Abstract
Global electric vehicle (EV) markets are rapidly expanding, and the efficient management of batteries has become increasingly important due to supply constraints of rare metals and other raw materials required for lithium-ion batteries. Accordingly, the reuse and recycling of used batteries from early EVs are emerging as key solutions. This study proposes a machine learning-based approach to rapidly and reliably estimate the static capacity of used batteries. While conventional methods require significant measurement time, this study demonstrates that accurate static capacity estimation is possible using only short-term partial discharge data (6 min under 1C-rate CC conditions) by leveraging an RNN (recurrent neural network) architecture specialized for time-series data processing. The proposed model achieves high prediction accuracy, with an average RMSE of 28.439 mAh, average MSE of 808.799 mAh2, average MAE of 13.049 mAh, and average R2 of 0.9993, while significantly reducing the evaluation time compared to conventional methods. This is expected to greatly enhance the efficiency and practicality of battery reuse and recycling processes.
1. Introduction
The growing popularity of electric vehicles (EVs) significantly contributes to reducing greenhouse gas emissions from internal combustion (IC) engine-based transportation systems, which account for a substantial portion of global emissions [1]. However, the dramatic increase in EV adoption raises concerns about the availability of raw materials needed for lithium-ion battery production. As a result, the efficient reuse or recycling of retired batteries has become a critical issue, not only due to raw material shortages but also because of the instability of supply chains for these materials [2,3]. Furthermore, for profitable business models in the reuse or recycling of lithium-ion batteries, fast and reliable estimation of the static capacity of retired batteries is essential, as the economic and environmental benefits heavily depend on the efficiency of the process. Several studies have addressed similar issues [4,5]. Battery health estimation techniques include electrochemical model-based and filter-based methods. The former are accurate but complex and sensitive to environmental variables, making then expensive. The latter, using mathematical modeling, are difficult to interpret [6]. It is well known in the research community that conventional methods for measuring static capacity, such as low-current (i.e., 0.1 C) full discharge, are time-consuming and costly [7].
Departing from these traditional models, research is actively being conducted on machine learning-based estimation methods to assess battery health across various environments [8,9]. These machine learning-based methods also leverage data on battery aging characteristics to develop estimation models for state of health (SOH), constructing extensive datasets (e.g., current, voltage, and resistance) for training and evaluation, and using various machine learning algorithms for estimation. Although this approach requires large amounts of training data to improve the accuracy of machine learning-based health estimation, it offers the advantage of being applicable across a variety of environmental conditions and operating factors. The estimation error, precision, and speed can vary significantly depending on the experimental design [9,10]. Therefore, to rapidly estimate the health status of lithium-ion batteries, this study focused on using the partial discharge voltage characteristics at a 1 C rate.
In this context, recent studies have reported methods for estimating the capacity and state of health (SOH) of lithium-ion batteries using not full charge/discharge cycles, but rather partial charge/discharge data or short-term partial discharge curves. For example, Zhang et al. (2025) demonstrated, using a large experimental dataset, that the available capacity of a battery can be accurately estimated using only incomplete charging data, specifically, fragmented data from partial charging segments [11]. In addition, Yao et al. (2023) showed that deep learning-based transfer learning techniques can effectively predict battery capacity using only partial charge/discharge data [12]. Similarly, various machine learning-based approaches have been actively explored to estimate battery capacity by extracting features from partial segments of voltage–capacity curves (or incremental capacity curves) [13,14,15].
The current study utilized a machine learning algorithm for time-series data to construct a quick and accurate estimation of battery capacity. For this research, battery data were gathered from cylindrical lithium-ion batteries covering various degrees of aging over a long period. The data, collected via 1 C-rate partial discharge for 6 min, were used for learning and validating the proposed methodology.
2. Experimental Set-Up and Data Acquisition
In this study, we used a cylindrical lithium-ion battery typically found in the market to acquire data for training and validation for machine learning algorithms. A picture of a battery cycler (APRO Co. Ltd., Anyang, Republic of Korea) is shown in Figure 1a, which was used for the data acquisition of traces of voltage drop during the partial discharge period of 6 min. As shown in Figure 1b, a picture of the ‘INR21700-40T’ model (Samsung SDI Co. Ltd., Yongin, Republic of Korea) of the sample SDI NCM series is provided. Table 1 and Table 2 summarize the specifications of each of Figure 1.

Figure 1.
Experimental set-up. (a) Cylindrical cell cycler; (b) ‘INR21700-40T’model battery.

Table 1.
Specification of cell cycler.

Table 2.
Specification of cylindrical cell.
