Effects of Boron-Incorporation in a V-Containing Zr-Based AB2 Metal Hydride Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Composition
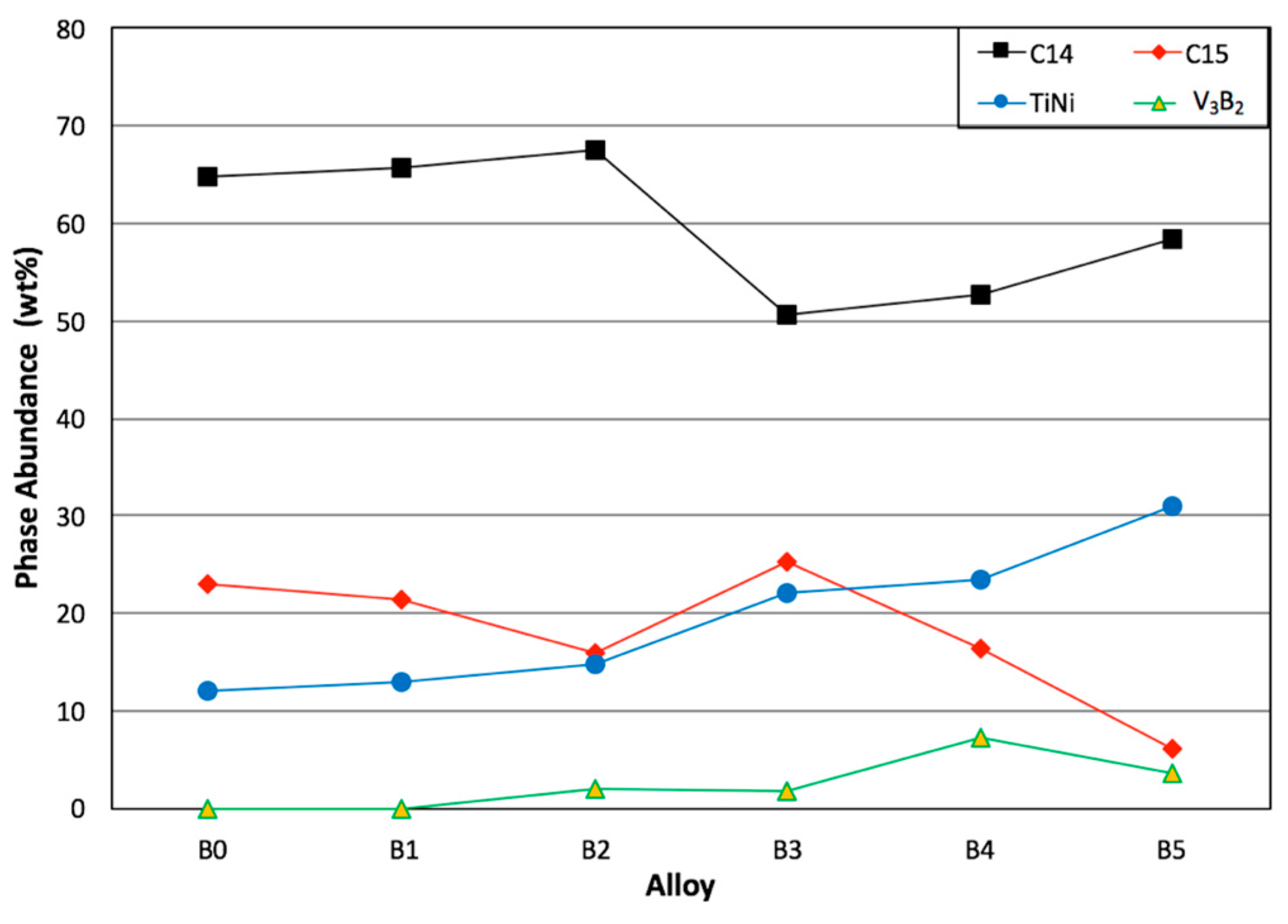
3.2. XRD Analysis
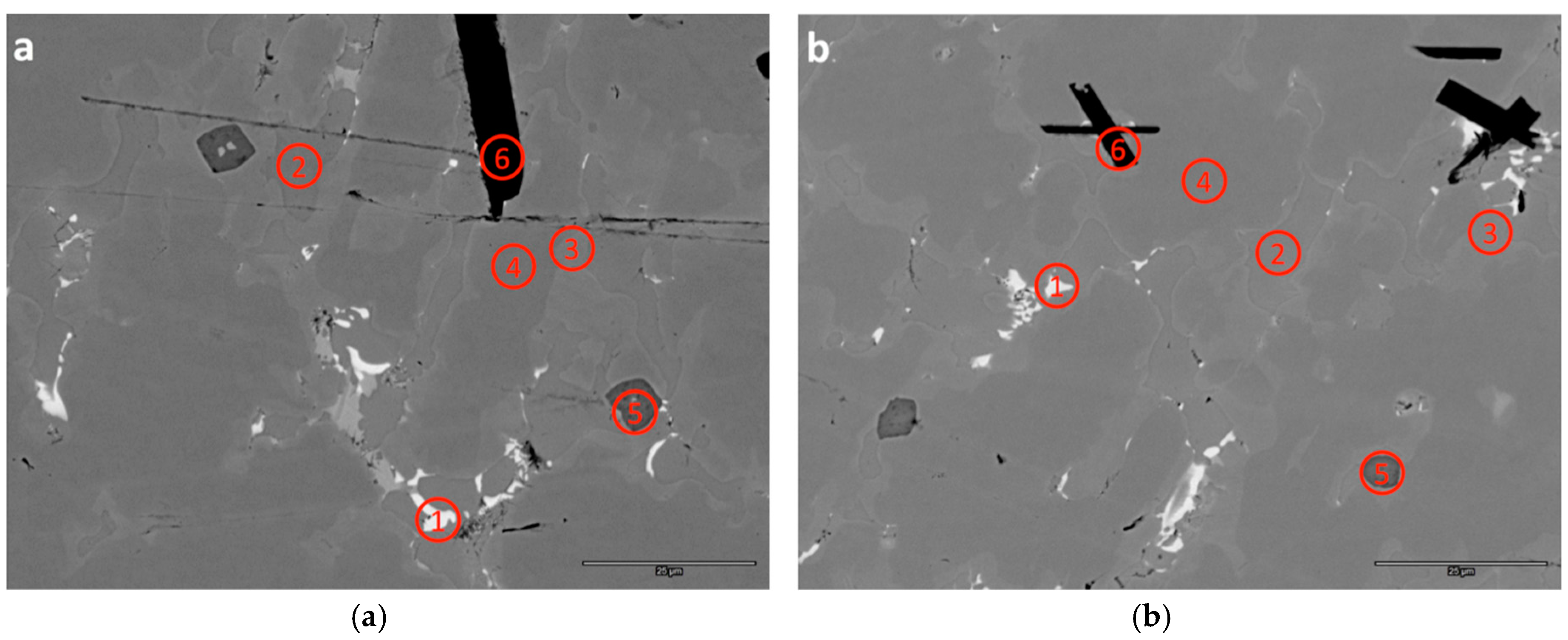
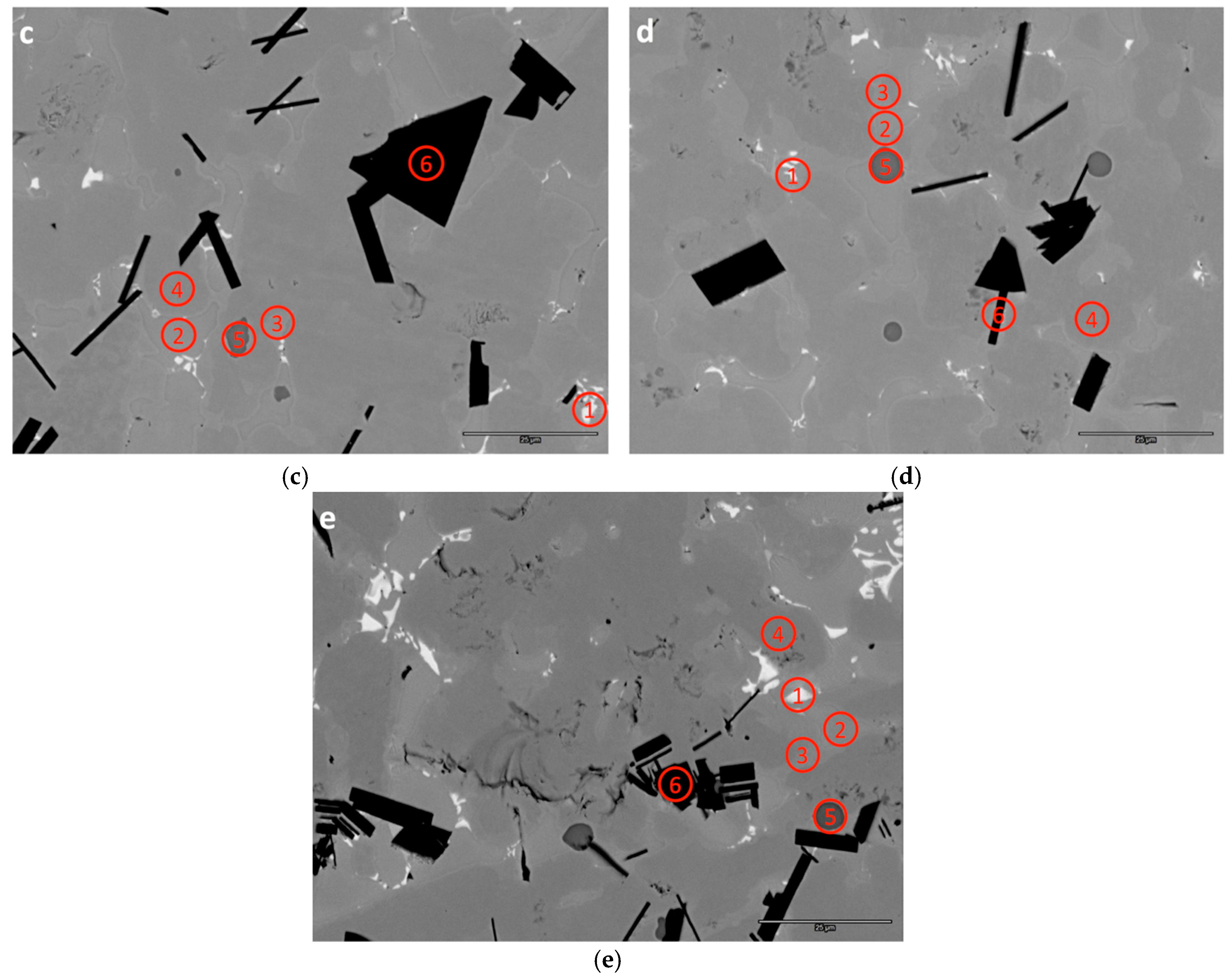
3.3. SEM/EDS Analysis
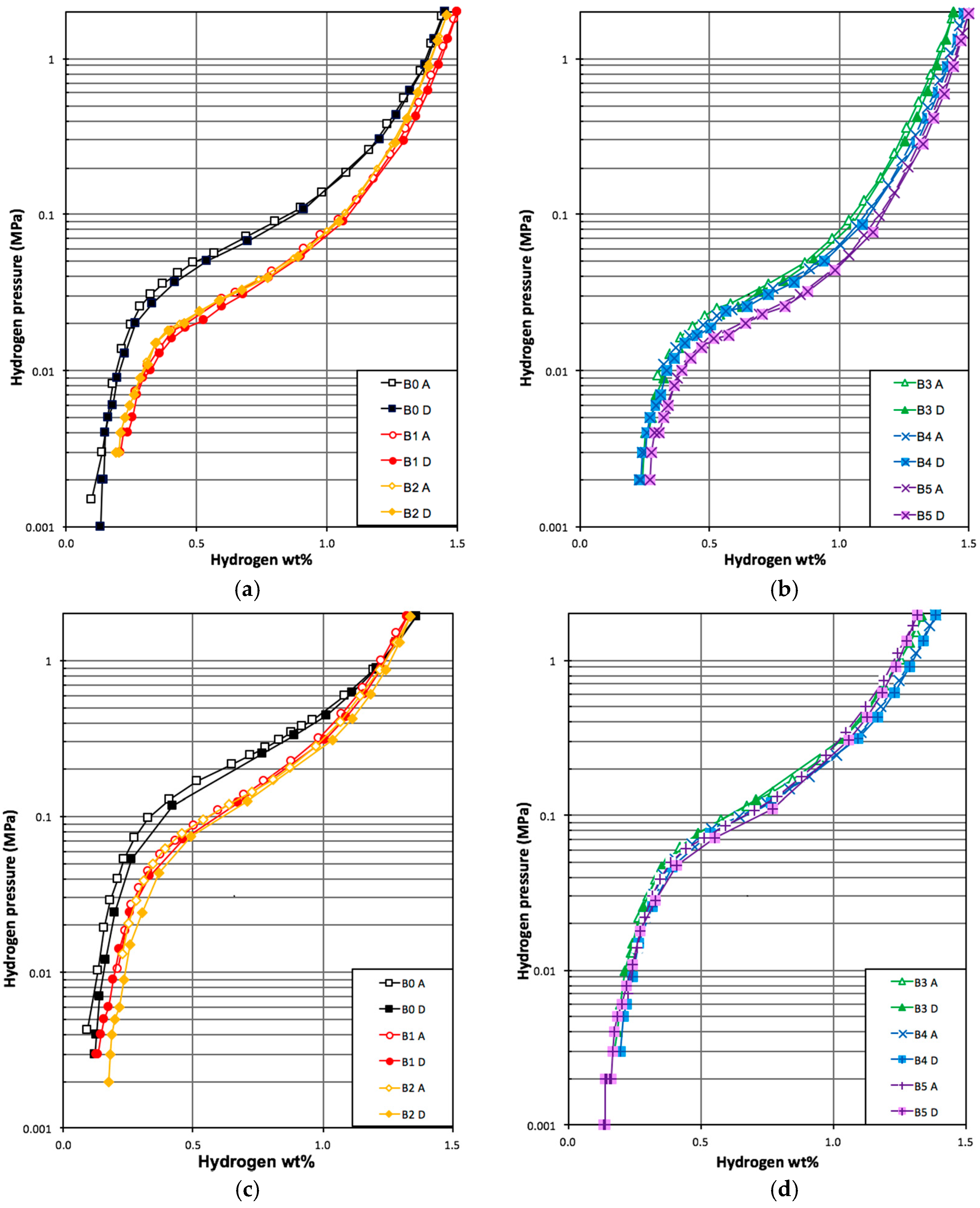
3.4. PCT Analysis
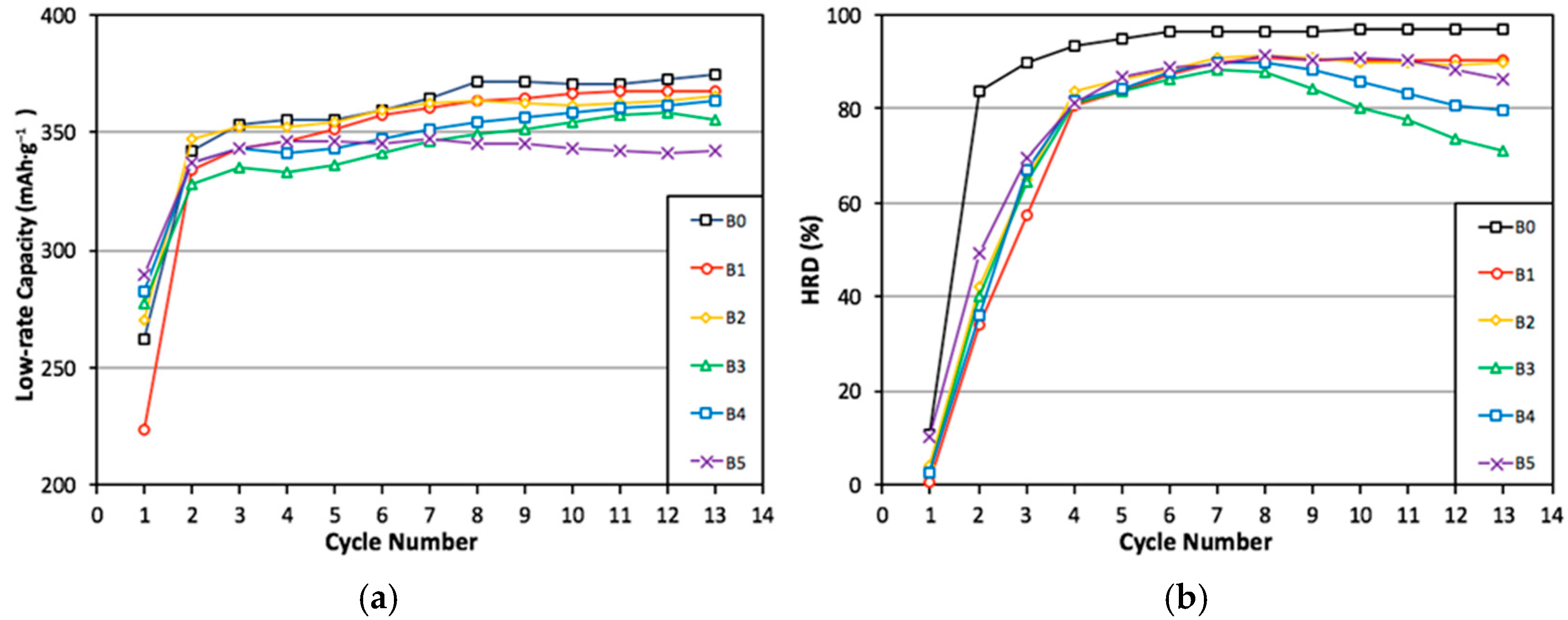
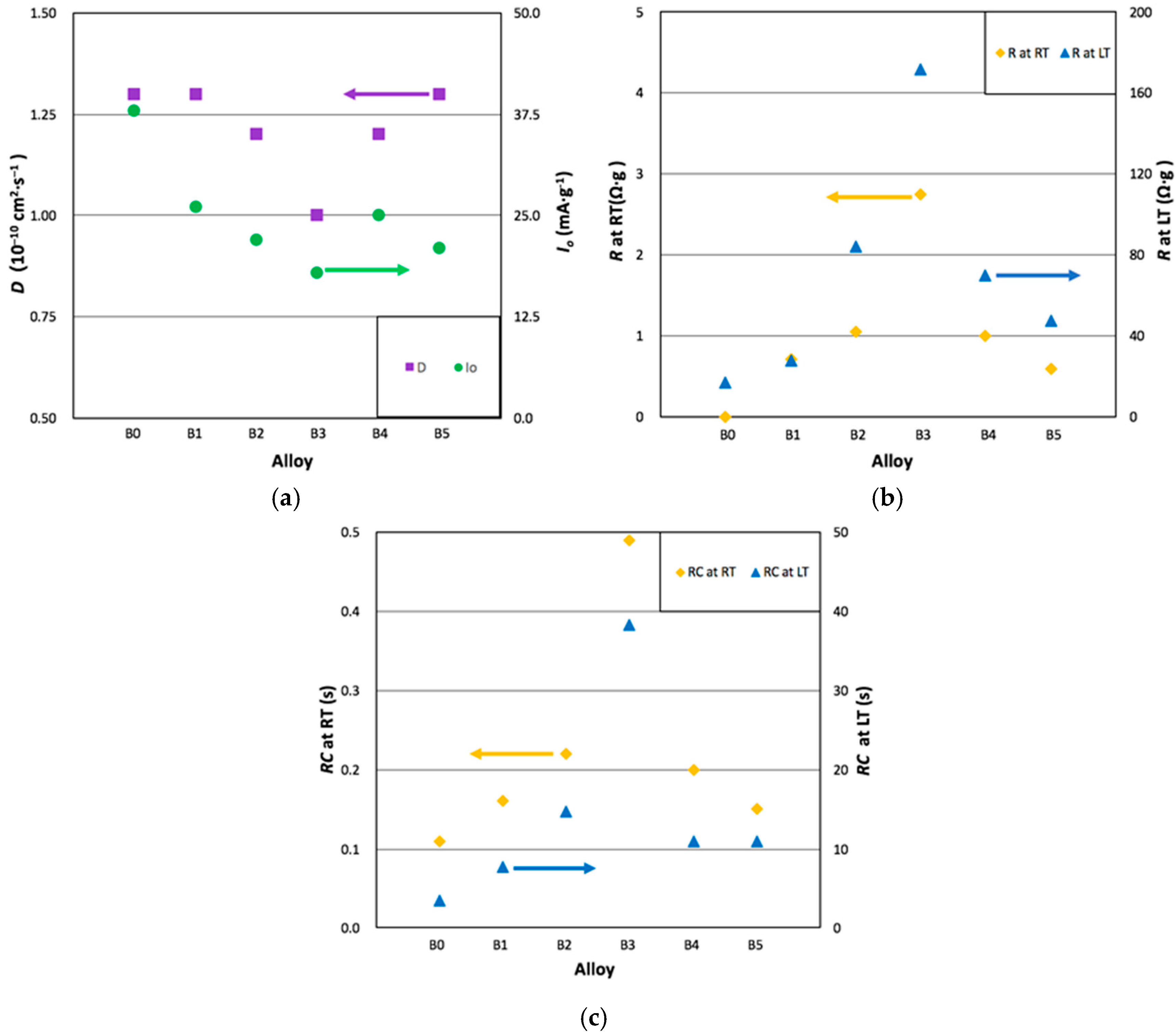
3.5. Electrochemical Analysis
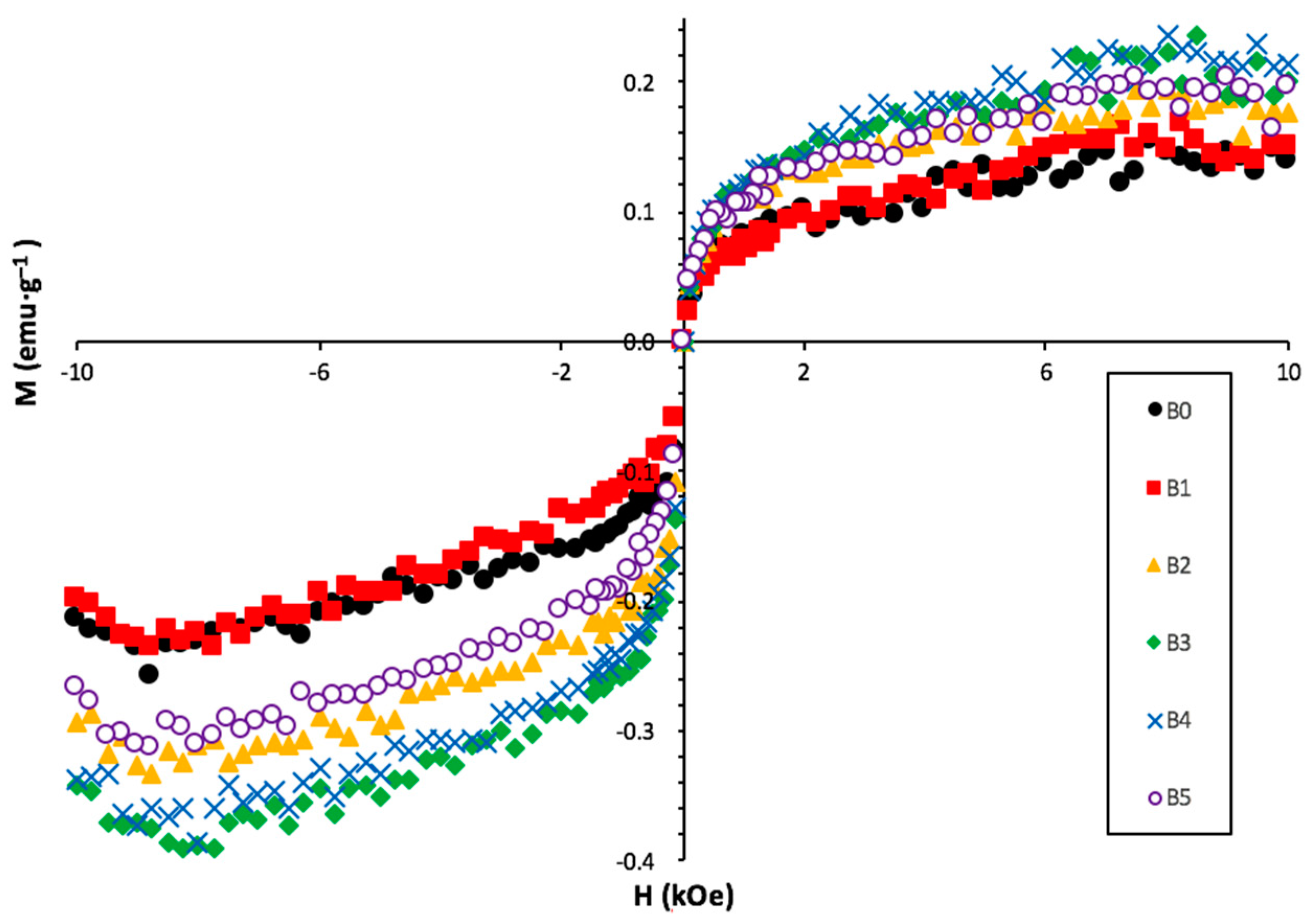
3.6. Magnetic Susceptibility
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ni/MH | Nickel/metal hydride |
| MH | Metal hydride |
| H-storage | Hydrogen-storage |
| ICP-OES | Inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometer |
