Abstract
Magnetic soft materials (MSMs) and magnetic shape memory polymers (MSMPs) have been some of the most intensely investigated newly developed material types in the last decade, thanks to the great and versatile potential of their innovative characteristic behaviors such as remote and nearly heatless shape transformation in the case of MSMs. With regard to a number of properties such as shape recovery ratio, manufacturability, cost or programming potential, MSMs and MSMPs may exceed conventional shape memory materials such as shape memory alloys or shape memory polymers. Nevertheless, MSMs and MSMPs have not yet fully touched their scientific-industrial potential, basically due to the lack of detailed knowledge on various aspects of their constitutive response. Therefore, MSMs and MSMPs have been developed slowly but their importance will undoubtedly increase in the near future. This review emphasizes the development of MSMs and MSMPs with a specific focus on the role of the magnetic particles which affect the shape memory recovery and programming behavior of these materials. In addition, the synthesis and application of these materials are addressed.
1. Introduction
Magnetic shape memory polymers (MSMPs) belong to the group of shape memory materials, a group that can change their shape back to their “remembered” shape when they are exposed to a stimulus [1]. Most commonly, this stimulus is a temperature change [2,3]. However, there are also shape memory materials that are activated by, for example, light [4,5], pH [6,7,8,9], or electricity [10,11,12]. There is an interest in magnetically activated shape memory materials in the biomedical domain because they require no heat and can be remotely controlled, which makes them safer and less drastic to bring inside a body [13]. Internal heating is also favorable for other applications, such as to speed up the curing process of thermoset adhesives by the use of induction-heated magnetic particles by an AC field [14].
Even though there are multiple shape memory materials that are activated by magnetic fields (e.g., gels, fluids, etc., [1]), this review will focus on MSMPs as well as MSMs. These two materials both exist out of a polymer or elastomer with incorporated magnetic particles that will activate the shape memory effect of the material when being placed in an external magnetic field. The difference between the two, however, is how the magnetic particles activate the shape change of the material.
MSMPs are essentially shape memory polymers whose shape memory effect is stimulated by heat. In the case of the MSMPs, magnetic particles are incorporated in the shape memory polymer. When the material is placed in an external alternating magnetic field, the magnetic particles heat up due to induction heating. The heated particles heat the shape memory polymer from the inside and when the activation temperature is reached, the shape memory effect is activated [15,16,17].
MSMs exist out of an elastomer with incorporated magnetic particles. The magnetic fields of these magnetic particles are set in specific magnetization patterns inside the elastomer during the fabrication process. When the magnetic soft material is placed inside an external static magnetic field, the magnetic fields of the magnetic particles align with the external magnetic field. This creates micro torques in the elastomer and pulls the elastomer matrix in a programmed shape [15,16].
MSMPs and MSMs in literature have many different names. This is especially the case for MSMs. Here we chose the names of MSMPs and MSMs through the study by Ma, Wu, Ze, Kuang, Zhang, Qi and Zhao [16], because this study worked with both of these materials. MSMs are not the same as soft magnetic materials. In MSM, the word ‘soft’ refers to the material body in which the magnetic particles are incorporated, like elastomers and silicones. In the term soft magnetic material, the word ‘soft’ refers to the magnet and its magnetic properties (it implies that the materials have a very coercive field, i.e., it has a very narrow hysteresis loop).
This review focuses on MSMPs and MSMs and the research done on their composition, manufacturing techniques, design considerations, computer models to predict and design shape transformations, and finally their applications.
2. MSMP Filled with Magnetic Fillers
In this section, different MSMPs will be addressed. Their shape change is caused by induction heating of the incorporated magnetic particles by AC magnetic fields. The section itself will focus on research on the performance of the material and the influence of the magnetic particles. The section is further divided into subsections addressing different types of magnetic particles.
2.1. MSMPs Filled with Fe3O4
Schmidt [17] tried to make remotely controllable shape memory polymers. She made a shape memory polymer with incorporated magnetic particles (Fe3O4). These magnetic particles are used to heat the shape memory polymer by induction heating the particles by an AC field. The Massart and Cabuil method was employed for the experimental part [18]. Magnetite nanoparticles between 2 and 12 wt% were used for magnetic heating. She succeeded in remotely activating the shape memory effect with the magnetic particles (see Figure 1), while also maintaining basic thermal and mechanical properties of the polymer matrix.

Figure 1.
Deformed magnetic shape memory polymer, induction heated magnetic shape memory polymer in the process of recovering its memorized shape, recovered memorized shape [17].
Mohr, et al. [19] also performed research to remotely activate the shape memory effect of a shape memory polymer. Shape changing from a temporary shape (corkscrew like spiral) to a permanent shape (plane stripe) happened within 22 s (see Figure 2). In this study, they made two types of MSMPs. One had a base of polyetheruerthane (TFX) and the other a biodegradable multi block copolymer (PDC). For the magnetic micro particles, Fe3O4 was used. They found that the 88 °C maximum temperatures reached by induction heating were dependent on the added magnetic particles and the shape made with the MSMP. All experiments were done with a constant cooling and heating rate of 10 K/min. Moreover, the shape recovery capabilities of induction-heated MSMPs with an AC magnetic field seemed very similar to that for conventional shape memory polymers activated by an environmental heat change, which makes them a promising candidate for smart implants and controlled medical instruments.
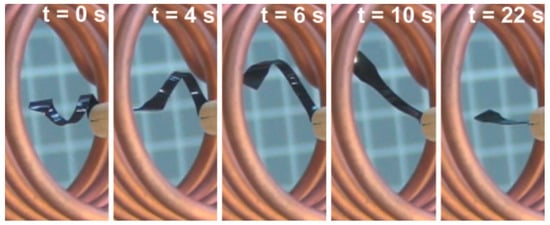
Figure 2.
Shape memory effect through induction heating [19].
Instead of using randomly distributed magnetic micron particles, Leng, et al. [20] fabricated a MSMP with the magnetic powder laying in chains by applying a 0.03 T field by an AC magnetic field. They confirmed the formation of clear chain structure in chained samples. These chains increase the electrical conductivity in the shape memory polymer. Due to this, a lower electric voltage is needed to heat the MSMP and activate the shape change. Furthermore, they reported that alignment of magnetic particle chains significantly improves the mechanical properties of the SMP.
In addition, Yakacki, et al. [21] did further research on the influence of the percentage of magnetic particles (Fe3O4) incorporated in the polymer matrix. There is a direct influence of the percentage of the added particles on the induction heating rate of the material by an AC magnetic field. The polymer did not influence the heating of the particles. Higher percentages of the magnetic powder also lowered the glass temperature of the material. Materials with a lower percentage of magnetic particles had more crosslinks and therefore had higher glass temperature. Finally, when a large percentage of magnetic particles was added to the polymer matrix, the material had some strains that could not be repaired and the material was more brittle.
Razzaq et al. [22] also investigated the thermal and electrical performance of a MSMP with various wt% of Fe3O4 particles. They found that the thermal conductivity of the polymer matrix increased with the increase of magnetic particle fraction. The thermal conductivity improved from 0.19 to 0.60 W/mK with the increase of magnetite volume fraction but the polymer specific electrical resistivity showed a reversed trend. The changes of resistivity could be due to a conversion of the morphology of the polymer matrix which leads to a faster separation of magnetic particles.
Yu, et al. [23] developed a MSMP made from poly(ε-caprolactone) (c-PCL) with incorporated Fe3O4 nanoparticles (5–25 wt%). One part of their study consisted of researching the results of crosslinking the polymer. These crosslinks increased the shape recovery of the polymer up to 70%. The MSMP was also activated by both hot water and by an alternating magnetic field. Figure 3 gives an intuitive contrast of the shape-recovery process in both an AC magnetic field and hot water. They observed that both magnetic nanoparticles and hot water stimulated the shape recovery of the helicoidal specimens. However, shape recovery time was significantly different. Thus, this revealed that the reactivity of c-PCL/Fe3O4 was better in hot water compared to an AC magnetic field. They believed that the faster recovery time was due to higher thermal transfer and lower heat loss in hot water.
