Studies on the Removal of Congo Red Dye by an Adsorbent Based on Fly-Ash@Fe3O4 Mixture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fly-Ash/NaOH Adsorbent Synthesis
2.2. Fly-Ash@Fe3O4 Adsorbent Synthesis
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Congo Red Dye Characteristics and Preparation
2.5. Batch Adsorption Experiments
2.6. Isotherm and Kinetics Adsorption Study
3. Results and Discussion
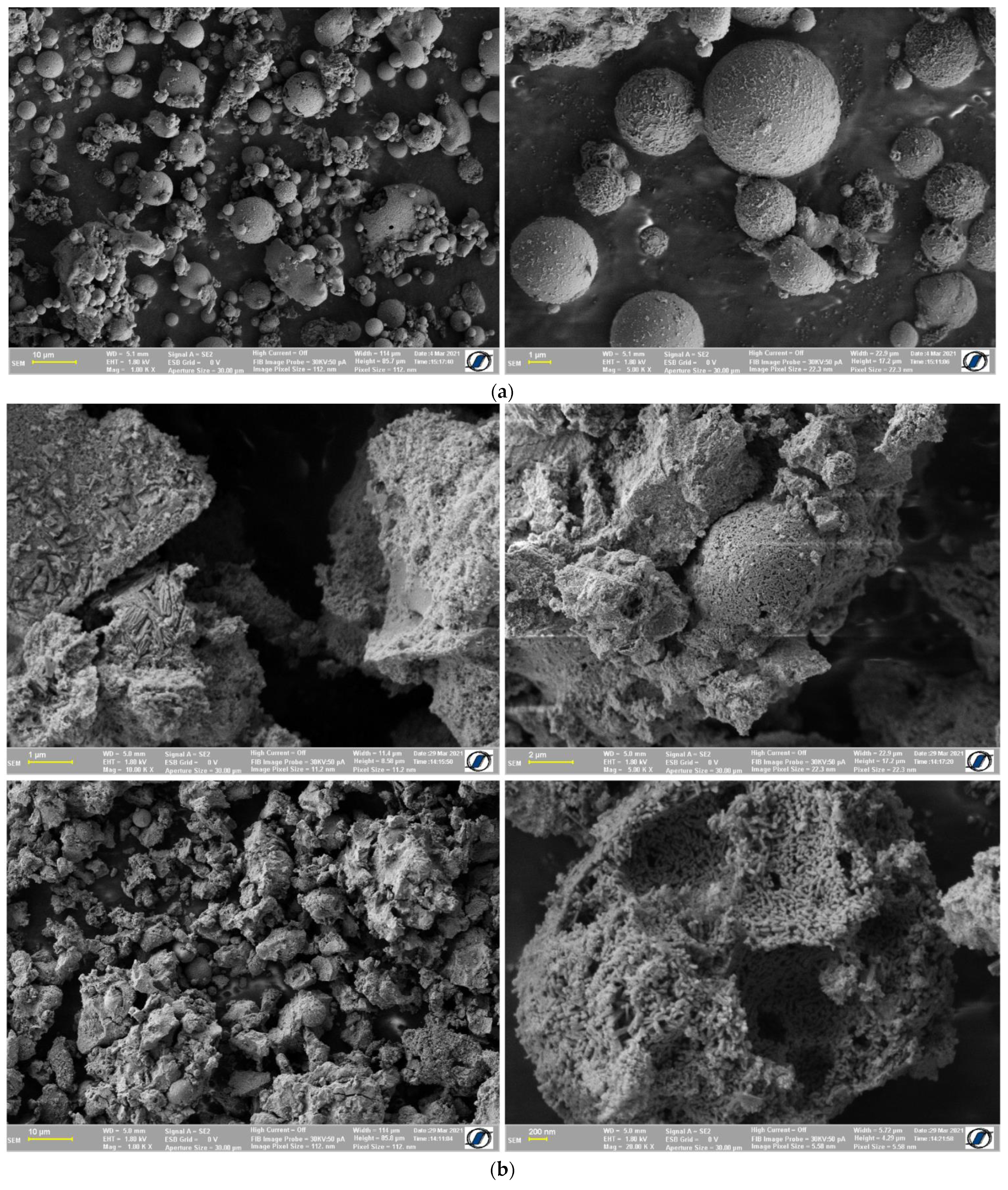
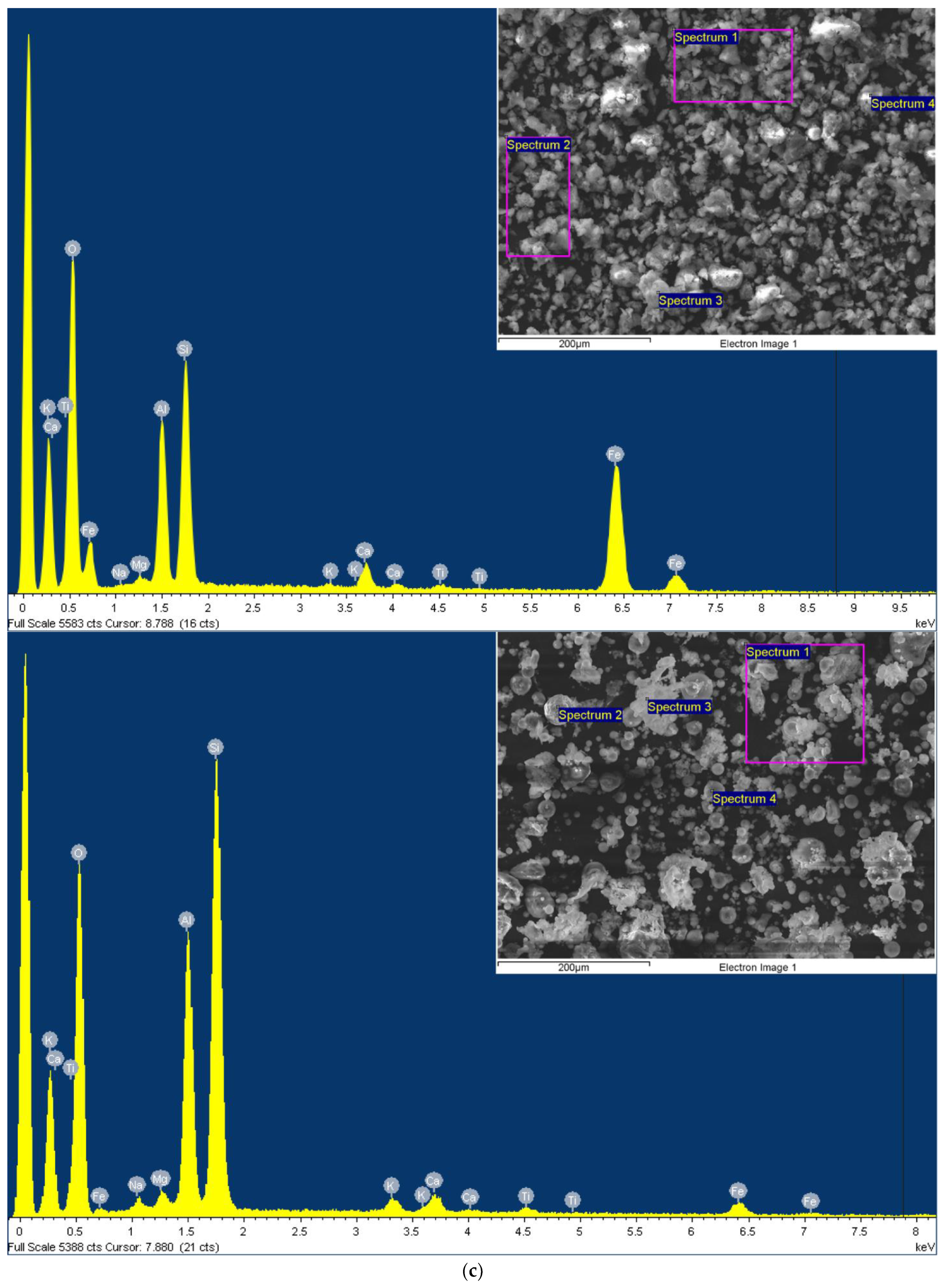
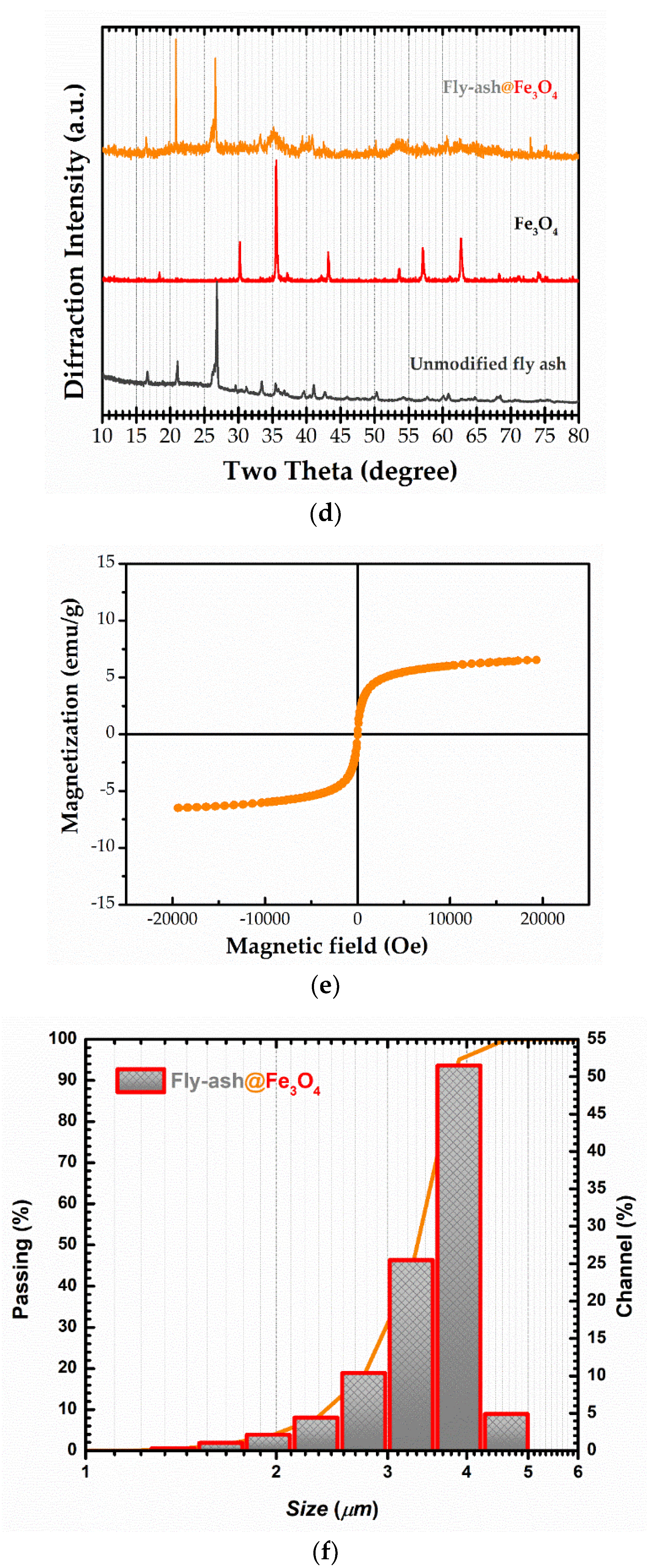
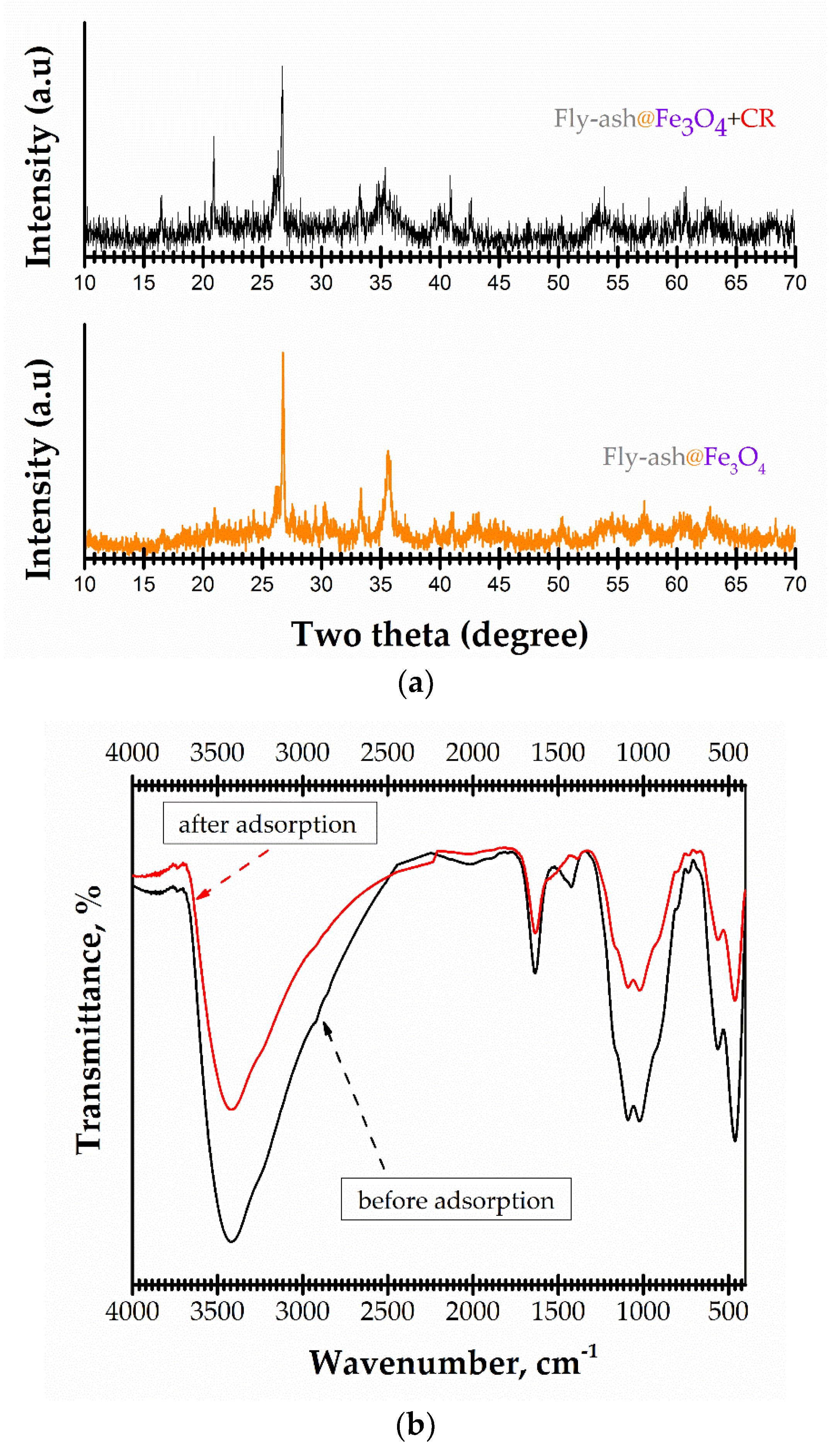
3.1. Characterization of Magnetic Adsorbent
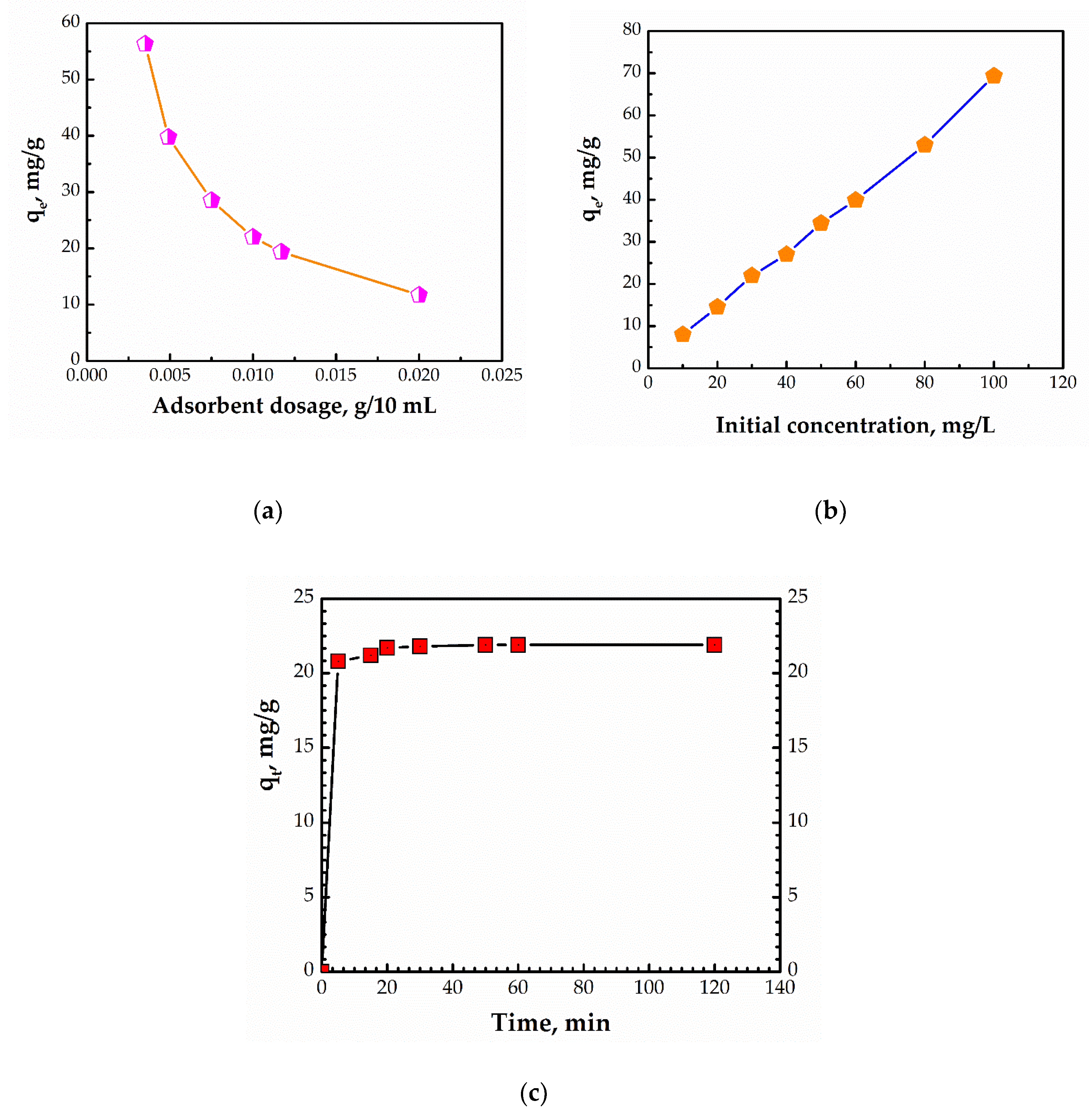
3.2. Effect of Working Parameters on the Adsorption Process
3.3. Comparison with the Available Literature and Circular Economy Concept
3.4. Characterization of Fly-Ash@Fe3O4 Loaded Adsorbent
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamd, A.; Dryaz, A.R.; Shaban, M.; AlMohamadi, H.; Abu Al-Ola, K.A.; Soliman, N.K.; Ahmed, S.A. Fabrication and Application of Zeolite/Acanthophora Spicifera Nanoporous Composite for Adsorption of Congo Red Dye from Wastewater. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshti, A.; Nozarian, K.; Ghamari, N.; Mayer, P.; Motamedi, H. Selective high capacity adsorption of Congo red, luminescence and antibacterial assessment of two new cadmium(II) coordination polymers. J. Solid State Chem. 2018, 258, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Gao, M.; Shen, T.; Zeng, H.; Yang Xiang, Y. Comparative study of organo-vermiculite, organo-montmorillonite and organo-silica nanosheets functionalized by an ether-spacer-containing Gemini surfactant: Congo red adsorption and wettability. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 349, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Meas, A.; Shan, S.; Yang, R.; Gai, X.; Wang, H.; Tsend, N. Characterization, isotherm and kinetic data for adsorption of Congo red and 2-naphthol on different bamboo hydrochars. Data Brief 2018, 19, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, S.; Biswas, B.K.; Rahman, M.A.; Rahman, M.H.; Anik, M.S.; Uddin, M.R. Study on adsorption of Congo red onto chemically modified egg shell membrane. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, J.; Wang, S.T.; Sun, J.; Guo, Y.M.; Wang, H.; Huang, S.G.; Li, Y.D.; Wang, C.C. Ultrahigh adsorption capacities of fluorescein sodium and Congo red achieved in mixed-halide [BiI3Cl2] and methylviologen dication. Mater. Lett. 2019, 254, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derouich, G.; Alami Younssi, S.; Bennazha, J.; Cody, J.A.; Ouammou, M.; El Rhazi, M. Development of low-cost polypyrrole/sintered pozzolan ultrafiltration membrane and its highly efficient performance for congo red dye removal. J. Env. