Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor Chip for Human Blood Groups Identification Assisted with Silver-Chromium-Hafnium Oxide
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. SPR Sensor Theoretical Modeling and Design Considerations
- 1.
- BK7 Prism selection
- 2.
- Silver (Ag) metal selection
- 3.
- Chromium (Cr) layers
- 4.
- Hafnium oxide (HfO2)
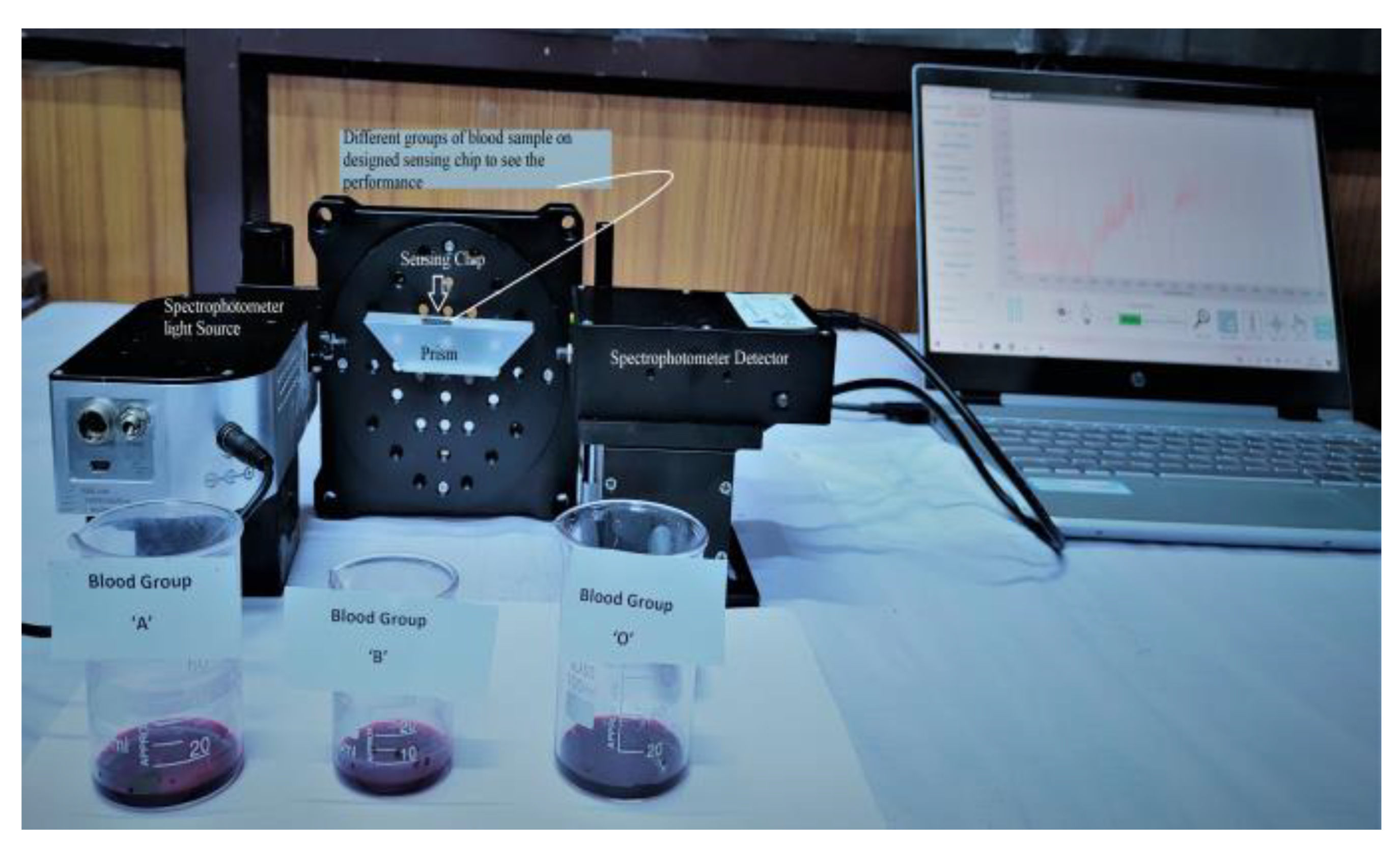
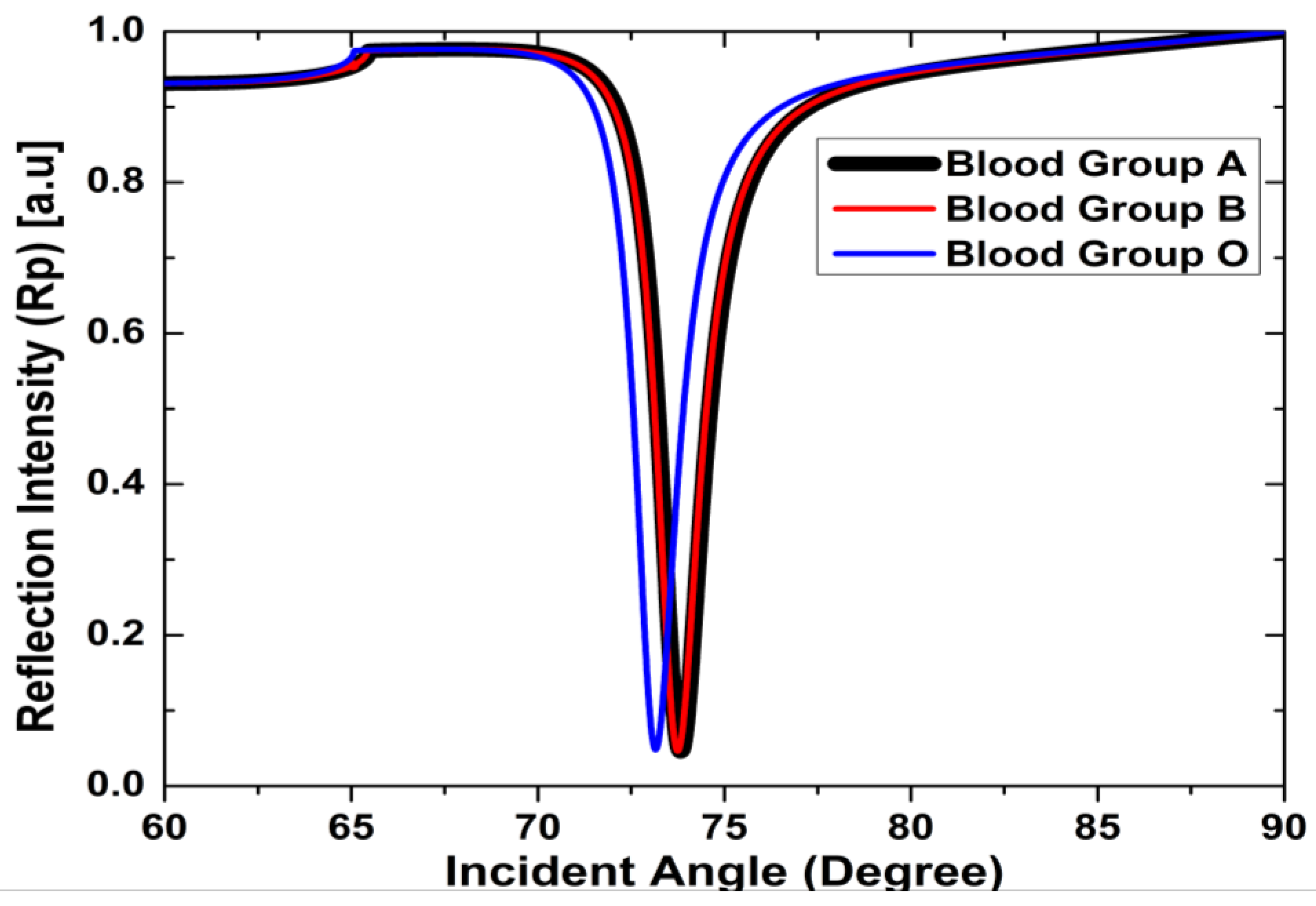
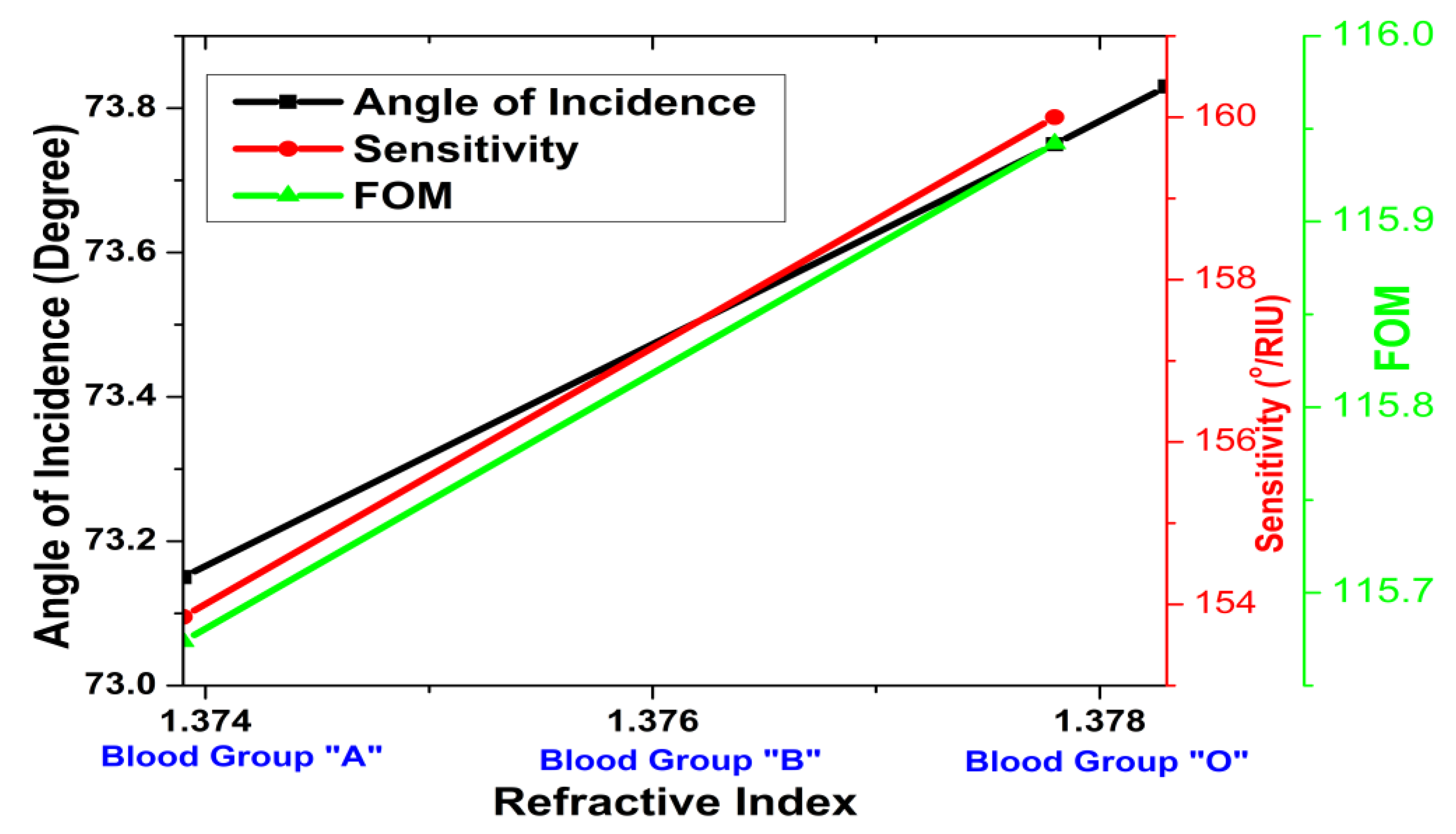
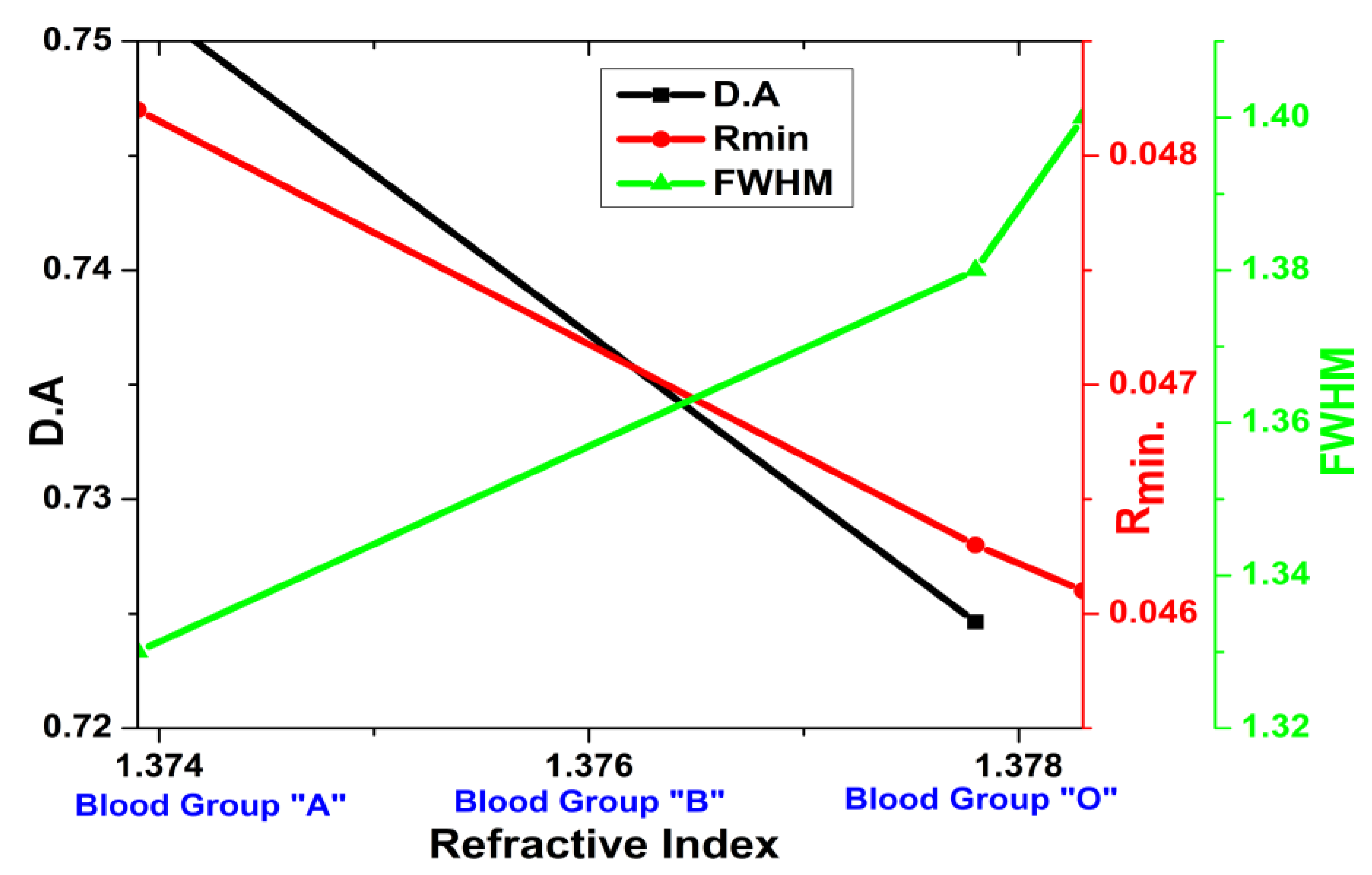
3. Results and Discussion
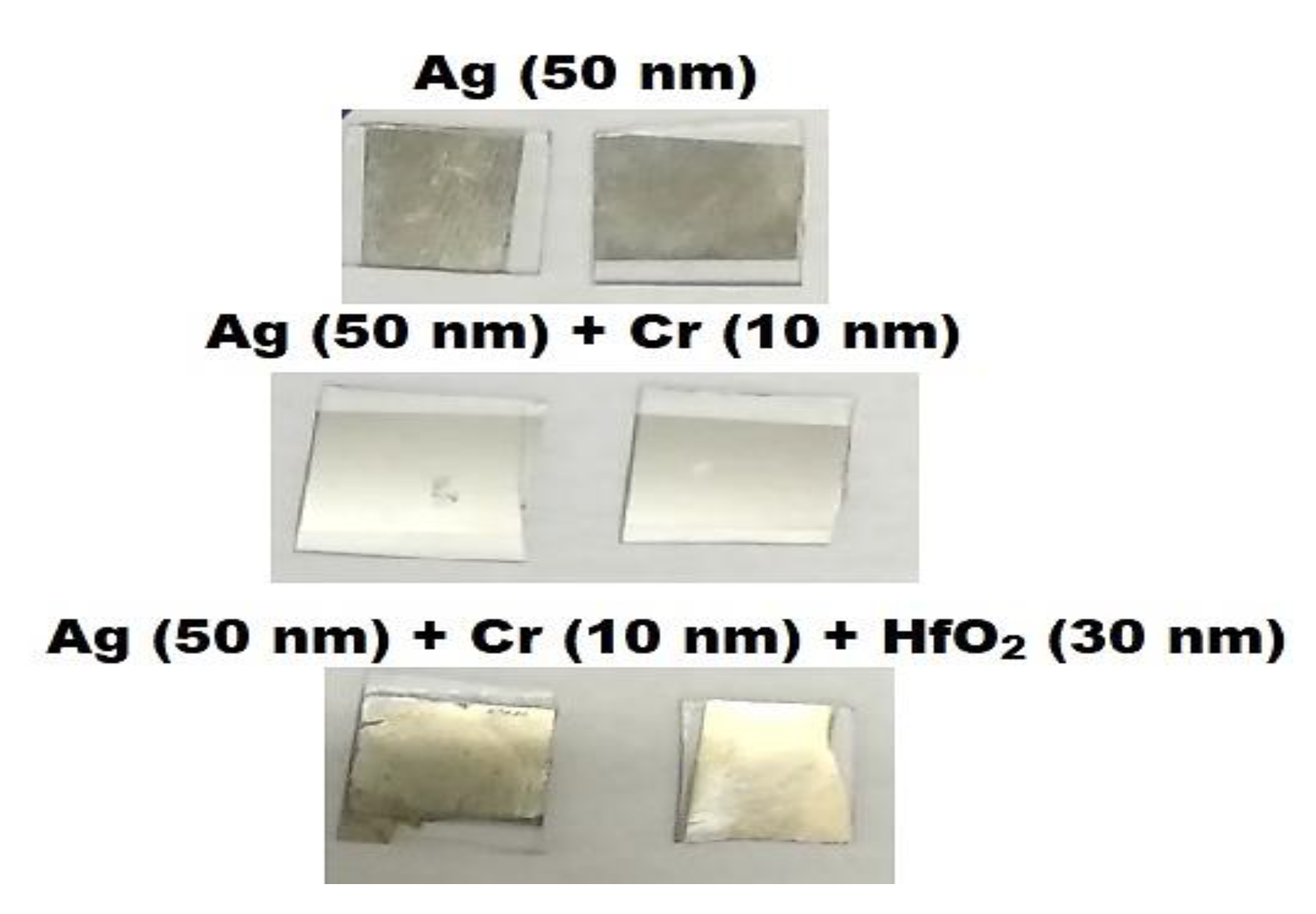
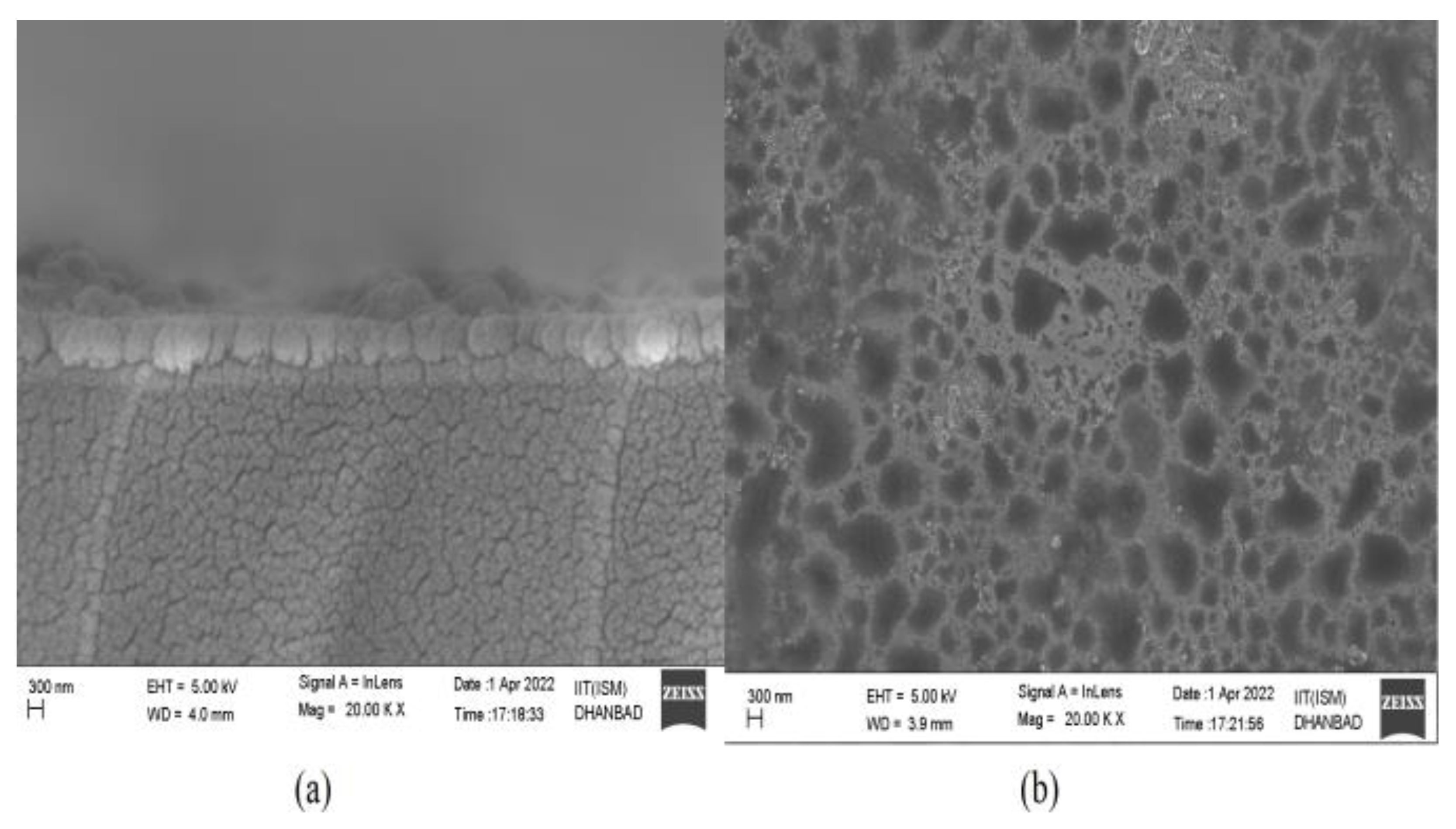
4. Fabrication Prospects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Holden, J.M.; Rao, A.M.; Eklund, P.C.; Venkateswaran, U.D.; Eastwood, D.; Lidberg, R.L.; Dresselhaus, G.; Dresselhaus, M.S. Optical absorption and photoluminescence in pristine and photopolymerized C 60 solid films. Phys. Rev. B 1995, 51, 4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajenski, P.J. Surface