Recent Advances in Non-Flammable Electrolytes for Safer Lithium-Ion Batteries
Abstract
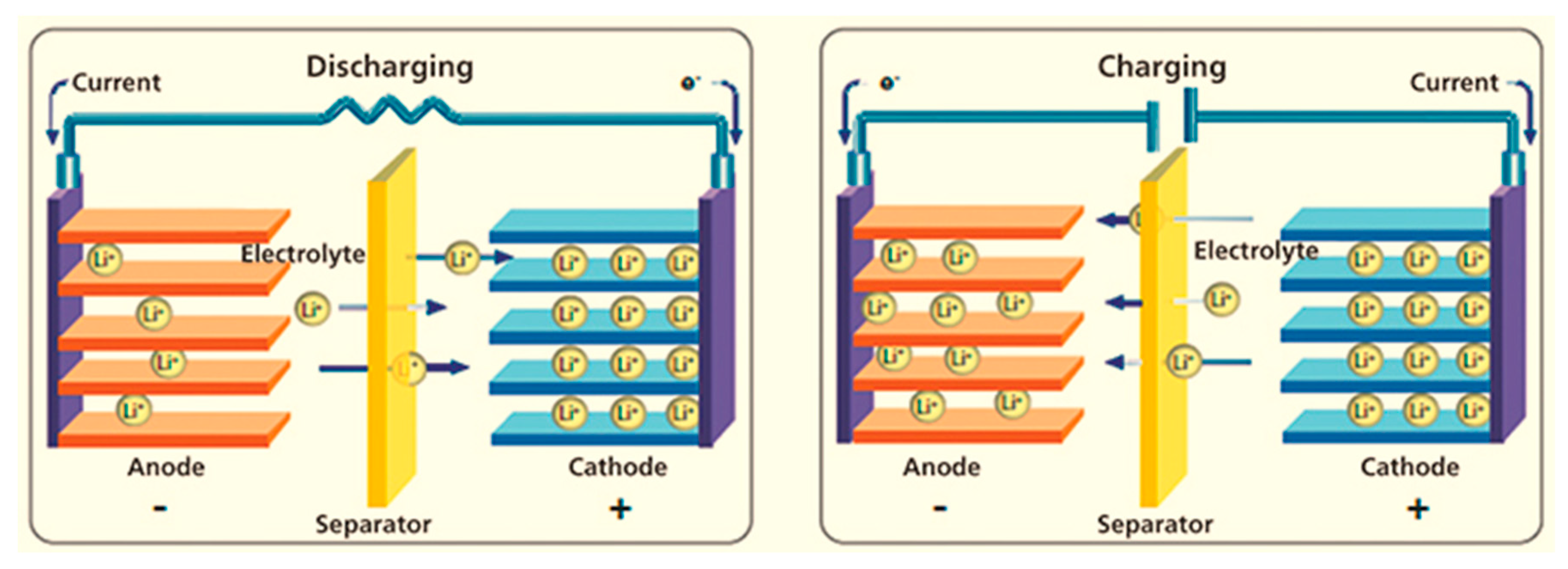
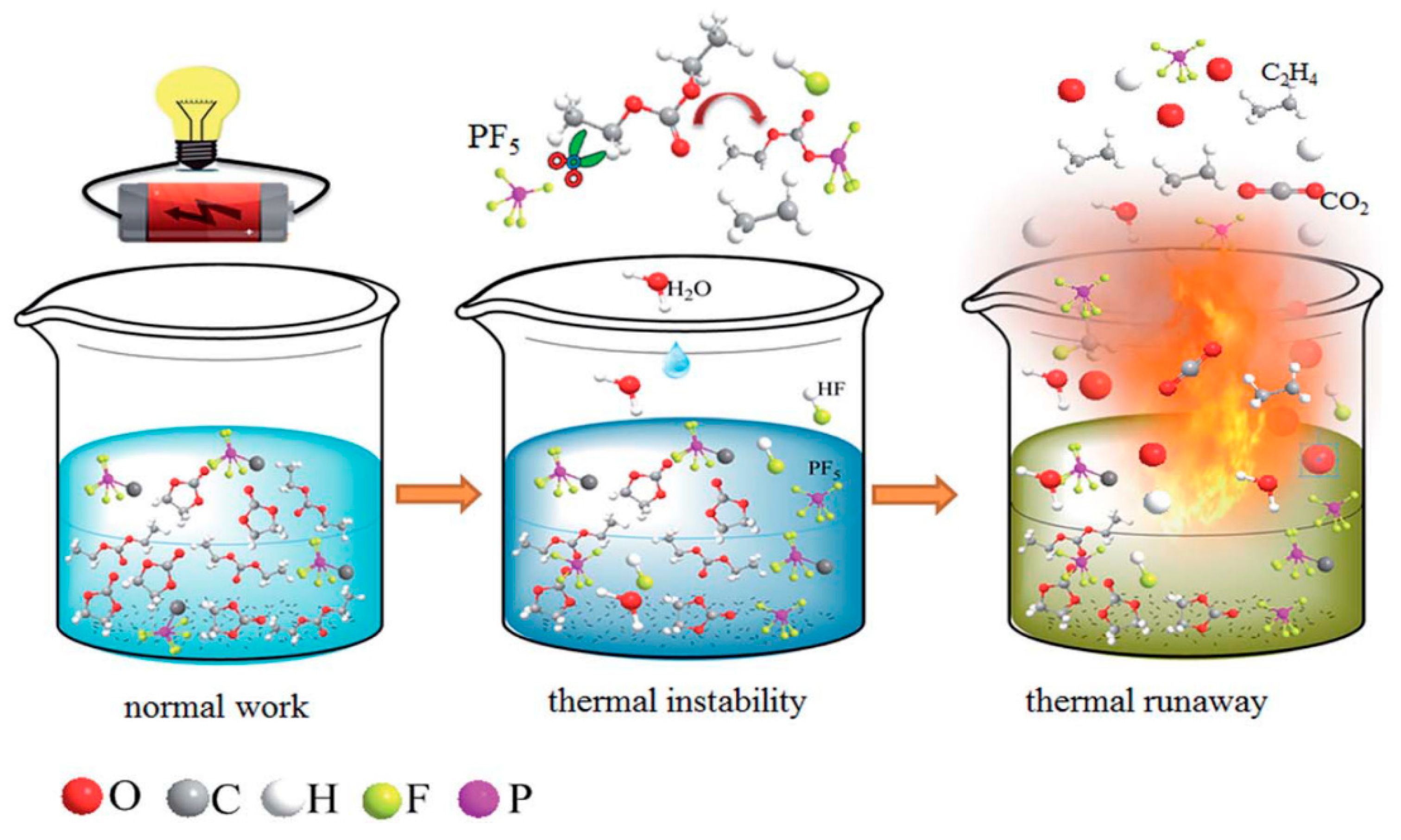
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Organosilicon-Containing Electrolytes
2.2. Ionic Liquid Electrolytes with/without Solvents
2.3. Flame-Retardant Solvents
2.4. Fire-Extinguishing Electrolyte
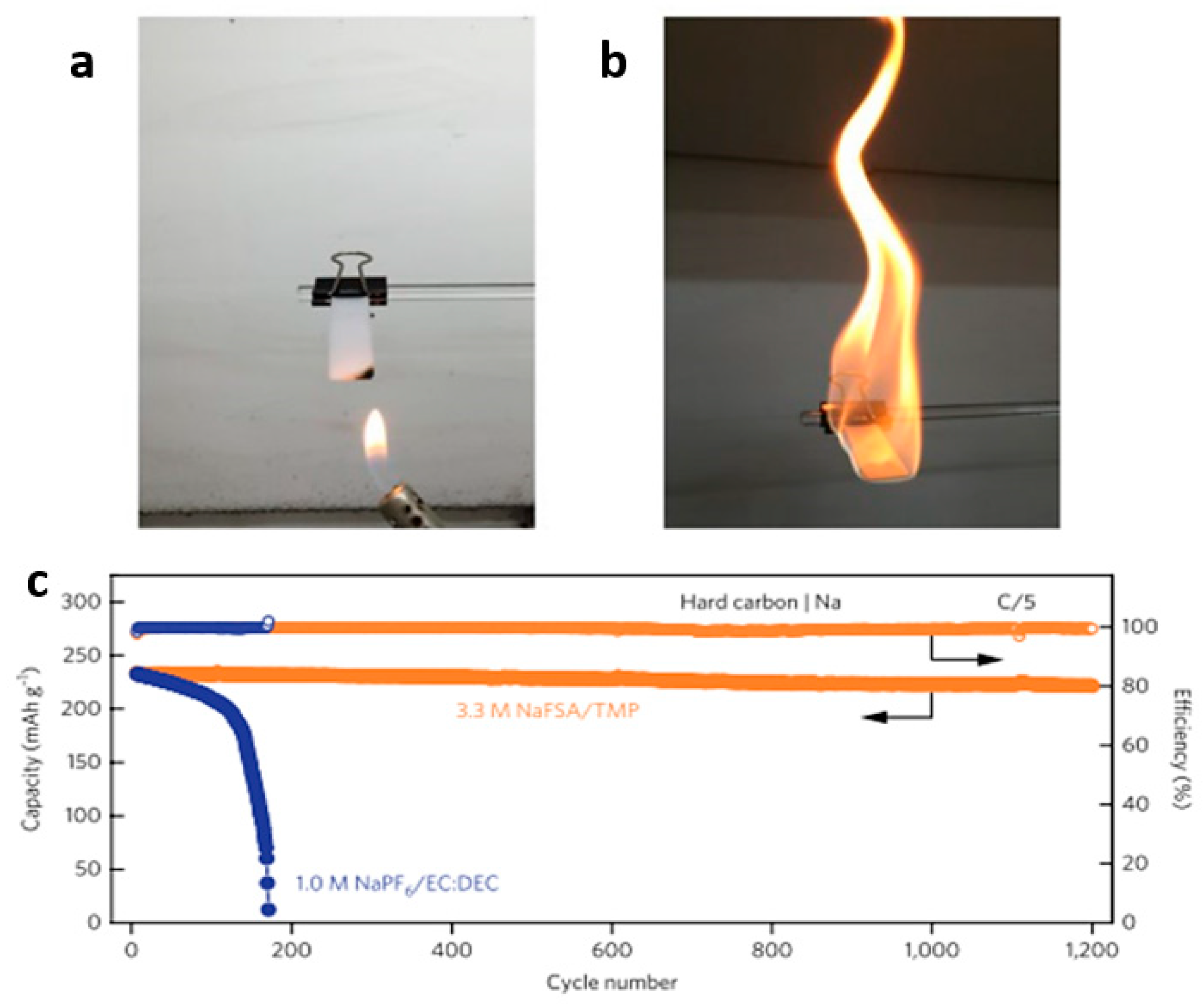
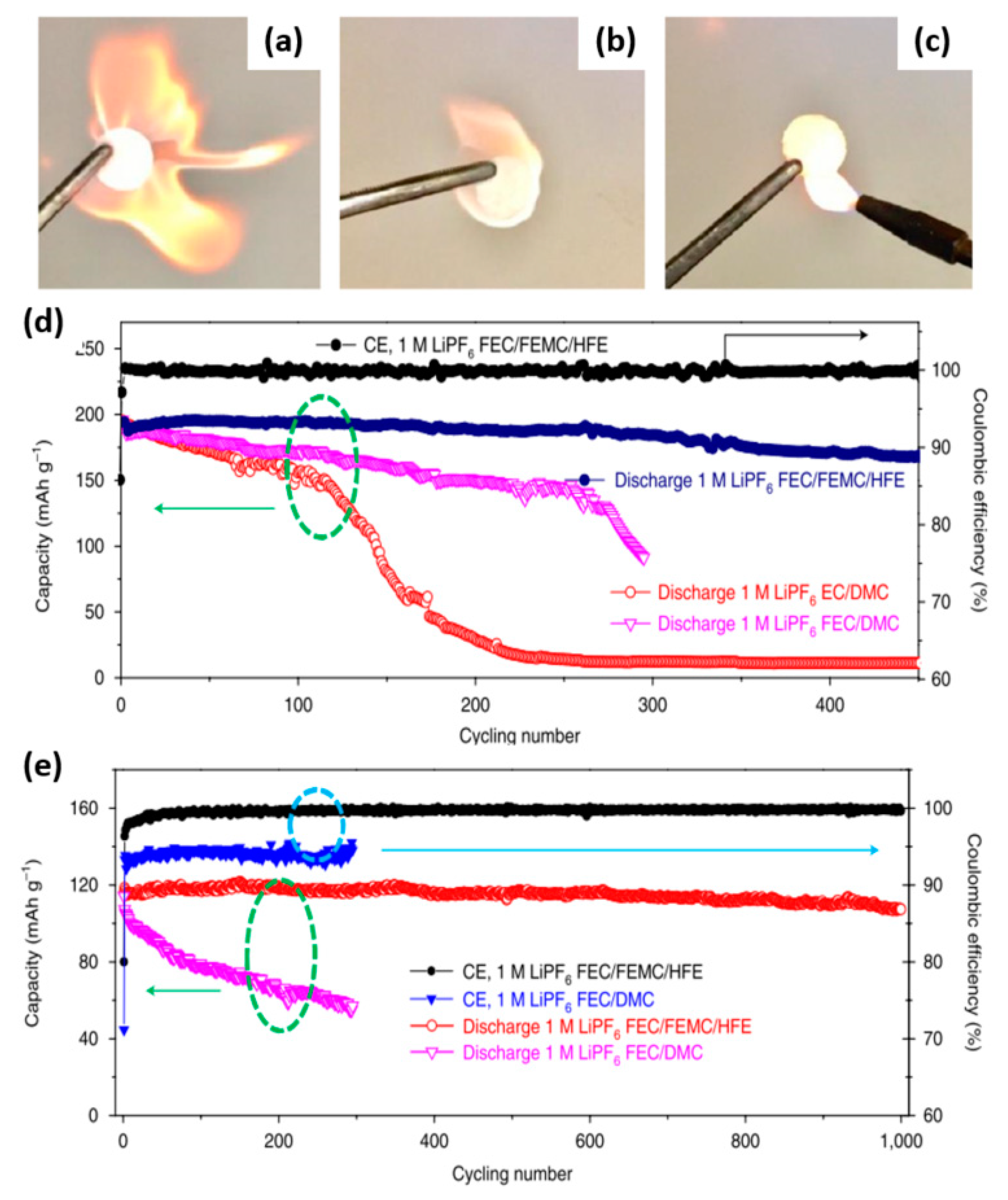
2.5. Fluorinated/Phosphonate Electrolyte
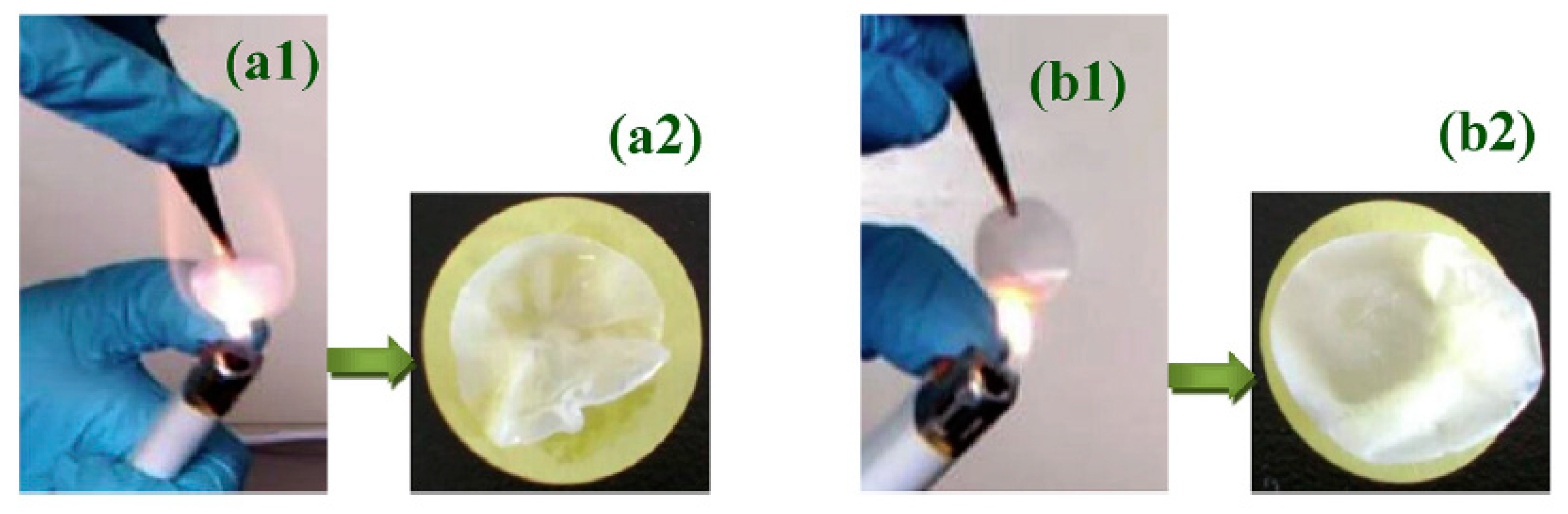
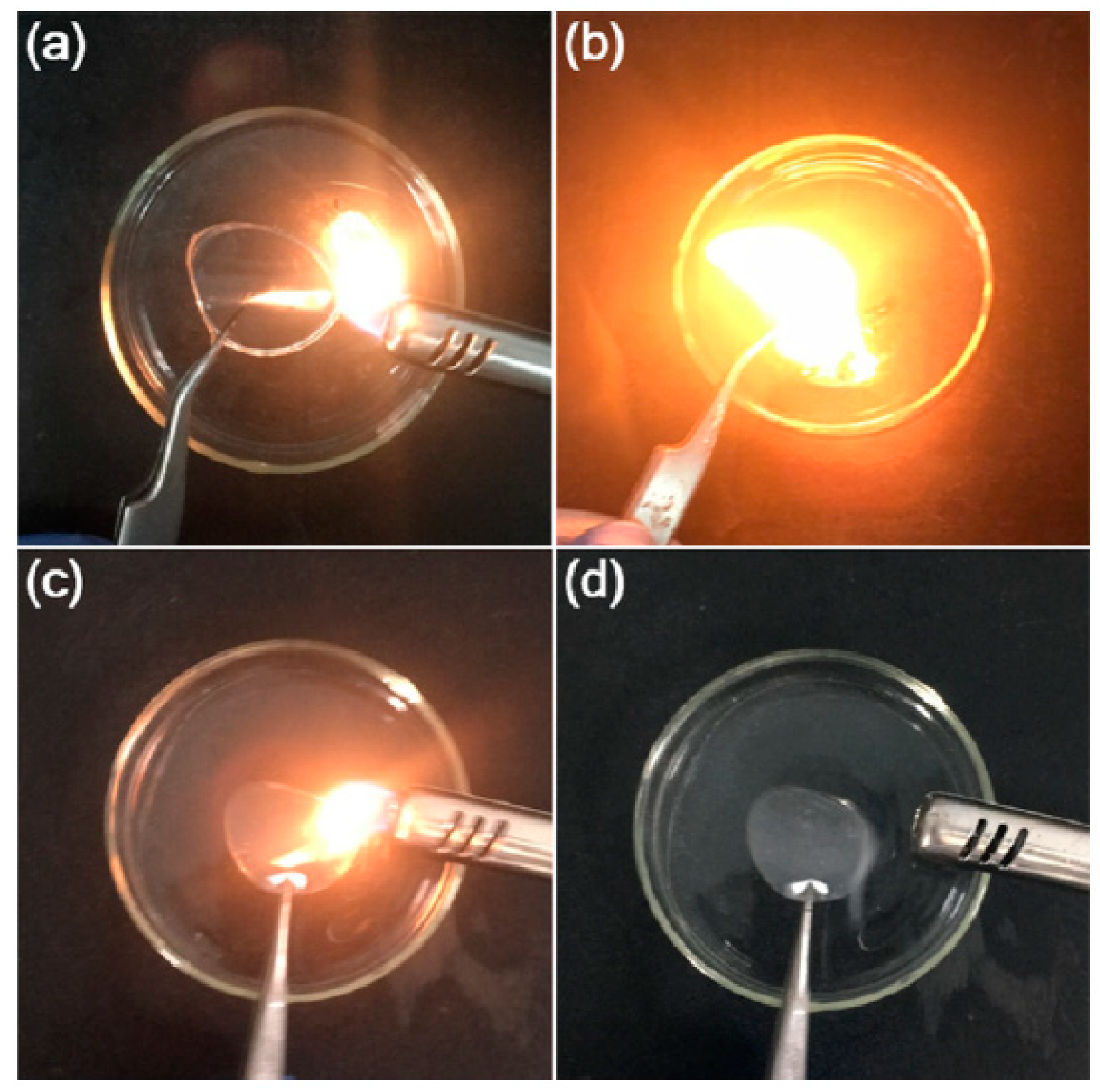
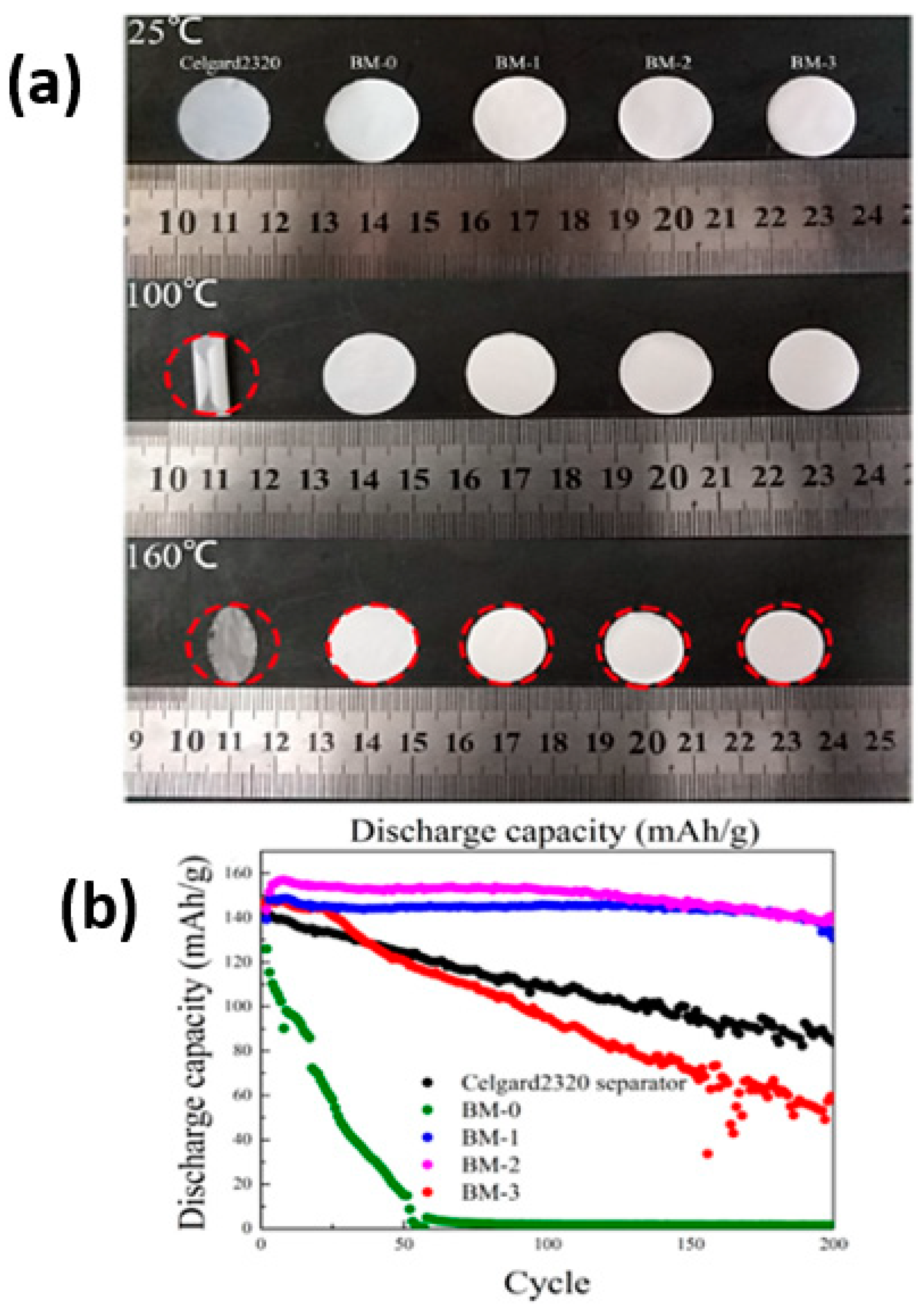
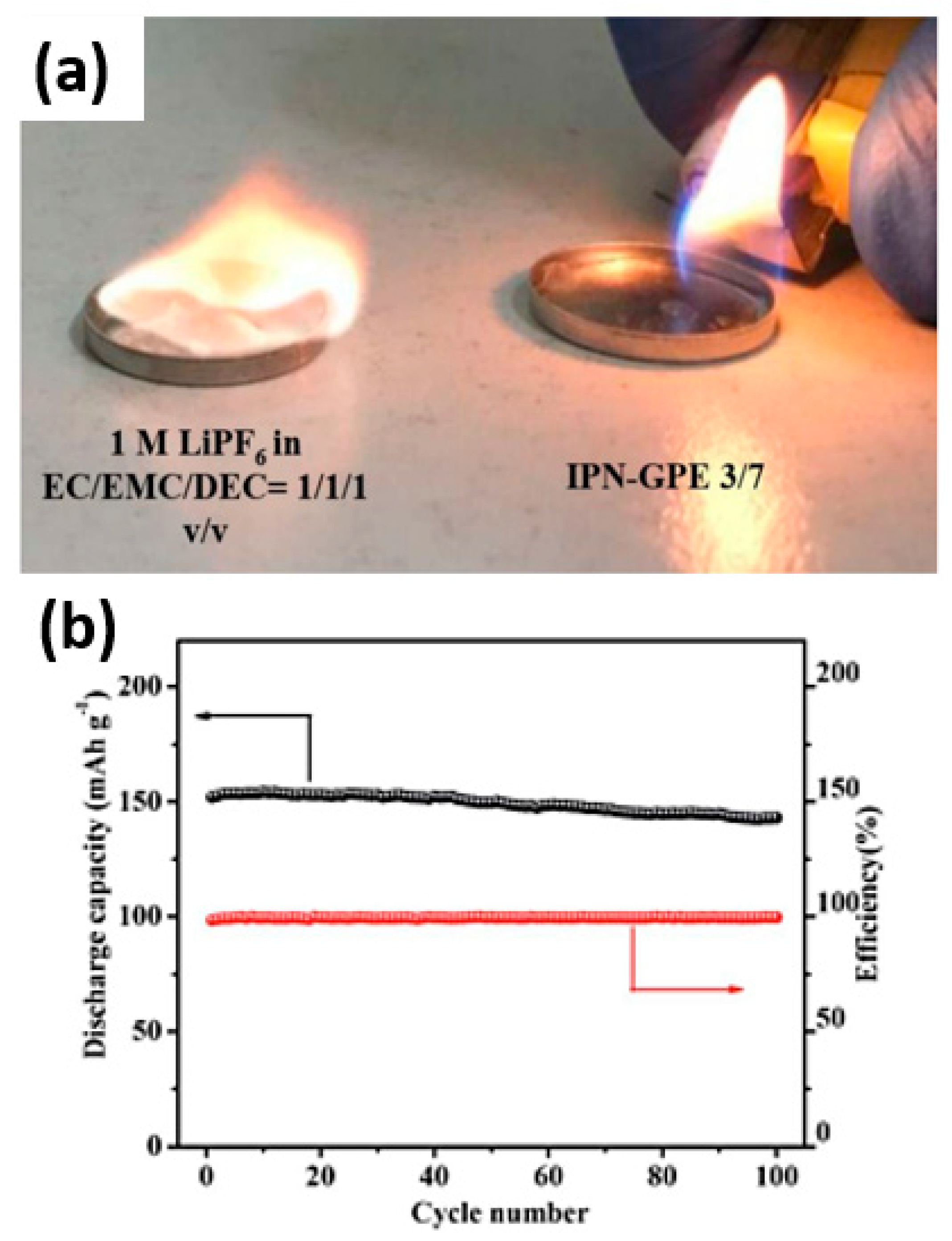
2.6. Gel Polymer Electrolytes
2.7. Additives for Electrolytes
3. Conclusions and Future Direction
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Full form/Chemical Name | Abbreviation | Full form/Chemical Name |
| LiPF6 | lithium hexafluorophosphate | DEC | diethyl carbonate |
| DMC | dimethyl carbonate | EMC | ethyl methyl carbonate |
| EC | ethylene carbonate | FEC | fluoroethylene carbonate |
| MFSM2 | fluoro(3-(2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethoxy)propyl) dimethylsilane | DFSM2 | difluoro(3-(2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethoxy)propyl) methylsilane |
| LCO | LiCoO2 (lithium cobalt oxide) | LiTFSI | lithium bis (trimethylsulfonyl) imide |
| LiODFB | lithium oxalydifluoroborate | IL | Ionic liquid |
| AN1IL-TFSI | IL with allyl group | CEN1IL-TFSI | IL with cynoethyl group |
| SN1IL | ((2-trimethylsililoxyethyl) trimethylammonium bis(trifluoromethanesulf-onyl)imide | LMNO | LiMn1.5Ni0.5O4 |
| PYR13FSI | N-methyl-N-propyl pyrrolidinium, bis(fluorosulfonyl) imide | PYR13TFSI | N-methyl-N-propyl pyrrolidinium, bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl) imide |
| LiFePO4 | Lithium iron phosphate | TMP | trimethyl phosphate |
| NaPF6 | sodium hexafluorophosphate | ADN | adiponitrile |
| LTO | Li4Ti5O12 | NMC | LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 |
| DMAC | N, N Dimethylacetamide | PFMP | perfluoro-2-methyl-3-pentanone |
