Microstructure Evolution of Ag/TiO2 Thin Film
Abstract
1. Introduction
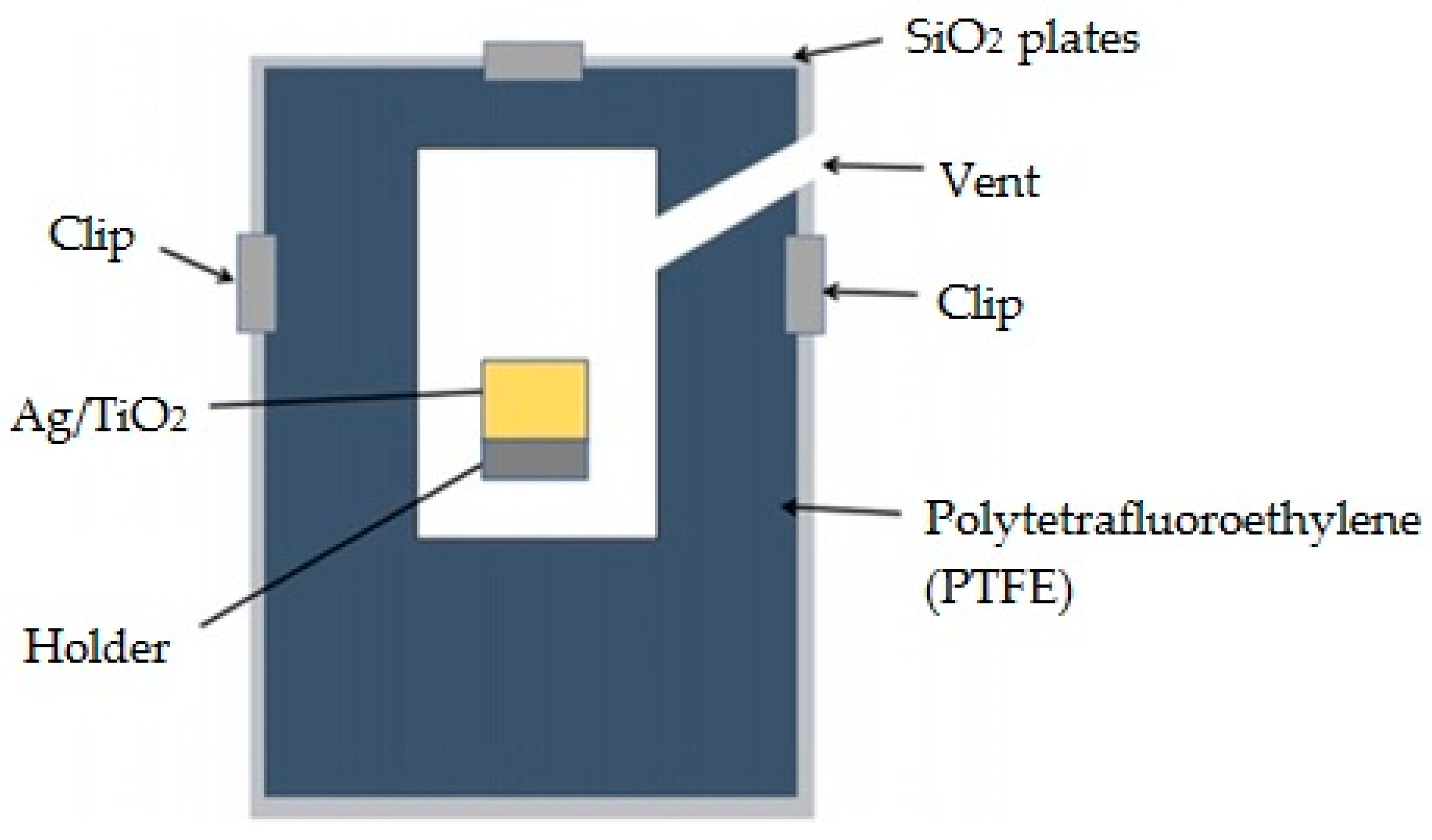
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparations of Ag/TiO2 Thin Film
2.3. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phase Composition
3.2. Microstructural and Topography Analysis
3.3. Growth Behavior of Ag/TiO2
