Artificial Intelligence—Engineering Magnetic Materials: Current Status and a Brief Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. AI—Hard/Soft Magnetic Materials: Why?
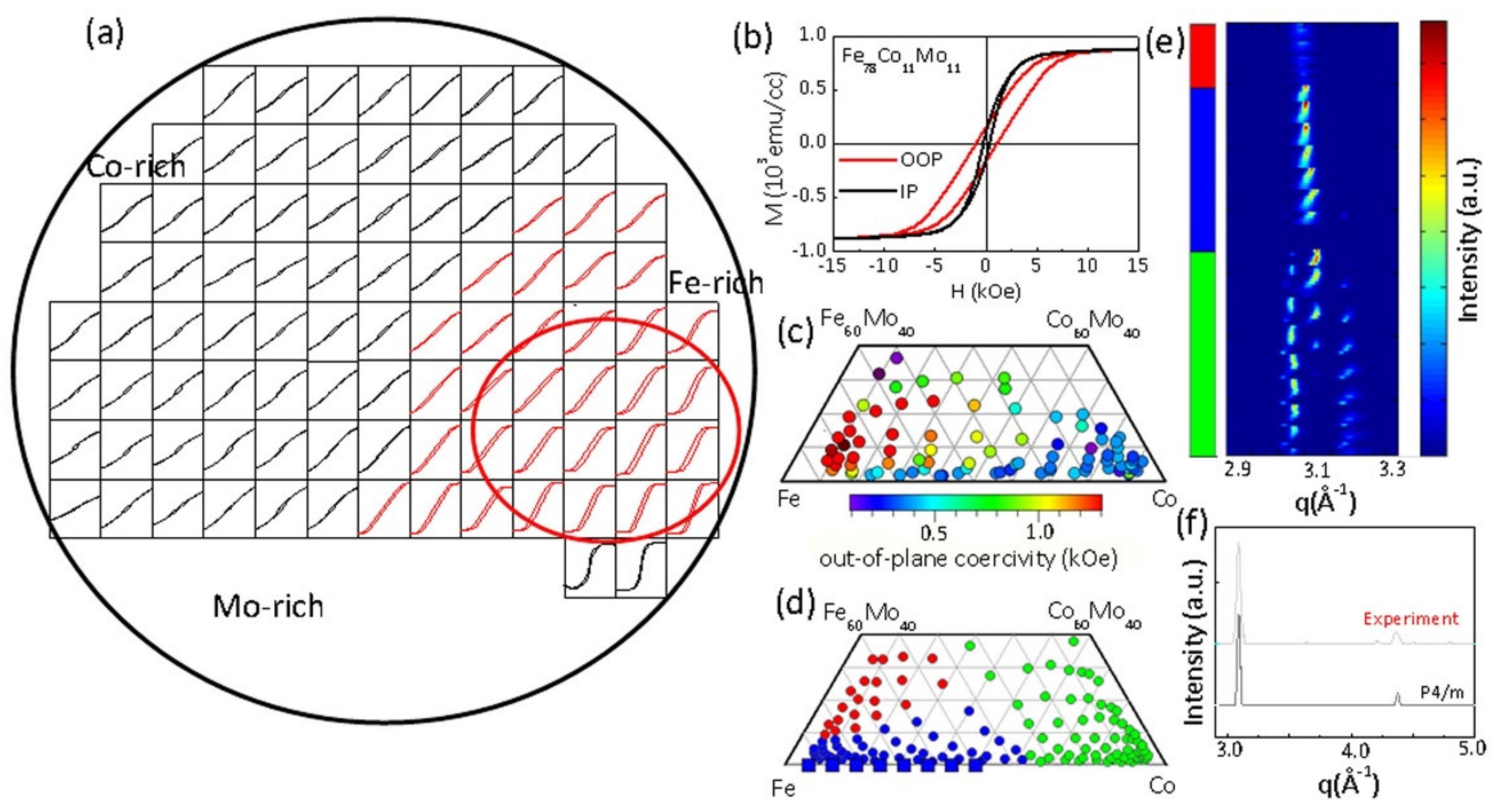
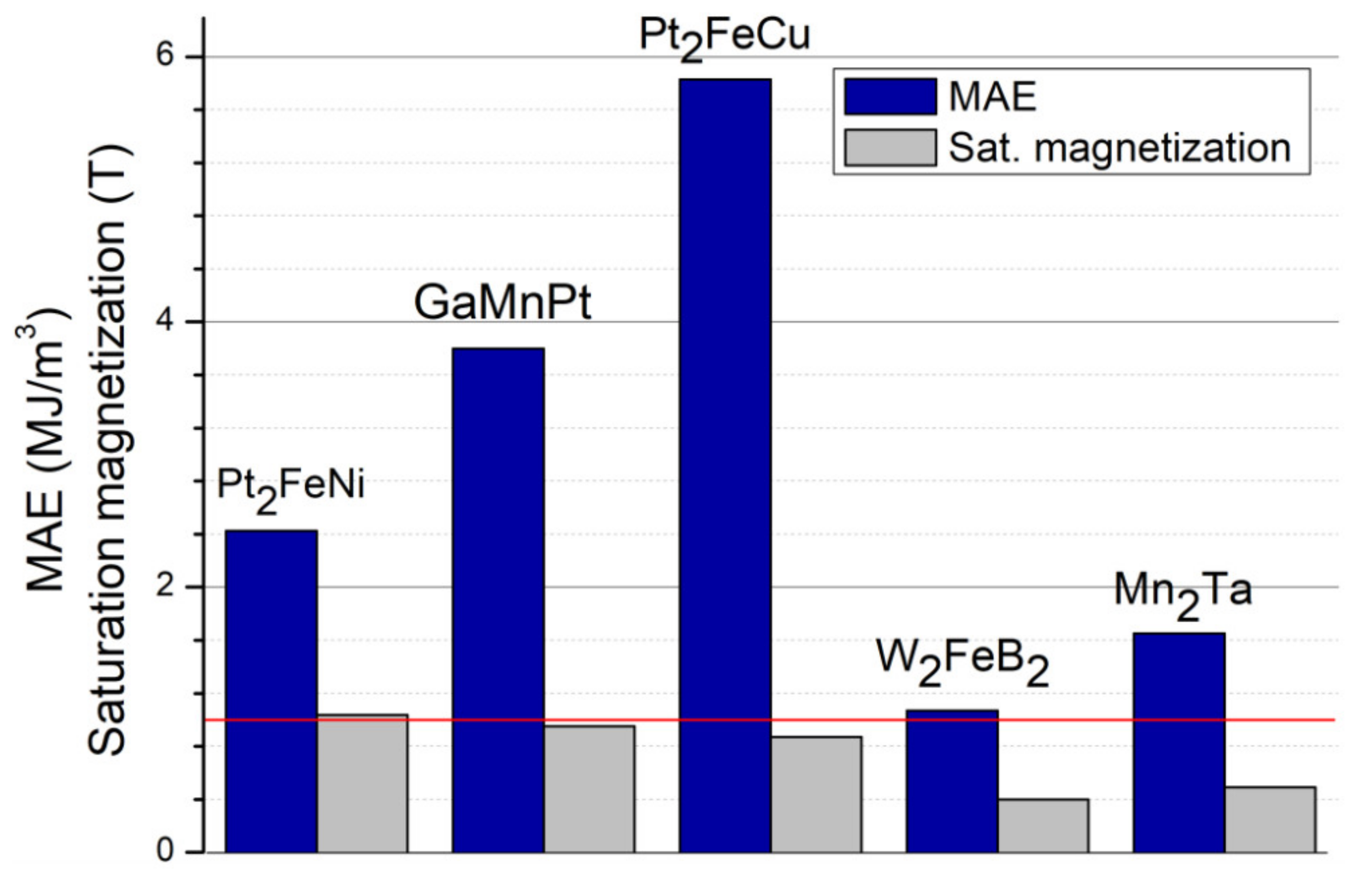
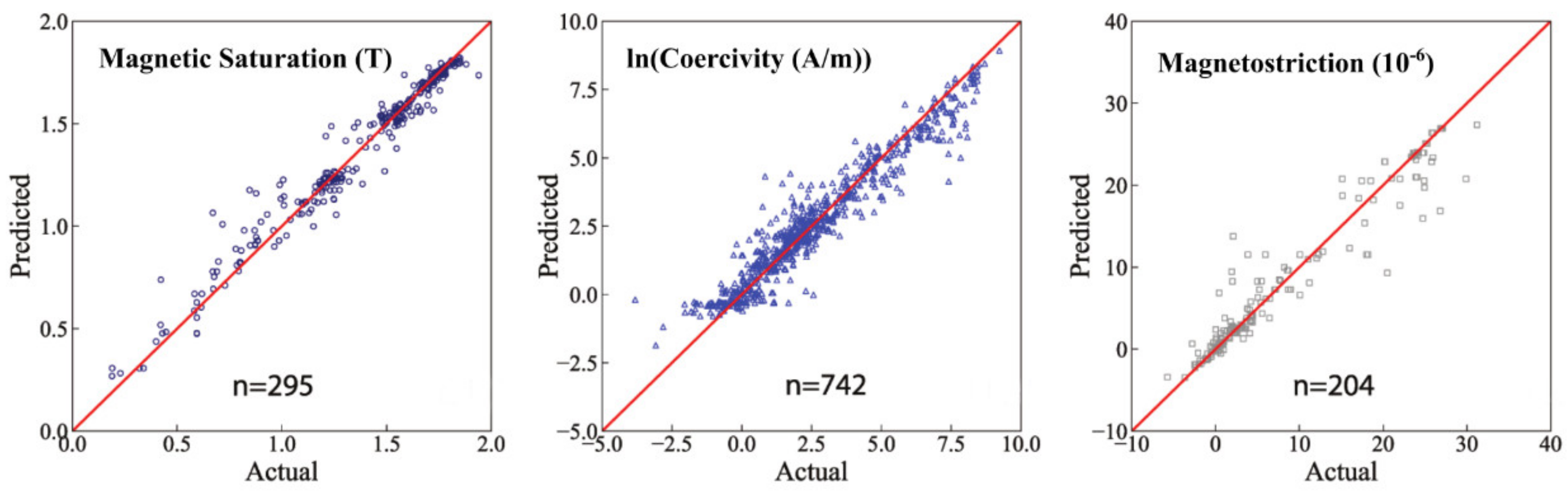
2.1. Discovery of Materials and/or Prediction of Properties
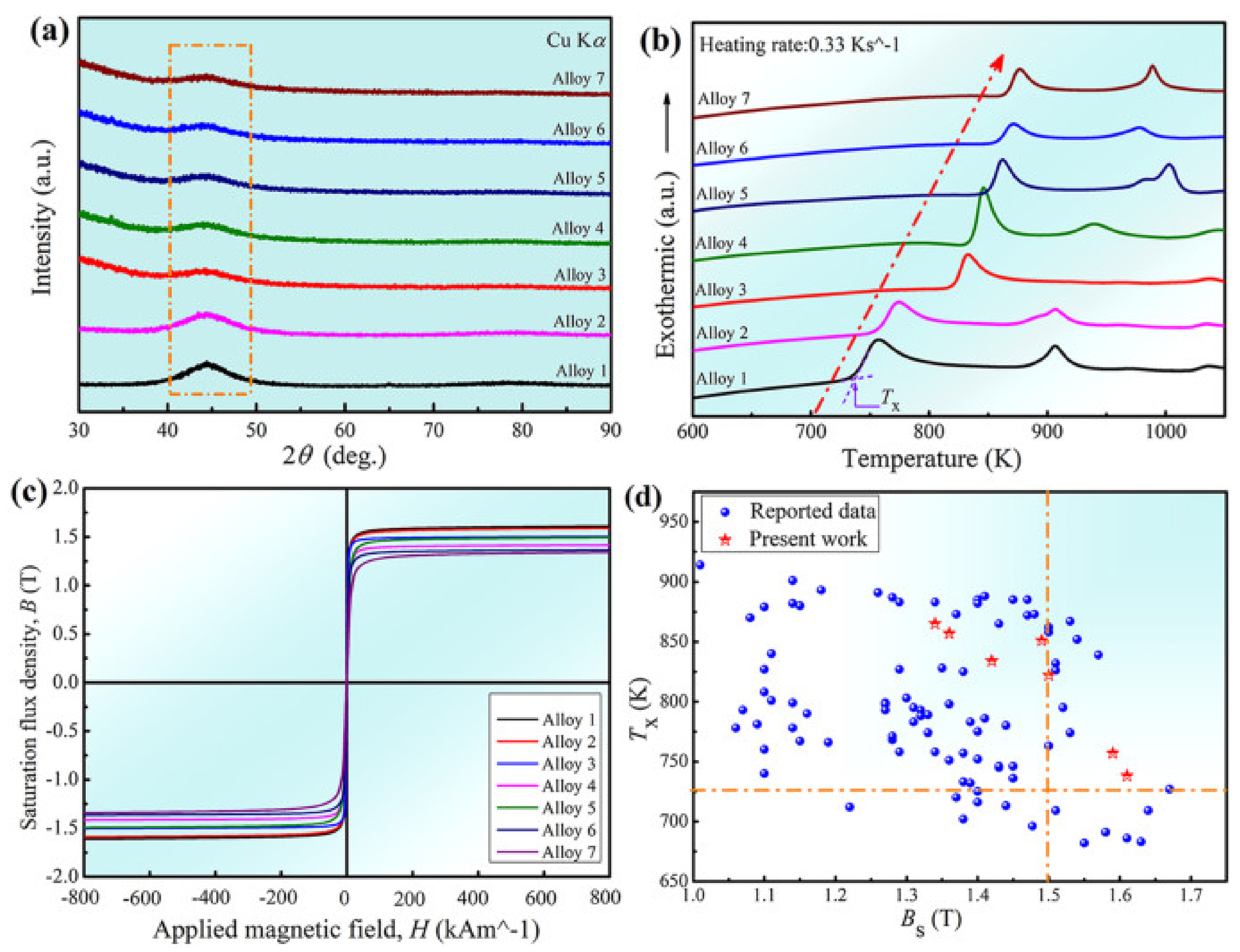
2.2. Characterization
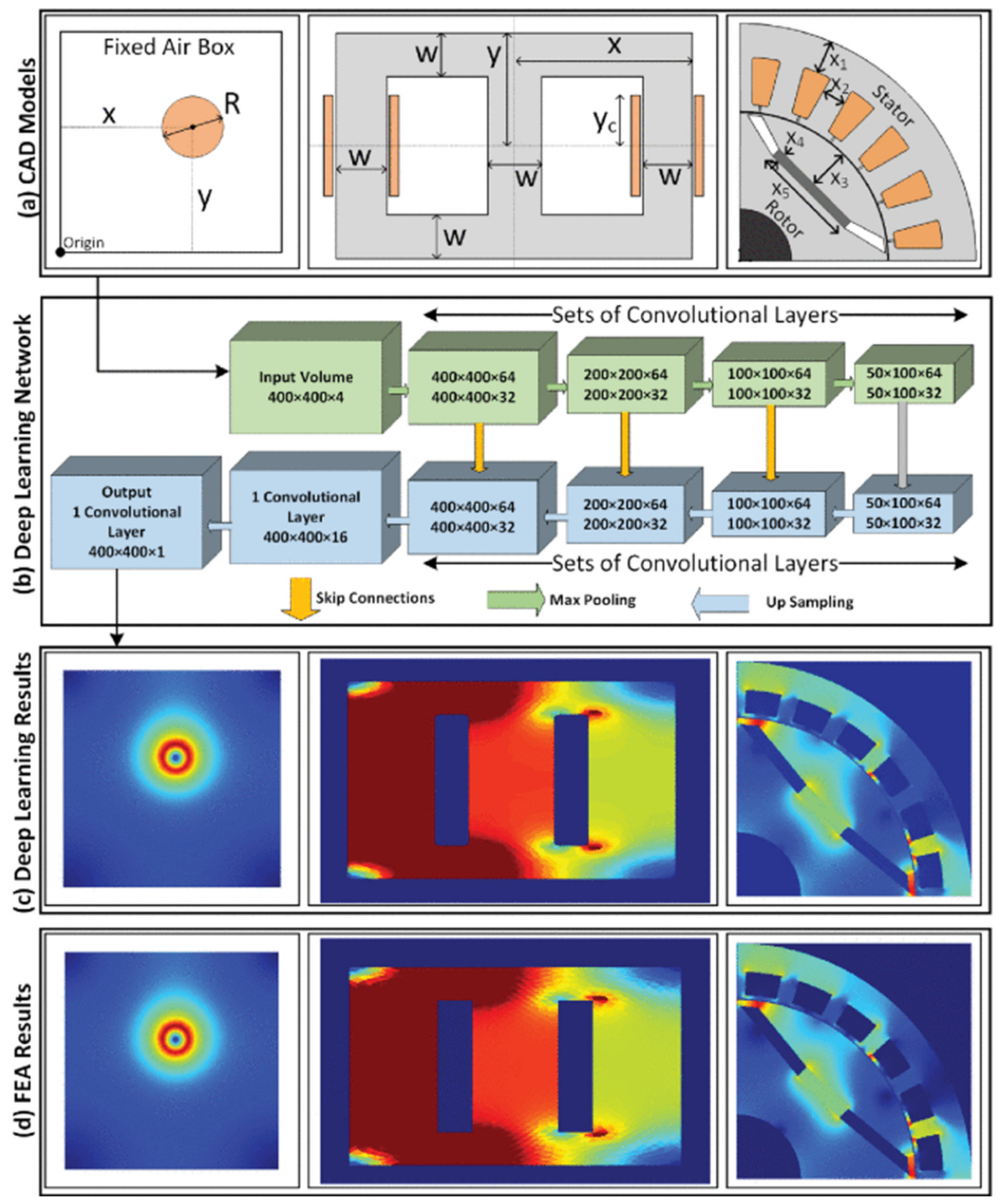
2.3. Applications
3. AI—Engineering Hard and Soft Magnetic Materials: Summarizing the Present and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ABB Website. Available online: https://new.abb.com/motors-generators/service/advanced-services/smart-sensor (accessed on 5 February 2021).
