Magnetic Properties and Coercivity Mechanism of Nanocrystalline Rare-Earth-Free Co74Zr16Mo4Si3B3 Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Phase Distribution and Microstructural Characterization
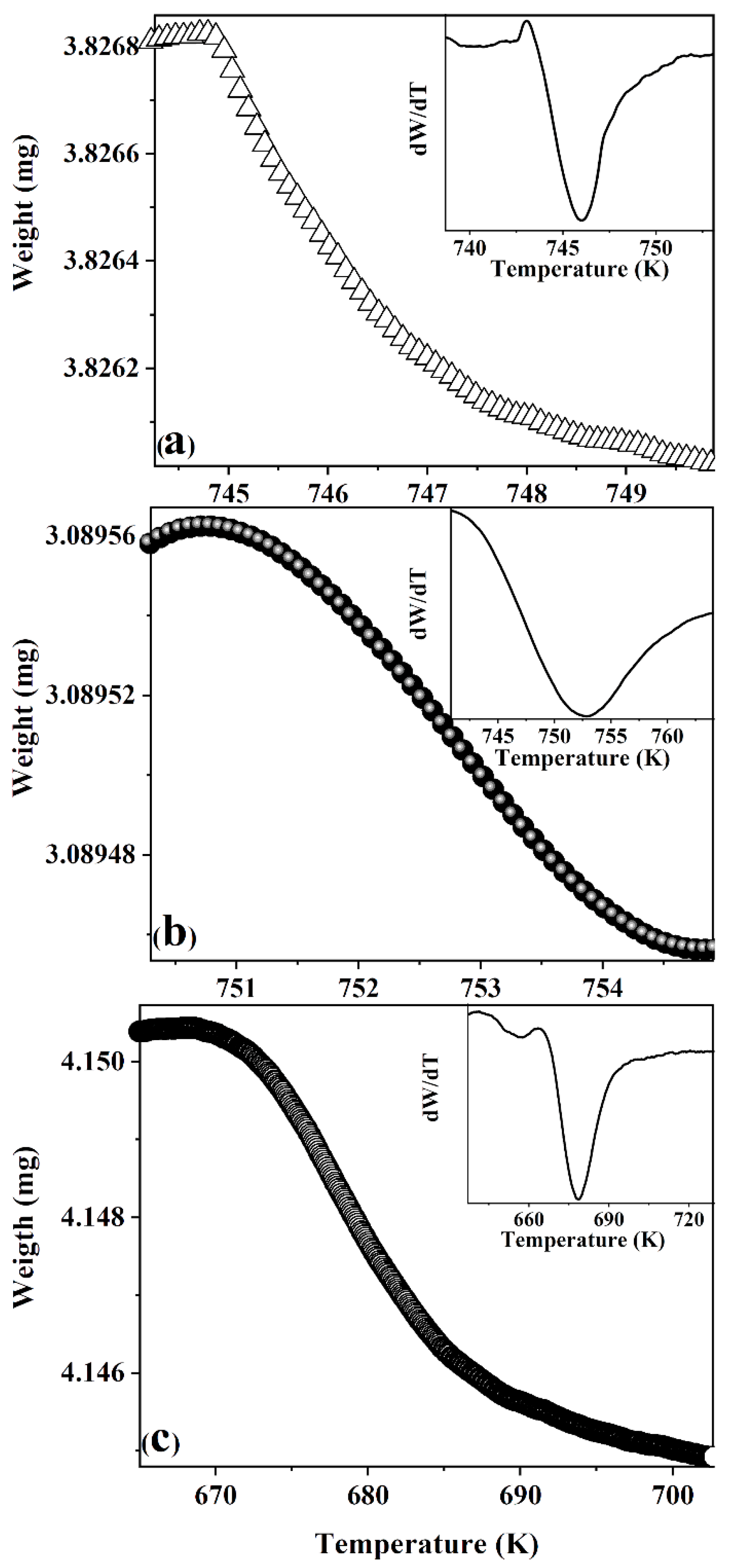
3.2. Magnetic Properties
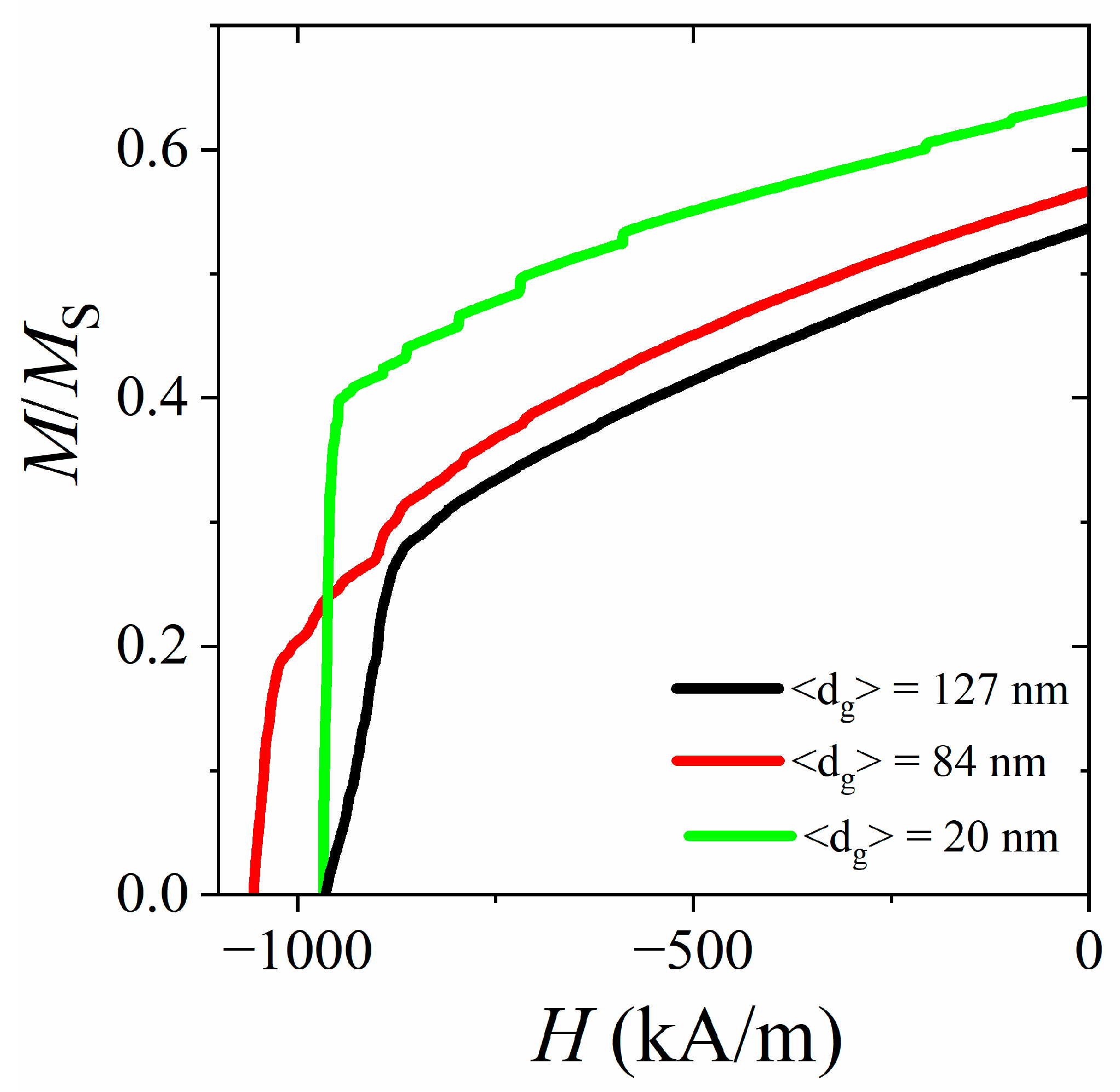
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spaldin, N.A. Magnetic Materials: Fundamentals and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010; pp. 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Madugundo, R.; Venkata, N.; Rao, R.; Schonhobel, A.M.; Salazar, D.; El-gendy, A.A. Recent Developments in Nanostructured Permanent Magnet Materials and Their Processing Methods. In Magnetic Nanostructured Materials; El-Gendy, A.A., Barandiaran, J.M., Hadimani, R.L., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 157–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zijlstra, H. Permanent Magnets Theory. In Handbook of Ferromagnetic Materials; Wohlfarth, E.P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1982; Volume 3, pp. 37–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschow, K.H.J. New permanent magnet materials. Mater. Sci. Rep. 1986, 1, 1–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjipanayis, G.C.; Hazelton, R.C.; Lawless, K.R. New iron-rare-earth based permanent magnet materials. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1983, 43, 797–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croat, J.J.; Herbst, J.F.; Lee, R.W.; Pinkerton, F.E. Pr-Fe and Nd-Fe-based materials: A new class of high-performance permanent magnets (invited). J. Appl. Phys. 1984, 55, 2078–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, J.F.; Croat, J.J. Neodymium-iron-boron permanent magnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1991, 100, 57–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Kramer, M.; Zhou, L.; Liu, F.; Gabay, A.; Hadjipanayis, G.; Balasubramanian, B.; Sellmyer, D. Current progress and future challenges in rare-earth-free permanent magnets. Acta Mater. 2018, 158, 118–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjoka, M.; Psycharis, V.; Devlin, E.; Niarchos, D.; Hadjipanayis, G. Effect of Zr substitution on the structural and magnetic properties of the series Nd1−xZrxFe10Si2 with the ThMn12 type structure. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 687, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołodziej, M.; Grenèche, J.M.; Auguste, S.; Idzikowski, B.; Zubko, M.; Bessais, L.; Śniadecki, Z. Influence of Nd Substitution on the Phase Constitution in (Zr,Ce)Fe10Si2 Alloys with the ThMn12 Structure. Materials 2023, 16, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, A.M.; Han, C.; Ni, C.; Lewis, L.H.; Hadjipanayis, G.C. Effect of vanadium on phase composition and hard magnetic properties of as-solidified and heat-treated Sm–Fe–(Ti,V) alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2025, 627, 173152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhu, M.G. Overview of composition and technique process study on 2:17-type Sm–Co high-temperature permanent magnet. Rare Metals. 