Advanced Algorithm for SOC, Internal Resistance, and SOH Co-Estimation of Lithium-Titanate-Oxide Batteries Using Neural Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
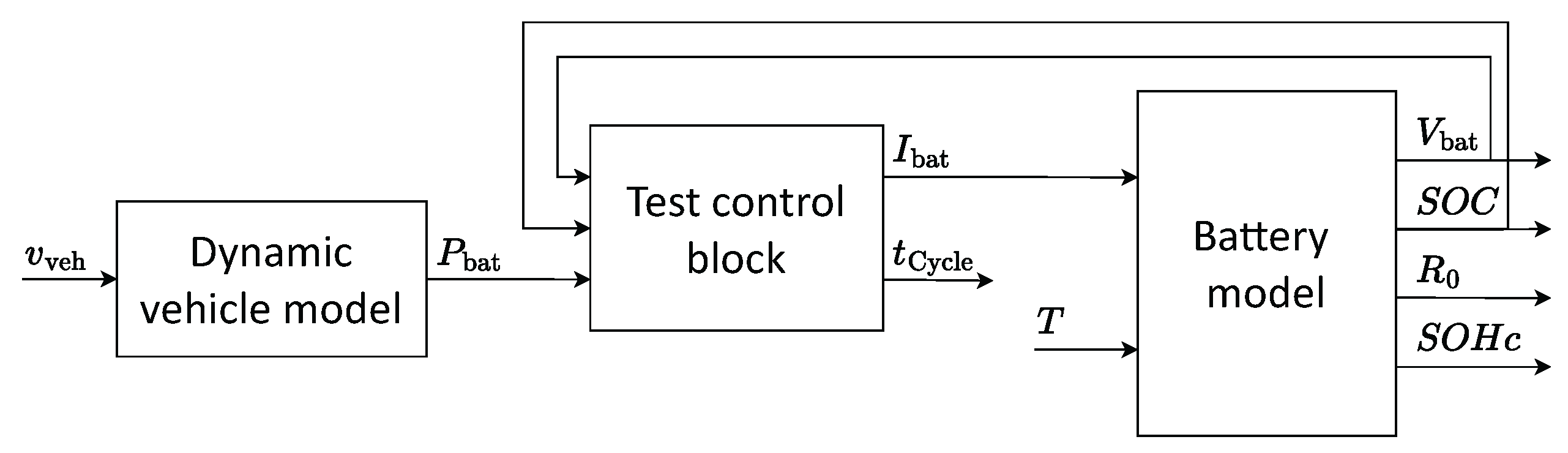
2. Simulation Platform and Synthetic Dataset Creation
2.1. Dynamic Vehicle Model
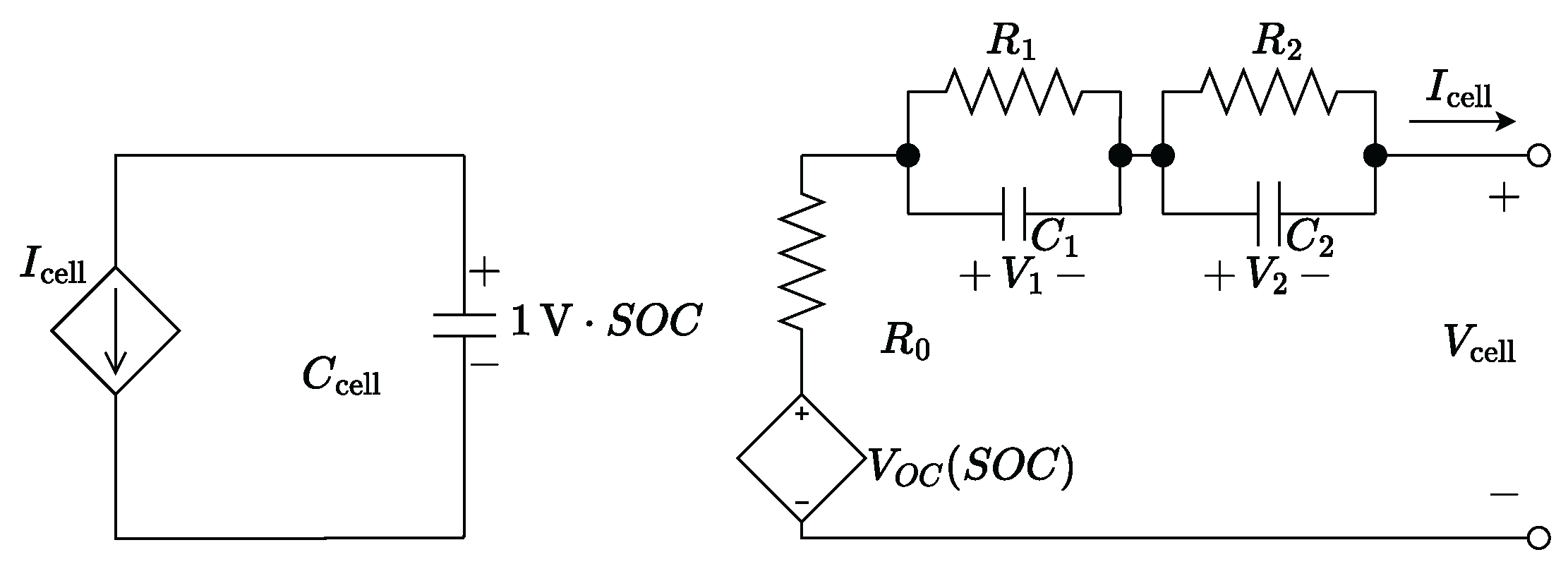
2.2. Battery Model
2.3. Test Control Block
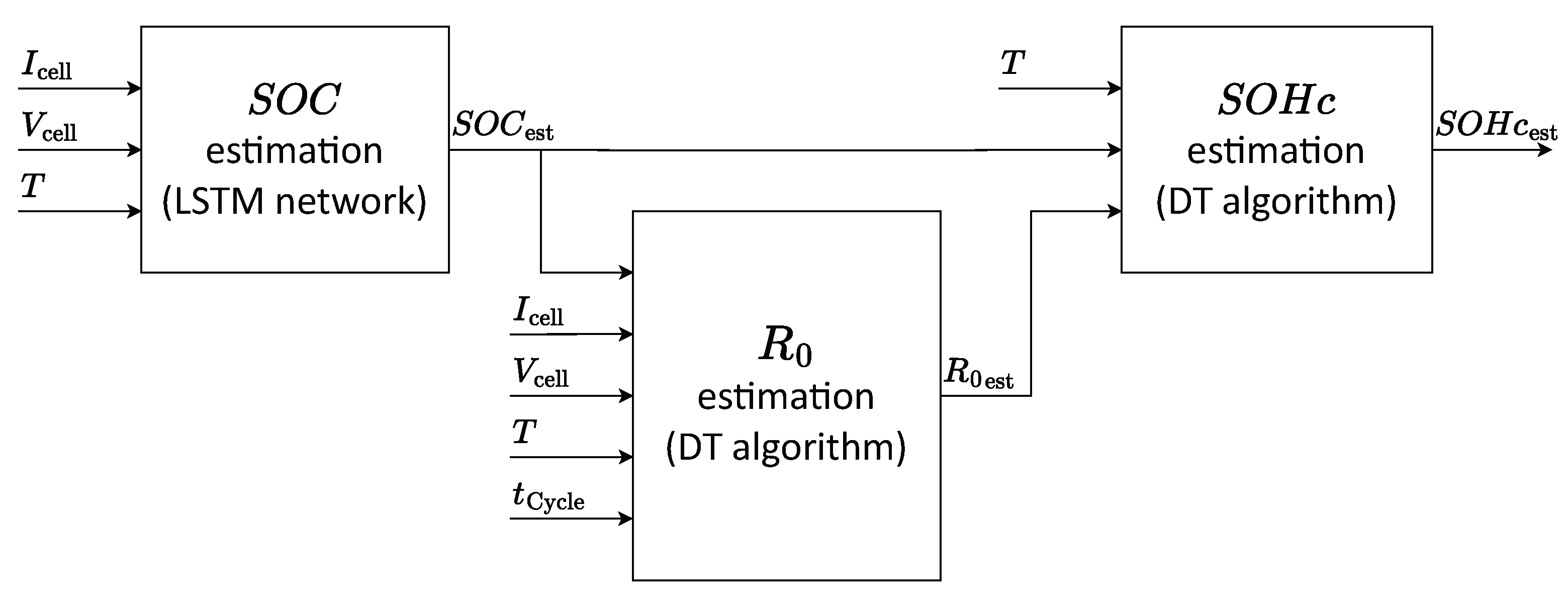
3. Co-Estimation Algorithm
3.1. SOC Estimation Block
3.2. Internal Resistance and SOHc Estimation Blocks
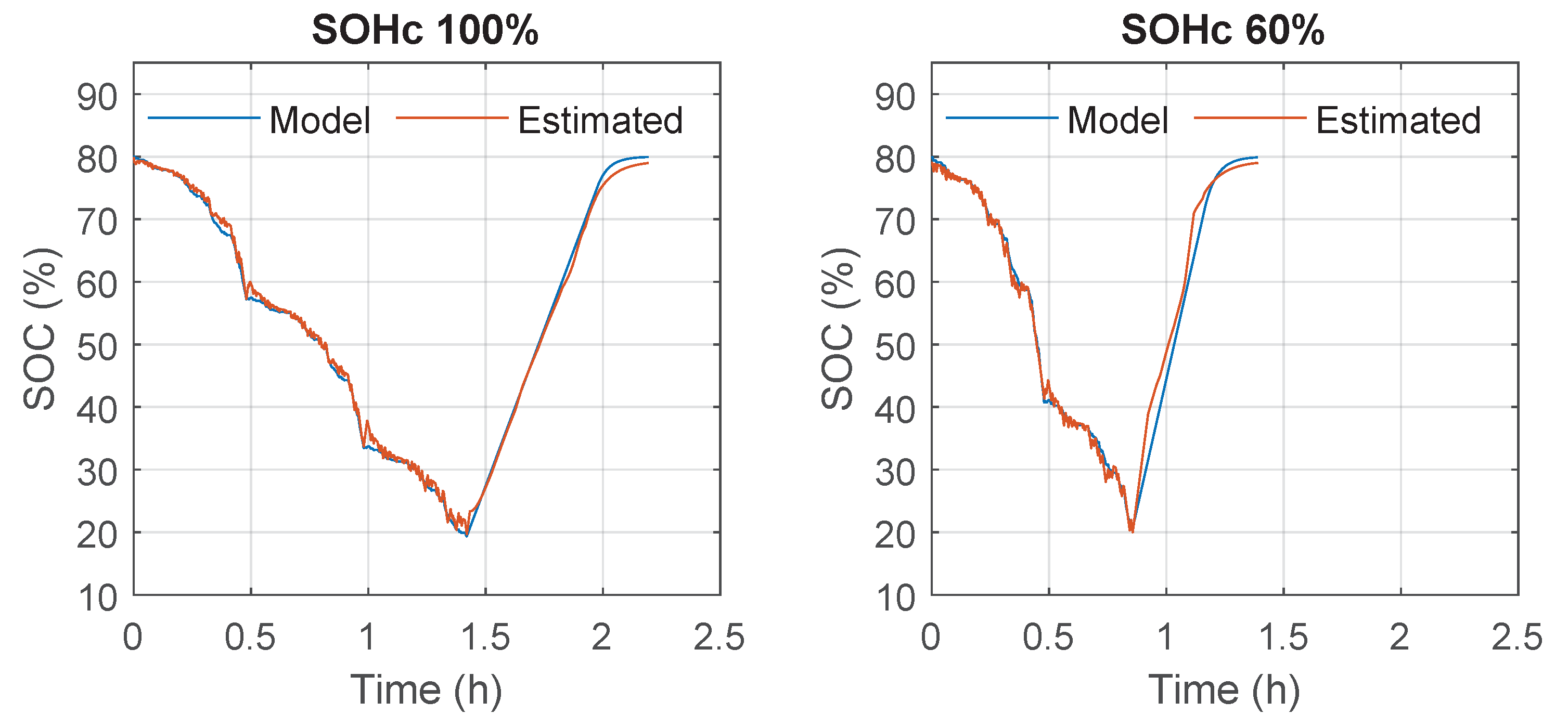
4. Test of the Developed Co-Estimation Algorithm
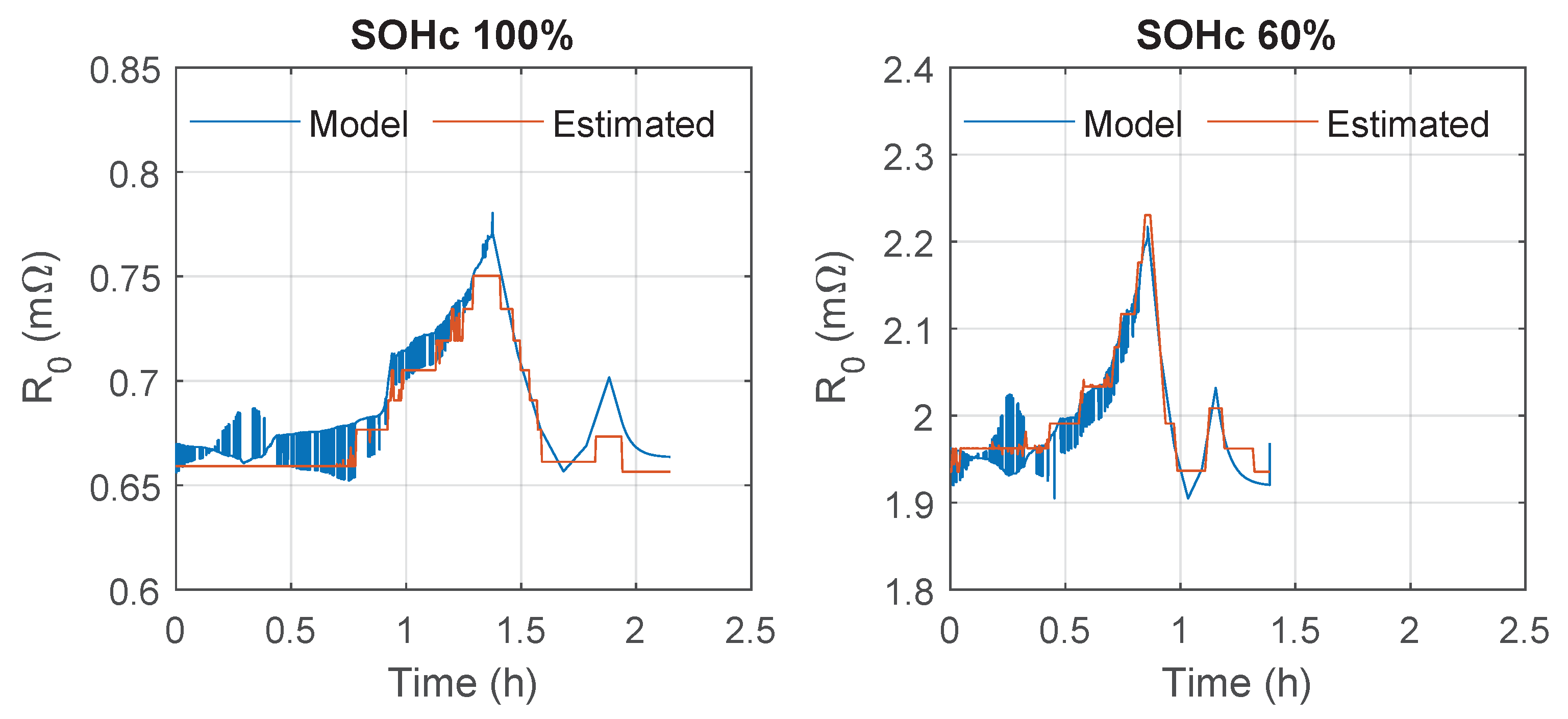
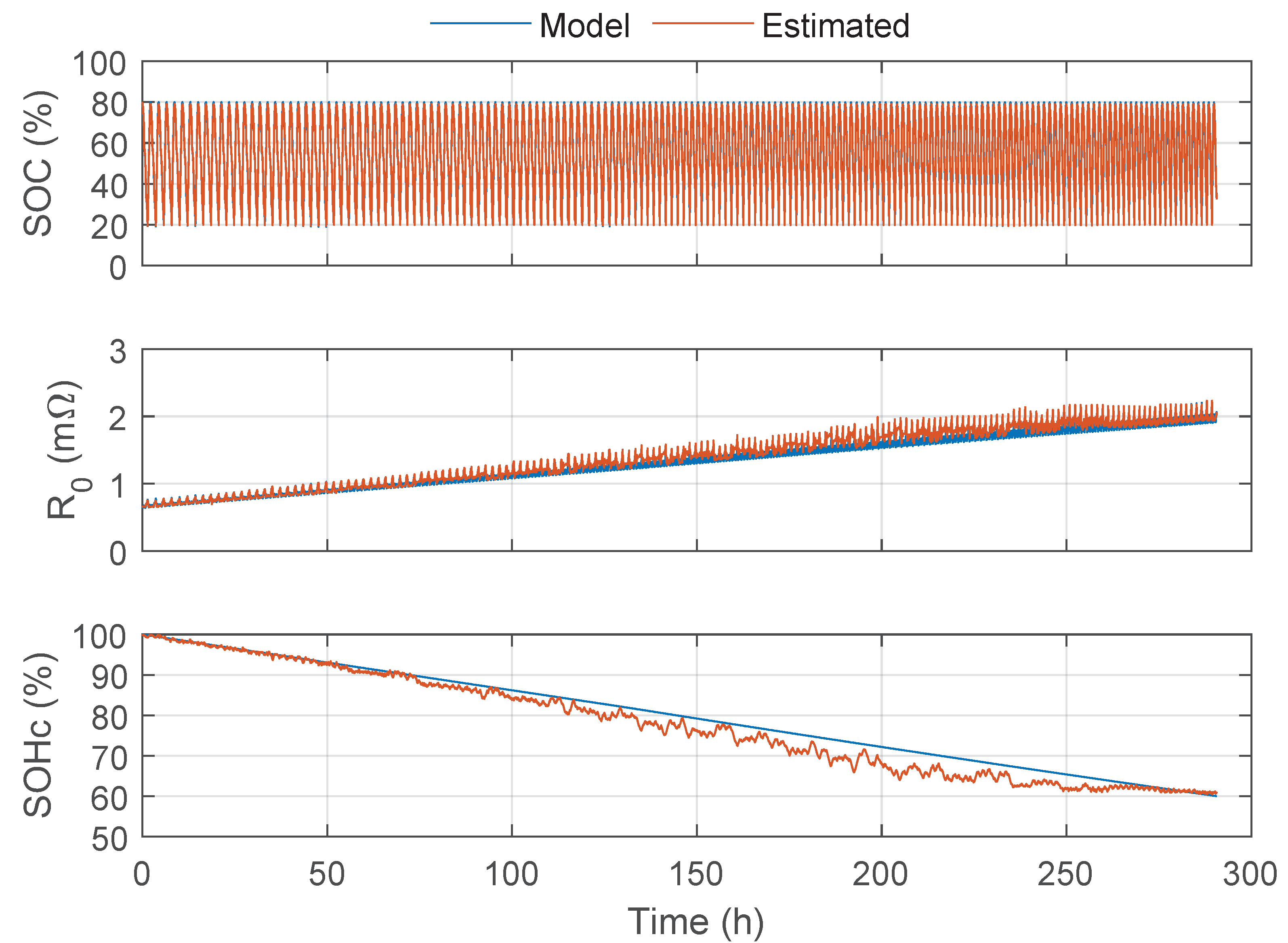
5. Result Discussion and Comparison
6. Conclusions
- Developing a reinforcement learning algorithm to improve the algorithm performance.
- Applying model compression and quantization techniques, which are aimed at reducing the model size and enhancing inference speed.
- Deployment on a microcontroller for practical application to a battery management system.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suganya, R.; Leo Joseph, L.M.I.; Kollem, S. Understanding lithium-ion battery management systems in electric vehicles: Environmental and health impacts, comparative study, and future trends: A review. Results Eng. 2024, 24, 103047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Yin, J.; Cao, Z.; Wu, L.; Wei, N.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Guo, D.; Zhang, Q.; Mao, H. Regional vehicle energy consumption evaluation framework to quantify the benefits of vehicle electrification in plateau city: A case study of Xining, China. Appl. Energy 2025, 377, 124626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zhou, Q.; Li, X.; Xiong, X. Fast-charging anodes for lithium ion batteries: Progress and challenges. Chem. Commun. 