- Wei, J.; Chu, X.; Sun, X.; Xu, K.; Deng, H.; Chen, J.; Wei, Z.; Lei, M. Machine learning in materials science. InfoMat 2019, 1, 338–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, C.P.; Selman, B.; Gregoire, J.M. Artificial intelligence for materials discovery. MRS Bull. 2019, 44, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waring, J.; Lindvall, C.; Umeton, R. Automated machine learning: Review of thestate-of-the-art and opportunities for healthcare. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020, 104, 101822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; DeSouza, K.C.; Butler, L.; Roozkhosh, F. Contributions and risks of artificial intelligence (AI) in building smarter cities: Insights from a systematic review of the literature. Energies 2020, 13, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngarambe, J.; Yun, G.Y.; Santamouris, M. The use of artificial intelligence (AI) methods in the prediction of thermal comfort in buildings: Energy implications of AI-based thermal comfort controls. Energy Build. 2020, 211, 109807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abduljabbar, R.; Dia, H.; Liyanage, S.; Bagloee, S.A. Applications of artificial intelligence in transport: An overview. Sustainability 2019, 11, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A. Machine learning algorithms: A review. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Technol. 2016, 7, 1174–1179. [Google Scholar]
- Alloghani, M.; Jumeily, D.A.; Mustafina, J.; Hussain, A.; Aljaaf, A.J. A systematic review on supervised and unsupervised machine learning algorithms for data science. In Supervised and Unsupervised Learning for Data Science; Berry, M.W., Mohamed, A., Yap, B.W., Eds.; Springer Link: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, S. A quick review on machine learning algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Machine Learning, Big Data, Cloud and Parallel Computing (COMITCon), Faridabad, India, 14–16 February 2019; p. 19046513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, J.J.; Körner, W.; Krugel, G.; Urban, D.F.; Elsässer, C. Compositional optimization of hard-magnetic phases with machine learning models. Acta Mater. 2018, 153, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraunhofer Press Release. Available online: https://www.fraunhofer.de/en/press/research-news/2018/September/MagnetPredictor-predicting-the-magnetic-properties-of-materials.html; http://153.97.176.35/magnetpredictor/ (accessed on 9 February 2021).
