Observations of Time-Domain Structures in the Plasmaspheric Plume by Van Allen Probes
Abstract
1. Inroduction
2. Instruments and Data
3. Observation
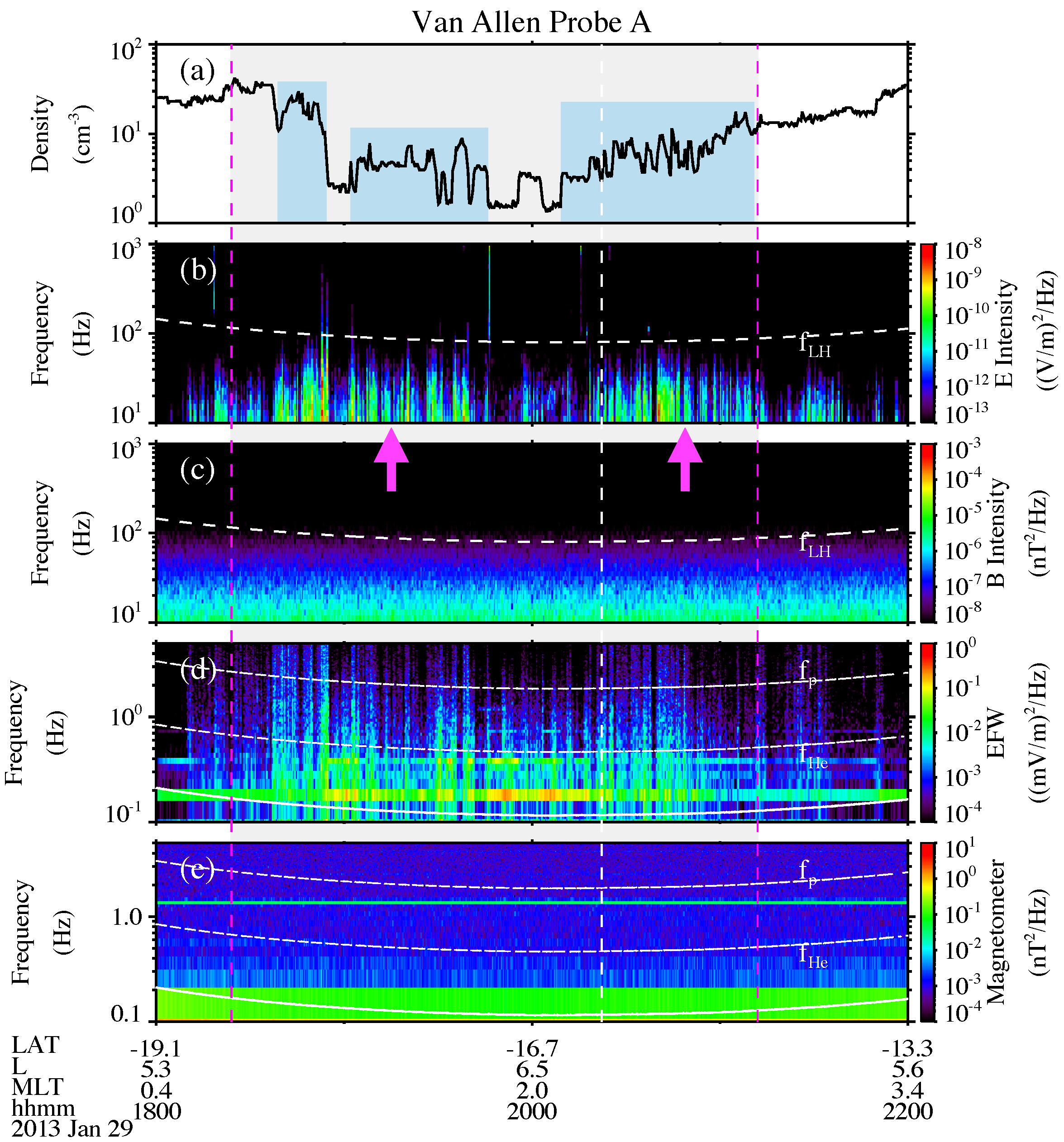
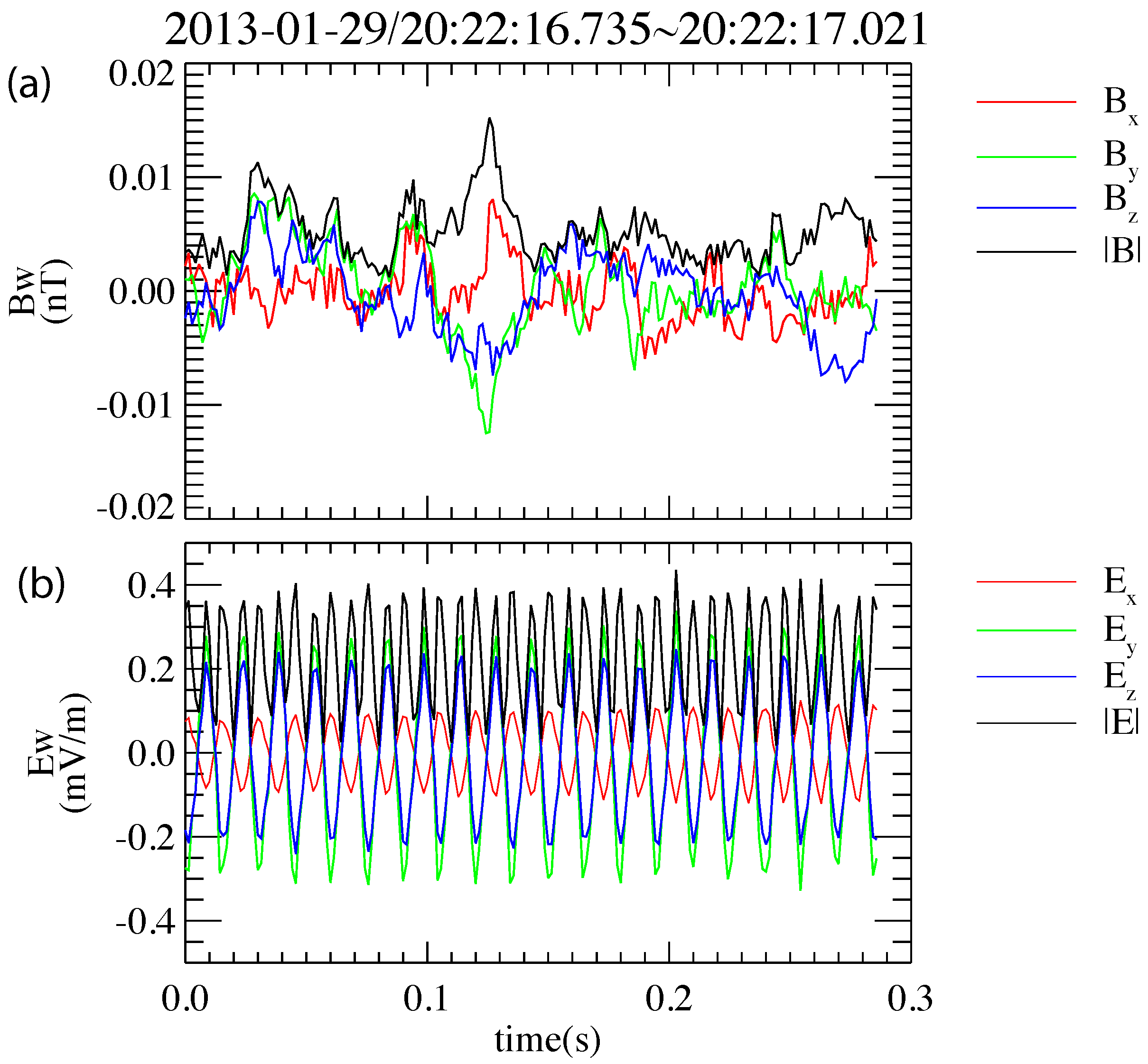
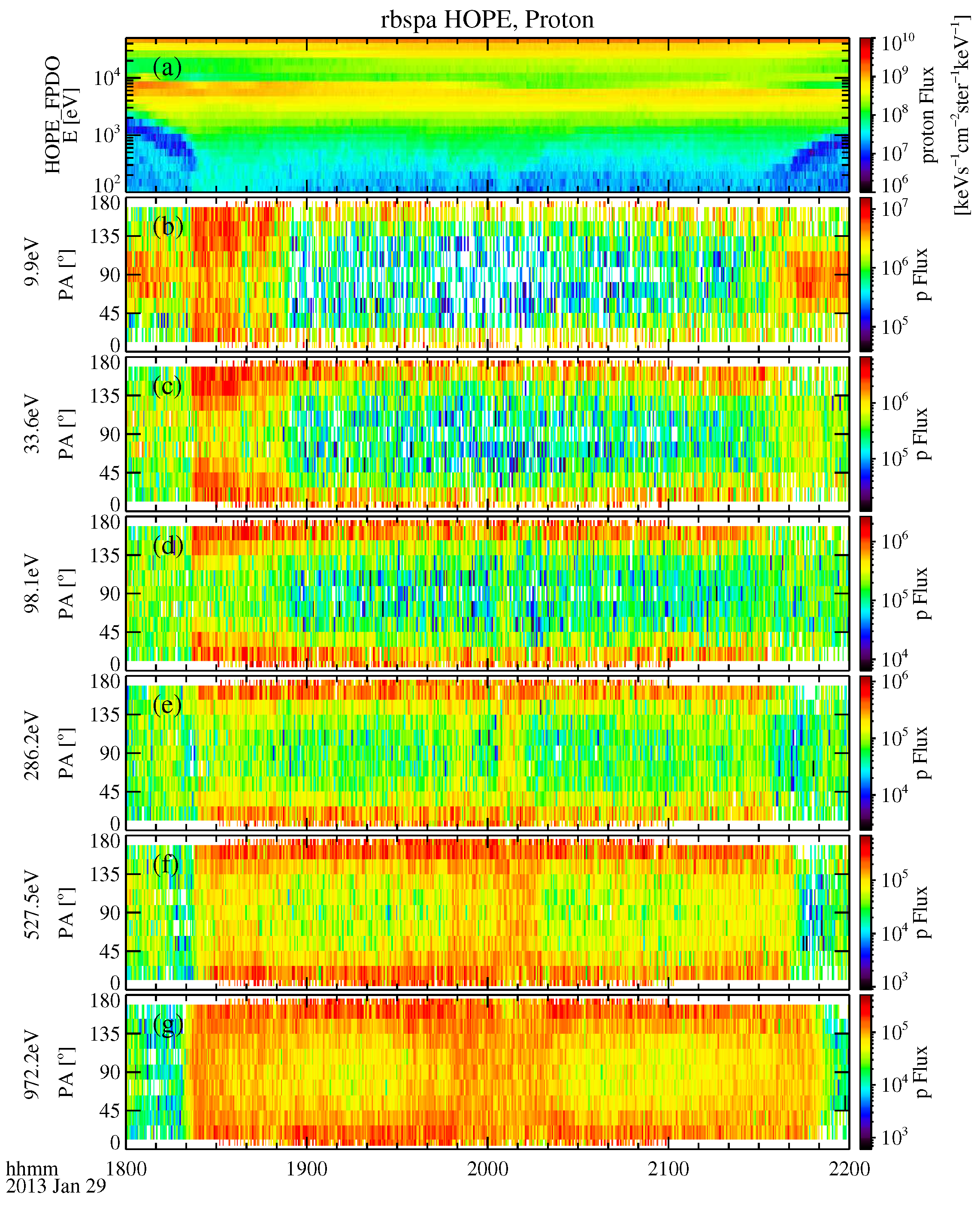
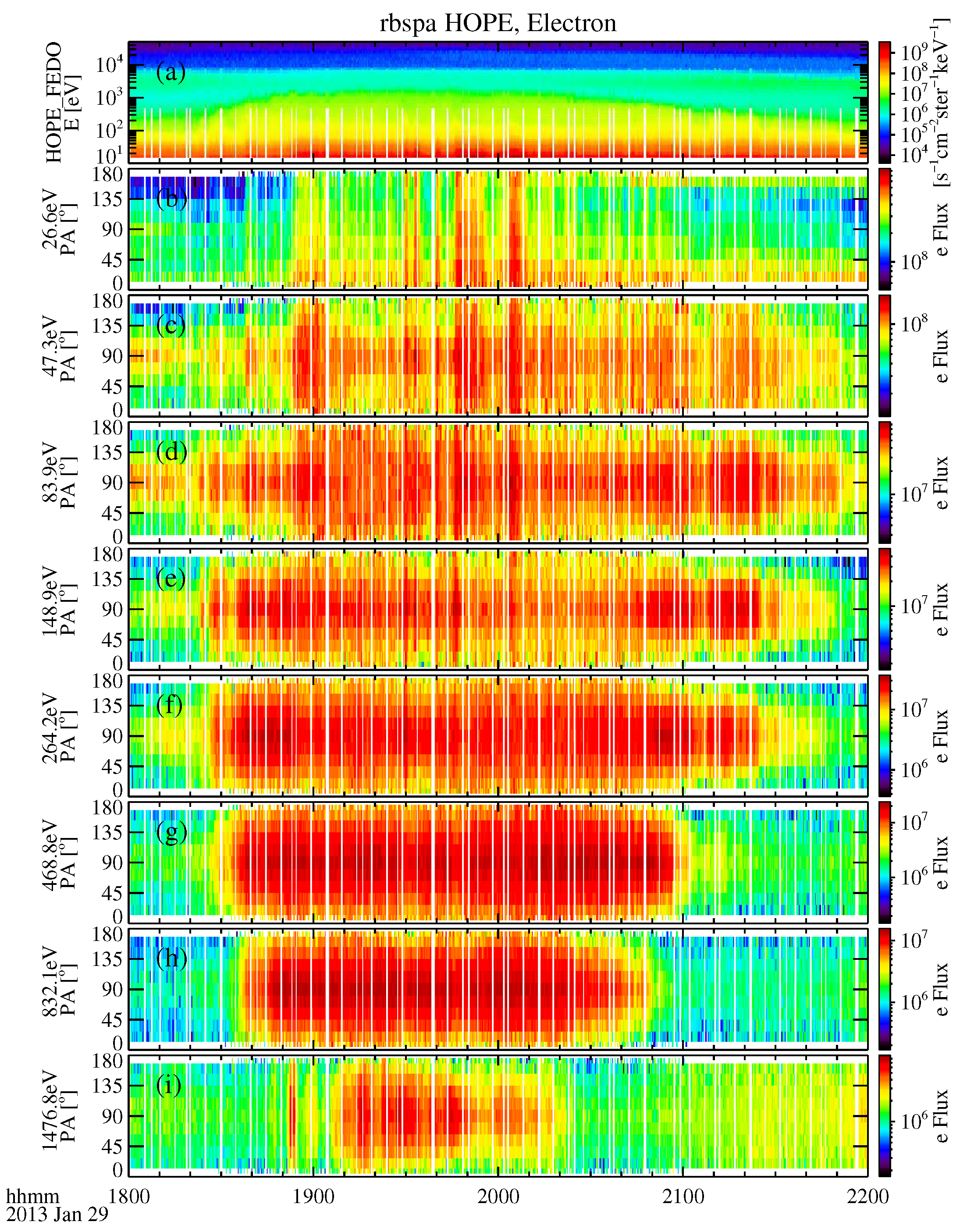
3.1. Example Event: 29 January 2013
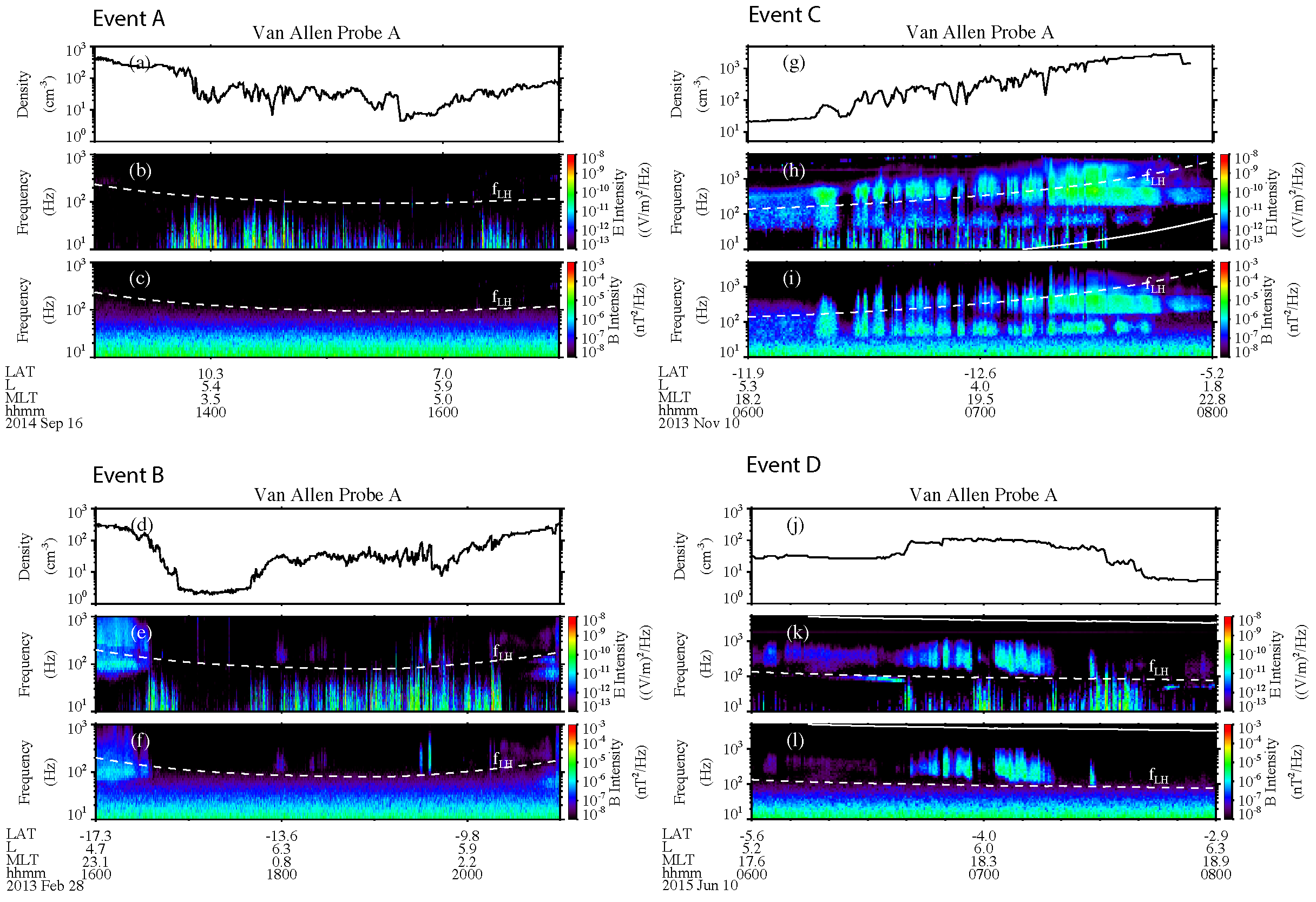
3.2. More events
4. Discussion and Conclusions
