Quantitative NMR as a Versatile Tool for the Reference Material Preparation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Basics of quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (qNMR)
2.1. Internal Standard Method
2.2. External Standard Method
2.3. Electronic Reference Method
2.4. Signal Processing
3. Recent Advances of qNMR
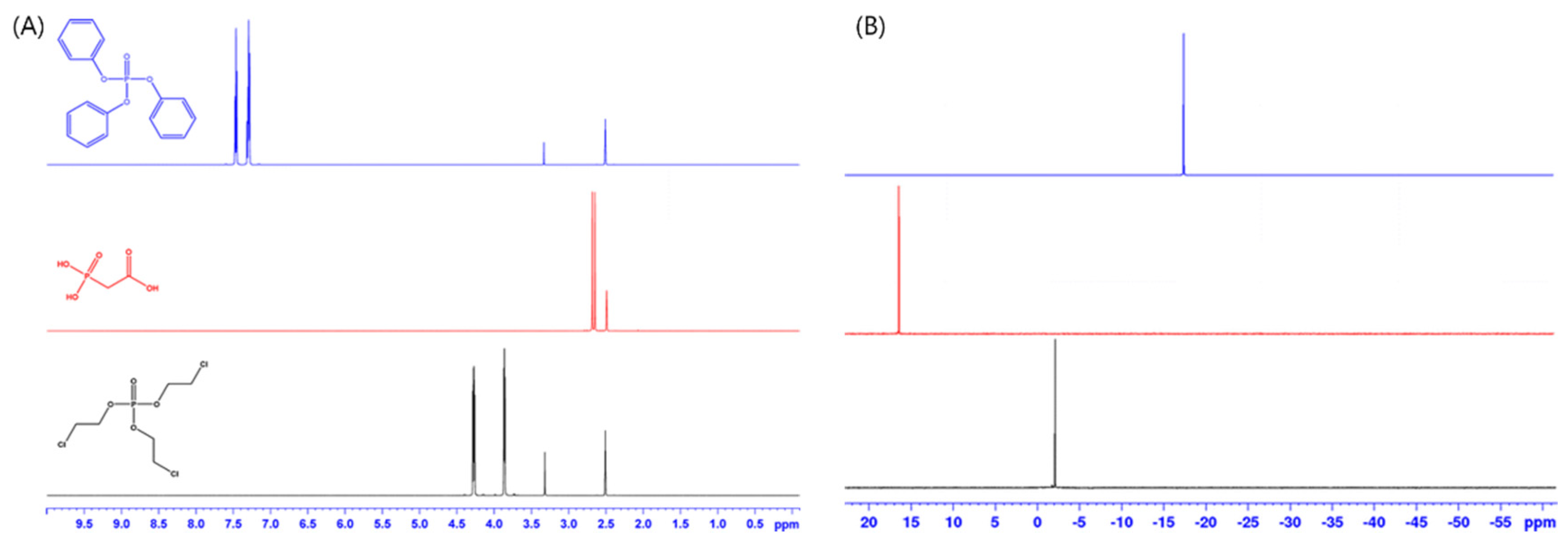
3.1. Heteroatoms
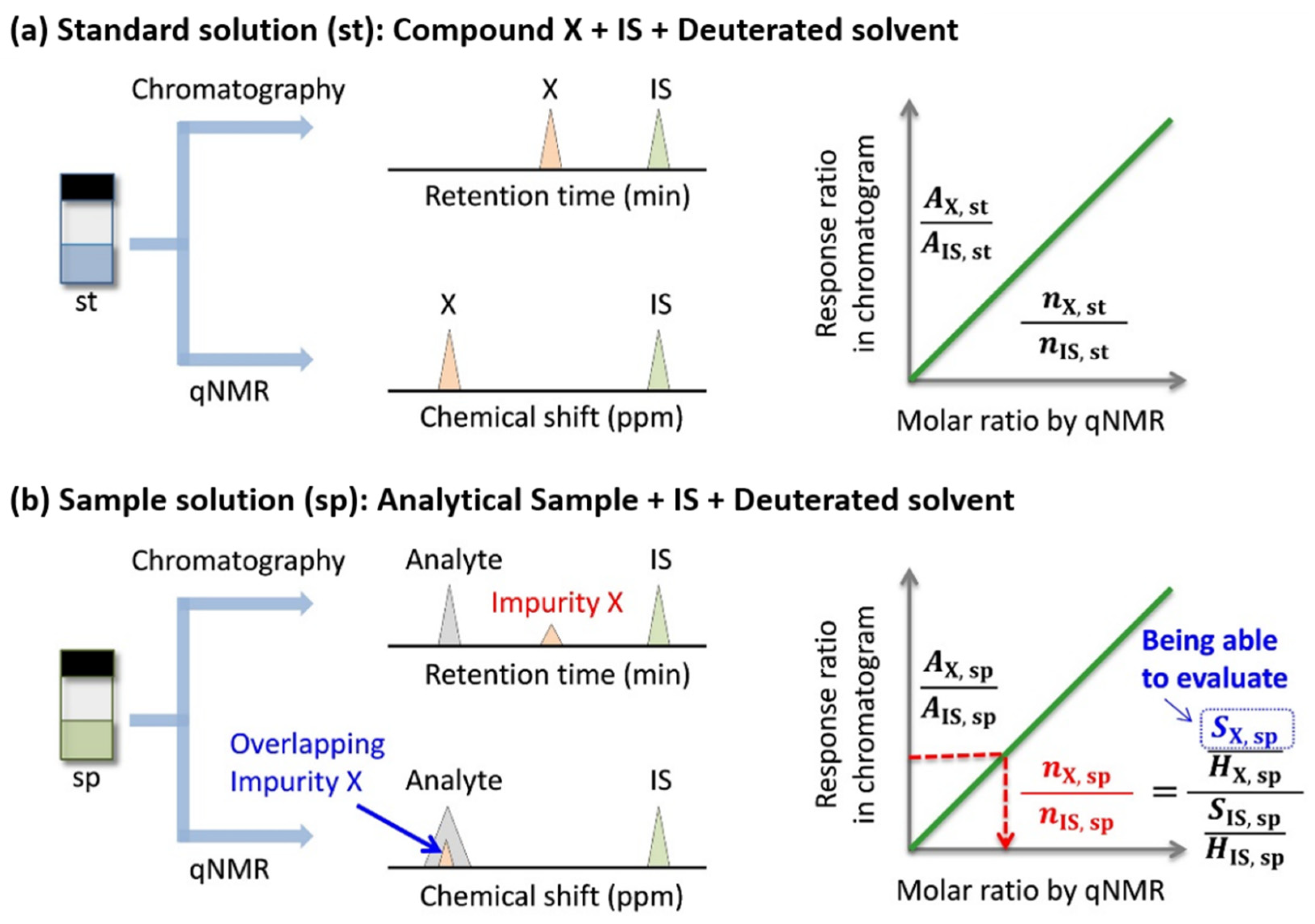
3.2. Coupling with Chromatography
3.3. Multidimensional NMR
4. Reference Material Development
4.1. Internal Standard
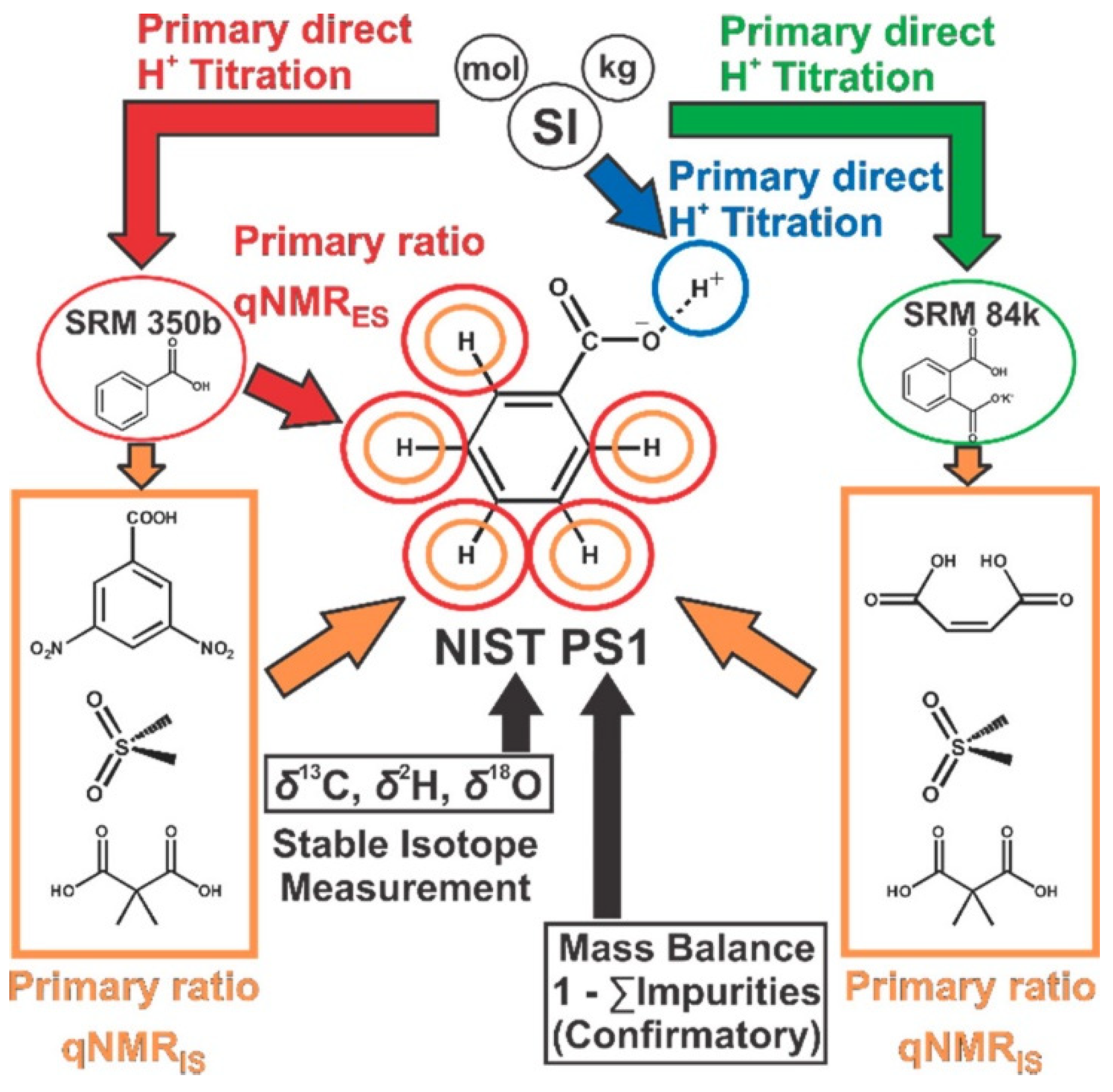
4.2. High Purity Reference Materials
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Bièvre, P.; Dybkær, R.; Fajgelj, A.; Hibbert, D.B. Metrological traceability of measurement results in chemistry: Concepts and implementation (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2011, 83, 1873–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westwood, S.; Choteau, T.; Daireaux, A.; Josephs, R.D.; Wielgosz, R.I. Mass Balance Method for the SI Value Assignment of the Purity of Organic Compounds. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 3118–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauli, G.F.; Chen, S.N.; Simmler, C.; Lankin, D.C.; Godecke, T.; Jaki, B.U.; Friesen, J.B.; McAlpine, J.B.; Napolitano, J.G. Importance of Purity Evaluation and the Potential of Quantitative 1H NMR as a Purity Assay. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 9220–9231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crook, A.A.; Powers, R. Quantitative NMR-Based Biomedical Metabolomics: Current Status and Applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diehl, B.; Holzgrabe, U.; Monakhova, Y.; Schonberger, T.J. Quo Vadis qNMR? Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 177, 112847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippa, K.A.; Duewer, D.L.; Nelson, M.A.; Davies, S.R.; Mackay, L.G. The role of the CCQM OAWG in providing SI traceable calibrators for organic chemical measurements. Accred. Qual. Assur. 2019, 24, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Yamazaki, T.; Numata, M. Development of nuclear magnetic resonance as a tool of quantitative analysis for organic materials. Metrologia 2019, 56, 054002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Numata, M.; Mackay, L.; Warren, J.; Jiao, H.; Westwood, S.; Song, D. Advanced approaches and applications of qNMR. Metrologia 2020, 57, 014004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pharmacopeia, T.U.S. The United States Pharmacopeia, USP 43/NF 38; The United States Pharmacopeial Convention: Rockville, MD, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pharmacopoeia, E. European Pharmacopoeia, 10th ed.; EDQM: Strasbourg, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki, T.; Nakamura, S.; Saito, T. Optimization of sample preparation for accurate results in quantitative NMR spectroscopy. Metrologia 2017, 54, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Nakaie, S.; Kinoshita, M.; Ihara, T.; Kinugasa, S.; Nomura, A.; Maeda, T. Practical guide for accurate quantitative solution state NMR analysis. Metrologia 2004, 41, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monakhova, Y.B.; Diehl, B.W.K. Practical guide for selection of 1H qNMR acquisition and processing parameters confirmed by automated spectra evaluation. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2017, 55, 996–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Bhavaraju, S.; Thibeault, M.P.; Melanson, J.; Blomgren, A.; Rundlof, T.; Kilpatrick, E.; Swann, C.J.; Rudd, T.; Aubin, Y.; et al. Survey of peptide quantification methods and comparison of their reproducibility: A case study using oxytocin. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 166, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, T.; Sugimoto, N.; Bhavaraju, S.; Yamazaki, T.; Nishizaki, Y.; Liu, Y.; Bzhelyansky, A.; Amezcua, C.; Ray, J.; Zailer, E.; et al. Collaborative Study to Validate Purity Determination by 1H quantitative NMR Spectroscopy by Using Internal Calibration Methodology. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 68, 868–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- qNMR Summit. Available online: http://www.qnmrsummit.com (accessed on 4 January 2021).
- ValidNMR. Available online: https://www.validnmr.com (accessed on 4 January 2021).
- Toman, B.; Nelson, M.A.; Lippa, K.A. Chemical purity using quantitative 1H-nuclear magnetic resonance: A hierarchical Bayesian approach for traceable calibrations. Metrologia 2016, 53, 1193–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullen, C.H.; Ray, G.J.; Szabo, C.M. A comparison of quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance methods: Internal, external, and electronic referencing. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2013, 51, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, T.J. Quantitative NMR Spectroscopy Using Coaxial Inserts Containing a Reference Standard: Purity Determinations for Military Nerve Agents. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, I.W.; Quilliam, M.A.; Walter, J.A. Quantitative 1H NMR with External Standards: Use in Preparation of Calibration Solutions for Algal Toxins and Other Natural Products. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 3123–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Klink, J.J. The NMR Reciprocity Theorem for Arbitrary Probe Geometry. J. Magn. Reson. 2001, 148, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wider, G.; Dreier, L.J. Measuring Protein Concentrations by NMR Spectroscopy. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2571–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monakhova, Y.B.; Kohl-Himmelseher, M.; Kuballa, T.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Determination of the purity of pharmaceutical reference materials by 1H NMR using the standardless PULCON methodology. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 100, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, O.; Kreissl, J.K.; Daschner, A.; Hofmann, T.J. Accurate Determination of Reference Materials and Natural Isolates by Means of Quantitative 1H NMR Spectroscopy. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 2506–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedito, L.E.C.; Maldaner, A.O.; Oliveira, A.L. An external reference 1H qNMR method (PULCON) for characterization of high purity cocaine seizures. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barantin, L.; Le Pape, A.; Akoka, S. A new method for absolute quantitation MRS metabolites. Magn. Reson. Med. 1997, 38, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akoka, S.; Barantin, L.; Trierweiler, M. Concentration Measurement by Proton NMR Using the ERETIC Method. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 2554–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestre, V.; Goupry, S.; Trierweiler, M.; Robins, R.; Akoka, S. Determination of Substrate and Product Concentrations in Lactic Acid Bacterial Fermentations by Proton NMR Using the ERETIC Method. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 1862–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehr, K.; John, B.; Russell, D.; Avizonis, D. Electronic Referencing Techniques for Quantitative NMR: Pitfalls and How To Avoid Them Using Amplitude-Corrected Referencing through Signal Injection. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 8320–8323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrant, R.D.; Hollerton, J.C.; Lynn, S.M.; Provera, S.; Sidebottom, P.J.; Upton, R.J. NMR quantification using an artificial signal. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2010, 48, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Kolpak, M.X.; Wu, J.; Leo, G.C. Automatic Analysis of Quantitative NMR Data of Pharmaceutical Compound Libraries. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 6914–6918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, M.A.; Sykora, S.; Peng, C.; Barba, A.; Cobas, C. Optimization and Automation of Quantitative NMR Data Extraction. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 5778–5786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monakhova, Y.B.; Diehl, B.W.K. Facilitating the performance of qNMR analysisusing automated quantification andresults verification. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2017, 55, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.; Hellriegel, C.; Rueck, A.; Wuethrich, J.; Jenks, P.; Obkircher, M. Method development in quantitative NMR towards metrologically traceable organic certified reference materials used as 31P qNMR standards. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 3115–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Power, J.E.; Foroozandeh, M.; Adams, R.W.; Nilsson, M.; Coombes, S.R.; Phillips, A.R.; Morris, G.A. Increasing the quantitative bandwidth of NMR measurements. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 2916–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhinderwala, F.; Evans, P.; Jones, K.; Laws, B.R.; Smith, T.G.; Morton, M.; Powers, R. Phosphorus NMR and Its Application to Metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 9536–9545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattes, A.O.; Russell, D.; Tishchenko, E.; Liu, Y.; Cichewicz, R.H.; Robinson, S.J. Application of 19F quantitative NMR to pharmaceutical analysis. Concepts Magn. Reson. Part A 2016, 45A, e21422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, T.; Saito, T.; Ihara, T. A new approach for accurate quantitative determination using fluorine nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Chem. Metrol. 