2021, 40, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dussa, S.; Joshi, S.S.; Sharma, S.; Krishna, K.V.M.; Radhakrishnan, M.; Dahotre, N.B. Additively Manufactured Alnico Permanent Magnet Materials—A Review. Magnetism 2024, 4, 125–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.U.; Liu, H.; Deng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Khan, A.J.; Li, J.; Yu, X.; Yang, M. Optimization of an isotropic Alnico 8 alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1010, 178142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Debata, M.; Sengupta, P.; Basu, S. L10 FeNi: A promising material for next generation permanent magnets. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2023, 48, 703–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, L.H.; Stamenov, P.S. Accelerating Nature: Induced Atomic Order in Equiatomic FeNi. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2302696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołodziej, M.; Śniadecki, Z. The formation of structural disorder in FeNi-based alloys—Theoretical approach. Mater. Lett. 2022, 326, 132917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, L.H.; Mubarok, A.; Poirier, E.; Bordeaux, N.; Manchanda, P.; Kashyap, A.; Skomski, R.; Goldstein, J.; Pinkerton, F.E.; Mishra, R.K.; et al. Inspired by nature: Investigating tetrataenite for permanent magnet applications. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2014, 26, 064213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kołodziej, M.; Śniadecki, Z.; Musiał, A.; Pierunek, N.; Ivanisenko, Y.; Muszyński, A.; Idzikowski, B. Structural transformations and magnetic properties of plastically deformed FeNi-based alloys synthesized from meteoritic matter. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 502, 166577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varvaro, G.; Imperatori, P.; Laureti, S.; Peddis, D.; Locardi, F.; Ferretti, M.; Cannas, C.; Angotzi, M.S.; Yaacoub, N.; Capobianchi, A. Facile and fast synthesis of highly ordered L10-FeNi nanoparticles. Scr. Mater. 2024, 238, 115754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaud, C. Polymorphisme du composé défini Mn Bi aux températures de disparition et de réapparition de l’aimantation spontanée. J. Phys. Radium. 1951, 12, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Stutius, W.E. The phase transformation and physical properties of the MnBi and Mn1.08Bi compounds. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1974, 10, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, A.J.J.; Hokkeling, P.; vd Steeg, M.G.; De Vos, K.J. New Material for Permanent Magnets on a Base of Mn and Al. J. Appl. Phys. 1960, 31, S75–S77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, D.H.; Yue, M.; Boyer, C.B.; Liu, X.B.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Wang, M.; Altounian, Z. The Magnetic and Crystal Structure of MnxGa (1.15 ≤ x ≤ 1.8) Alloys. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Wan, H.; Hadjipanayis, G.C. High coercivity in non-rare-earth containing alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 1990, 67, 4960–4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, A.M.; Zhang, Y.; Hadjipanayis, G.C. Cobalt-rich magnetic phases in Zr–Co alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2001, 236, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T. Magnetization process in Co-Zr-B permanent-magnet materials. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2004, 40, 2919–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.B.; Sun, Q.W.; Wang, W.Q.; Su, F. Effects of Mo additive on structure and magnetic properties of Co82Zr18 alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 474, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T. High performance Co–Zr–B melt-spun ribbons. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 2305–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Zhang, W.; Kharel, P.R.; Valloppilly, S.R.; Skomski, R.; Sellmyer, D.J. Effect of boron doping on nanostructure and magnetism of rapidly quenched Zr2Co11-based alloys. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 056002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Nguyen, M.C.; Zhang, W.Y.; Wang, C.Z.; Kramer, M.J.; Sellmyer, D.J.; Li, X.Z.; Zhang, F.; Ke, L.Q.; Antropov, V.P.; et al. Exploring the structural complexity of intermetallic compounds by an adaptive genetic algorithm. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 045502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demczyk, B.G.; Cheng, S.F. Structures of Zr2Co11 and HfCo7 intermetallic compounds. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1991, 24, 1023–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, B.; Das, B.; Skomski, R.; Zhang, W.Y.; Sellmyer, D.J. Novel nanostructured rare-earth-free magnetic materials with high energy products. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 6090–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Ohmori, K. Hard Magnetic Phase in Rapidly Quenched Zr-Co-B Alloys. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1990, 26, 1370–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellmyer Publications, D.; Zhang, W.; Valloppilly, S.R.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Michalski, S.A.; Zhang -Lincoln Wenyong Zhang, A.; George, T.A.; Skomski, R.A.; Sellmyer, D.J.; et al. Magnetic hardening of Zr2Co11(Ti, Si) nanomaterials. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 587, 578–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Valloppilly, S.R.; Li, X.; Skomski, R.; Shield, J.E.; Sellmyer, D.J. Coercivity enhancement in Zr2Co11—Based nanocrystalline materials due to Mo addition. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 3603–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, G.V.; Shchegoleva, N.N.; Gabay, A.M. Crystal structure of Zr2Co11 hard magnetic compound. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 432, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.L.; Zhang, W.Y.; Skomski, R.; Valloppilly, S.; Shield, J.E.; Sellmyer, D.J. Phase composition and nanostructure of Zr2Co11-based alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 17A739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Y.; Li, X.Z.; Valloppilly, S.; Skomski, R.; Shield, J.E.; Sellmyer, D.J. Magnetism of rapidly quenched rhombohedral Zr2Co11-based nanocomposites. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2013, 46, 135004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toby, B.H.; Von Dreele, R.B. GSAS-II: The genesis of a modern open-source all purpose crystallography software package. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2013, 46, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidler, J.; Schrefl, T. Micromagnetic modeling: The current state of the art. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2000, 33, R135–R145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Y.; Chang, H.W.; Chiu, C.H.; Chang, C.W.; Chang, W.C. Magnetic properties, phase evolution, and coercivity mechanism of CoxZr98−xB2 (x = 74–86) nanocomposites. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 10F307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Alarcos, V.; Pérez-Landazábal, J.I.; Recarte, V.; Rodríguez-Velamazn, J.A.; Chernenko, V.A. Effect of atomic order on the martensitic and magnetic transformations in Ni–Mn–Ga ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2010, 22, 166001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fdez-Gubieda, M.L.; Garcí A-Arribas, A.; Barandiará, J.M.; Lopez Anton, R.; Orue, I.; Gorria, P.; Pizzini, S.; Fontaine, A. Local structure and ferromagnetic character of Fe-B and Fe-P amorphous alloys. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 62, 5746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayana, C.; Inoue, A. Metallic Glasses. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinhem, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herlach, D.M. Metastable Solids from Undercooled Melts. Mater. Sci. Forum 2007, 539–543, 1977–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, J.W. The Theory of Transformations in Metals and Alloys; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Y.; Li, X.Z.; Valloppilly, S.; Skomski, R.; Sellmyer, D.J. Effect of annealing on nanostructure and magnetic properties of Zr2Co11 material. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2014, 186, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLaren, J.M.; Schulthess, T.C.; Butler, W.H.; Sutton, R.; McHenry, M. Electronic structure, exchange interactions, and Curie temperature of FeCo. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 85, 4833–4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksymowicz, A.Z. Curie temperature and short-range atomic order in amorphous ferromagnets. Phys. Status Solidi (b) 1982, 114, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinora, T. The Effect of Atomic Ordering on the Magnetic Properties of Fe-Al Alloys. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1964, 19, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorria, P.; Martínez-Blanco, D.; Pérez, M.J.; Blanco, J.A.; Hernando, A.; Laguna-Marco, M.A.; Haskel, D.; Souza-Neto, N.; Smith, R.I.; Marshall, W.G.; et al. Stress-induced large Curie temperature enhancement in Fe64Ni36 Invar alloy. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 80, 064421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jekal, S. Exchange Interactions and Curie Temperature of Ce-Substituted SmCo5. Condens. Matter 2019, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagawa, M.; Hiraga, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Matsuura, Y. Permanent magnet materials based on the rare earth-iron-boron tetragonal compounds. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1984, 20, 1584–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vial, F.; Joly, F.; Nevalainen, E.; Sagawa, M.; Hiraga, K.; Park, K.T. Improvement of coercivity of sintered NdFeB permanent magnets by heat treatment. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2002, 242–245, 1329–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancourt, I.; Davies, H.A. Exchange coupled nanocomposite hard magnetic alloys. Int. J. Mater. Eng. Tech. 2009, 1, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coey, J.M.D.; Stuart, S.S. Handbook of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials: Volume 1,2.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 53–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotopoulos, I.; Withanawasam, L.; Hadjipanayis, G.C. ‘Exchange spring’ behavior in nanocomposite hard magnetic materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1996, 152, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Shivakumara, C.; Anil Kumar, P.S. Observation of the exchange spring behavior in hard–soft-ferrite nanocomposite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, L11–L14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullerton, E.E.; Jiang, J.S.; Bader, S.D. Hard/soft magnetic heterostructures: Model exchange-spring magnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 200, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronmüller, H.; Fähnle, M. Micromagnetism and the Microstructure of Ferromagnetic Solids; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kronmüller, H. Micromagnetic Background of Hard Magnetic Materials. In Supermagnets, Hard Magnetic Materials; NATO Science Series C:ASIC; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1991; Volume 331, pp. 461–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goll, D.; Seeger, M.; Kronmüller, H. Magnetic and microstructural properties of nanocrystalline exchange coupled PrFeB permanent magnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1998, 185, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
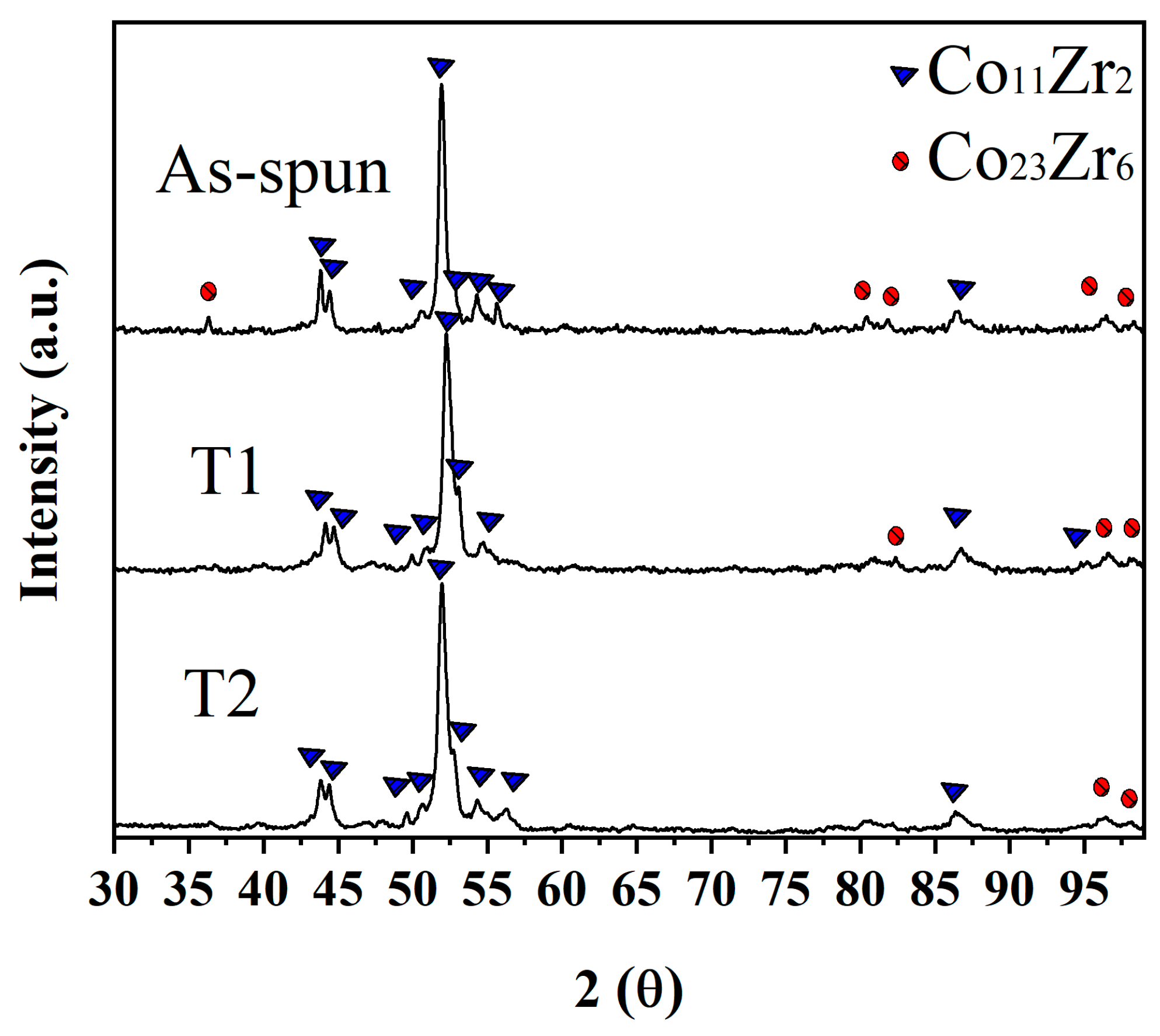


| Processing Conditions | Phase (wt.%) | a (Å) | c (Å) | V (Å3) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co11Zr2 | Co23Zr6 | Co11Zr2 | Co23Zr6 | Co11Zr2 | Co11Zr2 | Co23Zr6 | |
| As-spun | 84.2 | 15.8 | 4.752 ± 0.0027 | 11.4671 ± 0.0019 | 23.8695 ± 0.0039 | 466.9 ± 0.24 | 1507.8 ± 0.23 |
| T1 (903 K, 90 min) | 91.6 | 8.4 | 4.7152 ± 0.0013 | 11.5415 ± 0.0028 | 24.0266 ± 0.0038 | 462.6 ± 0.14 | 1537.4 ± 0.19 |
| T2 (903 K, 180 min) | 92.4 | 7.6 | 4.7494 ± 0.0023 | 11.5802 ± 0.0017 | 24.0324 ± 0.0058 | 469.4 ± 0.24 | 1552.9 ± 0.13 |
| Processing Conditions | Hc (kA/m) | μ0Mmax (T) | μ0Mr (T) | Mmax/Mr | TC (K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As-spun | 477 | 0.18 | 0.10 | 0.55 | 746 |
| T1 | 557 | 0.30 | 0.17 | 0.56 | 751 |
| T2 | 581 | 0.20 | 0.12 | 0.60 | 676 |
| Mean Grain Size (nm) | Hc (kA/m) | μ0Mmax (T) | μ0Mr (T) | Mr/Ms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 127 ± 24 | 971 | 0.35 | 0.25 | 0.54 |
| 85 ± 20 | 1050 | 0.36 | 0.26 | 0.56 |
| 20 ± 5 | 964 | 0.38 | 0.30 | 0.64 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miranda, A.; Betancourt, I. Magnetic Properties and Coercivity Mechanism of Nanocrystalline Rare-Earth-Free Co74Zr16Mo4Si3B3 Alloys. Magnetochemistry 2025, 11, 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11090078
Miranda A, Betancourt I. Magnetic Properties and Coercivity Mechanism of Nanocrystalline Rare-Earth-Free Co74Zr16Mo4Si3B3 Alloys. Magnetochemistry. 2025; 11(9):78. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11090078
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiranda, Aida, and Israel Betancourt. 2025. "Magnetic Properties and Coercivity Mechanism of Nanocrystalline Rare-Earth-Free Co74Zr16Mo4Si3B3 Alloys" Magnetochemistry 11, no. 9: 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11090078
APA StyleMiranda, A., & Betancourt, I. (2025). Magnetic Properties and Coercivity Mechanism of Nanocrystalline Rare-Earth-Free Co74Zr16Mo4Si3B3 Alloys. Magnetochemistry, 11(9), 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11090078






