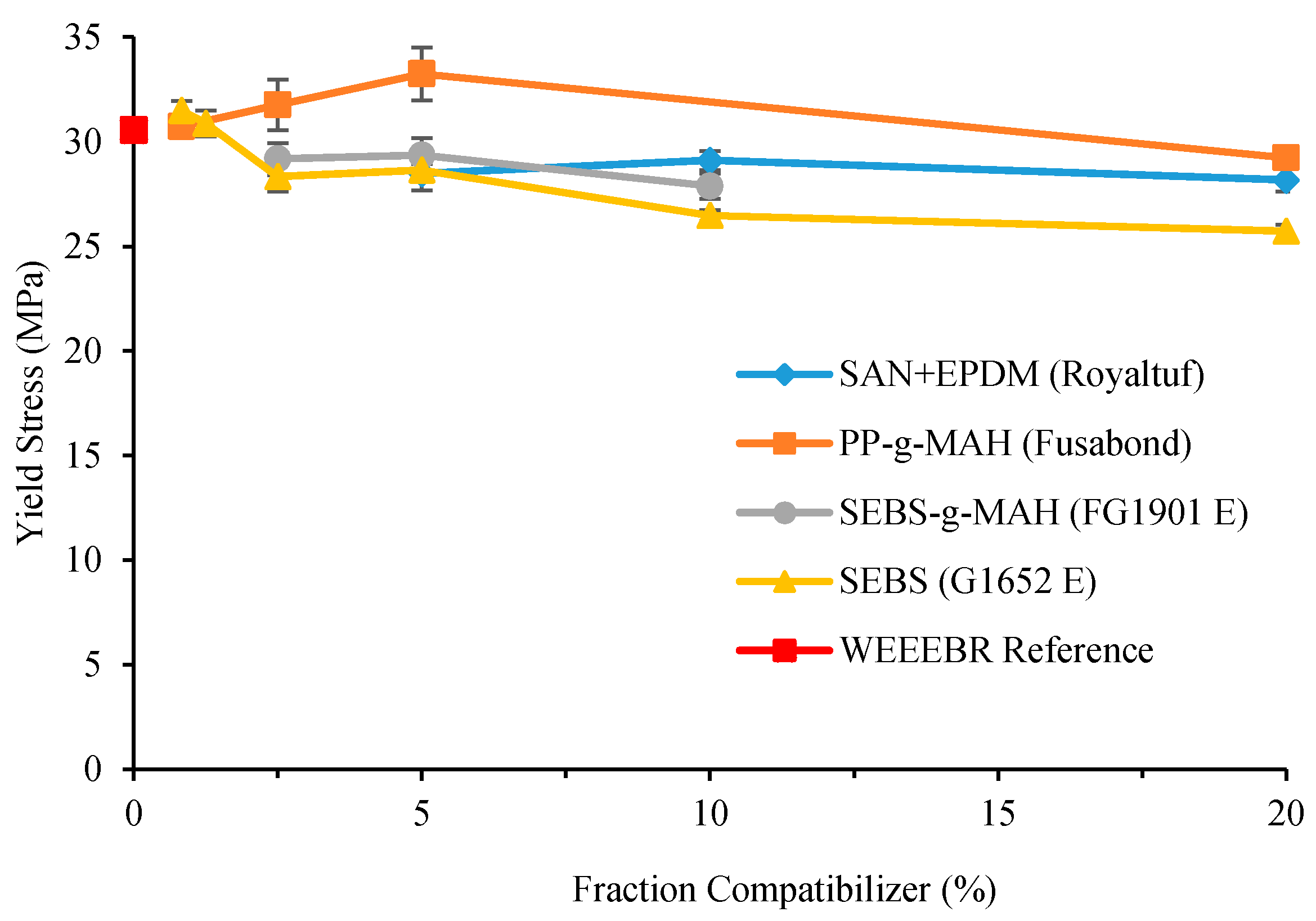
3.2. DMTA
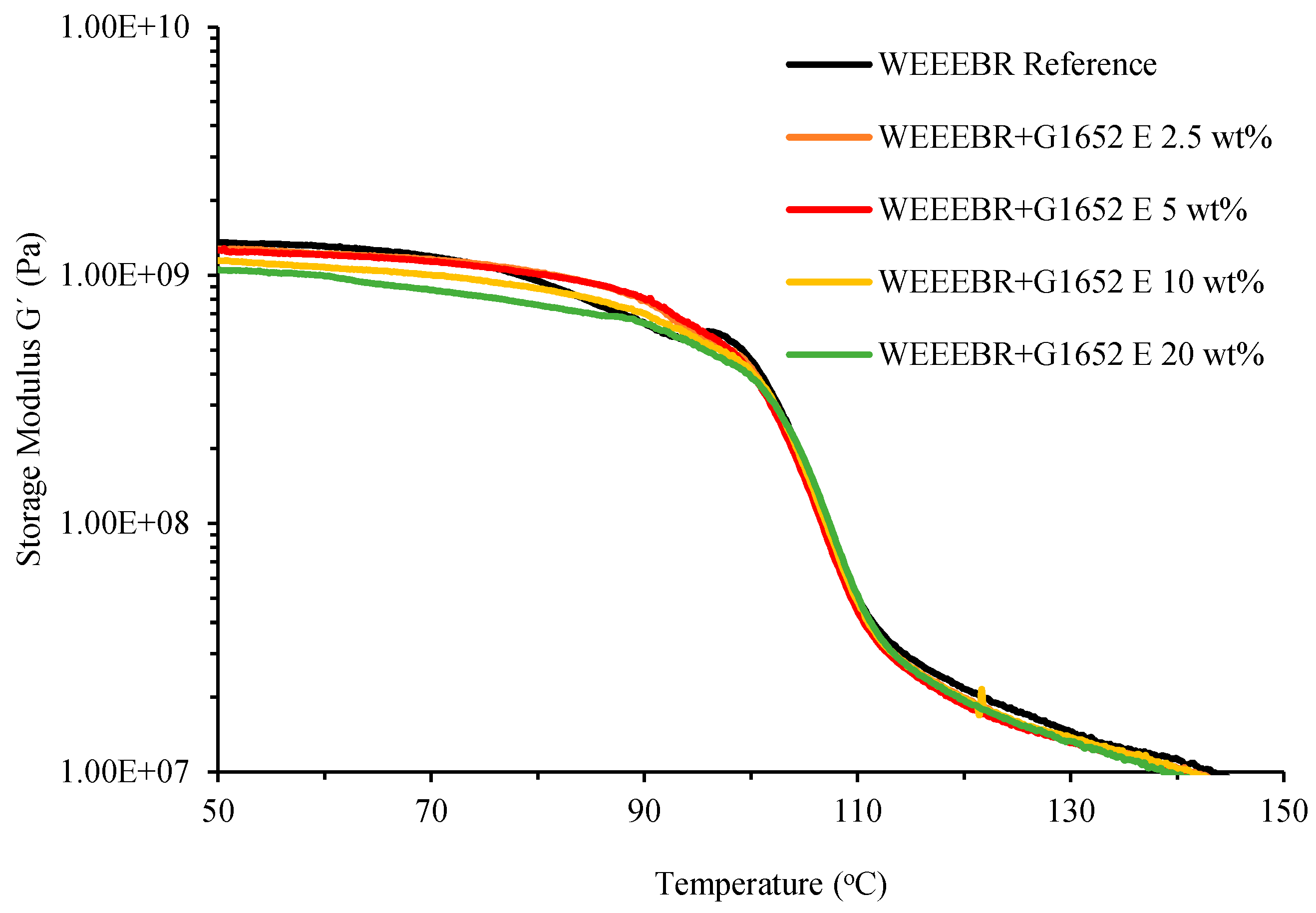
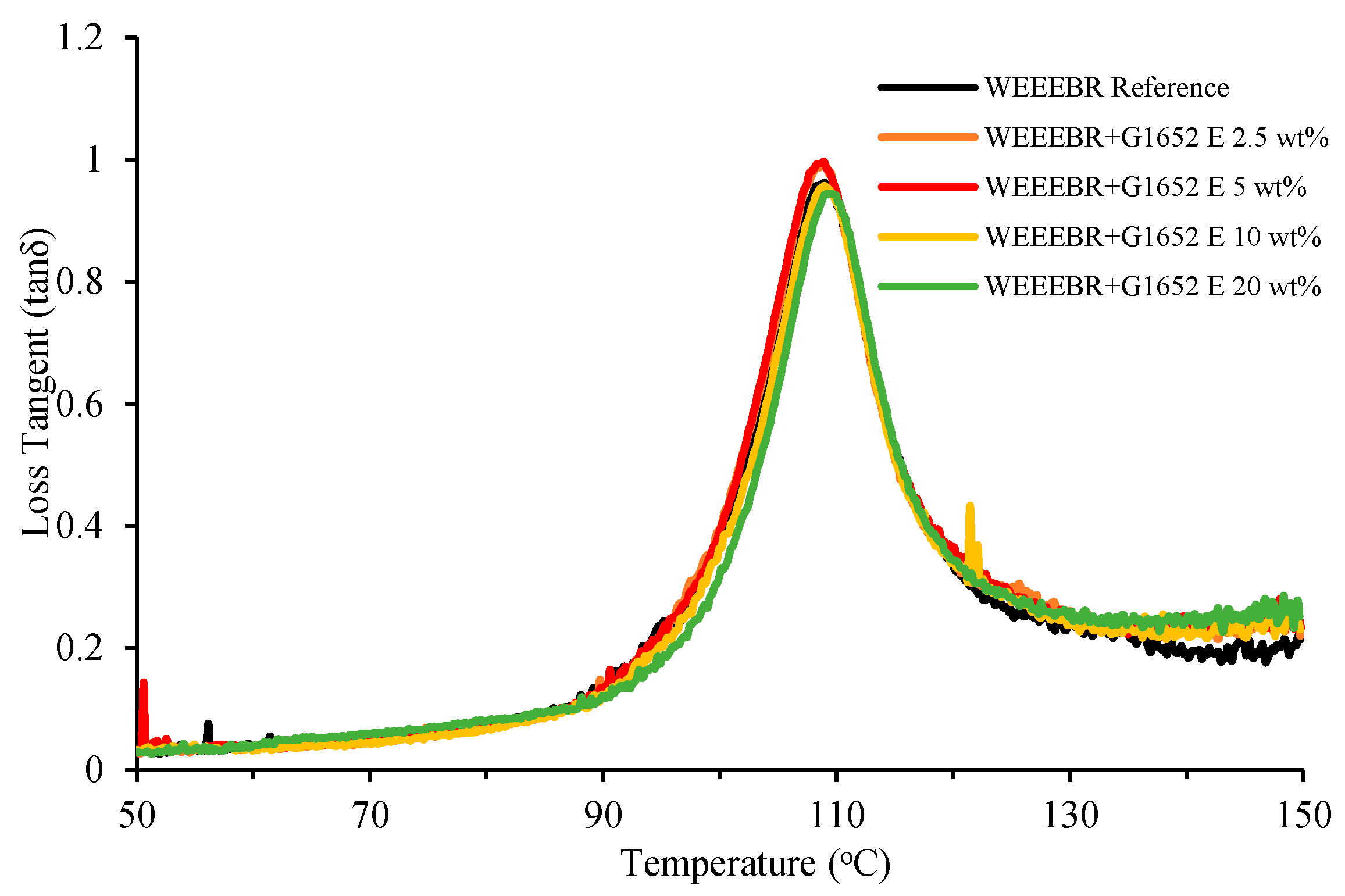
3.3. Impact Strength
| Material | Amount of Kraton® G1652 E (wt%) | Notched Samples | Un-Notched Samples | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kJ/m2 | Standard Deviation | kJ/m2 | Standard Deviation | ||
| WEEEBR reference | 0 | 2.1 | 0.3 | 7.9 | 1.0 |
| WEEEBR | 2.5 | 2.7 | 0.1 | 13.2 | 1.5 |
| WEEEBR | 5 | 3.8 | 0.3 | 16.8 | 2.0 |
| WEEEBR | 10 | 5.0 | 0.1 | 24.5 | 4.1 |
| WEEEBR (50 kGy) | 0 | 1.3 | 0.1 | 6.7 | 0.9 |
| WEEEBR (50 kGy) | 2.5 | 2.3 | 0.1 | 10.7 | 1.1 |
| WEEEBR (50 kGy) | 5 | 2.6 | 0.0 | 12.5 | 1.9 |
| WEEEBR (50 kGy) * | 0 | 2.1 | 0.5 | 8.0 | 1.1 |
| Material | Amount of Kraton® G1652 E (%) | Injection Molding Pressure (bar) | Increase in Injection Molding Pressure (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| WEEEEBR reference | 0 | 435 | - |
| WEEEBR | 2.5 | 508 | 17 |
| WEEEBR | 5 | 544 | 25 |
| WEEEBR | 10 | 544 | 25 |
| WEEEBR (50 kGy) | 0 | 435 | 0 |
| WEEEBR (50 kGy) | 2.5 | 471 | 8 |
| WEEEBR (50 kGy) | 5 | 508 | 17 |
3.4. Melt Flow Rate
| Material | Amount of Kraton® G1652 E (wt%) | Melt Flow Rate (g/10min) @220 °C, 5 kg | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Irradiated | 50 kGy Gamma-Irradiated | ||