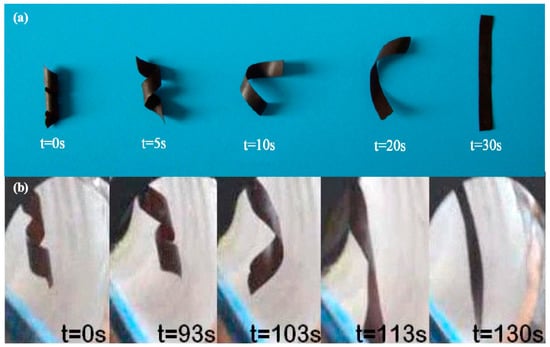
Figure 3.
(above, (a)) The shape memory effect activated in a heated environment (hot water), (below (b)) the shape memory effect remotely activated by an alternating magnetic fields [23].
Weigel, et al. [24] studied the effect of different parameters on the shape memory effect of MSMPs initiated by induction heating through an AC magnetic field. Parameters that were studied were the properties of the magnetic particles, what they were made of, how they were distributed in the polymer matrix, the heat transport conditions, and the surface to volume ratio. The investigated materials were polyetherurethane and a biodegradable multiblock copolymer (PDC) with integrated Fe3O4 particles. They found that with the addition of 10 wt% of magnetic particles in the polymer, the shape memory improved and the mechanical properties of the polymer were not changed.
Instead of making a one-way shape recovery MSMP, Kumar, et al. [25] made a MSMP that was triple-shape and could memorize two shapes; the shape memory effect was activated by an AC magnetic field. The magnetic triple-shape polymer was made of poly(3-caprolactone) (PCL) and poly(cyclohexyl methacrylate) (PCHMA) with incorporated Fe3O4 particles. The best triple-shape memory effect was achieved by a composite with 40 wt% PCL.
Yang, et al. [26] made a MSMP out of a polynorbornene copolymer and magnetite (Fe3O4) with a size of 55 nm. The shape memory effect was activated at a temperature of 51 °C, by the induction heating of magnetite by an AC magnetic field. Through the addition of the magnetic particles, the shape recovery of the material declined. The recovery time for the polymer was 186 s. The added magnetic particles also increased the thermal conductivity of the polymer.
Cai, et al. [27] also made a MSMP out of poly(ε-caprolactone)-polyurethane with incorporated Fe3O4. The nanocomposites were made by in situ polymerization at a molar ratio of PCL:MDI:BDO (1:4:3) with various content of Fe3O4 nanoparticles. The magnetic particles were homogeneously distributed in the polymer matrix. The shape memory effect was tested both by the activation of hot water and by the induction heating of the magnetic particles by an AC magnetic field (see Figure 4). It was found that the shape recovery started around 40 °C. The best shape recovery was of 97%. Their experiments confirmed that the shape change was faster in hot water compared to the ones heated by magnetic fields. In addition, they reported that shape recovery rate decreased with the more magnetic particles whereas shape recovery time increased.
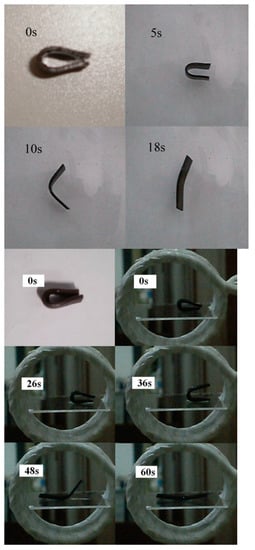
Figure 4.
(left) The shape recovery process in hot water, (right) the shape recovery process in an alternating magnetic field [27].
The development of models to further predict how the magnetic particles influence the shape change of the MSMPs was further studied by Yu, et al. [28]. They used a finite element model that was previously developed to model shape memory polymers. Parameters that they studied were particle size, particle volume fraction, particle heating temperature, and rate to magnetically induce shape recovery behavior. The overall outcome was that an increased volume percentage of the magnetic particles or the smaller the size of the particles increased the heating of the material which stimulated the shape memory effect. They also found that there was a limit to the added volume fraction of particles. When adding particles above this volume percentage, there was no increase in the heating rate of the material.
Liu, et al. [29] developed a dual-response shape memory polymer, which is the same as a MSMP. In this research, the carboxylic styrene butadiene rubber (XSBR)/ferriferrous oxide (Fe3O4)/zinc dimethacrylate (ZDMA) was synthesized and tested. The authors investigated how the shape memory effect of the polymer behaved through the two different types of actuation, a heated environment or by induction heating through an AC magnetic field of the magnetic particles (Fe3O4) (see Figure 5). The shape recovery ratio of both shape memory activation methods was 100% but with different response times. It is noticeable that the shape recovery rate under magnetic fields was lower at the initial stage and higher in the last phase. This might be due to the fact that heating by an AC magnetic field is a slow process in the early stage and fast in the end phase.

Figure 5.
(Left) shape memory activated by a heated environment, (right) shape memory activated by an AC magnetic field [29].
Zhang, Wang, Zheng, Liu and Leng [13] made a MSMP out of PLA with incorporated Fe3O4 particles, that is activated by an AC magnetic field. For this material, the shape memory behaviors were studied through a lens for biomedical applications. It was found that the developed bone support structure (see Figure 6) could very quickly return to its remembered shape, in a few seconds, and the surface temperature of the induction heated material was uniform and around 40 °C, which makes the material safe to use inside the human body. They reported that the shape recovery rate was about 96%. The bones could recover their initial shape within 100 s under a magnetic field. However, they confirmed that the shape recovery time in a hot water was much faster (about 10 s).
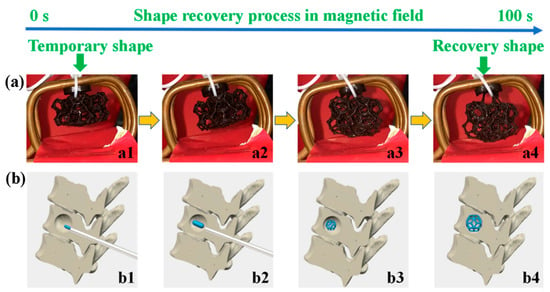
Figure 6.
The shape recovery of a printed structure (above (a1–a4)), the simulation of the shape recovery of a bone support structure in a bone (below, (b1–b4)) [13].
Zhao, et al. [30] also studied bone tissue scaffolds made out of PLA with incorporated Fe3O4 particles that were activated by an AC magnetic field. They mixed 20 wt% Fe3O4 with PLA. One of the noticed advantages of MSMPs is that in the context of biomedical design, these structures can be implemented in the body with minimally invasive surgery. Furthermore, this study found that the mechanical structure of the scaffolds was stable and could improve the attachment.
2.2. MSMP Filled with NdFeB
Golbang and Kokabi [31] fabricated a MSMP made out of polyethylene with incorporated NdFeB particles (5, 15, 40 wt%) and 2 wt% organoclay (cloisite 15A) that was activated by an AC magnetic field. The effect of different weight percentages of added NdFeB particles was studied. It was found that the highest generated heat by inductive heating was reliant on the magnetic particles. The sample that had a full shape recovery had 15 wt% of NdFeB particles.
2.3. MSMP Filled with Carbonyl Iron
In the study by Hassan, et al. [32], a MSMP was made with the use of high projection stereolithography with embedded iron carbonyl particles (CIPs). They used three-dimensional printing technology for the fabrication of novel functionally graded MSMPs. They mixed benzyl methacrylate as the monomer with a cross linker, and used poly(ethylene glycol) dimethacrylate (PEGDMA) and phenyl-bis(2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl)phosphine oxide as the crosslinker and photoiniator, respectively. Through the addition of the magnetic particles, they measured an increased thermal conductivity. Other tests they performed were thermo-mechanical and microstructural surface characterization. The outcome of these tests showed that MSMPs are good for remote controllability, an improvement in the thermal conductivity after embedding the CIPs and close interaction between the particles and the matrix. TGA and DMA results confirmed that the MSMPs have acceptable thermal stability and high mechanical strength.