2024, 60, 2472–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baronti, F.; Di Rienzo, R.; Moras, R.; Roncella, R.; Saletti, R.; Pede, G.; Vellucci, F. Implementation of the fast charging concept for electric local public transport: The case-study of a minibus. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 13th International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN), Cambridge, UK, 22–24 July 2015; pp. 1284–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Rienzo, R.; Baronti, F.; Vellucci, F.; Cignini, F.; Ortenzi, F.; Pede, G.; Roncella, R.; Saletti, R. Experimental analysis of an electric minibus with small battery and fast charge policy. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Electrical Systems for Aircraft, Railway, Ship Propulsion and Road Vehicles & International Transportation Electrification Conference (ESARS-ITEC), Toulouse, France, 2–4 November 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Deng, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, W.; Zhou, J.; Xiang, F.; Hu, X. State-of-health estimation for fast-charging lithium-ion batteries based on a short charge curve using graph convolutional and long short-term memory networks. J. Energy Chem. 2024, 98, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, L.; Yan, C.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Gao, G.; Ren, Z.; Li, S.; et al. A novel lithium-ion battery state-of-health estimation method for fast-charging scenarios based on an improved multi-feature extraction and bagging temporal attention network. J. Energy Storage 2024, 99, 113396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epding, B.; Rumberg, B.; Mense, M.; Jahnke, H.; Kwade, A. Aging-Optimized Fast Charging of Lithium Ion Cells Based on Three-Electrode Cell Measurements. Energy Technol. 