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.-H.; Ling, F.-X.; Wang, P.; Sui, B.-K.; Wang, S.-J.; Yuan, S.-H. Preparation of rod-like γ-alumina/volcanic rock porous material and preliminary study on the adsorption property of Congo red. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2021, 49, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, V.; Uthappa, U.T.; Arvind swami, O.R.; Han, S.S.; Jung, H.-Y.; Altalhi, T.; Kurkuri, M.D. Sustainable green functional nano aluminium fumarate-MOF decorated on 3D low-cost natural diatoms for the removal of Congo red dye and fabric whitening agent from wastewater: Batch & continuous adsorption process. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 32, 103887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.W.; An, L.; Chen, J.; Bae, J.H.; Kim, Y.S. Preparation of amine-functionalized lignins for the selective adsorption of Methylene blue and Congo red. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qiu, G.; Liu, Y.; Niu, Y.; Qu, R.; Ji, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, C. Fabrication of CoFe-MOF materials by different methods and adsorption properties for Congo red. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 360, 119405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harja, M.; Teodosiu, C.; Isopescu, D.N.; Gencel, O.; Lutic, D.; Ciobanu, G.; Cretescu, I. Using fly ash wastes for the development of new building materials with improved compressive strength. Materials 2022, 15, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawan, T.D.; Munawar, E.; Muchtar, S. Preparation and characterization of chemically activated adsorbent from the combination of coconut shell and fly ash. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 63, S40–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buema, G.; Harja, M.; Lupu, N.; Chiriac, H.; Forminte, L.; Ciobanu, G.; Bucur, D.; Bucur, R.D. Adsorption Performance of Modified Fly Ash for Copper Ion Removal from Aqueous Solution. Water 2021, 13, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.C.; Yoon, S.K.; Choi, N.J. Application of Fly Ash as an Adsorbent for Removal of Air and Water Pollutants. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahabadi, A.; Singh, P.; Raizada, P.; Anastopoulos, I.; Sivamani, S.; Dotto, G.L.; Landarani, M.; Ivanets, A.