2.4. MSMP Filled with Nickel Zinc Ferrite
With an increasing interest in making medical devices with shape memory polymers, Buckley, et al. [33] made a shape memory polymer with incorporated nickel zinc ferrite ferromagnetic particles that could be activated though induction heating by an alternating magnetic field. This interest in shape memory polymers for medical devices is because of the remote activation. The challenge for this type of device is to activate the shape memory effect safely and effectively in the body. They developed two in-house prototype devices to elaborate the impact of the added magnetic particles on SMP recovery. Their experiments highlighted that addition of 10 vol% of the magnetic particles made the material heat up uniformly and fast. This volume percentage did not compromise the shape recovery of the shape memory polymer.
In addition, Zhang, et al. [34] fabricated a MSMP with embedded nickel powder. The maximum volume percent of 20% was added to the base polymer. They observed that the homogeneous dispersion of powders had a noticeable effect on the thermal and mechanical abilities of the composite. The more nickel powder was added, the more the tensile strength of the polymer decreased. Two types of materials were made. One only had the added nickel particles. The other had the added nickel particles but it was treated before by a silane coupling agent. The samples with the silane coupling agent showed a better distribution of the particles throughout the material.
2.5. MSMP Filled with Ni-Mn-Ga
Aaltio, et al. [35] also made shape memory polymers with incorporated magnetic particles (Ni-Mn-Ga powder) laying in chains, like Leng, Lan, Liu, Du, Huang, Liu, Phee and Yuan [20]. They studied the damping capabilities of the material. Their developed material was tested on mechanical, structural, and magnetic properties and showed high passive damping for low frequencies. They also compared the damping of their developed material with the same polymeric matrix without magnetic particles and concluded that there was a significant difference between the two materials. They found an increment in the average grain size of the powder particles by the heat treatment. Their experiments confirmed that the magnetization improved more significantly parallel to the chained MSM particles rather than perpendicular to the chains.
2.6. MSMP Filled with Magnetite
Razzaq, et al. [36] studied the mechanical properties of shape memory polymers (polyurethane with 10–40 vol% magnetite). They mentioned the possibility of using AC induction heating. It was found that, with the inclusion of the magnetic particles, the shape memory polymer became more thermally stable but the glass temperature of the material decreased when more magnetite was added. Their report also concluded that the storage modulus of the material became higher when the amount of magnetite increased.
In a study by Puig, et al. [37], a MSMP was made out of magnetite particles that were coated with oleic acid and were embedded in an epoxy system inspired by diglycidylether of bisphenol A modified with oleic acid. The magnetic particles had a homogeneous distribution throughout the material. During the shape activation by an alternating magnetic field of the material, the surface became 25 °C warmer than when the material was not activated. This temperature was enough to activate the shape memory effect. They found the two-step reaction method to be essential to make a well dispersion of magnetics particles in the reactive solvent.
2.7. MSMP Filled with Iron
How the thermal and thermo-mechanical properties of the shape memory polymer were influenced by the addition of magnetic particles was also investigated by Cuevas, et al. [38]. They measured the shape recovery at 90%. Unlike other research, they found that the largest-sized sponged microparticles had a high capacity for the induction heating by an AC magnetic field of the material. Other outcomes of this research were that the stiffness of the shape memory polymer increased when adding more particles and that the material then also became more brittle.
2.8. MSMP Filled with Magnetite or Iron Oxide
Magnetite and iron oxide embedded in silica were compared as magnetic particles in a shape memory foam (Thermoset epoxy DP5.1) [39]. The shape memory effect was activated by the induction heating of the iron oxide by an AC magnetic field. Of these two particles, the iron oxide showed a better performance. It was found that adding a 10 wt% of magnetic particles to the foam did not influence the viscoelastic and thermo-mechanical properties of the material. In the performed experiments, the shapes were recovered within 10 to 20 s. Their results also confirmed that heat transfer between the filler nanoparticles and the bulk foam had a major role in increasing heating performance.
3. MSM
This section will focus on MSMs whose shape change is activated by the alignment of the incorporated magnetic particles in a soft substrate with an external magnetic field. This section will go into the composition of the material and the research carried out on it. In the history of these materials, silicones with embedded whole hard magnets are also taken into account because their working principle is the same as that of MSMs.
A predecessor of the magnetic soft material is presented in a study by Lagcore, et al. [40]. In that study, commercial epoxy resin bars were fabricated with embedded disc formed magnets (4 mm diameter and 90 µm thickness) (strontium ferrite powder). An 80% volume fraction of the hard ceramic ferrite powder was embedded in a commercial epoxy resin. The external magnetic field that was used to change the shape came from a planar coil. A finite element analysis and an analytical model were carried out, which showed good match results compared to the experimental tests.
Another example in which whole permanent magnets were added to a soft component can be seen in the study by Khoo and Liu [41], in which a micropump was developed from an elastomer with an incorporated magnet. By applying a magnetic field, the magnet moves and takes the elastomer with it creating a volume difference on either side of the elastomer. More than 80 mm displacement in the presence of the magnetics particles was reported. During the experiments, the external magnetic field was induced by a permanent disk-shaped NdFeB magnet that was moved near and away from the micro pump to vary the activation flux density.
Another example of hard magnets attached to each other with their magnetic fields pointed towards different directions can be seen in a study performed by [42]. They made different magnetic blocks, of which the magnetic axes (or directions) were orientated in different ways, by curing the materials under a static magnetic field of a permanent magnet. The external magnetic field in the experiment was homogeneous. By moving the permanent magnet, the external field changed its direction. Here, they have not yet made the transition to soft materials or attaching the two squares together by their sides instead of the wired connection.
Erb, et al. [43] also developed a type of magnetic self-shaped soft materials. In the study, they made a material that had a magnetization pattern existing out of two regions. They used a static permanent magnet during the curing process. They proposed a robust and universal technique to replicate this unusual shape-changing mechanism of original objects in an artificial bioinspired composite. They made it by first placing the uncured material in one mold and curing it under a permanent magnetic field. After that, more resin was added and cured under a permanent magnetic field in a different direction. Then, with prepared materials, they made bio-inspired structures. Hydrogel substrate containing aluminum oxide layers coated in Fe3O4 particles was added to a Teflon mold above which a permanent magnet was swiveled. The mold was cured with the magnetic field. To make a multi-layer structure, a second hydrogel substrate was merged to the mold and another orientation of magnetic field was imposed. The second layer of the solution was cured at a different orientation, after which the bilayer was extracted from the mold, Figure 7.
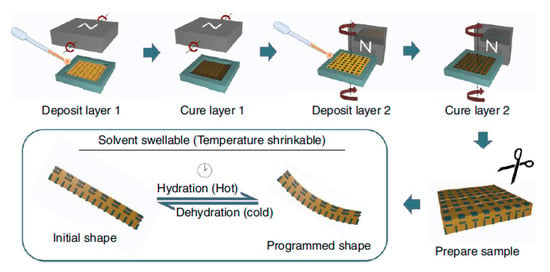
Figure 7.
The production process of the magnetic soft material [43].
Lum, et al. [44] were one of the first to develop a computer model to predict the shape memory behavior of MSMs. However, the model is not able to calculate all the shapes of the material over time and is restricted to only being able to define the shape with a 1D Fourier series. In addition, a fabrication process for the magnetic soft material was also presented, as shown in Figure 8. First, a beam of an elastomer (Ecoflex 10-00) with aluminum (non-magnetic; it had the same size as the NdFeB particles so that the elastomer had the same mechanical properties) particles was cast (Figure 8A,B). Depending on the preferred magnitude of shape change, a pater was laser cut out of this strip and filled with Ecofelx 10-00 with incorporated NdFeB (magnetic) particles (Figure 8C,D). After it was cured, the beam of magnetic soft material was folded in a jig (Figure 8E) and magnetized with a strong B field (~1 T) to get the right magnetization profile (Figure 8(Fi,Fii)). The external magnetic field was induced by an electromagnet.