2020, 8, 2000457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalk, A.; Leuthner, L.; Kupper, C.; Hiller, M. An Aging-Optimized State-of-Charge-Controlled Multi-Stage Constant Current (MCC) Fast Charging Algorithm for Commercial Li-Ion Battery Based on Three-Electrode Measurements. Batteries 2024, 10, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhong, C.; Xu, P.; Tian, Y. Deep Learning in the State of Charge Estimation for Li-Ion Batteries of Electric Vehicles: A Review. Machines 2022, 10, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain Lipu, M.; Ansari, S.; Miah, M.S.; Meraj, S.T.; Hasan, K.; Shihavuddin, A.; Hannan, M.; Muttaqi, K.M.; Hussain, A. Deep learning enabled state of charge, state of health and remaining useful life estimation for smart battery management system: Methods, implementations, issues and prospects. J. Energy Storage 2022, 55, 105752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Luo, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, H. State of Health Assessment for Lithium-Ion Batteries Using Incremental Energy Analysis and Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory. World Electr. Veh. J. 2023, 14, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Chen, C.; Shen, W.; Sun, F.; Xiong, R. Deep Learning Framework for Lithium-ion Battery State of Charge Estimation: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives. Energy Storage Mater. 2023, 61, 102883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Min, H.; Guo, H.; Yu, Y.; Sun, W.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, H. State of health estimation method for lithium-ion batteries using incremental capacity and long short-term memory network. J. Energy Storage 2023, 64, 107063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Dio, R.; Aurilio, G.; Di Rienzo, R.; Saletti, R. Machine Learning for SOC Estimation in Li-Ion Batteries. In Proceedings of the 2024 Applications in Electronics Pervading Industry, Environment and Society (Applepies), Turin, Italy, 19–20 September 2024; pp. 