Composite Cathodes Based on Lithium-Iron Phosphate and N-Doped Carbon Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
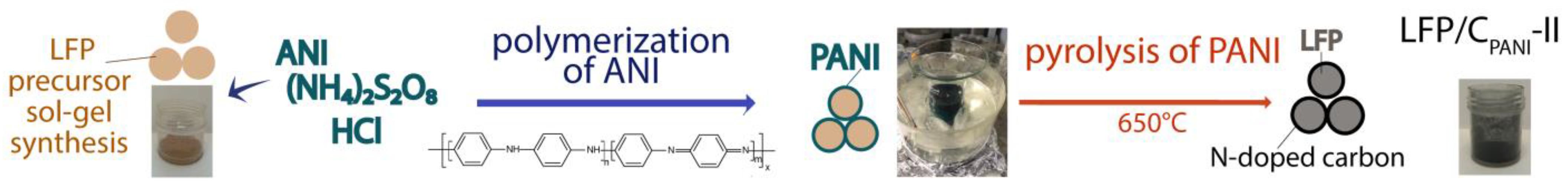
2.1. Material Manufacturing
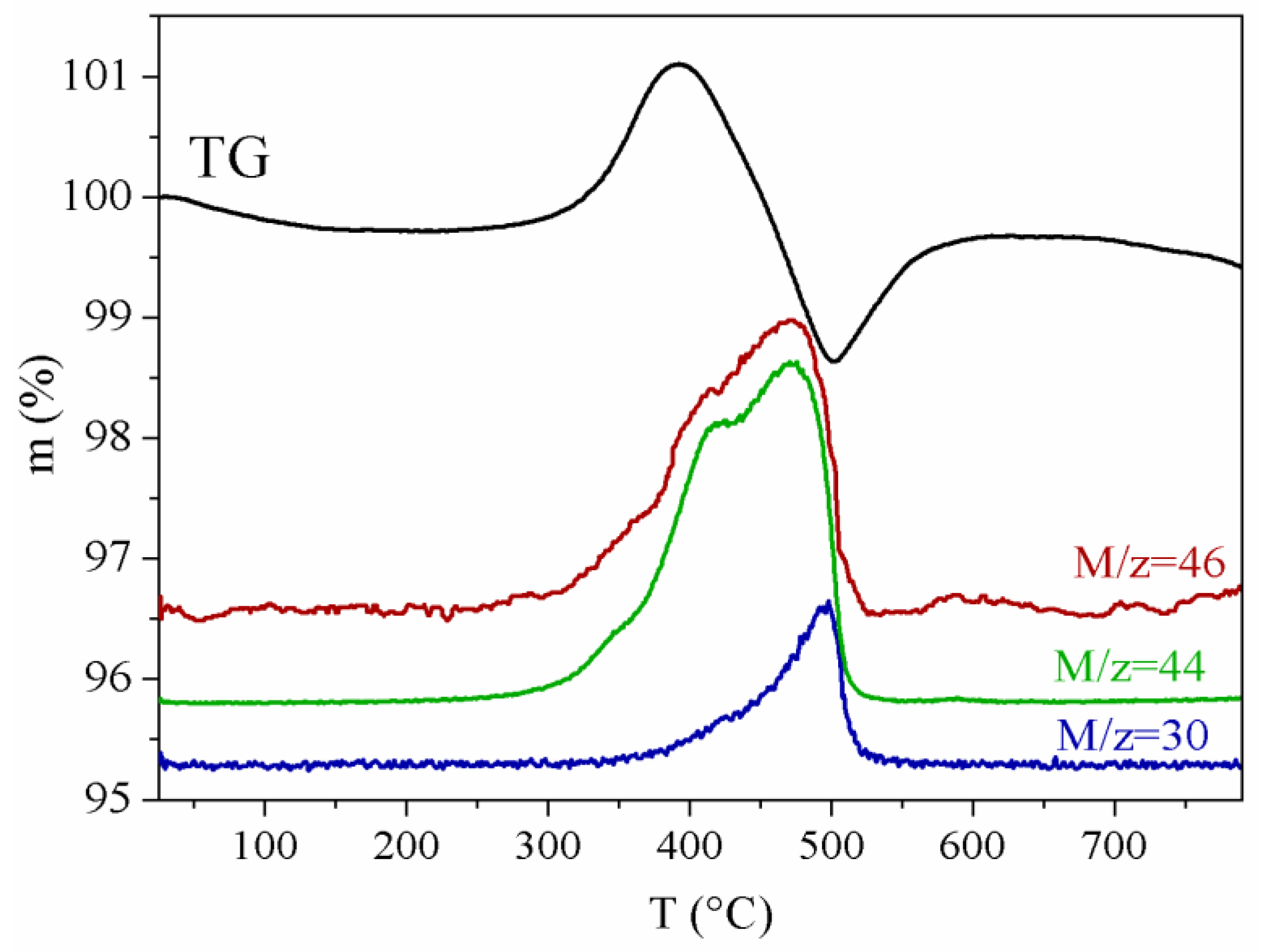
2.2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
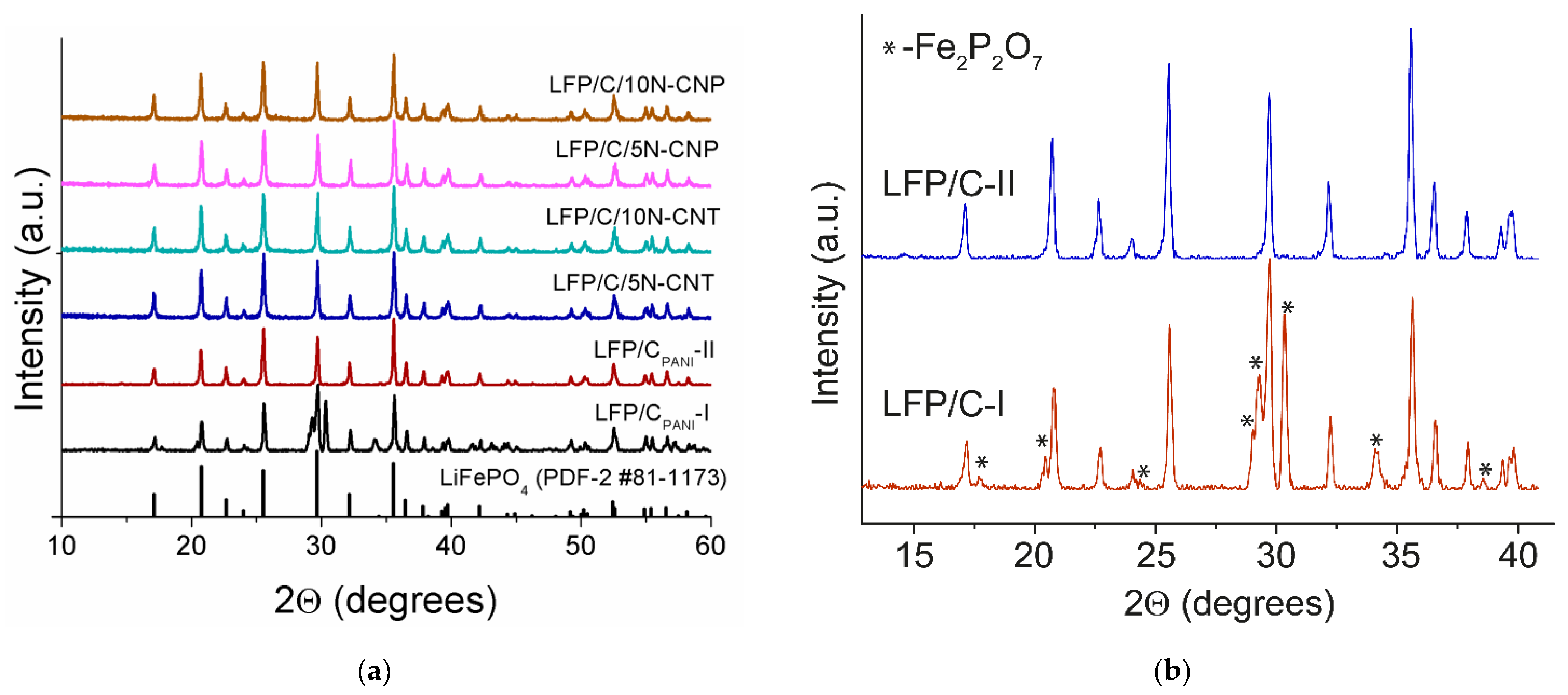
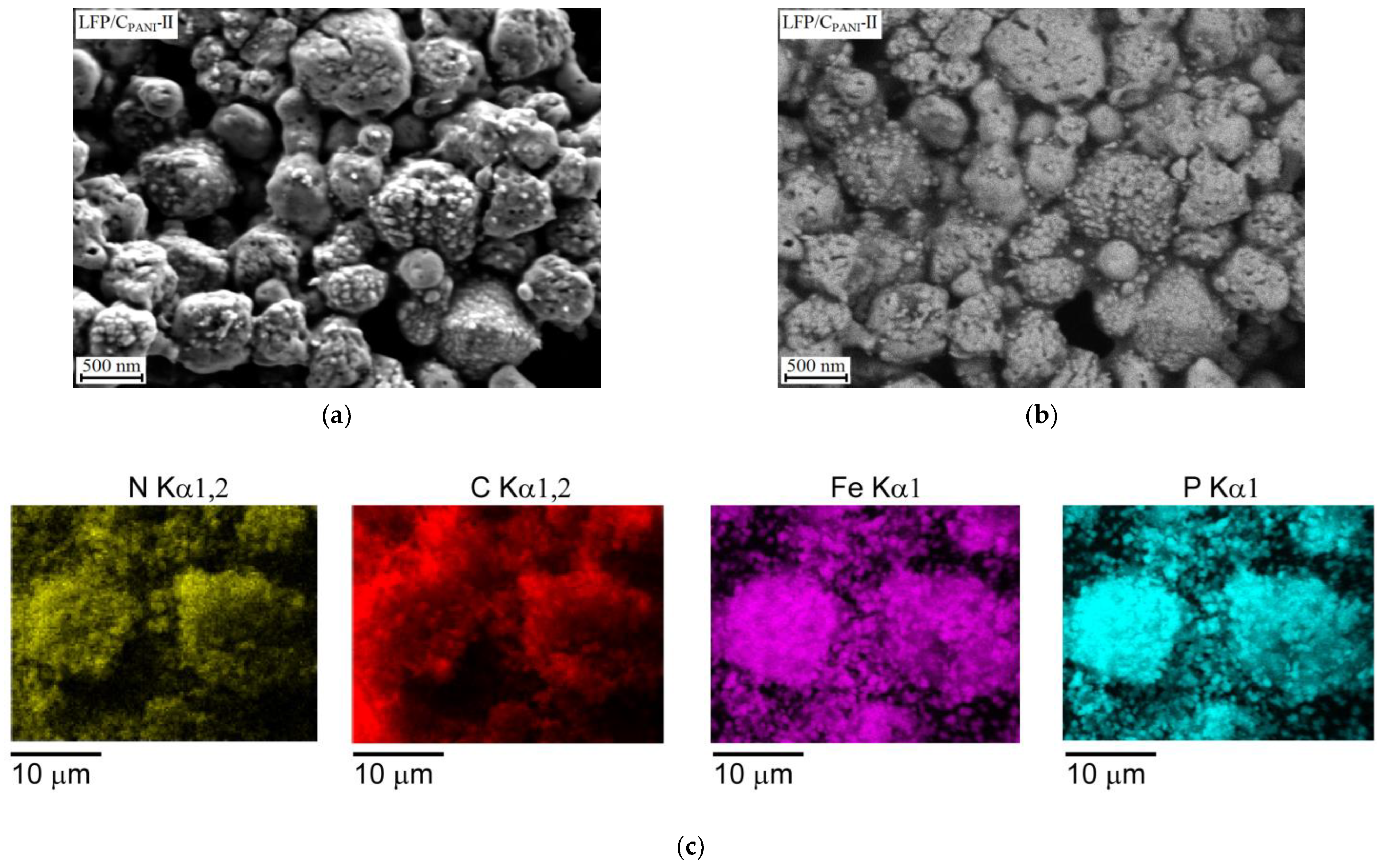
3.1. Composition and Morphology
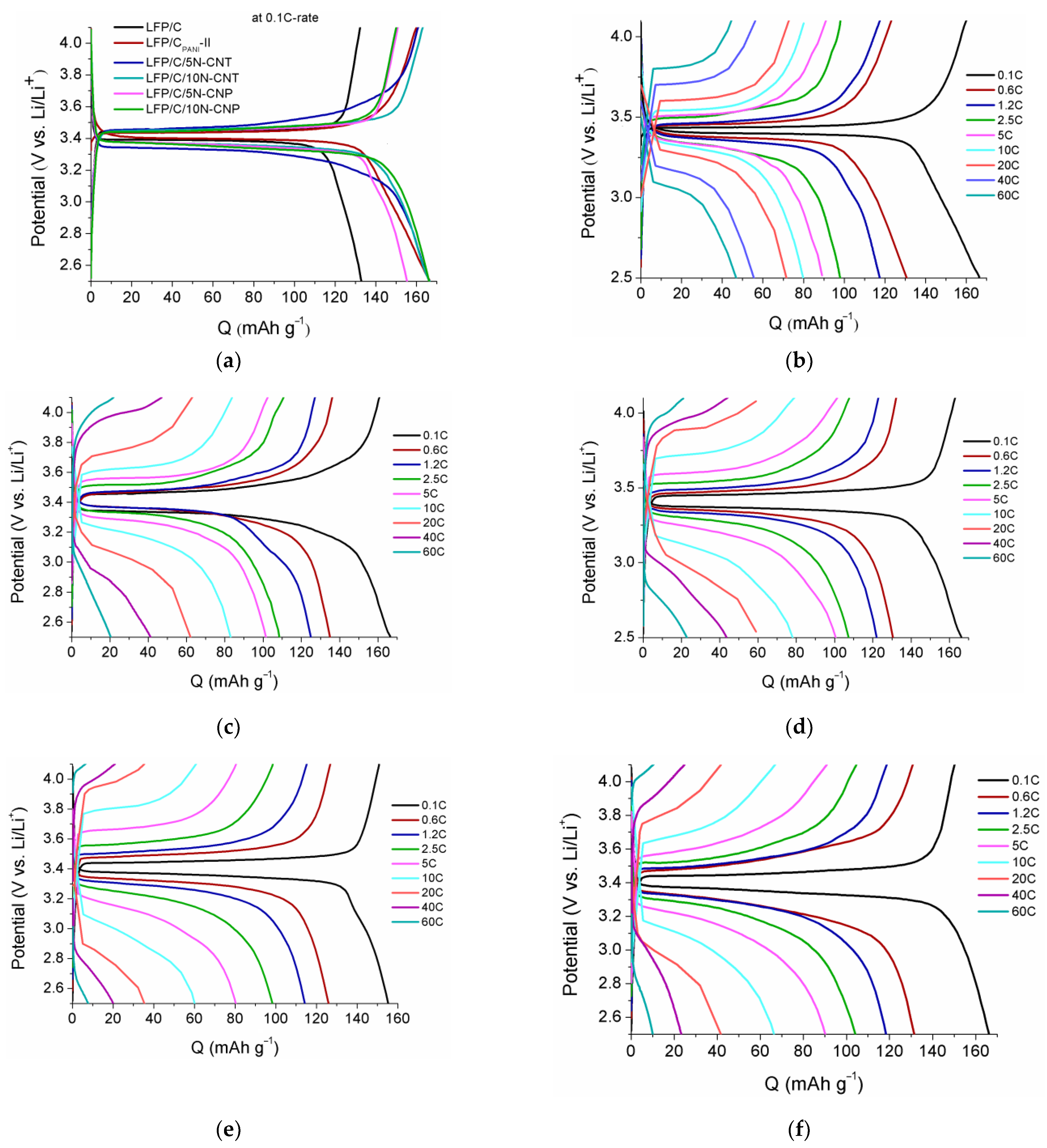
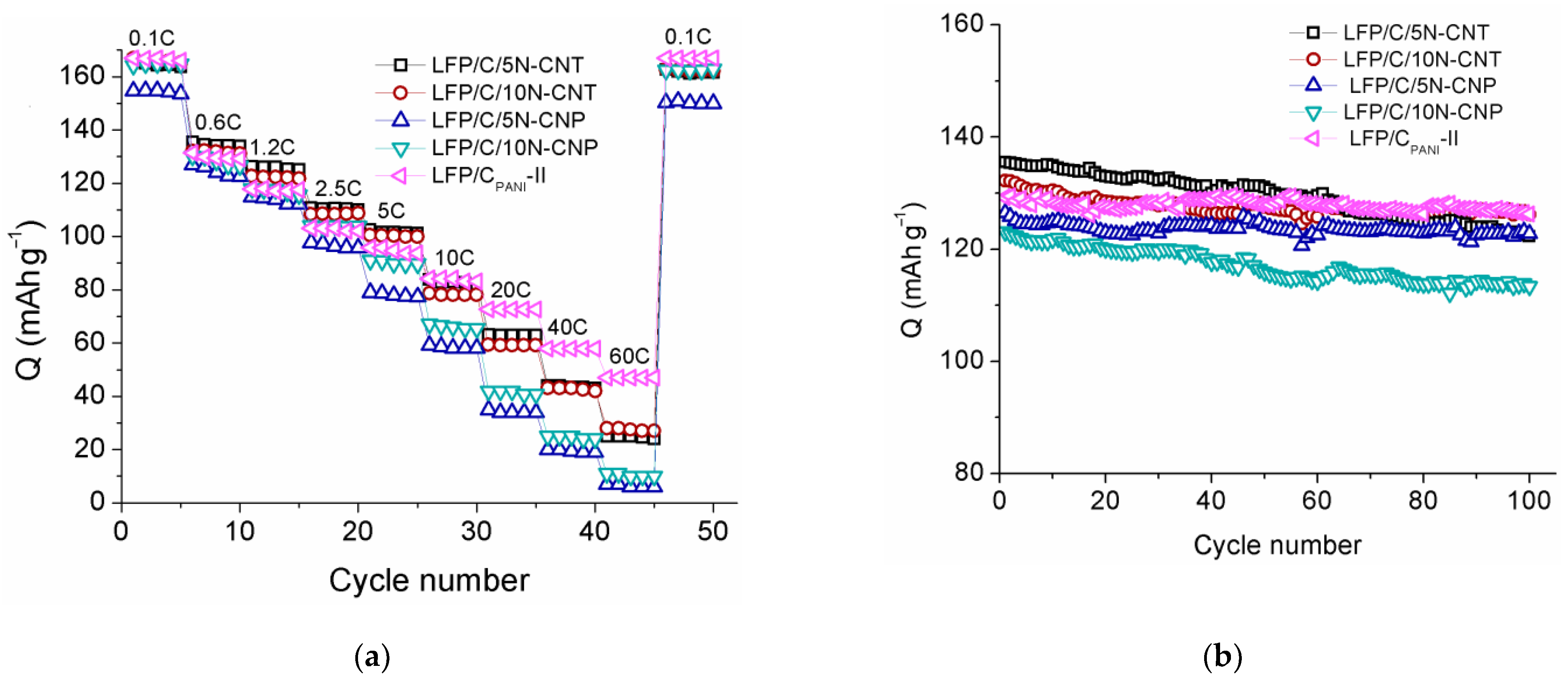
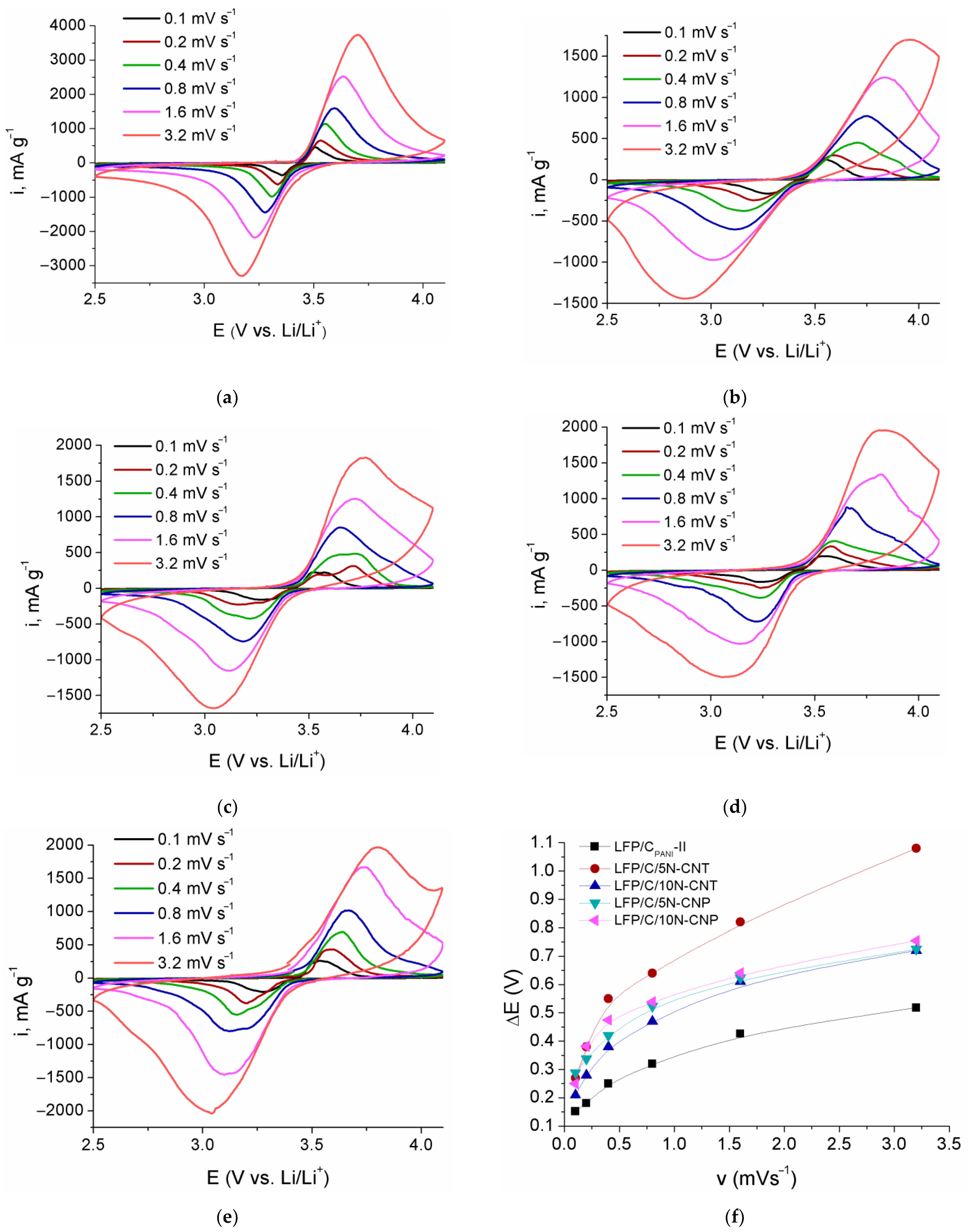
3.2. Electrochemical Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zaghib, K.; Guerfi, A.; Hovington, P.; Vijh, A.; Trudeau, M.; Mauger, A.; Goodenough, J.B.; Julien, C.M. Review and analysis of nanostructured olivine-based lithium recheargeable batteries: Status and trends. J. Power Sources 2013, 232, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, R.; Maier, J.; Balaya, P.; Chen, D.P.; Lin, C.T. Ionic and electronic transport in single crystalline LiFePO4 grown by optical floating zone technique. Solid State Ion. 2008, 179, 1683–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.L.; Zhao, X.X.; Hui, K.S.; Dinh, D.A.; Hui, K.N. Rechargeable batteries: Regulating electronic and ionic transports for high electrochemical performance. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7, 2101107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.B.; Xiong, X.Y.; Tan, L.; Yuan, B.; Hu, R.Z. Strategies for improving electrochemical reaction kinetics of cathode materials for subzero-temperature Li-ion batteries: A review. Energy Storage Mater. 2022, 44, 390–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftekhari, A. LiFePO4/C nanocomposites for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2017, 343, 395–411. [Google Scholar]
- Novikova, S.A.; Yaroslavtsev, A.B. Cathode materials based on olivine lithium iron phosphates for lithium-ion batteries. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2017, 49, 129–139. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, X.N.; Chen, W.H.; Jiang, Z.Q.; Jiang, Z.J. Porous carbon-coated LiFePO4 nanocrystals prepared by in situ plasma-assisted pyrolysis as superior cathode materials for lithium ion batteries. Ionics 2020, 26, 2715–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Raj, R.P.; Mohan, T.V.R.; Selvam, P. Electrochemical performance of nano-sized LiFePO4-embedded 3d-cubic ordered mesoporous carbon and nitrogenous carbon composites. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 30406–30414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Shinawi, H.; Cussen, E.J.; Corr, S.A. Morphology-directed synthesis of LiFePO4 and LiCoPO4 from nanostructured Li1+2xPO3+x. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 6946–6949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novikova, S.; Yaroslavtsev, S.; Rusakov, V.; Kulova, T.; Skundin, A.; Yaroslavtsev, A. LiFe1−xMIIxPO4/C (MII = Co, Ni, Mg) as cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 122, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozhzhin, O.A.; Sumanov, V.D.; Karakulina, O.M.; Abakumov, A.M.; Hadermann, J.; Baranov, A.N.; Stevenson, K.J.; Antipov, E.V. Switching between solid solution and two-phase regimes in the Li1-xFe1-yMnyPO4 cathode materials during lithium (de)insertion: Combined PITT, in situ XRPD and electron diffraction tomography study. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 191, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaroslavtsev, S.; Novikova, S.; Rusakov, V.; Vostrov, N.; Kulova, T.; Skundin, A.; Yaroslavtsev, A. LiFe1−xMgxPO4/C as cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Solid State Ion. 2018, 317, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Q.F.; Duan, J.F.; Zhu, H.L. Understanding the impact of K-doping on the structure and performance of LiFePO4/C cathode materials. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.Q.; Lai, A.J.; Huang, D.Q.; Chu, Y.Q.; Hu, S.J.; Pan, Q.C.; Liu, Z.H.; Zheng, F.H.; Huang, Y.G.; Li, Q.Y. Y-F co-doping behavior of LiFePO4/C nanocomposites for high-rate lithium-ion batteries. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 5695–5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wei, R.