Adjusting the Magnetic Properties of ZrO2:Mn Nanocrystals by Changing Hydrothermal Synthesis Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sample Preparation and Experimental Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. XRD and STEM Characterization
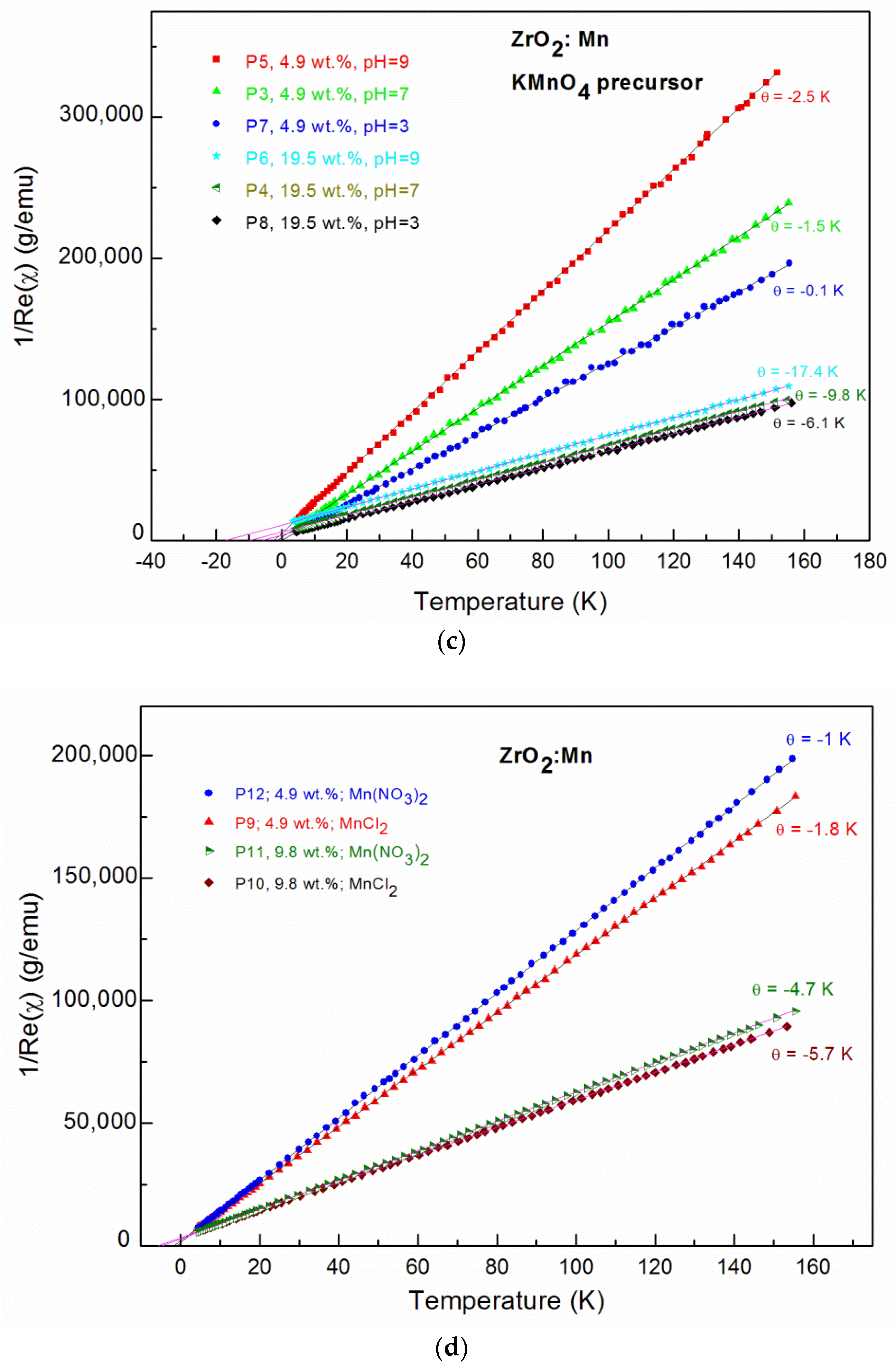
3.2. Magnetic Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yadav, G.D.; Nair, J.J. Sulfated zirconia and its modified versions as promising catalysts for industrial processes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 1999, 33, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.S.; Kim, W.S.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, J.; Lee, H.W.; Lee, J.H. Characterization of ZrO2 codoped with Sc2O3 and CeO2 electrolyte for the application of intermediate temperature SOFCs. Solid State Ion. 2005, 176, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badwal, S.P.S. Stability of Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Components. Solid State Ion. 2001, 143, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, N.Q. Ceramic Fuel Cells. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1993, 76, 563–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, R.H.; Glass, S.J.; Ohuchi, F.S.; Xu, Y.N.; Ching, W.Y. Experimental and theoretical determination of the electronic structure and optical properties of three phases of ZrO2. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 49, 5133–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashima, M.; Hirose, T.; Katano, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Kakihana, M.; Yoshimura, M. Structural changes of ZrO2-CeO2 solid solutions around the monoclinic-tetragonal phase boundary. Phys. Rev. B 1995, 51, 8018–8025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanese, E.; Leccese, M.; Di Valentin, C.; Pacchioni, G. Magnetic properties of nitrogen doped ZrO2: Theoretical evidence of absence of room temperature ferromagnetism. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31435–31445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacquet, G.; Dugas, J.; Escribe, C.; Rouanet, A. The system ZrO2 CaO studied by the electron spin resonance of Mn2+ ions. J. Solid State Chem. 1976, 19, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, C.C.; Bonanos, N.; Horsewell, A.; Linderoth, S. Ageing behaviour of zirconia stabilised by yttria and manganese oxide. J. Mater. Sci. 2001, 36, 4493–4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannink, R.H.J. Microstructural development of sub-eutectoid aged MgO-ZrO2 alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 1983, 18, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zippel, J.; Lorenz, M.; Lenzner, J.; Grundmann, M.; Hammer, T.; Jacquot, A.; Böttner, H. Electrical transport and optical emission of MnxZr1−xO2 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.5) MnxZr1−xO2 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.5) thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 110, 043706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimri, M.C.; Kooskora, H.; Pahapill, J.; Joon, E.; Heinmaa, I.; Subbi, J.; Stern, R. Search