4. Conclusions
- (a)
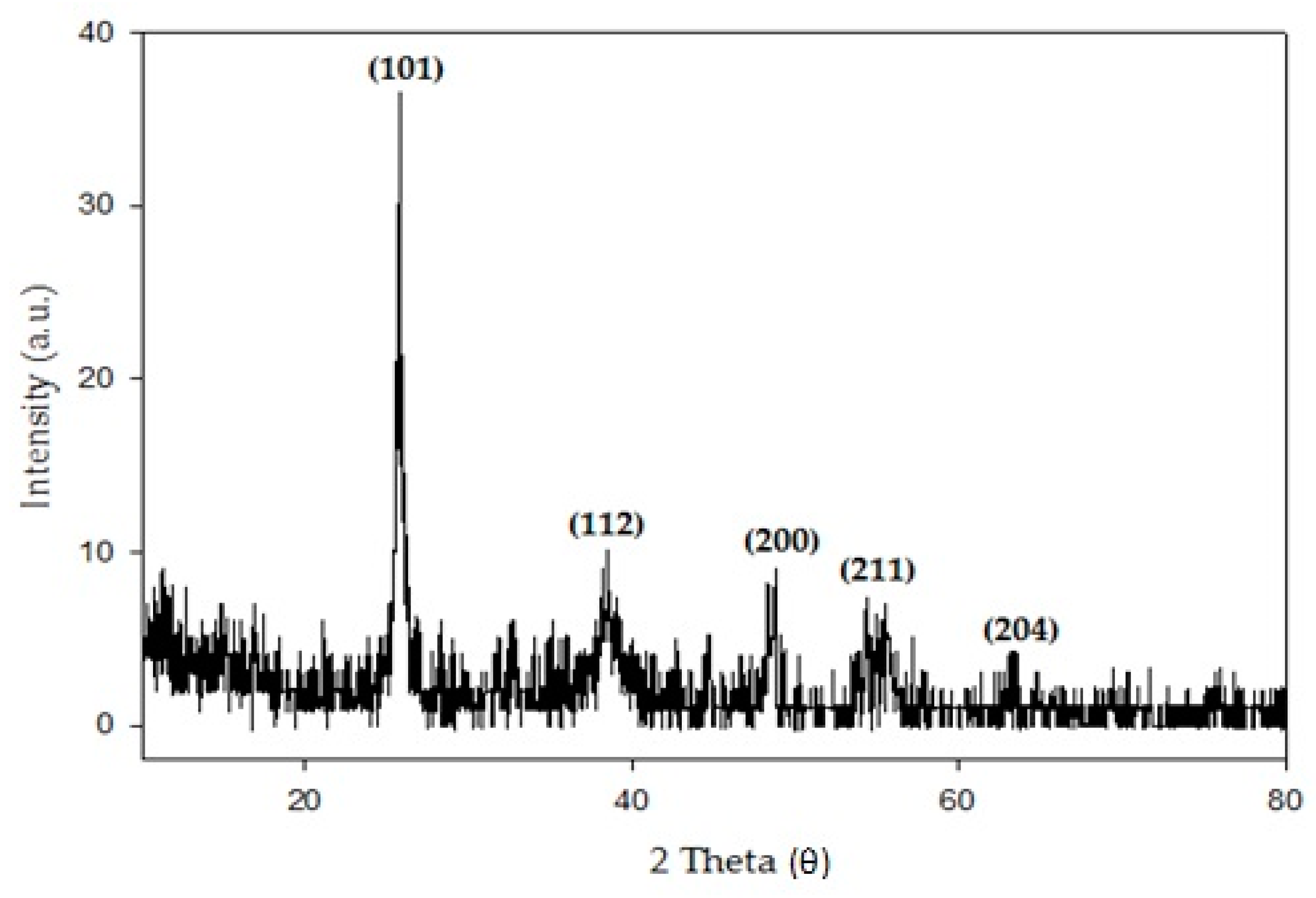
- The GIXRD pattern confirmed the presence of the anatase phase without any diffraction peak for Ag that can be clearly seen, even at a low annealing temperature. It is believed that the Ag peak is not present in the GIXRD due to the low concentration of AgNO3 added into the TiO2 parent solution.
