The Origin of Improved Cycle Stability of Li-O2 Batteries Using High-Concentration Electrolytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
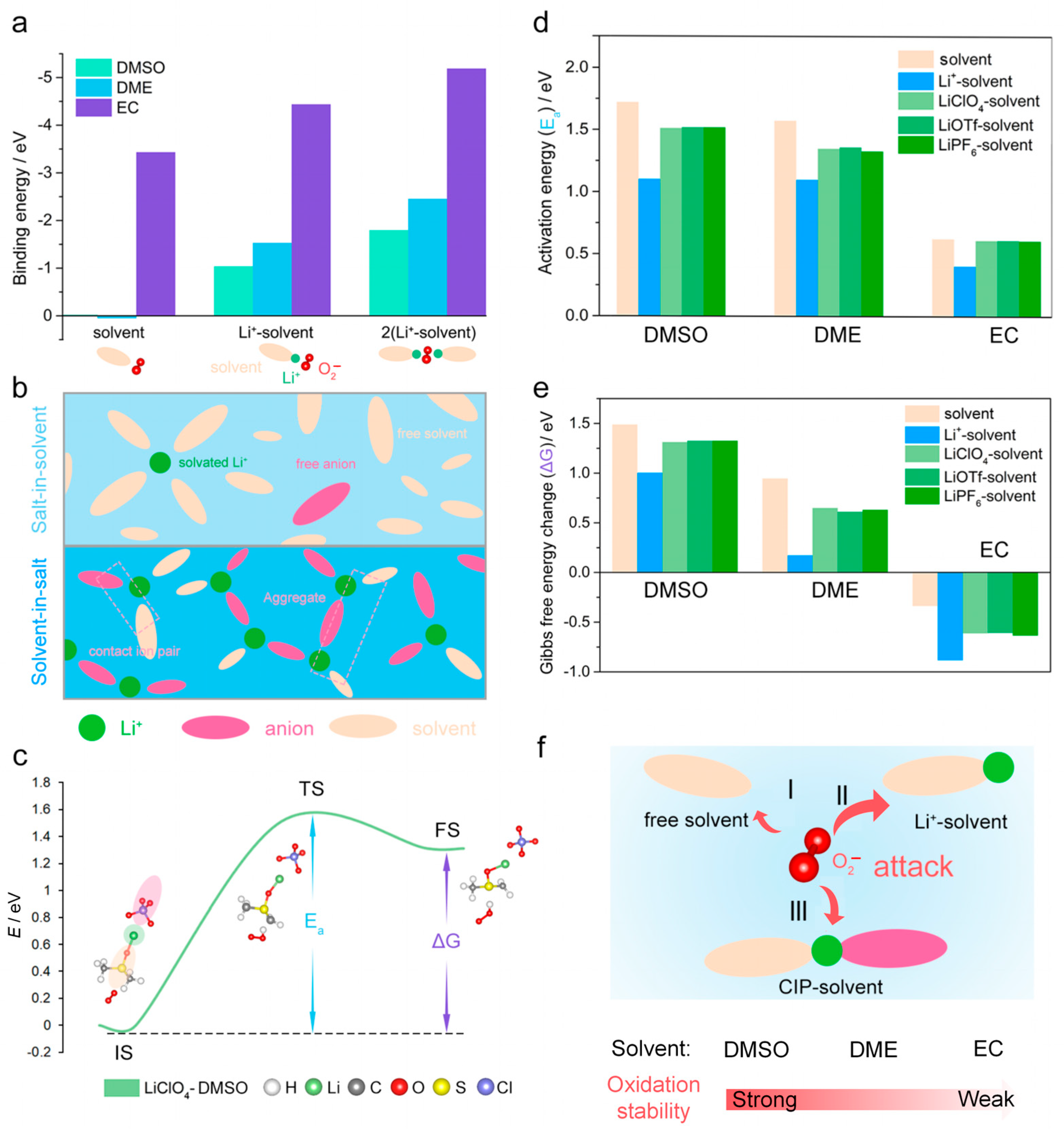
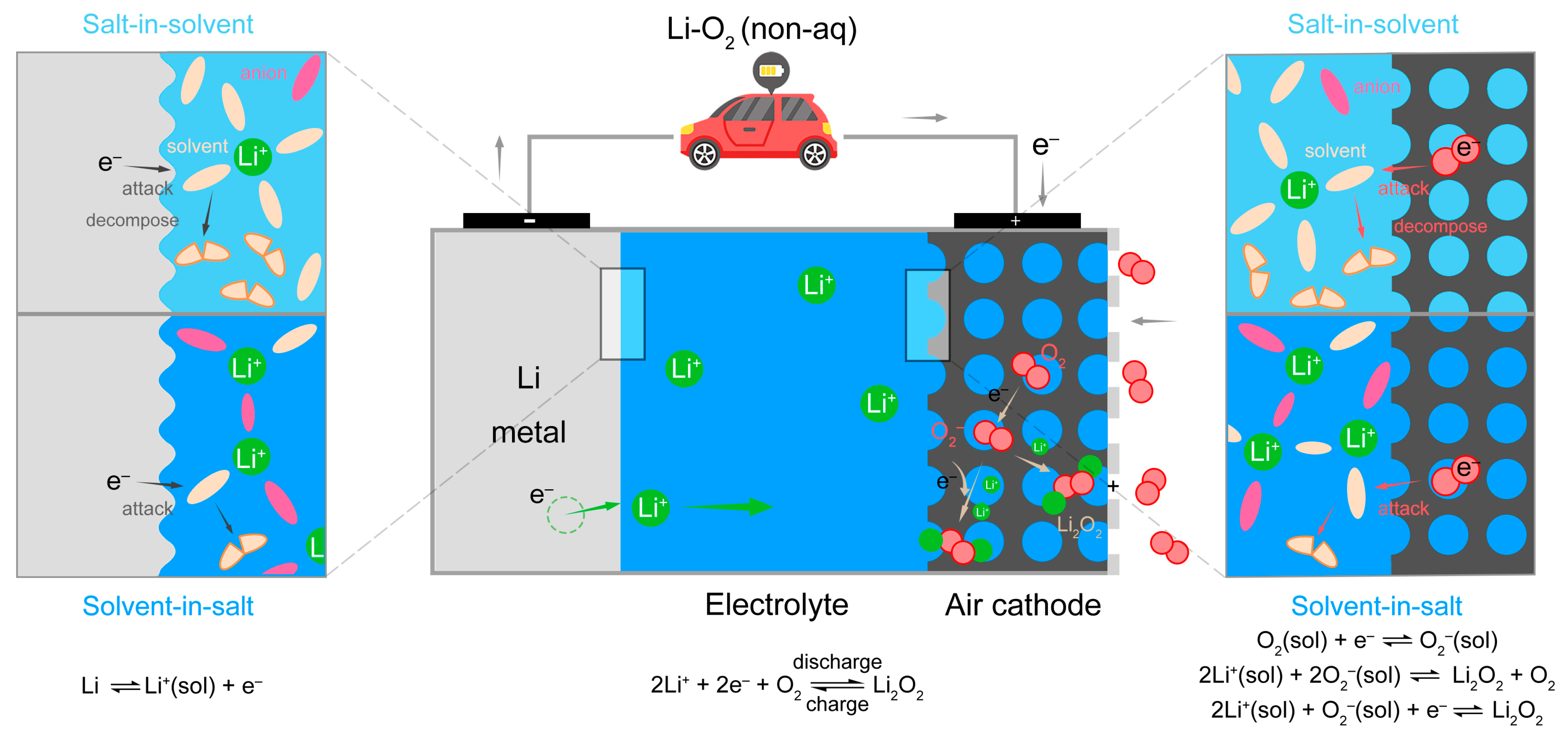
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, J.; Meng, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, S.; Luo, S. Advancements in Lithium–Oxygen Batteries: A Comprehensive Review of Cathode and Anode Materials. Batteries 2024, 10, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.; Hu, L.; Yu, X.; Wang, L.; Fernandez, C.; Yang, N.; Liang, Q.; Yang, Q.H. Engineering Triple-Phase Interfaces around the Anode toward Practical Alkali Metal-Air Batteries. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, e2400937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Liu, D.; Gao, L.; Yu, D.; Liu, X.; Li, L.; Kang, W. Novel Guidelines of Redox Mediators for Practical Lithium–Oxygen Batteries: Characterization Mechanisms, Design Principle, and Engineering Strategies. Adv. Energy Mater. 2025, 15, 2403406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Li, J.; Dahbi, M.; Alami, J.; Amine, K.; Lu, J. Understanding the Role of Lithium Iodide in Lithium–Oxygen Batteries. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2106148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, D.; Shen, X.; Wang, A.; Yu, F.; Wu, Y.; Shi, S.; Freunberger, S.A.; Chen, Y. Threshold potentials for fast kinetics during mediated redox catalysis of insulators in Li–O2 and Li–S batteries. Nat. Catal. 2022, 5, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Wen, B.; Huang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, F. New Reaction Pathway of Superoxide Disproportionation Induced by a Soluble Catalyst in Li-O2 Batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 136, e202315314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Song, L.; Wang, N.; Fu, Y.; Ren, R.; Li, Z.; Lu, Y.; Xu, J.; Liu, Q. Harnessing 4f Electron Itinerancy for Integrated Dual-Band Redox Systems Boosts Lithium-Oxygen Batteries Electrocatalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202414893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, X.; Tian, G.; Fan, F.; Wen, X.; Liu, P.; Shu, C. Manipulating Electron Delocalization of Metal Sites via a High-Entropy Strategy for Accelerating Oxygen Electrode Reactions in Lithium–Oxygen Batteries. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 27804–27816. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.4c11909 (accessed on 30 January 2025). [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, H.; Lin, Y.; Yu, K.; Nan, C.; Chen, C. Atomically Dispersed Ruthenium Catalysts with Open Hollow Structure for Lithium–Oxygen Batteries. Nano-Micro Lett. 2024, 16, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genorio, B.; Staszak-Jirkovský, J.; Assary, R.S.; Connell, J.G.; Strmcnik, D.; Diesendruck, C.E.; Lopes, P.P.; Stamenkovic, V.R.; Moore, J.S.; Curtiss, L.A.; et al. Superoxide (Electro)Chemistry on Well-Defined Surfaces in Organic Environments. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 15909–15914. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b12230 (accessed on 10 March 2024). [CrossRef]
- Bryantsev, V.S.; Blanco, M. Computational Study of the Mechanisms of Superoxide-Induced Decomposition of Organic Carbonate-Based Electrolytes. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 379–383. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jz1016526 (accessed on 20 April 2025). [CrossRef]
- Freunberger, S.A.; Chen, Y.; Peng, Z.; Griffin, J.M.; Hardwick, L.J.; Bardé, F.; Novák, P.; Bruce, P.G. Reactions in the Rechargeable Lithium–O2 Battery with Alkyl Carbonate Electrolytes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 8040–8047. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/ja2021747 (accessed on 15 April 2024). [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, E.; Peng, Z. Mechanistic Study on Oxygen Reduction Reaction in High-Concentrated Electrolytes for Aprotic Lithium–Oxygen Batteries. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2024, 15, 10111–10117. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jpclett.4c02455 (accessed on 18 July 2025). [CrossRef]
- Pranay Reddy, K.; Fischer, P.; Marinaro, M.; Wohlfahrt-Mehrens, M. Improved Li–Metal Cycling Performance in High Concentrated Electrolytes for Li-O2 Batteries. ChemElectroChem 2018, 5, 2758–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xu, W.; Yan, P.; Sun, X.; Bowden, M.E.; Read, J.; Qian, J.; Mei, D.; Wang, C.-M.; Zhang, J.-G. Enhanced Cycling Stability of Rechargeable Li–O2 Batteries Using High-Concentration Electrolytes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xu, W.; Yan, P.; Kim, S.T.; Engelhard, M.H.; Sun, X.; Mei, D.; Cho, J.; Wang, C.M.; Zhang, J.G. Stabilization of Li Metal Anode in DMSO-Based Electrolytes via Optimization of Salt–Solvent Coordination for Li–O2 Batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1602605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, H.R.; Shen, X.; Zhang, Q. The Origin of the Reduced Reductive Stability of Ion-Solvent Complexes on Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metal Anodes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 16643–16647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16 Rev. C.01, Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. Available online: https://gaussian.com/citation (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Hou, T.; Fong, K.D.; Wang, J.; Persson, K.A. The Solvation Structure, Transport Properties and Reduction Behavior of Carbonate-based Electrolytes of Lithium-Ion Batteries. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 14740–14751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Xu, H.; Cao, B.; Ma, J.; Yu, Z.W. In Situ Species Analysis of a Lithium-Ion Battery Electrolyte Containing LiTFSI and Propylene Carbonate. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2024, 15, 5047–5055. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jpclett.4c00641 (accessed on 16 May 2025). [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Shin, K.H.; Han, Y.K. Origin of Li+ Solvation Ability of Electrolyte Solvent: Ring Strain. Materials 2023, 16, 6995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon, D.; Afri, M.; Noked, M.; Garsuch, A.; Frimer, A.A.; Aurbach, D. Oxidation of Dimethyl Sulfoxide Solutions by Electrochemical Reduction of Oxygen. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 3115–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, J.M.; Horn, H.W.; Rice, J.E. Dominant Decomposition Pathways for Ethereal Solvents in Li–O2 Batteries. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 1795–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Zheng, X.; Schroeder, M.; Alvarado, J.; von Wald Cresce, A.; Xu, K.; Li, Q.; Li, W. Deciphering the Ethylene Carbonate–Propylene Carbonate Mystery in Li-Ion Batteries. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaumaux, P.; Yang, X.; Zhang, B.; Safaei, J.; Tang, X.; Zhou, D.; Wang, C.; Wang, G. Localized Water-In-Salt Electrolyte for Aqueous Lithium-Ion Batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 19965–19973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidi, S.S.H.; Douglas, J.T.; Li, X. Fluorobenzene-Diluted Localized Highly Concentrated Electrolyte for Enhanced Electrochemical Performance of Li–O2 Battery. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2024, 7, 8610–8621. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsaem.4c01566 (accessed on 14 February 2025). [CrossRef]