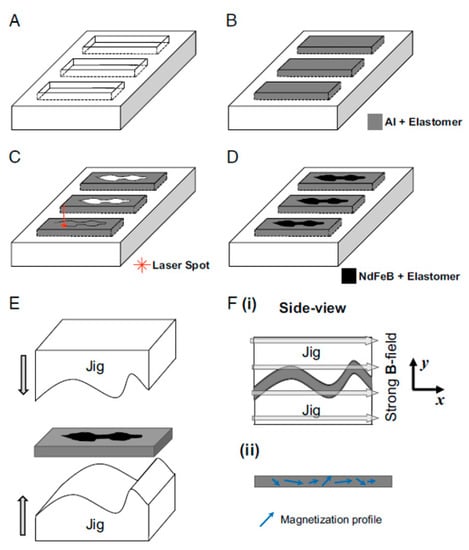
Figure 8.
The manufacturing process of magnetic soft materials in the study by Lum, Ye, Dong, Marvi, Erin, Hu and Sitti [44]. (A) a negative mold; (B) the passive component; (C) laser cutting; (D) NdFeB and Elastomer poured and cured in the mold (E) the beam bent into the jig; (Fi) the beam is magnetized with a strong B field (~1 T); (Fii) the beam is removed from the jig.
Kim et al. [15] reported one of the first 3D printing magnetic responsive materials by incorporating magnetic microparticles (NdFeB) in a soft compound and printing non-uniform magnetization patterns. This was previously done by embedding whole magnets into a soft compound. Their printing method was based on direct ink writing. During the printing procedure, a static magnetic field was applied at the nozzle to reorient the particles along that field (see Figure 9a) generated by either a permanent magnet or an electromagnet. The magnetic shield between the electromagnet and the printed material weakened the magnetic field from the electromagnet, so that the printed magnetic patterns were not disturbed by it. This ink with its created magnetic field directions could then be used to print complex structures, Figure 9b, which enabled structures that were not possible to make before. For the shape change activation, a permanent magnet was used. The magnetic responsive soft material could react fast, untethered, and in a revered way. They found that with the increase of the applied field at the nozzle tip, the magnetic moment density of produced samples through nozzles improved. Furthermore, the effect of nozzles’ diameters on the magnetic moment density was investigated with their custom-made set-up.
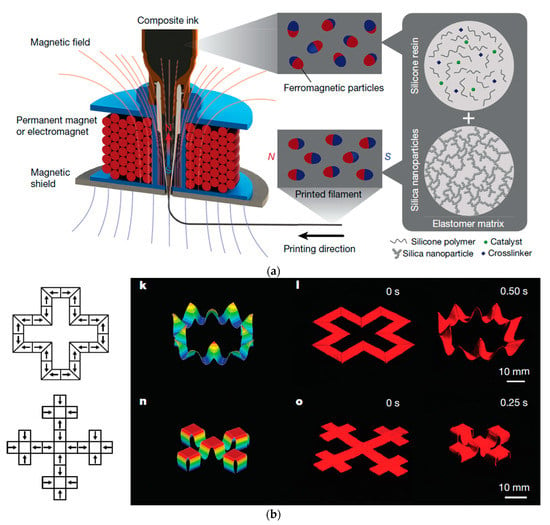
Figure 9.
(a): The manufacturing process of magnetic soft material developed by Kim, Yuk, Zhao, Chester and Zhao [15] by which the magnetic particles oriented with the magnetic field that was applied at the nozzle. (b): Complex structures printed out of magnetic soft material [15].
Instead of using direct ink writing with a 3D printer to create non-uniform magnetization patters, Xu, et al. [45] developed another system based on ultraviolet lithography. Like the 3D printer set up by Kim, Yuk, Zhao, Chester and Zhao [15], this ultraviolet lithography setup is also able to make more complex non-uniform magnetization patterns. The permanent magnet under the plate on which the UV resin with incorporated magnetic particles (NdFeB) lays rotates and changes the orientation of the particles in the uncured resin. When the hall sensors detect that the particles are oriented in the right position, the part of the UV resin that should have this direction for the particles is cured by the exposure to precise target UV light. The design concept for a microgripper magnetically actuated with six-degree-of-freedom can be seen in Figure 10. The six degrees of freedom actuator refers to movement in three dimensions added to grasping, pitch, and yaw motion. The microgripper includes a base segment and multiple arms to encapsulate the cargo. Once the arms are wrinkled, the gripper could be considered as a rigid body and could locomote using the magnetic gradient pulling force or rolling motion (Figure 10A). The shifting steps of a green triangular prism-shaped with the designed microgripper is shown in Figure 10B.
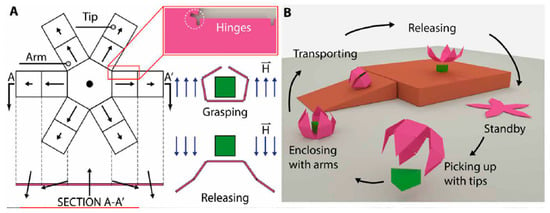
Figure 10.
(A) Geometry and working mechanism of microgripper; (B) the cargo transportation task [45].
Roh, et al. [46] also made structures with MSMs. The 3D printed objects could float on water. In one of the important experiments in this study, structures were printed with varying stiffness. The relation between deformations and material stiffness was reported by Roh et al. This varying stiffness showed different deformations in the activated material through a static magnetic field from an electromagnet. In places where the material was softer, the deformation was bigger and larger, while in the stiffer regions, there was less deformation.
Another study that used varying stiffness in the elastomers was performed by Lantean, et al. [47]. They employed digital light processing to print programmable magnet polymeric materials with acceptable magnetic and mechanical properties. To test their material, a permanent NdFeB magnet was used and moved manually. They varied of the mechanical properties from soft to hard by combination of urethane-acrylate resins and butyl acrylate as a diluent medium. This made it possible to create straight surfaces in the cube. They also changed the magnetization strength of parts of the created objects by changing the weight percentage of the added magnetic particles Fe3O4 between 0% and 6%.
Moreover, soft magnetic objects were fabricated to mimic animal movements by Venkiteswaran et al. [48]. Isotropic powder was used, made from praseodymium-iron-boron (PrFeB) magnets and a silicone rubber polymer (1:1 mass ratio). The fabricated soft magnetic strips were made in different formations to show different types of motions that are possible to create. To create the magnetic soft material strips, a magnetic field of 1T of an electromagnet was used. The motion of the robots was activated by static magnetic fields induced by six electromagnets with a magnetic field strength from 10 to 35 mT. By switching different pairs of coils on and off, a rotating external magnetic field was created. The robots with a length of 4 mm had a speed between 0.15 and 0.37 mm/s. Their interesting outcomes showed that bio-mimetic characteristic patterns were followed by all the specimens. Reliable movement of the specimens, from one end of the workspace to the other, is other exciting achievement [48].
Wu, et al. [49] developed different NdFeB particles types of joints for MSM. These joints are symmetric joints and asymmetric joints. The difference between them is a gap between the same two magnetic poles that lay next to each other. The difference of the gap makes the shape transformations of the material, round or angular. Combinations of these types of joints can enable more different types of shape transformations (see Figure 11). The shape transformations were activated by a homogeneous magnetic field induced by electromagnetic coils. The field strengths and directions were changed to obtain the intended shape change during the study. The S−S−S combination (either a “W” or a “M” configuration) was achieved with folding under the changing magnetic fields with amplitude B of 4 mT (Figure 11a,d,e). For the S−A−S combination (Figure 11b,f,g), an “M” mode with B = 6 mT and an arc mode with B = −23 mT was obtained. These required differences in magnetic fields were due to the higher bending stiffness as compared to the folding stiffness. The same trend can be seen in the A-S-A combination (Figure 11c,h,i).
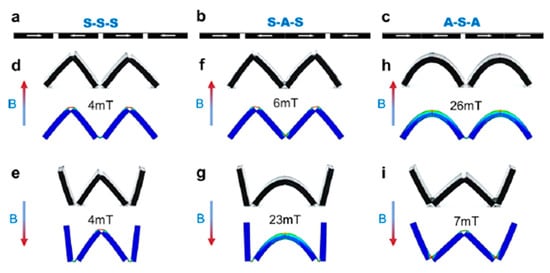
Figure 11.
A combination of symmetric (S) and asymmetric (A) joints [49]. (a) S−S−S (b) S−A−S (c) A−S−A. (d–i) Simulated deformations for the joint types in (a–c) with positive (d,f,h) and negative (e,g,i) magnetic field.