- TDS are often observed inside the plasmaspheric plumes. Plasmaspheric plumes tend to occur from the duskside to the midnight sector during active geomagnetic conditions. The events shown here occur in similar regions from the duskside to the midnight sector and dawnside.
- The generation mechanism of TDS has been discussed a lot in previous studies, such as current-driven and beam-related instabilities. The induced parametric interaction could also be one mechanism for quasiperiodic TDS generation [25]. The observation presented here suggests that density modulation may also affect the excitation of TDS.
- The representative event shows that TDS in plasmaspheric plumes have different effects on protons and electrons. During the occurrence of TDS, the flux of low-energy protons is significantly enhanced. Moreover, these enhanced low-energy protons exhibit field-aligned pitch-angle distributions. The fluxes of electrons are also enhanced, but these are mainly in the perpendicular direction.
- Plasmaspheric plumes in the inner magnetosphere are preferentially observed during moderate to strong geomagnetic storms. During periods of active geomagnetic activities, whether the cold plasma density and the fresh injection of energetic protons make it easier to generate the TDS generation remains to be discussed.
- The characteristics of TDS, including the wave amplitudes, types, and spatial distribution, should be determined. Comprehensive statistics of events observed in plasmaspheric plumes should also be used to estimate the importance of TDS in the particle dynamics of the radiation belt. Plasmaspheric hiss emissions are believed to be the dominant mechanism for pitch-angle scattering and the ultimate loss of energetic radiation belt electrons [44,45]. When TDS and plasmaspheric hiss emissions appear simultaneously, but whether there will be additional effects on energetic particles is unknown.