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamin, K.S.S.; Chen, Y.; Macii, E.; Poncino, M.; Vinco, S. A Machine Learning-based Digital Twin for Electric Vehicle Battery Modeling. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Omni-layer Intelligent Systems (COINS), Barcelona, Spain, 1–3 August 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleftheriadis, P.; Giazitzis, S.; Leva, S.; Ogliari, E. Data-Driven Methods for the State of Charge Estimation of Lithium-Ion Batteries: An Overview. Forecasting 2023, 5, 576–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azkue, M.; Miguel, E.; Martinez-Laserna, E.; Oca, L.; Iraola, U. Creating a Robust SoC Estimation Algorithm Based on LSTM Units and Trained with Synthetic Data. World Electr. Veh. J. 2023, 14, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattouti, L.A.; Di Rienzo, R.; Nicodemo, N.; Verani, A.; Baronti, F.; Roncella, R.; Saletti, R. Comparison of Lithium-Ion Battery SoC Estimation Accuracy of LSTM Neural Network Trained with Experimental and Synthetic Datasets. Lect. Notes Electr. Eng. 2024, 1110, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Jiang, B.; Wei, X.; Dai, H. A Systematic and Comparative Study of Distinct Recurrent Neural Networks for Lithium-Ion Battery State-of-Charge Estimation in Electric Vehicles. Energies 2023, 16, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Gulcehre, C.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Empirical Evaluation of Gated Recurrent Neural Networks on Sequence Modeling. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.3555. [Google Scholar]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Ma, L. A comparative study of different deep learning algorithms for lithium-ion batteries on state-of-charge estimation. Energy 2023, 263, 125872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islameka, M.; Budiman, B.A.; Juangsa, F.B.; Aziz, M. 