plasmon resonance based wavelength selector: Design considerations. Opt. Eng. 1997, 36, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sincerbox, G.T.; Gordon, J.C. Small fast large-aperture light modulator using attenuated total reflection. Appl. Opt. 1981, 20, 1491–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schildkraut, J.S. Long-range surface plasmon electrooptic modulator. Appl. Opt. 1988, 27, 4587–4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimoto, T.; Sasaki, S.; Ikebukuro, K.; Karube, I. Refractive-index and thickness sensitivity in surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 4058–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.-D.; Chen, S.J.; Yeh, T.L. Common-path phase-shift interferometry surface plasmon resonance imaging system. Opt. Lett. 2005, 30, 1488–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, C.E.; Greve, J. Differential S.P.R.immunosensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2000, 63, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stemmler, I.; Brecht, A.; Gauglitz, G. Compact surface plasmon resonance-transducers with spectral readout for biosensing applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1999, 54, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, R.H. Plasma losses by fast electrons in thin films. Phys. Rev. 1957, 106, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.K.; Gupta., B.D. Surface plasmon resonance based fiber optic sensor for the I.R. region using a conducting metal oxide film. JOSA A 2010, 27, 846–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homola, J. Surface plasmon resonance sensors for detection of chemical and biological species. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 462–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homola, J.; Piliarik, M. Surface Plasmon Resonance (S.P.R.) Sensors. In Surface Plasmon Resonance Based Sensors; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; pp. 45–67. [Google Scholar]