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A. Activated carbon from wood wastes for the removal of uranium and thorium ions through modification with mineral acid. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 607, 125516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Yang, Z.; Dai, H.; Lu, X.; Peng, L.; Tan, X.; Shi, L.; Fahim, R. Preparation and application of modified zeolites as adsorbents in wastewater treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 2017, 621–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruschi, M.L.; de Toledo, L.D.A.S. Pharmaceutical Applications of Iron-Oxide Magnetic Nanoparticles. Magnetochemistry 2019, 5, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbar, K.Q.; Barzinjy, A.A.; Hamad, S.M. Iron oxide nanoparticles: Preparation methods, functions, adsorption and coagulation/flocculation in wastewater treatment. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2022, 17, 100661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herea, D.D.; Chiriac, H.; Lupu, N. Preparation and characterization of magnetic nanoparticles with controlled magnetization. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 4357–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahdar, A.; Taboada, P.; Aliahmad, M.; Hajinezhad, M.R.; Sadeghfar, F. Iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, physical characterization, and intraperitoneal biochemical studies in Rattus norvegicus. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1173, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, X.; Liao, T.; Zhu, Y.; Tang, H.; Li, T.; Chen, J.S. Facile electrochemical fabrication of magnetic Fe3O4 for electrocatalytic synthesis of ammonia used for hydrogen storage application. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 24128–24134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jannah, N.R.; Onggo, D. Synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles for colour removal of printing ink solution. IOP Conf. Ser. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1245, 012040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herea, D.D.; Labusca, L.; Radu, E.; Chiriac, H.; Grigoras, M.; Dragos Panzaru, O.; Lupu, L. Human adipose-derived stem cells loaded with drug-coated magnetic nanoparticles for in-vitro tumor cells targeting. Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 94, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liandi, A.R.; Yunarti, R.T.; Nurmawan, M.F.; Cahyana, A.H. The Utilization of Fe3O4 Nanocatalyst in Modifying Cinnamaldehyde Compound to Synthesis 2-Amino-4H-Chromene Derivative. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 22, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Raza, T.; Ahmed, A.; Ali, M.S.; Liu, C.; Li, D.; Li, C. Facile synthesis of magnetically separable Fe3O4/GO/g-C3N4 composite for superior photocatalytic degradation of naphthalene. Synth. Met. 2022, 287, 117072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, Z.I.; Mustafa, M.K.; Asman, S.; Sekak, K.A. Preparation and Characterization of Magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles By Sol-Gel Method. Int. J. Nanoelectron. Mater. 2019, 12, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, P.; Chang, T.; Chen, W.J.; Deng, J.; Li, S.L.; Zuo, Y.G.; Kang, L.; Yang, F.; Hostetter, M.; Volinsky, A.A. Temperature effects on magnetic properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles synthesized by the sol-gel explosion-assisted method. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 773, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesus, A.C.B.; Jesus, J.R.; Lima, R.J.S.; Moura, K.O.; Almeida, J.M.A.; Duque, J.G.S.; Meneses, C.T. Synthesis and magnetic interaction on concentrated Fe3O4 nanoparticles obtained by the co-precipitation and hydrothermal chemical methods. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 11149–11153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herea, D.D.; Chiriac, H.; Lupu, N.; Grigoras, M.; Stoian, G.; Stoica, B.A.; Petreus, T. Study on iron oxide nanoparticles coated with glucose-derived polymers for biomedical applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 352, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govan, J. Recent Advances in Magnetic Nanoparticles and Nanocomposites for the Remediation of Water Resources. Magnetochemistry 2020, 6, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamasbi, N.; Mohammadi Ziarani, G.; Mohajer, F.; Darroudi, M.; Badiei, A.; Varma, R.S.; Karimi, F. Silica-coated modified magnetic nanoparticles (Fe3O4@SiO2@(BuSO3H)3) as an efficient adsorbent for Pd2+ removal. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koohi, P.; Rahbar-kelishami, A.; Shayesteh, H. Efficient removal of congo red dye using Fe3O4/NiO nanocomposite: Synthesis and characterization. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harja, M.; Buema, G.; Bucur, D. Recent advances in removal of Congo Red dye by adsorption using an industrial waste. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, S.; Guha, N.; Krishnan, S.; Singh, A.K.; Mathur, P.; Rai, D.K. Selective and Recyclable Congo Red Dye Adsorption by Spherical Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Functionalized with 1,2,4,5-Benzenetetracarboxylic Acid. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivalingam, S.; Sen, S. Rapid ultrasound assisted hydrothermal synthesis of highly pure nanozeolite X from fly ash for efficient treatment of industrial effluent. Chemosphere 2018, 210, 816–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buema, G.; Lupu, N.; Chiriac, H.; Ciobanu, G.; Bucur, R.D.; Bucur, D.; Favier, L.; Harja, M. Performance assessment of five adsorbents based on fly ash for removal of cadmium ions. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 333, 115932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harja, M.; Buema, G.; Lupu, N.; Chiriac, H.; Herea, D.D.; Ciobanu, G. Fly Ash Coated with Magnetic Materials: Improved Adsorbent for Cu (II) Removal from Wastewater. Materials 2021, 14, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cretescu, I.; Harja, M.; Teodosiu, C.; Isopescu, D.N.; Chok, M.F.; Sluser, B.M.; Salleh, M.A.M. Synthesis and characterisation of a binder cement replacement based on alkali activation of fly ash waste. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 119, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayat, A.R.P.; Sulistiono, D.O.; Murwani, I.K.; Endrawati, B.F.; Fansuri, H.; Zulfa, L.L.; Ratna Ediati, R. Linear and nonlinear isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic behavior of methyl orange adsorption using modulated Al2O3@UiO-66 via acetic acid. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 11313, Congo Red. 2022. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Congo-red (accessed on 21 July 2022).
- Hongsub, B.; Tanveer, A.; Ilsu, R.; Yongmin, C.; Seong-Uk, J.; Sungwook, H. Carbon-coated iron oxide nanoparticles as contrast agents in magnetic resonance imaging. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsani-Namin, Z.; Norouzbeigi, R.; Shayesteh, H. Green mediated combustion synthesis of copper zinc oxide using Eryngium planum leaf extract as a natural green fuel: Excellent adsorption capacity towards Congo red dye. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 20961–20973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungureanu, O.I.; Bulgariu, D.; Mocanu, A.M.; Bulgariu, L. Functionalized PET Waste Based Low-Cost Adsorbents for Adsorptive Removal of Cu(II) Ions from Aqueous Media. Water 2020, 12, 2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borth, K.W.; Galdino, C.W.; Teixeira, V.D.C.; Anaissi, F.J. Iron oxide nanoparticles obtained from steel waste recycling as a green alternative for Congo red dye fast adsorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 546, 149126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noli, F.; Avgerinou, A.; Kapashi, E.; Kapnisti, M. Uranium and Thorium Retention onto Sorbents from Raw and Modified Pomegranate Peel. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelfatah, A.; Abdel-Gawad, O.F.; Elzanaty, A.M.; Rabie, A.M.; Mohamed, F. Fabrication and optimization of poly(ortho-aminophenol) doped glycerol for efficient removal of cobalt ion from wastewater. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 345, 117034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonar, S.K.; Niphadkar, P.S.; Mayadevi, S.; Praphulla, N.; Joshi, P.N. Preparation and characterization of porous fly ash/NiFe2O4 composite: Promising adsorbent for the removal of Congo red dye from aqueous solution. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2014, 148, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tang, A.; Zhong, L.; Wen, X.; Yan, P.; Wang, J. Amino-modified γ-Fe2O3/sepiolite composite with rod-like morphology for magnetic separation removal of Congo red dye from aqueous solution. Powder Technol. 2018, 339, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etemadinia, T.; Barikbin, B.; Ali Allahresani, A. Removal of congo red dye from aqueous solutions using znfe2o4/sio2/Tragacanth gum magnetic nanocomposite as a novel adsorbent. Surf. Interfaces 2019, 14, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wo, R.; Li, Q.L.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, G.F.; Lei, K.Y.; Du, P.; Jiang, W. Preparation and characterization of functionalized metal-organic frameworks with core/shell magnetic particles (Fe3O4@SiO2@MOFs) for removal of Congo Red and Methylene Blue from water solution. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 2455–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabihi Sahebi, A.; Koushkbaghi, S.; Pishnamazi, M.; Askari, A.; Khosravi, R.; Irani, M. Synthesis of cellulose acetate/chitosan/SWCNT/Fe3O4/TiO2 composite nanofibers for the removal of Cr(VI), As(V), Methylene blue and Congo red from aqueous solutions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 1296–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Zhou, L.H.; Zhao, S.; Asuha, S. Direct synthesis of 3D flower-like maghemite particles and their properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 817, 152802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryee, A.A.; Dovi, E.; Han, R.; Li, Z.; Qu, L. One novel composite based on functionalized