for ferromagnetism in manganese-stabilized zirconia. Phys. Status Solidi A 2011, 208, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanakumra, S.; Kamalaveni, J.; Rani, M.P.; Saravanan, R. Solubility of Mn stabilized cubic zirconia nanostructures. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2014, 25, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucci, A.; Clavel, G.; Willinger, M.-G.; Zitoun, D.; Pinna, N. Transition metal-doped ZrO2 and HfO2 nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 12048–12052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearton, S.J.; Heo, W.H.; Ivill, M.; Norton, D.P.; Steiner, T. Dilute magnetic semiconducting oxides. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2004, 19, R59–R74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuryliszyn-Kudelska, I.; Hadžić, B.; Sibera, D.; Romčević, M.; Romčević, N.; Narkiewicz, U.; Dobrowolski, W. Dynamic magnetic properties of ZnO nanocrystals incorporating Fe. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 3756–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuryliszyn-Kudelska, I.; Dobrowolski, W.; Arciszewska, M.; Romčević, N.; Romčević, M.; Hadžić, B.; Sibera, D.; Narkiewicz, U.; Łojkowski, W. Transition metals in ZnO nanocrystals—Magnetic and structural properties. Sci. Sinter. 2013, 45, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, N.H.; Kanoun, M.B.; Goumri-Said, S.; Song, J.-H.; Chikoidze, E.; Dumont, Y.; Ruyter, A.; Kurisu, M. The origin of magnetism in transition metal-doped ZrO2 thin films: Experiment and theory. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2013, 25, 436003–436010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaresan, A.; Bhagavi, R.; Rangarajan, N.; Siddesh, U.; Rao, C.N.R. Ferromagnetism as a universal feature of nanoparticles of the otherwise nonmagnetic oxides. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 74, 161306(R). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, M.; Fitzgerald, C.B.; Coey, J.M.D. Thin films: Unexpected magnetism in a dielectric oxide. Nature 2004, 430, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostanin, S.; Ernst, A.; Sandratskii, L.M.; Bruno, P.; Dane, M.; Dughes, I.D.; Staunton, J.B.; Hergert, W.; Mertig, I.; Kudrnovsky, J. Mn-stabilized zirconia: From imitation diamonds to a new potential high-TC ferromagnetic spintronics material. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 016101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boujnah, M.; Zaari, H.; Benyoussef, A.; El Kenz, A.; Mounkachi, O. Understanding ferromagnetism and optical absorption in 3D transition metal-doped cubic ZrO2 with the modified Becke-Johnson exchange-correlation functional. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 123909–123916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Duan, L.B.; Yang, Y.C.; Rao, G.H. Absence of ferromagnetism in Mn- and Fe-stabilized zirconia nanoparticles. Physica B 2008, 403, 4264–4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavel, G.; Willinger, M.G.; Zioun, D.; Pinna, N. Manganese-doped zirconia nanocrystals. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 6, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.K.; Lejay, P.; Barbara, B.; Boisron, O.; Pailhes, S.; Bouzerar, G. Absence of ferromagnetism in Mn-doped tetragonal zirconia. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 043929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zippel, J.; Lorenz, M.; Setzer, A.; Wagner, G.; Sobolev, N.; Esquinazi, P.; Grundmann, M. Defect-induced ferromagnetism in undoped and Mn-doped zirconia thin films. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 125209–125214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, N.H.; Park, C.K.; Raghavender, A.T.; Ciftja, O.; Bingham, N.S.; Phan, M.H.; Srikanth, H. Room ferromagnetism in monoclinic Mn-doped ZrO2 thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 07C302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Ojha, A.K. Room temperature ferromagnetism in undoped and Mn doped t-ZrO2 nanostructures originated due to oxygen vacancy and effect of Mn doping on its optical properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 169, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuryliszyn-Kudelska, I.; Arciszewska, M.; Małolepszy, A.; Mazurkiewicz, M.; Stobiński, L.; Grabias, A.; Kopcewicz, M.; Paszkowicz, W.; Minikaev, R.; Domukhovski, V.; et al. Influence of Fe doping on magnetic properties of ZrO2 nanocrystals. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 632, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, A.L. The Scherrer Formula for X-ray Particle Size Determination. Phys. Rev. 1939, 56, 978–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschow, K.H.J.; de Boer, F.R. Physics of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials; Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2003; ISBN 978-0-306-48408-7. [Google Scholar]
- Spałek, J.; Lewicki, A.; Tarnawski, Z.; Furdyna, J.K.; Gałązka, R.R.; Obuszko, Z. Magnetic susceptibility of semiconductors: High-temperature regime and the role of superexchang. Phys. Rev. B 1986, 33, 3407–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaj, J.A.; Planel, R.; Fishman, G. Relation of magneto-optical properties of free excitonic to spin alignment of Mn2+ ions in Cd1−xMnxTe. Solid State Commun. 1979, 29, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
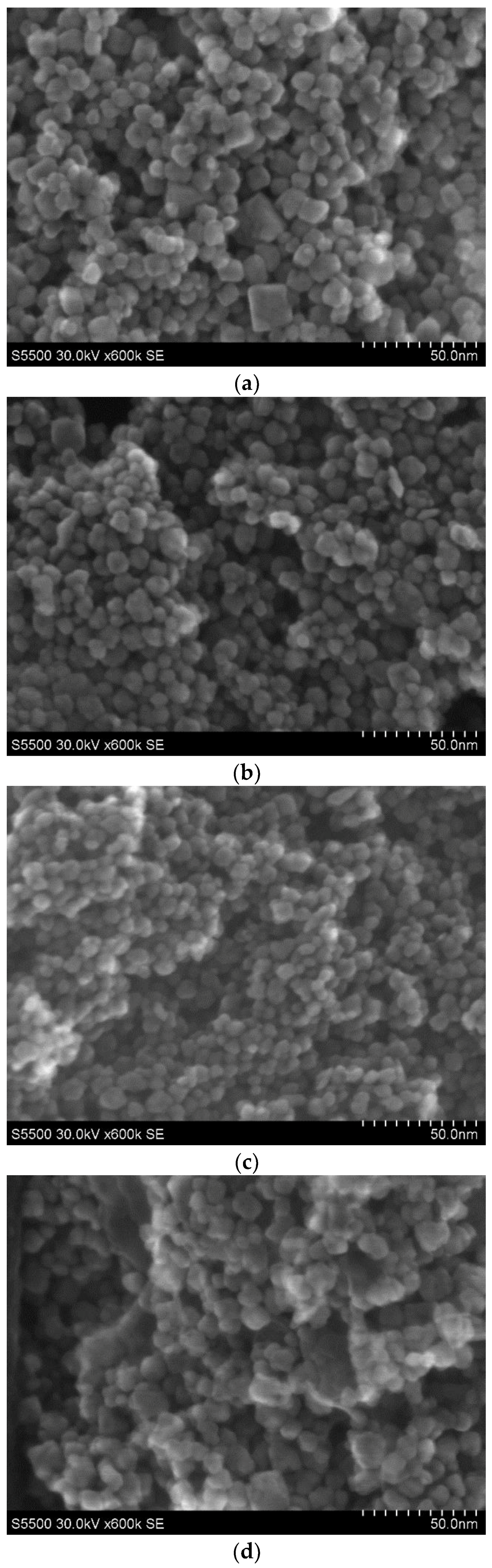
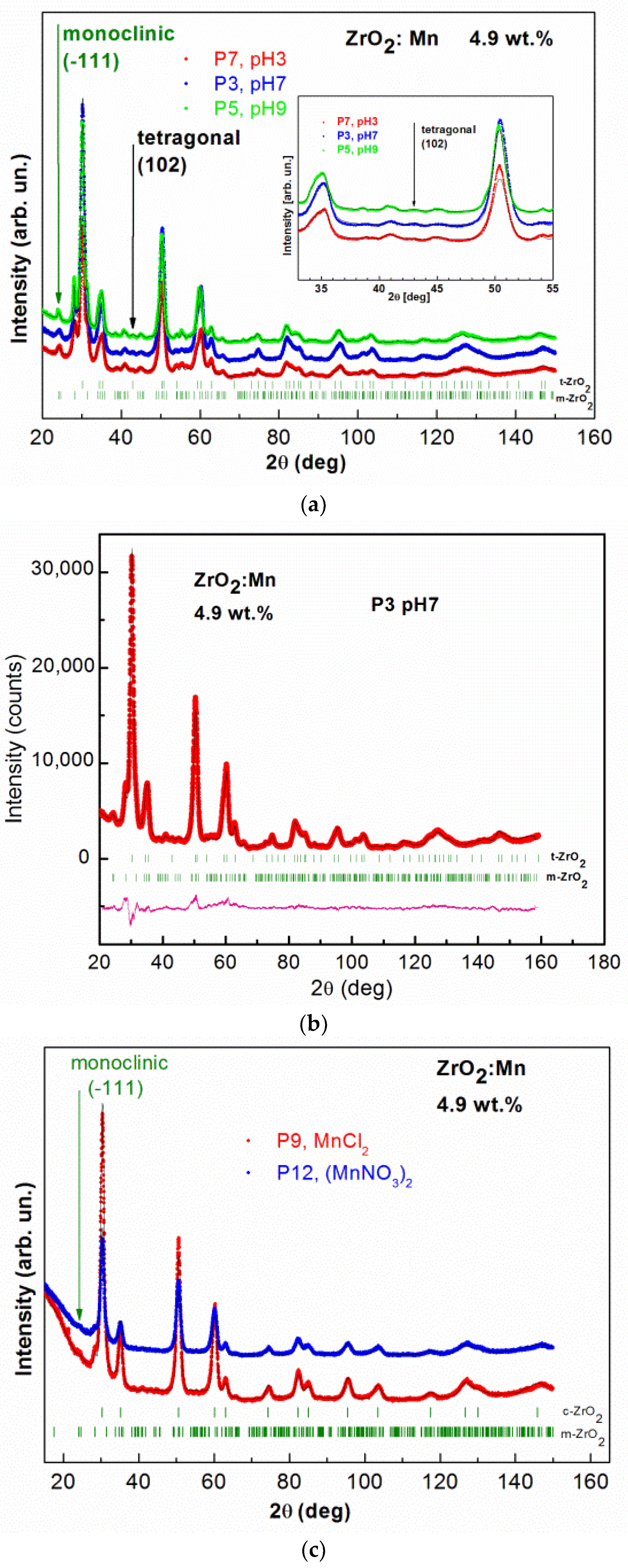
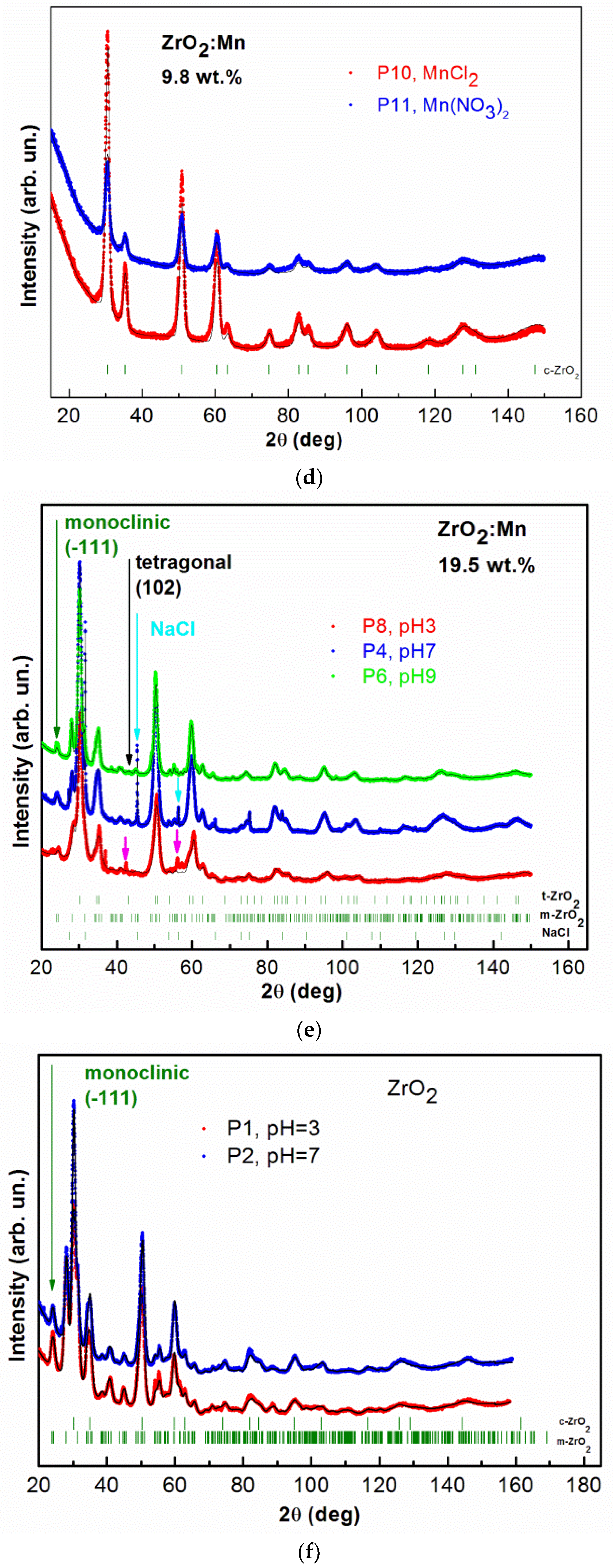

| Sample Name and Precursor | Nominal Content of Mn pH | ZrO2 (Cubic) | ZrO2 (Tetragonal) | ZrO2 (Monoclinic) | NaCl | Additional Phase | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | D (nm) | % | D (nm) | % | D (nm) | % | D (nm) | % | D (nm) | ||
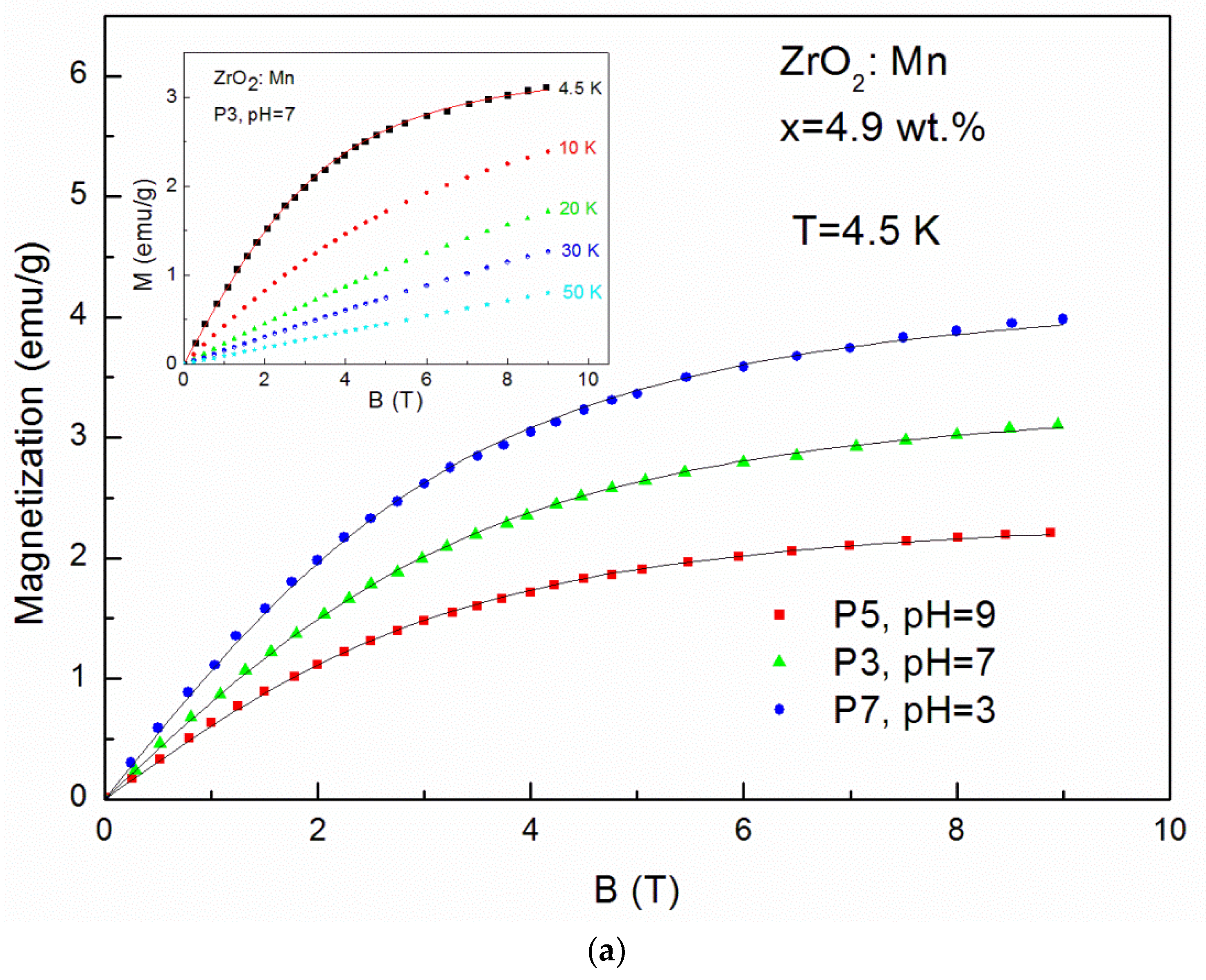
| P7 KMnO4 | 4.9 wt % pH 3 | - | - | 77.2 | 7 | 22.8 | 10.8 | - | - | - | - |
| P3 KMnO4 | 4.9 wt % pH 7 | - | - | 88.9 | 7.1 | 11.1 | 10.1 | - | - | - | - |
| P5 KMnO4 | 4.9 wt % pH 9 | - | - | 87.4 | 7.5 | 12.6 | 17 | - | - | - | - |
| P8 KMnO4 | 19.5 wt % pH 3 | - | - | + | + | + | + | - | - | + | + |