- Vasudevan, R.K.; Choudhary, K.; Mehta, A.; Smith, R.; Kusne, G.; Tavazza, F.; Vlcek, L.; Ziatdinov, M.; Kalinin, S.V.; Hattrick-Simpers, J. Materials science in the artificial intelligence age: High-throughput library generation, machine learning, and a pathway from correlations to the underpinning physics. MRS Commun. 2019, 9, 821–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.-L.; Nguyen, D.-N.; Ha, M.-Q.; Kino, H.; Miyake, T.; Dam, H.-C. Explainable machine learning for materials discovery: Predicting the potentially formable Nd-Fe-B crystal structures and extracting the structure-stability relationship. IUCrJ 2020, 7, 1036–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusne, A.G.; Gao, T.; A Mehta, A.; Ke, L.; Nguyen, M.C.; Ho, K.-M.; Antropov, V.; Wang, C.-Z.; Kramer, M.J.; Long, C.; et al. On-the-fly machine-learning for high-throughput experiments: Search for rare-earth-free permanent magnets. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vishina, A.; Vekilova, O.Y.; Björkman, T.; Bergman, A.; Herper, H.C.; Eriksson, O. High-throughput and data-mining approach to predict new rare earth free permanent magnets. Phys. Rev. B 2020, 101, 094407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Périgo, E.A.; Weidenfeller, B.; Kollar, P.; Fuzer, J. Past, present, and future of soft magnetic composites. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2018, 5, 031301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozorth, R.M. Ferromagnetism; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Kirk, T.; Laris, O.; Ross, J.H.; Noebe, R.D.; Keylin, V.; Arróyave, R. Accelerated design of Fe-based soft magnetic materials using machine learning and stochastic optimization. Acta Mater. 