| XRD | X-ray diffractometer |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| EDS | Energy dispersive spectroscopy |
| PCT | Pressure concentration temperature |
| RT | Room temperature |
| LT | Low temperature at −40 °C |
| M | Magnetic susceptibility |
| HRD | High-rate dischargeability |
| e/a | Average electron density |
| VC14 | Unit cell volume of the C14 phase |
| Unit cell volume of the V3B2 phase | |
| BEI | Back-scattering electron image |
| ∆Hh | Heat of hydride formation |
| ∆Sh | Change in entropy |
| SF | Slope factor |
| DOD | Degree of disorder |
| T | Absolute temperature |
| R | Ideal gas constant |
| Io | Surface exchange current |
| D | Bulk diffusion coefficient |
| R | Surface charge-transfer resistance |
| C | Surface double-layer capacitance |
| MS | Saturated magnetic susceptibility |
| H1/2 | Applied magnetic field strength corresponding to half of saturated magnetic susceptibility |
References
- Zelinsky, M.A.; Koch, J.M.; Young, K. Performance comparison of rechargeable batteries for stationary applications (Ni/MH vs. Ni-Cd and VRLA). Batteries. submitted.
- Young, K.; Ng, K.Y.S.; Bendersky, L.A. A technical report of the Robust Affordable Next Generation Energy Storage System-BASF program. Batteries 2016, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Nei, J. The current status of hydrogen storage alloy development for electrochemical applications. Materials 2013, 6, 4574–4608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Wu, Z.; Xia, B.; Xu, N. Influence of stoichiometry and alloying elements on the crystallography and hydrogen sorption properties of TiCr based alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 397, 284–287. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.M.; Jeon, S.W.; Lee, J.Y. A study of the development of a high capacity and high performance Zr–Ti–Mn–V–Ni hydrogen storage alloy for Ni–MH rechargeable batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 1998, 279, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Chang, S.; Lin, X. C14 Laves phase metal hydride alloys for Ni/MH batteries applications. Batteries 2017, 3, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilipedia. Laves Phase. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Laves_phase (accessed on 20 October 2017).
