Soft Chemistry Synthesis and Characterization of CoFe1.8RE0.2O4 (RE3+ = Tb3+, Er3+) Ferrite
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Synthesis of CoFe1.8RE0.2O4 (RE3+ = Tb3+, Er3+)
2.3. Characterization Techniques
2.4. Bioevaluation of the Obtained Nanoparticles
3. Results and Discussion
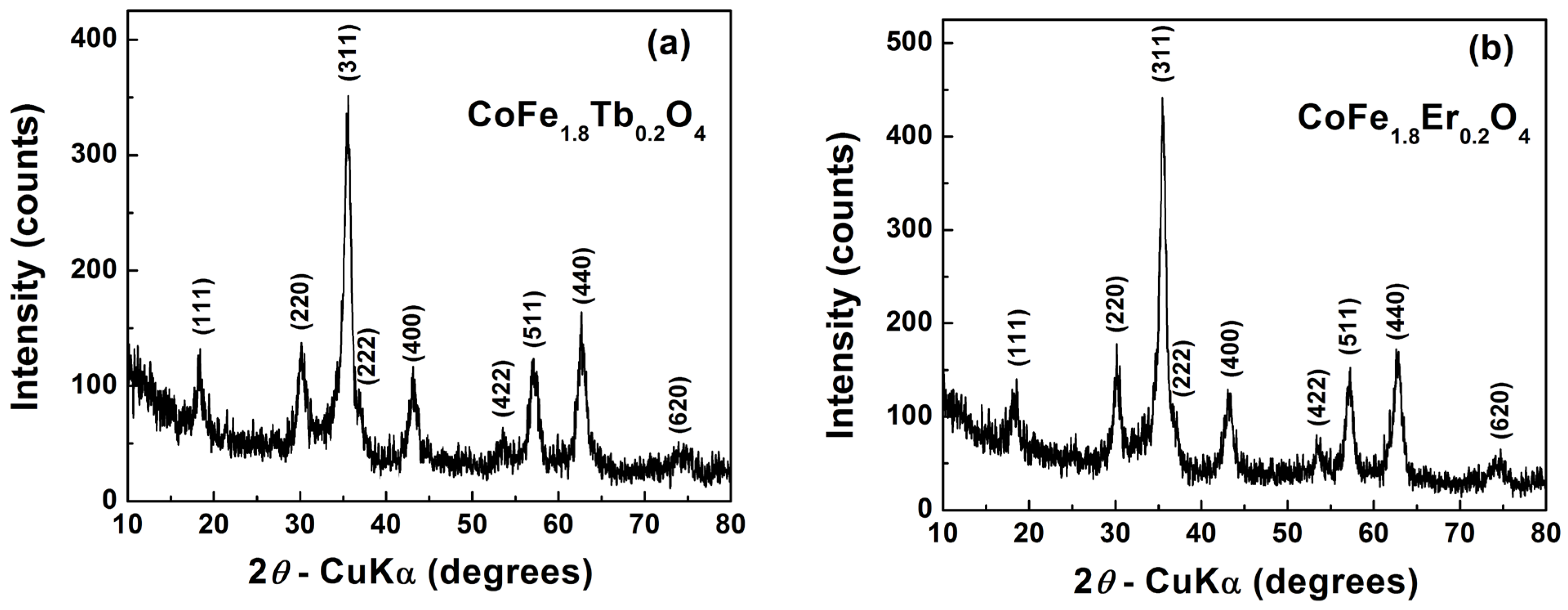
3.1. Structural Characterization
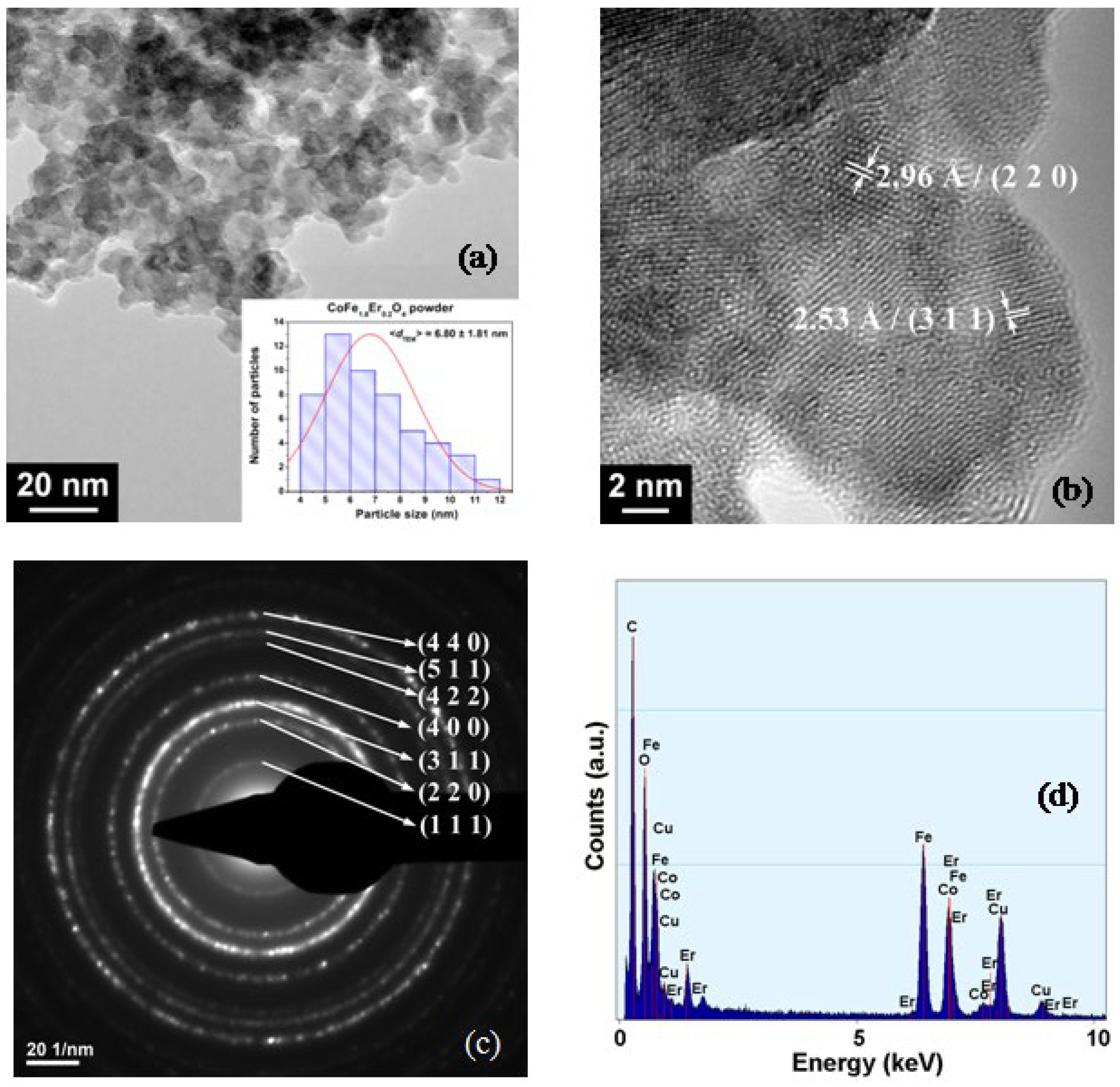
3.2. FE-SEM and TEM/HRTEM Investigations
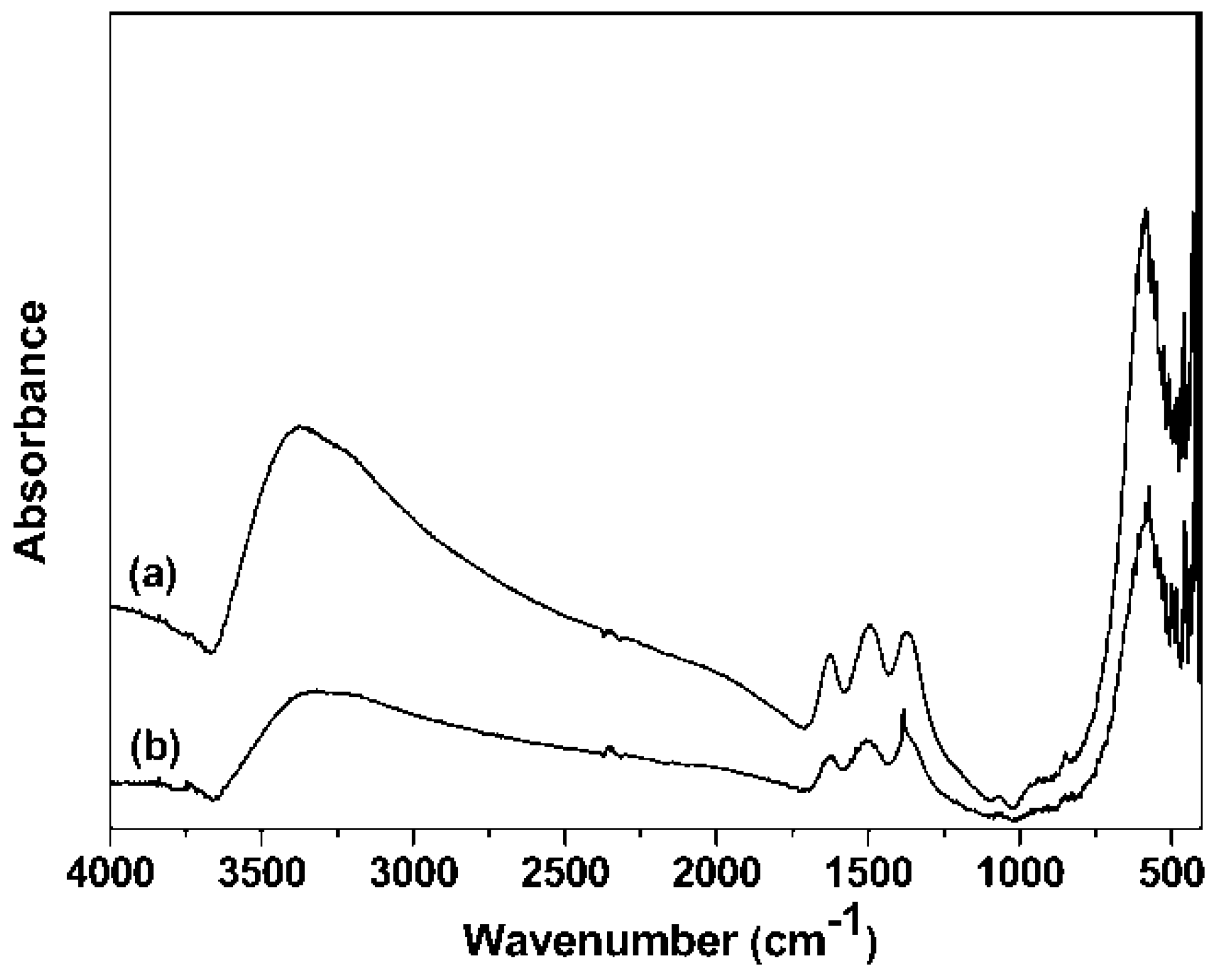
3.3. FTIR Spectra
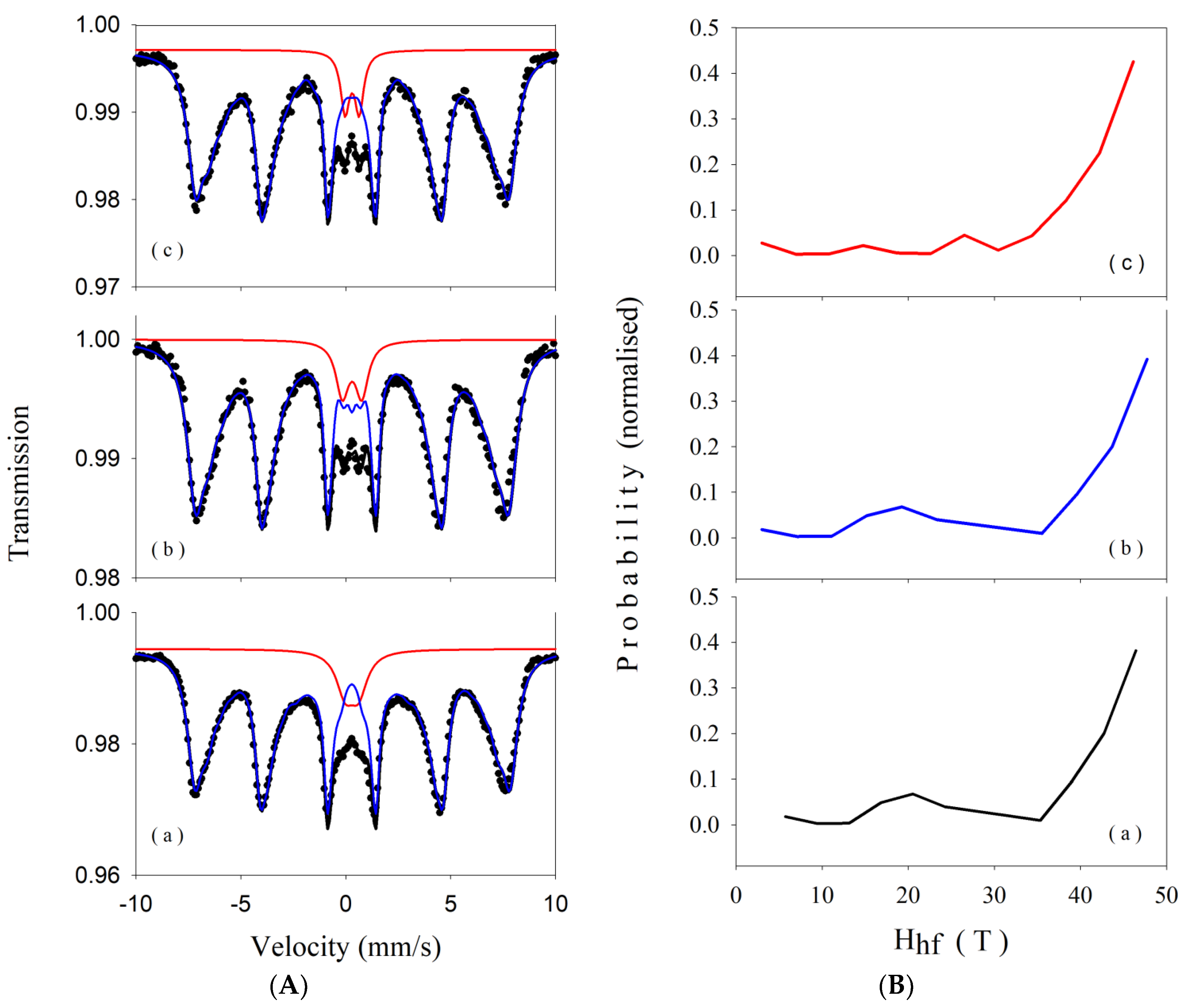
3.4. Mössbauer Spectroscopy
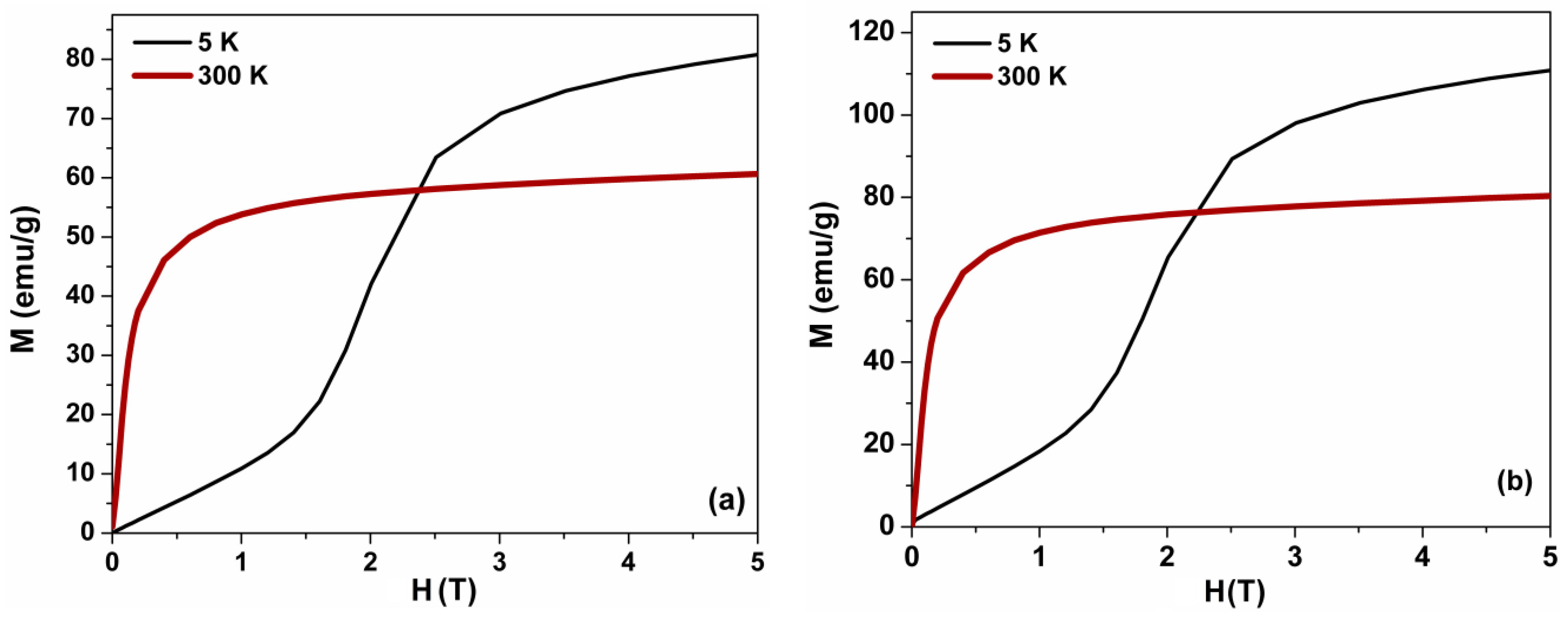
3.5. Magnetic Measurements
3.6. Antimicrobial Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kefeni, K.K.; Msagati, T.A.M.; Mamba, B.B. Ferrite nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and applications in electronic device. Mat. Sci. Eng. B 2017, 215, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.; Kim, S.; Park, J.E.; Jeon, J.; Wie, J.J. On-demand orbital maneuver of multiple soft robots via hierarchical magnetomotility. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carpenter, J.A.; Eberle, T.B.; Schuerle, S.; Rafsanjani, A.; Studart, A.R. Facile Manufacturing Route for Magneto-Responsive Soft Actuators. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2021, 3, 2000283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shobana, M.K. Nanoferrites in biosensors—A review. Mat. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 272, 115344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Nikles, D.E.; Johnson, D.T.; Brazel, C.S. Heat generation of aqueously dispersed CoFe2O4 nanoparticles as heating agents for magnetically activated drug delivery and hyperthermia. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320, 23–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, D.; Upadhyay, P.; Das, A.; Ghosh, A.; Adhikary, A.; Goswami, M.M. Studies on cancer cell death through delivery of dopamine as anti-cancer drug by a newly functionalized cobalt ferrite nano-carrier. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 627, 127202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, J.M.; Raza, W.; Amin, N.; Nadeem, K.; Arshad, M.I.; Khan, M.A. Synthesis and characterization of cobalt ferrites as MRI contrast agent. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 47, S50–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohar, A.; Geleta, D.D.; Krishnamoorthi, C.; Lee, J. Synthesis, characterization and magnetic hyperthermia properties of nearly monodisperse CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 28035–28041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikumbh, A.K.; Pawar, R.A.; Nighot, D.V.; Gugale, G.S.; Sangale, M.D.; Khanvilkar, M.B.; Nagawade, A.V. Structural, electrical, magnetic and dielectric properties of rare-earth substituted cobalt ferrites nanoparticles synthesized by the co-precipitation method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 355, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Yang, H.; Zhao, X.; Yu, L.; Cui, Y.; Feng, S. Magnetic properties of CoFe2O4 ferrite doped with rare earth ion. Mater. Lett. 2006, 60, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugesan, C.; Chandrasekaran, G. Impact of Gd3+-substitution on the structural, magnetic and electrical properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 73714–73725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ateia, E.E.; Abdelmaksoud, M.K.; Arman, M.M.; Shafaay, A.S. Comparative study on the physical properties of rare-earth-substituted nano-sized CoFe2O4. Appl. Phys. A 2020, 126, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almessiere, M.A.; Slimani, Y.; Korkmaz, A.D.; Guner, S.; Sertkol, M.; Shirsath, S.E.; Baykal, A. Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Tm3+ substituted cobalt spinel ferrites synthesized via sonochemical approach. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 54, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prathapani, S.; Vinitha, M.; Jayaraman, T.V.; Das, D. Effect of Er doping on the structural and magnetic properties of cobalt-ferrite. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 17A502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksoud, M.I.A.A.; El-Sayyad, G.S.; Ashour, A.H.; El-Batal, A.I.; Elsayed, M.A.; Gobara, M.; El-Khawaga, A.M.; Abdel-Khalek, E.K.; El-Okr, M.M. Antibacterial, antibiofilm, and photocatalytic activities of metals-substituted spinel cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 127, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chifiriuc, C.; Lazar, V.; Bleotu, C.; Calugarescu, I.