In this experiment, data from partial discharges of lithium-ion batteries, set to 6 min durations, were used to explore the effectiveness of estimating the batteries’ remaining capacities. The process involved an aging cycle with 2 C-rate constant current (CC) charging and discharging. During the data acquisition, parameters like DCIR, partial discharge data, and maximum capacity were measured utilizing conventional methodology. The data were then preprocessed using incremental capacity analysis (ICA) and differential voltage analysis (DVA) to create parameters reflecting the batteries’ aging characteristics for machine learning algorithms. This method estimates static capacity by analyzing voltage fluctuations and capacity changes over time, offering a more efficient approach to battery health assessment [16]. The experimental process illustrated in Figure 2 is divided into three major stages: the input data measurement step, the output data measurement step, and the aging step. In the first stage, standard charging is followed by a segmented discharge where the DCIR and partial voltage values are measured at every 10% decrement in SOC. A 1 h rest period is included to stabilize the electrochemical state, and this loop continues until SOC reaches 0%. In the second stage, after a standard charge, the discharge and charge capacities are measured to track degradation, and the loop exits when either 10 aging routines are completed or SOH drops below 80%. The third stage consists of accelerated aging through 2 C-rate constant current discharging and charging cycles, iterated up to 100 cycles or until the capacity loss threshold is reached. These structured routines ensure consistent data acquisition for subsequent analysis using ICA and DVA methods.
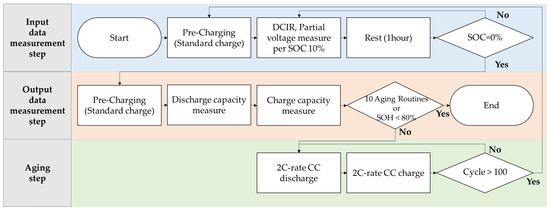
Figure 2.
Experiment flow chart.
3. Methodology–Machine Learning
3.1. Feature Extraction for Machine Learning
The experiment was aimed at aging the battery to below 80% SOH, and the aging was accelerated by 2 C-rate CC charge and discharge, which represents rapid charge and discharge. The experiments were conducted from 0 to 1000 cycles, and the measured partial discharge voltage characteristics per 100 cycle units and the change in SOH with aging are shown in Figure 3. Figure 3a shows the measured partial discharge voltage data for different states of charge (SOC), decreasing by 10% per aging cycle, which was extracted for machine learning training. The SOC calculation, based on Coulomb counting as described in Equation (1), indicates that a partial discharge of 6 min at a 1C rate theoretically results in a 10% SOC reduction. Figure 3b illustrates the corresponding change in SOH with aging.
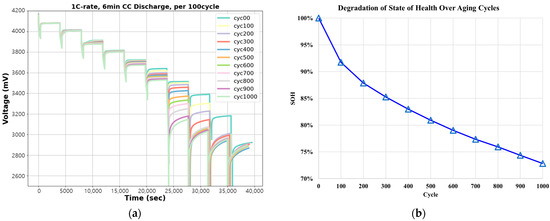
Figure 3.
Partial discharge voltage characteristics and SOH degradation in relation to aging cycles: (a) voltage characteristics; (b) change in SOH over cycle.
The data obtained from the experiments were preprocessed to train the machine learning-based model. The continuous voltage changes and the corresponding capacity change over a 6 min partial discharge period were detected and used as training parameters. This is derived from the concepts of ICA and DVA. An ICA is an analysis method that detects electrochemical changes through low-current CC charge or discharge and is characterized by analyzing data in all voltage bins.
In this study, only partial data were used instead of the whole discharge curve, and the data were extracted by voltage change rate, discharge time capacity change, etc., and then min-max normalized. Equations (2) and (3) show the expressions for ICA and DVA used for feature extraction, and Equation (4) shows the expression for min-max normalization. The data extracted from the short partial discharge voltage curve was used to train the machine learning model.
3.2. Machine Learning
This study employed recurrent neural networks (RNNs) for processing time-series data derived from partial discharge measurements. A distinguishing feature of RNNs is their ability to retain information across time steps through recurrent connections. This memory capability is particularly advantageous for SOH estimation, as it enables the model to utilize historical data to predict the ongoing degradation of batteries. Given that battery SOH degradation often follows complex and nonlinear patterns, the RNN’s proficiency in modeling such relationships is critical to achieving accurate predictions. Figure 4 illustrates the basic structure of the RNN, highlighting its recurrent architecture, which facilitates temporal data processing. Equations (5) and (6) show the basic RNN model. Figure 5 outlines the deep learning-based SOH estimation process, emphasizing the flow of time-series data through the network layers. Building upon established methodologies in battery health monitoring, this approach leverages the strengths of RNNs in capturing subtle temporal dynamics [17]. The model was constructed, and the testing environment was configured using MATLAB 2024a.
