Substitution Effects in Spin-Polarized (Cr4-xFex)0.5AC (A = Ge, Si, Al) MAX Phases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Computational Details
3. Results and Discussion
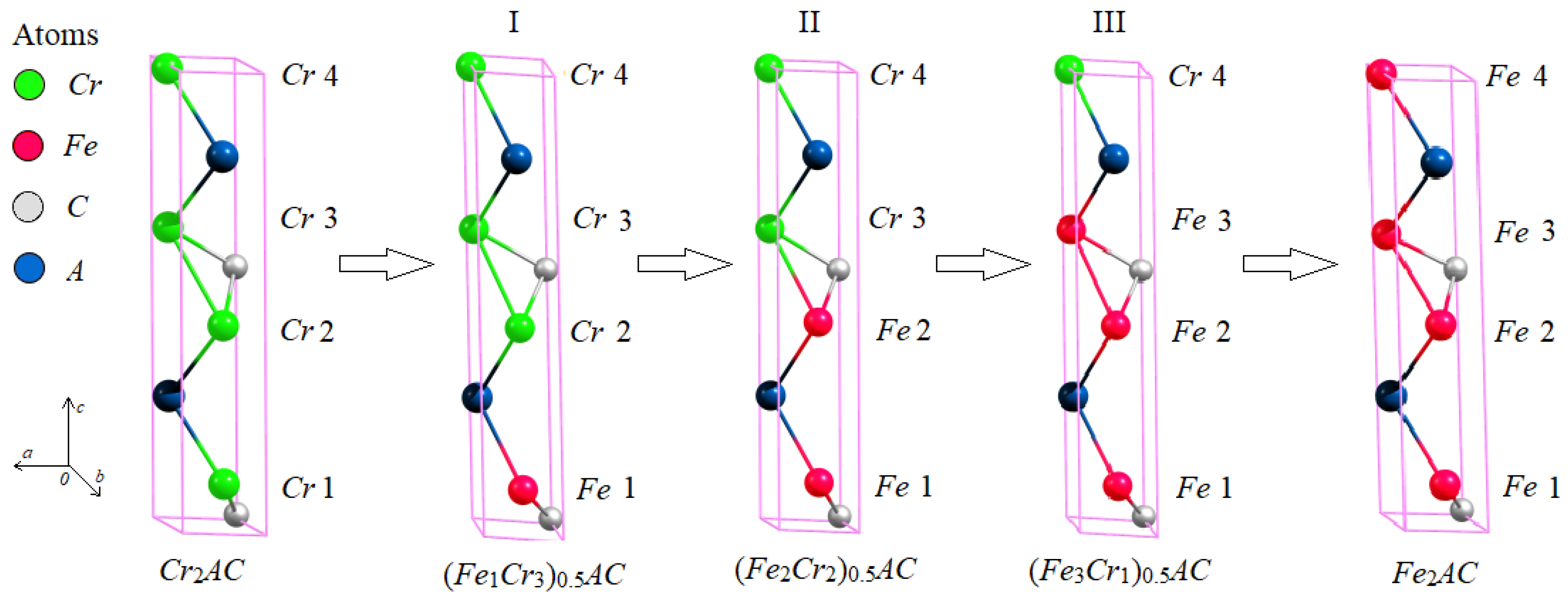
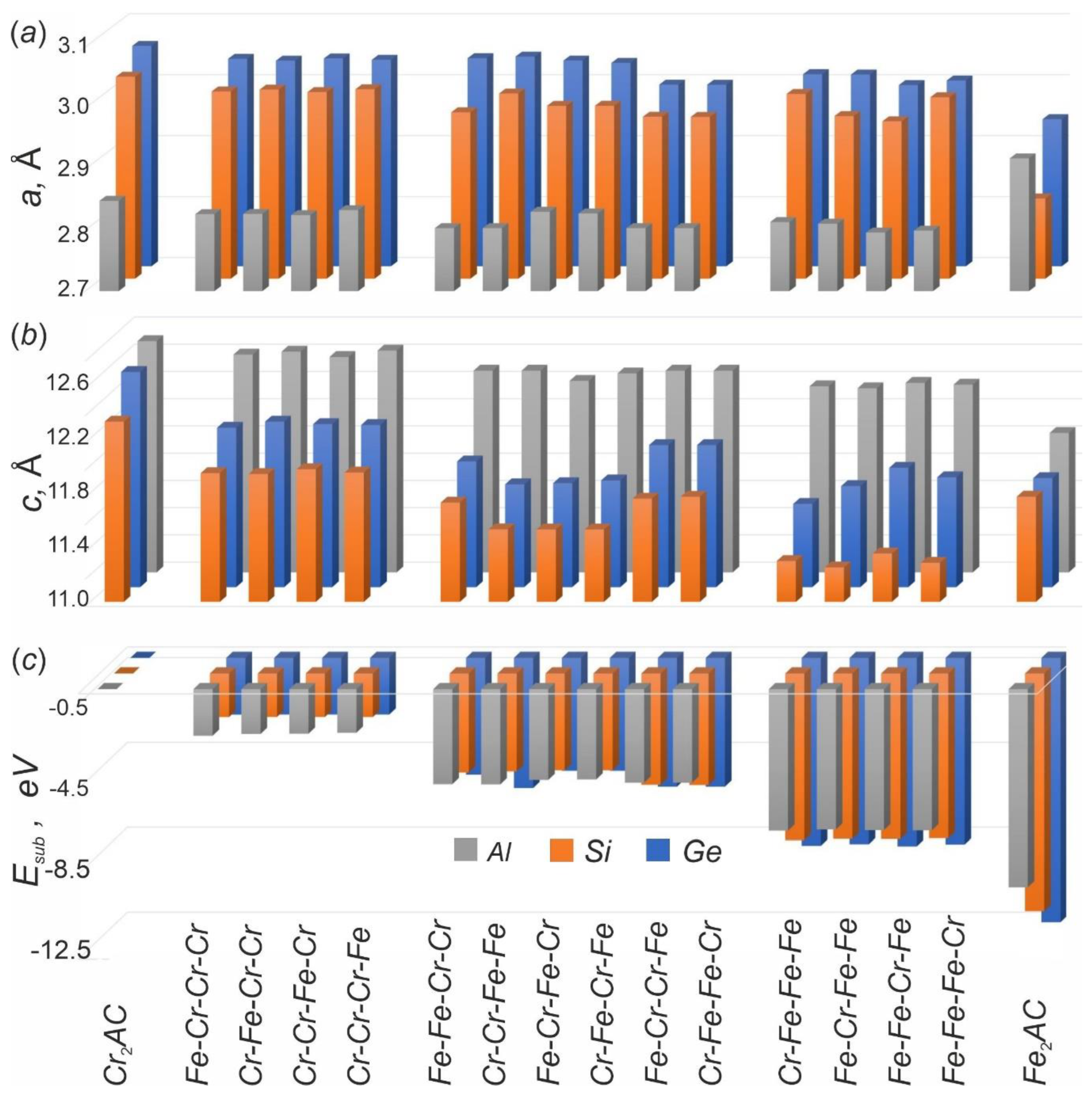
3.1. The Atomic Structure of Substituted MAX Phases
3.2. Energetic Characteristics
3.3. Band Structure
3.4. Density of Electronic States
3.5. Magnetic Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smetkin, A.; Maiorova, I. Properties of materials based on the MAX-phases (Review). PNIPU Bull. Mech. Eng. Mater. Sci. 2015, 17, 120–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Duan, X.; Jia, D.; Zhou, Y.; van der Zwaag, S. On the formation mechanisms and properties of MAX phases: A review. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 41, 3851–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, J.; Liu, D.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Zhong, B.; Ma, Y. MAX phase-derived woolen ball-like K2Ti8O17 with excellent surface-enhanced Raman scattering property. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 15145–15153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Wang, Z.; Ma, G.; Bai, X.; Li, Y.; Cheng, X.; Ke, P.; Wang, A. MAX phase forming mechanism of M–Al–C (M = Ti, V, Cr) coatings: In-situ X-ray diffraction and first-principle calculations. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 143, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsteinsson, E.B.; Ingason, A.S.; Magnus, F. Magnetic ordering and magnetocrystalline anisotropy in epitaxial Mn2GaC MAX phase thin films. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2023, 7, 34409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamm, C.M.; Bocarsly, J.D.; Seward, G.; Kramm, U.I.; Birkel, C.S. Non-conventional synthesis and magnetic properties of MAX phases (Cr/Mn)2AlC and (Cr/Fe)2AlC. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 5700–5708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinek, D.; Ito, T.; Ikemoto, M.; Yaji, K.; Nakatake, M.; Shin, S.; Ouisse, T. Unified description of the electronic structure of M2AC nanolamellar carbides. Phys. Rev. B 2019, 100, 75144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 15 Years of Graphene Electronics. Nat. Electron. 2019, 2, 369. [CrossRef]
