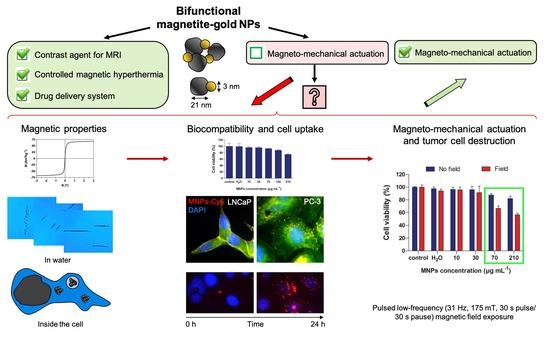
Bifunctional Magnetite–Gold Nanoparticles for Magneto-Mechanical Actuation and Cancer Cell Destruction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Magnetic Nanoparticles
2.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.3. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Measurements
2.4. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.5. Analysis of MNP Magnetic Properties
2.6. Cell Lines
2.7. Cell Incubation with MNPs
2.8. Dynamic of MNPs-Cy5 Accumulation in Cells
2.9. Immunofluorescent Staining
2.10. Scanning Surface Confocal Microscopy (SSCM)
2.11. Correlative Light-Electron Microscopy (CLEM)
2.12. Transmission Electron Microscopy of Cells
2.13. Cytotoxicity Assay of MNPs-Cy5
2.14. MNPs-Cy5 Behavior inside Cells under Low-Frequency Magnetic Field Exposure
2.15. MNPs-Cy5 Effect on Cells under Low-Frequency Magnetic Field Exposure
2.16. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
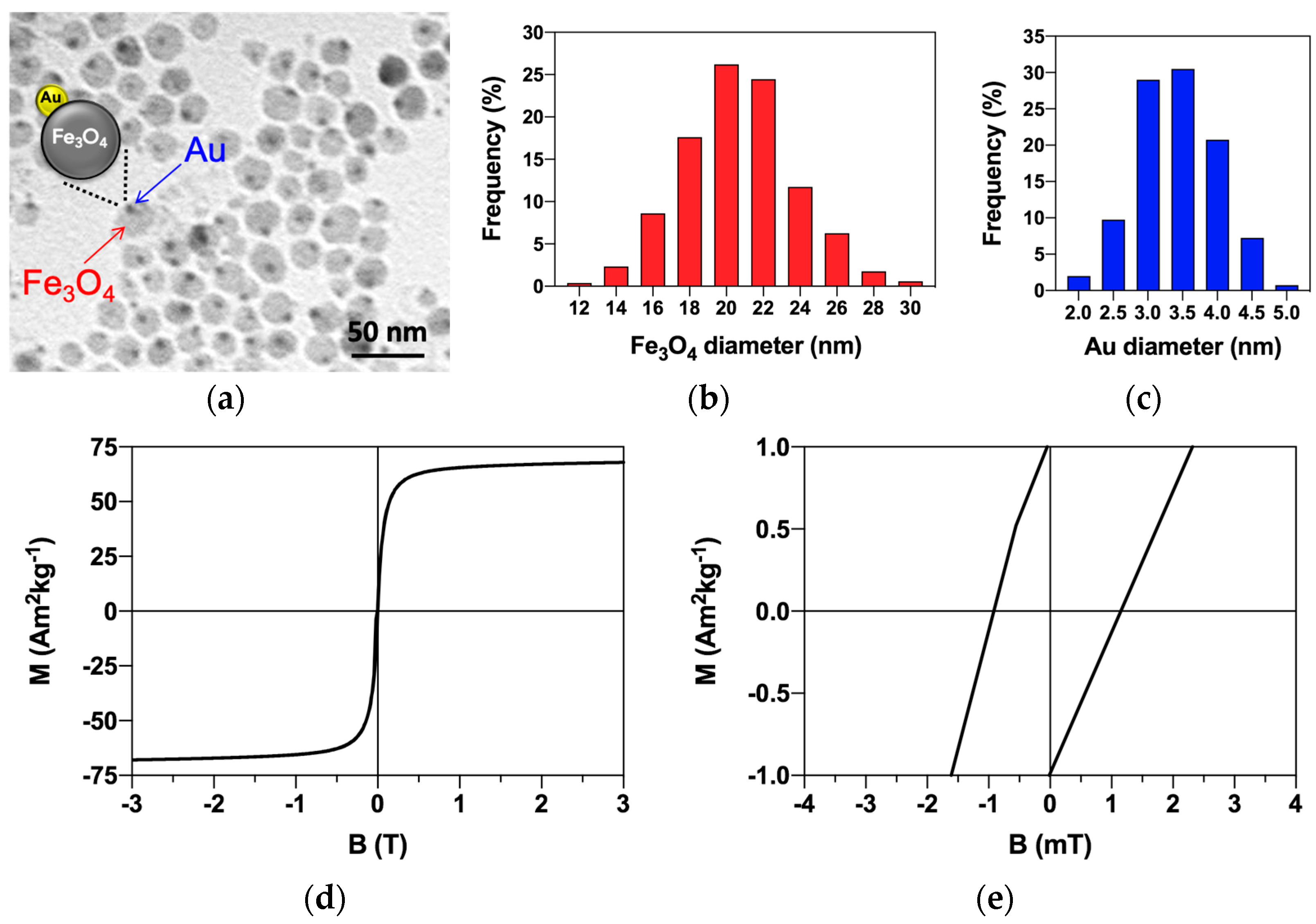
3.1. Magnetite–Gold Dumbbell Nanoparticle Characterization and Magnetic Properties
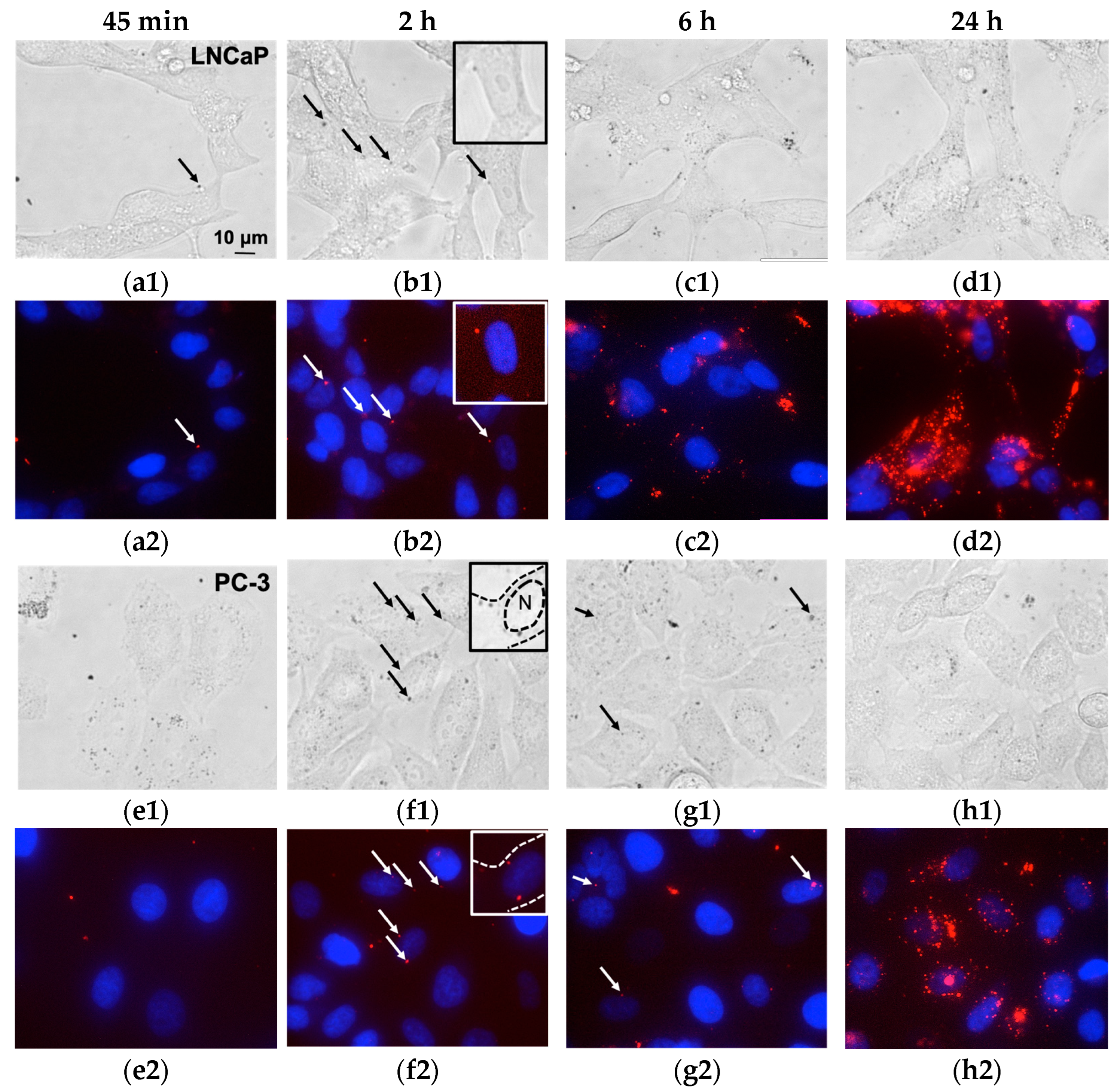
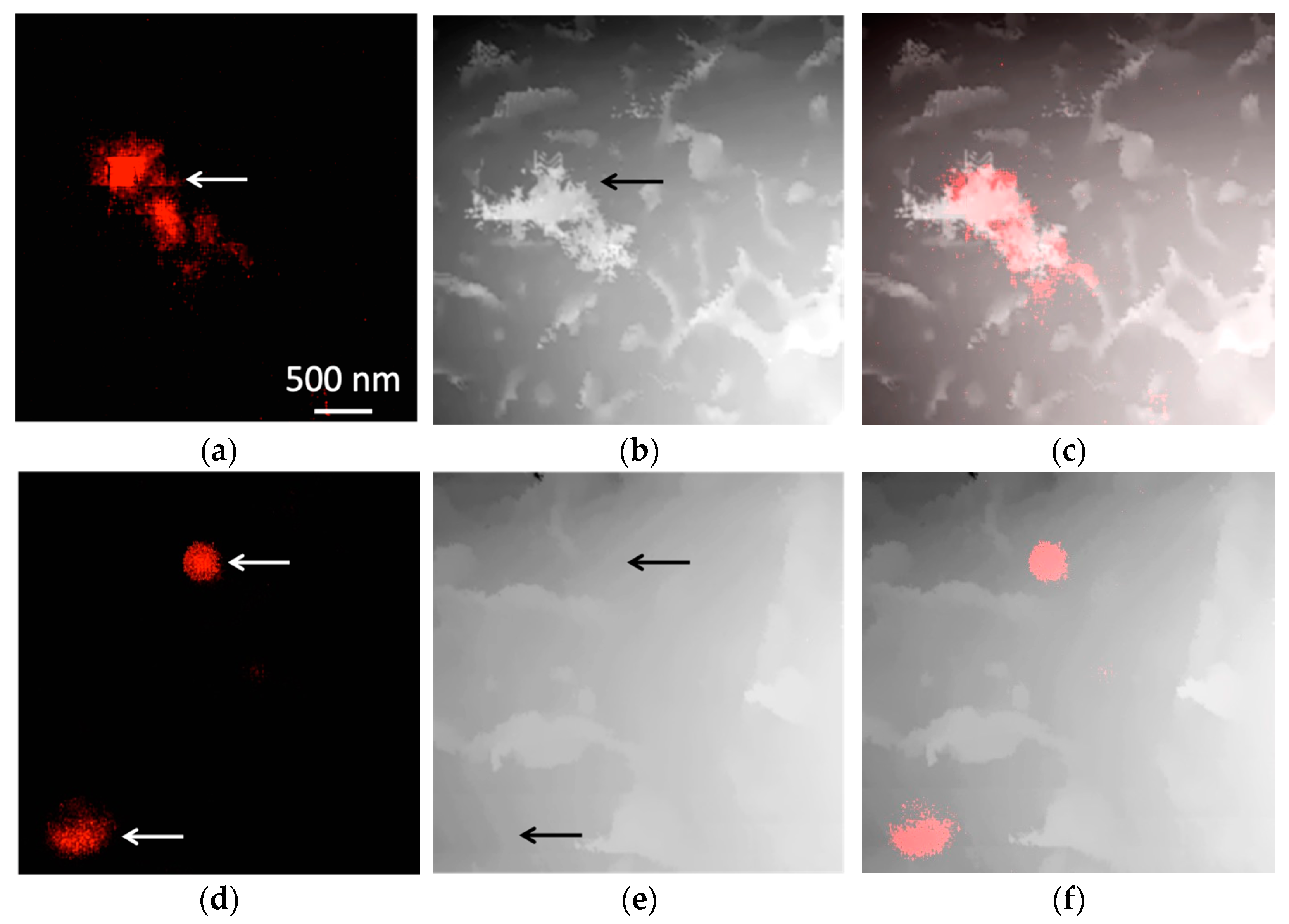
3.2. Magnetic Nanoparticles Accumulation in Cells
3.3. Magnetic Nanoparticles Uptake and Localization inside the Cell
3.4. Magnetic Nanoparticles Biocompatibility In Vitro
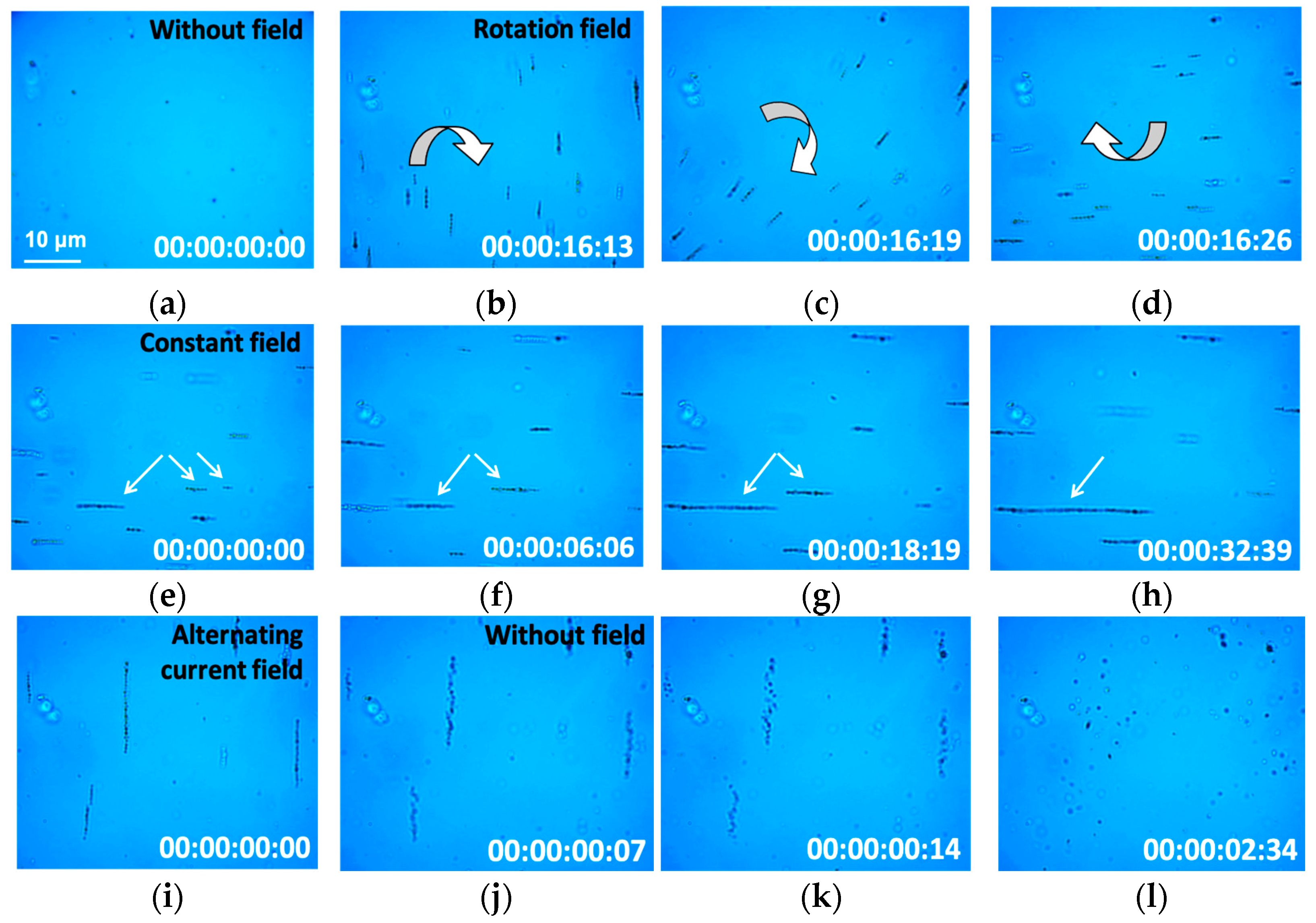
3.5. Magnetic Nanoparticle Impact on the Cells under Low-Frequency Magnetic Field Exposure
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Avasthi, A.; Caro, C.; Pozo-Torres, E.; Leal, M.P.; García-Martín, M.L. Magnetic Nanoparticles as MRI Contrast Agents. Top. Curr. Chem. 2020, 378, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, P.; Dong, Y.; Liang, G.; Yu, Y. Enzyme-instructed self-aggregation of Fe3O4 nanoparticles for enhanced MRI T2 imaging and photothermal therapy of tumors. Nanoscale 2020, 3, 1886–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raouf, I.; Khalid, S.; Khan, A.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, M.-H. A Review on Numerical Modeling for Magnetic Nanoparticle Hyperthermia: Progress and Challenges. J. Therm. Biol. 2020, 91, 102644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenea-Robin, M.; Marchalot, J. Basic Principles and Recent Advances in Magnetic Cell Separation. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, S.H.; Yuk, J.S.; Um, S.H. Regulation of cellular gene expression by nanomaterials. Nano Converg. 2018, 5, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, P.M.; Mahmoud, W.E.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A.; Bronstein, L.M. Magnetic Drug Delivery: Where the Field Is Going. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.F.; Jang, B.; Issadore, D.; Tsourkas, A. Use of magnetic fields and nanoparticles to trigger drug release and improve tumor targeting. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 11, e1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, S.; Hallali, N.; Lalatonne, Y.; Hillion, A.; Antunes, J.C.; Serhan, N.; Clerc, P.; Fourmy, D.; Motte, L.; Carrey, J.; et al. Magneto-mechanical destruction of cancer-associated fibroblasts using ultra-small iron oxide nanoparticles and low frequency rotating magnetic fields. Nanoscale Adv. 2022, 4, 421–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitin, A.A.; Ivanova, A.V.; Semkina, A.S.; Lazareva, P.A.; Abakumov, M.A. Magneto-Mechanical Approach in Biomedicine: Benefits, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzoneva, R.; Tsiapla, A.-R.; Uzunova, V.; Stoyanova, T.; Samaras, T.; Angelakeris, M.; Kalogirou, O. Synergistic Effect of Combined Treatment with Magnetic Hyperthermia and Magneto-Mechanical Stress of Breast Cancer Cells. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.W.; Gan, W.L.; Teo, Y.K.; Lew, W.S. Interplay of cell death signaling pathways mediated by alternating magnetic field gradient. Cell Death Discov. 2018, 4, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orel, V.E.; Dasyukevich, O.; Rykhalskyi, O.; Orel, V.B.; Burlaka, A.; Virko, S. Magneto-mechanical effects of magnetite nanoparticles on Walker-256 carcinosarcoma heterogeneity, redox state and growth modulated by an inhomogeneous stationary magnetic field. JMMM 2021, 538, 168314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiapla, A.