5-Energy management systems for battery electric vehicles. In Emerging Trends in Energy Storage Systems and Industrial Applications; Prabhansu, Kumar, N., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 113–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morello, R.; Di Rienzo, R.; Roncella, R.; Saletti, R.; Baronti, F. Hardware-in-the-Loop Platform for Assessing Battery State Estimators in Electric Vehicles. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 68210–68220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurilio, G.; Gallo, D.; Landi, C.; Luiso, M.; Rosano, A.; Landi, M.; Paciello, V. A battery equivalent-circuit model and an advanced technique for parameter estimation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC) Proceedings, Pisa, Italy, 11–14 May 2015; pp. 1705–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawuntu, N.N.; Mu, B.Q.; Doukhi, O.; Lee, D.J. Modeling of the Battery Pack and Battery Management System towards an Integrated Electric Vehicle Application. Energies 2023, 16, 7165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Qiao, W.; Qu, L. Real-time state of charge and electrical impedance estimation for lithium-ion batteries based on a hybrid battery model. In Proceedings of the 2013 Twenty-Eighth Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Long Beach, CA, USA, 17–21 March 2013; pp. 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo-Iglesias, E.; Venet, P.; Pelissier, S. Calendar and cycling ageing combination of batteries in electric vehicles. Microelectron. Reliab. 2018, 88–90, 1212–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadass, P.; Haran, B.; White, R.; Popov, B.N. Mathematical modeling of the capacity fade of Li-ion cells. J. Power Sources 2003, 123, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, G.; Haran, B.; Popov, B.N. Capacity