- (b)
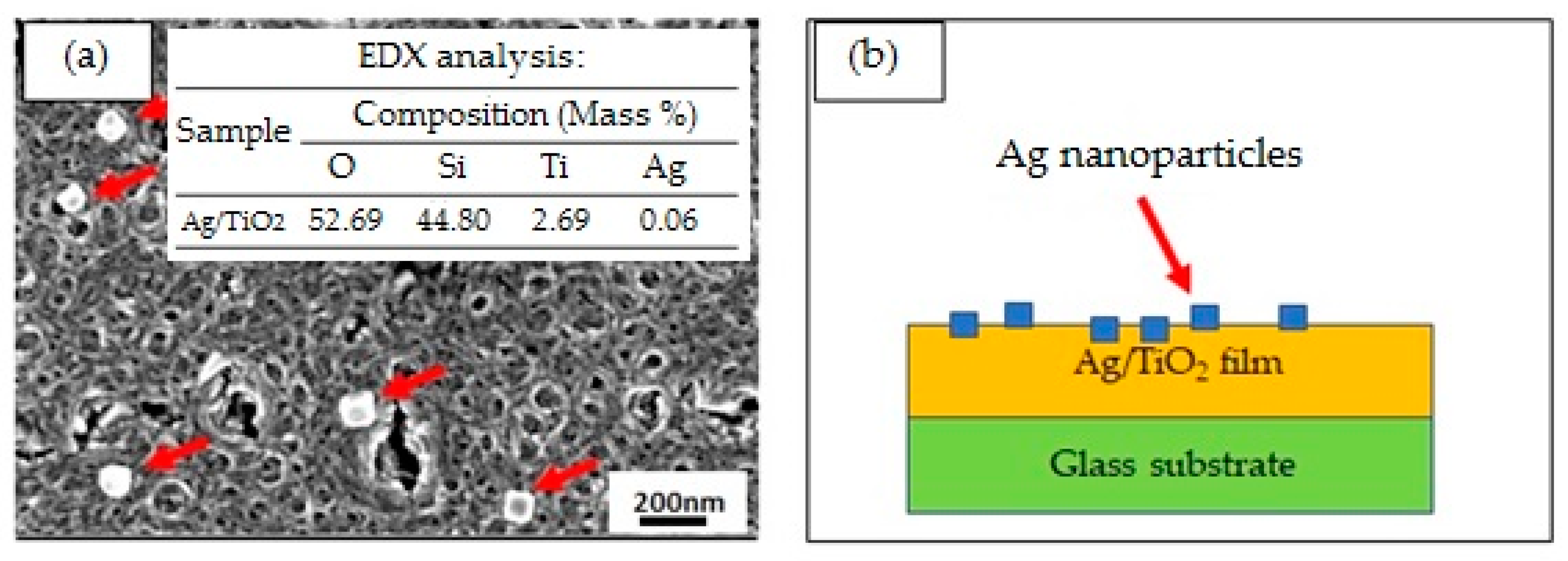
- The FESEM micrograph confirmed that the Ag particles were mostly cubical, while the TiO2 thin film resembled porous ring-like structures, where each ring coalesced to form a channel of ring. It was revealed that the coalescences of the porous ring-like TiO2 thin film structures and the formation of the cubical shape of Ag could be obtained even at a low annealing temperature. The EDX results confirmed the presence of a small amount of Ag particles.