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, K.; Liang, F.; Yao, Y.; Li, Y. B-Mg co-doping behavior of LiFePO4 cathode material: Balance of oxygen vacancy and enhancement of electrochemical performance. Ionics 2022, 28, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Goodenough, J.B. High-rate LiFePO4 lithium rechargeable battery promoted by electrochemically active polymers. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 7237–7241. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.Q.; Zhou, H.S. Enhancing the performances of Li-ion batteries by carbon-coating: Present and future. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 1201–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucinskis, G.; Bajars, G.; Kleperis, J. Graphene in lithium ion battery cathode materials: A review. J. Power Sources 2013, 240, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryzlov, D.; Novikova, S.; Kulova, T.; Skundin, A.; Yaroslavtsev, A. Behavior of LiFePO4/Cpvdf/Ag-based cathode materials obtained using polyvinylidene fluoride as the carbon source. Mater. Des. 2016, 104, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, X.F.; Zhou, Y.K.; Song, Y.J. Freeze-drying synthesis of three-dimensional porous LiFePO4 modified with well-dispersed nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes for high-performance lithium-ion batteries. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 400, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wu, L.; Wu, F.; Song, S.P.; Zhang, X.Q.; Fu, C.; Yuan, D.D.; Xiang, Y. Review-recent research progress in surface modification of LiFePO4 cathode materials. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, A2138–A2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenina, I.A.; Yaroslavtsev, A.B. Nanomaterials for lithium-ion batteries and hydrogen energy. Pure Appl. Chem. 2017, 89, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.P.; Zha, W.K.; Chen, D.C. Fabrication and electrochemical properties of 3d nano-network LiFePO4@multiwalled carbon nanotube composite using risedronic acid as the phosphorus source. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2019, 29, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwizerwa, J.P.; Liu, C.; Xu, K.; Zhao, N.; Chen, Z.; Shen, J. In-situ solution phase synthesis of LiFePO4@VSe2 composite as highly active cathode for li-ion batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 901, 163639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xiong, K.; Xu, H.; Zhu, B.F. Enhanced high-rate and low-temperature electrochemical properties of LiFePO4/polypyrrole cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2019, 14, 3408–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, N.; Haro, M.; Cintora-Juarez, D.; Perez-Vicente, C.; Tirado, J.L.; Ahmad, S.; Garcia-Belmonte, G. LiFePO4 particle conductive composite strategies for improving cathode rate capability. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 163, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozerova, V.V.; Stenina, I.A.; Kuz’mina, A.A.; Kulova, T.L.; Yaroslavtsev, A.B. Cathode materials based on lithium iron phosphate/PEDOT composites for lithium-ion batteries. Inorg. Mater. 2020, 56, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.Z.; Liu, Y.X.; Liu, P.; Wu, D.Q.; Zhuang, X.D.; Zhang, F.; Feng, X.L. Compact coupled graphene and porous polyaryltriazine-derived frameworks as high performance cathodes for lithium-ion batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 1812–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Lin, Y.; Zong, H.; Yang, H.; Wang, L.; Dai, Z. Three-dimensional architecture reduced graphene oxide- LiFePO4 composite: Preparation and excellent microwave absorption performance. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 2031–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Wen, L.; Guo, Z.-Q.; Piao, N.; Hu, G.-J.; Wu, M.-J.; Li, F. Application and prospects for using carbon materials to modify lithium iron phosphate materials used at low temperatures. New Carbon Mater. 2022, 37, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Liu, R.; Guo, H.; Tian, S.; Zhang, K.; Ren, X.; Wang, Y.; Liang, G. High-temperature solid-phase synthesis of lithium iron phosphate using polyethylene glycol grafted carbon nanotubes as the carbon source for rate-type lithium-ion batteries. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 907, 116049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.M.; Wang, Q.; Cao, Z.L.; Ren, S.J. Preparation and multifunctional applications of nitrogen-doped porous carbon materials. Acta Polym. Sin. 2020, 51, 1160–1168. [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa, K.; Tojo, T.; Muramatsu, H.; Elías, A.; Vega-Díaz, S.; Tristan Lopez, F.; Kim, J.; Hayashi, T.; Kim, Y.; Endo, M.; et al. Enhanced electrical conductivities of N-doped carbon nanotubes by controlled heat treatment. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 4359–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhou, H.; Meng, W.; Dai, L.; Wang, L. N-doped carbon coated LiTi2(PO4)3 as superior anode using PANi as carbon and nitrogen bi-sources for aqueous lithium ion battery. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 279, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avci, E.; Mazman, M.; Uzun, D.; Bicer, E.; Sener, T. High performance LiFePO4/CN cathode material promoted by polyaniline as carbon-nitrogen precursor. J. Power Sources 2013, 240, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, G.; Li, Z.C.; Sheng, W.J.; Zhang, Y.C.; Gu, J.J.; Zheng, X.S.; Cao, F.F. Improved electrochemical performance of LiFePO4@N-doped carbon nanocomposites using polybenzoxazine as nitrogen and carbon sources. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 26908–26915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaroslavtsev, A.B.; Stenina, I.A. Carbon coating of electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Surf. Innov. 2021, 9, 92–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Xi, F.; Wang, T.; He, W. The synthesis of LiFePO4/C with polyaniline as coated carbon source and sucrose as reducing carbon source. Ionics 2022, 28, 1559–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Z.X.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, F.Q.; Chen, J.T.; Cao, A.M.; Wan, L.J. Optimizing the carbon coating on LiFePO4 for improved battery performance. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 7795–7798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.-Y.; Gu, Y.-J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.-L.; Huo, Y.