fade study of lithium-ion batteries cycled at high discharge rates. J. Power Sources 2003, 117, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröer, P.; van Faassen, H.; Nemeth, T.; Kuipers, M.; Sauer, D.U. Challenges in modeling high power lithium titanate oxide cells in battery management systems. J. Energy Storage 2020, 28, 101189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, H.; Eze, C.; Wang, J.; Lian, Y.; Burke, A.F. Cloud-Based Deep Learning for Co-Estimation of Battery State of Charge and State of Health. Energies 2023, 16, 3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arandhakar, S.; Nakka, J. State of charge estimation of lithium ion battery for electric vehicle using cutting edge machine learning algorithms: A review. J. Energy Storage 2024, 103, 114281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Kerb weight M | 1525 kg |
| Surface area S | 2.27 m2 |
| Drag coefficient | 0.29 |
| Rolling resistance | 0.01 |
| Air density | 1.2 kg/m3 |
| Road slope | 0 |
| Gravitational acceleration g | 9.82 m/s2 |
| System efficiency | 0.7 |
| Symbol | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| q | Electron elementary charge | C |
| K | Boltzmann constant | |
| Terminal resistance constant gain for voltage | 0.0594 | |
| Terminal resistance constant offset for voltage | −0.0713 | |
| Terminal resistance temperature-dependent exponential increase | 0.4985 | |
| Terminal resistance constant gain for current | 2.5867 | |
| Terminal capacity constant gain for voltage | 0.0594 | |
| Terminal capacity constant offset for voltage | −0.0713 | |
| Terminal capacity temperature-dependent exponential increase | 0.4985 | |
| Terminal capacity constant gain for current | 0.4533 |
| Drive Cycle | Scenario | Distance | Duration | Average Speed | Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (km) | (min) | (km/h) | |||