- Shoemaker, D.P.; Shoemaker, C.B. Concerning atomic sites and capacities for hydrogen absorption in the AB2 Friauf-Laves phases. J. Less-Common Met. 1979, 68, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, I.; Stern, A.; Moran, A.; Shaltiel, D.; Davidov, D. Hydrogen absorption in (ZrxTi1−x)B2 (B = Cr, Mn) and the phenomenological model for the absorption capacity in pseudo-binary Laves-phase compounds. J. Less-Common Met. 1980, 73, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Ouchi, T.; Koch, J.; Fetcenko, M.A. The role of Mn in C14 Laves phase multi-component alloys for NiMH battery application. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 477, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehn, C.-C.; Chou, J.C.-P.; Li, H.-C.; Wu, Y.-P.; Perng, T.-P. Effect of interstitial boron and carbon on the hydrogenation properties of Ti25V35Cr40 alloy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 2010, 35, 11975–11980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, B.; Chu, N.; Zhao, H.J.; Liu, H.K.; Dou, S.X. Effects of potassium-boron addition on the performance of titanium based hydrogen storage alloy electrodes. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 1996, 21, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-H.; Dong, X.-P.; Wang, G.-Q.; Guo, S.-H.; Ren, J.-Y.; Wang, X.-L. Effect of boron additive on electrochemical cycling life of La-Mg-Ni alloys prepared by casting and rapid quenching. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 2007, 32, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leela, A.M.R.; Ramaprabhu, S. Hydrogen diffusion studies in Zr-based Laves phase AB2 alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 460, 268–271. [Google Scholar]
- Young, K.; Ouchi, T.; Huang, B.; Fetcenko, M.A. Effects of B, Fe, Gd, Mg, and C on the structure, hydrogen storage, and electrochemical properties of vanadium-free AB2 metal hydride alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 511, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Fetcenko, M.A.; Li, F.; Ouchi, T. Structural, thermodynamics, and electrochemical properties of TixZr11–x(VNiCrMnCoAl)2 C14 Laves phase alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 464, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Fetcenko, M.A.; Koch, J.; Morii, K.; Shimizu, T. Studies of Sn, Co, Al, and Fe additives in C14/C15 Laves alloys for NiMH battery application by orthogonal arrays. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 486, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Ouchi, T.; Huang, B.; Reichman, B.; Fetcenko, M.A. Studies of copper as a modifier in C14-predominant AB2 metal hydride alloys. J. Power Sources 2012, 204, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Ouchi, T.; Huang, B.; Reichman, B.; Fetcenko, M.A. The structure, hydrogen storage, and electrochemical properties of Fe-doped C14-predominating AB2 metal hydride alloys. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 12296–12304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Ouchi, T.; Huang, B.; Reichman, B. Effect of molybdenum content on structural, gaseous storage, and electrochemical properties of C14-predominant AB2 metal hydride alloys. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 8815–8821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erika, T.; Ricardo, F.; Fabricio, R.; Fernando, Z.; Verónica, D. Electrochemical and metallurgical characterization of ZrCr1-xNiMox AB2 metal hydride alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 649, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Ouchi, T.; Lin, X.; Reichman, B. Effects of Zn-addition to C14 metal hydride alloys and comparisons to Si, Fe, Cu, Y, and Mo-additives. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 655, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.L.; Hoffmann, R. Z. Structure-bonding relationships in the Laves Phases. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1992, 616, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.T.; Zhu, J.H.; Brady, M.P.; McKamey, C.G.; Pike, L.M. Physical metallurgy and mechanical properties of transition-metal Laves phase alloys. Intermetallics 2000, 8, 1119–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nei, J.; Young, K.; Salley, S.O.; Ng, K.Y.S. Determination of C14/C15 phase abundance in Laves phase alloys. Mat. Chem. Phys. 2012, 136, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power Diffraction File (PDF) Database; MSDS No. 04-003-6123; International Centre for Diffraction Data: Newtown Square, PA, USA, 2011.