2017, 11, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, A.; Raza, M.; Melanson, J.E. Metrologically traceable quantification of trifluoroacetic acid content in peptide reference materials by 19F solid-state NMR. Metrologia 2019, 56, 024002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, C.; Hemmann, F. EASY: A simple tool for simultaneously removing background, deadtime and acoustic ringing in quantitative NMR spectroscopy—Part I: Basic principle and applications. Solid State Nucl. Magn. Reson. 2014, 57–58, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeger, C.; Hemmann, F. “EASY: A simple tool for simultaneously removing background, deadtime and acoustic ringing in quantitative NMR spectroscopy. Part II: Improved ringing suppression, application to quadrupolar nuclei, cross polarisation and 2D NMR”. Solid State Nucl. Magn. Reson. 2014, 63–64, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godejohann, M.; Preiss, A.; Mügge, C. Quantitative Measurements in Continuous-Flow HPLC/NMR. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Iwasawa, R.; Ihara, T.; Kinugasa, S.; Nomura, A.; Maeda, T. Evaluation of accuracy for the quantitative analysis using nuclear magnetic resonance as a detector of HPLC. Chromatography 2003, 24, 117–120. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.; Zhang, W.; Dai, X.; Li, N.; Huang, L.; Quan, C.; Li, H.; Yang, Y. High performance liquid chromatography-quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance (HPLC-qNMR) with a two-signal suppression method for purity assessment of avermectin B1a. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 4482–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, T.; Li, H.; Dai, X.; Quan, C.; He, Y. Determination of avermectins by the internal standard recovery correction - high performance liquid chromatography - quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance method. Talanta 2017, 172, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, W.; Huang, T.; He, Y.; Li, H.; Su, P.; Yang, Y. Purity determination of pyributicarb by internal standard correction–high-performance liquid chromatography–quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 6983–6993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, N.; Kitamaki, Y.; Otsuka, S.; Yamanaka, N.; Nishizaki, Y.; Sugimoto, N.; Imura, H.; Ihara, T. Extended internal standard method for quantitative 1H NMR assisted by chromatography (EIC) for analyte overlapping impurity on 1H NMR spectra. Talanta 2018, 184, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkinen, S.; Toikka, M.M.; Karhunen, P.T.; Kilpeläinen, I.A. Quantitative 2D HSQC (Q-HSQC) via Suppression of J-Dependence of Polarization Transfer in NMR Spectroscopy: Application to Wood Lignin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 4362–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, D.J.; Loening, N.M. QQ-HSQC: A quick, quantitative heteronuclear correlation experiment for NMR spectroscopy. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2007, 45, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskela, H.; Kilpeläinen, I.; Heikkinen, S.J. Some aspects of quantitative 2D NMR. Magn. Reson. 2005, 174, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskela, H.; Heikkilä, O.; Kilpeläinen, I.; Heikkinen, S.J. Quantitative two-dimensional HSQC experiment for high magnetic field NMR spectrometers. Magn. Reson. 2010, 202, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Westler, W.M.; Markley, J.L. Simultaneous Quantification and Identification of Individual Chemicals in Metabolite Mixtures by Two-Dimensional Extrapolated Time-Zero 1H−13C HSQC (HSQC0). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 1662–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Ellinger, J.J.; Chylla, R.A.; Markley, J.L. Measurement of Absolute Concentrations of Individual Compounds in Metabolite Mixtures by Gradient-Selective Time-Zero 1H−13C HSQC with Two Concentration References and Fast Maximum Likelihood Reconstruction Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 9352–9360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, R.K.; Tripathi, P.; Sinha, N. Quantification of Metabolites from Two-Dimensional Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy: Application to Human Urine Samples. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 10232–10238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gronwald, W.; Klein, M.S.; Kaspar, H.; Fagerer, S.R.; Nurnberger, N.; Dettmer, K.; Bertsch, T.; Oefner, P.J. Urinary Metabolite Quantification Employing 2D NMR Spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 9288–9297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fardus-Reid, F.; Warren, J.; LeGresley, A. Validating heteronuclear 2D quantitative NMR. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 2013–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, G.; Evrard, B.; de Tullio, P. 2D-Cosy NMR Spectroscopy as a Quantitative Tool in Biological Matrix: Application to Cyclodextrins. AAPS J. 2015, 17, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, M.; Hellriegel, C.; Rück, A.; Sauermoser, R.; Wüthrich, J. Using high-performance quantitative NMR (HP-qNMR®) for certifying traceable and highly accurate purity values of organic reference materials with uncertainties <0.1 %. Accred. Qual. Assur. 2013, 18, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.; Hellriegel, C.; Rueck, A.; Wuethrich, J.; Jenks, P.J. Using high-performance 1H NMR (HP-qNMR®) for the certification of organic reference materials under accreditation guidelines—Describing the overall process with focus on homogeneity and stability assessment. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 93, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westwood, S.; Yamazaki, T.; Huang, T.; Garrido, B.; Ün, I.; Zhang, W.; Martos, G.; Stoppacher, N.; Saito, T.; Wielgosz, R. Development and validation of a suite of standards for the purity assignment of organic compounds by quantitative NMR spectroscopy. Metrologia 2019, 56, 064001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.A.; Waters, J.F.; Toman, B.; Lang, B.E.; Rück, A.; Breitruck, K.; Obkircher, M.; Windust, A.; Lippa, K.A. A New Realization of SI for Organic Chemical Measurement: NIST PS1 Primary Standard for Quantitative NMR (Benzoic Acid). Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 10510–10517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigger, R.; Rück, A.; Hellriegel, C.; Sauermoser, R.; Morf, F.; Breitruck, K.; Obkircher, M.J. Certified reference material for use in 1H, 31P, and 19F quantitative NMR, ensuring traceability to the International System of Units. AOAC Int. 2017, 100, 1365–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, C. Establishment of the purity values of carbohydrate certified reference materials using quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance and mass balance approach. Food Chem. 2014, 153, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Ihara, T.; Miura, T.; Yamada, Y.; Chiba, K. Efficient production of reference materials of hazardous organics using smart calibration by nuclear magnetic resonance. Accred. Qual. Assur. 2011, 16, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josephs, R.D.; Stoppacher, N.; Daireaux, A.; Choteau, T.; Lippa, K.A.; Phinney, K.W.; Westwood, S.; Wielgosz, R.I. State-of-the-art and trends for the SI traceable value assignment of the purity of peptides using the model compound angiotensin I. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 101, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melanson, J.E.; Thibeault, M.-P.; Stocks, B.B.; Leek, D.M.; McRae, G.; Meija, J. Purity assignment for peptide certified reference materials by combining qNMR and LC-MS/MS amino acid analysis results: Application to angiotensin II. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 6719–6731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, T.; Takatsu, A. Quantitative NMR spectroscopy for accurate purity determination of amino acids, and uncertainty evaluation for different signals. Accred. Qual. Assur. 2014, 19, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, P.M.; Ding, J.; Leek, D.M.; Mester, Z.; Robertson, G.; Windust, A.; Meija, J. Determination of chemical purity and isotopic composition of natural and carbon-13-labeled arsenobetaine bromide standards by quantitative 1H-NMR. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 7413–7421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; He, Y.; He, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, J.; Dai, Z.; Ma, S.; Lin, R.J. Application of quantitative 1H NMR for the calibration of protoberberine alkaloid reference standards. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 90, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, J.; Feng, R.; Yu, C.; Wu, X.; Shen, W.; Chen, Y.; Di, B.; Su, M. Quantitative Assessment of the Absolute Purity of Thiopeptcin Reference Standard by 1H-NMR. Anal. Sci. 2018, 34, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Y.; Hu, C.Q. A comparative uncertainty study of the calibration of macrolide antibiotic reference standards using quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance and mass balance methods. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 602, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Ihara, T.; Koike, M.; Kinugasa, S.; Fujimine, Y.; Nose, K.; Hirai, T. A new traceability scheme for the development of international system-traceable persistent organic pollutant reference materials by quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance. Accred. Qual. Assur. 2009, 14, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Analyte | NMR Method | Standard | Comparison Method | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amino acids | 1H qNMR | KHP | [68] | |
| Arsenobetaine bromide | 1H qNMR | Benzoic acid | [69] | |
| Carbohydrates | 1H qNMR | Benzoic acid | Mass balance | [64] |
| Benzoic acid | 1H qNMR | Benzoic acid, 2,2- dimethylpropanedioic acid, dimethyl sulfone, 3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid, maleic acid | Mass balance | [62] |
| Internal standards | 1H qNMR | Benzoic acid, dimethyl sulfone, KHP, maleic acid, nitrobenzoic acid | [59] | |
| Internal standards | 1H qNMR | Benzoic acid, 1,4-bis(trimethylsilyl)benzene, BTFMBA, dimethyl sulfone, DMTP, KHP, maleic acid, | [61] | |
| Internal standards | 1H qNMR 31P qNMR 19F qNMR | Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, benzoic acid, BTFMBA, KHP | [63] | |
| Pesticides | 1H qNMR | 1,4-dichlorobenzne, benzoic acid, dimethyl sulfone, 3-(trimethylsilyl)-1-propanesulfonic acid-d6, and 1,4-bis(trimethylsilyl)benzene-d4 | Differential Scanning Calorimetry | [65] |
| Phosphonoacetic acid, triphenyl phosphate | 1H qNMR | Ammoinum dihydrogen phosphate, benzoic acid, dimethyl terephtalate | [35] | |
| Protoberberine alkaloid | 1H qNMR | KHP | Mass balance | [70] |
| Pharmaceuticals | 1H qNMR PULCON | 3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid | [24] | |
| Thiopeptcin | 1H qNMR | Sulfadoxine | Mass balance | [71] |
| Macrolide antibiotics | 1H qNMR | 1,4-Dinitrobenzene, antracene | Mass balance | [72] |
| Nerve agents | 31P qNMR | Triethyl phosphate | [20] | |
| Persistent organic pollutants | 1H qNMR | Benzoic acid, Dimethyl sulfone | Differential Scanning Calorimetry, GC/FID | [73] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, K.; Myoung, S.; Seo, Y.; Ahn, S. Quantitative NMR as a Versatile Tool for the Reference Material Preparation. Magnetochemistry 2021, 7, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7010015
Choi K, Myoung S, Seo Y, Ahn S. Quantitative NMR as a Versatile Tool for the Reference Material Preparation. Magnetochemistry. 2021; 7(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Kihwan, Sangki Myoung, Yejin Seo, and Sangdoo Ahn. 2021. "Quantitative NMR as a Versatile Tool for the Reference Material Preparation" Magnetochemistry 7, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7010015
APA StyleChoi, K., Myoung, S., Seo, Y., & Ahn, S. (2021). Quantitative NMR as a Versatile Tool for the Reference Material Preparation. Magnetochemistry, 7(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7010015