- Goossens, N.; Tunca, B.; Lapauw, T.; Lambrinou, K.; Vleugels, J. MAX Phases, Structure, Processing, and Properties; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlqvist, M.; Alling, B.; Abrikosov, I.A.; Rosén, J. Magnetic nanoscale laminates with tunable exchange coupling from first principles. Phys. Rev. B—Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2011, 84, 220403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlqvist, M.; Rosén, J. Predictive theoretical screening of phase stability for chemical order and disorder in quaternary 312 and 413 MAX phases. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mockute, A.; Dahlqvist, M.; Emmerlich, J.; Hultman, L.; Schneider, J.M.; Persson, P.O.Å.; Rosén, J. Synthesis and ab initio calculations of nanolaminated (Cr,Mn)2AlC compounds. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 87, 94113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salikhov, R.; Semisalova, A.S.; Petruhins, A.; Ingason, Á.S.; Rosén, J.; Wiedwald, U.; Farle, M. Magnetic anisotropy in the (Cr0.5Mn0.5)2Gac MAX phase. Mater. Res. Lett. 2015, 3, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salikhov, R.; Meshkian, R.; Weller, D.; Zingsem, B.; Spoddig, D.; Lu, J.; Ingason, Á.S.; Zhang, H.; Rosén, J.; Wiedwald, U.; et al. Magnetic properties of nanolaminated (Mo0.5Mn0.5)2GaC MAX phase. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 121, 163904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmer, D.; Opahle, I.; Singh, H.K.; Zhang, H. Stability predictions of magnetic M2AX compounds. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2019, 31, 405902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Q.; Lu, J.; Dahlqvist, M.; Mockute, A.; Calder, S.; Petruhins, A.; Meshkian, R.; Rivin, O.; Potashnikov, D.; Caspi, E.N.; et al. Atomically Layered and Ordered Rare-Earth i -MAX Phases: A New Class of Magnetic Quaternary Compounds. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 2476–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruhins, A.; Ingason, Á.S.; Lu, J.; Magnus, F.; Olafsson, S.; Rosén, J. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic (Cr0.5Mn0.5)2GaC thin films. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 4495–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselova, I.P.; Petruhins, A.; Wiedwald, U.; Weller, D.; Rosén, J.; Farle, M.; Salikhov, R. Long-term stability and thickness dependence of magnetism in thin (Cr0.5Mn0.5)2GaC MAX phase films. Mater. Res. Lett. 2019, 7, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselova, I.P.; Petruhins, A.; Wiedwald, U.; Ingason, Á.S.; Hase, T.; Magnus, F.; Kapaklis, V.; Palisaitis, J.; Spasova, M.; Farle, M.; et al. Large uniaxial magnetostriction with sign inversion at the first order phase transition in the nanolaminated Mn2GaC MAX phase. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyaschenko, S.; Maximova, O.; Shevtsov, D.; Varnakov, S.; Tarasov, I.; Wiedwald, U.; Rosén, J.; Ovchinnikov, S.G.; Farle, M. Optical and magneto-optical properties of epitaxial Mn2GaC MAX phase thin film. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2021, 528, 167803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowotny, H. Strukturchemie einiger Verbindungen der Übergangsmetalle mit den elementen C, Si, Ge, Sn. Prog. Solid State Chem. 1971, 5, 27–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingason, Á.S.; Mockute, A.; Dahlqvist, M.; Magnus, F.; Olafsson, S.; Arnalds, U.B.; Alling, B.; Abrikosov, I.A.; Hjörvarsson, B.; Persson, P.O.Å.; et al. Magnetic Self-Organized Atomic Laminate from First Principles and Thin Film Synthesis. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 195502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklund, P.; Bugnet, M.; Mauchamp, V.; Dubois, S.; Tromas, C.; Jensen, J.; Piraux, L.; Gence, L.; Jaouen, M.; Cabioc’h, T. Epitaxial growth and electrical transport properties of Cr2GeC thin films. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 75424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, G.; He, X.; Li, M.; Han, W.; He, F.; Du, S. Synthesis and mechanical properties of high-purity Cr2AlC ceramic. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 2635–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Li, S.; Song, G.; Sloof, W.G. Synthesis and thermal stability of Cr2AlC. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 31, 1497–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzan, M.; Lebègue, S.; Ahuja, R. Electronic and mechanical properties of Cr2GeC with hybrid functional and correlation effects. Solid State Commun. 2012, 152, 1147–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized Gradient Approximation Made Simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisimov, V.I.; Aryasetiawan, F.; Lichtenstein, A.I. First-principles calculations of the electronic structure and spectra of strongly correlated systems: The LDA + U method. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1997, 9, 767–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyd, J.; Scuseria, G.E.; Ernzerhof, M. Hybrid functionals based on a screened Coulomb potential. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 118, 8207, Erratum in J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 124, 219906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guido, C.A.; Brémond, E.; Adamo, C.; Cortona, P. Communication: One third: A new recipe for the PBE0 paradigm. J. Chem. Phys. 2013, 138, 21104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Yang, W.; Parr, R.G. Development of the Colle-Salvetti correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron density. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 37, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D.G. The M06 suite of density functionals for main group thermochemistry, thermochemical kinetics, noncovalent interactions, excited states, and transition elements: Two new functionals and systematic testing of four M06-class functionals and 12 other functionals. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2008, 120, 215–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D.G. A new local density functional for main-group thermochemistry, transition metal bonding, thermochemical kinetics, and noncovalent interactions. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 125, 194101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilela Oliveira, D.; Laun, J.; Peintinger, M.F.; Bredow, T. BSSE-correction scheme for consistent gaussian basis sets of double- and triple-zeta valence with polarization quality for solid-state calculations. J. Comput. Chem. 2019, 40, 2364–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, T.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y. Chemical bonding and mechanical properties of M2AC (M = Ti, V, Cr, A = Al, Si, P, S) ceramics from first-principles investigations. J. Mater. Res. 2009, 24, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metadjer, N.; Beldi, L.; Bouhafs, B.; Ruterana, P. Electronic and magnetic properties of Fe2SiC. Eur. Phys. J. B 2014, 87, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piskunov, S.; Heifets, E.; Eglitis, R.I.; Borstel, G. Bulk properties and electronic structure of SrTiO3, BaTiO3, PbTiO3 perovskites: An ab initio HF/DFT study. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2004, 29, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladik, J.; Bogar, F.; Penke, B. Comparison of HF, HF + MP2, LDA, BLYP, and B3LYP band structures of the homopolypeptides. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2004, 98, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovesi, R.; Erba, A.; Orlando, R.; Zicovich-Wilson, C.M.; Civalleri, B.; Maschio, L.; Rérat, M.; Casassa, S.; Baima, J.; Salustro, S.; et al. Quantum-mechanical condensed matter simulations with CRYSTAL. WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci. 2018, 8, e1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovesi, R.; Saunders, V.R.; Roetti, C.; Orlando, R.; Pascale, F.; Civalleri, B.; Doll, K.; Harrison, N.M.; Bush, I.J.; Arco, P.D.; et al. User’s Manual. 2017. Available online: http://www.crystal.unito.it/Manuals/crystal17.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2023).