- (c)
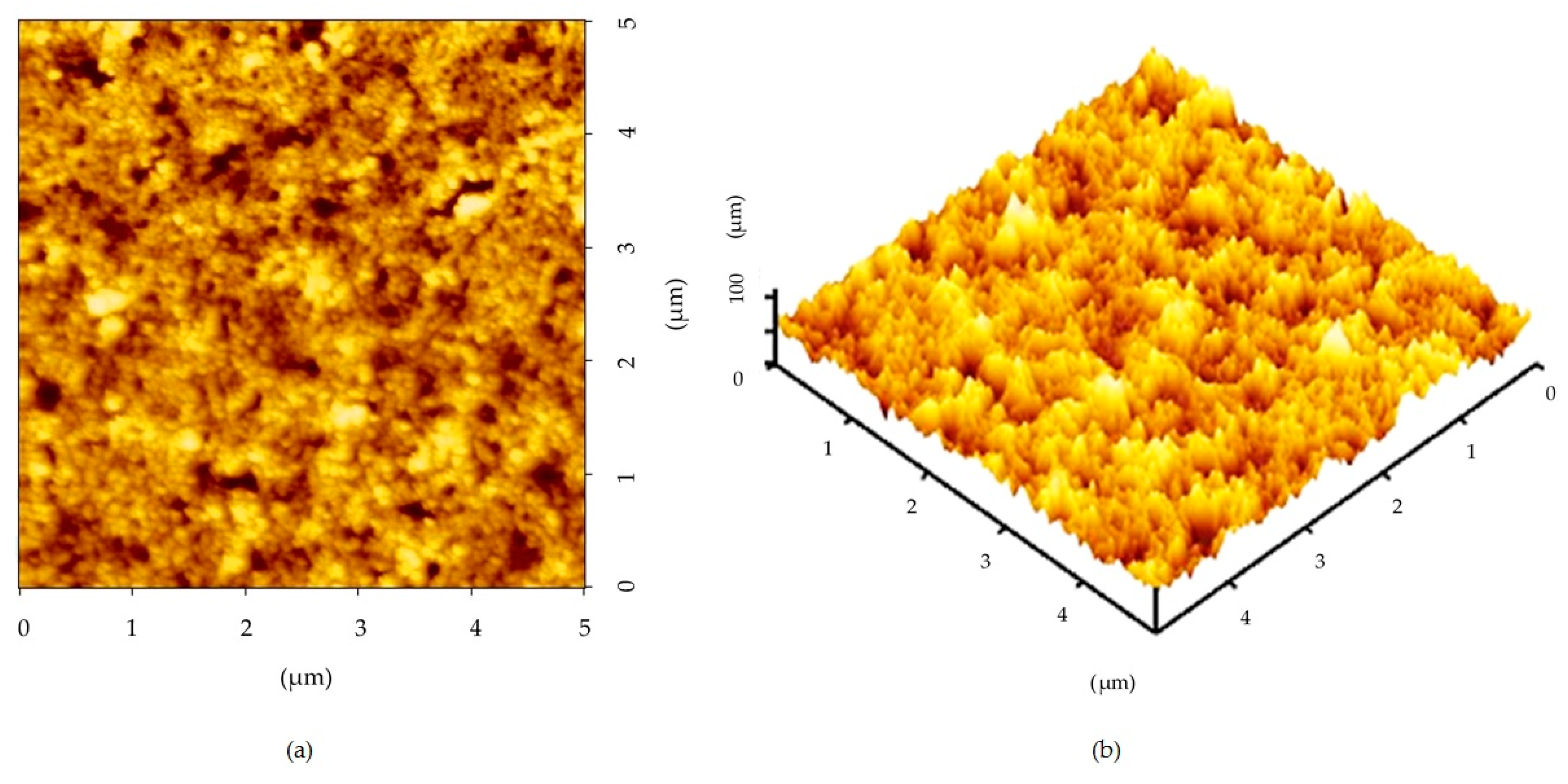
- The surface topographical profile shows that the root mean square (RMS) roughness values obtained by the AFM for the film are 10.52 × 10−3 μm with a thickness of 83.72 × 10−3 μm. The film’s surface was rough due to the limited surface diffusion, caused by the relatively low thermal energy and the crystallite size effect.