- Notten, P.H.L.; Einerhand, R.E.F.; Daams, J.L.C. How to achieve long-term electrochemical cycling stability with hydride-forming electrode materials. J. Alloys Compd. 1995, 231, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Fetcenko, M.A.; Li, F.; Ouchi, T.; Koch, J. Effect of vanadium substitution in C14 Laves phase alloys for NiMH battery application. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 468, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Ouchi, T.; Fetcenko, M.A.; Mays, W.; Reichman, B. Structural and electrochemical properties of Ti1.5Zr5.5VxNi10–x. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 8695–8706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Young, K. Microstructure investigation on metal hydride alloys by electron backscatter Diffraction Technique. Batteries 2016, 2, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovshinsky, S.R.; Fetcenko, M.A. Electrochemical Hydrogen Storage Alloys and Batteries Fabricated from Mg Containing Base Alloys. U.S. Patent 5,506,069, 9 April 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Young, K.; Huang, B.; Ouchi, T. Studies of Co, Al, and Mn substitutions in NdNi5 metal hydride alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 543, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlapbach, L.; Züttel, A. Hydrogen-storage materials for mobile applications. Nature 2001, 414, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Züttel, A. Materials for hydrogen storage. Mater. Today 2003, 6, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastri, M.V.C. Introduction to metal hydrides: basic chemistry and thermodynamics of their formation. In Metal Hydride; Sastri, M.V.C., Viswanathan, B., Murthy, S.S., Eds.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1998; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Young, K.; Ouchi, T.; Meng, T.; Wong, D.F. Studies on the synergetic effects in multi-phase metal hydride alloys. Batteries 2016, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Ouchi, T.; Fetcenko, M.A. Pressure-composition-temperature hysteresis in C14 Laves phase alloys: Part 1. Simple ternary alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 480, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.F.; Young, K.; Nei, J.; Wang, L.; Ng, K.Y.S. Effects of Nd-addition on the structural, hydrogen storage, and electrochemical properties of C14 metal hydride alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 647, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholtus, N.A.; Hall, W.K. Hysteresis in the palladium-hydrogen system. J. Chem. Phys. 1963, 39, 868–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makenas, B.J.; Birnbaum, H.K. Phase changes in the niobium-hydrogen system 1: Accommodation effects during hydride precipitation. Acta Metall. Mater. 1980, 28, 979–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramaniam, R. Accommodation effects during room temperature hydrogen transformations in the niobium-hydrogen system. Acta Metall. Mater. 1993, 41, 3341–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lide, D.R. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 74th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993; pp. 6–22. [Google Scholar]
- Jeng, R.; Lee, S.; Hsu, C.; Wu, Y.; Lin, J. Effects of the addition of Pd on the hydrogen absorption-desorption characteristics of Ti33V33Cr34 alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 464, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Ouchi, T.; Nei, J.; Moghe, D. The importance of rare-earth additions in Zr-based AB2 metal hydride alloys. Batteries 2016, 2, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Wong, D.F.; Ouchi, T.; Huang, B.; Reichman, B. Effects of La-addition to the structure, hydrogen storage, and electrochemical properties of C14 metal hydride alloys. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 174, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renz, W.; Majer, G.; Skripov, A.V.; Seeher, A. A pulsed-field-gradient NMR study of hydrogen diffusion in the Laves-phase compounds ZrCr2Hx. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 1994, 6, 6367–6474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, S.I.; Kemali, M.; Ross, D.K.; Bull, D.J.; Fernandez, J.F.; Johnson, M.R. Quasi-elastic neutron scattering study of the hydrogen diffusion in the C15 Laves structure, TiCr1.85. J. Alloys Compd. 1999, 293–295, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stucki, F.; Schlapbach, L. Magnetic properties of LaNi5, FeTi, Mg2Ni and their hydrides. J. Less-Common Met. 1980, 74, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
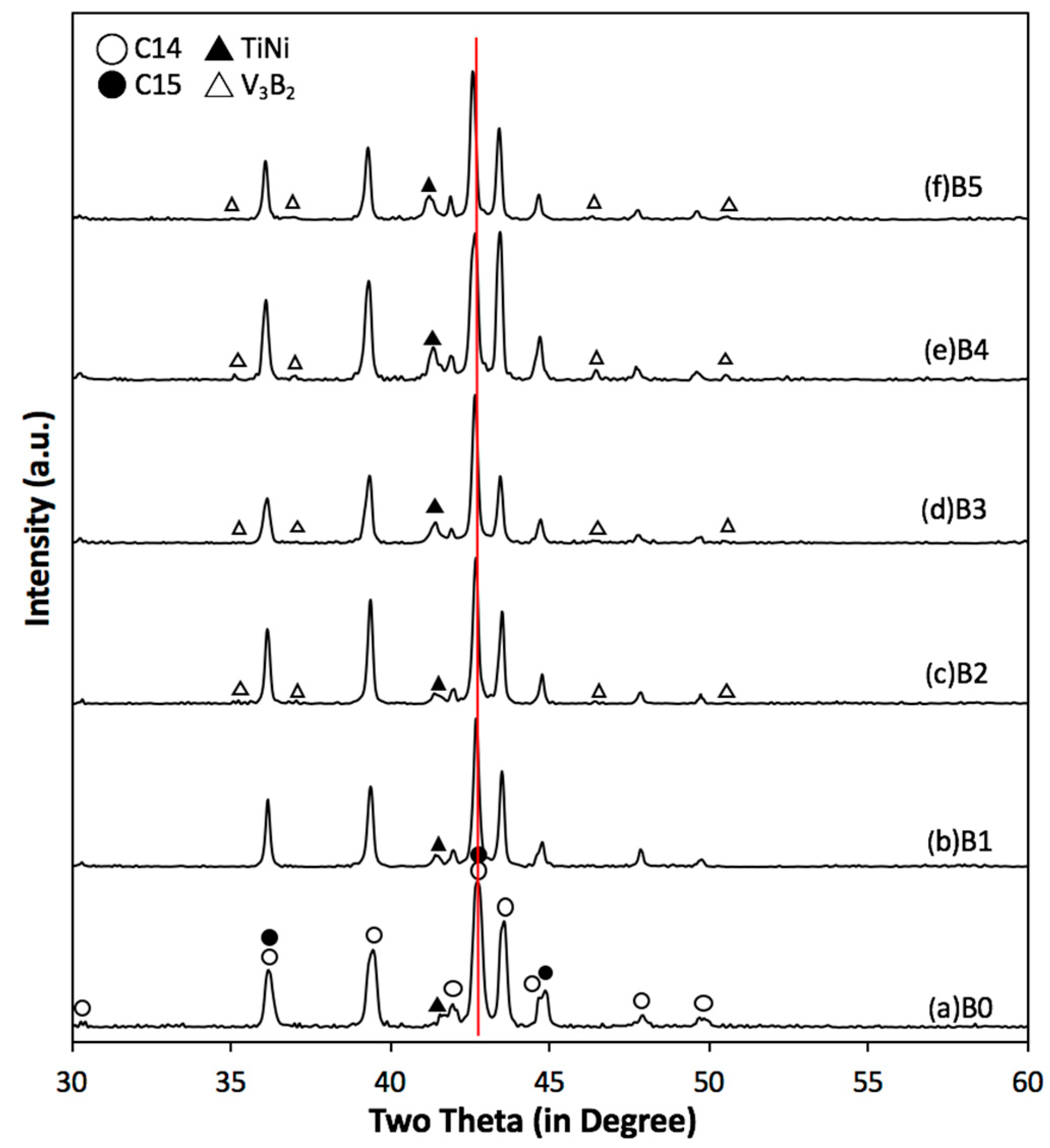