- Tangkawsakul, W.; Srikhirin, T.; Shinbo, K.; Kato, K.; Kaneko, F.; Baba, A. Application of long-range surface plasmon resonance for ABO blood typing. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2016, 2016, 1432781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munawar, A.; Ong, Y.; Schirhagl, R.; Tahir, M.A.; Khan, W.S.; Bajwa, S.Z. Nanosensors for diagnosis with optical, electric and mechanical transducers. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 6793–6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Jayatissa, A.H. Perovskites-based solar cells: A review of recent progress, materials and processing methods. Materials 2018, 11, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, P.S.; Raghuwanshi, S.K.; Singh, Y. Enhancement of the sensitivity of a surface plasmon resonance sensor using a nobel structure based on barium titanate–graphene-silver. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2022, 54, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Jia, Y.; Jiang, L.; Guo, J.; Dai, X.; Xiang, Y.; Fan, D. Sensitivity improved S.P.R. biosensor based on the MoS2/graphene–aluminum hybrid structure. J. Light. Technol. 2017, 35, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, N.R.; Mei, G.S.; Jamil, N.A.; Majlis, B.; Menon, P.S. Influence of ultrathin chromium adhesion layer on different metal thicknesses of SPR-based sensor using F.D.T.D. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 7, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, C.F.; Clothier, W.K. Optical properties of thin chromium films. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1974, 64, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, J.L.; Hernandez, H.M.; Habibi, S.; Kendrick, C.E.; Wang, Z.; Bihari, N.; Bergstrom, P.L.; Minerick, A.R. Electrical and chemical characterizations of hafnium (IV) oxide films for biological lab-on-a-chip devices. Thin Solid Films 2018, 662, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, P.S.; Gan, S.M.; Mohamad, N.R.; Jamil, N.A.; Tarumaraja, K.A.; Razak, N.R.; Bakar, A.A.A.; Mukhtar, W.M.; Murat, N.F.; Mohamed, R.; et al. Kretschmann Based Surface Plasmon Resonance for Sensing in Visible Region. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 9th International Nanoelectronics Conferences (INEC), Piscataway, NJ, USA, 3–5 July 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Bo, L.; Metiu, H. The effect of island coalescence on island density during epitaxial growth. Surf. Sci. 1997, 392, L56–L62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, K.; Sharma, S.C.; Hozhabri, N. Hafnium dioxide as a dielectric for highly-sensitive waveguide-coupled surface plasmon resonance sensors. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 045217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghuwanshi, S.K.; Pandey, P.S. A Numerical Study of different Metal and Prism Choices in the Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor Chip for Human blood group identification. IEEE Trans. NanoBiosci. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
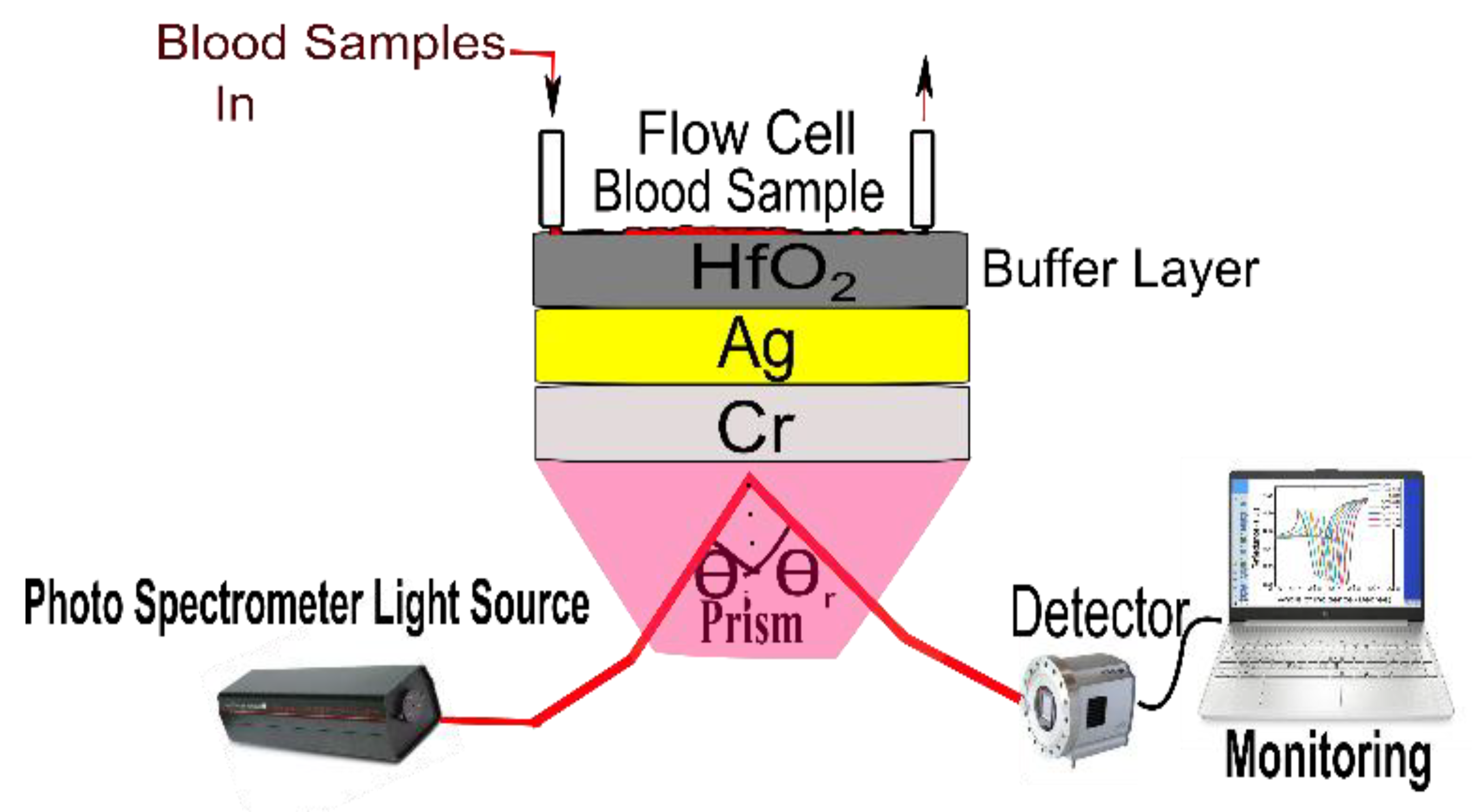


| a1 | a2 | a3 |
| 1.03961212 | 0.231792344 | 1.03961212 |