-l.; Wu, F.-Z.; Mai, Y.; Dai, X.-Y.; Deng, Y. Electrochemical performance of in situ LiFePO4 modified by N-doped graphene for Li-ion batteries. Ceramics Int. 2021, 47, 11332–11339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Jiang, L. Olivine LiFePO4 nanocrystals grown on nitrogen-doped graphene sheets as high-rate cathode for lithium-ion batteries. Solid State Ion. 2018, 325, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Raj, R.P.; Mohan, T.V.R.; Bhuvaneswari, S.; Varadaraju, U.V.; Selvam, P. Electrochemical performance of nano-LiFePO4 embedded ordered mesoporous nitrogenous carbon composite as cathode material for Li-ion battery applications. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 848, 113242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenina, I.; Minakova, P.; Kulova, T.; Yaroslavtsev, A. Electrochemical Properties of LiFePO4 Cathodes: The Effect of Carbon Additives. Batteries 2022, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, Z. In situ FTIR-attenuated total reflection spectroscopic investigations on the base-acid transitions of polyaniline-base-acid transition in the emeraldine form of polyaniline. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1996, 92, 3063–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenina, I.A.; Il'ina, A.A.; Pinus, I.Y.; Sergeev, V.G.; Yaroslavtsev, A.B. Cation mobility in systems based on high-molecular-weight sulfonic acids and polyaniline. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2008, 57, 2261–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svitan'ko, A.; Scopets, V.; Novikova, S.; Yaroslavtsev, A. The effect of composite formation with oxides on the ion conductivity of NASICON-type LiTi2(PO4)3 and olivine-type LiFePO4. Solid State Ion. 2015, 271, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, J.D.; Doeff, M.M.; Marcinek, M.; Kostecki, R. Factors influencing the quality of carbon coatings on LiFePO4. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 154, A389–A395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenina, I.A.; Sobolev, A.N.; Kuz’mina, A.A.; Kulova, T.L.; Skundin, A.M.; Tabachkova, N.Y.; Yaroslavtsev, A.B. Electrochemical properties of Li4Ti5O12/C and Li4Ti5O12/C/Ag nanomaterials. Inorg. Mater. 