| WEEEBR reference | 0 | 29 | 45 |
| WEEEBR | 2.5 | 21.7 | 38.2 |
| WEEEBR | 5 | 21.1 | 34 |
| WEEEBR | 10 | 19.6 | - |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflict of Interest
References and Notes
- El-Kretsen. El-Kretsen Verksamheten 2014; El-Kretsen: Stockholm, Sweden, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Menikpura, S.N.M.; Santo, A.; Hotta, Y. Assessing the climate co-benefits from Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) recycling in Japan. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 74, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toxics Link. Improving Plastic Management in Delhi—A Report on WEEE Plastic Recycling; Toxics Link: Delhi, India, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hirayama, D.; Saron, C. Characterisation of recycled acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene and high-impact polystyrene from waste computer equipment in Brazil. Waste Manag. Res. 2015, 33, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Xu, Z. Recycling of non-metallic fractions from waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE): A review. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 1455–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waste & Resources Action Programme. Separation of Mixed WEEE Plastics Final Report (WRAP Project MDD018 and MDD023); WRAP: Scotland, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dascalescu, L.; Samuila, A.; Iuga, A.; Morar, R.; Csorvasy, I. Influence of material superficial moisture on insulation-metal electroseparation. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 1992 IEEE Industry Applications Society Annual Meeting, Huston, TX, USA, 4–9 October 1992; Volume 2, pp. 1472–1478.
- Stenvall, E.; Tostar, S.; Boldizar, A.; Foreman, M.R.S.J.; Moller, K. An analysis of the composition and metal contamination of plastics from waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE). Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, V.; Biswal, M.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. Recycling of engineering plastics from waste electrical and electronic equipments: Influence of virgin polycarbonate and impact modifier on the final performance of blends. Waste Manag. Res. ISWA 2014, 32, 379–388. [Google Scholar]
- Wäger, P.A.; Böni, H.; Buser, A.; Morf, L.; Schluep, M.; Streicher, M. Recycling of Plastics from Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE)—Tentative Results of a Swiss study; R‘09 World Congress: Davos, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Freegard, K.; Tan, G.; Morton, R. Develop a Process to Separate Brominated Flame Retardants from WEEE Polymers; Waste Resources Action Programme: Banbury, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Schlummer, M.; Gruber, L.; Maeurer, A.; Woiz, G.; van Eldik, R. Characterisation of polymer fractions from waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) and implications for waste management. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 1866–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenvall, E. Functional Properties and Morphology of Recycled Post-Consumer WEEE Thermoplastic Blend; Chalmers University of Technology: Gothenburg, Sweden, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Clegg, D.W.; Collyer, A.A. Irradiation Effects on Polymers; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Zheng, K.; Tong, B. Nonisothermal Crystallization Behavior of Polypropylene Grafted Silane and Styrene Using gamma-Ray Irradiation. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B Phys. 2011, 50, 942–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directive 2011/65/EU. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32011L0065 (accessed on 8 June 2011).