magnetic peanut husk as adsorbent for efficient sequestration of phosphate and Congo red from solution: Characterization, equilibrium, kinetic and mechanism studies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 598, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taher, T.; Putra, R.; Palapa, N.R.; Lesbani, A. Preparation of magnetite-nanoparticle-decorated NiFe layered double hydroxide and its adsorption performance for congo red dye removal. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2021, 777, 138712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavani, Y.; Chitti Babu, N.; Uday Kumar, K. Decolorisation of Congo red synthetic solution using Fe doped ZnO nano particles and optimization using response surface methodology. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.E.F.; Amira, M.F.; Azab, M.M.H.M.; Abdelfattah, A.M. An innovative amino-magnetite@graphene oxide@amino-manganese dioxide as a nitrogen-rich nanocomposite for removal of Congo red dye. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2022, 121, 108744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onizuka, T.; Iwasaki, T. Low-temperature solvent-free synthesis of polycrystalline hematite nanoparticles via mechanochemical activation and their adsorption properties for Congo red. Solid State Sci. 2022, 129, 106917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyan, V.V.; Kumar, N.; Narayanasamy, S. Toxicological assessment and adsorptive removal of lead (Pb) and Congo red (CR) from water by synthesized iron oxide/activated carbon (Fe3O4/AC) nanocomposite. Chemosphere 2022, 294, 133758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zourou, A.; Ntziouni, A.; Adamopoulos, N.; Roman, T.; Zhang, F.; Terrones, M.; Kordatos, K. Graphene oxide-CuFe2O4 nanohybrid material as an adsorbent of Congo red dye. Carbon Trends 2022, 7, 100147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzyk, P.; Phuong, N.T.; Olusegun, S.J.; Hong Nam, N.; Thanh, D.T.M.; Giersig, M.; Krysiński, P.; Osial, M. Titan Yellow and Congo Red Removal with Superparamagnetic Iron-Oxide-Based Nanoparticles Doped with Zinc. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
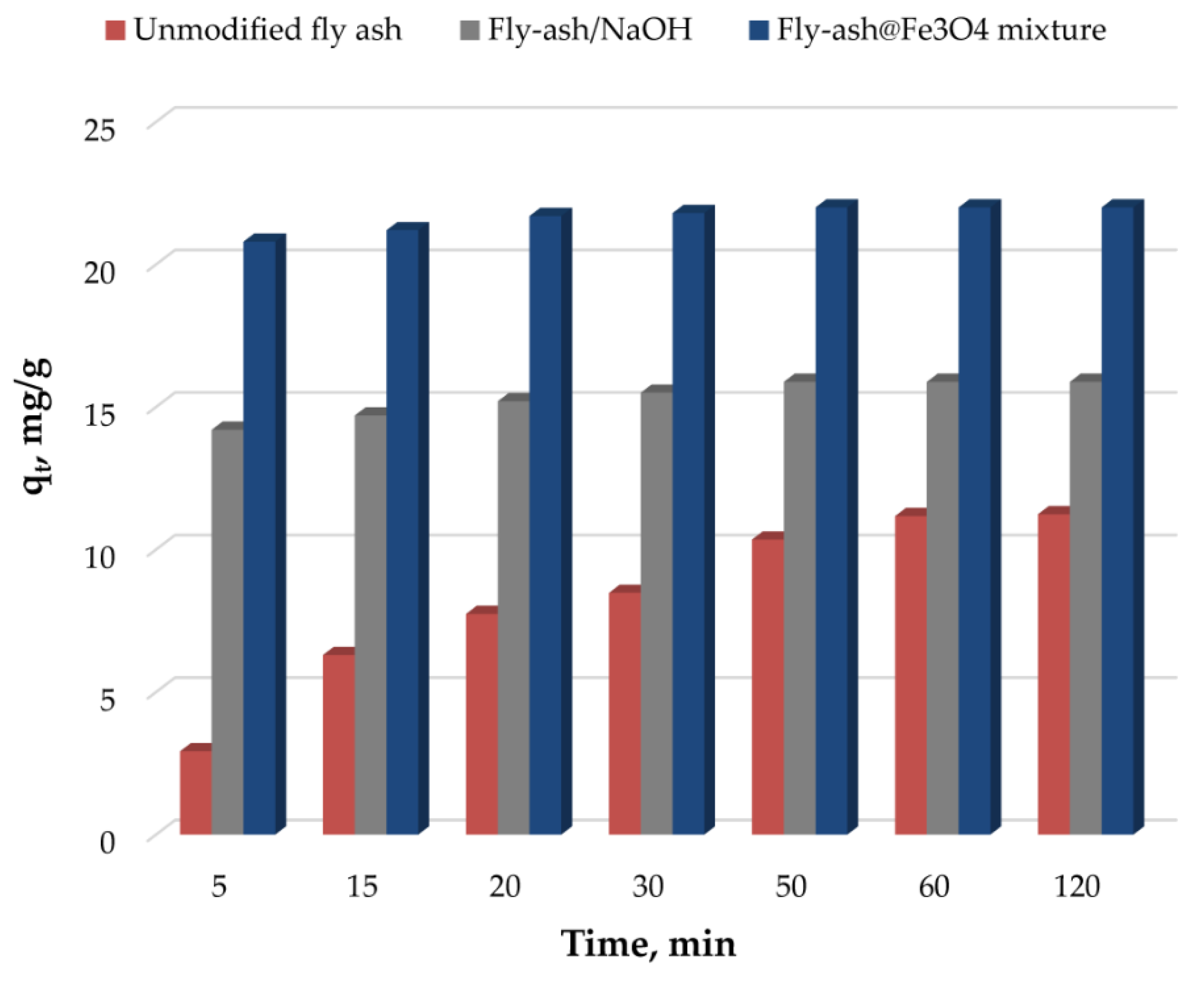


| Adsorbent Dosage, mg | Initial Congo Red Dye Concentration, mg/L | Contact Time, min |
|---|---|---|
| 3.5–20 | 10–100 | 5–120 |
| conc: 30 mg/L, contact time: 24 h | adsorbent dosage: 10 mg, contact time: 24 h | adsorbent dosage: 10 mg, conc: 30 mg/L |
| Langmuir | |
| Freundlich | |
| Pseudo-first-order model | |
| Pseudo-second-order model | |