2017, 53, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doeff, M.M.; Hu, Y.Q.; McLarnon, F.; Kostecki, R. Effect of surface carbon structure on the electrochemical performance of LiFePO4. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2003, 6, A207–A209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.T.; Zhang, H.Y.; Chen, Y.M.; Qin, G.; Lei, X.L.; Liu, L.Y. Graphene-carbon nanotubes-modified LiFePO4 cathode materials for high-performance lithium-ion batteries. Mater. Sci. Forum 2018, 913, 818–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Deng, Q.; Fang, B.; Li, Y.; Deng, L.; Yang, B.; Ren, X.; Zhang, P. Carbon-coated LiFePO4 synthesized by a simple solvothermal method. CrystEngComm 2016, 18, 7537–7543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Wang, D.; Liu, J.; Liang, G.; Gauthier, M.; Li, Y.; Geng, D.; Li, R.; et al. Hierarchically porous LiFePO4/nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes composite as a cathode for lithium ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 7537–7543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Feng, Z.; Huang, J.; Deng, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Wen, Z. Graphene-decorated carbon-coated LiFePO4 nanospheres as a high-performance cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. Carbon 2018, 127, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | Crystallite Size, nm | Content, wt.% | Electronic Conductivity, S/cm | Specific Surface Area, m2/g | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | N | ||||
| LFP/C | 75 | 4.7 | - | 4.6 × 10–7 | 35 |
| LFP/CPANI-II (molar ratio ANI: LFP = 1) | 44 | 5.0 | 0.5 | 4.0 × 10–5 | 103 |
| LFP/C/5N-CNT | 61 | 9.8 | 0.2 | 8.6 × 10–3 | 48 |
| LFP/C/10N-CNT | 57 | 14.3 | 0.4 | 1.8 × 10–2 | 57 |
| LFP/C/5N-CNP | 62 | 9.3 | 1.1 | 1.3 × 10–5 | 49 |
| LFP/C/10N-CNP | 54 | 13.1 | 1.8 | 4.1 × 10–5 | 60 |
| Cathode Composition | LFP Synthesis Method | Carbon Source | LFP, wt.% | Capacity at C-Rate, mAh g−1 | Ref. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 C | 1 C | 5 C | 10 C | 20 C | ≥30 C | |||||