| P4 KMnO4 | 19.5 wt % pH 7 | - | - | 73.5 | 7.3 | 15.1 | 10.8 | 11.4 | + | - | - |
| P6 KMnO4 | 19.5 wt % pH 9 | - | - | 84.8 | 8.1 | 15.2 | 17 | - | - | - | - |
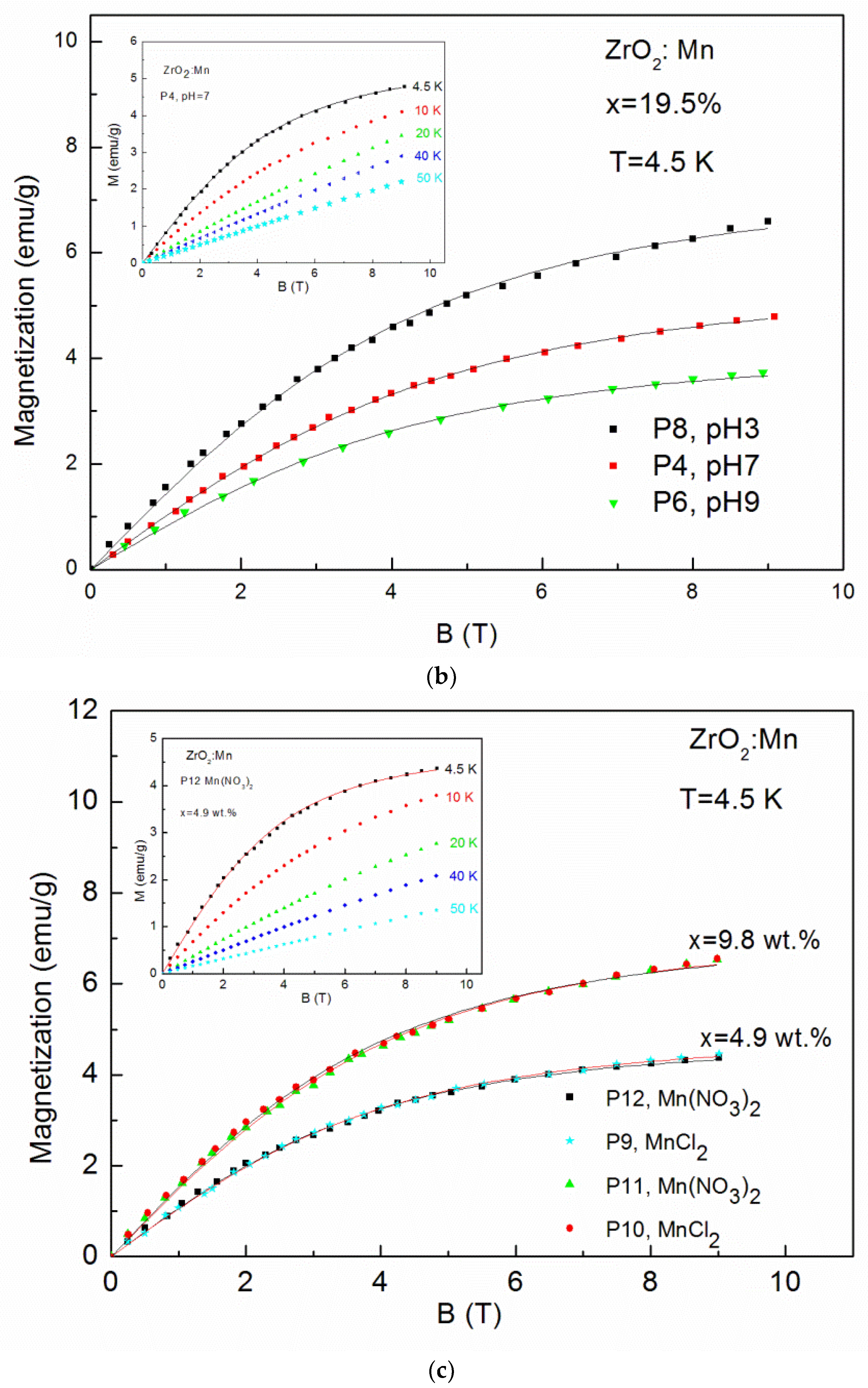
| P9 MnCl2 | 4.9 wt % pH 9 | 95.4 | 7.1 | - | - | 4.6 | + | - | - | - | - |
| P12 Mn(NO3)2 | 4.9 wt % pH 9 | 94.2 | 6.7 | - | - | 5.8 | + | - | - | - | - |
| P10 MnCl2 | 9.8 wt % pH 9 | 100 | 6.6 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| P11 Mn(NO3)2 | 9.8 wt % pH 9 | 100 | 5.8 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| P1 ZrOCl2 | - pH 3 | 50 | 5 | - | - | 50 | 7.3 | - | - | - | - |
| P2 ZrOCl2 | - pH 7 | 64 | 6.1 | - | - | 36 | 8.2 | - | - | - | - |
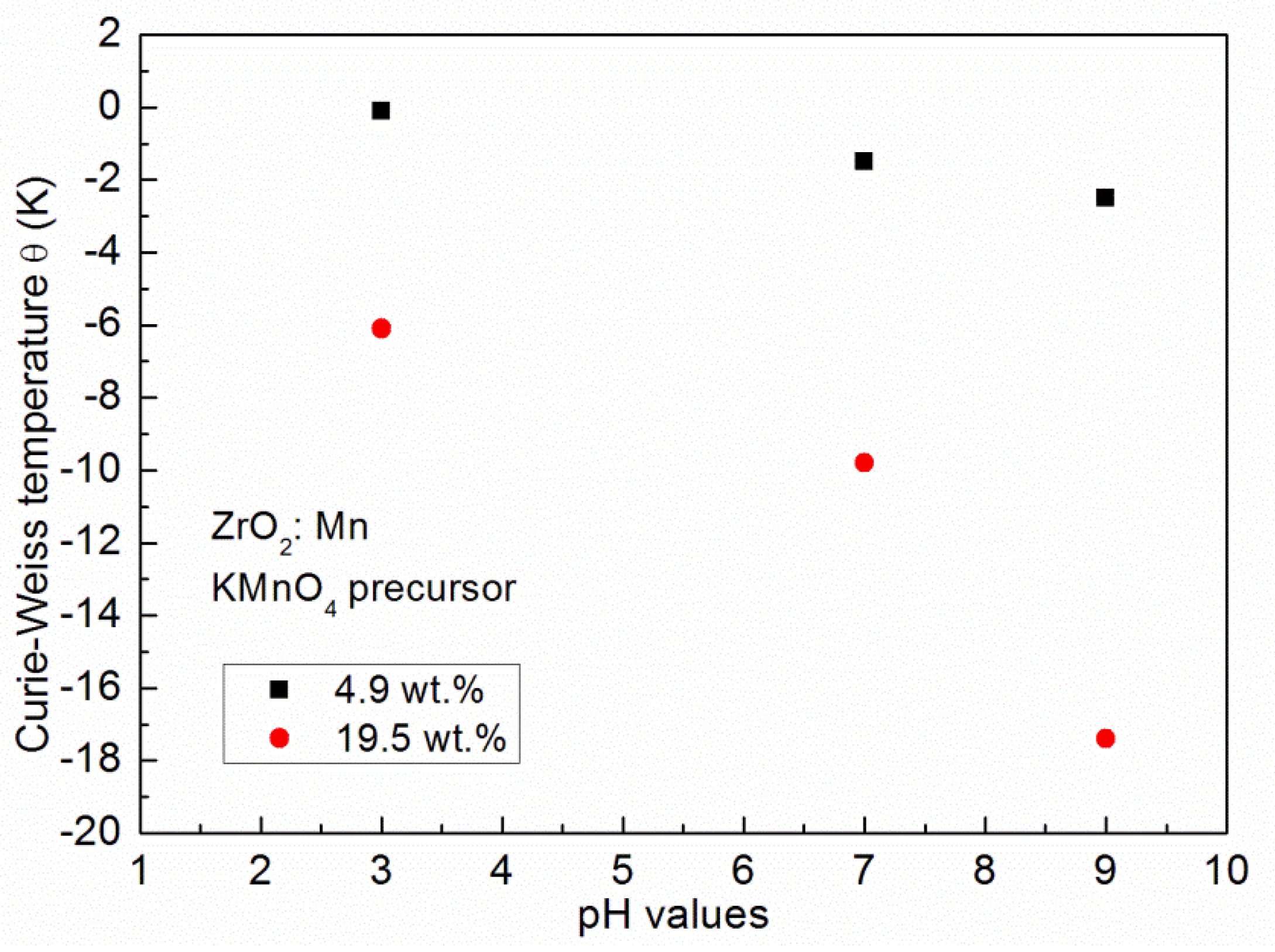
| Sample | θ (K) | C (emuK/g) | x | xeff | Teff (K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P7 4.9 wt % pH 3; KMnO4 | −0.1 | 0.00080 | 0.022 (0.99 wt %) | 0.018 (0.81 wt %) | 1.48 |
| P3 4.9 wt % pH 7; KMnO4 | −1.5 | 0.00066 | 0.018 (0.80 wt %) | 0.015 (0.67 wt %) | 1.77 |
| P5 4.9 wt % pH 9; KMnO4 | −2.5 | 0.00470 | 0.013 (0.58 wt %) | 0.010 (0.45 wt %) | 1.36 |
| P8 19.5 wt % pH 3; KMnO4 | −6.1 | 0.00167 | 0.046 (2.08 wt %) | 0.032 (1.44 wt %) | 3.13 |
| P4 19.5 wt % pH 7; KMnO4 | −9.8 | 0.00164 | 0.045 (2.01 wt %) | 0.024 (1.08 wt %) | 3.71 |
| P6 19.5 wt % pH 9; KMnO4 | −17.4 | 0.00158 | 0.044 (2.00 wt %) | 0.018 (0.81 wt %) | 3.21 |
| P9 4.9 wt % pH 9; MnCl2 | −1.8 | 0.00086 | 0.024 (1.08 wt %) | 0.021 (0.94 wt %) | 2.56 |
| P12 4.9 wt % pH 9; Mn(NO3)2 | −1 | 0.00079 | 0.022 (0.99 wt %) | 0.021 (0.94 wt %) | 2.29 |
