Superparamagnetism of Baked Clays Containing Polymorphs of Iron Oxides: Experimental Study and Theoretical Modeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental and Theoretical Methods
3. Experimental Results
3.1. Structure-Phase Composition: Results and Interpretation
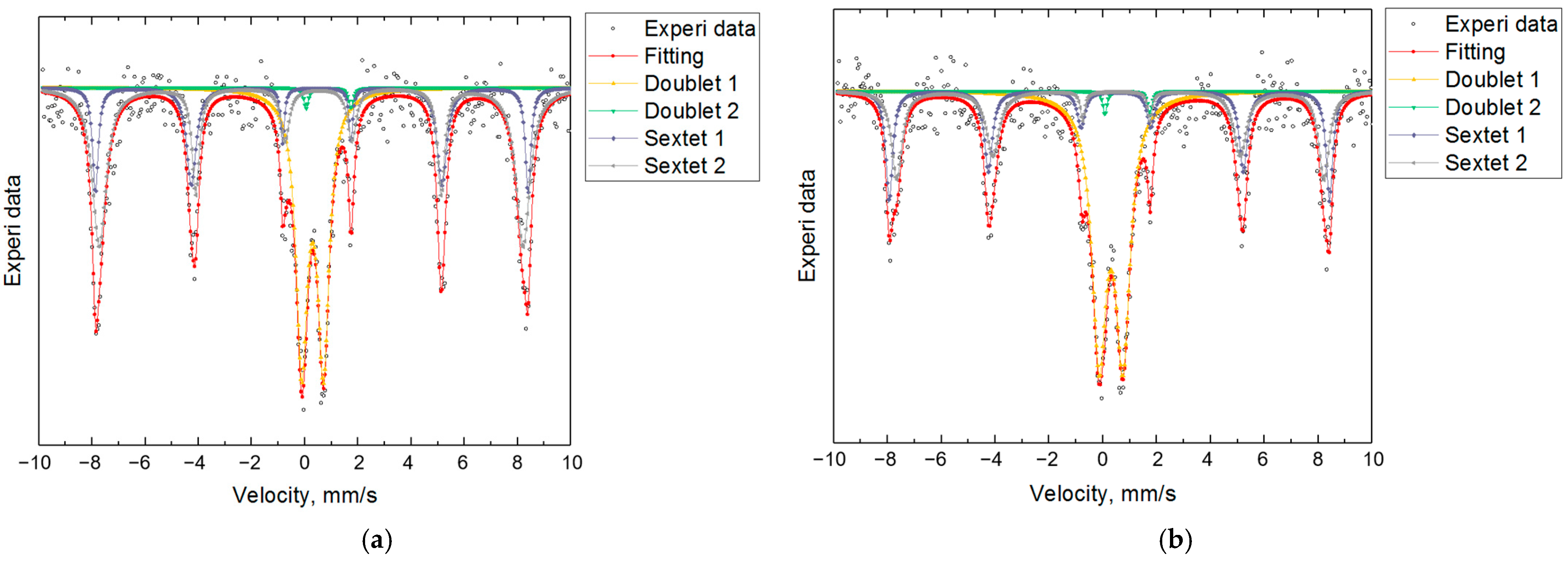
3.2. Mössbauer Spectroscopy: Fe Valence and Magnetic Ordering
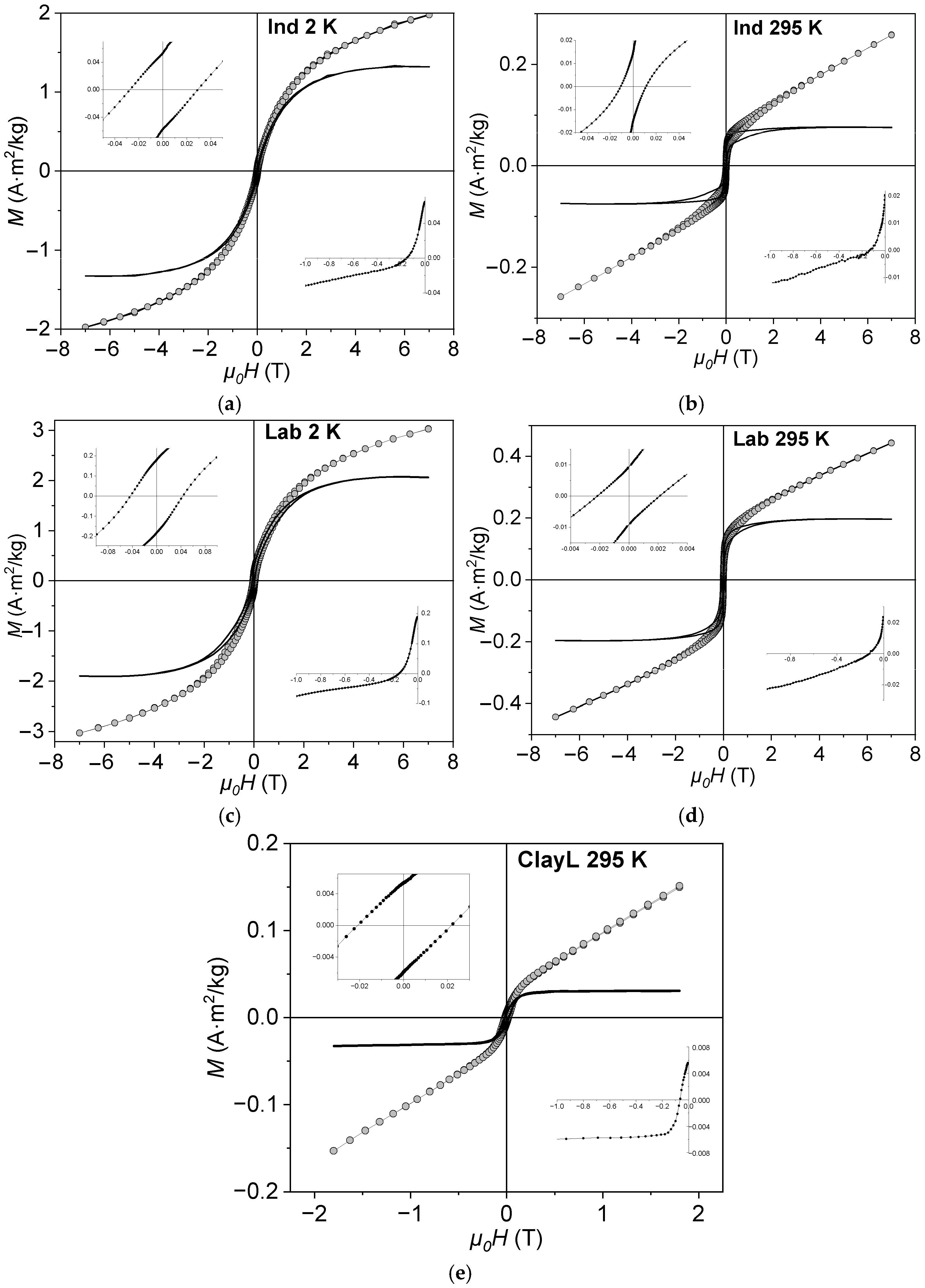
3.3. Field Dependencies of Magnetization
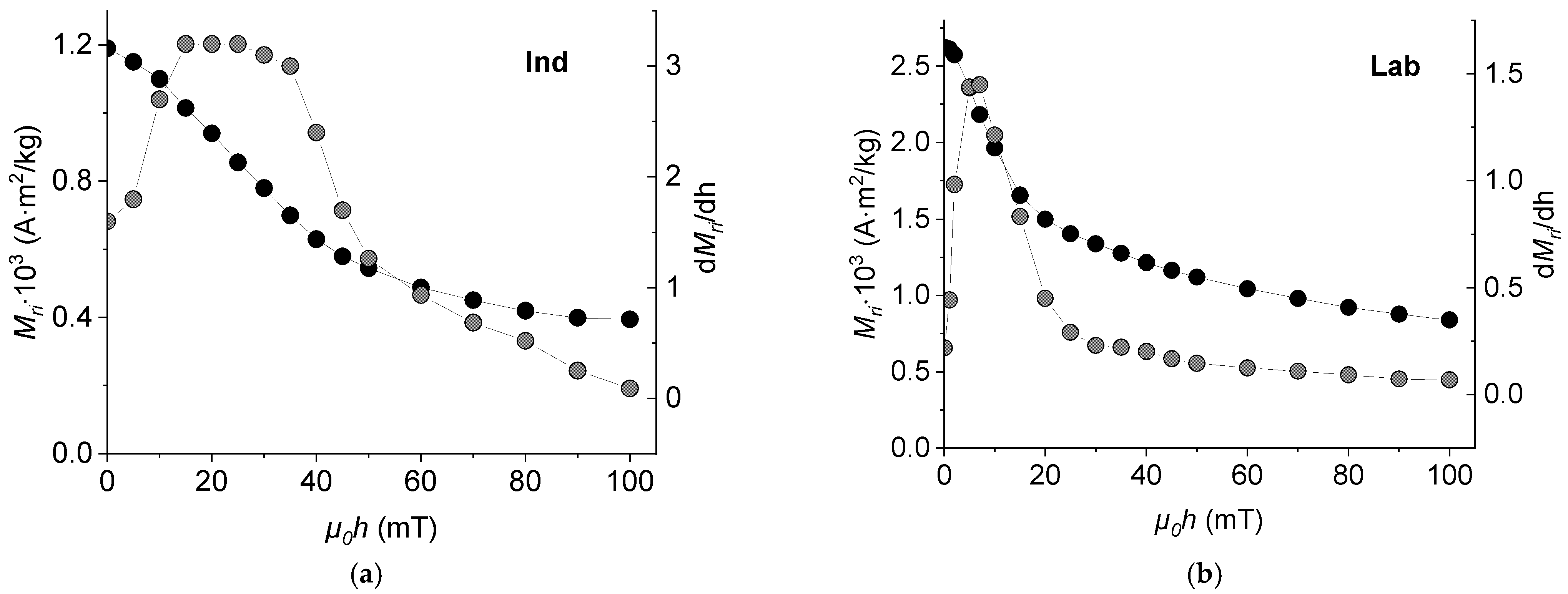
3.4. Coercivity Spectra and Remanent Magnetization
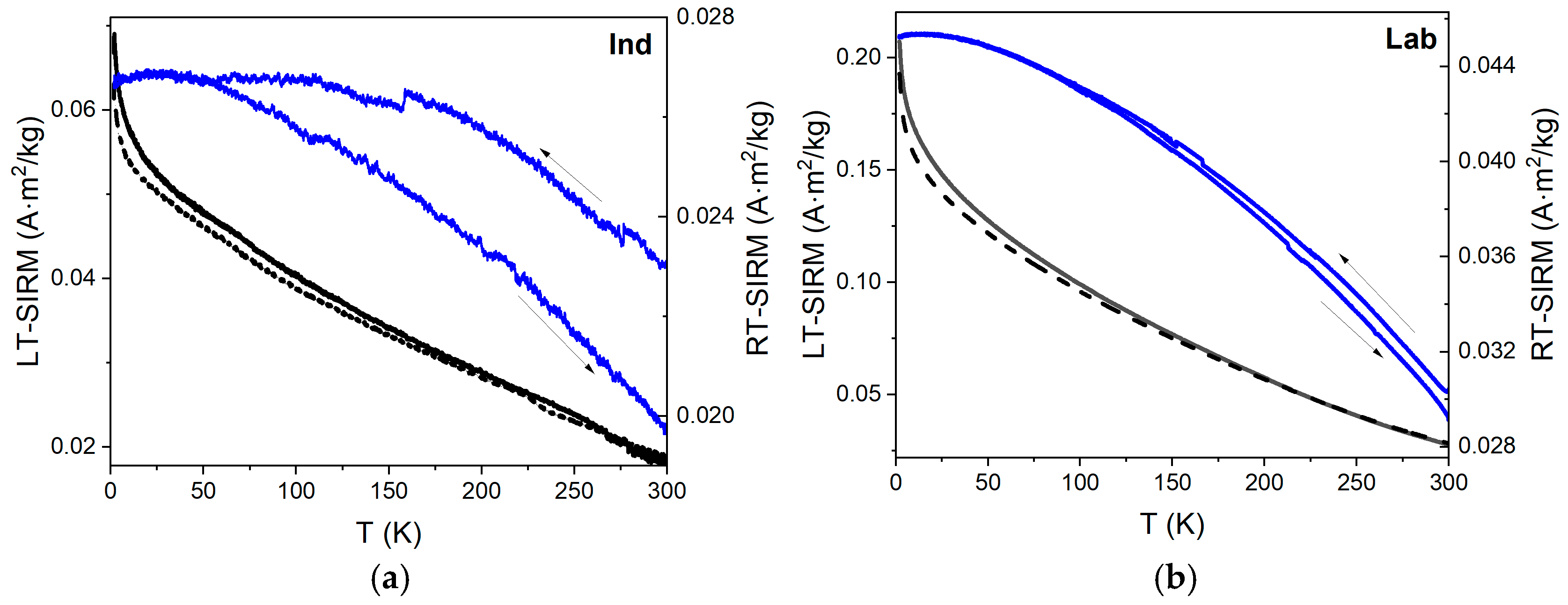
3.5. Low-Temperature Magnetization
3.6. Impulse and Frequency Characteristics of Susceptibility
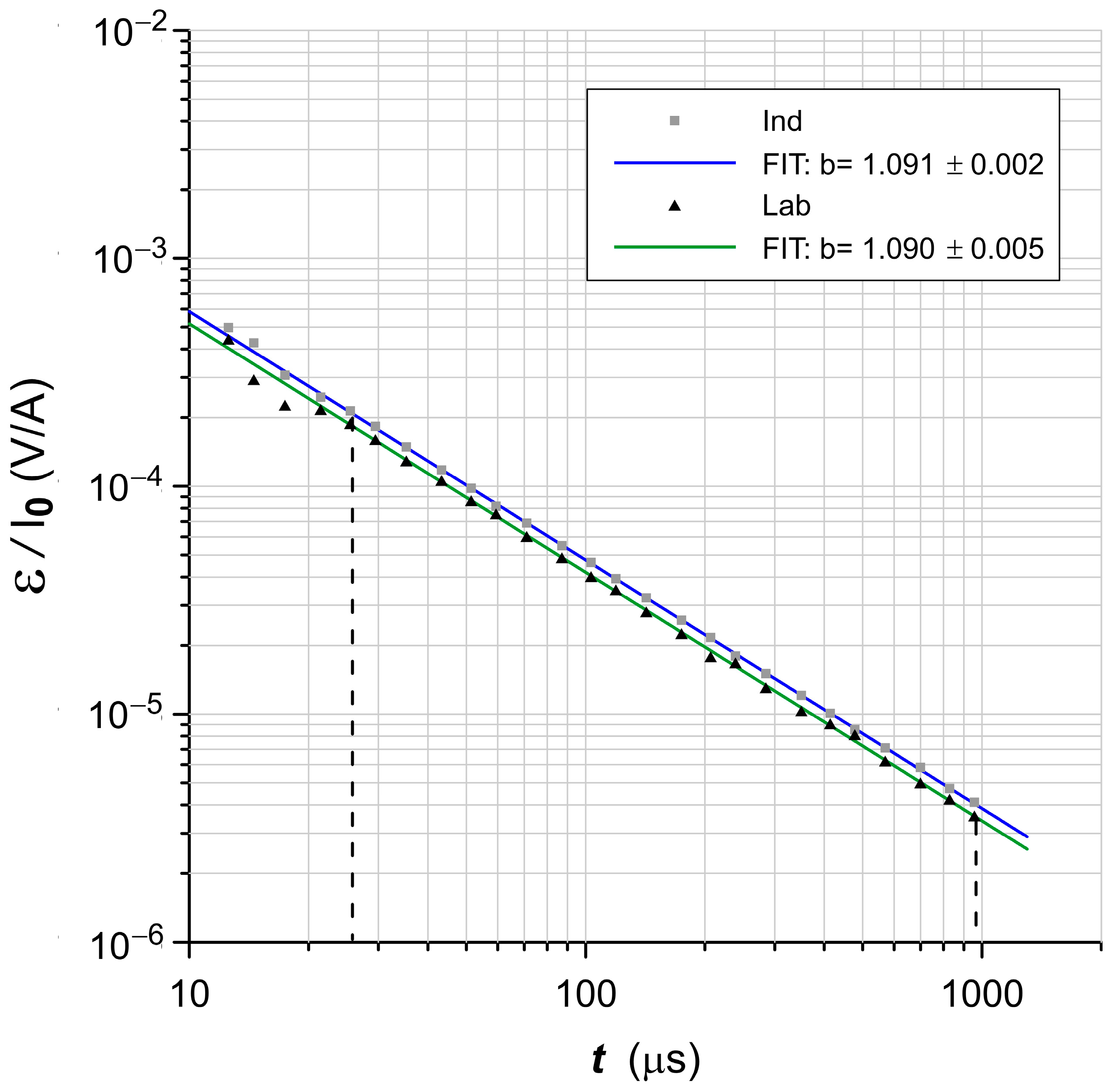
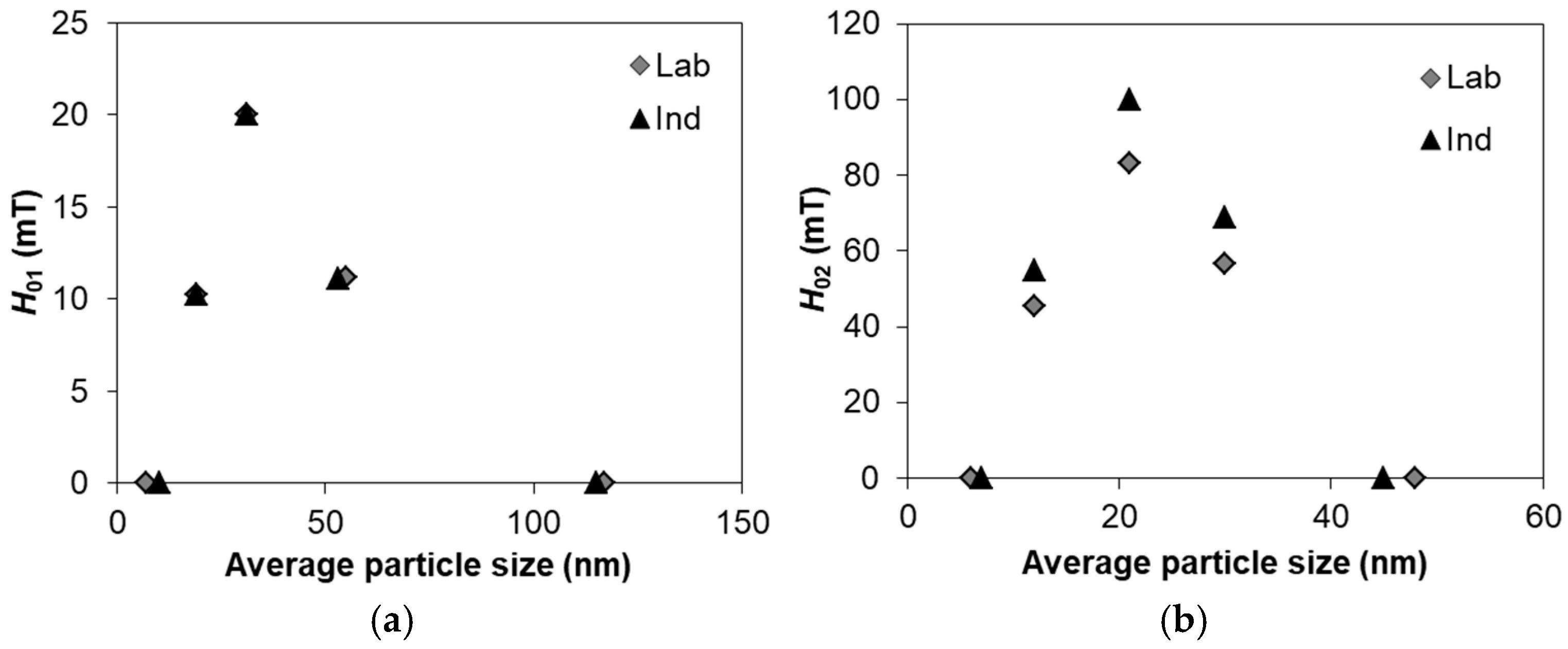
3.6.1. Impulse Characteristics
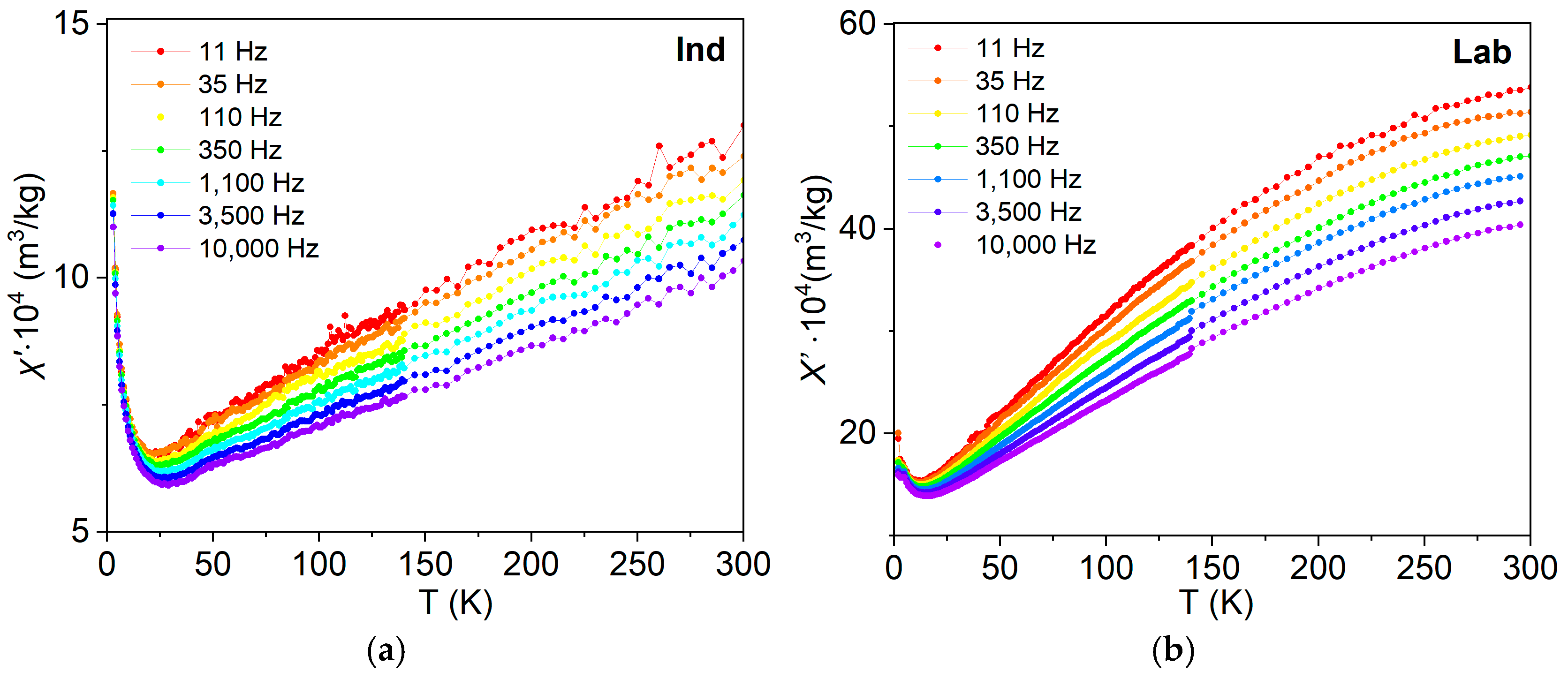
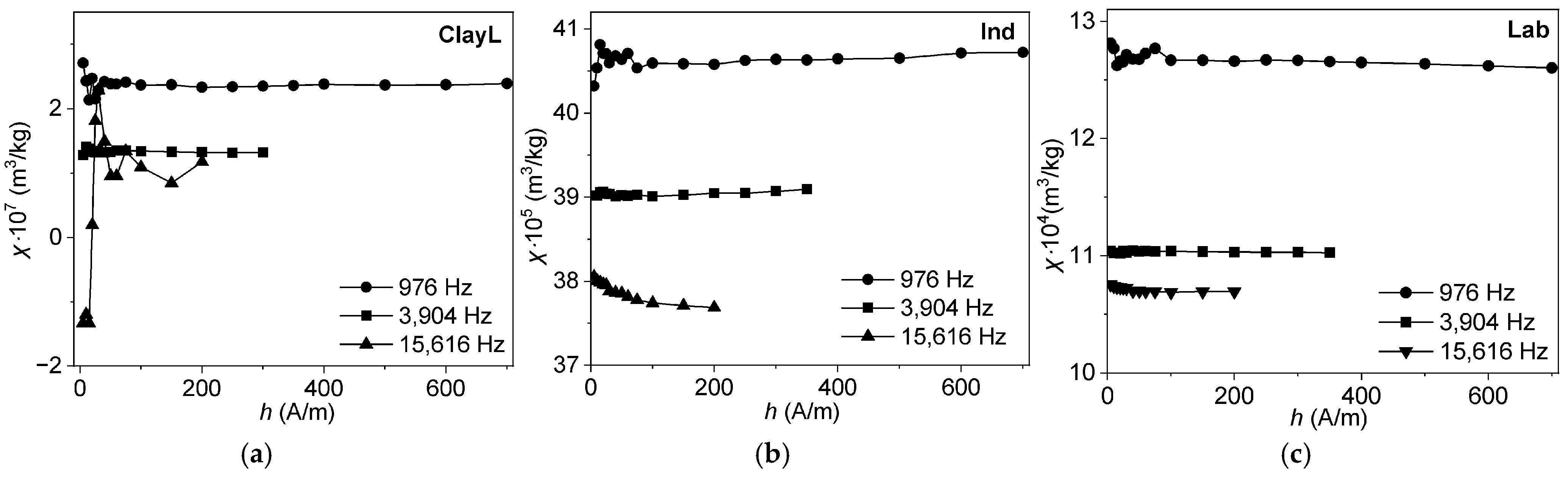
3.6.2. Frequency–Temperature and Frequency–Field Dependencies of Magnetic Susceptibility
3.7. FD Factor and SP Contributions
4. Discussion of the Experimental Results
4.1. Structure-Phase Basis of Magnetic Microheterogeneity
4.2. Magnetic Parameters as Indicators of a Multicomponent Ensemble of Particles
4.3. Temperature Dependencies of ARM and IRM Coercivity
4.4. Low-Temperature Magnetic Behavior
4.5. Frequency-Dependent and Transient Susceptibility Signatures of SP Particles
5. Theoretical Modeling
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rancourt, D.G. Magnetism of Earth, Planetary, and Environmental Nanomaterials. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2001, 44, 217–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.E.; Heller, F. Environmental Magnetism: Principles and Applications of Enviromagnetics; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2003; ISBN 0122438515. [Google Scholar]
- Jordanova, N. Soil Magnetism: Applications in Pedology, Environmental Science and Agriculture; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; ISBN 0128092394. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, C.; Thompson, R. Supermagnetic Enhancement, Superparamagnetism, and Archaeological Soils. Geoarchaeology-An Int. J. 1999, 14, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Li, G.; Liu, M.; Ge, W.; Wu, G.; Zhan, C. The Firing Temperatures of Burnt Clay from the Chinese Neolithic Cultural Relics and Its Paleoenvironmental Imprints. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordanova, N.; Jordanova, D.; Kostadinova-Avramova, M. Synergy of Environmental Magnetism and Archaeomagnetism for the Benefit of Archaeology—State of the Art in Bulgaria. In World Archaeo-Geophysics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, B.A. Palaeoclimatic Records of the Loess/Palaeosol Sequences of the Chinese Loess Plateau. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2016, 154, 23–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermenidou, M.; Balcells, L.; Martinez-Boubeta, C.; Chatziavramidis, A.; Konstantinidis, I.; Samaras, T.; Sarigiannis, D.; Simeonidis, K. Magnetic Nanoparticles: An Indicator of Health Risks Related to Anthropogenic Airborne Particulate Matter. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 116309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Néel, L. Théorie Du Traînage Magnétique Des Ferromagnétiques En Grains Fins Avec Application Aux Terres Cuites. Ann. Geophys. 1949, 5, 99–136. [Google Scholar]
- Kharitonskiǐ, P.V. Magnetostatic Interaction of Superparamagnetic Particles Dispersed in a Thin Layer. Phys. Solid State 1997, 39, 162–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharitonskii, P.V.; Gareev, K.G.; Ionin, S.A.; Ryzhov, V.A.; Bogachev, Y.V.; Klimenkov, B.D.; Kononova, I.E.; Moshnikov, V.A. Microstructure and Magnetic State of Fe3O4-SiO2 Colloidal Particles. J. Magn. 2015, 20, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsukov, P.; Soupios, P.; Gorokhovich, Y. Application of Special SPM Loop in Archaeological Prospection. In Proceedings of the 20th International Geophysical Congress and Exhibition of Turkey, Antalya, Turkey, 25–27 November 2013; pp. 90–93. [Google Scholar]
- Kozhevnikov, N.O.; Antonov, E.Y. Aftereffects in the Transient Electromagnetic Method: Magnetic Viscosity. Russ. Geol. Geophys. 2022, 63, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, D.C.; Song, L.P.; Oldenburg, D.W. Transient VRM Response From a Large Circular Loop Over a Conductive and Magnetically Viscous Half-Space. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 3669–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsukov, P.O.; Fainberg, E.B. Study of the Environment by the Transient Electromagnetic Method Using the Induced Polarization and Superparamagnetic Effects. Izv. Phys. Solid Earth 2002, 38, 981–984. [Google Scholar]
- Thiesson, J.; Tabbagh, A.; Flageul, S. TDEM Magnetic Viscosity Prospecting Using a Slingram Coil Configuration. Near Surf. Geophys. 2007, 5, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeill, J.D. The Magnetic Susceptibility of Soils Is Definitely Complex; Technical Note TN-36; Geonix Limited: London, UK, 2013; 27p. [Google Scholar]
- Finco, C.; Rejiba, F.; Schamper, C.; Cavalcante Fraga, L.H.; Wang, A. Calibration of near-surface multi-frequency electromagnetic induction data. Geophys. Prospect. 2023, 71, 765–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozhevnikov, N.O.; Kharinsky, A.V.; Kozhevnikov, O.K. An Accidental Geophysical Discovery of an Iron Age Archaeological Site on the Western Shore of Lake Baikal. J. Appl. Geophys. 2001, 47, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faivre, D. Iron Oxides: From Nature to Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; ISBN 9783527691395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machala, L.; Tuček, J.; Zbořil, R. Polymorphous Transformations of Nanometric Iron(III) Oxide: A Review. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 3255–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.H.; Kim, H.H.; Lee, J.G.; Baek, Y.K. Epsilon Iron Oxide (ε-Fe2O3) as an Electromagnetic Functional Material: Properties, Synthesis, and Applications. J. Powder Mater. 2024, 31, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharitonskii, P.; Kamzin, A.; Gareev, K.; Valiullin, A.; Vezo, O.; Sergienko, E.; Korolev, D.; Kosterov, A.; Lebedev, S.; Gurylev, A.; et al. Magnetic Granulometry and Mössbauer Spectroscopy of FemOn–SiO2 Colloidal Nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 461, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurylev, A.; Kharitonskii, P.; Kosterov, A.; Berestnev, I.; Sergienko, E. Magnetic Properties of Fired Clay (Bricks) Possibly Containing Epsilon Iron (III) Oxide. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1347, 012034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharitonskii, P.; Bobrov, N.; Gareev, K.; Kosterov, A.; Nikitin, A.; Ralin, A.; Sergienko, E.; Testov, O.; Ustinov, A.; Zolotov, N. Magnetic Granulometry, Frequency-Dependent Susceptibility and Magnetic States of Particles of Magnetite Ore from the Kovdor Deposit. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 553, 169279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrov, N.; Sergienko, E.; Yanson, S.; Kosterov, A.; Karpinsky, V.; Kharitonskii, P.; Ralin, A. Magnetic Viscosity of Suevites from the Zhamanshin Impact Crater. In Problems of Geocosmos—2022; Springer Proceedings in Earth and Environmental Sciences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; Volume 2023, pp. 85–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharitonskii, P.; Sergienko, E.; Ralin, A.; Setrov, E.; Sheidaev, T.; Gareev, K.; Ustinov, A.; Zolotov, N.; Yanson, S.; Dubeshko, D. Superparamagnetism of Artificial Glasses Based on Rocks: Experimental Data and Theoretical Modeling. Magnetochemistry 2023, 9, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doebelin, N.; Kleeberg, R. Profex: A Graphical User Interface for the Rietveld Refinement Program BGMN. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2015, 48, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowrie, W. Identification of Ferromagnetic Minerals in a Rock by Coercivity and Unblocking Temperature Properties. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1990, 17, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applied Electromagnetic Research. Applied Electromagnetic Research. Available online: http://www.aemr.net/ (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Kharitonskii, P.V.; Setrov, E.A.; Ralin, A.Y. Modeling of Hysteresis Characteristics of a Dilute Magnetic with Dipole-Dipole Interaction of Particles. Mater. Phys. Mech. 2024, 52, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abert, C. Micromagnetics and Spintronics: Models and Numerical Methods. Eur. Phys. J. B 2019, 92, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leliaert, J.; Mulkers, J. Tomorrow’s Micromagnetic Simulations. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 125, 180901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, C.; Hierro-Rodríguez, A.; Abert, C.; Witte, K.; Skoric, L.; Sanz-Hernández, D.; Finizio, S.; Meng, F.; McVitie, S.; Raabe, J.; et al. Complex Free-Space Magnetic Field Textures Induced by Three-Dimensional Magnetic Nanostructures. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2022, 17, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharitonskii, P.; Zolotov, N.; Kirillova, S.; Gareev, K.; Kosterov, A.; Sergienko, E.; Yanson, S.; Ustinov, A.; Ralin, A. Magnetic Granulometry, Mössbauer Spectroscopy, and Theoretical Modeling of Magnetic States of FemOn–Fem-XTixOn Composites. Chin. J. Phys. 2022, 78, 271–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olin, M.; Anttila, T.; Dal Maso, M. Using a Combined Power Law and Log-Normal Distribution Model to Simulate Particle Formation and Growth in a Mobile Aerosol Chamber. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 7067–7090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujihara, A.; Tanimoto, S.; Yamamoto, H.; Ohtsuki, T. Log-Normal Distribution in a Growing System with Weighted and Multiplicatively Interacting Particles. J. Phys. Soc. Japan 2018, 87, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrouda, F. Models of Frequency-Dependent Susceptibility of Rocks and Soils Revisited and Broadened. Geophys. J. Int. 2011, 187, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostadinova-Avramova, M.; Kovacheva, M. The Magnetic Properties of Baked Clays and Their Implications for Past Geomagnetic Field Intensity Determinations. Geophys. J. Int. 2013, 195, 1534–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putnis, A.; McConnell, J.D.C. Principles of Mineral Behaviour; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1980; 257p. [Google Scholar]
- Murad, E.; Wagner, U. The Mössbauer Spectrum of Illite. Clay Miner. 1994, 29, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Sánchez, J.; Palencia-Ortas, A.; del Campo, A.; McIntosh, G.; Kovacheva, M.; Martín-Hernández, F.; Carmona, N.; Rodríguez de la Fuente, O.; Marín, P.; Molina-Cardín, A.; et al. Further Progress in the Study of Epsilon Iron Oxide in Archaeological Baked Clays. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2020, 307, 106554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, G.; Kovacheva, M.; Catanzariti, G.; Donadini, F.; Lopez, M.L.O. High Coercivity Remanence in Baked Clay Materials Used in Archeomagnetism. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2011, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosterov, A.; Kovacheva, M.; Kostadinova-Avramova, M.; Minaev, P.; Salnaia, N.; Surovitskii, L.; Yanson, S.; Sergienko, E.; Kharitonskii, P. High-Coercivity Magnetic Minerals in Archaeological Baked Clay and Bricks. Geophys. J. Int. 2021, 224, 1256–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberghe, R.E.; De Grave, E. Application of Mössbauer Spectroscopy in Earth Sciences. In Mössbauer Spectroscopy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 91–185. [Google Scholar]
