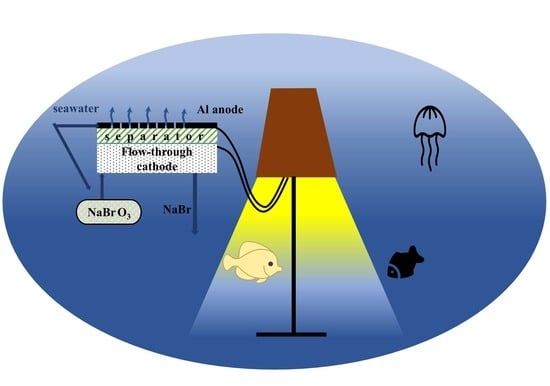
Aluminum/Bromate and Aluminum/Iodate Mechanically Rechargeable Batteries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussions
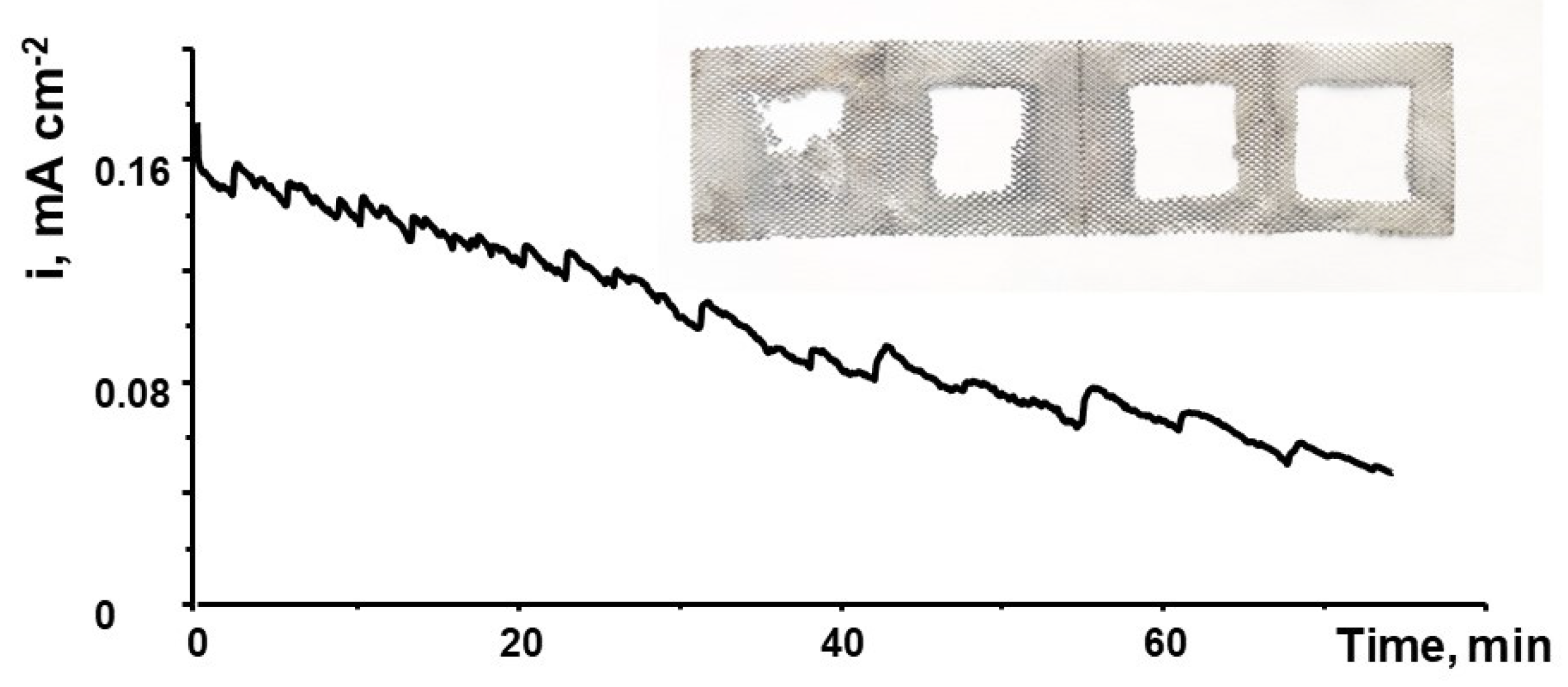
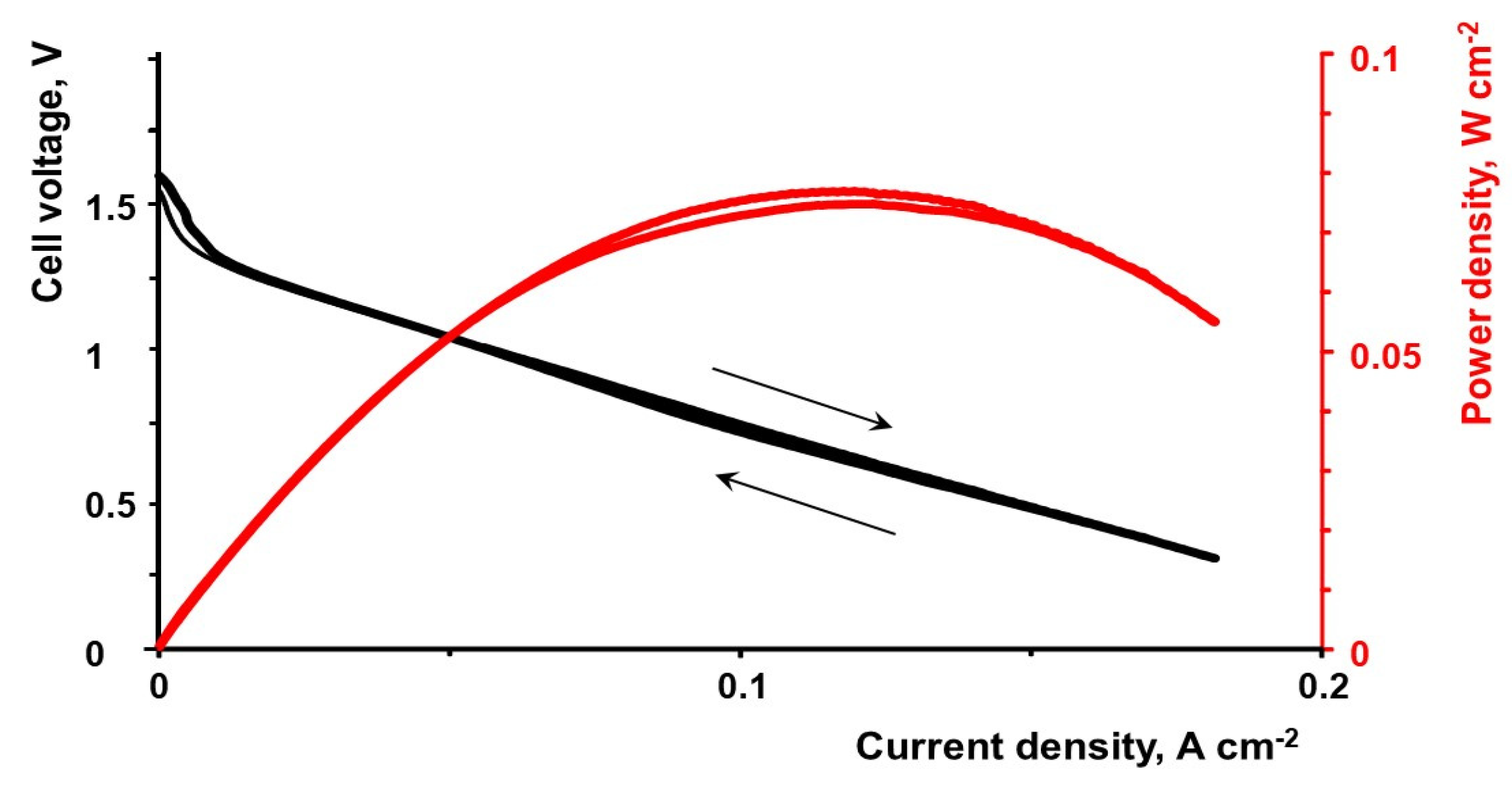
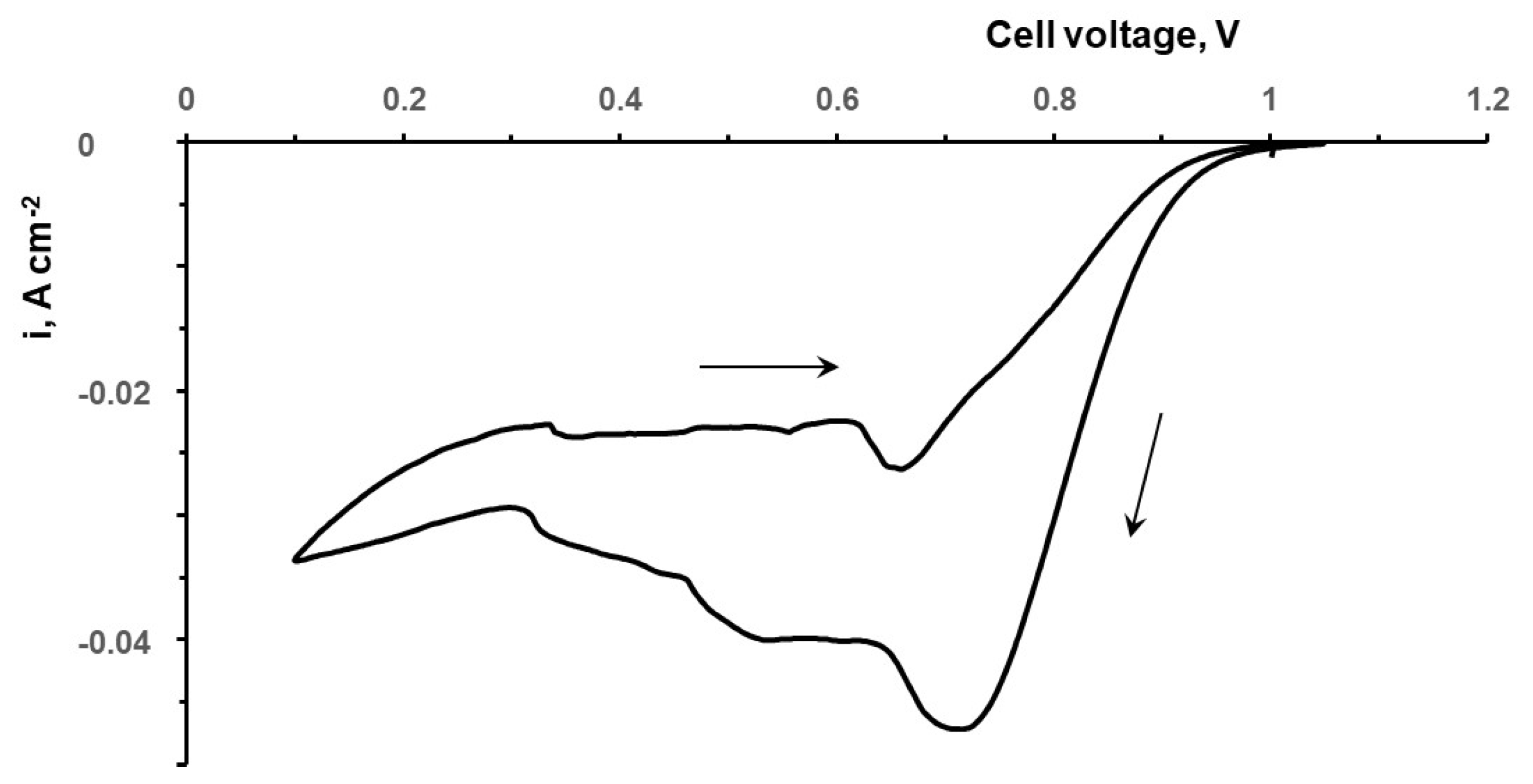
3.1. Flow Cell Performance
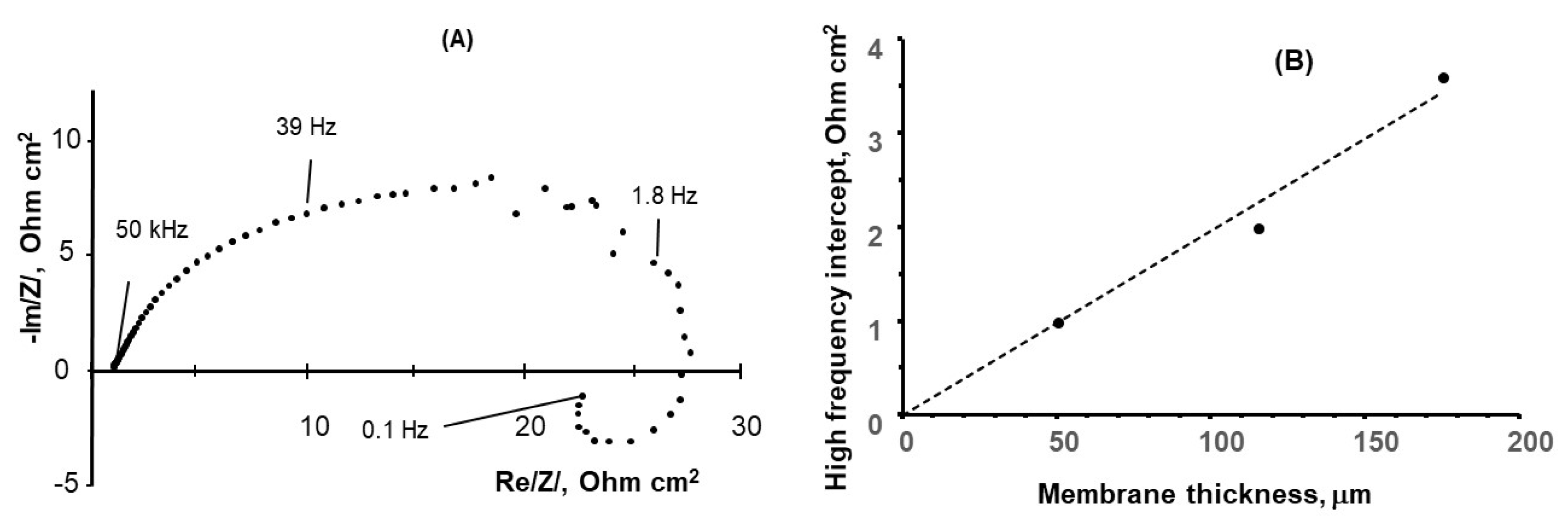
3.2. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Measurements
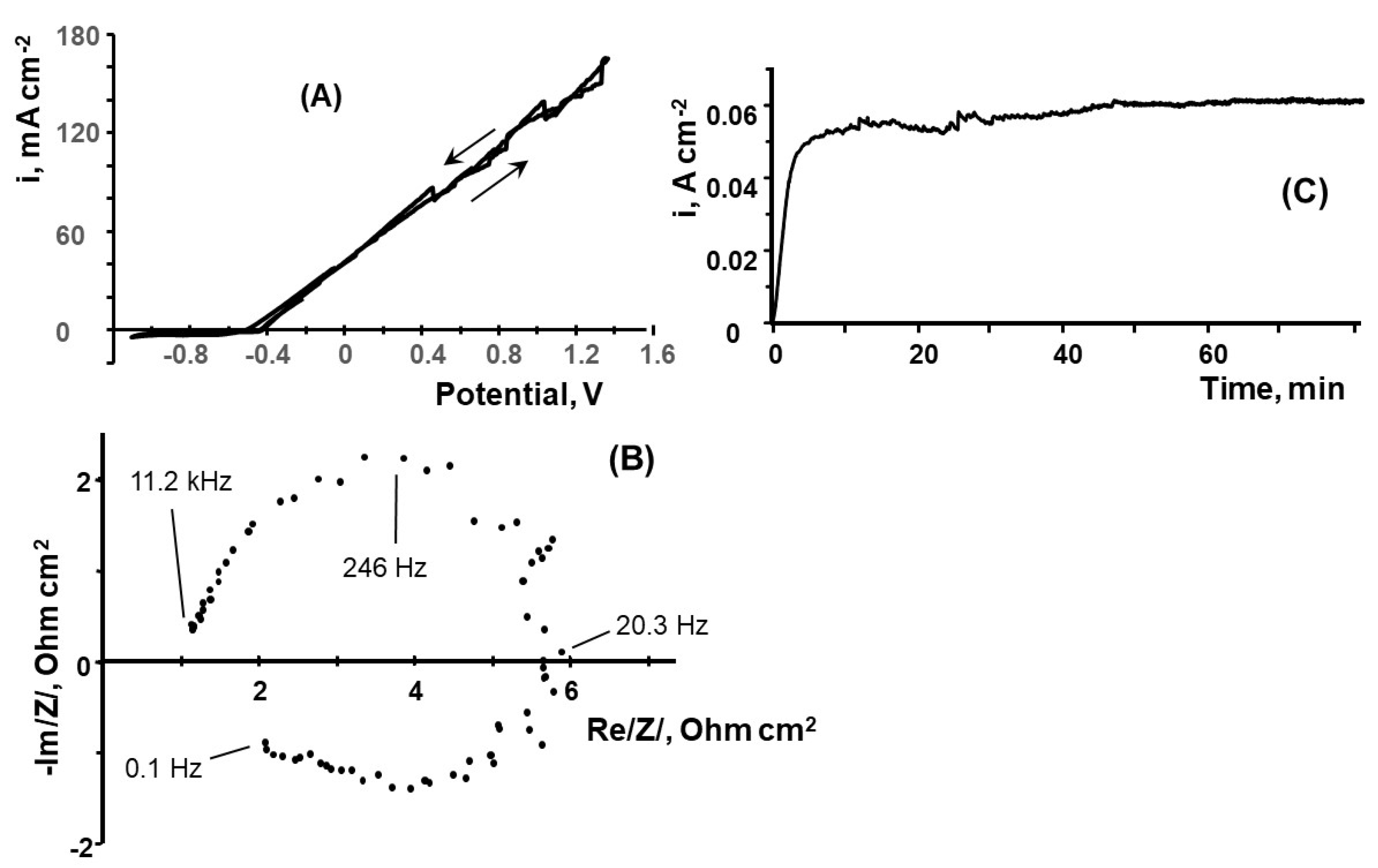
3.3. Electrodissolution of Al in 0.5 M NaCl
3.4. Reduction of the Iodate on a Porous Carbonaceous Electrode
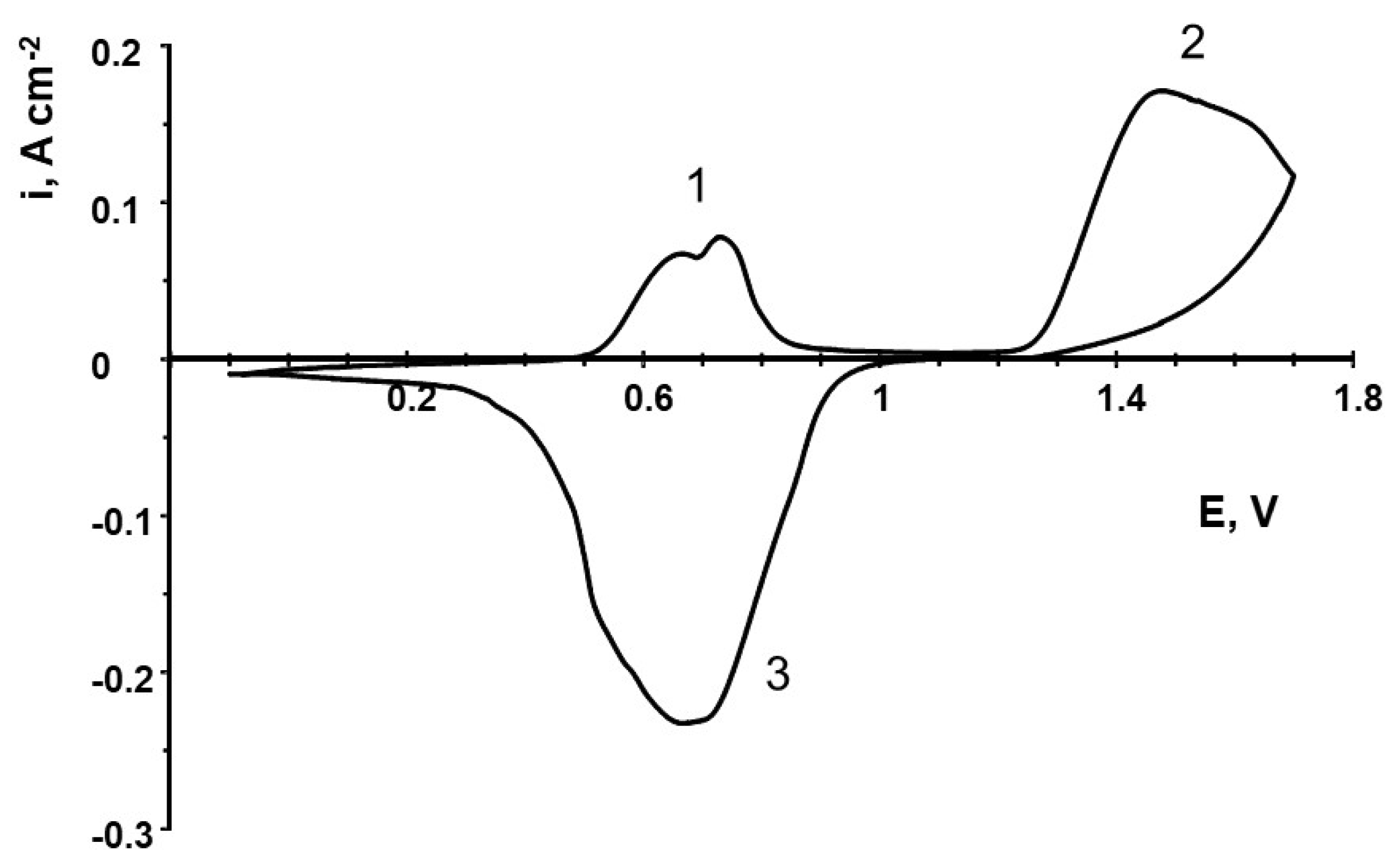
3.5. Iodide–Iodine–Iodate Transformations on the Carbonaceous Electrode in the Acidic Electrolytes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pantoja, W.; Perez-Taborda, J.A.; Alba Avila, A. Tug-of-War in the Selection of Materials for Battery Technologies. Batteries 2022, 8, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Yuan, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Huang, J.; Yu, D.; Liu, Y.; Titirici, M.; Chueh, Y.; et al. A review of rechargeable batteries for portable electronic devices. InfoMat 2019, 1, 6–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsukov, Y.; Qian, J. Battery Power Management for Portable Devices; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2013; 241p. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.A.; Wang, X.; Wen, C.J. High Energy Density Metal-Air Batteries: A Review. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 160, A1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Tan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Feng, J.; Qian, Y. Towards better Mg metal anodes in rechargeable Mg batteries: Challenges, strategies, and perspectives. Energy Storage Mater. 2022, 52, 299–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwater, T.B.; Dobley, A. Metal/air batteries. In Linden’s Handbook of Batteries, 4th ed.; Reddy, T.B., Linden, D., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2011; Chapter 33. [Google Scholar]
- Arai, H. Metal Storage/metal air (Zn, Fe, Al, Mg). In Encyclopedia of Electrochemical Power Sources; Moseley, P.T., Garche, J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 337–344. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Li, B.-Q.; Zhao, C.-X.; Zhang, Q. Seawater electrolyte-based metal–air batteries: From strategies to applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 3253–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Pan, Z.; Wang, E.; An, L.; Sun, G. Aqueous metal-air batteries: Fundamentals and applications. Energy Storage Mater. 2020, 27, 478–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chang, Z.-W.; Zhang, X.-B. Recent progress on the development of metal-air batteries. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2017, 1, 1700036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olabi, A.G.; Sayed, E.T.; Wilberforce, T.; Jamal, A.; Alami, A.H.; Elsaid, K.; Rahman, S.M.A.; Shah, S.K.; Abdelkareem, M.A. Metal-air batteries—A review. Energies 2021, 14, 7373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Li, X.; White, J.; Zhong, C.; Deng, Y.; Hu, W.; Ma, T. Metal–air batteries: From static to flow system. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1801396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, L. Metallic negatives. In Handbook of Battery Materials, 2nd ed.; Daniel, C., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2008; Chapter 8; Volume 2, pp. 219–238. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Bjerrum, N.J. Aluminum as anode for energy storage and conversion: A review. J. Power Sources 2002, 110, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, G.S. Thermodynamics of Electrolytic Corrosion. In Encyclopedia of Electrochemistry. Corrosion and Oxide Films; Bard, A.J., Stratmann, M., Frankel, G.S., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2003; Volume 4, pp. 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargel, C. Corrosion of Aluminium, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; 858p. [Google Scholar]
- Schütze, M.; Wieser, D.; Bender, R. (Eds.) Corrosion Resistance of Aluminium and Aluminium Alloys; Wiley-VCH: Frankfurt, Germany, 2010; 636p. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, J.R. (Ed.) Corrosion of Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys; ASM International: Almere, The Netherlands, 1999; 313p. [Google Scholar]
- Sivashanmugam, A.; Prasad, S.R.; Thirunakaran, R.; Gopukumar, S. Electrochemical Performance of Al/MnO2 Dry Cells: An Alternative to Lechlanche Dry Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2008, 155, A725–A728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaromb, S. The Use and Behavior of Aluminum Anodes in Alkaline Primary Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1962, 109, 1125–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasvold, Ø.; Johansen, K.H.; Molestad, O.; Forseth, S.; Størkersen, N. The alkaline aluminium/hydrogen peroxide power source in the Hugin II unmanned underwater vehicle. J. Power Sources 1999, 80, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasvold, Ø.; Størkersen, N.J.; Forseth, S.; Lian, T. Power sources for autonomous underwater vehicles. J. Power Sources 2006, 162, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Knickle, H. Design and analysis of aluminum/air battery system for electric vehicles. J. Power Sources 2002, 112, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zuo, C.; Liu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Song, Y. All-solid-state Al–air batteries with polymer alkaline gel electrolyte. J. Power Sources 2014, 251, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Li, W.; Adair, K.R.; Li, J.; Sun, X. A comprehensive review on recent progress in aluminum-air batteries. Green Energy Environ. 2017, 2, 246–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, B.M.L.; Hoge, W.H.; Zakrzewski, J.; Shah, S.; Hamlen, R.P.; Halliop, W. Aluminum-sea water battery for undersea vehicle. In Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Unmanned Untethered Submersible Technology, Durham, NH, USA, 12–14 June 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeriote, E.M.L.; Gallop, L.D. High pressure effects on the EMF of seawater battery electrodes in chloride electrolyte. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1974, 121, 1245–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heise, G.W.; Schumacher, E.A.; Cahoon, N.C. A heavy duty chlorine-depolarized cell. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1948, 94, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modestov, A.D.; Andreev, V.N.; Antipov, A.E.; Petrov, M.M. Novel aqueous zinc–halogenate flow batteries as an offspring of zinc–air fuel cells for use in oxygen-deficient environment. Energy Technol. 2021, 9, 2100233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modestov, A.D.; Konev, D.V.; Tripachev, O.V.; Antipov, A.E.; Tolmachev, Y.V.; Vorotyntsev, M.A. A hydrogen–bromate flow battery for air-deficient environments. Energy Technol. 2018, 6, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modestov, A.D.; Konev, D.V.; Antipov, A.E.; Vorotyntsev, M.A. Hydrogen-bromate flow battery: Can one reach both high bromate utilization and specific power? J. Solid. State Electrochem. 2019, 23, 3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modestov, A.; Kartashova, N.; Pichugov, R.; Petrov, M.; Antipov, A.; Abunaeva, L. Bromine crossover in operando analysis of proton exchange membranes in hydrogen−bromate flow batteries. Membranes 2022, 12, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mussini, T.; Longhi, P. Bromine. In Standard Potentials in Aqueous Solutions; Bard, A.J., Parsons, R., Jordan, J., Eds.; IUPAC: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 78–84. [Google Scholar]