Ma [16] developed a magnetic multi-material printing technique to combine the MSMP and the MSM into one object. The printing was performed with two printing heads under a static magnetic field induced by a permanent magnet for different materials. MSMPs and MSMs could be structurally integrated into the design by adjusting the on-off switching among the syringes and the printing directions. The magnetization of the printed substrate and the direction of the printing ink can be seen in Figure 12a. The created multi-material was able to transform in multiple shapes through the different activation methods of the different materials. They used a one-dimensional MSM/MSMP stripe to investigate the mechanical behavior and four possible deformation modes (Figure 12b,c). They found that only the MSM deformed under actuation magnetic fields at room temperature and the MSMP stayed without deformation due to the higher stiffness (mode 1-U shape). At the elevated temperature (above room temperature), both MSM and MSMP were deformed (Mode 2-W shape). Subsequently, by keeping the magnetic field and cooling the stripe to below room temperature, the MSMP part was locked into the deformed shape whereas the MSM part changed to its original shape once the magnetic field was eliminated (Mode 3 with a peak in the center). In the end, they applied a reversed magnetic field and obtained a wavy configuration (mode 4). The shape memory effect of the MSMP was activated by the induction heating of the incorporated magnetic particles (Fe3O4) by an AC magnetic field. The MSMs, on the other hand, transformed to their programmed shape through the alignment of NdFeB magnetic particles with a specific external magnetic field.
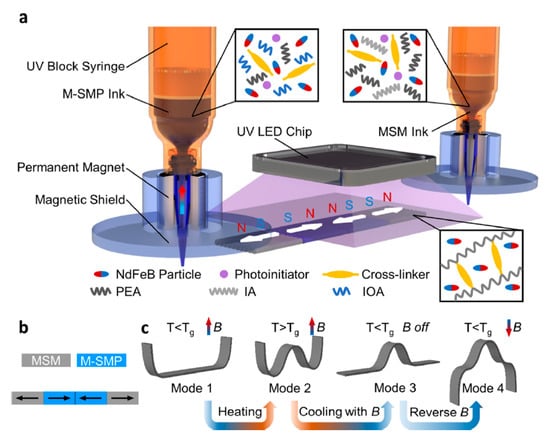
Figure 12.
(a) The multi-material printing setup with two printer heads for the two different materials. The permanent magnet around the nozzle orients the magnetic particles while printing. (b) The pattern printed with the different materials and the directions of the magnetic fields [16].
A magnetic shape memory and stiffening composite elastomer combined material was made by Testa, et al. [50]. The elastomer base incorporated carbonyl iron particles. When the material was placed in a uniform magnetic field from a permanent magnet, the particles aligned with the magnetic field and stiffened the material up to almost 30-fold so that the magnetic shape memory composite elastomer could carry a weight under the influence of a magnetic field but was not capable of doing this without the magnetic field.
Another interesting study on composite MSMs was done by Scheerbaum, et al. [51]. They made a polymer (polyester) with incorporated Ni-Mn-Ga particles. The magnetic particles were aligned by being cured under the influence of a magnetic field from a permanent magnet. They found that the perfect orientation of the MSMs was obtained once the magnetic field was applied during the curing of the substrate. They also found that the compressed MSMs magnetized more easily once the magnetic particle direction was parallel in comparison to the perpendicular direction. One of the applications for this material could be magnetic field-controlled dampers. It was also suggested to make this composite with a softer matrix to make actuators of the material.
A good example of hard magnets that have the same working principles as MSMs can be seen in a study by Alharbi, et al. [52]. The square-shaped magnets had their magnetic poles mirrored to the magnet next to them. This formed a zig-zag shape when a DC magnetic field generated by a neodymium permanent magnet was applied over the magnets. In their experimental study, they embedded NdFeB in a soft silicone base and coated e-thread antennas on it. They achieved a stable magnetic property as well as good programmable polarity. They performed mechanical and thermal testing to confirm their results. Various volume percentages of NdFeB particles (5 to 30 vol%) were examined, the results showing a tiny reduction in flexibility due to increasing magnetic particles volume fraction.
In addition, Qi, et al. [53] presented a method to design biomimetic applications from magnetic responsive soft material. This method was developed to design the preferred programmed shape fast. They used inspiration from nature and started designing from the preferred programmed shape and the direction of the magnetic field. From there on, they determined the direction of the magnetic fields that were incorporated in the silicone. The results showed that the soft materials 3D printed filament had reversible, fast, and acceptable deformation properties. They employed the Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) technique to print the oriented magnetic structural elements and encapsulated mold. To activate the shape change, both a permanent magnet controlled by a linear motor and an electromagnet were used. By the movement of the permanent magnet and the current change in the electromagnet, the magnetic flux density was adjusted to make the material move.
4. MSMP Composite
In this section, some studies are mentioned that show a combination of MSMPs and MSMs by means of their activation principles. These materials are also very interesting but could not be placed in the two previous sections. These combined structures could not be described in the above-mentioned sections due to their specific characterizations.
Ze, et al. [54] presented a material that can have multiple shape manipulations, which can also be locked in place. To do this, they used an amorphous shape memory matrix with two types of incorporated magnetic microparticles (see Figure 13). For the shape change, the matrix was first softened by the inductive heating of Fe3O4 particles by an AC field. When the material was soft, the shape could be manipulated by applying a DC magnetic field generated by an electromagnet on which the NdFeB particles moved to align their magnetic fields. These fields had a nonuniform magnetization pattern through which the shape was activated. The stripe could not deform under an actuation magnetic field (Ba) at room temperature because of stiffness of the ink (Figure 13a). Once a high AC magnetic field (Bh) was added, the induction heating in a magnetic particle made the MSMP composite hot (above room temperature) and dropped the modulus of the MSMP noticeably. Subsequently, a tiny Ba could simply stop the stripe (Figure 13b). When the inductive heating was removed, the polymer cooled down and locked its shape in place (Figure 13c). To allow a different actuation, the magnetization pattern of the MSMP can be reconfigured (Figure 13d). The unique advantages of this material are the shape locking abilities without the constant need for a magnetic field.
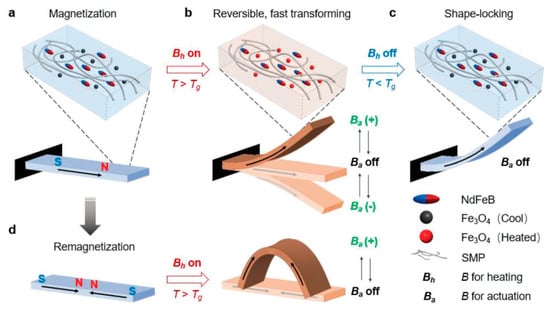
Figure 13.
Magnetic shape memory polymer composite. (a) Before actuation. (b) After induction heating. (c) Shape locking of the MSMP composite [54].
Zhang, et al. [55] developed a combination between shape memory materials and MSMs by incorporating magnetic particles laying in magnetization fields in a liquid crystal elastomer. First, the elastomer had the shape of half a circle which could walk with the help of an alternating magnetic field. When the sample reached the heated liquid (around 70 °C), the shape of the elastomer transformed in a helix and the material could use this shape to swim while also being exposed to a magnetic field. The combination of these two materials could allow for even more complex movements and shape transformations. The magnetic field for the movement was a rotating field made from a Halbach array mounted on a stepper motor.
A performance metric of the magnetic particles and variety of them for both MSMP and MSM application has been summarized in Table 1 and Table 2. The most-used particle for MSMP application is Fe3O4 and for MSM is NdFeB, based on most research reports.

Table 1.
Summarized performance metrics of the magnetic particles.

Table 2.
Variety of Magnetic Particles.
5. Modeling
The available modeling studies of MSMPs and MSMs are very limited. This section will go further into studies that developed computer models to predict the shape memory effect. It is divided into two sub-sections. One focuses on the computer models developed for MSMP, the other is about the computer models developed for MSMs.