- Maher, B.A.; Ahmed, I.A.M.; Karloukovski, V.; MacLaren, D.A.; Foulds, P.G.; Allsop, D.; Mann, D.M.A.; Torres-Jardón, R.; Calderon-Garciduenas, L. Magnetite Pollution Nanoparticles in the Human Brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10797–10801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokanov, A.; Manakova, I.; Vereshchak, M.; Migunova, A. Characterization of Kazakhstan’s Clays by Mössbauer Spectroscopy and X-ray Diffraction. Minerals 2024, 14, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuček, J.; Zbořil, R.; Namai, A.; Ohkoshi, S.I. ε-Fe2O3: An Advanced Nanomaterial Exhibiting Giant Coercive Field, Millimeter-Wave Ferromagnetic Resonance, and Magnetoelectric Coupling. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 6483–6505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Sánchez, J.; McIntosh, G.; Osete, M.L.; del Campo, A.; Villalaín, J.J.; Pérez, L.; Kovacheva, M.; Rodríguez de la Fuente, O. Epsilon Iron Oxide: Origin of the High Coercivity Stable Low Curie Temperature Magnetic Phase Found in Heated Archeological Materials. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2017, 18, 2646–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.; Oldfield, F. Environmental Magnetism; Springer: Dordrecht, Germany, 2012; ISBN 978-94-011-8038-2. [Google Scholar]
- Nogués, J.; Sort, J.; Langlais, V.; Doppiu, S.; Dieny, B.; Muñoz, J.S.; Suriñach, S.; Baró, M.D.; Stoyanov, S.; Zhang, Y. Exchange Bias in Ferromagnetic Nanoparticles Embedded in an Antiferromagnetic Matrix. Int. J. Nanotechnol. 2005, 2, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ortega, A.; Estrader, M.; Salazar-Alvarez, G.; Roca, A.G.; Nogués, J. Applications of Exchange Coupled Bi-Magnetic Hard/Soft and Soft/Hard Magnetic Core/Shell Nanoparticles. Phys. Rep. 2015, 553, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaev, D.A.; Krasikov, A.A.; Dubrovskiy, A.A.; Popkov, S.I.; Stolyar, S.V.; Iskhakov, R.S.; Ladygina, V.P.; Yaroslavtsev, R.N. Exchange Bias in Nano-Ferrihydrite. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 120, 183903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi, T.N.; Van, P.C.; Artavazd, K.; Hwang, C.; Choi, J.; Kim, H.; Jeong, J.R. Effect of Heat-Treatment Temperature on the Formation of ε-Fe2O3 Nanoparticles Encapsulated by SiO2. J. Magn. 2023, 28, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauxe, L.; Mullender, T.A.T.; Pick, T. Potbellies, Wasp-Waists, and Superparamagnetism in Magnetic Hysteresis. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1996, 101, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, Ö.; Dunlop, D.J. Hysteresis and Coercivity of Hematite. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2014, 119, B02101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.P.; Cui, Y.; Verosub, K.L. Wasp-Waisted Hysteresis Loops: Mineral Magnetic Characteristics and Discrimination of Components in Mixed Magnetic Systems. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 17909–17924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlop, D.J. Theory and application of the Day plot (Mrs/Ms versus Hcr/Hc) 2. Application to data for rocks, sediments, and soils. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2002, 107, EPM 5-1–EPM 5-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabian, K. Some Additional Parameters to Estimate Domain State from Isothermal Magnetization Measurements. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2003, 213, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muxworthy, A.R.; Williams, W. Critical Superparamagnetic/Single-Domain Grain Sizes in Interacting Magnetite Particles: Implications for Magnetosome Crystals. J. R. Soc. Interface 2009, 6, 1207–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Roberts, A.P.; Torrent, J.; Horng, C.S.; Larrasoaña, J.C. What Do the HIRM and S-Ratio Really Measure in Environmental Magnetism? Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2007, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehring, A.U.; Fischer, H.; Louvel, M.; Kunze, K.; Weidler, P.G. High Temperature Stability of Natural Maghemite: A Magnetic and Spectroscopic Study. Geophys. J. Int. 2009, 179, 1361–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlop, D.J.; Özdemir, Ö. Rock Magnetism. Fundamentals and Frontiers. Cambridge Studies in Magnetism Series; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997; ISBN 978-0521000987. [Google Scholar]
- Özdemir, Ö.; Banerjee, S.K. High Temperature Stability of Maghemite (γ-Fe2O3). Geophys. Res. Lett. 1984, 11, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskowitz, B.M.; Frankel, R.B.; Bazylinski, D.A. Rock Magnetic Criteria for the Detection of Biogenic Magnetite. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1993, 120, 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Housen, B.A.; Banerjee, S.K.; Moskowitz, B.M. Low-Temperature Magnetic Properties of Siderite and Magnetite in Marine Sediments. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1996, 23, 2843–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, A.V.; Tarduno, J.A. Low-Temperature Magnetic Properties of Pelagic Sediments (Ocean Drilling Program Site 805C): Tracers of Maghemitization and Magnetic Mineral Reduction. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2000, 105, 16457–16471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, Ö.; Dunlop, D.J. Hallmarks of Maghemitization in Low-Temperature Remanence Cycling of Partially Oxidized Magnetite Nanoparticles. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, B02101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearing, J.A.; Dann, R.J.L.; Hay, K.; Lees, J.A.; Loveland, P.J.; Maher, B.A.; O’Grady, K. Frequency-Dependent Susceptibility Measurements of Environmental Materials. Geophys. J. Int. 1996, 124, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurshid, H.; Lampen-Kelley, P.; Iglesias, Ò.; Alonso, J.; Phan, M.H.; Sun, C.J.; Saboungi, M.L.; Srikanth, H. Spin-Glass-like Freezing of Inner and Outer Surface Layers in Hollow γ-Fe2O3 Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugiraneza, S.; Hallas, A.M. Tutorial: A Beginner’s Guide to Interpreting Magnetic Susceptibility Data with the Curie-Weiss Law. Commun. Phys. 2022, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Gupta, P. Halloysite-Based Magnetic Nanostructures for Diverse Applications: A Review. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 13824–13868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaev, D.A.; Semenov, S.V.; Dubrovskiy, A.A.; Knyazev, Y.V.; Kirillov, V.L.; Shaykhutdinov, K.A.; Martyanov, O.N. Size Effect and Temperature of Magnetic Ordering in ε-Fe2O3 Nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2025, 38, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, S.; Namai, A.; Hashimoto, K.; Ohkoshi, S. First Observation of Phase Transformation of All Four Fe2O3 Phases (γ → ε → β → α-Phase). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 18299–18303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kneller, E.F.; Luborsky, F.E. Particle Size Dependence of Coercivity and Remanence of Single-Domain Particles. J. Appl. Phys. 1963, 34, 656–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoner, E.C.; Wohlfarth, E.P. A Mechanism of Magnetic Hysteresis in Heterogeneous Alloys. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London. Ser. A, Math. Phys. Sci. 1948, 240, 599–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.P.; Almeida, T.P.; Church, N.S.; Harrison, R.J.; Heslop, D.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Muxworthy, A.R.; Williams, W.; Zhao, X. Resolving the Origin of Pseudo-Single Domain Magnetic Behavior. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2017, 122, 9534–9558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
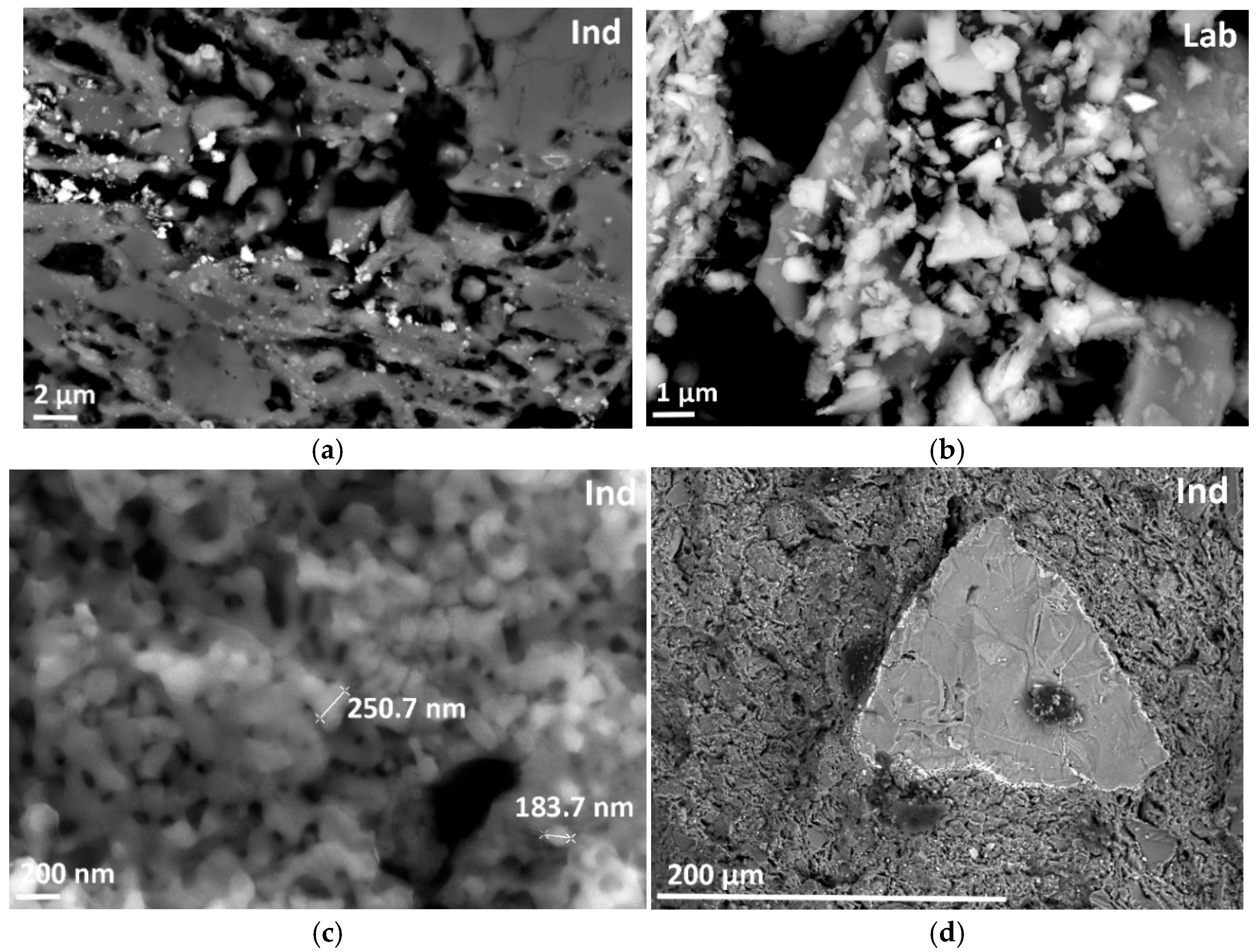

| ClayL | Ind | Lab | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quartz | 40 | 44 | 49 |
| Feldspar (microcline + plagioclase) | 23 | 39 | 41 |
| Mica | 20 | 3 | 4 |
| Amphibole | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Hematite | — | 5 | 5 |
| Spinel | — | 8 | — |
| Kaolinite | 9 | — | — |
| Pyroxene | 2 | — | — |
| Chlorite | 5 | — | — |
| Dolomite | 1 | — | — |
| Rp (*) (%) | 4.4 | 5.9 | 5.4 |
| Sample | Component | Fe | IS (mm/s) | QS (mm/s) | BHf (T) | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lab | Doublet Fe(1) | Fe3+ | 0.305 ± 0.009 | 0.882 ± 0.016 | — | 50.11 |