| FS | Fluorocarbon surfactant | F-EPE | 1,1,2,2-tetrafluoroethyl-2,2,3,3-tetrafluoropropyl ether |
| LiBOB | lithium bis(oxalato)borate | GBL | gamma-butyrolactone |
| FEC | fluoroethylene carbonate | FEMC | 3,3,3-fluoroethylmethyl carbonate |
| HFE | 1,1,2,2-tetrafluoroethyl-2′,2′,2′-trifluoroethyl ether | TEP | Triethyl phosphate |
| DFDEC | di-(2,2,2 trifluoroethyl) carbonate | PC | Propylene carbonate |
| DMMP | dimethyl methyl-phosphonate | FAP | fluorinated alkyl phosphates |
| TFEP | tris(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl) phosphate | LiNTF2 | lithium bis(trifluoromethane sulphonyl) imide |
| TMS | tetramethylene sulfone | VC | vinylene carbonate |
| PEO | poly(ethylene oxide) | PMHS | poly-methyl hydrogen-siloxane |
| NHC-BF3 | 1,3-dimethylimidazolidin-2-mm-trifluoroborate | NMC111 | LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 |
| NHC-PF4CF3 | 1,3-dimethylimidazolidin-2-mm-tetrafluorotrifluoromethylphosphate | GPE | gel polymer electrolytes |
| PVDF | polyvinylidene fluoride | HNT | halloysite nanotube |
| P(MMA-AN-EA) | poly(methyl methacrylate-acrylonitrile-ethyl acrylate) | EMITFSI | 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesolfonyl) imide |
| GPE-SN | gel polymer electrolyte containing succinonitrile | GPE-SN-IM | GPE-SN by immersion method |
| PAN | polyacrylonitrile | PVA | poly(vinyl alcohol) |
| NIPS | non-solvent induced phase separation | IPN-GPE | Gel polymer electrolyte with interpenetrating polymer network |
| EMS | ethyl-methyl sulfone | PDLLA | poly(d,l-lactide) |
| PEGMA | poly(ethylene glycol)methyl ether methacrylate | LAGP | Li1.5Al0.5Ge1.5(PO4)3 |
| ILGPE | ionic liquid gel polymer electrolytes | PEM | polymer electrolyte membrane |
| PEGBCDMA | polyethylene glycolbiscarbamate dimethacrylate | PAMM | poly(acrylic anhydride-2-methyl-acrylic acid-2-oxirane-ethyl ester-methyl methacrylate) |
| PCL/SN | Poly(ε-caprolactone)/Succinonitrile | CPE | composite polymer electrolyte |
| Mg(OH)2 | Magnesium hydroxide | PAEKNW | poly (aryl ether ketone) nonwovens |