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Mihaiescu, D.E.; Mogosanu, D.E.; Buteica, A.S.; Buteica, E. Bacterial adherence to the cellular and inert substrate in the presence of CoFe2O4 and Fe3O4/oleic acid–core/shell. Dig. J. Nanomater. Bios. 2011, 6, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Gingasu, D.; Mindru, I.; Mocioiu, O.C.; Preda, S.; Stanica, N.; Patron, L.; Ianculescu, A.; Oprea, O.; Nita, S.; Paraschiv, I.; et al. Synthesis of nanocrystalline cobalt ferrite through soft chemistry methods: A green chemistry approach using sesame seed extract. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 182, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gingasu, D.; Mindru, I.; Patron, L.; Calderon-Moreno, J.M.; Mocioiu, O.C.; Preda, S.; Stanica, N.; Nita, S.; Dobre, N.; Popa, M.; et al. Green synthesis methods of CoFe2O4 and Ag-CoFe2O4 nanoparticles using hibiscus extracts. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 2106756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naik, M.M.; Naik, H.S.B.; Nagaraju, G.; Vinuth, M.; Vinu, K.; Viswanath, R. Green synthesis of zinc doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: Structural, optical, photocatalytic and antibacterial studies. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2019, 19, 100322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, Ç.E.; Manna, P.K.; Wroczynskyj, Y.; Aktürk, S.; van Lierop, J. Lanthanum ion substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles and their hyperthermia efficiency. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 458, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsoumbou, X.; Tsiaoussis, I.; Bulai, G.A.; Caltun, O.F.; Kalogirou, O.; Sarafidis, C. CoFe2-xRExO4 (RE=Dy, Yb, Gd) magnetic nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Phys. B 2021, 606, 412849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žalnėravičius, R.; Paškevičius, A.; Kurtinaitiene, M.; Jagminas, A. Size-dependent antimicrobial properties of the cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 2016, 18, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elayakumar, K.; Dinesh, A.; Manikandan, A.; Palanivelu, M.; Kavitha, G.; Prakash, S.; Kumar, R.T.; Jaganathan, S.K.; Baykal, A. Structural, morphological, enhanced magnetic properties and antibacterial bio-medical activity of rare earth element (REE) Cerium (Ce3+) doped CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 476, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Tahar, J.L.; Artus, M.; Ammar, S.; Smiri, L.S.; Herbst, F.; Vaulay, M.