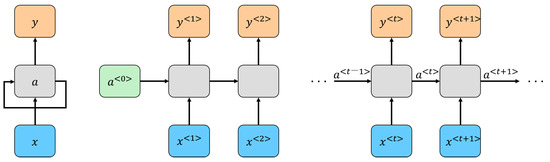
Figure 4.
Structure of RNN.
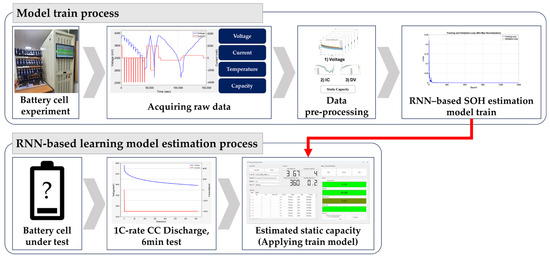
Figure 5.
Overall process flow of current research.
3.3. Evaluation Indicators
In this paper, a study was conducted to quickly and accurately estimate the static capacity of lithium-ion batteries from short partial discharges alone, based on the results of an RNN-based estimation model trained on data acquired through short partial discharges of 1 C rate for 6 min. Data were collected at all SOC intervals during aging and the model was trained.
To evaluate the estimation performance of the RNN-based model, we compared and analyzed the root mean square error (RMSE), mean square error (MSE), and mean absolute error (MAE) metrics throughout the experiments. We additionally considered the coefficient of determination (R2) in evaluating the model’s performance, which analyzes how well the model explains the variability in the data. The RMSE was calculated using the formula presented in Equation (7), while the formulas for MSE and MAE are shown in Equations (8) and (9), respectively. The coefficient of determination (R2) was calculated using Equation (10) and was utilized as an important metric to evaluate the explanatory power of the model.
4. Results and Discussion
To assess the model’s generalization performance, performance metrics were evaluated over 50 iterations. Table 3 shows summarized the resulting data. The RMSE results indicated a minimum of 15.486 mAh, a maximum of 44.366 mAh, and an average error of 28.439 mAh. The MSE, representing the mean squared difference between predicted and actual capacity values, was used as a metric to evaluate the dispersion of the error, with values ranging from 239.836 mAh2 to 1968.836 mAh2 and an average of 808.799 mAh2. The MAE, which provides an intuitive measure of the difference between the actual and predicted data, showed a minimum value of 20.734 mAh, a maximum of 33.795 mAh, and an average of 13.049 mAh, indicating a relatively small divergence between the actual and predicted values. The R2 metric, which reflects the variance of the estimated capacity (dependent variable) explained by the actual capacity (independent variable), averaged 0.9993. This high R2 value suggests that the estimated capacity closely aligns with the actual capacity. However, when considered in isolation, the R2 metric may give an inflated sense of model performance, particularly on the training dataset, while potentially overlooking underperformance on the validation or test datasets. Therefore, it is essential to evaluate R2 in conjunction with other metrics such as RMSE, MSE, and MAE to provide a comprehensive assessment of the model’s generalization performance. The model used in this study, as evaluated by these metrics, demonstrated significant estimation accuracy when developed using data from a brief 6 min partial discharge under a 1 C-rate CC.

Table 3.
Discharging data estimation results.
The estimation accuracy of battery capacity was evaluated using partial discharge data obtained from various SOC ranges. As shown in Figure 6a, the estimation errors did not exhibit significant variation across different SOC intervals. Notably, each point in Figure 6a represents a capacity estimate derived from a specific initial SOC condition, based on 10% partial discharge data. These results indicate that the proposed capacity estimation method does not strongly depend on the specific SOC range of the input data, suggesting that reliable estimation can be achieved under a wide range of SOC conditions. Figure 6b highlights the differences in estimation errors across various aging cycle groups, while Figure 6c shows the distribution of discrepancies between the estimated and actual capacities across all aging cycles. Figure 6d presents the performance metric of R2 in graphical form. When compared and analyzed alongside Figure 6a–c, it generally suggests accuracy while minimizing errors. However, when analyzed with Figure 6d, it reveals that the high R2 value may indicate tendencies of overestimation in certain segments of the aging cycle.
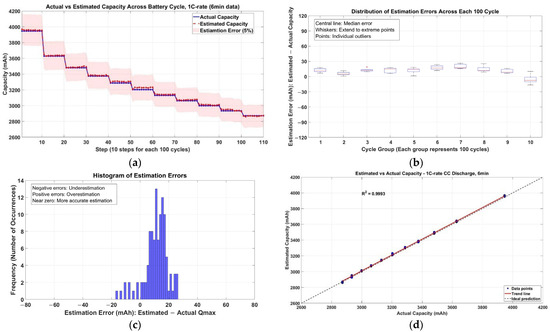
Figure 6.