5.1. Modeling of MSMPs
Further development of MSMPs was done by creating models to predict real-life behavior [22]. The material was composed of thermoplastic polyurethane with different volume fractions of Fe3O4 particles (0–40 vol% magnetite particles) and fabricated through injection molding. In this research, they compared the measured values of the samples with multiple theoretical models, such as Rayleigh, Lewis–Nielsen, Hashin–Shtrikman, and Agri-Uno correlations for thermal conductivity, to see if there was a correlation. They found good agreement between experimental and theoretical data. However, they did not develop a new computational model and used available theoretical correlation to evaluate their results.
Conti, et al. [58] also reported on modeling and simulating the behavior of MSMP composites. They studied how the magnetic field changed the shape of the composites. Their results were based on macroscopic material properties. In the conclusion, it was pointed out that the orientation of the magnetic particles was more important than the alignment. The shape of the particles was also important and elongated particles had better properties than the round-shaped particles. Finally, a softer polymer gave better results than the incorporated magnetic particles. They developed a numerical method based on the boundary-element method to solve the model for two dimensions and with a linear geometrical matrix.
Moreover, in the study by Yu, Westbrook, Kao, Leng and Qi [28], a model was developed to further predict how the round magnetic particles influence the shape change effect of MSMPs. A finite element model that was previously used to predict the shape change effect of shape memory polymers was altered to accommodate this. They investigated several parameters including particle size, the volume of the magnetic particle fraction, the heating of the particles, and the speed of the shape recovery process. They found that smaller particle sizes or more volume fractions could bring faster shape recovery rate. In addition, they pointed out that there were critical points for each parameter.
5.2. Modeling of MSM
In the study by Crivaro, et al. [59], a finite element analysis model was developed to predict the required magnetic field strength to activate magnetic soft material. The finite element analysis model was also developed to determine if the made mechanism was bistable. They used magneto active elastomer (MAE) patches bonded to a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) substrate that was activated by a DC magnetic field generated by an electromagnet. The magnetic soft material that they used was made out of a 70 vol% Dow Corning HS II RTV silicone rubber compound. The catalyst was added in a 20:1 weight ratio. The other 30% of the volume consisted of the magnetic particles (325 mesh M-type barium hexaferrite). Their experimental outcome validated the proposed model, although they observed some issues with the fabrication procedure to enhance the design of the mechanisms involved in making an accurate prediction field to actuate the device.
In the study by Lum, Ye, Dong, Marvi, Erin, Hu and Sitti [44], a computer model was developed to predict the behavior of MSMs. The formulae they used were based on the deflection of a beam. Restrictions of their model that were pointed out were that the model does not show the shape transformation of the beam of magnetic soft material over time, but only its end state of the shape recovery. The shape transformation was activated by an electromagnet.
In the research by Kim, Yuk, Zhao, Chester and Zhao [15], aside from developing the 3D printer system for MSMs, they also developed a computer model to predict the shape changes of complex structures. The model was based on the torques created in the material by the embedded magnetic particles when the material was placed in an external magnetic field and how those torques created stresses in the elastomer surrounding them. The shape change of the material was activated by the use of a manually moved permanent magnet.
Zhao, et al. [60] continued the studies of Kim, Yuk, Zhao, Chester and Zhao [15]. They developed a constitutive model in a finite-element framework to design and predict the behavior of MSMs. They used permanent magnets and a pair of electromagnets for shape activation. With this model, complex structures can be designed out of MSMs which have almost the same shape transformations as their real-life objects (see Figure 14). They adopted a nonlinear field theory to explain the finite deformation coupled with magnetic fields. They developed an eight-node continuum brick element to explore the induced deformation magnetically in MSMs. They investigated three different scenarios: (i) extreme bending up to 180°, (ii) large bending up to 90°, and (iii) small-deflection beam bending. They remarked that the good effective media for a magnetically shape response material could also be a “non-classical” media such as polar media.
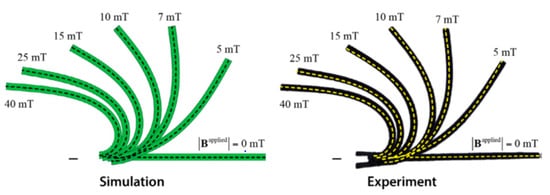
Figure 14.
Validation of the developed finite element analysis model [60].
Chen, et al. [61] also developed a computational model that can be used for the development of transformation and movements of MSMs that were activated by cylindrical permanent NdFeB magnets. This was based on the torque equilibrium and iteration in a computational model. The model was tested by developing physical prototypes that could be compared with the prediction of the shape transformation. A model was developed for static shapes as well as the locomotion of magnetic soft material objects.
The summaries of modeling of MSMPs and MSMs are given in Table 3.

Table 3.
Summarized models of MSMP and MSM.
6. Application
This section emphasizes various applications of MSMPs and MSMs and is divided into two parts. One of the most important advantages of these materials is that they can be remotely activated and have no or almost no surface heat. Differences between the two are that MSMPs are probably stiffer than magnetic soft material, do not change their shape as fast, and transform only one way. MSMs, on the other hand, are less stiff, can transform fast, and are reversible. These differences can also be seen in their applications.
In MSMPs, the active memory material is the polymer, which has a typical response time of tens of seconds [23]. In MSMs, the memory effect is induced by magnetic particles, which have a much faster response time (<1 s). In the research by Kim et al. [15], it could be seen that the shape change was completed within a fraction of a second (0.50 s and 0.25 s).
Additionally, in MSMPs, the magnetic particles need some time to increase the temperature of the shape memory polymer. The time it takes to reach this temperature depends on the type of shape memory polymer [1] and multiple particle parameters such as their size and volume fraction in the material [28]. That is why there is some delay in the activation of the shape memory effect. The research by Mohr et al. [19] (Figure 2) showed that the shape change of the MSMP under an alternating magnetic field took 22 s. In Figure 3, the shape changes took 130 s [23].
6.1. MSMP Applications
Applications for MSMPs are mostly thought of in the biomedical domain. Advantages of the MSMPs over the shape memory polymers in this domain are that the shape change can be remotely activated by an AC field and that the environment does not have to heat up. Zhao, Huang, Liu, Wang, Leng and Liu [30] also mentioned that shape memory polymers could be used for minimally invasive surgeries, because of being able to compress the shape before implementing or using it inside a body. Even though the environment does not have to heat up for the activation of MSMPs, the material itself should. Zhang, Wang, Zheng, Liu and Leng [13] developed a MSMP that had a uniform surface temperature of 40 °C during the activation of the shape change. With this temperature that is close to the body temperature, it would not harm the body in which the material is used. They developed a bone support structure that would be brought into the body in a compressed state. When it was placed at the right location in the body, a magnetic field was applied to heat the particles and make the bone support structure expand. Bone support structures were also developed in the study by Zhao, Huang, Liu, Wang, Leng and Liu [30]. In the study by Buckley, McKinley, Wilson, Small, Bennett, Bearinger, McElfresh and Maitland [33], other biomedical devices were made that were activated by an alternating magnetic field, such as a flower-shaped endovascular thrombectomy device and an expandable MSMP foam device for aneurysm embolization.
6.2. MSM Applications
As described earlier, in the study by Khoo and Liu [41], they developed micropumps out of an elastomer with an incorporated magnet. The advantages of the magnetic soft material that were used are the fast and reversible shape transformation. These are unique characteristics of the magnetic soft material. Another unique thing about this application is that the pumps could be made very small. This is partially due to the reduction of components needed to make a pump. This reduction in product components is also one of the advantages of using MSMs. In the experiment, the pumps were activated by a manually controlled permanent magnet.
Grippers and other star-shaped objects are also a recurring application of MSMs. One of the grippers was made by Xu, Zhang, Salehizadeh, Onaizah and Diller [45] and rotated by a rotating field generated by an electromagnet. Another gripper that was made to catch a ball was developed by Kim, Yuk, Zhao, Chester and Zhao [15] and activated by a manually controlled permanent magnet. In the study by Ze, Kuang, Wu, Wong, Montgomery, Zhang, Kovitz, Yang, Qi and Zhao [54], they used two types of magnetic particles. First, Fe3O4 particles were used to inductively heat and soften up the polymer matrix, and second, the particles (NdFeB) were used to change the shape through the alignment with the particles with the external magnetic field generated by an electromagnet. They found out that without locking the shape (by removing the magnetic field that inductively heats the material), the force of the gripper was not enough to carry the ball. While locking the shape, the same material was able to carry it.
