Correlation of Mechanical and Electrical Behavior of Polyethylene Oxide-Based Solid Electrolytes for All-Solid State Lithium-Ion Batteries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
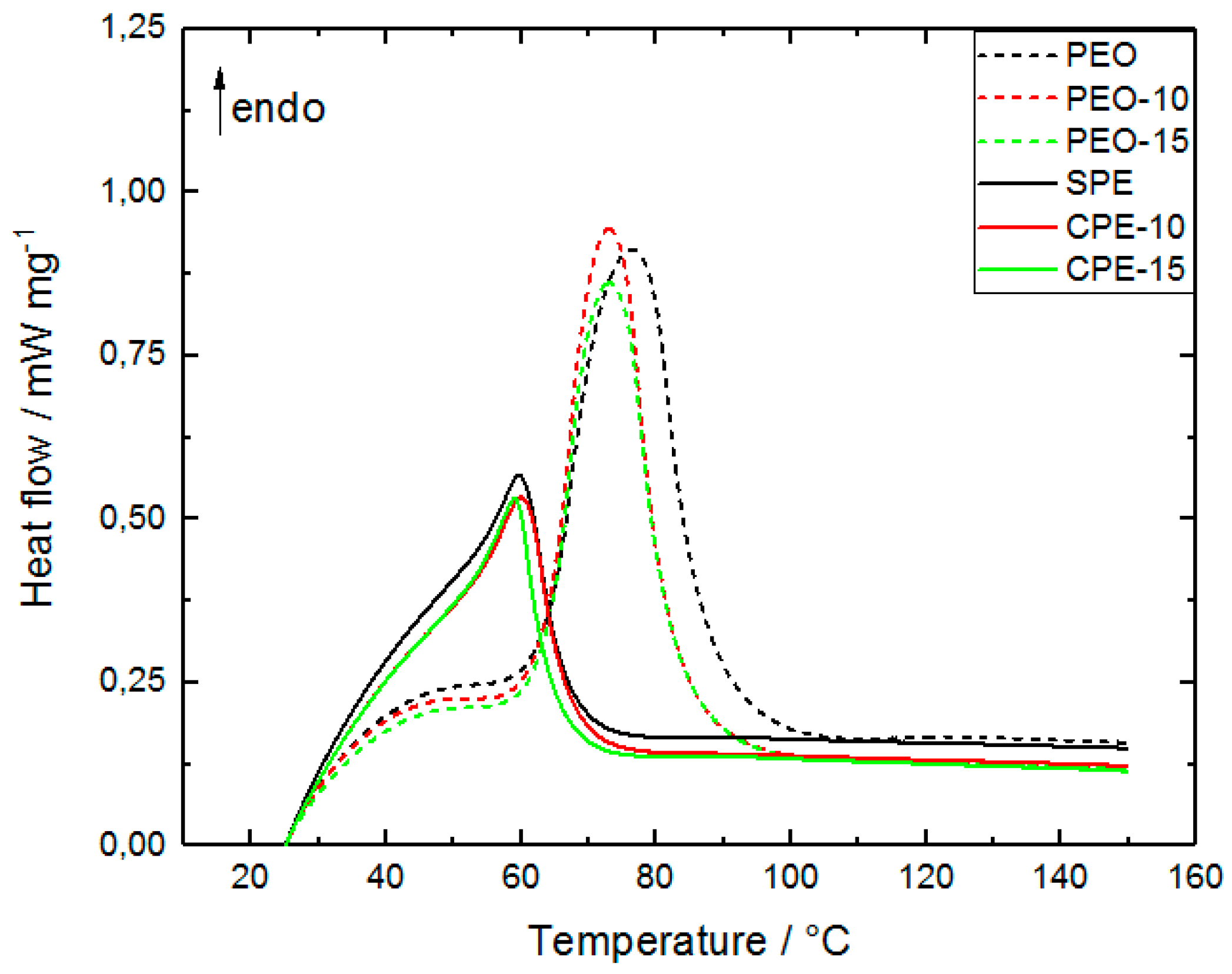
2.1. Influence of Li Salt and Alumina on PEO Thermal Properties
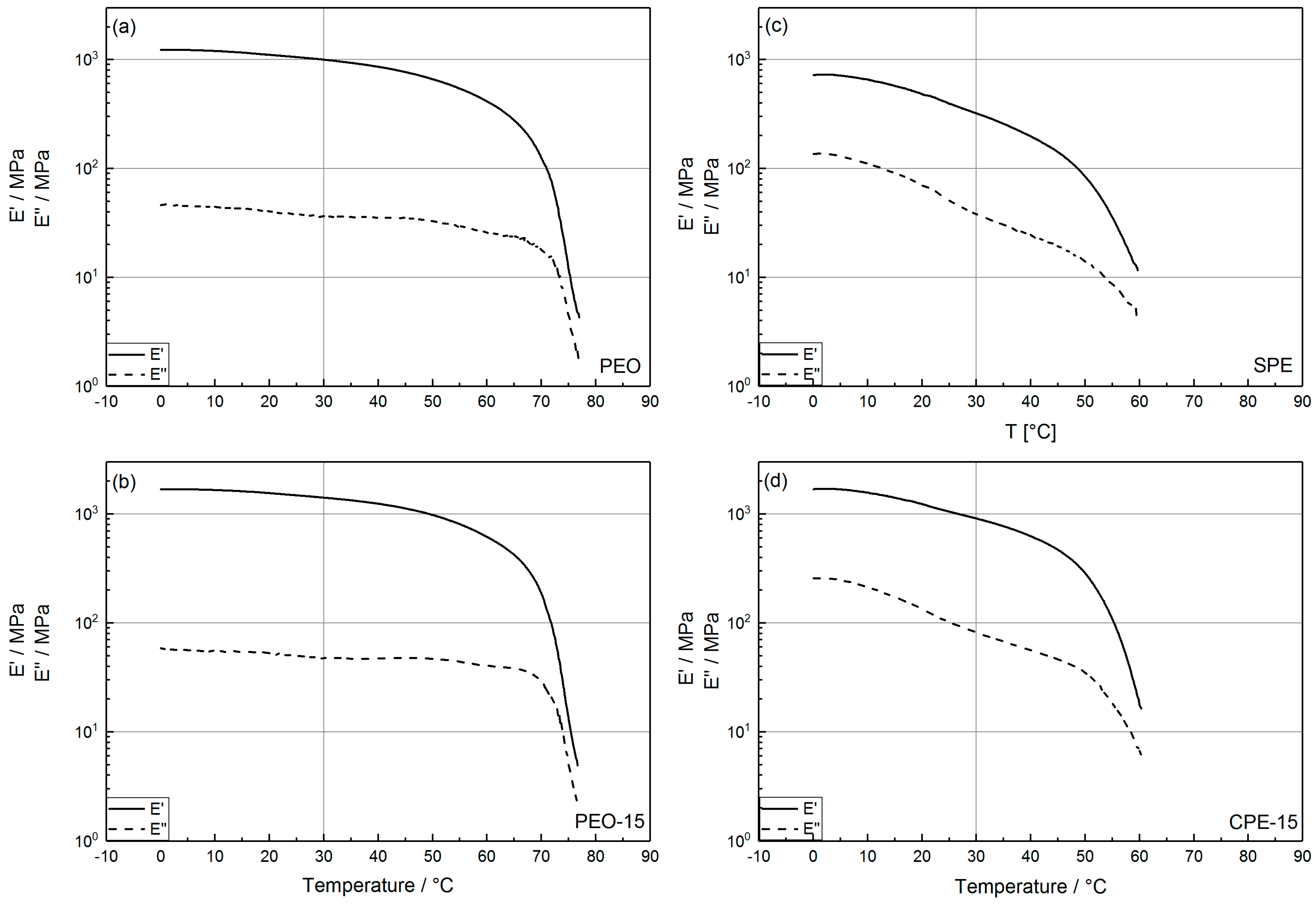
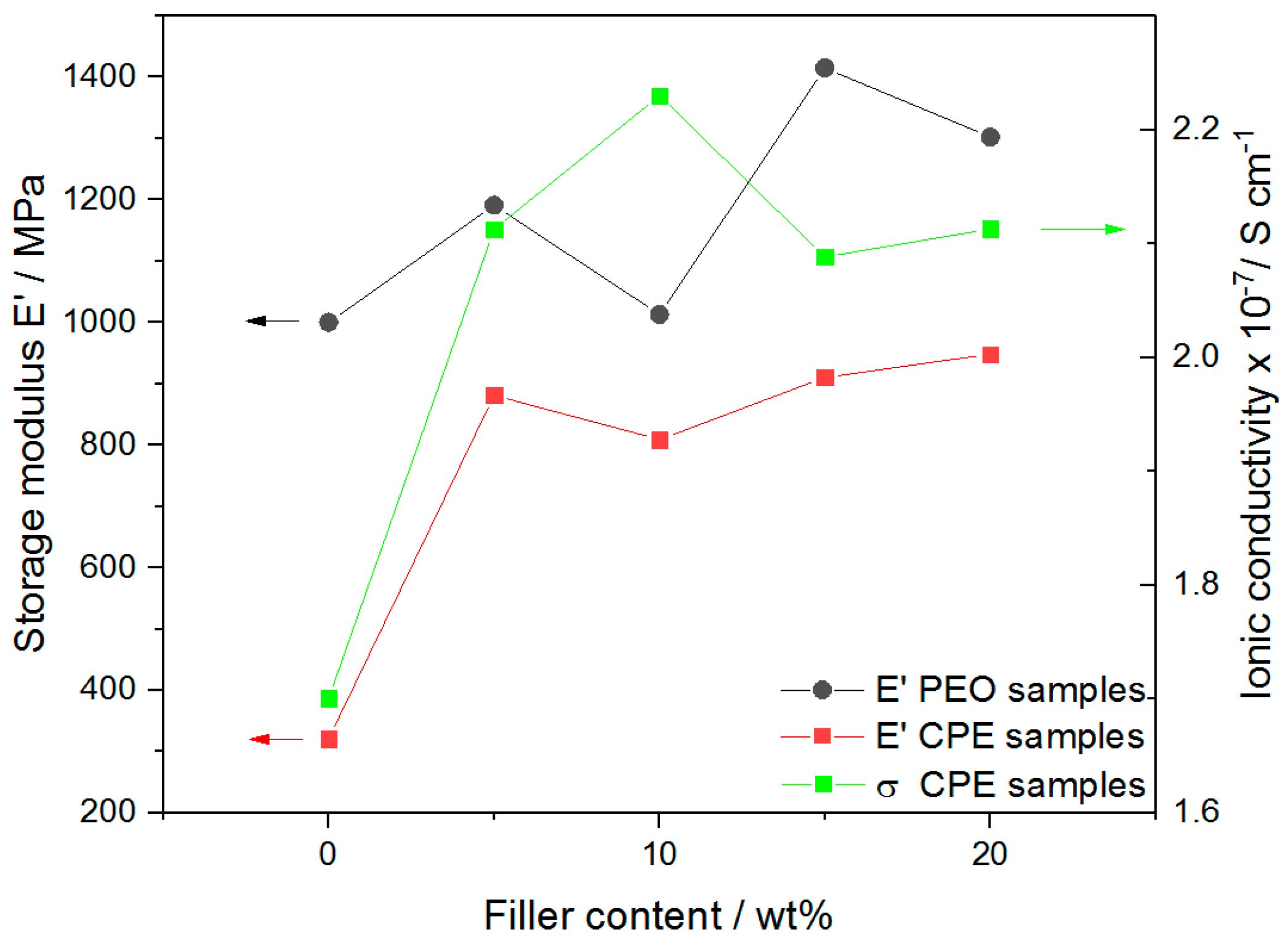
2.2. Thermomechanical Properties
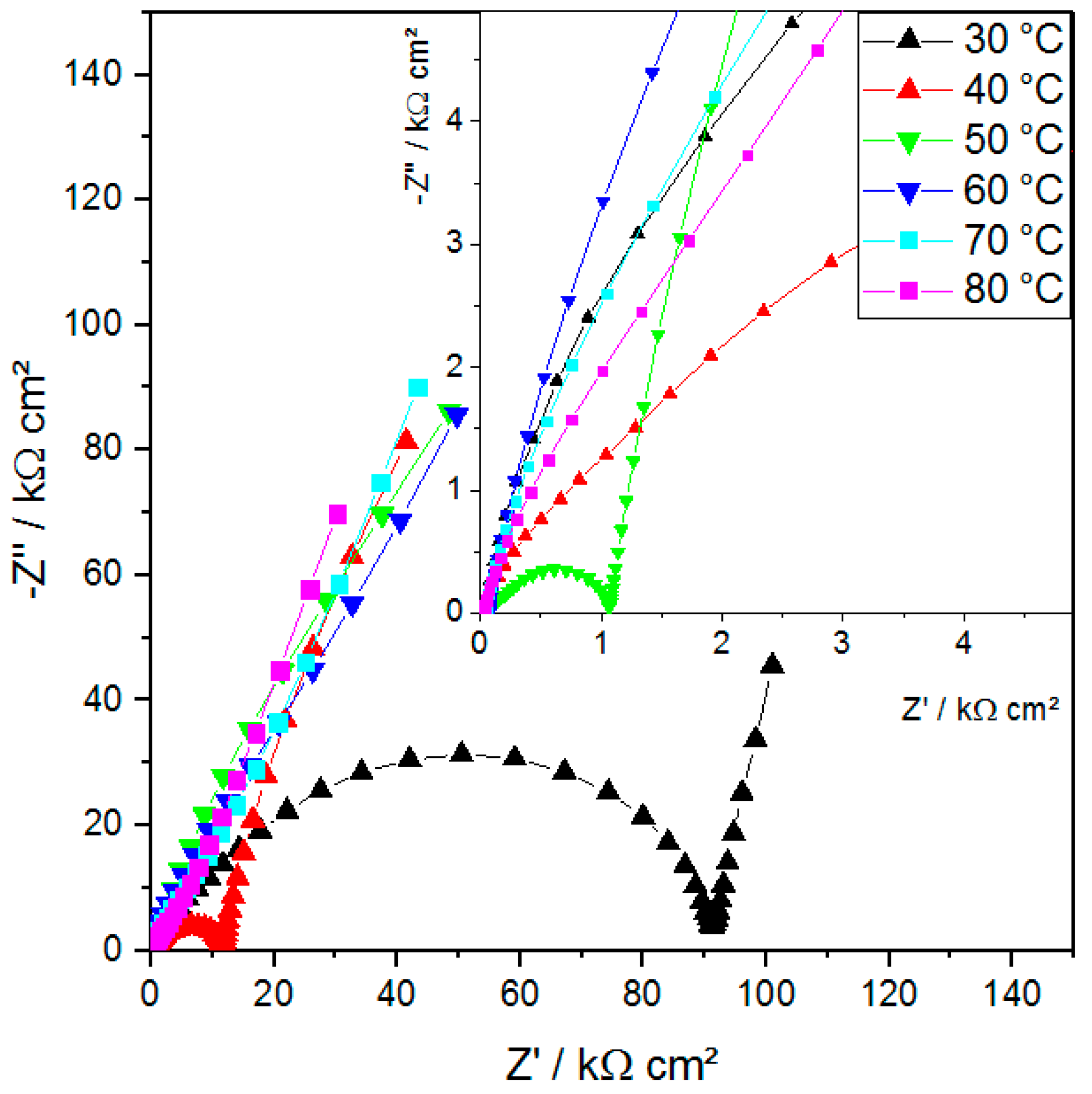
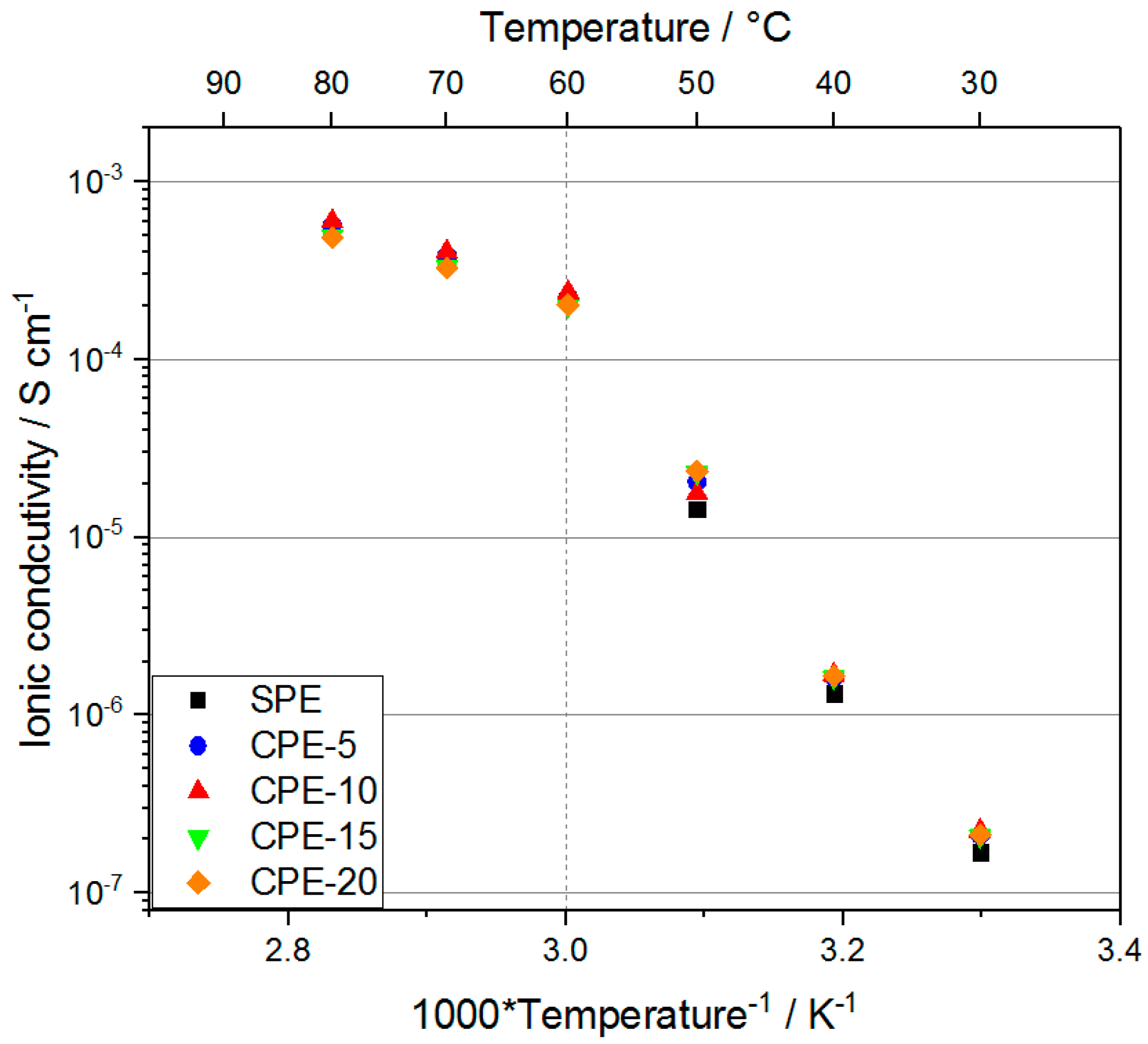
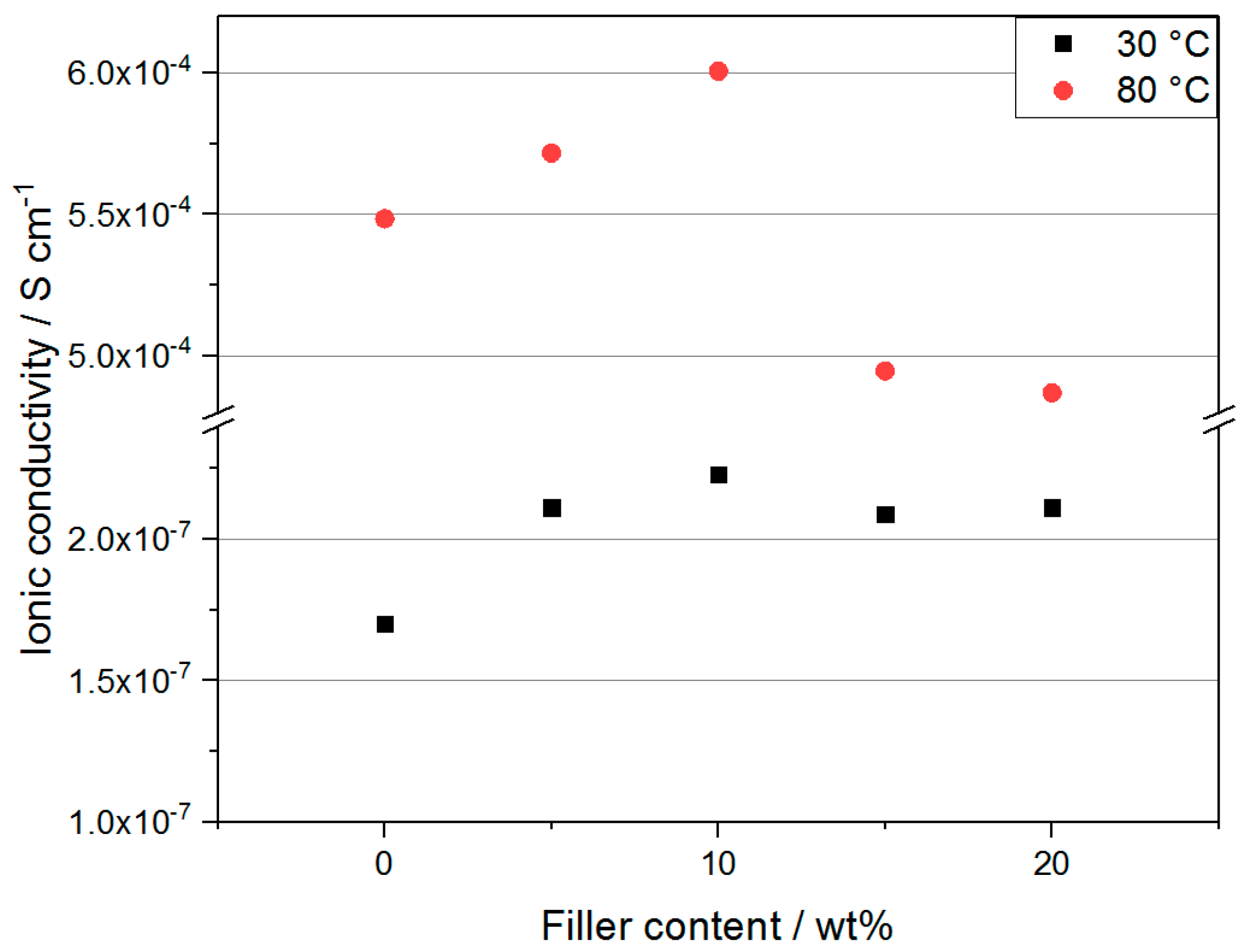
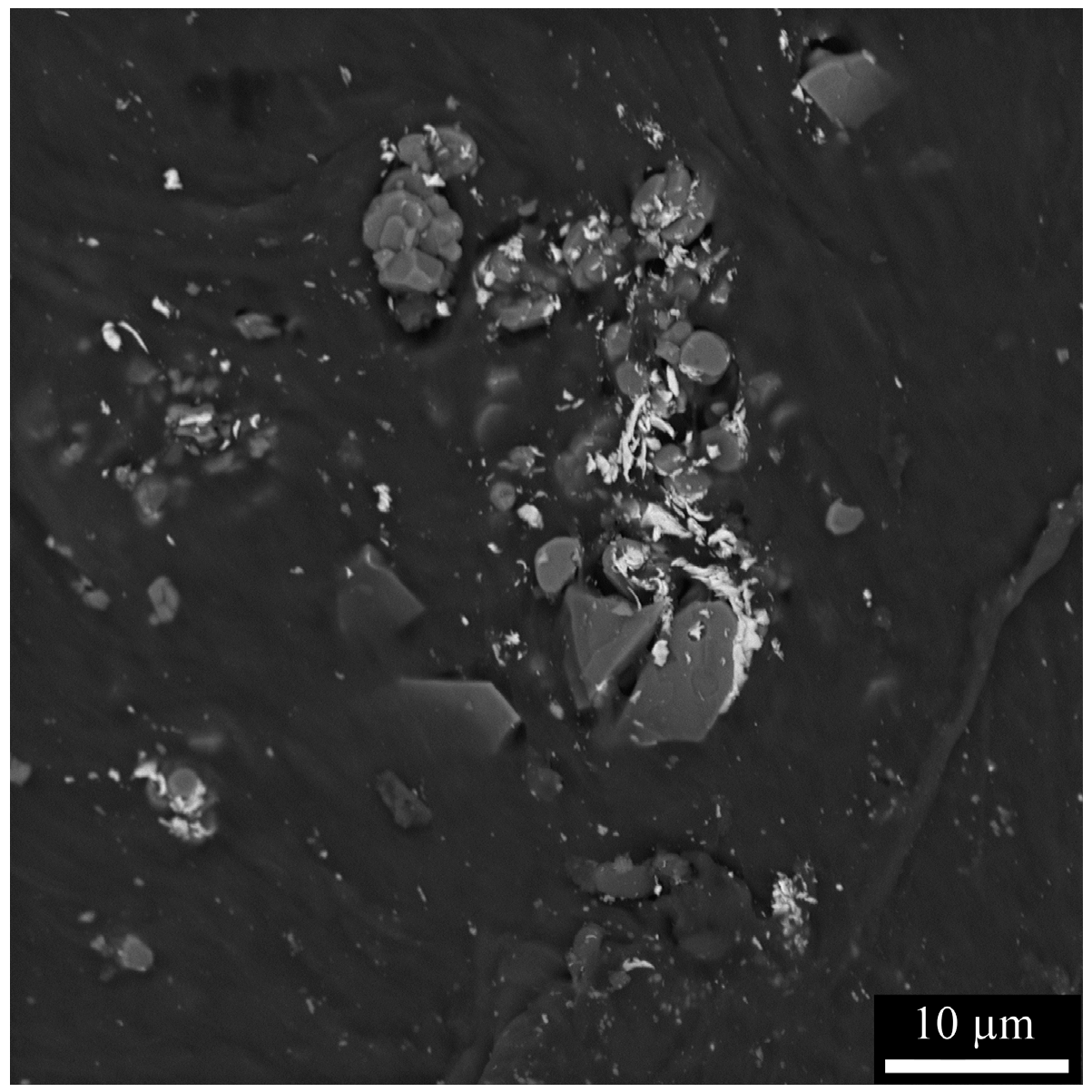
2.3. EIS—Li-ion Conductivity Versus Mechanical Integrity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of Solid Electrolyte Samples
3.2. Analytical Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Janek, J.; Zeier, W.G. A solid future for battery development. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monchak, M.; Hupfer, T.; Senyshyn, A.; Boysen, H.; Chernyshov, D.; Hansen, T.; Schell, K.G.; Bucharsky, E.C.; Hoffmann, M.J.; Ehrenberg, H. Lithium Diffusion Pathway in Li(1.3)Al(0.3)Ti(1.7)(PO4)3 (LATP) Superionic Conductor. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 2941–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dashjav, E.; Tietz, F. Neutron Diffraction Analysis of NASICON-type Li1+xAlxTi2−xP3O12. Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie 2014, 640, 3070–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, R.; Thangadurai, V.; Weppner, W.J.F. Schnelle Lithiumionenleitung in granatartigem Li7La3Zr2O12. Angew. Chem. 2007, 119, 7925–7928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, F.; Glenneberg, J.; Bardenhagen, I.; Kun, R. Synthesis of single phase cubic Al-substituted Li7La3Zr2O12 by solid state lithiation of mixed hydroxides. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 645, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Hori, S.; Saito, T.; Suzuki, K.; Hirayama, M.; Mitsui, A.; Yonemura, M.; Iba, H.; Kanno, R. High-power all-solid-state batteries using sulfide superionic conductors. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhu, W.; Feng, Z.; Guerfi, A.; Vijh, A.; Zaghib, K. Recent progress in sulfide-based solid electrolytes for Li-ion batteries. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2016, 213, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenneberg, J.; Andre, F.; Bardenhagen, I.; Langer, F.; Schwenzel, J.; Kun, R. A concept for direct deposition of thin film batteries on flexible polymer substrate. J. Power Sources 2016, 324, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, M.B. Polymers with Ionic Conductivity. Adv. Mater. 1990, 2, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; He, D.; Xie, X. Poly(ethylene oxide)-based electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 19218–19253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bron, P.; Johansson, S.; Zick, K.; Schmedt auf der Günne, J.; Dehnen, S.; Roling, B. Li10SnP2S12: An affordable lithium superionic conductor. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 135, 15694–15697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, S.; Weber, D.A.; Leichtweiss, T.; Busche, M.R.; Sann, J.; Janek, J. Interphase formation and degradation of charge transfer kinetics between a lithium metal anode and highly crystalline Li7P3S11 solid electrolyte. Solid State Ion. 2016, 286, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, S.; Randau, S.; Leichtweiß, T.; Weber, D.A.; Sann, J.; Zeier, W.G.; Janek, J. Direct Observation of the Interfacial Instability of the Fast Ionic Conductor Li10GeP2S12 at the Lithium Metal Anode. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 2400–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, E.J.; Sharafi, A.; Sakamoto, J. Intergranular Li metal propagation through polycrystalline Li6.25Al0.25La3Zr2O12 ceramic electrolyte. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 223, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porz, L.; Swamy, T.; Sheldon, B.W.; Rettenwander, D.; Frömling, T.; Thaman, H.L.; Berendts, S.; Uecker, R.; Carter, W.C.; Chiang, Y.-M. Mechanism of Lithium Metal Penetration through Inorganic Solid Electrolytes. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 414, 1701003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-L.; Roddatis, V.; Chandran, C.V.; Ma, Q.; Uhlenbruck, S.; Bram, M.; Heitjans, P.; Guillon, O. Li7La3Zr2O12 Interface Modification for Li Dendrite Prevention. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 10617–10626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mindemark, J.; Sun, B.; Törmä, E.; Brandell, D. High-performance solid polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries operational at ambient temperature. J. Power Sources 2015, 298, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.; Liu, X.-M.; Cai, F.; Yang, H.; Shen, X.-D.; Liu, G. A novel all-solid electrolyte based on a co-polymer of poly-(methoxy/hexadecal-poly(ethylene glycol) methacrylate) for lithium-ion cell. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 22265–22271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Matsui, M.; Takeda, Y.; Yamamoto, O.; Im, D.; Lee, D.; Imanishi, N. Interface Properties between Lithium Metal and a Composite Polymer Electrolyte of PEO18Li(CF3SO2)2N-Tetraethylene Glycol Dimethyl Ether. Membranes 2013, 3, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, B.-K.; Kim, Y.-W. Conductivity relaxation in the PEO–salt polymer electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 49, 2307–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, F.; Scrosati, B. Nanocomposite Lithium Ion Conducting Membranes. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 984, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fergus, J.W. Ceramic and polymeric solid electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 4554–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, F.; Bardenhagen, I.; Glenneberg, J.; Kun, R. Microstructure and temperature dependent lithium ion transport of ceramic–polymer composite electrolyte for solid-state lithium ion batteries based on garnet-type Li7La3Zr2O12. Solid State Ion. 2016, 291, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, R.C.; Pandey, G.P. Solid polymer electrolytes: Materials designing and all-solid-state battery applications: An overview. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 223001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes-Pereira, J.; Costa, C.M.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Polymer composites and blends for battery separators: State of the art, challenges and future trends. J. Power Sources 2015, 281, 378–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetjen, M.; Kim, G.-T.; Joost, M.; Winter, M.; Passerini, S. Temperature dependence of electrochemical properties of cross-linked poly(ethylene oxide)–lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide–N-butyl-N-methylpyrrolidinium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide solid polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 87, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appetecchi, G.B.; Carewska, M.; Alessandrini, F.; Prosini, P.P.; Passerini, S. Characterization of PEO-Based Composite Cathodes. I. Morphological, Thermal, Mechanical, and Electrical Properties. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2000, 147, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, F.; Persi, L.; Ronci, F.; Scrosati, B. Nanocomposite polymer electrolytes and their impact on the lithium battery technology. Solid State Ion. 2000, 135, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitra, M.; Sinha, M.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Middya, T.; De, U.; Tarafdar, S. Ion-conductivity and Young’s modulus of the polymer electrolyte PEO–ammonium perchlorate. Solid State Ion. 2007, 178, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, N.; Kawakage, S.; Ogihara, T. Structure and thermal/mechanical properties of poly(ethylene oxide)-clay mineral blends. Polymer 1997, 38, 5115–5118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdari, F.; Carreau, P.J.; Heuzey, M.C.; Kamal, M.R.; Sain, M.M. Enhanced properties of poly(ethylene oxide)/cellulose nanofiber biocomposites. Cellulose 2017, 24, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, F.; Appetecchi, G.B.; Persi, L.; Scrosati, B. Nanocomposite polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. Nature 1998, 394, 456–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Alexandridis, P. Composite Polymer Electrolytes: Nanoparticles Affect Structure and Properties. Polymers 2016, 8, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlich, B. (Ed.) Macormolecular Physics; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Malathi, M.; Tamilarasan, K.; Ganesan, V. Role of ceramic reinforcement in composite polymer electrolyte. Polym. Compos. 2015, 36, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weston, J.; Steele, B. Effects of inert fillers on the mechanical and electrochemical properties of lithium salt-poly(ethylene oxide) polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ion. 1982, 7, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrosati, B.; Croce, F. Composite polymer ionics: Advanced electrolyte materials for thin-film batteries. Polym. Adv. Technol. 