2020, 194, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Chen, X.; Liu, X.; Lin, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Jiang, S.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; et al. Interpretable machine-learning strategy for soft magnetic property and thermal stability in Fe-based metallic glasses. NPJ Comput. Mater. 2020, 6, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
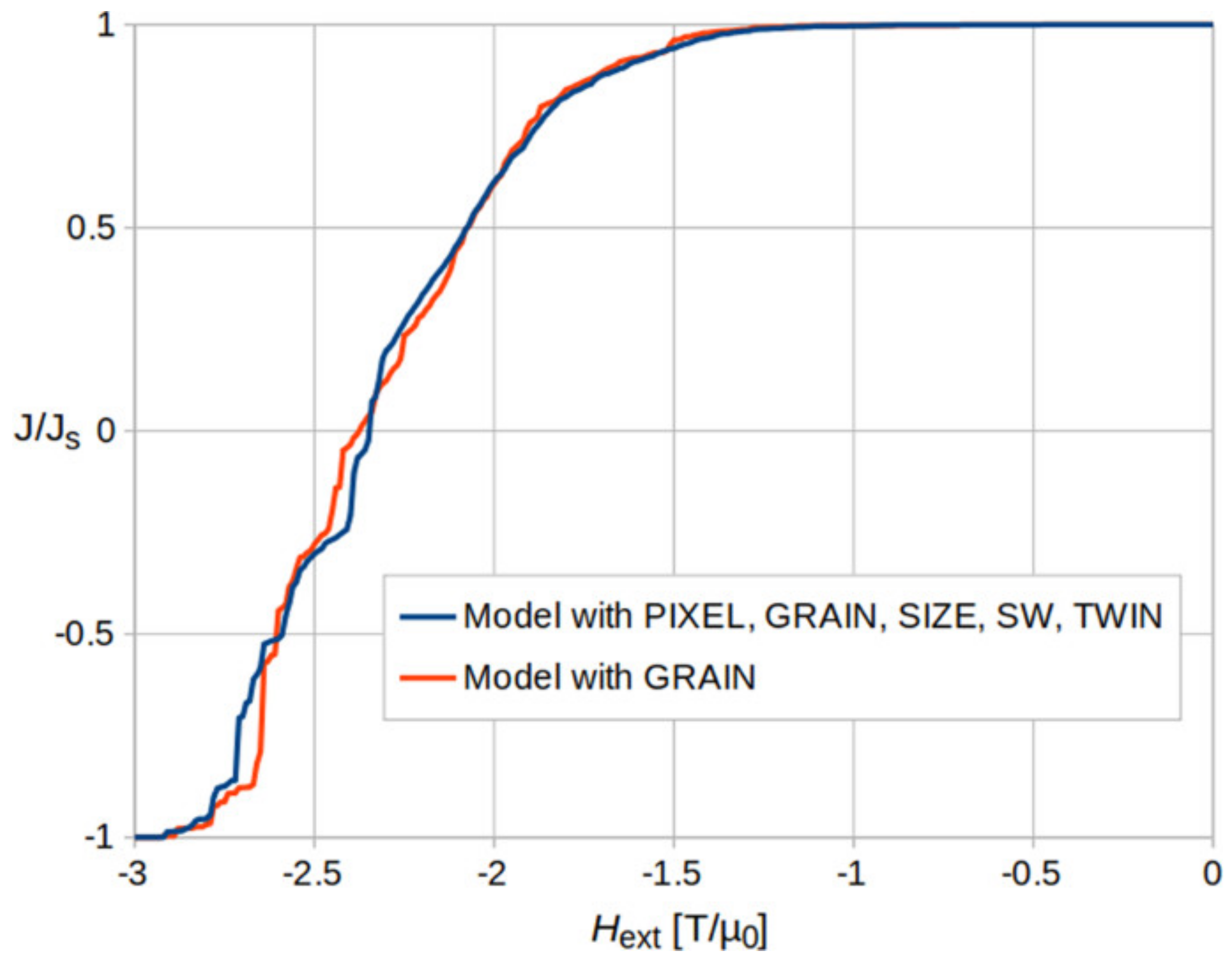
- Exl, L.; Fischbacher, J.; Kovacs, A.; Özelt, H.; Gusenbauer, M.; Yokota, K.; Shoji, T.; Hrkac, G.; Schrefl, T. Magnetic microstructure machine learning analysis. J. Phys. Mater. 2018, 2, 014001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
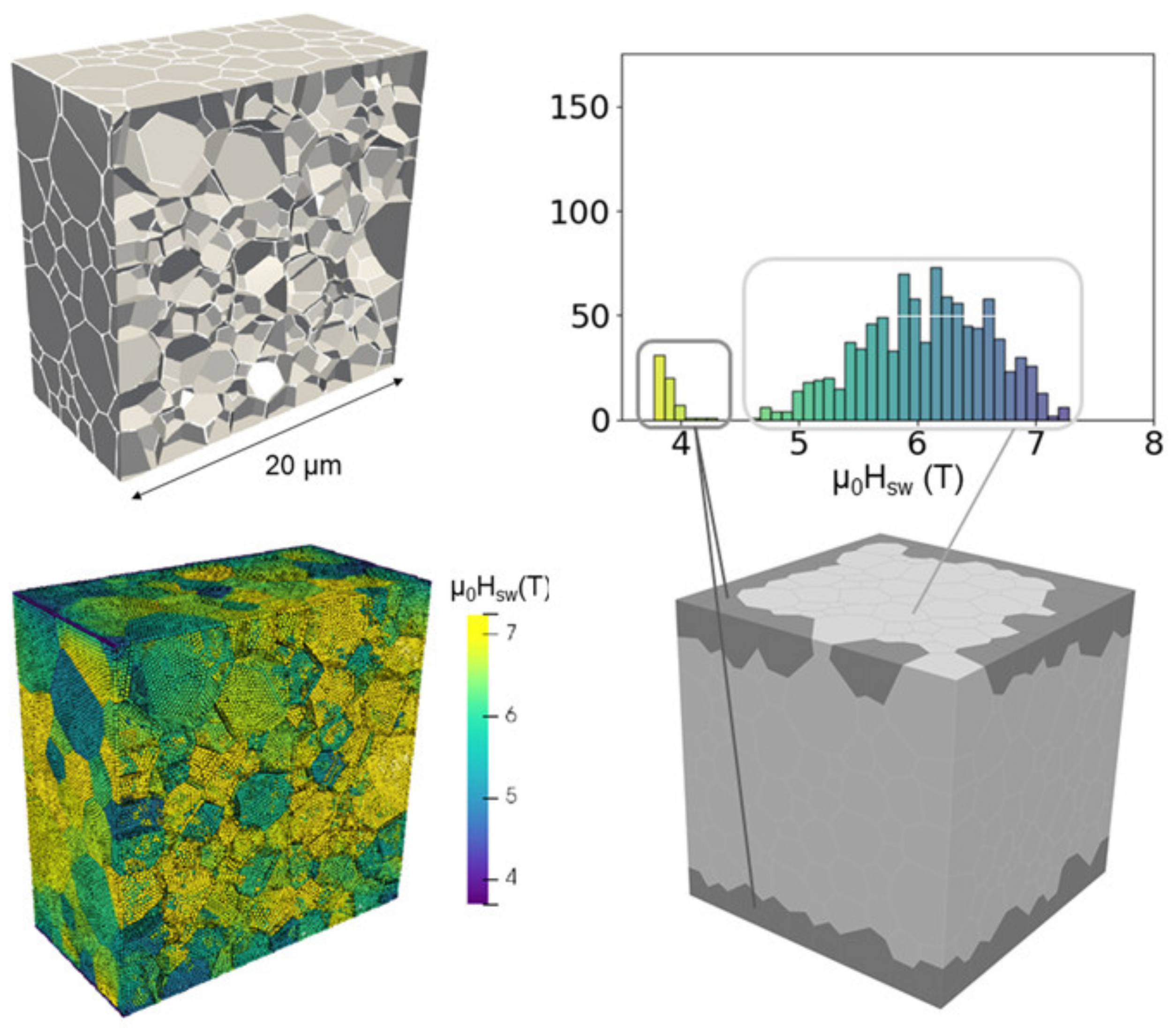
- Gusenbauer, M.; Oezelt, H.; Fischbacher, J.; Kovacs, A.; Zhao, P.; Woodcock, T.G.; Schrefl, T. Extracting local nucleation fields in permanent magnets using machine learning. NPJ Comput. Mater. 2020, 6, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
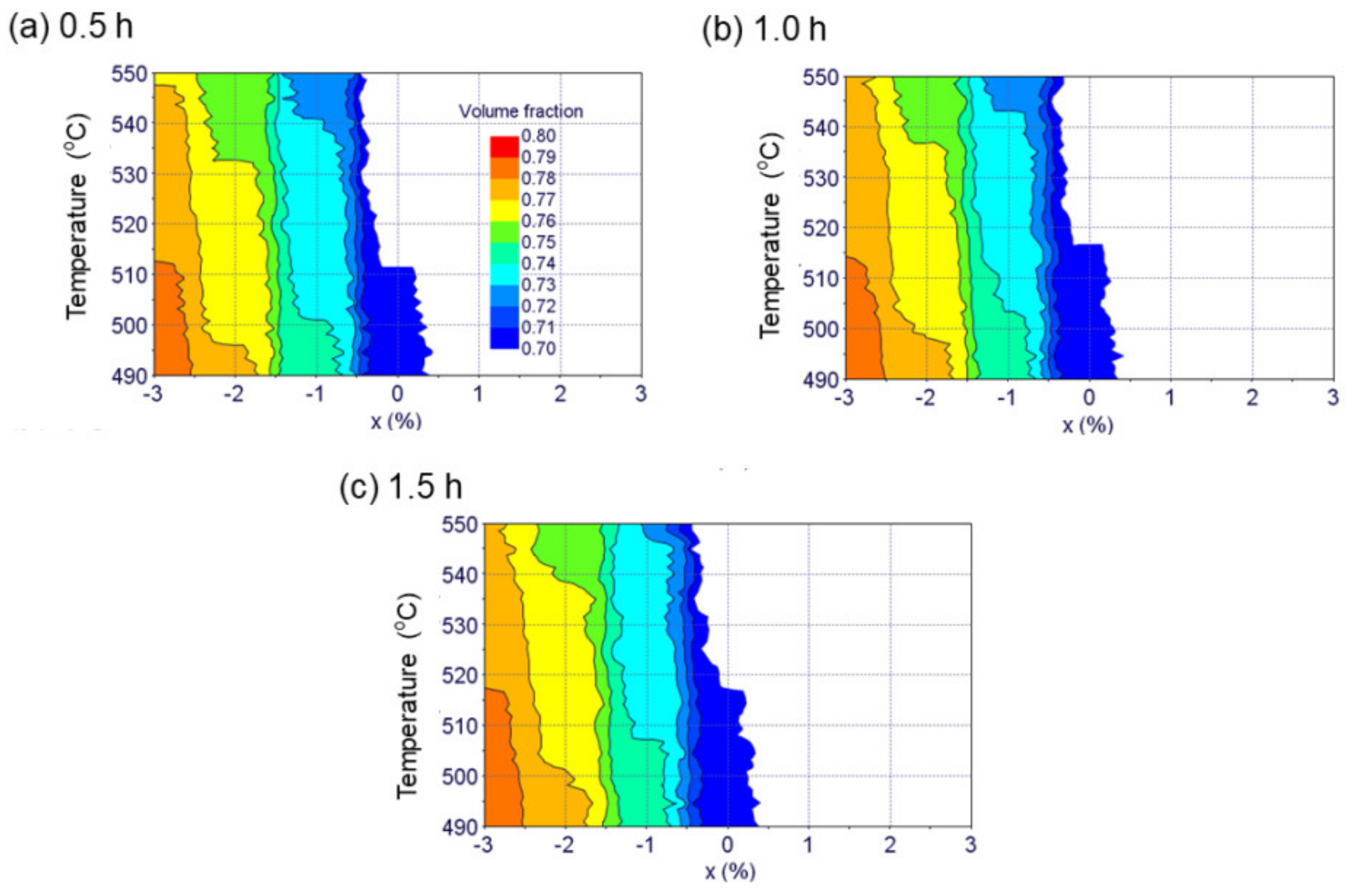
- Jha, R.; Chakraborti, N.; Diercks, D.R.; Stebner, A.P.; Ciobanu, C.V. Combined machine learning and CALPHAD approach for discovering processing-structure relationships in soft magnetic alloys. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2018, 150, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
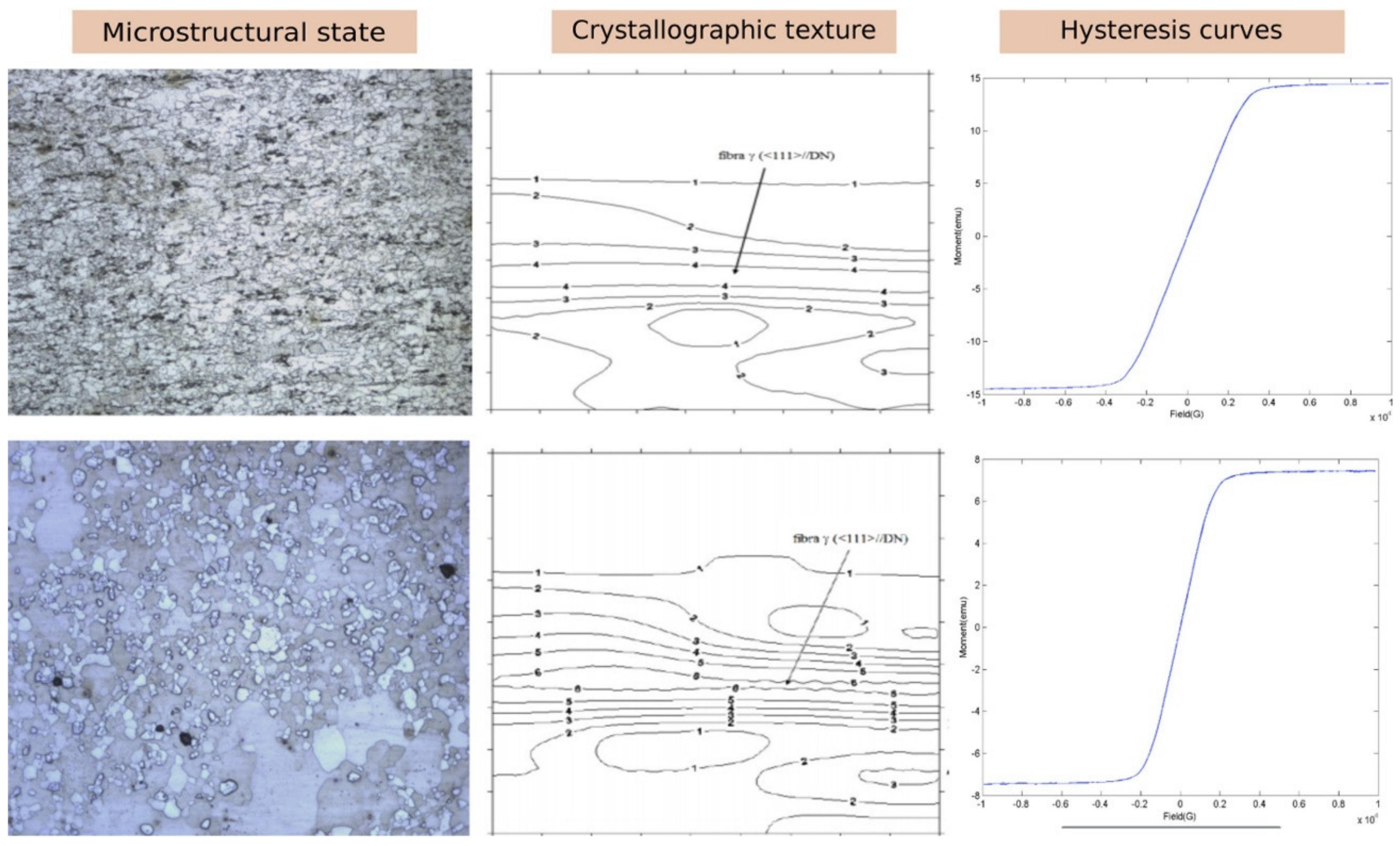