- (d)
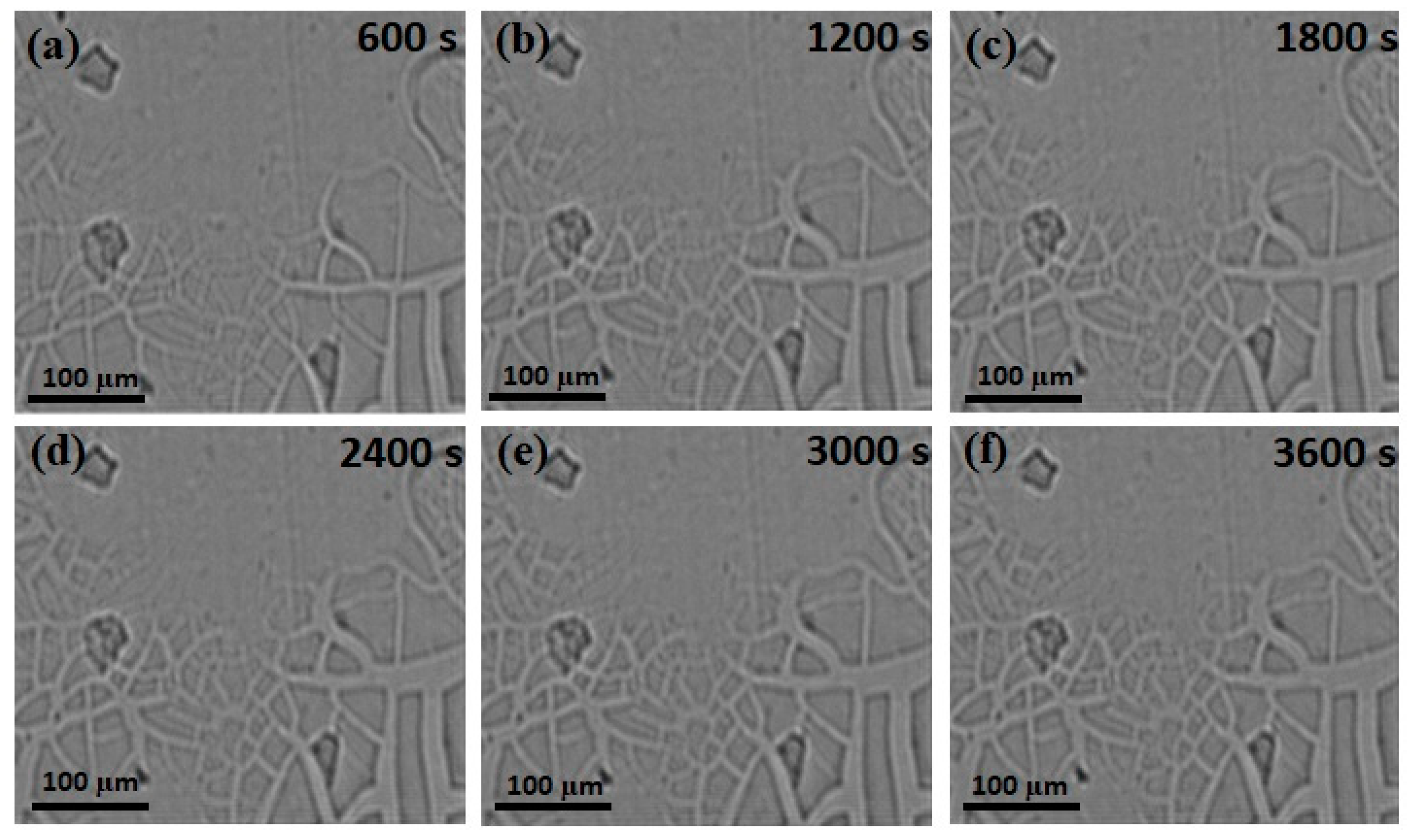
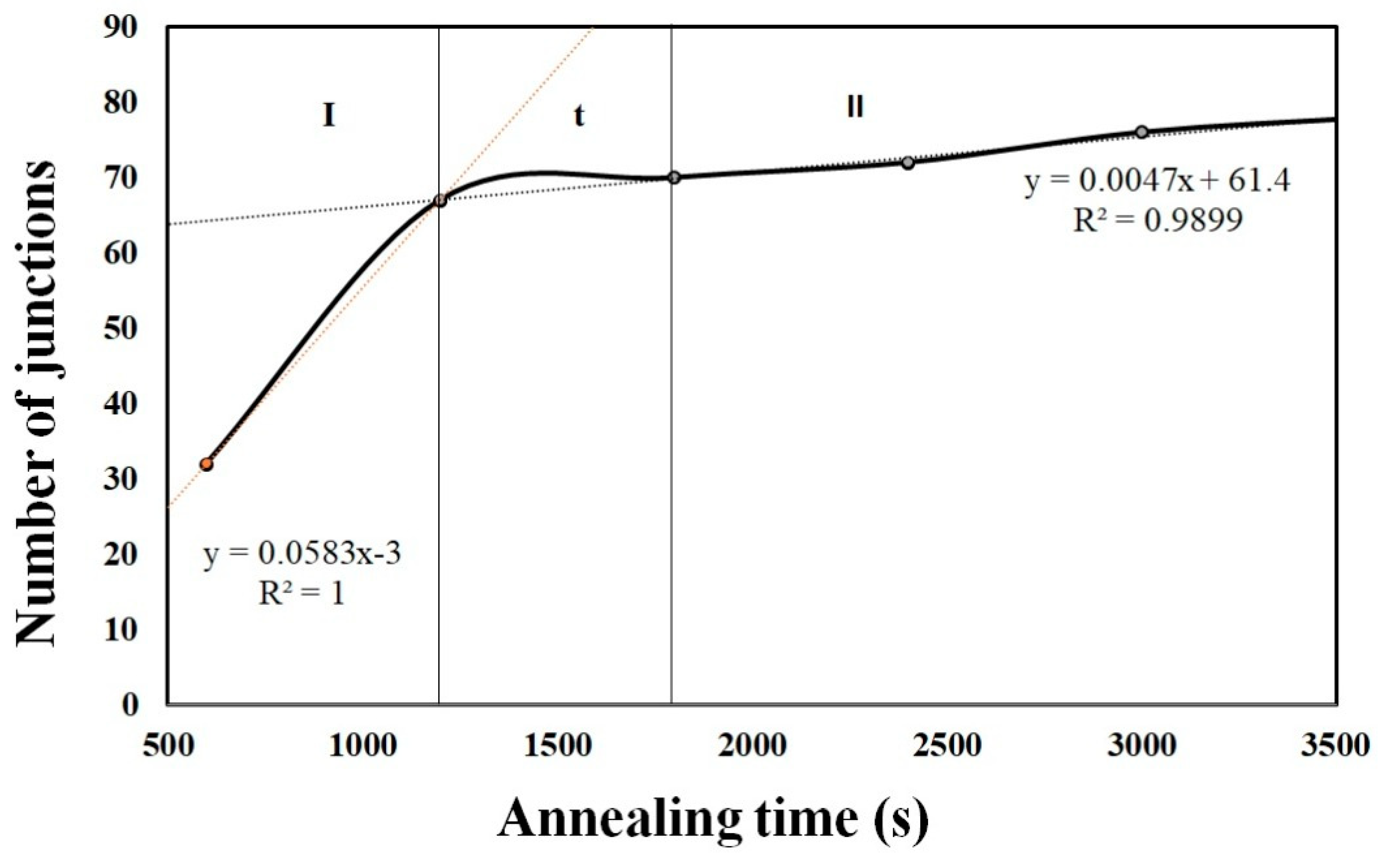
- From the in-situ synchrotron radiation images, the formation of junctions was also quantified. It was observed that as the annealing time increased, the growth of Ag/TiO2 also increased in terms of area and the number of junctions. It was clearly seen that the growth rate of Ag/TiO2 at 600 s was 47.26 µm2/s, and that after 1200 s it decreased to 11.50 µm2/s and to 11.55 µm2/s at 1800 s. Prolonged annealing will further decrease the growth rate to 5.94 µm2/s, 4.12 µm2/s and 4.86 µm2/s at 2400 s, 3000 s and 3600 s, respectively. This shows that at the early stages of the annealing process, the area was increasing steadily and started to become constant towards the end.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, B.H.; An, J.H.; Kang, B.A.; Hwang, K.S.; Oh, J.S. Nickel-doped titanium oxide films prepared by chemical solution deposition. J. Ceram. Proc. Res. 2004, 5, 53–57. [Google Scholar]
- Zaharescu, M.; Crisan, M.; Muševič, I. Atomic force microscopy study of TiO2 films obtained by the sol-gel method. J. Sol–Gel Sci. Tech. 1998, 13, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishide, T.; Sato, M.; Hara, H. Crystal structure and optical property of TiO2 gels and films prepared from Ti-edta complexes as titania precursors. J. Mater. Sci. 2000, 35, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, K.; Fujishima, A. TiO2 photocatalysis: Design and applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2012, 13, 169–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, A.; Rao, T.N.; Tryk, D.A. Titanium Dioxide Photocatalysis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2000, 1, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.; Matsuoka, M.; Takeuchi, M.; Zhang, J.; Horiuchi, Y.; Anpo, M.; Bahnemann, D.W. Understanding TiO2 photocatalysis: Mechanisms and materials. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 9919–9986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhail, M.H.; Mohan Rao, G.; Mohan, S. dc reactive magnetron sputtering of titanium-structural and optical characterization of TiO2 films. J. Appl. Phys. 1992, 71, 1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyorgy, E.; del Pino, A.P.; Sauthier, G.; Figueras, A.; Alsina, F.; Pascual, J. Structural, morphological and local electric properties of TiO2 thin films grown by pulsed laser deposition. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 5246–5251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzamani, M.; Shokuhfar, A.; Eghdam, E.; Mastali, S. Influence of catalyst on structural and morphological properties of TiO2 nanostructured films prepared by sol–gel on glass. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2013, 23, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, H. Recent applications of TiO2 nanomaterials in chemical sensing in aqueous media. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 160, 875–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Liu, X.; Hu, L.; Xu, L.; He, J. Effects of Nb doping on microstructure and photocatalytic properties of TiO2 thin film. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 6910–6915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azani, A.; Che Halin, D.S.; Abdul Razak, K.; Abdullah MM, A.; Mohd Salleh MA, A.; Mahmed, N.; Abdul Razak MF, S.; Ramli, M.M.; Azhari, A.W.; Chobpattana, V. Effect of graphene oxide on microstructure and optical properties of TiO2 thin film. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 701, 012011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M.I.; Gandhi, V.G.; Mishra, M.; Tripathi, S.; Shripathi, T.; Joshi, P.A.; Shah, D.O. Single-Step Synthesis of Silver-Doped Titanium Dioxide: Influence of Silver on Structural, Textural, and Photocatalytic Properties. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 5749–5758. [Google Scholar]
- Abdul Razak, K.; Che Halin, D.S.; Azani, A.; Abdullah, M.M.A.; Mohd Salleh, M.A.A.; Mahmed, N.; Abdul Razak, M.F.S.; Ramli, M.M.; Azhari, A.W.; Chobpattana, V. Microstructural studies of doped PEG Ag/TiO2 thin film. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 701, 012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reidy, D.J.; Holmes, J.D.; Morris, M.A. The critical size mechanism for the anatase to rutile transformation in TiO2 and doped-TiO2. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 26, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.P.; Keizer, K.; Buggraaf, A.J.; Okubo, T.; Nagamoto, H. Textural Evolution and Phase Transformation in Titania Membranes: Part 2. J. Mater. Chem. 1993, 3, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Yoko, T.; Kozuka, H.; Sakka, S. Effects of solvent on properties of sol—gel-derived TiO2 coating films. Thin Solid Film. 1992, 219, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajutvichyanukul, P.; Ananpattarachai, J.; Pongpom, S. Sol–gel preparation and properties study of TiO2 thin film for photocatalytic reduction of chromium (VI) in photocatalysis process. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2005, 6, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Leung, K.M.; Guo, Q.; Lau, W.M.; Yang, J. Synthesis of Ag–TiO2 composite nano thin film for antimicrobial application. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 115603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-C.; Chen, J.-Y.; Hsu, T.-L.; Lin, C.-K.; Chan, C.-C. Photocatalytic properties of porous TiO2/Ag thin films. Thin Solid Film. 2008, 516, 1743–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seery, M.K.; George, R.; Floris, P.; Pillai, S.C. Silver doped titanium dioxide nanomaterials for enhanced visible light photocatalysis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2007, 189, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckertová, L. Mechanism of Film Formation. Phys. Thin Film. 1977, 72–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, U.H.; Kim, M.H.; Kwon, Y.U. Mesoporous thin films with accessible pores from surfaces. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2006, 27, 808–816. [Google Scholar]
- Tijani, J.O.; Totito, T.C.; Fatoba, O.O.; Babajide, O.O.; Petrik, L.F. Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity of Ag metallic particles deposited carbon-doped TiO2 nanocomposites supported on stainless steel mesh. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2017, 83, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Mahendra, S.; Lyon, D.Y.; Brunet, L.; Liga, M.V.; Li, D.; Alvarez, P.J. Antimicrobial nanomaterials for water disinfection and microbial control: Potential applications and implications. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4591–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Xiong, J.; Xiong, Y.; Xiao, H. A novel biomaterial—Fe3O4:TiO2 core-shell nano particle with magnetic performance and high visible light photocatalytic activity. Opt. Mater. 