| b1 | b2 | b3 |
| 0.00600069867 µm2 | 0.0200179144 µm2 | 103.560653 µm2 |
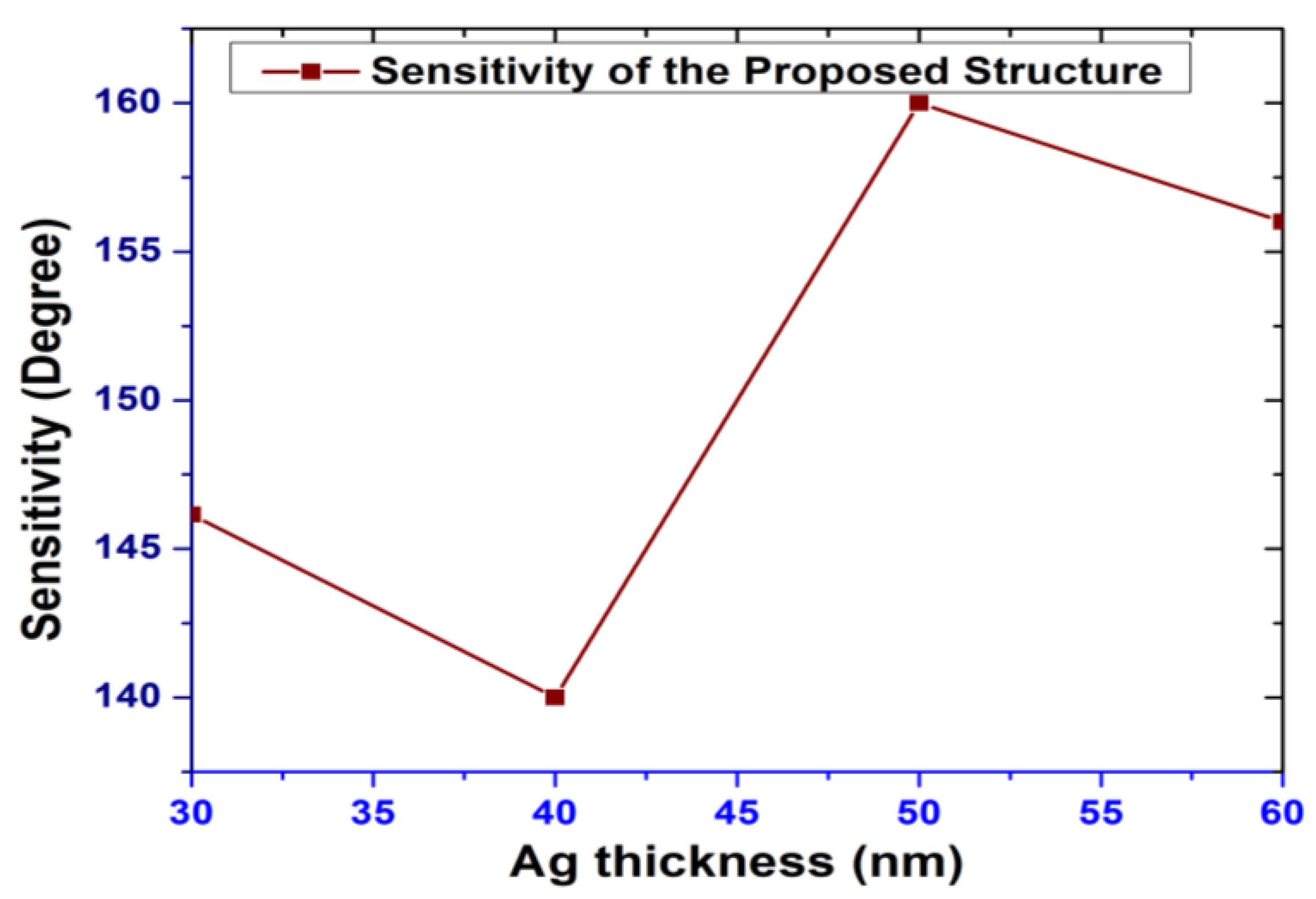
| Au Thickness (nm) | Sensitivity (°/RIU) | Ag Thickness (nm) | Sensitivity (°/RIU) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 136.41 | 30 | 146.15 |
| 40 | 148.91 | 40 | 140 |
| 50 | 158.21 | 50 | 160 |
| 60 | 151.23 | 60 | 156 |
| Layers | Materials | Refractive Index | Thickness (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | BK7 Prism | 1.5151 | - |
| II | Ag | 0.0562 + 1i × 4.2776 | 50 nm |
| III | Chromium | 3.1395 + 1i × 3.3152 | 10 nm |
| IV | HfO2 | 2.042 | 30 nm |
| V | Sensing layer | nA = 1.3739, nB = 1.3783, nO = 1.3778 | - |
| Types of Vacuum | Pressure Range (Torr) |
|---|---|
| Low | 760–0 |
| Medium | 0–10−3 |
| High | 10−3–10−8 |
| Outer Space | ≈10−16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pandey, P.S.; Raghuwanshi, S.K.; Singh, R.; Kumar, S. Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor Chip for Human Blood Groups Identification Assisted with Silver-Chromium-Hafnium Oxide. Magnetochemistry 2023, 9, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9010021
Pandey PS, Raghuwanshi SK, Singh R, Kumar S. Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor Chip for Human Blood Groups Identification Assisted with Silver-Chromium-Hafnium Oxide. Magnetochemistry. 2023; 9(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9010021
Chicago/Turabian StylePandey, Purnendu Shekhar, Sanjeev Kumar Raghuwanshi, Rajesh Singh, and Santosh Kumar. 2023. "Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor Chip for Human Blood Groups Identification Assisted with Silver-Chromium-Hafnium Oxide" Magnetochemistry 9, no. 1: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9010021
APA StylePandey, P. S., Raghuwanshi, S. K., Singh, R., & Kumar, S. (2023). Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor Chip for Human Blood Groups Identification Assisted with Silver-Chromium-Hafnium Oxide. Magnetochemistry, 9(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9010021