- Shu, C.; Wang, J.; Long, J.; Liu, H.K.; Dou, S.X. Understanding the Reaction Chemistry during Charging in Aprotic Lithium-Oxygen Batteries: Existing Problems and Solutions. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1804587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Vatamanu, J.; Ji, X.; Pollard, T.P.; Cui, C.; Hou, S.; Chen, J.; Yang, C.; et al. A 63 m Superconcentrated Aqueous Electrolyte for High-Energy Li-Ion Batteries. ACS Energy Lett. 2020, 5, 968–974. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsenergylett.0c00348 (accessed on 13 February 2025). [CrossRef]
- Khetan, A.; Arjmandi, H.R.; Pande, V.; Pitsch, H.; Viswanathan, V. Understanding Ion Pairing in High-Salt Concentration Electrolytes Using Classical Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Its Implications for Nonaqueous Li–O2 Batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 8094–8101. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b00944 (accessed on 29 March 2024). [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, W.; Liu, X.; Li, G.; Yu, K.; Wang, P.; Lei, M.; Zhen, C.; Miao, L.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; et al. The Origin of Improved Cycle Stability of Li-O2 Batteries Using High-Concentration Electrolytes. Batteries 2025, 11, 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries11100349
Fan W, Liu X, Li G, Yu K, Wang P, Lei M, Zhen C, Miao L, Wang J, Li C, et al. The Origin of Improved Cycle Stability of Li-O2 Batteries Using High-Concentration Electrolytes. Batteries. 2025; 11(10):349. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries11100349
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Wei, Xu Liu, Guangqian Li, Ke Yu, Peng Wang, Min Lei, Ce Zhen, Lei Miao, Jialiang Wang, Chun Li, and et al. 2025. "The Origin of Improved Cycle Stability of Li-O2 Batteries Using High-Concentration Electrolytes" Batteries 11, no. 10: 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries11100349
APA StyleFan, W., Liu, X., Li, G., Yu, K., Wang, P., Lei, M., Zhen, C., Miao, L., Wang, J., Li, C., Hou, J., Ji, H., & Miao, L. (2025). The Origin of Improved Cycle Stability of Li-O2 Batteries Using High-Concentration Electrolytes. Batteries, 11(10), 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries11100349