-R.; Uzunova, V.; Oreshkova, T.; Angelakeris, M.; Samaras, T.; Kalogirou, O.; Tzoneva, R. Cell Behavioral Changes after the Application of Magneto-Mechanical Activation to Normal and Cancer Cells. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Qian, Z.; Yang, Y. Evaluation of Tumor Treatment of Magnetic Nanoparticles Driven by Extremely Low Frequency Magnetic Field. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Master, A.M.; Williams, P.N.; Pothayee, N.; Zhang, R.; Vishwasrao, H.M.; Golovin, Y.I.; Riffle, J.S.; Sokolsky, M.; Kabanov, A.V. Remote Actuation of Magnetic Nanoparticles for Cancer Cell Selective Treatment Through Cytoskeletal Disruption. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.W.; Gan, W.L.; Liu, N.; Lew, W.S. Magneto-actuated cell apoptosis by biaxial pulsed magnetic field. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiriac, H.; Radu, E.; Țibu, M.; Stoian, G.; Ababei, G.; Lăbușcă, L.; Herea, D.-D.; Lupu, N. Fe-Cr-Nb-B ferromagnetic particles with shape anisotropy for cancer cell destruction by magneto-mechanical actuation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alieva, I.; Kireev, I.; Rakhmanina, A.; Garanina, A.; Strelkova, O.; Zhironkina, O.; Cherepaninets, V.; Davydov, V.; Khabashesku, V.; Agafonov, V.; et al. Magnetinduced behavior of iron carbide (Fe7C3@C) nanoparticles in the cytoplasm of living cells. Nanosyst. Phys. Chem. Math. 2016, 7, 158160. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Wu, C.; Uyeda, T.Q.P.; Plaza, G.R.; Liu, B.; Han, Y.; Lesniak, M.S.; Cheng, Y. Elongated Nanoparticle Aggregates in Cancer Cells for Mechanical Destruction with Low Frequency Rotating Magnetic Field. Theranostics 2017, 7, 1735–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garanina, A.S.; Kireev, I.I.; Zhironkina, O.A.; Strelkova, O.S.; Shakhov, A.; Alieva, I.B.; Davydov, V.A.; Murugesan, S.; Khabashesku, V.N.; Majouga, A.G.; et al. Long-term live cells observation of internalized fluorescent Fe@C nanoparticles in constant magnetic field. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 17, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naud, C.; Thébault, C.; Carrière, M.; Hou, Y.; Morel, R.; Berger, F.; Diény, B.; Joisten, H. Cancer treatment by magneto-mechanical effect of particles, a review. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 3632–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, E.; Kircher, M.F.; Koch, M.; Eliasson, L.; Goldberg, S.N.; Renström, E. Dynamic magnetic fields remote-control apoptosis via nanoparticle rotation. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 3192–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vegerhof, A.; Barnoy, E.A.; Motiei, M.; Malka, D.; Danan, Y.; Zalevsky, Z.; Popovtzer, R. Targeted magnetic nanoparticles for mechanical lysis of tumor cells by low-amplitude alternating magnetic field. Materials 2016, 9, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremova, M.V.; Naumenko, V.A.; Spasova, M.; Garanina, A.S.; Abakumov, M.A.; Blokhina, A.D.; Melnikov, P.A.; Prelovskaya, A.O.; Heidelmann, M.; Li, Z.-A.; et al. Magnetite-Gold nanohybrids as ideal all-in-one platforms for theranostics. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremova, M.V.; Nalench, Y.A.; Myrovali, E.; Garanina, A.S.; Grebennikov, I.S.; Gifer, P.K.; Abakumov, M.A.; Spasova, M.; Angelakeris, M.; Savchenko, A.G.; et al. Size-selected Fe3O4–Au hybrid nanoparticles for improved magnetism-based theranostics. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2684–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machulkin, A.E.; Garanina, A.S.; Zhironkina, O.A.; Beloglazkina, E.K.; Zyk, N.V.; Savchenko, A.G.; Kotelyanskii, V.E.; Mazhuga, A.G. Nanohybride Materials Based on Magnetite-Gold Nanoparticles for Diagnostics of Prostate Cancer: Synthesis and In Vitro Testing. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2016, 161, 706–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Chen, M.; Rice, P.M.; Wang, S.X.; White, R.L.; Sun, S. Dumbbell-like bifunctional Au-Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romodina, M.N.; Lyubin, E.V.; Fedyanin, A.A. Detection of Brownian Torque in a Magnetically-Driven Rotating Microsystem. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavaev, E.S.; Novoselova, M.; Shchelkunov, N.M.; German, S.; Komlev, A.S.; Mokrousov, M.D.; Zelepukin, I.V.; Burov, A.M.; Khlebtsov, B.N.; Lyubin, E.V.; et al. CaCO3 Nanoparticles Coated with Alternating Layers of Poly-L-Arginine Hydrochloride and Fe3O4 Nanoparticles as Navigable Drug Carriers and Hyperthermia Agents. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 2994–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korchev, Y.E.; Bashford, C.L.; Milovanovic, M.; Vodyanoy, I.; Lab, M.J. Scanning ion conductance microscopy of living cells. Biophys. J. 1997, 73, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korchev, Y.E.; Milovanovic, M.; Bashford, C.L.; Bennett, D.C.; Sviderskaya, E.V.; Vodyanoy, I.; Lab, M.J. Specialized scanning ion-conductance microscope for imaging of living cells. J. Microsc. 1997, 188, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorelik, J.; Shevchuk, A.; Ramalho, M.; Elliott, M.; Lei, C.; Higgins, C.F.; Lab, M.J.; Klenerman, D.; Krauzewicz, N.; Korchev, Y. Scanning surface confocal microscopy for simultaneous topographical and fluorescence imaging: Application to single virus-like particle entry into a cell. PNAS 2002, 99, 16018–16023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salikhov, S.V.; Savchenko, A.G.; Grebennikov, I.S.; Yurtov, E.V. Phase composition and structure of iron oxide nanopowders prepared by chemical means. Bull. Russ. Acad. Sci. Phys. 2015, 79, 1106–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Walle, A.; Perez, J.E.; Abou-Hassan, A.; Hémadi, M.; Luciani, N.; Wilhelm, C. Magnetic nanoparticles in regenerative medicine: What of their fate and impact in stem cells? Mater. Today Nano 2020, 11, 100084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribanovsky, S.L.; Zhigachev, A.O.; Golovin, D.Y.; Golovin, Y.I.; Klyachko, N.L. Mechanisms and conditions for mechanical activation of magnetic nanoparticles by external magnetic field for biomedical applications. JMMM 2022, 553, 169278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ning, P.; Gao, R.; Feng, O.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, C.; Qin, Y.; Plaza, G.R.; et al. Programmable ROS-Mediated Cancer Therapy via Magneto-Inductions. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1902933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yang, W.; Pu, G.; Zhu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, B.; Chu, M. Low frequency vibrating magnetic field-triggered magnetic microspheres with a nanoflagellum-like surface for cancer therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanavio, B.; Stellacci, F. Recent Advances in the Synthesis and Applications of Multimodal Gold-Iron Nanoparticles. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantechi, E.; Innocenti, C.; Bertoni, G.; Sangregorio, C.; Pineider, F. Modulation of the magnetic properties of gold-spinel ferrite heterostructured nanocrystals. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmi, G.R.; Saleem, K.; Baig, M.M.F.A.; Aamir, M.N.; Wang, M.; Gao, X.; Abbas, M.; Rehman, M.U. Recent Advances of Magnetic Gold Hybrids and Nanocomposites, and Their Potential Biological Applications. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, S.; Prabaharan, M. Theranostics Based on Iron Oxide and Gold Nanoparticles for Imaging-Guided Photothermal and Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1858–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzzi, B.; Albino, M.; Gabbani, A.; Omelyanchik, A.; Kozenkova, E.; Petrecca, M.; Innocenti, C.; Balica, E.; Lavacchi, A.; Scavone, F.; et al. Star-Shaped Magnetic-Plasmonic Au@Fe3O4 Nano-Heterostructures for Photothermal Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 29087–29098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathore, B.; Sunwoo, K.; Jangili, P.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.H.; Huang, M.; Xiong, J.; Sharma, A.; Yang, Z.; Qu, J.; et al. Nanomaterial designing strategies related to cell lysosome and their biomedical applications: A review. Biomaterials 2019, 211, 25–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzhytchak, M.; Smolková, B.; Lunova, M.; Jirsa, M.; Frtús, A.; Kubinová, Š.; Dejneka, A.; Lunov, O. Iron Oxide Nanoparticle-Induced Autophagic Flux Is Regulated by Interplay between p53-mTOR Axis and Bcl-2 Signaling in Hepatic Cells. Cells 2020, 9, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foroozandeh, P.; Aziz, A.A. Insight into Cellular Uptake and Intracellular Trafficking of Nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portilla, Y.; Mulens-Arias, V.; Paradela, A.; Ramos-Fernández, A.; Pérez-Yagüe, S.; Morales, M.P.; Barber, D.F. The surface coating of iron oxide nanoparticles drives their intracellular trafficking and degradation in endolysosomes differently depending on the cell type. Biomaterials 2022, 281, 121365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alieva, I.B.; Kireev, I.; Garanina, A.S.; Alyabyeva, N.; Ruyter, A.; Strelkova, O.S.; Zhironkina, O.A.; Cherepaninets, V.D.; Majouga, A.G.; Davydov, V.A.; et al. Magnetocontrollability of Fe7C3@C superparamagnetic nanoparticles in living cells. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 14, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Lai, K.; Wu, Y.; Gu, Z. Protein corona on magnetite nanoparticles and internalizationof nanoparticle–protein complexes into healthy and cancer cells. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2014, 37, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, C.; Pernemalm, M.; Kohonen, P.; Laurent, S.; Hultenby, K.; Vahter, M.; Lehtiö, J.; Toprak, M.S.; Fadeel, B. Proteomics Analysis Reveals Distinct Corona Composition on Magnetic Nanoparticles with Different Surface Coatings: Implications for Interactions with Primary Human Macrophages. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brollo, M.E.F.; Flores, P.H.; Gutierrez, L.; Johansson, C.; Barber, D.F.; Morales, M.P. Magnetic properties of nanoparticles as a function of their spatial distribution on liposomes and cells. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 17829–17838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalandari, B.; Asadollahi, K.; Shakerizadeh, A.; Komeili, A.; Riazi, G.; Kamrava, S.K.; Attaran, N. Microtubule network as a potential candidate for targeting by gold nanoparticle-assisted photothermal therapy. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2019, 192, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikitin, A.A.; Yurenya, A.Y.; Zatsepin, T.S.; Aparin, I.O.; Chekhonin, V.P.; Majouga, A.G.; Farle, M.; Wiedwald, U.; Abakumov, M.A. Magnetic Nanoparticles as a Tool for Remote DNA Manipulations at a Single-Molecule Level. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 14458–14469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, S.; Sun, Y.; Squires, J.M.; Zhang, H.; Oh, W.K.; Liang, C.-Z.; Huang, J. PC3 is a cell line characteristic of prostatic small cell carcinoma. Prostate 2011, 71, 1668–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hope, J.M.; Bersi, M.R.; Dombroski, J.A.; Clinch, A.B.; Pereles, R.S.; Merryman, W.D.; King, M.R. Circulating prostate cancer cells have differential resistance to fluid shear stress-induced cell death. J. Cell Sci. 2021, 134, jcs251470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garanina, A.S.; Efremova, M.V.; Machulkin, A.E.; Lyubin, E.V.; Vorobyeva, N.S.; Zhironkina, O.A.; Strelkova, O.S.; Kireev, I.I.; Alieva, I.B.; Uzbekov, R.E.; et al. Bifunctional Magnetite–Gold Nanoparticles for Magneto-Mechanical Actuation and Cancer Cell Destruction. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8120185
Garanina AS, Efremova MV, Machulkin AE, Lyubin EV, Vorobyeva NS, Zhironkina OA, Strelkova OS, Kireev II, Alieva IB, Uzbekov RE, et al. Bifunctional Magnetite–Gold Nanoparticles for Magneto-Mechanical Actuation and Cancer Cell Destruction. Magnetochemistry. 2022; 8(12):185. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8120185
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaranina, Anastasiia S., Maria V. Efremova, Alexey E. Machulkin, Evgeny V. Lyubin, Natalia S. Vorobyeva, Oxana A. Zhironkina, Olga S. Strelkova, Igor I. Kireev, Irina B. Alieva, Rustem E. Uzbekov, and et al. 2022. "Bifunctional Magnetite–Gold Nanoparticles for Magneto-Mechanical Actuation and Cancer Cell Destruction" Magnetochemistry 8, no. 12: 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8120185
APA StyleGaranina, A. S., Efremova, M. V., Machulkin, A. E., Lyubin, E. V., Vorobyeva, N. S., Zhironkina, O. A., Strelkova, O. S., Kireev, I. I., Alieva, I. B., Uzbekov, R. E., Agafonov, V. N., Shchetinin, I. V., Fedyanin, A. A., Erofeev, A. S., Gorelkin, P. V., Korchev, Y. E., Savchenko, A. G., & Abakumov, M. A. (2022). Bifunctional Magnetite–Gold Nanoparticles for Magneto-Mechanical Actuation and Cancer Cell Destruction. Magnetochemistry, 8(12), 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8120185