| P10 9.8 wt % pH 9; MnCl2 | −5.7 | 0.00178 | 0.049 (2.20 wt %) | 0.031 (1.40 wt %) | 2.58 |
| P11 9.8 wt % pH 9; Mn(NO3)2 | −4.7 | 0.00167 | 0.046 (2.08 wt %) | 0.031 (1.40 wt %) | 2.87 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuryliszyn-Kudelska, I.; Dobrowolski, W.; Arciszewska, M.; Małolepszy, A.; Stobinski, L.; Minikayev, R. Adjusting the Magnetic Properties of ZrO2:Mn Nanocrystals by Changing Hydrothermal Synthesis Conditions. Magnetochemistry 2018, 4, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry4020028
Kuryliszyn-Kudelska I, Dobrowolski W, Arciszewska M, Małolepszy A, Stobinski L, Minikayev R. Adjusting the Magnetic Properties of ZrO2:Mn Nanocrystals by Changing Hydrothermal Synthesis Conditions. Magnetochemistry. 2018; 4(2):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry4020028
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuryliszyn-Kudelska, Izabela, Witold Dobrowolski, Monika Arciszewska, Artur Małolepszy, Leszek Stobinski, and Roman Minikayev. 2018. "Adjusting the Magnetic Properties of ZrO2:Mn Nanocrystals by Changing Hydrothermal Synthesis Conditions" Magnetochemistry 4, no. 2: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry4020028
APA StyleKuryliszyn-Kudelska, I., Dobrowolski, W., Arciszewska, M., Małolepszy, A., Stobinski, L., & Minikayev, R. (2018). Adjusting the Magnetic Properties of ZrO2:Mn Nanocrystals by Changing Hydrothermal Synthesis Conditions. Magnetochemistry, 4(2), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry4020028