| MDPCT | methyl diethyl phospho- noacetate | CETPE | Carbethoxy ethylidene triphenylphosphorane |
| TFPCT | triethyl2-fluoro-2-phosphonoacetate | Tetra PEG | Tetra-armed poly(ethylene glycol) |
| NCA | LiNi0.8Co0.15Al0.05O2 | PVDF-HFP | polyvinylidenefluoride-hex- afluoropropylene |
| PBO | poly [benzyl methacrylate-co-oligo(ethylene glycol)ether methacrylate] | c-PPO | cross-linked poly[dimethyl-p- vinyl benzyl phosphonate-co-oligo (ethylene glycol) meth acrylate] co-polymer (c-PPO) |
| DTYP | diethyl(thiophen-2-ylmethyl) phosphonate | PFN | Fluorinated phosphazene derivative, ethoxy-(pentafluoro)-cyclotriphosphazene |
| PFPN | ethoxy(pentafluoro) cyclotriphosphazene | EEEP | Poly[bis-(ethoxyethoxyethoxy)phosphazene] |
References
- Hahn, M.; Wieboldt, D.; Ruff, I. Techniques for Raman Analysis of Lithium-Ion Batteries. Spectroscopy 2015, 30, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Samuelson, K. A Brief History of Samsung’s Troubled Galaxy Note 7 Smartphone. 2016. Available online: http://time.com/4526350/samsung-galaxy-note-7-recall-problems-overheating-fire/ (accessed on 11 November 2018).
- Pappalardo, J. No One is Fixing Flying’s Fire Problem. 2018. Available online: https://www.popularmechanics.com/flight/airlines/a22629210/faa-laptop-battery-fire-danger-regulations/ (accessed on 3 August 2018).
- Jansen, B. Crash investigators trace UPS plane fire to batteries. USA TODAY, 25 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Exploding Camera Battery Causes Panic at Orlando International Airport, Police Say. 2017. Available online: https://www.wftv.com/news/local/exploding-camera-battery-causes-panic-at-orlando-international-airport-police-say/645230506 (accessed on 11 November 2017).
- Economy, P. Lithium-Ion Battery on Delta Air Lines Flight Explodes, Catches Fire (Quick-Thinking Crew Averts Disaster). Available online: https://www.inc.com/peter-economy/lithium-ion-battery-on-delta-air-lines-flight-explodes-catches-fire-quick-thinking-crew-averts-disaster.html (accessed on 18 May 2018).