-J.; Richard, V.; Grenèche, J.-M.; Villain, F.; Fiévet, F. Magnetic properties of CoFe1.9 RE0.1O4 nanoparticles (RE = La, Ce, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Ho) prepared in polyol. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320, 643–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ding, Z.; Song, N.; Li, L.; Wang, W. Effect of the rare-earth substitution on the structural, magnetic, and adsorption properties in cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 4246–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumalatha, E.; Nyathani, M.; Babu, T.A.; Ravinder, D.; Prasad, N.V.K.; Katlakunta, S. Eco-Friendly Synthesis, TEM and Magnetic Properties of Co-Er Nano-Ferrites. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2022, 12, 910–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, T.; Matijevic, E. Formation of uniform spherical magnetite particle by crystallization from ferrous hydroxide gels. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 1980, 74, 227–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, T.A.S.; Waerenborgh, J.C.; Mendonça, M.H.R.M.; Nunes, M.R.; Costa, F.M. Structural and morphological characterization of FeCo2O4 and CoFe2O4 spinels prepared by a coprecipitation method. Solid State Sci. 2003, 5, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, H.; Navrotsky, A. Simple spinels: Crystallographic parameters, cation radii, lattice energies, and cation distribution. Am. Mineral. 1983, 68, 181–194. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Cryst. A 1976, 32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodan, A.M.; Iconaru, S.L.; Ciobanu, C.S.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; Stoicea, M.; Predoi, D. Iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles: Characterization and toxicity evaluation by in vitro and in vivo assays. J. Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 587021. [Google Scholar]