- Ivo, R.F.; Rodrigues, D.D.A.; Bezerra, G.M.; Freitas, F.N.; de Abreu, H.F.G.; Filho, P.P.R. Non-grain oriented electrical steel photomicrograph classification using transfer learning. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 8580–8591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, P.P.R.; Dos Santos, J.C.; Freitas, F.N.C.; Rodrigues, D.D.A.; Ivo, R.F.; Herculano, L.F.G.; de Abreu, H.F.G. New approach to evaluate a non-grain oriented electrical steel electromagnetic performance using photomicrographic analysis via digital image processing. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivo, R.F.; Rodrigues, D.D.A.; Dos Santos, J.C.; Freitas, F.N.C.; Herculano, L.F.G.; de Abreu, H.F.G.; Filho, P.P.R. Study and classification of the crystallographic orientation distribution function of a non-grain oriented electrical steel using computer vision system. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 1070–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EWI Website. Available online: https://ewi.org/application-of-micro-magnetic-material-characterization-for-metal-stamping/ (accessed on 12 March 2021).
- Khan, A.; Ghorbanian, V.; Lowther, D. Deep learning for magnetic field estimation. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2019, 55, 7202304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEPower Website. Available online: https://eepower.com/news/artificial-intelligence-designs-magnetic-materials-geometries-with-minimum-energy-loss/# (accessed on 12 March 2021).