- Loveday, E. Tesla Model S Catches Fire During Test Drive In France. Electrek, 15 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, F. Tesla Model S battery caught on fire “without accident”, says owner—Tesla is investigating. Electrek, 16 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, K.; Ping, P. A self-cooling and flame-retardant electrolyte for safer lithium ion batteries. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2018, 2, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Fang, S.; Huang, J.; Luo, D.; Yang, L.; Hirano, S. A novel mixture of lithium bis(oxalato)borate, gamma-butyrolactone and non-flammable hydrofluoroether as a safe electrolyte for advanced lithium ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 19982–19990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Mai, Y.; Luo, H.; Yan, X.; Zhang, L. Fluorosilane compounds with oligo (ethylene oxide) substituent as safe electrolyte solvents for high-voltage lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2016, 334, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, T.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Mai, Y.; Yan, X. Novel choline-based ionic liquids as safe electrolytes for high-voltage lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2016, 328, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, N.; Abu-lebdeh, Y. Non-Flammable Electrolyte Mixtures of Ringed Ammonium-Based Ionic Liquids and Ethylene Carbonate for High Voltage Li-Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, A1593–A1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Wang, B.; Wang, L.; Liu, G.; Wang, F.; Luo, H.; Wang, D. LiAlCl4·3SO2 as a high conductive, non-flammable and inorganic non-aqueous liquid electrolyte for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 286, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safa, M.; Chamaani, A.; Chawla, N.; El-Zahab, B. Polymeric Ionic Liquid Gel Electrolyte for Room Temperature Lithium Battery Applications. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 213, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceder, G.; Supervisor, T.; Schuh, C. First Principles Design and Investigation of Lithium-Ion Battery Cathodes and Electrolytes. Ph.D. Dissertation, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Liao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xu, J.; Sun, P.; Shi, H. Application of the imidazolium ionic liquid based nano-particle decorated gel polymer electrolyte for high safety lithium ion battery. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 284, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, M.; Simonetti, E.; Appetecchi, G.B.; Carewska, M.; Montanino, M.; Kim, G.; Loeffler, N.; Passerini, S. Ionic Liquid Electrolytes for Safer Lithium Batteries I. Investigation around Optimal Formulation. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, 6026–6031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L.; Yang, J.; Xiong, S.; Qian, Y. Ether-based nonflammable electrolyte for room temperature sodium battery. J. Power Sources 2015, 284, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yasukawa, E.; Kasuya, S. Nonflammable trimethyl phosphate solvent-containing electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries: I. Fundamental properties. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2001, 148, A1058–A1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, E.G.; Nam, T.H.; Kim, J.G.; Kim, H.; Moon, S. Effect of the concentration of diphenyloctyl phosphate as a flame-retarding additive on the electrochemical performance of lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 2276–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, H.; Ochida, M.; Domi, Y.; Doi, T.; Tsubouchi, S.; Yamanaka, T.; Abe, T.; Ogumi, Z. Electrochemical Raman study of edge plane graphite negative-electrodes in electrolytes containing trialkyl phosphoric ester. J. Power Sources 2012, 212, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yamada, Y.; Sodeyama, K.; Watanabe, E.; Takada, K.; Tateyama, Y.; Yamada, A. Fire-extinguishing organic electrolytes for safe batteries. Nat. Energy 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Co, L.; Nmc, M.O. Adiponitrile-Lithium Bis(trimethylsulfonyl)imide Solutions as Alkyl Carbonate-free Electrolytes for Li4 Ti5 O12 (LTO)/LiNi1/3 Co1/3 Mn1/3 O2 (NMC) Li-Ion Batteries. ChemPhysChem 2017, 12, 1333–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Fang, S.; Luo, D.; Yang, L.; Hirano, S. A Safe Electrolyte Based on Propylene Carbonate and Non-Flammable Hydrofluoroether for High-Performance Lithium Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, 1991–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Chen, L.; Borodin, O.; Ji, X.; Chen, J.; Hou, S.; Deng, T.; Zheng, J.; Yang, C.; Liou, S.; et al. batteries with aggressive cathode chemistries. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Murugesan, V.; Han, K.S.; Jiang, X.; Cao, Y.; Xiao, L. Non-flammable electrolytes with high salt-to-solvent ratios for Li-ion and Li-metal batteries. Nat. Energy 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quang, H.; Lee, H.; Hwang, E.; Kwon, Y.; Song, S. Non-flammable organic liquid electrolyte for high-safety and high-energy density Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2018, 404, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yamada, C.; Naito, H.; Segami, G.; Kibe, K. High-Concentration Trimethyl Phosphate-Based Nonflammable Electrolytes with Improved Charge—Discharge Performance of a Graphite Anode for Lithium-Ion Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Nakahara, K.; Inoue, K.; Iwasa, S. Performance Improvement of Li Ion Battery with Non-Flammable TMP Mixed Electrolyte by Optimization of Lithium Salt Concentration and SEI Preformation Technique on Graphite Anode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, 831–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalavi, S.; Xu, M.; Ravdel, B.; Zhou, L.; Lucht, B.L. Nonflammable Electrolytes for Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinov, Y.; Aoki, M.; Mimura, H.; Fujii, K.; Yoshimoto, N.; Morita, M. Thermal and electrochemical properties of nonflammable electrolyte solutions containing fluorinated alkylphosphates for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2016, 332, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurc, B. Electrolyte Working in a lithium-ion batteries with a LiNiO2 Cathode. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 13, 5938–5955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fan, C.; Zhang, J.; Wu, X. A promising PMHS/PEO blend polymer electrolyte for all-solid-state lithium ion batteries. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 14932–14937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, P.; Zheng, H.; Liang, X.; Sun, Y.; Cheng, S.; Chen, C.; Xiang, H. A highly concentrated phosphate-based electrolyte for high-safety rechargeable lithium batteries. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 4453–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, P.; Streipert, B.; Krafft, R.; Murmann, P.; Wagner, R.; Winter, M.; Cekic-laskovic, I. Shutdown potential adjustment of modi fi ed carbene adducts as additives for lithium ion battery electrolytes. J. Power Sources 2017, 367, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamaani, A.; Safa, M.; Chawla, N.; El-Zahab, B. Composite Gel polymer electrolyte for improved cyclability in lithium-oxygen batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 33819–33826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safa, M.; Hao, Y.; Chamaani, A.; Adelowo, E.; Chawla, N.; Wang, C.; El-Zahab, B. Capacity Fading Mechanism in Lithium-Sulfur Battery using Poly(ionic liquid) Gel Electrolyte. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 258, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamaani, A.; Chawla, N.; Safa, M.; El-Zahab, B. One-Dimensional Glass Micro-Fillers in Gel Polymer Electrolytes for Li-O2 Battery Applications. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 235, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamaani, A.; Safa, M.; Chawla, N.; Herndon, M.; El-zahab, B. Stabilizing e ff ect of ion complex formation in lithium—Oxygen battery electrolytes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 815, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, M.; Janakiraman, S.; Ghosh, S.; Venimadhav, A.; Anandhan, S. PVDF/Halloysite Nanocomposite-Based Non-Wovens as Gel Polymer Electrolyte for High Safety Lithium Ion Battery. Polym. Compos. 2018, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, P.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, G.; Liu, H.; Li, S.; Tang, C.; Mei, J.; Li, Y. Robust Succinonitrile-Based Gel Polymer Electrolyte for Lithium-Ion Batteries Withstanding Mechanical Folding and High Temperature. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 25384–25392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Zhu, F.; Zhao, H. Blending based polyacrylonitrile/poly (vinyl alcohol) membrane for rechargeable lithium ion batteries. J. Memb. Sci. 2018, 560, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Que, M.; Xiao, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Yuan, K.; Chen, Y. A facile in situ approach to ion gel based polymer electrolytes for flexible lithium batteries. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 54391–54398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilbig, P.; Ibing, L.; Wagner, R.; Winter, M.; Cekic-Laskovic, I. Ethyl Methyl Sulfone-Based Electrolytes for Lithium Ion Battery Applications. Energies 2017, 10, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lou, H.; Xu, H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Q.; Shi, Q.; Deng, Y. High voltage, solvent-free solid polymer electrolyte based on a star-comb PDLLA–PEG copolymer for lithium ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 6373–6380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.; Ok, D.; Kim, S.; Ho, J.; Man, K.; Oh, J.; Kim, J.; Ju, M.; Yang, Y.; Lee, S.; et al. Reversible thixotropic gel electrolytes for safer and shape-versatile lithium- ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2018, 401, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Han, Y.; Wang, H.; Xiong, S.; Sun, W.; Zheng, C.; Xie, K. Liquid Gel Polymer Electrolytes for High Safety Rechargeable Solid- State Lithium Metal Batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 10334–10342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Soucek, M.D.; Kyu, T. Fully flexible lithium ion battery based on a flame retardant, solid-state polymer electrolyte membrane. Solid State Ionics 2018, 320, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ma, J.; Chai, J.; Liu, Z.; Ding, G.; Xu, G.; Liu, H. Two Players Make a Formidable Combination: In Situ Generated Poly(acrylic anhydride-2-methyl-acrylic acid-2-oxirane-ethyl ester-methyl methacrylate) Cross-Linking Gel Polymer Electrolyte toward 5 V High-Voltage Batteries. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 41462–41472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, L.; Yang, K.; Wang, H.; Yu, C.; Xu, D.; Xu, B.; Wang, L. Superior Blends Solid Polymer Electrolyte with Integrated Hierarchical Architectures for All-Solid-State Lithium-Ion Batteries. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 36886–36896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Han, T.; Jeong, J.; Lee, H.; Ryou, M.; Min, Y. A Flame-Retardant Composite Polymer Electrolyte for Lithium-Ion Polymer Batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 241, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, R.; Chen, N.; Chen, Y.; Ye, Y. Ionic liquid-based electrolyte with binary lithium salts for high performance lithium e sulfur batteries. J. Power Sources 2015, 296, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Saka, T.; Yosh, N.; Fuj, K. Electrochemical Properties of a Tetra PEG-based Gel Electrolyte Containing a Nonflammable Fluorinated Alkyl Phosphate for Safer Lithium-ion Batteries. Chem. Lett. 2018, 909–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Chen, X.; Miao, L.; Chen, J.; Zheng, J. A hybridized solid-gel nonflammable Li-Battery. J. Power Sources 2018, 394, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Onishi, H.; Wagner, R.; Winter, M.; Cekic-laskovic, I. Intrinsically Safe Gel Polymer Electrolyte Comprising Flame- Retarding Polymer Matrix for Lithium Ion Battery Application. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 42348–42355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Du, C.; Wang, S.; Chen, S. Three new bifunctional additive for safer nickel-cobalt-aluminum based lithium ion batteries. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2018, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
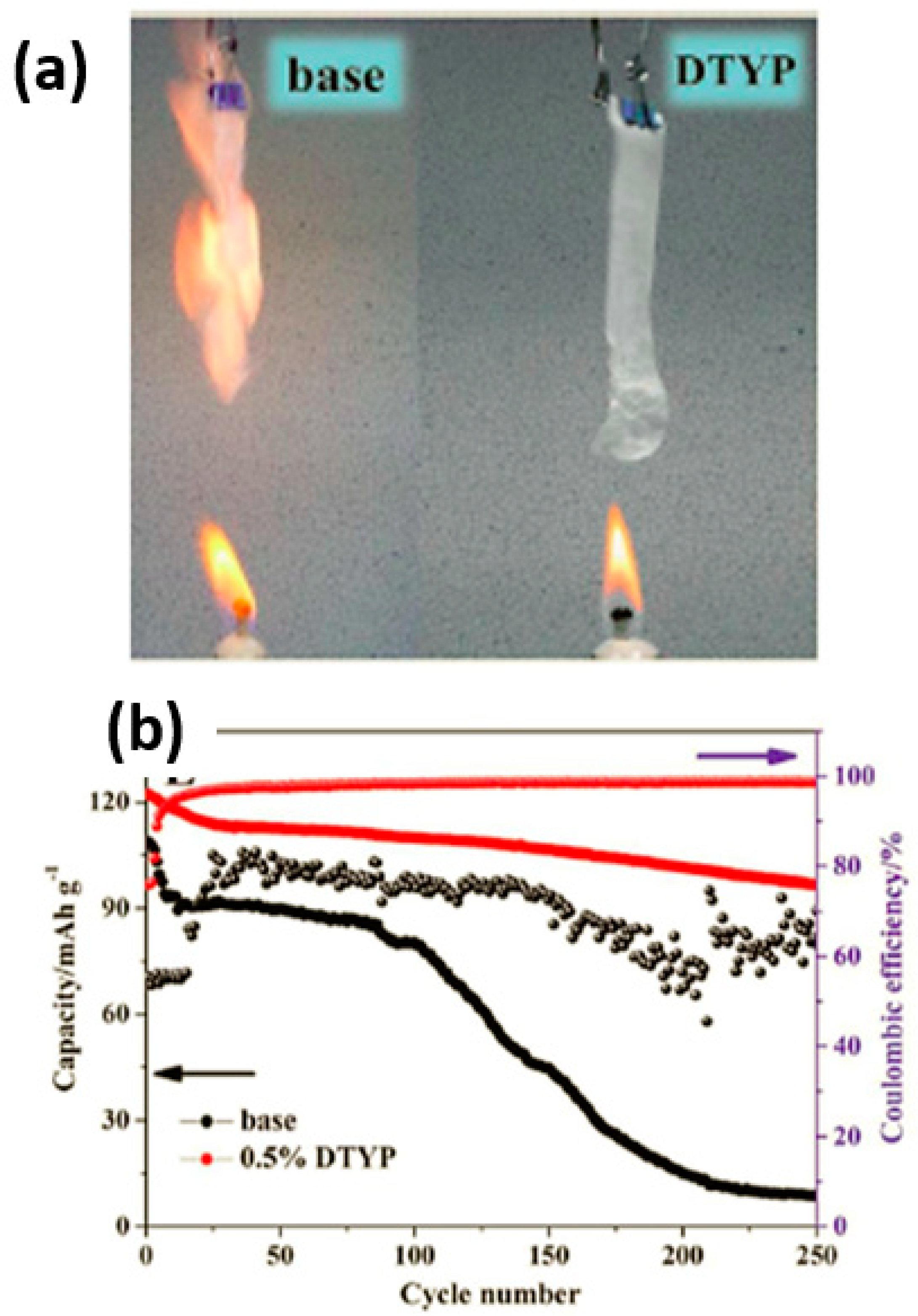
- Zhu, Y.; Luo, X.; Zhi, H.; Liao, Y.; Xing, L.; Xu, M.; Liu, X.; Xu, K.; Li, W. Diethyl(thiophen-2-ylmethyl)phosphonate: A novel multifunctional electrolyte additive for high voltage batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 10990–11004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
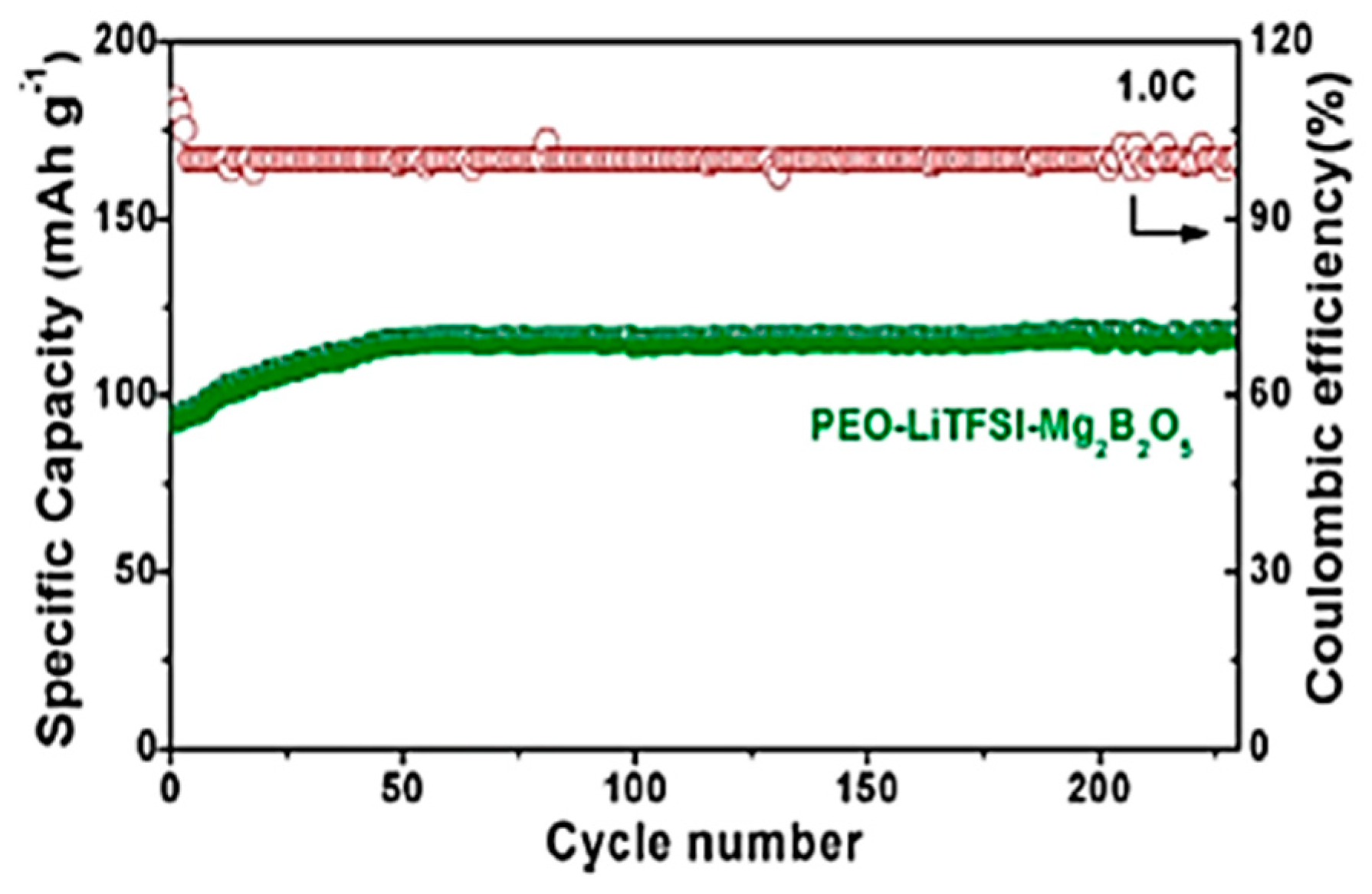
- Sheng, O.; Jin, C.; Luo, J.; Yuan, H.; Huang, H.; Gan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xia, Y.; Liang, C.; Zhang, W.; et al. Mg2B2O5 Nanowire Enabled Multifunctional Solid-State Electrolytes with High Ionic Conductivity, Excellent Mechanical Properties, and Flame-Retardant Performance. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 3104–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
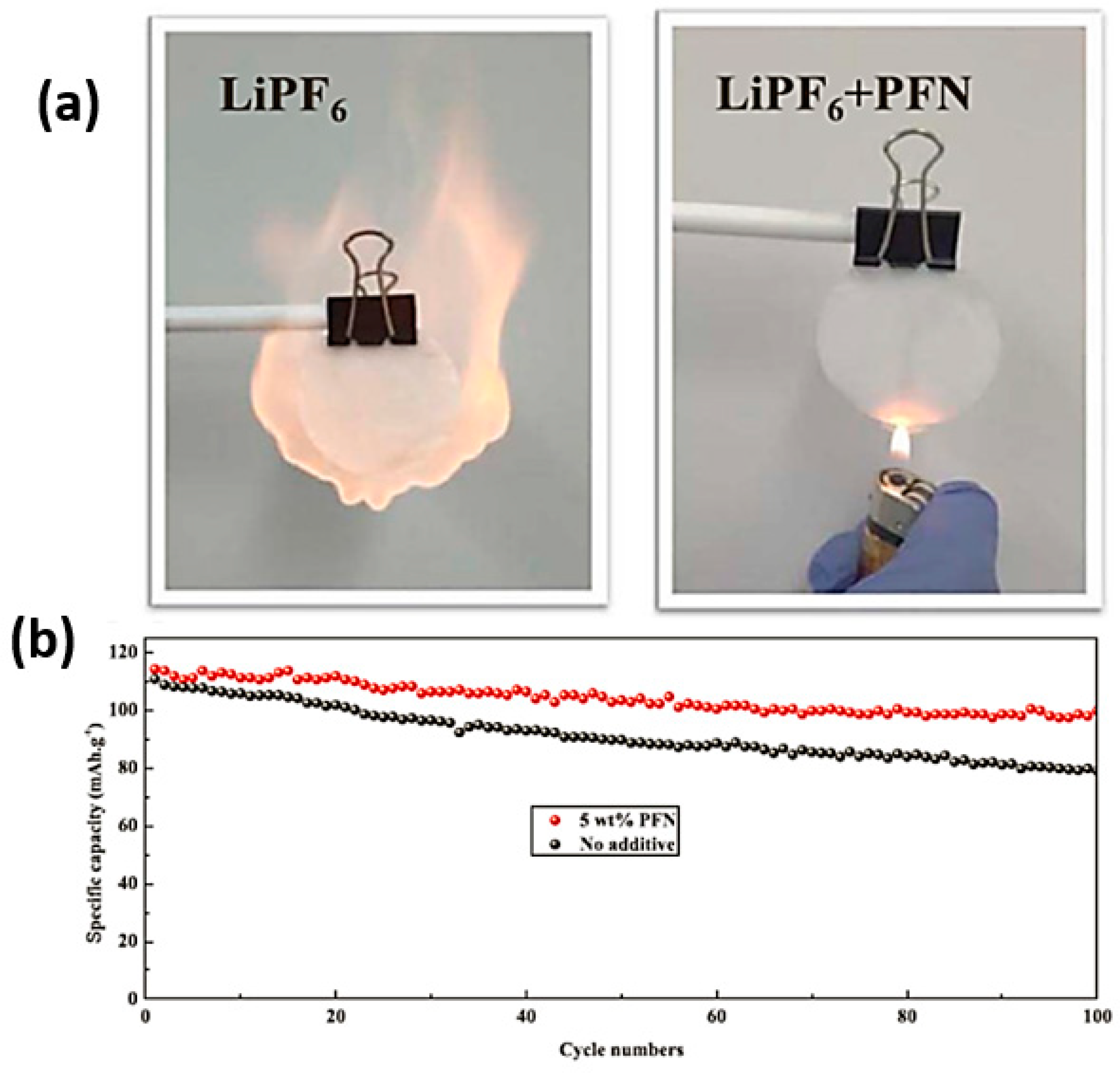
- Liu, J.; Song, X.; Zhou, L.; Wang, S.; Song, W.; Liu, W.; Long, H. Nano Energy Fluorinated phosphazene derivative—A promising electrolyte additive for high voltage lithium ion batteries: From electrochemical performance to corrosion mechanism. Nano Energy 2018, 46, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, W.; Chen, L.; Lu, Y.; Su, Y.; Bao, L.; Wang, J. Ethoxy (penta fluoro) cyclotriphosphazene (PFPN) as a multi-functional flame retardant electrolyte additive for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2018, 378, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Qin, C.; Liu, Z.; Feng, L.; Su, X.; Chen, Y.; Xia, L.; Xia, Y.; Liu, Z. Applied Surface Science Enhanced high voltage cyclability of LiCoO2 cathode by adopting poly [bis-(ethoxyethoxyethoxy) phosphazene] with flame-retardant property as an electrolyte additive for lithium-ion batteries. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 403, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Suo, L.; Wang, F.; Eidson, N.; Yang, C.; Han, F.; Ma, Z.; Gao, T.; Zhu, M.; Wang, C. “Water-in-Salt” electrolyte enabled LiMn2O4/TiS2Lithium-ion batteries. Electrochem. Commun. 2017, 82, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
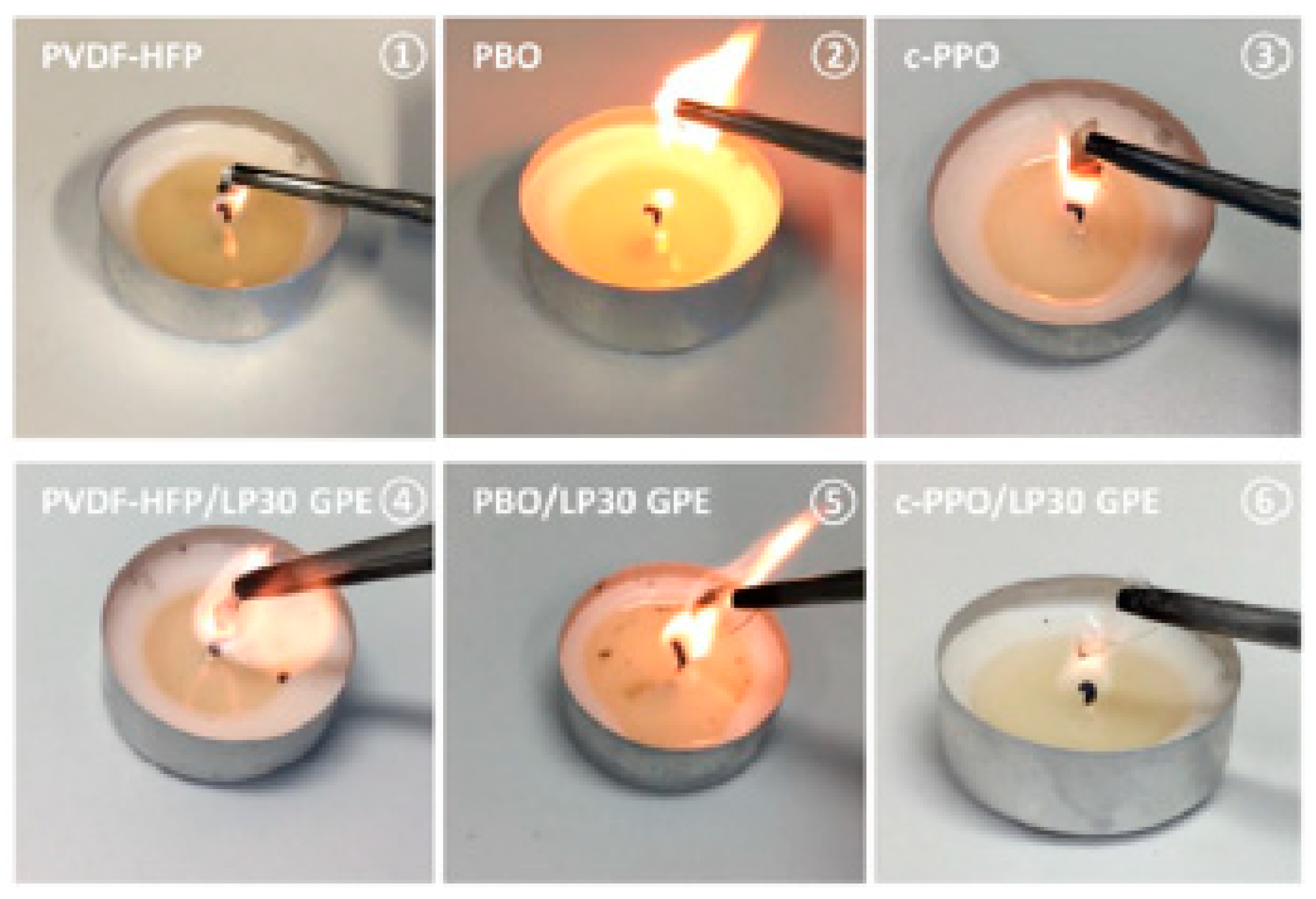
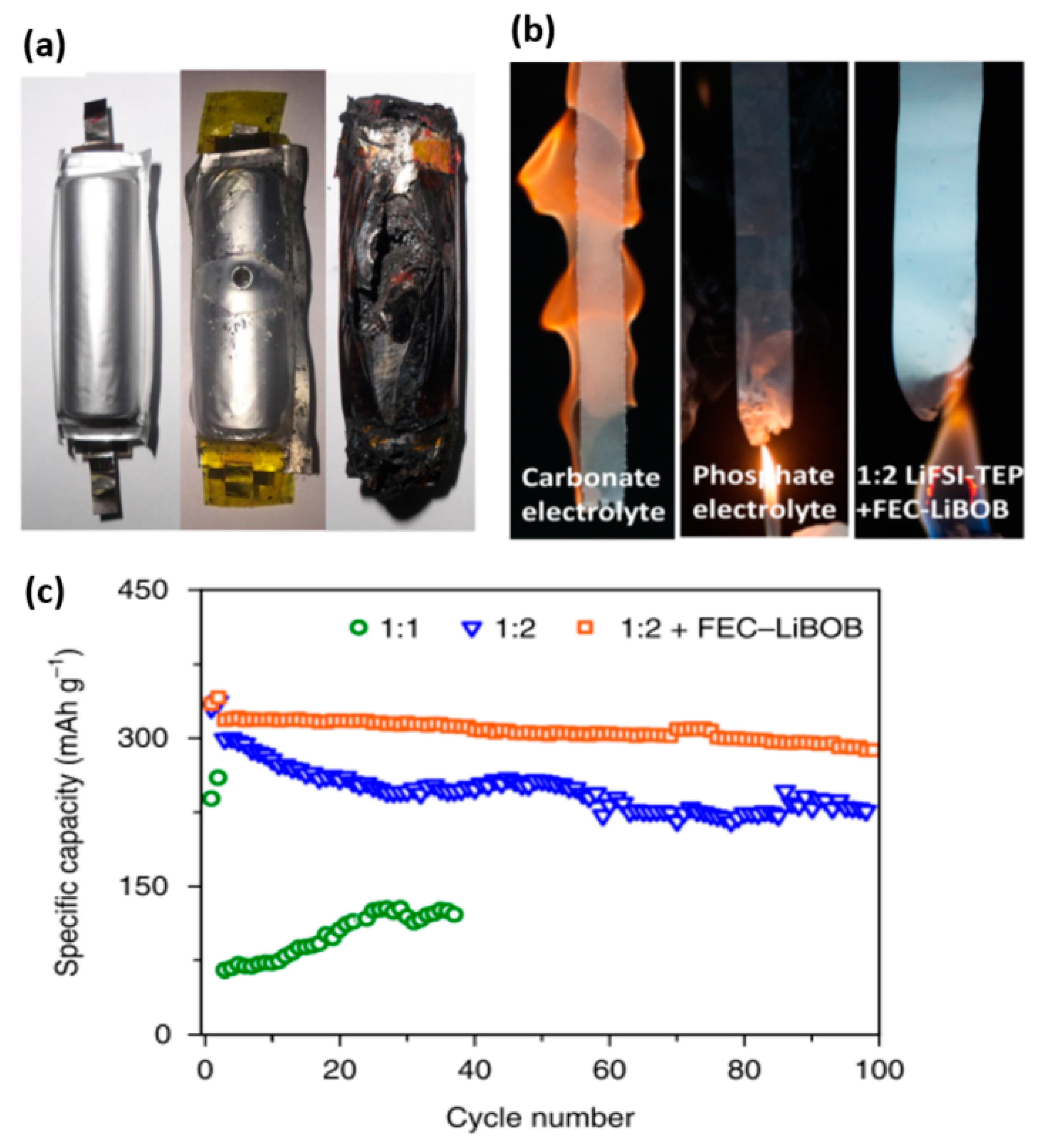
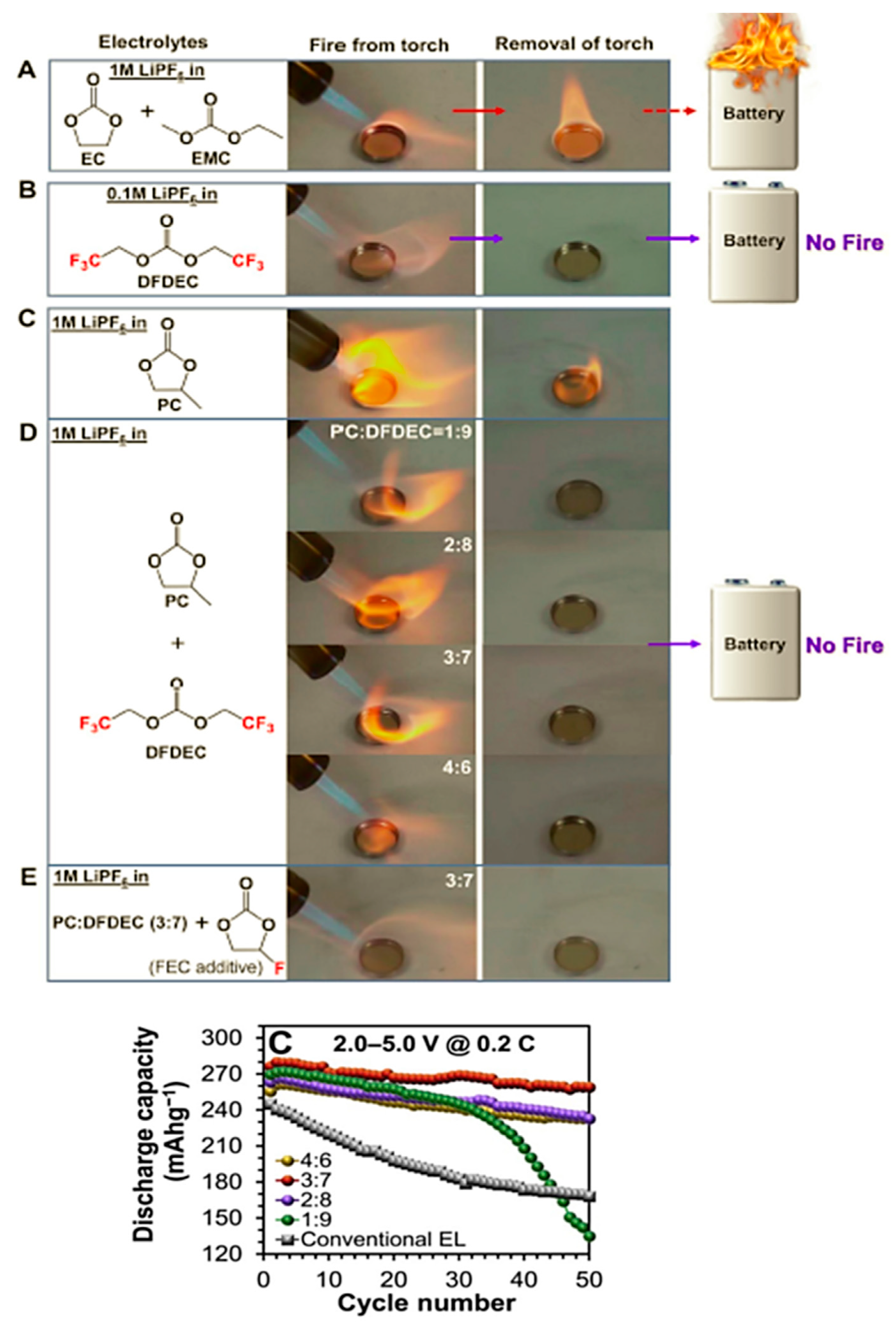
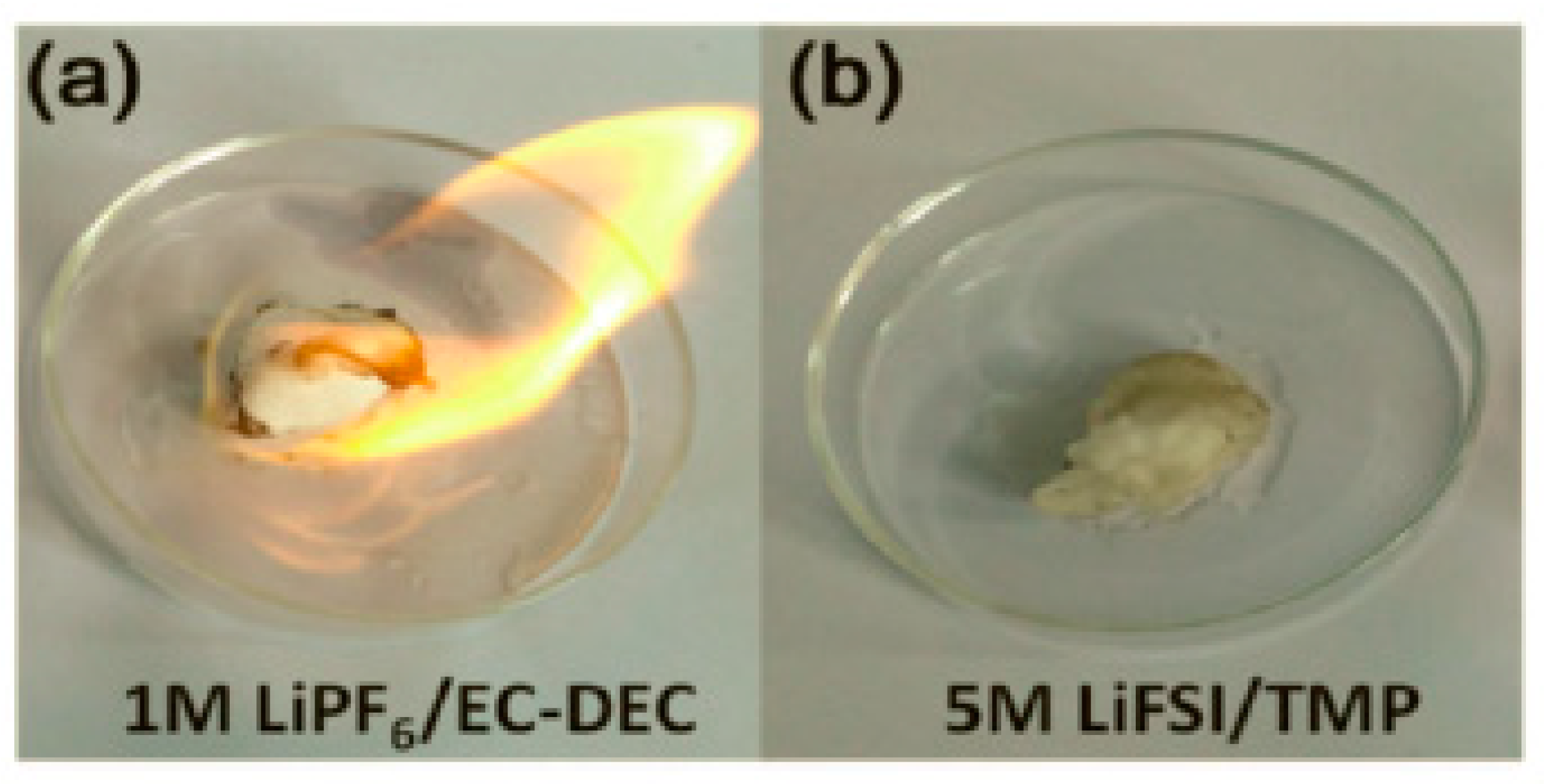
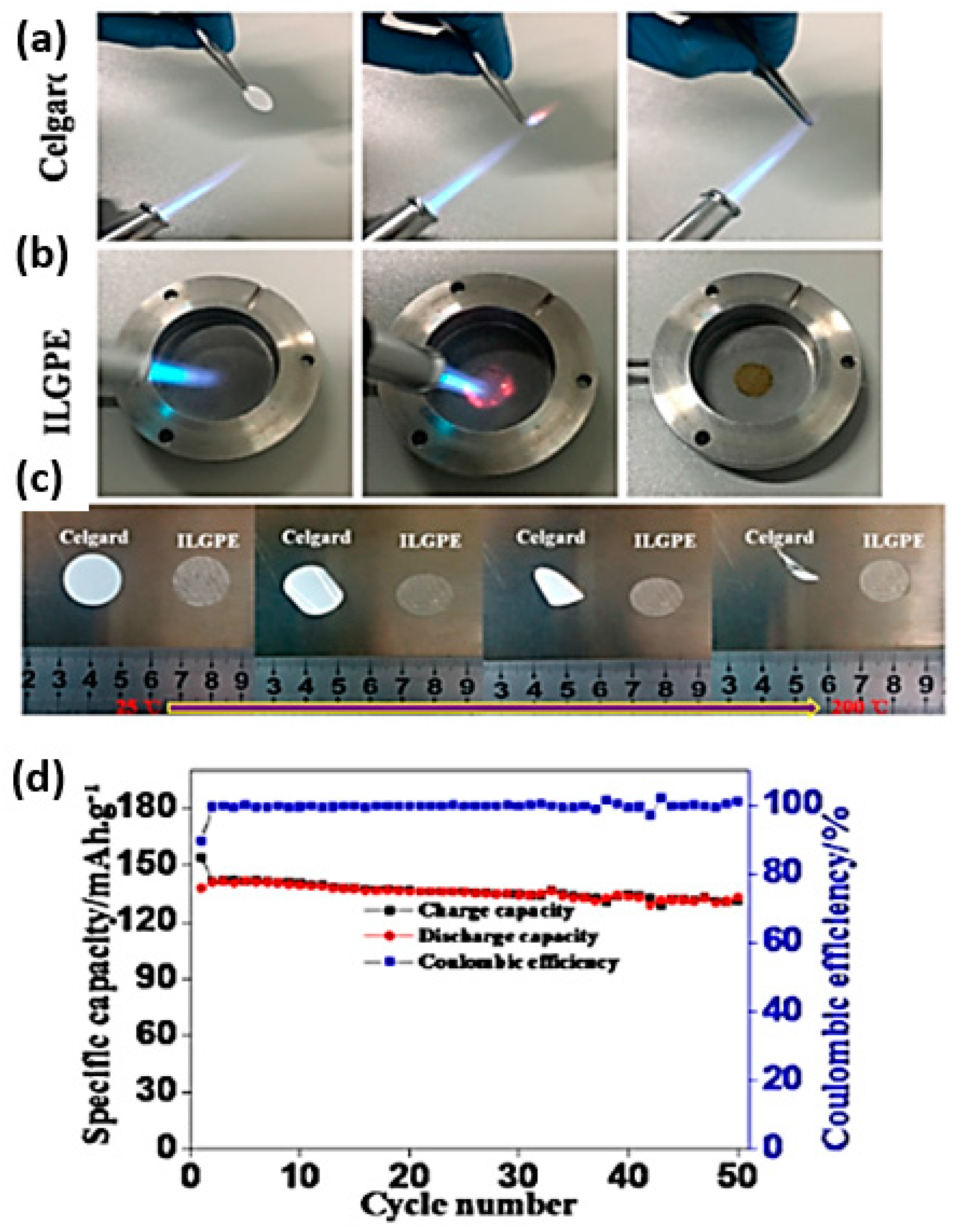
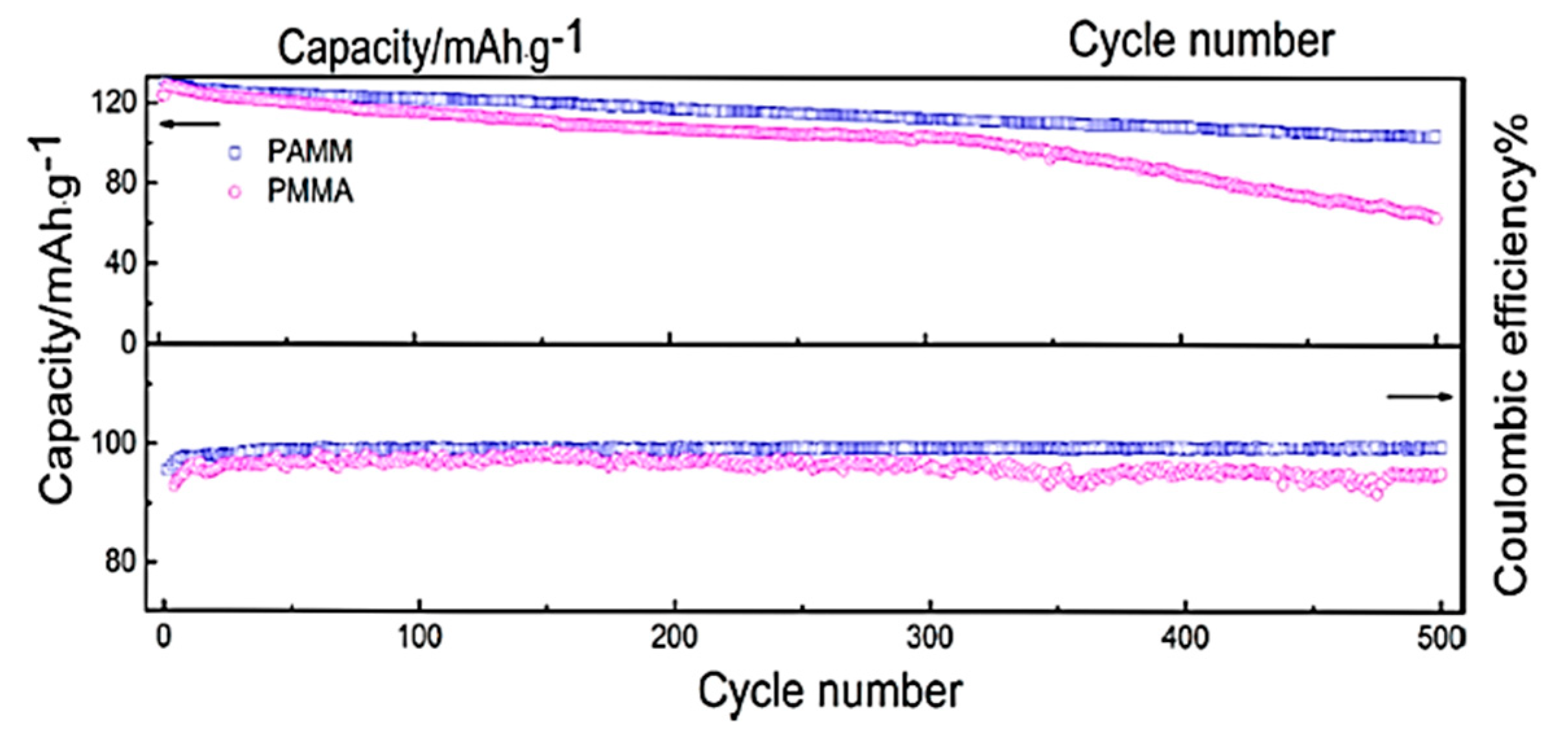
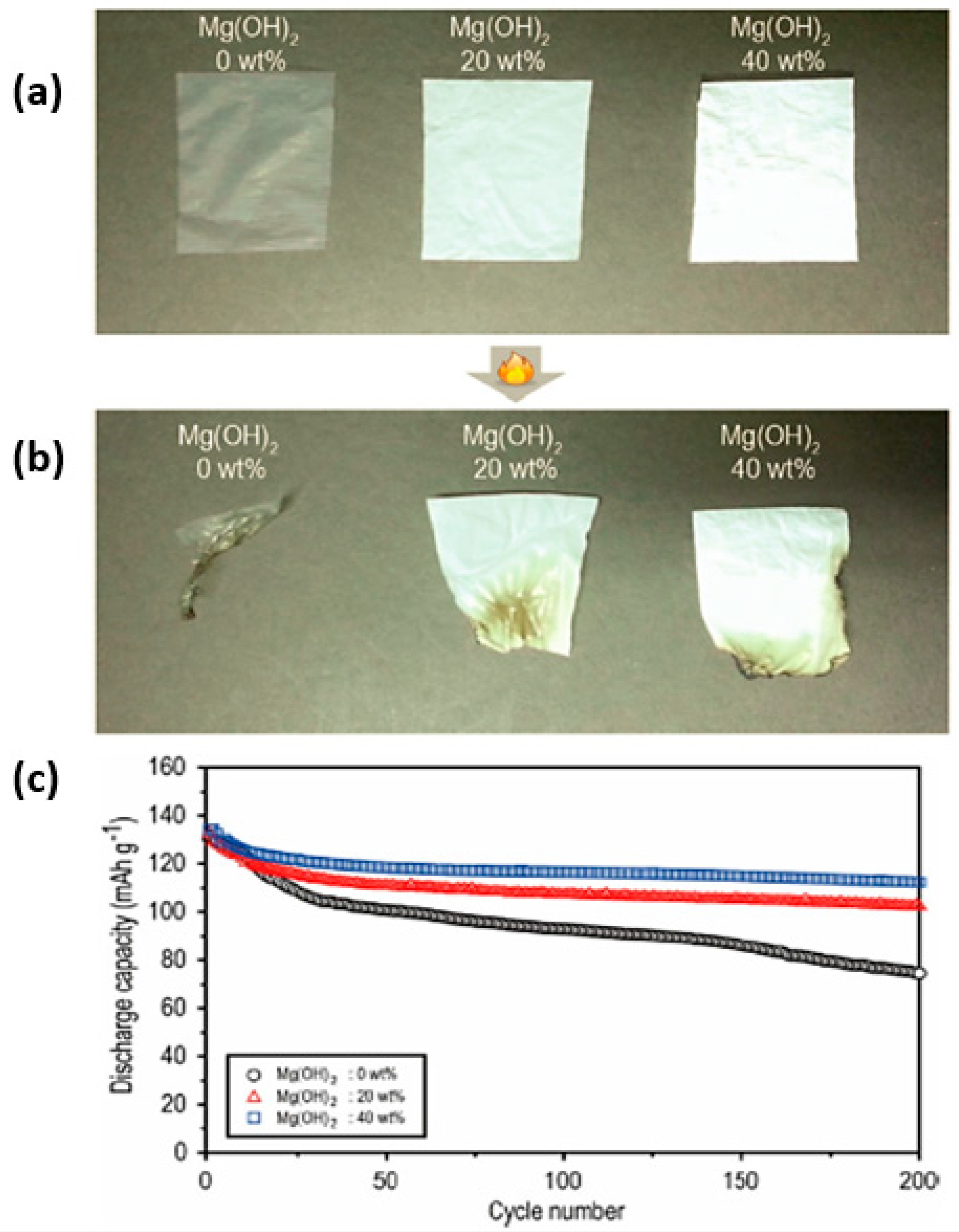
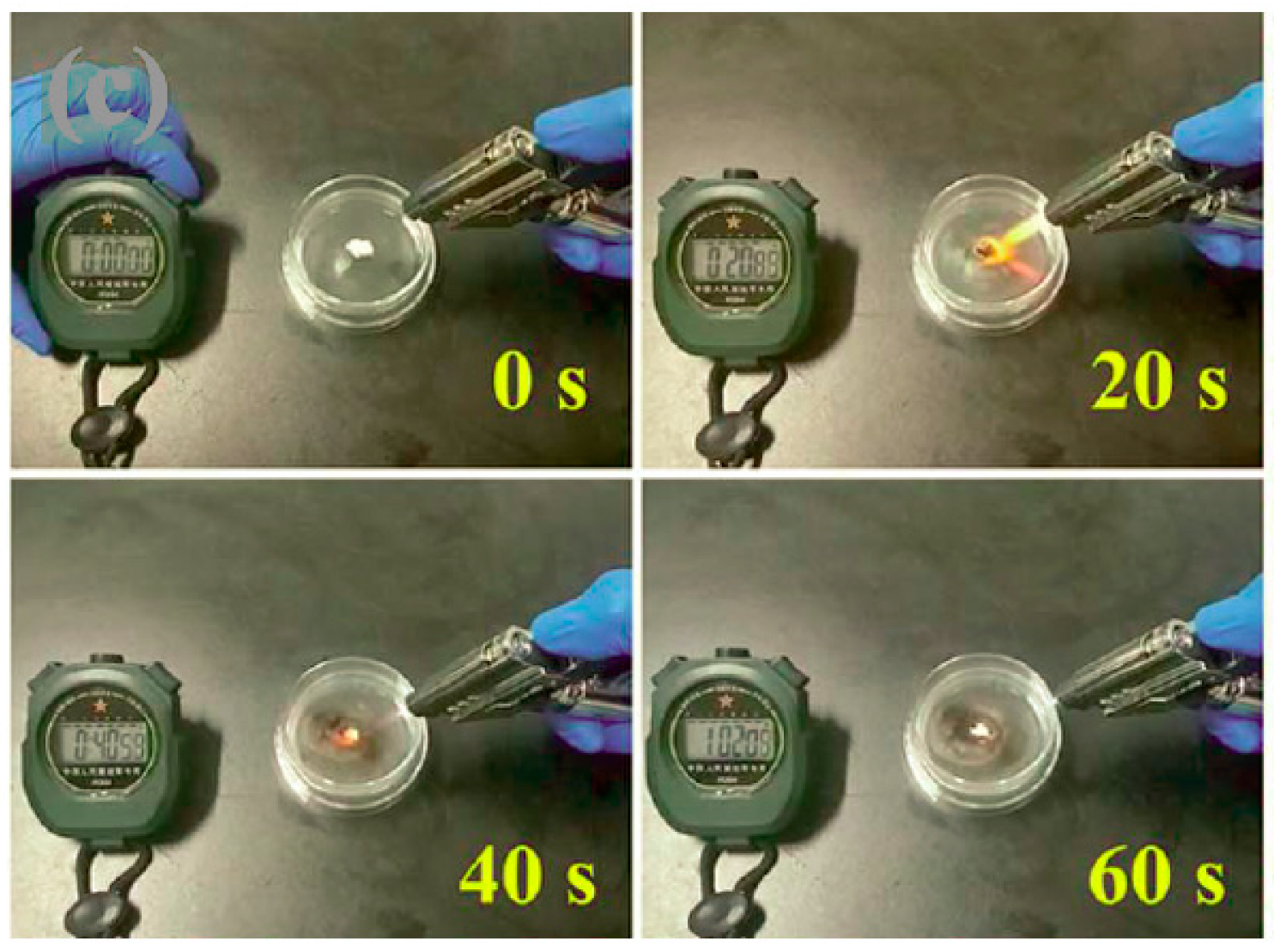

| Electrolyte Composition | Cathode/Battery Type | Discharge Capacity (mAh·g−1) | Number of Cycles | Capacity Retention | Rate | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DFSM2/EMC (2/3/5 in vol.) + 5 wt% FEC | LiCoO2(LCO)/graphite full cell | 135 | 92% | [11] | ||
| SN1IL/DMC (v/v = 1/1) doped with 0.6 M LiPF6/0.4 M LiODFB salts | LiCoO2/graphite full cell | 152 | ~90 | 72% | 2C | [12] |
| 1 M LiPF6 P13-TFSI/EC (1/1) w/w 5% FEC | Graphite/Li half batteries | 115 | ~100 | 95% | C/12 | [13] |
| inorganic non-aqueous liquid electrolyte-LiAlCl4,3SO2 (IE) | LiFePO4 | 113 | ~100 | 94% | 5C | [14] |