| La92short | Urban | 11.1 | 16 | 41.8 | Training |
| J1015 | Urban | 6.4 | 15 | 25.6 | Training |
| HWFET | Highway | 16.8 | 13 | 77.5 | Training |
| ArtMw150 | Motorway | 29.8 | 18 | 99.5 | Training |
| ArtUrban | Urban | 5.0 | 17 | 17.6 | Training |
| FTP | Urban | 17.6 | 31 | 34.1 | Validation |
| ArtRoad | Rural road | 17.2 | 18 | 57.4 | Validation |
| WLTP | Mixed | 23.3 | 30 | 46.5 | Test |
| Chunk Size | Learning Rate | Hidden Units | MAE (%) | MAPE (%) | RMSE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 0.01 | 20 | 3.0553 | 7.7688 | 4.2216 |
| 100 | 0.01 | 32 | 27.4707 | 80.6835 | 32.9009 |
| 100 | 0.01 | 50 | 6.3870 | 25.1024 | 10.0717 |
| 100 | 0.02 | 20 | 17.2782 | 31.8322 | 19.9990 |
| 100 | 0.02 | 32 | 20.4943 | 33.5117 | 24.5322 |
| 1000 | 0.01 | 50 | 1.5717 | 4.8987 | 1.8302 |
| 1000 | 0.02 | 20 | 1.6536 | 5.1177 | 2.0221 |
| 1000 | 0.02 | 32 | 3.9563 | 7.8092 | 5.2773 |
| 1000 | 0.02 | 50 | 24.5365 | 44.8146 | 28.2875 |
| Temperature | RMSE | MAE | MAPE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOC | 25 ∘C | 2.0% | 1.5% | 3.4% |
| 35 ∘C | 1.8% | 1.3% | 3.0% | |
| 25 ∘C | 80 μΩ | 58 μΩ | 3.8% | |
| 35 ∘C | 71 μΩ | 55 μΩ | 4.2% | |
| SOHc | 25 ∘C | 2.9% | 2.2% | 3.22% |
| 35 ∘C | 2.9% | 2.4% | 3.3% |
| Ref. | Algorithm | Condition | RMSE (%) | MAE (%) | MAPE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| our | LSTM | Fresh cell, 25 ∘C | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.4 |
| Fresh cell, noise, 25 ∘C | 1.0 | 0.8 | 1.7 | ||
| Fresh cell, noise, 35 ∘C | 0.9 | 0.7 | 1.5 | ||
| SOH 60%, noise, 25 ∘C | 2.9 | 2.2 | 4.2 | ||
| SOH 60%, noise, 35 ∘C | 2.4 | 1.9 | 3.7 | ||
| [20] | GRU | Fresh cell, 25 ∘C | 6.3 | 4.9 | 15.8 |
| SOH 98%, 25 ∘C | 6.4 | 5.0 | 16.1 | ||
| LSTM | Fresh cell, 25 ∘C | 5.7 | 4.4 | 15.9 | |
| SOH 98%, 25 ∘C | 5.7 | 4.5 | 16.2 | ||
| BGRU | Fresh cell, 25 ∘C | 5.4 | 4.5 | 14.7 | |
| SOH 98%, 25 ∘C | 5.5 | 4.6 | 15.0 | ||