- Park, H.-K.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.-K. Optimizing machine learning models for granular NdFeB magnets by very fast simulated annealing. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcedo-Gallo, J.S.; Galindo-Gonzalez, C.C.; Restrepo-Parra, E. Deep learning approach for image classification of magnetic phases in chiral magnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 501, 166482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazato, I.; Tanaka, Y.; Takahashi, K. Accelerating the discovery of hidden two-dimensional magnets using machine learning and first principle calculations. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2018, 30, 06LT01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabiraj, A.; Kumar, M.; Mahapatra, S. High-throughput discovery of high Curie point two-dimensional ferromagnetic materials. NPJ Comput. Mater. 2020, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Périgo, E.A.; Faria, R.N.d. Artificial Intelligence—Engineering Magnetic Materials: Current Status and a Brief Perspective. Magnetochemistry 2021, 7, 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7060084
Périgo EA, Faria RNd. Artificial Intelligence—Engineering Magnetic Materials: Current Status and a Brief Perspective. Magnetochemistry. 2021; 7(6):84. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7060084
Chicago/Turabian StylePérigo, Elio A., and Rubens N. de Faria. 2021. "Artificial Intelligence—Engineering Magnetic Materials: Current Status and a Brief Perspective" Magnetochemistry 7, no. 6: 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7060084
APA StylePérigo, E. A., & Faria, R. N. d. (2021). Artificial Intelligence—Engineering Magnetic Materials: Current Status and a Brief Perspective. Magnetochemistry, 7(6), 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7060084