| 5.3 M LiFSA/TMP | LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4/graphite/Li half batteries | 250 | 1200 | 99% | C/5 | [23] |
| ADN + LiTFSI | LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 (NMC) | 165 | ~200 | 98% | 0.5C | [24] |
| LiBOB-based electrolyte | graphite/LiCo1/3Mn1/3Ni1/3O2 full cell | 108 | ~500 | 80% | 1C | [10] |
| 1 M LiPF6 in FEC:FEMC:HFE (w/w/w = 2/6/2) | Li/LCP cell | 1000 | 93% | 1C | [26] | |
| 1:2 LiFSI–TEP with FEC–LiBOB composite additives | Li–Cu half cells | 135 | 350 | 88% | 0.05C | [27] |
| 1 M Li-LiPF6 in PC and fluorinated linear carbonate co-solvents | LMNC/graphite full cell | 250 | 100 | 72% | 0.2C | [28] |
| 2 M LiPF6 in EC:DEC:TMP | LiMn2O4 cathode | 34 | 50 | 97% | 0.2C | [30] |
| 1 M LiPF6 in TMS + 10% VC electrolyte | LiNiO2 | 145 | 195 | [33] | ||
| 5 M LiFSI/TMP | Li/LiFePO4 battery | 118 | 400 | 99% | 0.5C | [35] |
| GPE based on electro-spun PVDF/HNT nano-composite non-wovens | LiCoO2 | 138 | 50 | 97% | 0.1C | [41] |
| P(MMA-AN-EA) + EMITFSI | LiFePO4 | 100 | 95% | 0.2C | [13] | |
| GPE-SN-IM | LiCoO2/Li4Ti5O12 film battery | 132 | 100 | 92% | 0.2C | [42] |
| PAN/PVA (20:80 ratio) blending membrane-based GPE | LiCoO2 | 160 | 200 | 96% | 1C | [43] |
| IPN-GPE with 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC/DEC ¼ 1/1/1, v/v/v, liquid electrolyte | LiFePO4 | 143 | 100 | 94% | [44] | |
| 4% FEC to the 1 MLiPF6 in EMS electrolyte | NMC/graphite cells | 325 | 100 | 99% | 0.1C | [45] |
| LFP/PDLLA–SPE/Li | LiFePO4 | 144.7 | 250 | 87% | [46] | |
| 1.0 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC mixed with 700 wt.% polymer | LiCoO2/graphite electrodes | 300 | 74% | 0.1C | [47] | |
| ILGPEs supported by 10% LAGP | LiFePO4 | 131 | 50 | 0.05C | [48] | |
| PEM based on PEGBCDMA | LiFePO4 | 125 | 250 | 80% | C/3 | [49] |
| PAMM-based gel polymer electrolyte | LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4/Li and LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4/Li4Ti5O12 batteries | 128 | 100 | 96% | 0.1C | [50] |
| Solid polymer electrolyte: PCL/SN blends with PAN-skeleton | LiFePO4 | 101 | 400 | 100% | 1C | [51] |
| 40 wt.% Mg(OH)2 added to electrolyte | LiCoO2/graphite | 112 | 200 | 83% | 0.5C | [52] |
| Ionogel electrolyte | LiFePO4 | 136 | 200 | [53] | ||
| Tetra PEG gel mixed with 1.0 M LiPF6 in an EC + DEC + TFEP mixture (v/v/v = 53/27/20) electrolyte | LiFePO4 | 128 | 10 | 95% | 0.1C | [54] |
| PAEKNW) cross-linked with poly(ethylene glycol) dimethacrylate electrolyte | LiFePO4 | 128 | 200 | 90% | 1C | [55] |
| 5 wt.% TFPCT | NCA/Li half-cell | 120 | 100 | 92% | 0.5C | [57] |
| 0.5% DTYP additive in base electrolyte | LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4/graphite full cells | 125 | 280 | 1C | [58] | |
| poly (ethylene oxide)-LiTFSi-Mg2B2O5 electrolyte | LiFePO4 | 120 | 230 | 1C | [59] | |
| 5 wt.% PFN-containing electrolyte | LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode | ~110 | 100 | 1C | [60] | |
| 5% PFPN | LiCoO2 | 150.7 | 30 | 99% | 0.1C | [61] |
| 5 wt.% EEEP in electrolyte | LiCoO2 | 100 | 91% | [62] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chawla, N.; Bharti, N.; Singh, S. Recent Advances in Non-Flammable Electrolytes for Safer Lithium-Ion Batteries. Batteries 2019, 5, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries5010019
Chawla N, Bharti N, Singh S. Recent Advances in Non-Flammable Electrolytes for Safer Lithium-Ion Batteries. Batteries. 2019; 5(1):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries5010019
Chicago/Turabian StyleChawla, Neha, Neelam Bharti, and Shailendra Singh. 2019. "Recent Advances in Non-Flammable Electrolytes for Safer Lithium-Ion Batteries" Batteries 5, no. 1: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries5010019
APA StyleChawla, N., Bharti, N., & Singh, S. (2019). Recent Advances in Non-Flammable Electrolytes for Safer Lithium-Ion Batteries. Batteries, 5(1), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries5010019