- Giles, H.F.J.; Wagner, J.R.J.; Mount, E.M.I. Extrusion—The Definitive Processing Guide and Handbook; William Andrew Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sani Amril, S.; Hassan, A.; Mokhtar, M.; Syed Mustafa Syed, J. Effect of SEBS on the mechanical properties and miscibility of polystyrene rich polystyrene/polypropylene blends. Prog. Rubber Plast. Recycl. Technol. 2005, 21, 261–276. [Google Scholar]
- Kallel, T.; Massardier-Nageotte, V.; Jaziri, M.; Gerard, J.F.; Elleuch, B. Compatibilization of PE/PS and PE/PP blends. I. Effect of processing conditions and formulation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 90, 2475–2484. [Google Scholar]
- Deanin, R.D.; Manion, M.A. Handbook of Polyolefins, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- La Mantia, F.P. Recycling of heterogeneous plastics wastes. II—The role of modifier agents. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1993, 42, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parameswaranpillai, J.; Joseph, G.; Jose, S.; Hameed, N. Phase morphology, thermomechanical, and crystallization behavior of uncompatibilized and PP-g-MAH compatibilized polypropylene/polystyrene blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettini, S.H.P.; de Mello, L.C.; Munoz, P.A.R.; Ruvolo-Filho, A. Grafting of maleic anhydride onto polypropylene, in the presence and absence of styrene, for compatibilization of poly(ethylene terephthalate)/(ethylene-propylene) blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.Y.; Zhao, S.F.; Cheng, L.; Li, B.M. Synthesis and reaction kinetics model of suspension phase grafting polypropylene with dual monomers. Polym. Bull. 2010, 64, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xie, X.M.; Guo, B.H. Study on styrene-assisted melt free-radical grafting of maleic anhydride onto polypropylene. Polymer 2001, 42, 3419–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Guo, Z.F.; Zhang, L.M.; Pan, L.S.; Tian, Z.; Pang, S.J.; Xu, N.; Lin, Q. Mechanochemistry: A novel approach to graft polypropylene with dual monomers (PP-g-(MAH-co-St)). Polym. Bull. 2015, 72, 1949–1960. [Google Scholar]
- Metals, A.S.O. Characterization and Failure Analysis of Plastics; ASM International: Novelty, OH, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Colombani, J.; Labed, V.; Joussot-Dubien, C.; Perichaud, A.; Raffi, J.; Kister, J.; Rossi, C. High doses gamma radiolysis of PVC: Mechanisms of degradation. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2007, 265, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, G. Environmental stability of polymers. In Polymers and the Environment; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 1999; pp. 38–67. [Google Scholar]
- Choppin, G.; Liljenzin, J.-O.; Rydberg, J. Radiochemistry and Nuclear Chemistry, 3rd ed.; Butterwort-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Swallow, A.J. Radiation Chemistry of Organic Compounds; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1960; p. 380. [Google Scholar]
- Santana, R.M.C.; Manrich, S. Studies on morphology and mechanical properties of PP/HIPS blends from postconsumer plastic waste. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 87, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tall, S.; Karlsson, S.; Albertsson, A.C. Improvements in the properties of mechanically recycled thermoplastics. Polym. Polym. Compos. 1998, 6, 261–267. [Google Scholar]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tostar, S.; Stenvall, E.; Foreman, M.R.S.J.; Boldizar, A. The Influence of Compatibilizer Addition and Gamma Irradiation on Mechanical and Rheological Properties of a Recycled WEEE Plastics Blend. Recycling 2016, 1, 101-110. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling1010101
Tostar S, Stenvall E, Foreman MRSJ, Boldizar A. The Influence of Compatibilizer Addition and Gamma Irradiation on Mechanical and Rheological Properties of a Recycled WEEE Plastics Blend. Recycling. 2016; 1(1):101-110. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling1010101
Chicago/Turabian StyleTostar, Sandra, Erik Stenvall, Mark R. St J. Foreman, and Antal Boldizar. 2016. "The Influence of Compatibilizer Addition and Gamma Irradiation on Mechanical and Rheological Properties of a Recycled WEEE Plastics Blend" Recycling 1, no. 1: 101-110. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling1010101
APA StyleTostar, S., Stenvall, E., Foreman, M. R. S. J., & Boldizar, A. (2016). The Influence of Compatibilizer Addition and Gamma Irradiation on Mechanical and Rheological Properties of a Recycled WEEE Plastics Blend. Recycling, 1(1), 101-110. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling1010101