| LFP/C LFP/C/N-CNT | sol–gel | PANI N-doped CNTs, sucrose | 95 91 | 167 166 | 114 126 | 96 102 | 84 84 | 73 63 | 47 25 (56 C) | this work |
| LFP/C | sol–gel | Sucrose | 95 | 136 | 105 | 65 | - | - | - | [10] |
| LFP/C | solvothermal | Glucose | 86 | 147 | 111 | 73 | - | - | - | [51] |
| LFP/C | solid state reaction | PANI-Cl | 82.6 | 163 | 148 | - | 100 | - | - | [35] |
| LFP/C | carbothermal reduction | PANI, sucrose | - | 164 | 140 | 50 | 5 | - | - | [38] |
| LFP/N-CNT | sol–gel | N-doped CNTs | 89 | 138 | 110 | 68 | 48 | - | - | [52] |
| LFP/N-CNT | freeze-drying | N-doped CNTs | 88.5 | 158 | 143 | 103 | 71 | - | - | [20] |
| LFP/G/CNT | hydrothermal | Graphene, CNT | 95 | 168 | 155 | 133 | 120 | 113 | 103 (40 C) | [50] |
| LFP/C/G | high-energy ball milling/ solid state reaction | Glucose, graphene | 97 | 164 | 147 | 127 | 112 | 81 | - | [53] |
| LFP/C/NG | hydrothermal | N-doped graphene, glucose | 92 | 156 | 129 | 105 | 88 | - | - | [40] |
| LFP/NG | hydrothermal | N-doped graphene | 95 | 163 | 157 | 136 | 114 | - | - | [41] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stenina, I.; Safikanov, D.; Minakova, P.; Novikova, S.; Kulova, T.; Yaroslavtsev, A. Composite Cathodes Based on Lithium-Iron Phosphate and N-Doped Carbon Materials. Batteries 2022, 8, 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries8120256
Stenina I, Safikanov D, Minakova P, Novikova S, Kulova T, Yaroslavtsev A. Composite Cathodes Based on Lithium-Iron Phosphate and N-Doped Carbon Materials. Batteries. 2022; 8(12):256. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries8120256
Chicago/Turabian StyleStenina, Irina, Danis Safikanov, Polina Minakova, Svetlana Novikova, Tatiana Kulova, and Andrey Yaroslavtsev. 2022. "Composite Cathodes Based on Lithium-Iron Phosphate and N-Doped Carbon Materials" Batteries 8, no. 12: 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries8120256
APA StyleStenina, I., Safikanov, D., Minakova, P., Novikova, S., Kulova, T., & Yaroslavtsev, A. (2022). Composite Cathodes Based on Lithium-Iron Phosphate and N-Doped Carbon Materials. Batteries, 8(12), 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries8120256