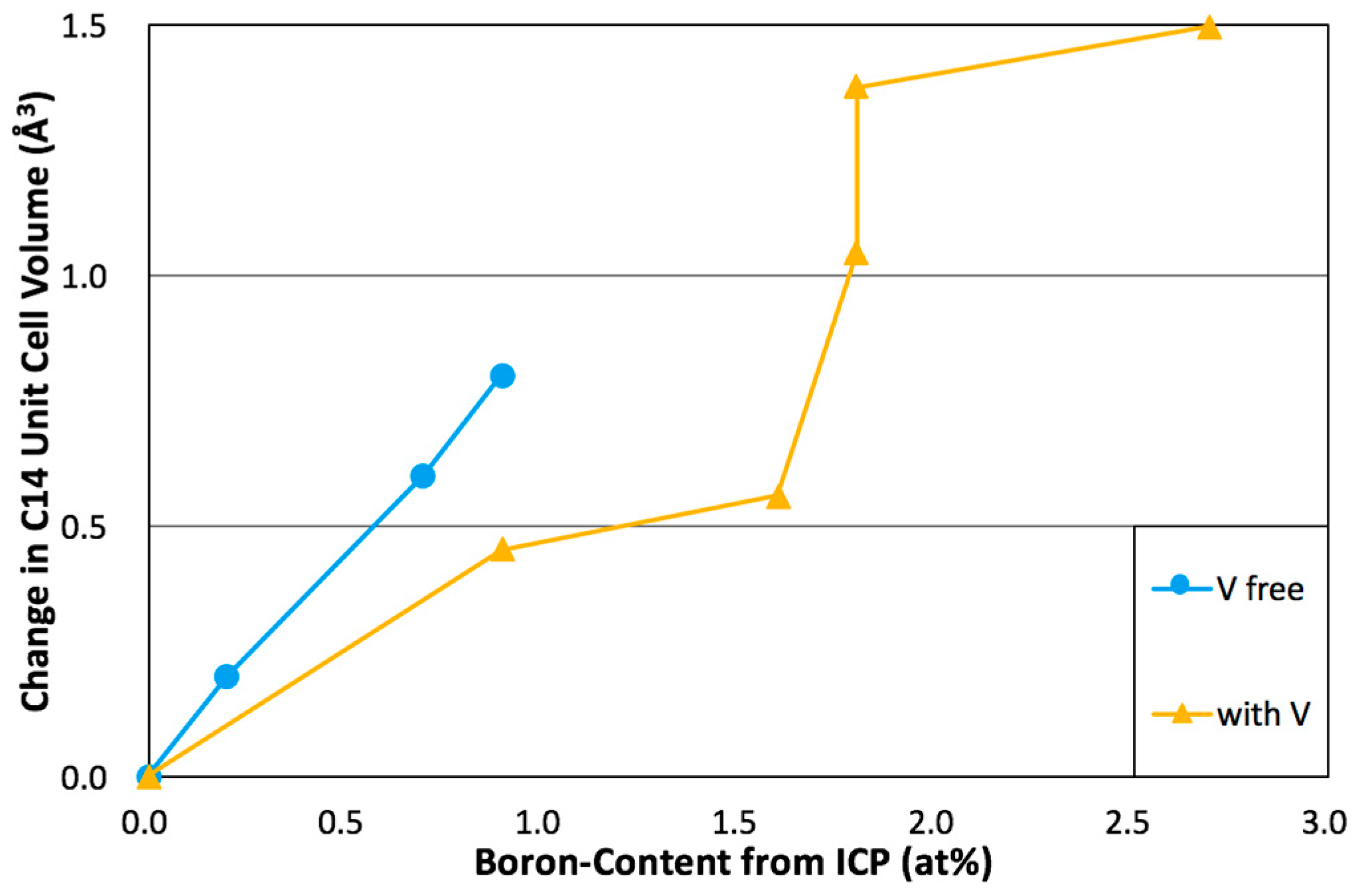
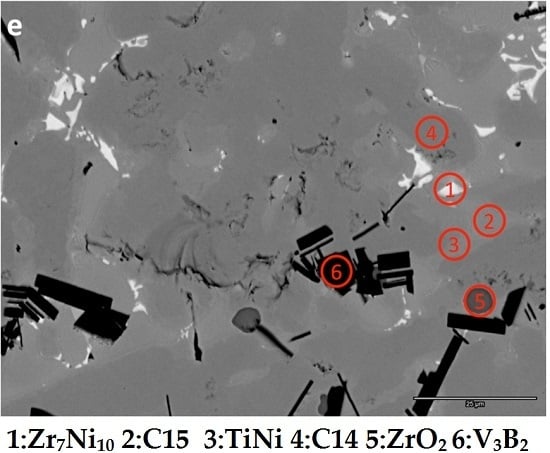
| Alloy | Source | Ti | Zr | V | Cr | Mn | Co | Ni | Al | Sn | B | e/a | B/A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B0 | Design | 12.0 | 21.5 | 10.0 | 7.5 | 8.1 | 8.0 | 32.2 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 6.82 | 1.99 |
| ICP | 12.0 | 21.5 | 10.0 | 7.5 | 8.1 | 8.0 | 32.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 6.82 | 1.99 | |
| B1 | Design | 12.0 | 21.5 | 9.6 | 7.5 | 8.1 | 8.0 | 31.6 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 1.0 | 6.77 | 1.99 |
| ICP | 12.1 | 21.5 | 9.7 | 7.3 | 7.9 | 8.0 | 31.6 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.9 | 6.76 | 1.98 | |
| B2 | Design | 12.0 | 21.5 | 9.2 | 7.5 | 8.1 | 8.0 | 31.0 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 2.0 | 6.72 | 1.99 |
| ICP | 12.0 | 21.4 | 9.7 | 7.2 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 31.1 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 1.6 | 6.72 | 2.00 | |
| B3 | Design | 12.0 | 21.5 | 8.8 | 7.5 | 8.1 | 8.0 | 30.4 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 3.0 | 6.67 | 1.99 |
| ICP | 12.1 | 21.7 | 9.2 | 7.1 | 8.0 | 8.1 | 31.0 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 1.8 | 6.72 | 1.96 | |
| B4 | Design | 12.0 | 21.5 | 8.4 | 7.5 | 8.1 | 8.0 | 29.8 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 4.0 | 6.62 | 1.99 |
| ICP | 12.2 | 22.1 | 8.6 | 6.9 | 8.1 | 8.3 | 31.0 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 1.8 | 6.72 | 1.92 | |
| B5 | Design | 12.0 | 21.5 | 8.0 | 7.5 | 8.1 | 8.0 | 29.2 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 5.0 | 6.57 | 1.99 |
| ICP | 12.1 | 22.8 | 8.0 | 7.0 | 8.7 | 8.1 | 29.5 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 2.7 | 6.62 | 1.86 |
| Alloy | C14 a (Å) | C14 c (Å) | C14 a/c | VC14 (Å3) | C14 Crystallite Size (Å) | C15 a (Å) | TiNi a (Å) | V3B2 a (Å) | V3B2 c (Å) | V3B2 a/c | (Å3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B0 | 4.9635 | 8.0906 | 0.6135 | 172.62 | 260 | 7.0002 | 3.0637 | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| B1 | 4.9655 | 8.0959 | 0.6133 | 172.87 | 591 | 7.0077 | 3.0770 | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| B2 | 4.9667 | 8.0961 | 0.6135 | 172.96 | 643 | 7.0087 | 3.0775 | 5.7125 | 3.0232 | 1.8896 | 98.66 |
| B3 | 4.9702 | 8.1072 | 0.6131 | 173.44 | 487 | 7.0148 | 3.0813 | 5.7089 | 3.0486 | 1.8726 | 99.36 |
| B4 | 4.9744 | 8.1110 | 0.6133 | 173.81 | 496 | 7.0154 | 3.0841 | 5.7193 | 3.0330 | 1.8857 | 99.21 |
| B5 | 4.9845 | 8.1330 | 0.6129 | 174.99 | 571 | 7.0293 | 3.0916 | 5.7287 | 3.0397 | 1.8846 | 99.76 |
| Location | Ti | Zr | V | Cr | Mn | Co | Ni | Al | Sn | O | e/a | B/A | Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1-1 | 4.8 | 35.9 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 40.3 | 0.4 | 15.3 | 0.0 | - | 1.44 | Zr7Ni10 |
| B1-2 | 25.3 | 18.9 | 1.2 | 0.4 | 2.3 | 7.5 | 43.8 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.0 | - | 1.21 | TiNi |
| B1-3 | 11.8 | 22.9 | 6.8 | 3.4 | 7.0 | 6.5 | 40.6 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 7.10 | 1.88 | C15 |
| B1-4 | 9.6 | 22.4 | 11.9 | 9.7 | 9.6 | 8.7 | 27.2 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 6.65 | 2.12 | C14 |
| B1-5 | 0.2 | 33.8 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 64.9 | - | 1.94 | ZrO2 |
| B1-6 | 18.5 | 0.5 | 56.9 | 16.0 | 4.8 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | - | - | V3B2 |
| B2-1 | 6.8 | 34.6 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 1.8 | 2.2 | 39.6 | 0.4 | 13.7 | 0.0 | - | 1.38 | Zr7Ni10 |
| B2-2 | 24.7 | 19.7 | 1.1 | 0.4 | 2.3 | 7.3 | 43.8 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.0 | - | 1.20 | TiNi |
| B2-3 | 11.5 | 23.3 | 6.5 | 3.7 | 7.1 | 6.6 | 40.2 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 7.08 | 1.87 | C15 |
| B2-4 | 9.6 | 22.8 | 11.3 | 10.9 | 10.0 | 9.0 | 25.9 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 6.64 | 2.09 | C14 |
| B2-5 | 0.1 | 34.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 64.5 | - | 1.91 | ZrO2 |
| B2-6 | 10.4 | 0.4 | 62.2 | 21.1 | 3.6 | 1.0 | 1.3 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | - | - | V3B2 |
| B3-1 | 6.2 | 34.4 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 1.9 | 2.3 | 38.5 | 0.4 | 13.4 | 1.9 | - | 1.38 | Zr7Ni10 |
| B3-2 | 23.7 | 21.0 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 2.2 | 7.3 | 43.5 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.0 | - | 1.18 | TiNi |
| B3-3 | 11.4 | 24.0 | 6.0 | 3.8 | 7.4 | 6.8 | 39.7 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 7.08 | 1.83 | C15 |