- Modestov, A.D.; Konev, D.V.; Antipov, A.E.; Petrov, M.M.; Pichugov, R.D.; Vorotyntsev, M.A. Bromate electroreduction from sulfuric acid solution at rotating disk electrode: Experimental study. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 259, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desideri, P.G. Reduction of iodate in sulphuric medium. I. Reduction mechanism. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1965, 9, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badea, G.E. Autocatalytic reduction of iodate at the platinum electrode in 0.5 M H2SO4 solutions. Rev. Roum. Chim. 2007, 52, 491–498. [Google Scholar]
- Vanleugenhagne, C.; Valensi, V.; Pourbaix, M. Iodine. In Atlas of Electrochemical Equilibria in Aqueous Solutions, 2nd ed.; Pourbaix, M., Ed.; NACE International and CEBELCOR: Houston, TX, USA, 1974; pp. 614–626. [Google Scholar]
- Xhanari, K.; Finšgar, M. Organic corrosion inhibitors for aluminum and its alloys in chloride and alkaline solutions: A review. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 4646–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusoglu, A.; Weber, A.Z. New insights into perfluorinated sulfonic-acid ionomers. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 987–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongsirikarn, K.; Goodwin, J.G., Jr.; Greenway, S.; Creager, S. Effect of cations (Na+, Ca2+, Fe3+) on the conductivity of a Nafion membrane. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 7213–7220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, A. (Ed.) Handbook of Membrane Reactors: Reactor Types and Industrial Applications; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Sawston, UK, 2013; Volume 2, p. 407. [Google Scholar]
- Metikoš-Huković, M.; Babić, R.; Grubač, Z.; Brinć, S. Impedance spectroscopic study of aluminium and Al-alloys in acid solution: Inhibitory action of nitrogen containing compounds. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1994, 24, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wit, J.H.W.; Lenderink, H.J.W. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy as a tool to obtain mechanistic information on the passive behaviour of aluminium. Electrochim. Acta 1996, 41, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, C.M.A. The application of electrochemical impedance techniques to aluminium corrosion in acidic chloride solution. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1990, 20, 1000–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treacy, G.M.; Rudd, A.L.; Breslin, C.B. Electrochemical behaviour of aluminium in the presence of EDTA-containing chloride solutions. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2000, 30, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Myung, N.; Sumodjo, P.T.A.; Nobe, K. A comparative electrodissolution and localized corrosion study of 2024Al in halide media. Electrochim. Acta 1999, 44, 2751–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, F.J.; Cheek, G.T.; O’Grady, W.E.; Natishan, P.M. Impedance studies of the passive film on aluminium. Corros. Sci. 2005, 47, 3187–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolics, A.; Besing, A.S.; Baradlai, P.; Haasch, R.; Wieckowski, A. Effect of pH on Thickness and Ion Content of the Oxide Film on Aluminum in NaCl Media. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2001, 148, B251–B259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.X. Hydrogen oxidation and evolution on platinum in acids. In Encyclopedia of Applied Electrochemistry; Kreysa, G., Ota, K.-I., Savinell, R.F., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Modestov, A.; Andreev, V.; Antipov, A. Aluminum/Bromate and Aluminum/Iodate Mechanically Rechargeable Batteries. Batteries 2022, 8, 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries8120270
Modestov A, Andreev V, Antipov A. Aluminum/Bromate and Aluminum/Iodate Mechanically Rechargeable Batteries. Batteries. 2022; 8(12):270. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries8120270
Chicago/Turabian StyleModestov, Alexander, Vladimir Andreev, and Anatoliy Antipov. 2022. "Aluminum/Bromate and Aluminum/Iodate Mechanically Rechargeable Batteries" Batteries 8, no. 12: 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries8120270
APA StyleModestov, A., Andreev, V., & Antipov, A. (2022). Aluminum/Bromate and Aluminum/Iodate Mechanically Rechargeable Batteries. Batteries, 8(12), 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries8120270