- Monkhorst, H.J.; Pack, J.D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilat, G.; Raubenheimer, L.J. Accurate Numerical Method for Calculating Frequency-Distribution Functions in Solids. Phys. Rev. 1966, 144, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civalleri, B.; D’Arco, P.; Orlando, R.; Saunders, V.R.; Dovesi, R. Hartree–Fock geometry optimisation of periodic systems with the Crystal code. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2001, 348, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghebouli, M.A.; Ghebouli, B.; Fatmi, M.; Bouhemadou, A. Theoretical prediction of the structural, elastic, electronic and thermal properties of the MAX phases X2SiC (X = Ti and Cr). Intermetallics 2011, 19, 1936–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomilin, F.N.; Shubin, A.A.; Kozak, V.V.; Ivanova, D.A.; Fedorova, N.A.; Ol’shevskaya, Y.S.; Kovaleva, A.V.; Avramov, P.V.; Ovchinnikov, S.G. Effect of Substitution on Magnetic Moments of Iron and Chromium Atoms in MAX Phases of Type (Cr4–xFex)0.5SiC: Theoretical Calculation. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2022, 123, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazniak, A.; Stevens, M.; Dahlqvist, M.; Zingsem, B.; Kibkalo, L.; Felek, M.; Varnakov, S.; Farle, M.; Rosén, J.; Wiedwald, U. Phase Stability of Nanolaminated Epitaxial (Cr1−xFex)2 AlC MAX Phase Thin Films on MgO(111) and Al2O3 (0001) for Use as Conductive Coatings. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 13761–13770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setyawan, W.; Curtarolo, S. High-throughput electronic band structure calculations: Challenges and tools. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2010, 49, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.; Jaegermann, W. Review—Electronic Properties of 2D Layered Chalcogenide Surfaces and Interfaces grown by (quasi) van der Waals Epitaxy. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 93012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begunovich, L.V.; Kuklin, A.V.; Visotin, M.A.; Kuzubov, A.A.; Tomilin, F.N.; Tarasov, A.S.; Mikhalev, Y.G.; Avramov, P.V. Triple VTe2/graphene/VTe2 heterostructures as perspective magnetic tunnel junctions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 510, 145315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Txoperena, O.; Llopis, R.; Dery, H.; Hueso, L.E.; Casanova, F. A two-dimensional spin field-effect switch. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alymov, G.; Vyurkov, V.; Ryzhii, V.; Svintsov, D. Abrupt current switching in graphene bilayer tunnel transistors enabled by van Hove singularities. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatten, T.; Matthes, F.; Petruhins, A.; Salikhov, R.; Wiedwald, U.; Farle, M.; Rosén, J.; Bürgler, D.E.; Schneider, C.M. Direct measurement of anisotropic conductivity in a nanolaminated (Mn0.5Cr0.5)2GaC thin film. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 115, 94101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattesini, M.; Magnuson, M. Electronic correlation effects in the Cr2GeC Mn+1AXn phase. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2013, 25, 35601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnuson, M.; Mattesini, M. Magnetic anisotropy in Cr2GeC investigated by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and ab initio calculations. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 501, 166470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benouis, M.; Azzaz, Y.; Ameri, M.; Arbouche, O.; Bennadji, A.; Bensaid, D.; Al-Douri, Y. Electronic and Magnetic Properties of Cr2GeC with GGA + U Approximation. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2016, 29, 1267–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Waki, T.; Tabata, Y.; Nakamura, H. Mn-doping-induced itinerant-electron ferromagnetism in Cr2GeC. Phys. Rev. B—Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2014, 89, 54435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlqvist, M.; Rosén, J. The rise of MAX phase alloys—Large-scale theoretical screening for the prediction of chemical order and disorder. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 10958–10971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsley, J. The Elements, 3rd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1989; p. 264. [Google Scholar]

| MAX Phase | ∆EFiM-FM | ∆EAFM-n-FM | MO | μB |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr2GeC | a | a | FM | 11.57 |
| (Fe-Cr-Cr-Cr)0.5GeC | −0.13 b | — | FiM-3 | 6.09 |
| (Cr-Fe-Cr-Cr)0.5GeC | −0.13 b | — | FiM-2 | 6.09 |
| (Cr-Cr-Fe-Cr)0.5GeC | −0.13 b | — | FiM-4 | 6.09 |
| (Cr-Cr-Cr-Fe)0.5GeC | −0.13 b | — | FiM-1 | 6.09 |
| Fe2GeC | −0.10 | FiM | 5.86 | |
| Cr2SiC | −1.15 | −1.39 | FiM c | 1.38 |
| (Fe-Cr-Cr-Cr)0.5SiC | 0.07 | — | FM | 9.58 |
| (Cr-Fe-Cr-Cr)0.5SiC | −0.01 | — | FiM-3 | 5.1 |
| (Cr-Cr-Fe-Cr)0.5SiC | 0.02 | — | FM | 9.6 |
| (Cr-Cr-Cr-Fe)0.5SiC | 0.19 | — | FM | 9.61 |
| Fe2SiC | 0.07 | — | FM | 6.46 |
| Cr2AlC | −0.80 | −0.56 | FiM | 1.8 |
| (Fe-Cr-Cr-Cr)0.5AlC | −0.14 | −0.20 | FiM d | −0.42 |
| (Cr-Fe-Cr-Cr)0.5AlC | −0.06 | −0.14 | FiM d | 0.36 |
| (Cr-Cr-Fe-Cr)0.5AlC | −0.08 | −0.31 | FiM d | −1.31 |
| (Cr-Cr-Cr-Fe)0.5AlC | −0.02 | −0.25 | FiM d | 1.31 |
| Fe2AlC | −0.50 | −0.28 | FiM | 3.32 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fedorova, N.A.; Kovaleva, A.V.; Olshevskaya, J.S.; Ivanova, D.A.; Kozak, V.V.; Shubin, A.A.; Tarasov, A.S.; Varnakov, S.N.; Ovchinnikov, S.G.; Moshkina, E.M.; et al. Substitution Effects in Spin-Polarized (Cr4-xFex)0.5AC (A = Ge, Si, Al) MAX Phases. Magnetochemistry 2023, 9, 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9060147
Fedorova NA, Kovaleva AV, Olshevskaya JS, Ivanova DA, Kozak VV, Shubin AA, Tarasov AS, Varnakov SN, Ovchinnikov SG, Moshkina EM, et al. Substitution Effects in Spin-Polarized (Cr4-xFex)0.5AC (A = Ge, Si, Al) MAX Phases. Magnetochemistry. 2023; 9(6):147. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9060147
Chicago/Turabian StyleFedorova, Natalja A., Alena V. Kovaleva, Julia S. Olshevskaya, Daria A. Ivanova, Victoria V. Kozak, Alexander A. Shubin, Anton S. Tarasov, Sergey N. Varnakov, Sergei G. Ovchinnikov, Evgeniya M. Moshkina, and et al. 2023. "Substitution Effects in Spin-Polarized (Cr4-xFex)0.5AC (A = Ge, Si, Al) MAX Phases" Magnetochemistry 9, no. 6: 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9060147
APA StyleFedorova, N. A., Kovaleva, A. V., Olshevskaya, J. S., Ivanova, D. A., Kozak, V. V., Shubin, A. A., Tarasov, A. S., Varnakov, S. N., Ovchinnikov, S. G., Moshkina, E. M., Maximova, O. A., Avramov, P. V., & Tomilin, F. N. (2023). Substitution Effects in Spin-Polarized (Cr4-xFex)0.5AC (A = Ge, Si, Al) MAX Phases. Magnetochemistry, 9(6), 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9060147