1993, 4, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capiglia, C.; Yang, J.; Imanishi, N.; Hirano, A.; Takeda, Y.; Yamamoto, O. Composite polymer electrolyte: The role of filler grain size. Solid State Ion. 2002, 154–155, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Li, S.-P.; Fan, L.-Z.; Nan, C.-W.; Goodenough, J.B. PEO/garnet composite electrolytes for solid-state lithium batteries: From “ceramic-in-polymer” to “polymer-in-ceramic”. Nano Energy 2018, 46, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appetecchi, G.B.; Croce, F.; Persi, L.; Ronci, F.; Scrosati, B. Transport and interfacial properties of composite polymer electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2000, 45, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| w/o LiClO4 | PEO | PEO-5 | PEO-10 | PEO-15 | PEO-20 |
| PEO/wt% | 100 | 95 | 90 | 85 | 80 |
| Al2O3/wt% | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 |
| w LiClO4 | SPE | CPE-5 | CPE-10 | CPE-15 | CPE-20 |
| PEO/wt% | 87 | 82.5 | 78.2 | 73.9 | 69.5 |
| LiClO4/wt% | 13 | 12.5 | 11.8 | 11.1 | 10.5 |
| Al2O3/wt% | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 |
| w/o LiClO4 | PEO | PEO-10 | PEO-15 |
| Melting temp. Tm/°C | 76 | 73 | 73 |
| Enthalpy ΔHm,N/J g−1 | 143 | 113 | 99 |
| Crystallinity Xc,N/% | 73 | 57 | 50 |
| w LiClO4 | SPE | CPE-10 | CPE-15 |
| Melting temp. Tm/°C | 60 | 60 | 60 |
| Enthalpy ΔHm,N/J g−1 | 70 | 53 | 39 |
| Crystallinity Xc,N/% | 36 | 27 | 20 |