- Kakade, S.G.; Ma, Y.-R.; Devan, R.S.; Kolekar, Y.D.; Ramana, C.V. Dielectric, complex impedance, and electrical transport properties of erbium (Er3+) ion-substituted nanocrystalline, cobalt-rich ferrite (Co1.1Fe1.9−xErxO4). J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 5682–5693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.-X.; Jia, J.-T.; Xu, Z.-G.; Zhou, B.; Liao, C.-S.; Yan, C.-H. Microstructure, magnetic, and magneto-optical properties of chemical synthesized Co–RE (RE = Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu) ferrite nanocrystalline films. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 86, 2727–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wen, D. Influence of RE/Mn (RE = La, Nd and Gd) ratios on the infrared absorption and emission properties of Co-Zn ferrites. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 217–218, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, S.R.; Salker, A.V. Change in the magnetostructural properties of rare earth doped cobalt ferrites relative to the magnetic anisotropy. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 2740–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prathapani, S.; Jayaraman, T.V.; Varaprasadarao, E.K.; Das, D. Structural and ambient/sub-ambient temperature magnetic properties of Er-substituted cobalt-ferrites synthesized by sol-gel assisted auto-combustion method. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 023908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khana, A.; Javid ur Rehman, M.; Mahmood, K.; Ali, I.; Akhtar, M.N.; Murtaza, G.; Shakir, I.; Warsig, M.F. Impacts of Tb substitution at cobalt site on structural, morphological and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrites synthesized via double sintering method. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 2286–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharibshahian, M.; Mirzaee, O.; Nourbakhsh, M.S. Evaluation of superparamagnetic and biocompatible properties of mesoporous silica coated cobalt ferrite nanoparticles synthesized via microwave modified Pechini method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 425, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, N.N.; Gibb, T.C. Mössbauer Spectroscopy; Chapman and Hall Ltd.: London, UK, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Fock, J.; Hansen, M.F.; Frandsen, C.; Mørup, S. On the interpretation of Mössbauer spectra of magnetic nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 445, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duong, G.V.; Hanh, N.; Linh, D.V.; Groessinger, R.; Weinberger, P.; Schafler, E.; Zehetbauer, M. Monodispersed nanocrystalline Co1–xZnxFe2O4 particles by forced hydrolysis: Synthesis and characterization. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 311, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gözüak, F.; Köseoğlu, Y.; Baykal, A.; Kavas, H. Synthesis and characterization of CoxZn1−xFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles via a PEG-assisted route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 2170–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manova, E.; Kunev, B.; Paneva, D.; Mitov, I.; Petrov, L.; Estournès, C.; D’Orleans, C.; Rehspringer, J.L.; Kurmoo, M. Mechano-synthesis, characterization, and magnetic properties of nanoparticles of cobalt ferrite, CoFe2O4. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 5689–5696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, D.; Adeyeye, A.O.; Boothroyd, C.B.; Piramanayagam, S.N. Magnetic and transport properties of Co-doped Fe3O4 films. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 013904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Liao, C.; Kuang, J.; Xu, Z.; Yana, C.; Chen, L.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Z. Nanostructure magneto-optical thin films of rare earth (RE=Gd, Tb, Dy) doped cobalt spinel by sol–gel synthesis. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 85, 2782–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, M.L.; Zhang, Z.J. Synthesis and magnetic properties of CoFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanoparticles doped with lanthanide ions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 78, 3651–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, R.N.; Shih, J.C.; Chin, T.S. Magnetic properties of nano-crystalline Gd- or Pr-substituted CoFe2O4 synthesized by the citrate precursor technique. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2003, 257, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, J.; Hojamberdiev, M.; Xu, Y.; Cao, B.; Wang, J.; Wu, H. Hydrothermal synthesis and magnetic properties of gadolinium-doped CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2011, 323, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazer, B.H.; Gebhardt, J.R.; Ali, N. Magnetic phase diagrams of erbium. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 85, 6100–6102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reddy, R.A.; Rao, K.R.; Babu, B.R.; Kumar, G.K.; Rajesh, C.; Chatterjee, A.; Jyothi, N.K. Structural, electrical and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite with Nd3+ doping. Rare Met. 2022, 41, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szotek, Z.; Temmerman, W.M.; Ködderitzsch, D.; Svane, A.; Petit, L.; Winter, H. Electronic structures of normal and inverse spinel ferrites from first principles. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 74, 174431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, Y.H.; Huang, Y.L.; Hou, S.J.; Ma, S.C.; Liu, Z.W.; Ouyang, Y.F. Structural, electronic and magnetic properties of RE3+-doping in CoFe2O4: A first-principles study. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 421, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telcian, A.; Mohammed, D.H.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; Bleotu, C.; Holban, A.M.; Curutiu, C.; Grosu, E.; Ficai, A.; Mihaescu, G.; Grigore, R.; et al. Assessment of the anti-biofilm activity and biocompatibility of novel PE and PVC polymers. Rom. Biotech. Lett. 2017, 22, 12997–13004. [Google Scholar]


| Structural/Microstructural Parameters | Composition | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CoFe2O4 (ICDD 01-080-6487) | CoFe1.8Er0.2O4 | CoFe1.8Tb0.2O4 | |
| Unit cell parameters (cubic Fd3m) a = b = c (Å) | 8.3554 | 8.3751 ± 0.0051 | 8.3775 ± 0.0018 |
| α(◦) = β (◦) = γ (◦) | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| No. molecules/unit cell, Z | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| Unit cell volume, V (Å3) | 583.31 | 587.45 | 587.95 |
| Oxygen occupancy, u | 0.25664 | 0.258455 | 0.260472 |
| Average cation radius of the tetrahedral sublattice, rT (Å) | 0.5251 | 0.5559 | 0.5857 |
| Average cation radius of the octahedral sublattice, rO (Å) | 0.6549 | 0.64545 | 0.6305 |
| Theoretical density, ρt (g/cm3) | 5.343 | 5.809 | 5.766 |
| Average crystallite size, <D> (nm) | - | 6.42 ± 0.63 | 5.77 ± 0.50 |
| Microstrains (%) | - | 1.41 ± 0.54 | 1.57 ± 0.62 |
| Degree of inversion | 0.61 | 0.25 | 0 |
| Formula obtained for the estimated degree of inversion, λ | |||
| Goodness of fit, χ2 | - | 2.34845 | 1.49297 |
| Average particle size, <dTEM> (nm) | - | 6.80 ± 1.81 | 5.91 ± 2.13 |