| BLSTM | Fresh cell, 25 ∘C | 4.5 | 3.6 | 14.1 | |
| SOH 98%, 25 ∘C | 4.5 | 3.6 | 14.3 | ||
| [23] | FCNN | Fresh cell, 25 ∘C | 3.1 | 2.34 | |
| Fresh cell, 40 ∘C | 3.0 | 2.3 | |||
| LSTM | Fresh cell, 25 ∘C | 0.8 | 0.7 | ||
| Fresh cell, 40 ∘C | 0.6 | 0.5 | |||
| GRU | Fresh cell, 25 ∘C | 0.6 | 0.4 | ||
| Fresh cell, 40 ∘C | 0.5 | 0.3 | |||
| TCN | Fresh cell, 25 ∘C | 0.85 | 0.7 | ||
| Fresh cell, 40 ∘C | 0.6 | 0.4 | |||
| [33] | BERT | Fresh cell | 0.81 | 2.5 | |
| [34] | FNN | Fresh cell | 2.24 | ||
| GRU | Fresh cell | 1.13 | |||
| LSTM | Fresh cell | 1.5 | |||
| [18] | LSTM | Fresh cell | 1.64 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Dio, R.; Di Rienzo, R.; Aurilio, G.; Cavaliere, D.; Saletti, R. Advanced Algorithm for SOC, Internal Resistance, and SOH Co-Estimation of Lithium-Titanate-Oxide Batteries Using Neural Networks. Batteries 2025, 11, 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries11060235
Di Dio R, Di Rienzo R, Aurilio G, Cavaliere D, Saletti R. Advanced Algorithm for SOC, Internal Resistance, and SOH Co-Estimation of Lithium-Titanate-Oxide Batteries Using Neural Networks. Batteries. 2025; 11(6):235. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries11060235
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Dio, Riccardo, Roberto Di Rienzo, Gianluca Aurilio, Davide Cavaliere, and Roberto Saletti. 2025. "Advanced Algorithm for SOC, Internal Resistance, and SOH Co-Estimation of Lithium-Titanate-Oxide Batteries Using Neural Networks" Batteries 11, no. 6: 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries11060235
APA StyleDi Dio, R., Di Rienzo, R., Aurilio, G., Cavaliere, D., & Saletti, R. (2025). Advanced Algorithm for SOC, Internal Resistance, and SOH Co-Estimation of Lithium-Titanate-Oxide Batteries Using Neural Networks. Batteries, 11(6), 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries11060235