| B3-4 | 10.1 | 23.1 | 10.4 | 9.8 | 10.0 | 9.1 | 27.0 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 6.67 | 2.02 | C14 |
| B3-5 | 1.2 | 31.5 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 2.2 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 64.1 | - | 2.04 | ZrO2 |
| B3-6 | 11.4 | 1.2 | 59.5 | 21.2 | 3.5 | 0.9 | 2.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | - | - | V3B2 |
| B4-1 | 7.1 | 34.2 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 2.3 | 2.5 | 40.0 | 0.4 | 12.4 | 0.0 | - | 1.38 | Zr7Ni10 |
| B4-2 | 22.8 | 21.9 | 0.9 | 0.4 | 2.4 | 7.6 | 43.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.0 | - | 1.20 | TiNi |
| B4-3 | 11.0 | 24.3 | 5.7 | 3.6 | 8.1 | 7.0 | 39.3 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 7.07 | 1.83 | C15 |
| B4-4 | 9.7 | 23.2 | 10.3 | 10.1 | 10.7 | 9.4 | 26.0 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 6.66 | 2.04 | C14 |
| B4-5 | 0.1 | 32.6 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 66.1 | - | 2.04 | ZrO2 |
| B4-6 | 14.8 | 1.8 | 52.0 | 23.4 | 4.1 | 1.2 | 2.6 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | - | - | V3B2 |
| B5-1 | 4.5 | 36.5 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 2.4 | 2.3 | 39.2 | 0.6 | 13.9 | 0.0 | - | 1.42 | Zr7Ni10 |
| B5-2 | 21.3 | 23.5 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 2.5 | 7.2 | 43.6 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.0 | - | 1.20 | TiNi |
| B5-3 | 10.9 | 24.6 | 5.1 | 3.5 | 9.1 | 7.6 | 38.4 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 7.08 | 1.82 | C15 |
| B5-4 | 9.7 | 23.4 | 9.3 | 9.6 | 11.9 | 9.7 | 25.9 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 6.68 | 2.03 | C14 |
| B5-5 | 0.1 | 32.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 66.5 | - | 2.08 | ZrO2 |
| B5-6 | 17.5 | 2.0 | 48.2 | 22.8 | 4.6 | 1.5 | 3.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.0 | - | - | V3B2 |
| Alloy | Maximum Capacity at 30 °C wt % | Reversible Capacity at 30 °C wt % | Desorption PRESSURE at 0.75 wt %, 30 °C MPa | Slope Factor at 30 °C % | Hysteresis at 0.75 wt %, 30 °C | -∆Hh kJ·mol H2−1 | -∆Sh J·mol H2−1·K−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B0 | 1.45 | 1.32 | 0.078 | 60 | 0.04 | 32.8 | 107 |
| B1 | 1.50 | 1.29 | 0.037 | 54 | 0.08 | 38.9 | 120 |
| B2 | 1.46 | 1.27 | 0.038 | 53 | 0.06 | 37.5 | 116 |
| B3 | 1.44 | 1.21 | 0.036 | 55 | 0.07 | 35.3 | 108 |
| B4 | 1.46 | 1.23 | 0.032 | 58 | 0.05 | 35.5 | 108 |
| B5 | 1.50 | 1.22 | 0.025 | 50 | 0.05 | 42.9 | 130 |
| Alloy | 10th Cycle High-Rate Discharge Capacity mAh·g−1 | 10th Cycle Full Discharge Capacity mAh·g−1 | 10th Cycle HRD % | Number of Activation Cycles to Reach 85% HRD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B0 | 359 | 371 | 97 | 3 |
| B1 | 330 | 366 | 90 | 4 |
| B2 | 325 | 362 | 90 | 5 |
| B3 | 284 | 354 | 80 | 6 |
| B4 | 307 | 359 | 86 | 6 |
| B5 | 311 | 343 | 91 | 6 |
| Alloy | D at RT 10−10 cm2·s−1 | Io at RT mA·g−1 | R at RT Ω·g | C at RT F·g−1 | RC Product at RT s | R at LT Ω·g | C at LT F·g−1 | RC Product at LT s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B0 | 1.3 | 38 | 0.44 | 0.24 | 0.11 | 16.5 | 0.21 | 3.5 |
| B1 | 1.3 | 26 | 0.71 | 0.22 | 0.16 | 27.4 | 0.28 | 7.7 |
| B2 | 1.2 | 22 | 1.04 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 83.9 | 0.18 | 15.1 |
| B3 | 1.0 | 18 | 2.74 | 0.18 | 0.49 | 171.5 | 0.22 | 37.7 |
| B4 | 1.2 | 25 | 0.99 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 70.0 | 0.16 | 11.2 |
| B5 | 1.3 | 21 | 0.59 | 0.24 | 0.15 | 47.1 | 0.23 | 10.8 |
| Alloy | MS emu·g−1 | H1/2 kOe |
|---|---|---|
| B0 | 0.064 | 0.064 |
| B1 | 0.059 | 0.120 |
| B2 | 0.093 | 0.138 |
| B3 | 0.099 | 0.139 |
| B4 | 0.101 | 0.106 |
| B5 | 0.090 | 0.139 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, S.; Young, K.-H.; Ouchi, T.; Nei, J.; Wu, X. Effects of Boron-Incorporation in a V-Containing Zr-Based AB2 Metal Hydride Alloy. Batteries 2017, 3, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries3040036
Chang S, Young K-H, Ouchi T, Nei J, Wu X. Effects of Boron-Incorporation in a V-Containing Zr-Based AB2 Metal Hydride Alloy. Batteries. 2017; 3(4):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries3040036
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Shiuan, Kwo-Hsiung Young, Taihei Ouchi, Jean Nei, and Xin Wu. 2017. "Effects of Boron-Incorporation in a V-Containing Zr-Based AB2 Metal Hydride Alloy" Batteries 3, no. 4: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries3040036
APA StyleChang, S., Young, K.-H., Ouchi, T., Nei, J., & Wu, X. (2017). Effects of Boron-Incorporation in a V-Containing Zr-Based AB2 Metal Hydride Alloy. Batteries, 3(4), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries3040036