- Waves in plasmaspheric plumes may also have an influence on ionospheric irregularities. TDS can provide seed electrons that are further accelerated by whistler waves to relativistic energies [46]. It is necessary to determine the relative importance of each source on particle acceleration and on loss, as well as their contributions to auroras when more than one wave mode exists. Through a joint observation from magnetospheric and ionospheric satellites, and ground measurements, the quantitative evaluation of TDS in plasmaspheric plumes can be obtained.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goldstein, J.; Pascuale, S.D.; Kletzing, C.; Kurth, W.; Genestreti, K.J.; Skoug, R.M.; Larsen, B.A.; Kistler, L.M.; Mouikis, C.; Spence, H. Simulation of Van Allen Probes plasmapause encounters. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2014, 119, 7464–7484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldwin, M.B.; Downward, L.; Rassoul, H.; Amin, R.; Anderson, R. A new model of the location of the plasmapause: CRRES results. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2002, 107, SMP-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, C.R. Detached plasma regions in the magnetosphere. J. Geophys. Res. (1896–1977) 1974, 79, 1861–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, D.L.; Giles, B.L.; Chappell, C.R.; Décréau, P.M.E.; Anderson, R.R.; Persoon, A.M.; Smith, A.J.; Corcuff, Y.; Canu, P. Plasmasphere dynamics in the duskside bulge region: A new look at an old topic. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1993, 98, 19243–19271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darrouzet, F.; De Keyser, J.; Décréau, P.M.E.; El Lemdani-Mazouz, F.; Vallières, X. Statistical analysis of plasmaspheric plumes with Cluster/WHISPER observations. Ann. Geophys. 2008, 26, 2403–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Zhang, H.; Zong, Q.G.; Otto, A.; Rème, H.; Liebert, E. A statistical study of plasmaspheric plumes and ionospheric outflows observed at the dayside magnetopause. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2016, 121, 492–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Fu, T.; Tang, R.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, Z.; Ouyang, Z.; Deng, X. Statistical study and corresponding evolution of plasmaspheric plumes under different levels of geomagnetic storms. Ann. Geophys. 2022, 40, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laakso, H.; Santolik, O.; Horne, R.; Kolmasová, I.; Escoubet, P.; Masson, A.; Taylor, M. Identifying the source region of plasmaspheric hiss. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 3141–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Liu, N.; Zheng, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S. Large-Amplitude Extremely Low Frequency Hiss Waves in Plasmaspheric Plumes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Pang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Deng, X.; Trotignon, J.G.; Lucek, E.; Wang, J. Wave-particle interaction in a plasmaspheric plume observed by a Cluster satellite. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, A03205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, S.; Li, W.; Tao, X.; Shen, X.C.; Ma, Q. Characteristics of rising tone whistler mode waves inside the Earth’s plasmasphere, plasmaspheric plumes, and plasmatrough. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 7121–7130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grison, B.; Hanzelka, M.; Breuillard, H.; Darrouzet, F.; Santolík, O.; Cornilleau-Wehrlin, N.; Dandouras, I. Plasmaspheric Plumes and EMIC Rising Tone Emissions. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2018, 123, 9443–9452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Deng, X.; Lin, X.; Pang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Décréau, P.M.E.; Trotignon, J.G.; Lucek, E.; Frey, H.U.; Wang, J. Link between EMIC waves in a plasmaspheric plume and a detached sub-auroral proton arc with observations of Cluster and IMAGE satellites. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, D.; Ni, B.; Meredith, N.P.; Horne, R.B.; Thorne, R.M.; Moldwin, M.B.; Anderson, R.R. Electron scattering by whistler-mode ELF hiss in plasmaspheric plumes. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, A04219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Fu, S.; Gu, X.; Ni, B.; Xiang, Z.; Summers, D.; Zou, Z.; Cao, X.; Lou, Y.; Hua, M. Electron Scattering by Plasmaspheric Hiss in a Nightside Plume. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 4618–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozer, F.S.; Agapitov, O.V.; Artemyev, A.; Drake, J.F.; Krasnoselskikh, V.; Lejosne, S.; Vasko, I. time-domain structures: What and where they are, what they do, and how they are made. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 3627–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaspina, D.M.; Andersson, L.; Ergun, R.E.; Wygant, J.R.; Bonnell, J.W.; Kletzing, C.; Reeves, G.D.; Skoug, R.M.; Larsen, B.A. Nonlinear electric field structures in the inner magnetosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 5693–5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaspina, D.M.; Wygant, J.R.; Ergun, R.E.; Reeves, G.D.; Skoug, R.M.; Larsen, B.A. Electric field structures and waves at plasma boundaries in the inner magnetosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2015, 120, 4246–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozer, F.S.; Carlson, C.W.; Hudson, M.K.; Torbert, R.B.; Parady, B.; Yatteau, J.; Kelley, M.C. Observations of paired electrostatic shocks in the polar magnetosphere. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1977, 38, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temerin, M.; Cerny, K.; Lotko, W.; Mozer, F.S. Observations of double layers and solitary waves in the auroral plasma. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1982, 48, 1175–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasko, I.Y.; Agapitov, O.V.; Mozer, F.S.; Artemyev, A.V. Thermal electron acceleration by electric field spikes in the outer radiation belt: Generation of field-aligned pitch-angle distributions. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2015, 120, 8616–8632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozer, F.; Artemyev, A.; Agapitov, O.; Mourenas, D.; Vasko, I. Near-relativistic electron acceleration by Landau trapping in time domain structures. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Artemyev, A.; Zhang, X.; Vasko, I.Y.; Runov, A.; Angelopoulos, V.; Knudsen, D. Potential Evidence of Low-Energy Electron Scattering and Ionospheric Precipitation by time-domain structures. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, J.F.; Agapitov, O.V.; Mozer, F.S. The development of a bursty precipitation front with intense localized parallel electric fields driven by whistler waves. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 2563–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agapitov, O.V.; Krasnoselskikh, V.; Mozer, F.S.; Artemyev, A.V.; Volokitin, A.S. Generation of nonlinear electric field bursts in the outer radiation belt through the parametric decay of whistler waves. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 3715–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, H.; Kojima, H.; Miyatake, T.; Omura, Y.; Okada, M.; Nagano, I.; Tsutsui, M. Electrostatic solitary waves (ESW) in the magnetotail: BEN wave forms observed by GEOTAIL. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1994, 21, 2915–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergun, R.E.; Andersson, L.; Tao, J.; Angelopoulos, V.; Bonnell, J.; McFadden, J.P.; Larson, D.E.; Eriksson, S.; Johansson, T.; Cully, C.M.; et al. Observations of double layers in earth’s plasma sheet. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 155002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattell, C.A.; Crumley, J.; Dombeck, J.; Wygant, J.R.; Mozer, F.S. Polar observations of solitary waves at the Earth’s magnetopause. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 9-1–9-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauk, B.; Fox, N.J.; Kanekal, S.; Kessel, R.; Sibeck, D.; Ukhorskiy, a.A. Science objectives and rationale for the Radiation Belt Storm Probes mission. Space Sci. Rev. 2013, 179, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kletzing, C.; Kurth, W.; Acuna, M.; MacDowall, R.; Torbert, R.; Averkamp, T.; Bodet, D.; Bounds, S.; Chutter, M.; Connerney, J.; et al. The electric and magnetic field instrument suite and integrated science (EMFISIS) on RBSP. In The Van Allen Probes Mission; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 127–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurth, W.S.; De Pascuale, S.; Faden, J.B.; Kletzing, C.A.; Hospodarsky, G.B.; Thaller, S.; Wygant, J.R. Electron densities inferred from plasma wave spectra obtained by the Waves instrument on Van Allen Probes. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2015, 120, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wygant, J.; Bonnell, J.; Goetz, K.; Ergun, R.; Mozer, F.; Bale, S.; Ludlam, M.; Turin, P.; Harvey, P.; Hochmann, R.; et al. The Electric Field and Waves Instruments on the Radiation Belt Storm Probes Mission. Space Sci. Rev. 2013, 179, 183–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funsten, H.; Skoug, R.; Guthrie, A.; MacDonald, E.; Baldonado, J.; Harper, R.; Henderson, K.; Kihara, K.; Lake, J.; Larsen, B.; et al. Helium, Oxygen, Proton, and Electron (HOPE) mass spectrometer for the Radiation Belt Storm Probes mission. In The Van Allen Probes Mission; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 423–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, J.; Carranza, P.; Claudepierre, S.; Clemmons, J.; Crain, W.; Dotan, Y.; Fennell, J.; Fuentes, F.; Galvan, R.; George, J.; et al. The magnetic electron ion spectrometer (MagEIS) instruments aboard the radiation belt storm probes (RBSP) spacecraft. In The Van Allen Probes Mission; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 383–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, D.N.; Kanekal, S.; Hoxie, V.; Batiste, S.; Bolton, M.; Li, X.; Elkington, S.; Monk, S.; Reukauf, R.; Steg, S.; et al. The Relativistic Electron-Proton Telescope (REPT) instrument on board the Radiation Belt Storm Probes (RBSP) spacecraft: Characterization of Earth’s radiation belt high-energy particle populations. Space Sci. Rev. 2013, 179, 337–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheeley, B.W.; Moldwin, M.B.; Rassoul, H.K.; Anderson, R.R. An empirical plasmasphere and trough density model: CRRES observations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2001, 106, 25631–25641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasko, I.Y.; Agapitov, O.V.; Mozer, F.S.; Bonnell, J.W.; Artemyev, A.V.; Krasnoselskikh, V.V.; Reeves, G.; Hospodarsky, G. Electron-acoustic solitons and double layers in the inner magnetosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 4575–4583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.H.; Hoffman, R.A. Direct observations in the dusk hours of the characteristics of the storm time ring current particles during the beginning of magnetic storms. J. Geophys. Res. (1896–1977) 1974, 79, 966–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallat, C.; Ganushkina, N.; Dandouras, I.; Escoubet, C.P.; Taylor, M.G.G.T.; Laakso, H.; Masson, A.; Sauvaud, J.A.; Rème, H.; Daly, P. Ion multi-nose structures observed by Cluster in the inner Magnetosphere. Ann. Geophys. 2007, 25, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozer, F.S.; Agapitov, O.; Krasnoselskikh, V.; Lejosne, S.; Reeves, G.D.; Roth, I. Direct observation of radiation-belt electron acceleration from electron-volt energies to megavolts by nonlinear whistlers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 035001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artemyev, A.V.; Vasiliev, A.A.; Mourenas, D.; Agapitov, O.V.; Krasnoselskikh, V.; Boscher, D.; Rolland, G. Fast transport of resonant electrons in phase space due to nonlinear trapping by whistler waves. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 5727–5733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorne, R.M.; Smith, E.J.; Burton, R.K.; Holzer, R.E. Plasmaspheric Hiss. J. Geophys. Res. 1973, 78, 1581–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Thorne, R.M.; Li, W.; Bortnik, J.; Turner, D.; Angelopoulos, V. Modulation of plasmaspheric hiss intensity by thermal plasma density structure. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, L.R.; Thorne, R.M.; Kennel, C.F. Pitch-angle diffusion of radiation belt electrons within the plasmasphere. J. Geophys. Res. (1896–1977) 1972, 77, 3455–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, N.P.; Horne, R.B.; Glauert, S.A.; Thorne, R.M.; Summers, D.; Albert, J.M.; Anderson, R.R. Energetic outer zone electron loss timescales during low geomagnetic activity. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, A05212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Mourenas, D.; Artemyev, A.; Li, W.; Thorne, R.M.; Bortnik, J. Strong enhancement of 10–100 keV electron fluxes by combined effects of chorus waves and time-domain structures. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 4683–4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teng, S.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Q.; Han, D. Observations of Time-Domain Structures in the Plasmaspheric Plume by Van Allen Probes. Magnetochemistry 2023, 9, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9010022
Teng S, Chen H, Zhang Q, Han D. Observations of Time-Domain Structures in the Plasmaspheric Plume by Van Allen Probes. Magnetochemistry. 2023; 9(1):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9010022
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeng, Shangchun, Huayue Chen, Qiang Zhang, and Desheng Han. 2023. "Observations of Time-Domain Structures in the Plasmaspheric Plume by Van Allen Probes" Magnetochemistry 9, no. 1: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9010022
APA StyleTeng, S., Chen, H., Zhang, Q., & Han, D. (2023). Observations of Time-Domain Structures in the Plasmaspheric Plume by Van Allen Probes. Magnetochemistry, 9(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9010022