Estimation errors across aging cycles at 10% SOC discharge: (a) actual and estimated battery capacity at each evaluation step across 1000 cycles using 6 min 1C-rate discharge data; (b) distribution of estimation errors for each 100-cycle group; (c) histogram of capacity estimation errors across all cycles and steps; (d) correlation between actual and estimated capacity across all evaluated steps.
In this study, a total of five battery samples were utilized to develop the model. Data from three samples were used for training, one sample was used for validation, and one sample was reserved for testing. This approach underscores the significant impact of data quantity and quality on the model’s estimation accuracy. Specifically, the imbalanced data distribution during the battery aging process can increase estimation errors in certain aging cycles, leading to overestimation. Therefore, future work should focus on enhancing the model’s generalization capability by increasing data diversity through additional data collection and improving preprocessing techniques.
This study made a significant contribution to the rapid estimation of the static capacity of degraded Li-ion batteries by training a machine learning-based model using 6 min partial discharge data at a 1 C rate. However, since the experimental data were collected and aged only under room temperature (RT) conditions, the findings have limitations in their applicability to a wide range of environments, regardless of diagnostic location. For future research, we plan to expand the dataset by collecting data under various temperature (−10~30 °C) conditions to broaden the model’s applicability. Additionally, experiments will be conducted not only with cylindrical batteries, but also with pouch and prismatic battery types to further enhance the practical utility of the model.
Funding
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program for Automotive Industry (20022377), funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE, Republic of Korea).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Mala, P.; Palanivel, M.; Priyan, S.; Anbazhagan, N.; Acharya, S.; Joshi, G.P.; Ryoo, J. Sustainable decision-making approach for dual-channel manufacturing systems under space constraints. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.D.; Lim, O.T. Policy suggestion for fostering the industry of using end-of-life EV batteries. Trans. Korean Hydrog. New Energy Soc. 2021, 32, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, G.; Sommerville, R.; Kendrick, E.; Chong, W.; Curran, S.M.D.; Roberts, D.A.; Anderson, P.; Scarr, M.O.; Gaines, P.S.J.; Denton, L.A.J.; et al. Recycling lithium-ion batteries from electric vehicles. Nature 2019, 575, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Tian, J.; Sun, Z.; Wang, L.; Xu, R.; Li, M.; Chen, Z. A comprehensive review of battery modeling and state estimation approaches for advanced battery management systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 131, 110015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Xu, S.; Tang, A.; Zhou, F.; Hou, J.; Xiao, Y.; Fu, Z. A review of lithium-ion battery state of health estimation and prediction methods. World Electr. Veh. J. 2021, 12, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Kumar, R. Electric vehicle battery capacity degradation and health estimation using machine-learning techniques: A review. Clean Energy 2023, 7, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.; Choi, W. Rapid estimation of battery storage capacity through multiple linear regression. Batteries 2023, 9, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Yu, J.; Mao, L. Multisource domain adaptation for health degradation monitoring of lithium-ion batteries. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2021, 7, 2279–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, C.; Meng, Y.; Zhu, J.; Duan, Y. Capacity estimation of Li-ion battery based on transformer-adversarial discriminative domain adaptation. AIP Adv. 2023, 13, 075203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, K.; Foley, A.M.; Zülke, A.; Berecibar, M.; Nanini-Maury, E.; Hoster, H.E. Data-driven health estimation and lifetime prediction of lithium-ion batteries: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 113, 109254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Gu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, T.; Gong, Y.; Shang, Y. Data-driven available capacity estimation of lithium-ion batteries using fragmented charge capacity. Nat. Commun. Eng. 2025, 32, 2731–3395. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, J.; Han, T. Data-driven lithium-ion batteries capacity estimation based on deep transfer learning using partial segments of charging/discharging data. Energy 2023, 271, 127033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, X.; Kang, L.; Xie, D.; Zhang, X. State of health estimation for lithium-ion battery using partial incremental capacity curves and transfer learning. Batteries 2024, 10, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Xu, B.; Zheng, L.; Xu, J. Robustness enhanced capacity estimation method for lithium-ion batteries based on multi-voltage-interval incremental capacity peaks. Front. Energy Res. 2023, 11, 1207194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Duan, W.; He, Y.; Wang, S.; Fernandez, C. A hybrid data driven framework considering feature extraction for battery state of health estimation and remaining useful life prediction. Green Energy Intell. Transp. 2024, 3, 100160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran, H.; Sansano, E.; Pecht, M. Machine learning techniques suitability to estimate the retained capacity in lithium-ion batteries from partial charge/discharge curves. J. Energy Storage 2023, 59, 106346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharath, Y.K.; Anandu, V.P.; Vinatha, U.; Sudeep, S. Long-term estimation of SoH using cascaded LSTM-RNN for lithium batteries subjected to aging and accelerated degradation. Energy Storage 2024, 10, 70066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).