Ren, et al. [62] developed an untethered jellyfish-inspired soft milli swimmer. It was made from a magnetic soft material existing out of Ecoflex 10-00 and NdFeB particles with a size of 5 µm. The swimmer was activated by a magnetic field induced by a custom-made electromagnet coil system that, through a difference in magnitude, frequency, and direction changes, changed the swimming behavior. In this research, it was highlighted how the swimmer can perform different tasks, such as drug delivery and moving through small tubes.
Another gripper-like robot made of magnetic soft material was developed by Goudu, et al. [63]. This gripper was made out of a biodegradable matrix for the use of the gripper in a human body with incorporated iron oxide particles. The robot was also activated by the direction and frequencies of an external magnetic field as was the case by Ren, Wang, Hu and Sitti [62]. The magnetic field was generated by a custom-made electromagnetic coil setup. By enclosing the magnetic soft material structure around an object, rolling it can deliver the object to a specific place.
A frequent application for MSMs is a strip that is able to swim for the biomedical field [64,65,66]. These strips often have sinusoidal magnetic field patterns. The type of magnetic particles in all three studies was NdFeB, except for one which used NdPrFeb [64]. Even though the three studies had similar magnetization patterns, only the study by Hu, Lum, Mastrangeli and Sitti [65] also showed other ways of locomotion (e.g., walking, crawling, jumping). All the robots were activated by frequently changing and rotating magnetic fields generated by different types of DC coil setups. The type of locomotion was determined by the orientation of the external magnetic field and its strength.
The summarized application for MSMPs and MSMs are given in Table 4.

Table 4.
Summarized applications for MSMPs and MSMs.
7. Summary and Conclusions
In the last twenty years, MSMPs and MSMs have been developed to serve the purposes of a number of specific design applications. This review reports on the research of these two materials. Parameters that have been studied are their material composition, shape recovery, and shape recovery simulation, with specific emphasis on manufacturing methods and applications. The magnetic shape memory effect activation makes it able to activate shape change remotely and with (almost) no surface heat. This makes shape memory materials useful for more applications than the heat-activated shape memory polymers by conduction or convection. MSMPs often have only one remembered shape and no reversible shape change activated by the magnetic field. It can also take some time to activate the shape change. However, these drawbacks can be avoided by MSMs which offer fast and reversible shape changes. In comparison to MSMPs, MSMs have not yet been investigated to the same level of detail. As MSMs are of a more complicated nature (both in production and application), they pose a major challenge for the future of these materials. In addition, 3D printing is a promising manufacturing technique for both MSMPs and MSMs, although there is not yet sufficient knowledge available about the optimum printing parameters.
In addition, the effect of the magnetic properties of the magnetic components (Curie temperature, coercivity, remanence) on the shape memory function of these materials is as yet largely unknown and needs to be the subject of future research.
Although several successful applications have already been reported (predominantly in the biomedical field), it can be concluded that magnetic shape memory alloys (both MSMs and MSMPs) are merely at the beginning of their developing stage and still need to find their way to large-scale market applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.J.M.v.V., H.Y. and S.G.; writing—original draft preparation, S.J.M.v.V. and H.Y.; writing—review and editing, S.G.; supervision S.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by an internal funding from Delft University of Technology (TU Delft).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bengisu, M.; Ferrara, M. Materials that Move Smart Materials, Intelligent Design; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lendleind, A.; Kelch, S. Shape-Memory Polymers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 2034–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Singh, C.; Singh, S.; Jha, K.; Prakash, C. 3D printed biodegradable functional temperature-stimuli shape memory polymer for customized scaffoldings. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 108, 103781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lendlein, A.; Jiang, H.; Jünger, O.; Langer, R. Light-induced shape-memory polymers. Nature 2005, 434, 879–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Ikeda, T. Photodeformable Polymers: A New kind of Promising Smart Material for Micro and Nano-Applications. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2005, 206, 1705–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, D.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, S. pH-Responsive Shape Memory Poly(ethylene glycol)−Poly(εcaprolactone)-based Polyurethane/Cellulose Nanocrystals Nanocomposite. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 12988–12999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.-J.; Dong, X.-Q.; Fan, M.-M.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.-H.; Wang, Y.-F.; Yuan, X.-J.; Li, B.-J.; Zhang, S. pH-Induced Shape-Memory Polymers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2012, 33, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gong, T.; Wang, L.; Zhou, S. Highly pH-sensitive polyurethane exhibiting shape memory and drug release. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 5168–5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Chen, H.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, K.; Wang, B.; Hu, P. Thermo- and pH-sensitive shape memory polyurethane containing carboxyl groups. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 1739–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courty, S.; Mine, J.; Tajbakhsh, A.R.; Terentjev, E.M. Nematic elastomers with aligned carbon nanotubes: New electromechanical actuators. Europhys. Lett. 2003, 65, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, J.W.; Kim, J.W.; Jung, Y.C.; Goo, N.S. Electroactive Shape-Memory Polyurethane Composites Incorporating Carbon Nanotubes. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2005, 26, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, W.; Skupin, H.; Tolksdorf, C.; Gebhard, E.; Zentel, R.; Krüger, P.; Lösche, M.; Kremer, F. Giant lateral electrostriction in ferroelectric liquid-crystalline elastomers. Nature 2001, 410, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, L.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J. Magnetic programming of 4D printed shape memory composite structures. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, R.; Chaudhary, V.; Ramanujan, R.V.; Steele, T.W.J. Magnetocuring of temperature failsafe epoxy adhesives. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Yuk, H.; Zhao, R.; Chester, S.A.; Zhao, X. Printing ferromagnetic domains for untethered fast-transforming soft materials. Nature 2018, 558, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Wu, S.; Ze, Q.; Kuang, X.; Zhang, R.; Qi, H.J.; Zhao, R. Magnetic Multimaterial Printing for Multimodal Shape Transformation with Tunable Properties and Shiftable Mechanical Behaviors. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 13, 12639–12648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, A.M. Electromagnetic Activation of Shape Memory Polymer Networks Containing Magnetic Nanoparticles. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2006, 27, 1168–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massart, R.; Cabuil, V. Synthèse en milieu alcalin de magnétite colloïdale: Contrôle du rendement et de la taille des particules. J. De Chim. Phys. 1987, 84, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, R.; Kratz, K.; Weigel, T.; Lucka-Gabor, M.; Moneke, M.; Lendlein, A. Initiation of shape-memory effect by inductive heating of magnetic nanoparticles in thermoplastic polymers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3540–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leng, J.S.; Lan, X.; Liu, Y.J.; Du, S.Y.; Huang, W.M.; Liu, N.; Phee, S.J.; Yuan, Q. Electrical conductivity of thermoresponsive shape-memory polymer with embedded micron sized Ni powder chains. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 014104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yakacki, C.M.; Satakar, N.S.; Call, K.; Likos, R.; Hilt, J.Z. Shape-Memory Polymer Networks with Fe3O4 Nanoparticles for Remote Activation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 112, 3166–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaq, M.Y.; Anhalt, M.; Frormann, L.; Weidenfeller, B. Thermal, electrical and magnetic studies of magnetite filled polyurethane shape memory polymers. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2007, 444, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhou, S.; Zheng, X.; Guo, T.; Xiao, Y.; Song, B. A biodegradable shape-memory nanocomposite with excellent magnetism sensitivity. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 235702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigel, T.; Mohr, R.; Lendlein, A. Investigation of parameters to achieve temperatures required to initiate the shape-memory effect of magnetic nanocomposites by inductive heating. Smart Mater. Struct. 2009, 18, 025011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, U.N.; Kratz, K.; Wagermaier, W.; Behl, M.; Lendlein, A. Non-contact actuation of triple-shape effect in multiphase polymer network nanocomposites in alternating magnetic field. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 3404–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Huang, W.; He, X.; Xie, M. Electromagnetic activation of a shape memory copolymer matrix incorporating ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Polym. Int. 2012, 61, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Jian, J.-S.; Zheng, B.; Xie, M.-R. Synthesis and properties of magnetic sensitive shape memory Fe3O4/poly(ε-caprolactone)-polyurethane nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 12, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Westbrook, K.K.; Kao, P.H.; Leng, J.; Qi, H.J. Design considerations for shape memory polymer composites with magnetic particles. J. Compos. Mater. 2012, 47, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Huang, J.; Yuan, D.; Chen, Y. Design of a High-Strength XSBR/Fe3O4/ZDMA Shape-Memory Composite with Dual Response. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 14527–14534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Huang, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, W.; Leng, J.; Liu, Y. Porous bone tissue scaffold concepts based on shape memory PLA/Fe3O4. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 203, 108563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golbang, A.; Kokabi, M. Magnetic Field Actuation of Shape Memory Nanocomposites. Adv. Mater. Res. 2010, 123–125, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.U.; Jo, S.; Seok, J. Fabrication of a functionally graded and magnetically responsive shape memory polymer using a 3D printing technique and its characterization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 45997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, P.R.; McKinley, G.H.; Wilson, T.S.; Small, W.; Bennett, W.J.; Bearinger, J.P.; McElfresh, M.W.; Maitland, D.J. Inductively Heated Shape Memory Polymer for the Magnetic Actuation of Medical Devices. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 53, 2075–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J. Magnetic field activation of SMP networks containing micro nickel (Ni) powder. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Smart Materials and Nanotechnology in Engineering, Weihai, China, 8–11 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Aaltio, I.; Nilsén, F.; Lehtonen, J.; Ge, Y.; Spoljaric, S.; Seppälä, J.; Hannula, S.-P. Magnetic Shape Memory—Polymer Hybrids. Mater. Sci. Forum 2016, 879, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaq, M.Y.; Anhalt, M.; Frormann, L.; Weidenfeller, B. Mechanical spectroscopy of magnetite filled polyurethane shape memory polymers. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2007, 471, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, J.; Hoppe, C.E.; Fasce, L.A.; Pérez, C.J.; Piñeiro-Rendondo, Y.; Bañobre-López, M.; López-Quintela, M.A.; Rivas, J.; Williams, R.J.J. Superparamagnetic Nanocomposites Based on the Dispersion of Oleic Acid-Stabilized Magnetite Nanoparticles in a Diglycidylether of Bisphenol A-Based Epoxy Matrix: Magnetic Hyperthermia and Shape Memory. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 13421–13428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, J.M.; Alonso, J.; German, L.; Iturrondobeitia, M.; Laza, J.M.; Vilas, J.L.; León, L.M. Magneto-active shape memory composites by incorporating ferromagnetic microparticles in a thermo-responsive polyalkenamer. Smart Mater. Struct. 2009, 18, 075003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vialle, G.; Prima, M.D.; Hocking, E.; Gall, K.; Garmestani, H.; Sanderson, T.; Arzberger, S.C. Remote activation of nanomagnetite reinforced shape memory polymer foam. Smart Mater. Struct. 2009, 18, 115014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagcore, L.K.; Brand, O.; Allen, M.G. Magnetic microactuators based on polymer magnets. J. Microelectromechanical Syst. 1999, 8, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khoo, M.; Liu, C. Micro magnetic silicone elastomer membrane actuator. Sens. Actuators A 2001, 89, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Chung, S.E.; Choi, S.-E.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.; Kwon, S. Programming magnetic anisotropy in polymeric microactuators. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erb, R.M.; Sander, J.S.; Grisch, R.; Studart, A.R. Self-shaping composites with programmable bioinspired microstructures. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lum, G.Z.; Ye, Z.; Dong, X.; Marvi, H.; Erin, O.; Hu, W.; Sitti, M. Shape-programmable magnetic soft matter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E6007–E6015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, T.; Zhang, J.; Salehizadeh, M.; Onaizah, O.; Diller, E. Millimeter-scale flexible robots with programmable three-dimensional magnetization and motions. Sci. Robot. 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, S.; Okello, L.B.; Golbasi, N.; Hankwitz, J.P.; Liu, J.A.-C.; Tracy, J.B.; Velev, O.D. 3D-Printed Silicone Soft Architectures with Programmed Magneto-Capillary Reconfigurations. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lantean, S.; Barrera, C.; Pirri, C.F.; Tiberto, P.; Sangermano, M.; Roppolo, I.; Rizza, G. 3D Printing of Magnetoresponsive Polymeric Materials with Tunable Mechanical and Magnetic Properties by Digital Light Processing. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1900505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkiteswaran, V.K.; Samaniego, L.F.P.; Sikorski, J.; Misra, S. Bio-Inspired Terrestrial Motion of Magnetic Soft Millirobots. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 1753–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.; Ze, Q.; Zhang, R.; Hu, N.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhao, R. Symmetry-Breaking Actuation Mechanism for Soft Robotics and Active Metamaterials. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 41649–44658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Testa, P.; Style, R.W.; Cui, J.; Donnelly, C.; Borisova, E.; Derlet, P.M.; Dufresne, E.R.; Heyderman, L.J. Magnetically Addressable Shape-Memory and Stiffening in a Composite Elastomer. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheerbaum, N.; Hinz, D.; Gutfleisch, O.; Müller, K.-H.; Schultz, L. Textured polymer bonded composites with Ni-Mn-Ga magnetic shape memory particles. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 2707–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, S.; Ze, Q.; Zhao, R.; Kiourti, A. Magnetoactuated Reconfigurable Antennas on Hard-Magnetic Soft Substrates and E-Threads. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2020, 68, 5882–5892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Guo, H.; Fu, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhu, M.; Yu, M. 3D printed shape-programmable magneto-active soft matter for biomimetic applications. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 188, 107973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ze, Q.; Kuang, X.; Wu, S.; Wong, J.; Montgomery, S.M.; Zhang, R.; Kovitz, J.M.; Yang, F.; Qi, H.J.; Zhao, R. Magnetic Shape Memory Polymers with Integrated Multifunctional Shape Manipulation. Adv. Sci. News 2020, 32, 1906657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, Y.; Hu, W.; Soon, R.H.; Davidson, Z.S.; Sitti, M. Liquid Crystal Elastomer-Based Magnetic Composite Films for Reconfigurable Shape-Morphing Soft Miniature Machines. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2006191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yi, S.; Lin, Z.; Wang, C.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, L. 4D Printing of Magnetoactive Soft Materials for On-Demand Magnetic Actuation Transformation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 4174–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagorce, L.K.; Allen, M.G. Magnetic and mechanical properties of micromachined strontium ferrite/polyimide composites. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 1997, 6, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conti, S.; Lenz, M.; Rumpf, M. Modelling and simulation of magnetic-shape memory polymer composites. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2007, 55, 1462–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crivaro, A.; Sheridan, R.; Frecker, M.; Simpson, T.W.; Lockette, P.V. Bistable compliant mechanism using magneto active elastomer actuation. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2015, 27, 2049–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Kim, Y.; Chester, S.A.; Sharma, P.; Zhao, X. Mechanics of hard-magnetic soft materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2019, 124, 244–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Lin, Y.; Zheng, G.; Yang, Y.; Zhag, Y.; Zheng, S.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Ren, L.; Jiang, L. Programmable Transformation and Controllable Locomotion of Magnetoactive Soft Materials with 3D-Patterned Magnetization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 58179–58190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Wang, T.; Hu, W.; Sitti, M. A Magnetically-Actuated Untethered Jellyfish-Inspired Soft Milliswimmer. In Proceedings of the Robotics: Science and Systems, Freiburg im Breisgau, Germany, 22–26 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Goudu, S.R.; Yasa, I.C.; Hu, X.; Ceylan, H.; Hu, W.; Sitti, M. Biodegradable Untethered Magnetic Hydrogel Milli-Grippers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2004975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jain, P.; Diller, E. Independent Control of Two Millimeter-Scale Soft-Bodied Magnetic Robotic Swimmers. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.; Lum, Q.Z.; Mastrangeli, M.; Sitti, M. Small-scale soft-bodied robot with multimodal locomotion. Nature 2018, 554, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diller, E.; Zhuang, J.; Lum, G.Z.; Edwards, M.R.; Sitti, M. Continuously distributed magnetization profile for millimeter-scale elastomeric undulatory swimming. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 174101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).