| Intraparticle diffusion model |
| Linear Models | Non-Linear Models | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | Freundlich | Langmuir | Freundlich |
| = 153.85 | = 4.33 | = 157.21 | = 4.028 |
| = 0.0201 | 1/n = 0.7617 | = 0.0179 | 1/n = 0.774 |
| R2 = 0.5716 | R2 = 0.9816 | R2 = 0.9829 | R2 = 0.9905 |
| Experimental qe, mg/g | Pseudo-First Order Model | Pseudo-Second Order Model | Intraparticle Diffusion Stage I | Intraparticle Diffusion Stage II |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21.9 | = 0.1018 | qe cal = 21.93 | = 0.3691 | = 0.0147 |
| = 0.2079 | = 19.932 | 21.76 | ||
| R2 = 0.9178 | R2 = 1 | R2 = 0.8975 | R2 = 0.4578 |
| Adsorbent | qmax, mg/g | References |
|---|---|---|
| FANiFe50 | 22.73 | [48] |
| γ-Fe2O3-sepolite-NH2 | 126.4 | [49] |
| ZnFe2O4/SiO2/Tragacanth gum magnetic nanocomposite | 128.2 | [50] |
| Fe3O4@SiO2 | 14.76 | [51] |
| Fe3O4@SiO2@Zn−TDPAT | 17.73 | [51] |
| Cellulose acetate/chitosan/SWCNT/Fe3O4/TiO2 composite nanofibers | 74.2 | [52] |
| 3D flower-like maghemite particles | 102.7 | [53] |
| Magnetic peanut husk | 56.3–79 | [54] |
| Magnetite-nanoparticle-decorated NiFe layered double hydroxide | 79.6 | [55] |
| Fe doped ZnO nano particles | 93.75 | [56] |
| NH2-Fe3O4-GO-MnO2-NH2 | 54.95 | [57] |
| Polycrystalline α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles | 58.2 | [58] |
| Iron oxide/activated carbon (Fe3O4/AC) nanocomposite | 122.22 | [59] |
| Graphene oxide-CuFe2O4 nanohybrid | 114.21 | [60] |
| Fe3O4@10%Zn | 59 | [61] |
| Fly-ash@Fe3O4 | 153 | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Harja, M.; Lupu, N.; Chiriac, H.; Herea, D.-D.; Buema, G. Studies on the Removal of Congo Red Dye by an Adsorbent Based on Fly-Ash@Fe3O4 Mixture. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8100125
Harja M, Lupu N, Chiriac H, Herea D-D, Buema G. Studies on the Removal of Congo Red Dye by an Adsorbent Based on Fly-Ash@Fe3O4 Mixture. Magnetochemistry. 2022; 8(10):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8100125
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarja, Maria, Nicoleta Lupu, Horia Chiriac, Dumitru-Daniel Herea, and Gabriela Buema. 2022. "Studies on the Removal of Congo Red Dye by an Adsorbent Based on Fly-Ash@Fe3O4 Mixture" Magnetochemistry 8, no. 10: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8100125
APA StyleHarja, M., Lupu, N., Chiriac, H., Herea, D.-D., & Buema, G. (2022). Studies on the Removal of Congo Red Dye by an Adsorbent Based on Fly-Ash@Fe3O4 Mixture. Magnetochemistry, 8(10), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8100125