| w/o LiClO4 | PEO | PEO-5 | PEO-10 | PEO-15 | PEO-20 |
| E′/MPa | 1000 | 1191 | 1013 | 1415 | 1302 |
| w LiClO4 | SPE | CPE-5 | CPE-10 | CPE-15 | CPE-20 |
| E′/MPa | 321 | 881 | 809 | 910 | 948 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peters, F.; Langer, F.; Hillen, N.; Koschek, K.; Bardenhagen, I.; Schwenzel, J.; Busse, M. Correlation of Mechanical and Electrical Behavior of Polyethylene Oxide-Based Solid Electrolytes for All-Solid State Lithium-Ion Batteries. Batteries 2019, 5, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries5010026
Peters F, Langer F, Hillen N, Koschek K, Bardenhagen I, Schwenzel J, Busse M. Correlation of Mechanical and Electrical Behavior of Polyethylene Oxide-Based Solid Electrolytes for All-Solid State Lithium-Ion Batteries. Batteries. 2019; 5(1):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries5010026
Chicago/Turabian StylePeters, Fabian, Frederieke Langer, Nikolai Hillen, Katharina Koschek, Ingo Bardenhagen, Julian Schwenzel, and Matthias Busse. 2019. "Correlation of Mechanical and Electrical Behavior of Polyethylene Oxide-Based Solid Electrolytes for All-Solid State Lithium-Ion Batteries" Batteries 5, no. 1: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries5010026
APA StylePeters, F., Langer, F., Hillen, N., Koschek, K., Bardenhagen, I., Schwenzel, J., & Busse, M. (2019). Correlation of Mechanical and Electrical Behavior of Polyethylene Oxide-Based Solid Electrolytes for All-Solid State Lithium-Ion Batteries. Batteries, 5(1), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries5010026