| Sample | IS * (mm/s) | ΔEQ (mm/s) | Hhf (T) | Site/Phase Assignment | Relative Areas (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoFe2O4 | 0.374 ± 0.002 | 0.036 ± 0.038 | 5.75–46.44 | Hhf distribution | 92 ± 0.96 |
| 0.361 ± 0.018 | 0.641 ± 0.037 | - | Paramagnetic | 8 ± 0.99 | |
| CoFe1.8Er0.2O4 | 0.368 ± 0.002 | 0.012 ± 0.004 | 4.32–45.74 | Hhf distribution | 93 ± 1.0 |
| 0.371 ± 0.016 | 0.916 ± 0.036 | - | Paramagnetic | 7 ± 1.02 | |
| CoFe1.8Tb0.2O4 | 0.367 ± 0.002 | 0.022 ± 0.004 | 4.24–46.14 | Hhf distribution | 94 ± 0.98 |
| 0.386 ± 0.021 | 0.603 ± 0.041 | - | Paramagnetic | 6 ± 1.01 |
| MIC | S. aureus | E. faecalis | E. coli | P. aeruginosa | C. albicans |
| CoFe1.8Er0.2O4 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.125 | 1 |
| CoFe1.8Tb0.2O4 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.125 | 1 |
| MBEC | S. aureus | E. faecalis | E. coli | P. aeruginosa | C. albicans |
| CoFe1.8Er0.2O4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.125 | 1 |
| CoFe1.8Tb0.2O4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.125 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gingasu, D.; Mindru, I.; Ianculescu, A.-C.; Diamandescu, L.; Surdu, V.-A.; Marinescu, G.; Bartha, C.; Preda, S.; Popa, M.; Chifiriuc, M.C. Soft Chemistry Synthesis and Characterization of CoFe1.8RE0.2O4 (RE3+ = Tb3+, Er3+) Ferrite. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8020012
Gingasu D, Mindru I, Ianculescu A-C, Diamandescu L, Surdu V-A, Marinescu G, Bartha C, Preda S, Popa M, Chifiriuc MC. Soft Chemistry Synthesis and Characterization of CoFe1.8RE0.2O4 (RE3+ = Tb3+, Er3+) Ferrite. Magnetochemistry. 2022; 8(2):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8020012
Chicago/Turabian StyleGingasu, Dana, Ioana Mindru, Adelina-Carmen Ianculescu, Lucian Diamandescu, Vasile-Adrian Surdu, Gabriela Marinescu, Cristina Bartha, Silviu Preda, Marcela Popa, and Mariana Carmen Chifiriuc. 2022. "Soft Chemistry Synthesis and Characterization of CoFe1.8RE0.2O4 (RE3+ = Tb3+, Er3+) Ferrite" Magnetochemistry 8, no. 2: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8020012
APA StyleGingasu, D., Mindru, I., Ianculescu, A.-C., Diamandescu, L., Surdu, V.-A., Marinescu, G., Bartha, C., Preda, S., Popa, M., & Chifiriuc, M. C. (2022). Soft Chemistry Synthesis and Characterization of CoFe1.8RE0.2O4 (RE3+ = Tb3+, Er3+) Ferrite. Magnetochemistry, 8(2), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8020012