| Doublet Fe(2) | Fe2+ | 0.910 ± 0.044 | 1.663 ± 0.089 | — | 1.29 | |
| Sextet Fe(3) | Fe3+ | 0.363 ± 0.012 | 0.241 ± 0.023 | 50.796 ± 0.097 | 22.82 | |
| Sextet Fe(4) | Fe3+ | 0.388 ± 0.017 | 0.228 ± 0.034 | 49.285 ± 0.205 | 25.78 | |
| Ind | Doublet Fe(1) | Fe3+ | 0.293 ± 0.007 | 0.819 ± 0.012 | — | 36.92 |
| Doublet Fe(2) | Fe2+ | 0.895 ± 0.057 | 1.675 ± 0.115 | — | 1.13 | |
| Sextet Fe(3) | Fe3+ | 0.353 ± 0.010 | 0.183 ± 0.021 | 50.543 ± 0.085 | 20.84 | |
| Sextet Fe(4) | Fe3+ | 0.372 ± 0.010 | 0.274 ± 0.021 | 49.496 ± 0.132 | 41.11 |
| Sample | Ms, A·m2/kg | Mrs, A·m2/kg | Mrs/Ms | μ0Hc, mT | μ0Hcr, mT | Hcr/Hc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ClayL (Lake Shore 295) | 0.03 | 0.005 | 0.17 | 17 | 64 | 3.8 |
| Ind (MPMS 2) | 1.30 | 0.060 | 0.05 | 28 | 150 | 5.4 |
| Ind (MPMS 295) | 0.08 | 0.020 | 0.25 | 10 | 139 | 13.9 |
| Lab (MPMS 2) | 2.00 | 0.190 | 0.10 | 45 | 150 | 3.3 |
| Lab (MPMS 295) | 0.20 | 0.020 | 0.10 | 2 | 119 | 59.5 |
| Sample | fd, % | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| MFK1-FA | PPMS-9 | Average Value | |
| Ind | 5.2 | 7.8 | 6.5 |
| Lab | 12.5 | 8.5 | 10.5 |
| ClayL | 50 (estimation) | – | – |
| Sample | Δ1, % | cf, 10−3 | Ieff rs, kA/m | Ieff rs1, kA/m | δ1, % | δ2, % | δ3, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lab | 76–84 | 0.80–0.93 | 37–43 | 33–41 | 67.4–78.3 | 31.9–21.2 | 0.7–0.5 |
| Ind | 52–63 | 0.42–0.50 | 66–79 | 82–102 | 65.8–76.4 | 33.4–23.0 | 0.8–0.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kharitonskii, P.; Krasilin, A.; Belskaya, N.; Yanson, S.; Bobrov, N.; Ralin, A.; Gareev, K.; Zolotov, N.; Zaytsev, D.; Sergienko, E. Superparamagnetism of Baked Clays Containing Polymorphs of Iron Oxides: Experimental Study and Theoretical Modeling. Magnetochemistry 2025, 11, 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11120103
Kharitonskii P, Krasilin A, Belskaya N, Yanson S, Bobrov N, Ralin A, Gareev K, Zolotov N, Zaytsev D, Sergienko E. Superparamagnetism of Baked Clays Containing Polymorphs of Iron Oxides: Experimental Study and Theoretical Modeling. Magnetochemistry. 2025; 11(12):103. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11120103
Chicago/Turabian StyleKharitonskii, Petr, Andrei Krasilin, Nadezhda Belskaya, Svetlana Yanson, Nikita Bobrov, Andrey Ralin, Kamil Gareev, Nikita Zolotov, Dmitry Zaytsev, and Elena Sergienko. 2025. "Superparamagnetism of Baked Clays Containing Polymorphs of Iron Oxides: Experimental Study and Theoretical Modeling" Magnetochemistry 11, no. 12: 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11120103
APA StyleKharitonskii, P., Krasilin, A., Belskaya, N., Yanson, S., Bobrov, N., Ralin, A., Gareev, K., Zolotov, N., Zaytsev, D., & Sergienko, E. (2025). Superparamagnetism of Baked Clays Containing Polymorphs of Iron Oxides: Experimental Study and Theoretical Modeling. Magnetochemistry, 11(12), 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11120103