2008, 31, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahl, A.; Veziroglu, S.; Henkel, B.; Strunskus, T.; Polonskyi, O.; Aktas, O.C.; Faupel, F. Pathways to Tailor Photocatalytic Performance of TiO2 Thin Films Deposited by Reactive Magnetron Sputtering. Materials 2019, 12, 2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Kumar Parashar, K.; Kumar Tandi, S.; Kumar, T.; Agarwal, D.C.; Pathak, A. Fabrication of Ag:TiO2 Nanocomposite Thin Films by Sol-Gel Followed by Electron Beam Physical Vapour Deposition Technique. J. Spectrosc. 2013, 491716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bade, B.R.; Rondiya, S.; Bhopale, S.R.; Dzade, N.Y.; Kamble, M.M.; Rokade, A.; Nasane, M.P.; More, M.A.; Jadkar, S.R.; Funde, A.M. Investigation of growth mechanism for highly oriented TiO2 nanorods: The role of reaction time and annealing temperature. Sn Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Halin, D.S.C.; Razak, K.A.; Mohd Salleh, M.A.A.; Ramli, M.I.I.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Azhari, A.W.; Nogita, K.; Yasuda, H.; Nabiałek, M.; Wysłocki, J.J. Microstructure Evolution of Ag/TiO2 Thin Film. Magnetochemistry 2021, 7, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7010014
Halin DSC, Razak KA, Mohd Salleh MAA, Ramli MII, Abdullah MMAB, Azhari AW, Nogita K, Yasuda H, Nabiałek M, Wysłocki JJ. Microstructure Evolution of Ag/TiO2 Thin Film. Magnetochemistry. 2021; 7(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7010014
Chicago/Turabian StyleHalin, Dewi Suriyani Che, Kamrosni Abdul Razak, Mohd Arif Anuar Mohd Salleh, Mohd Izrul Izwan Ramli, Mohd Mustafa Al Bakri Abdullah, Ayu Wazira Azhari, Kazuhiro Nogita, Hideyuki Yasuda, Marcin Nabiałek, and Jerzy J. Wysłocki. 2021. "Microstructure Evolution of Ag/TiO2 Thin Film" Magnetochemistry 7, no. 1: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7010014
APA StyleHalin, D. S. C., Razak, K. A., Mohd Salleh, M. A. A., Ramli, M. I. I., Abdullah, M. M. A. B., Azhari, A. W., Nogita, K., Yasuda, H., Nabiałek, M., & Wysłocki, J. J. (2021). Microstructure Evolution of Ag/TiO2 Thin Film. Magnetochemistry, 7(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7010014








