Microwave-Assisted Combustion Synthesized Sm2Co17 Magnetic Particles for Permanent Magnetic Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
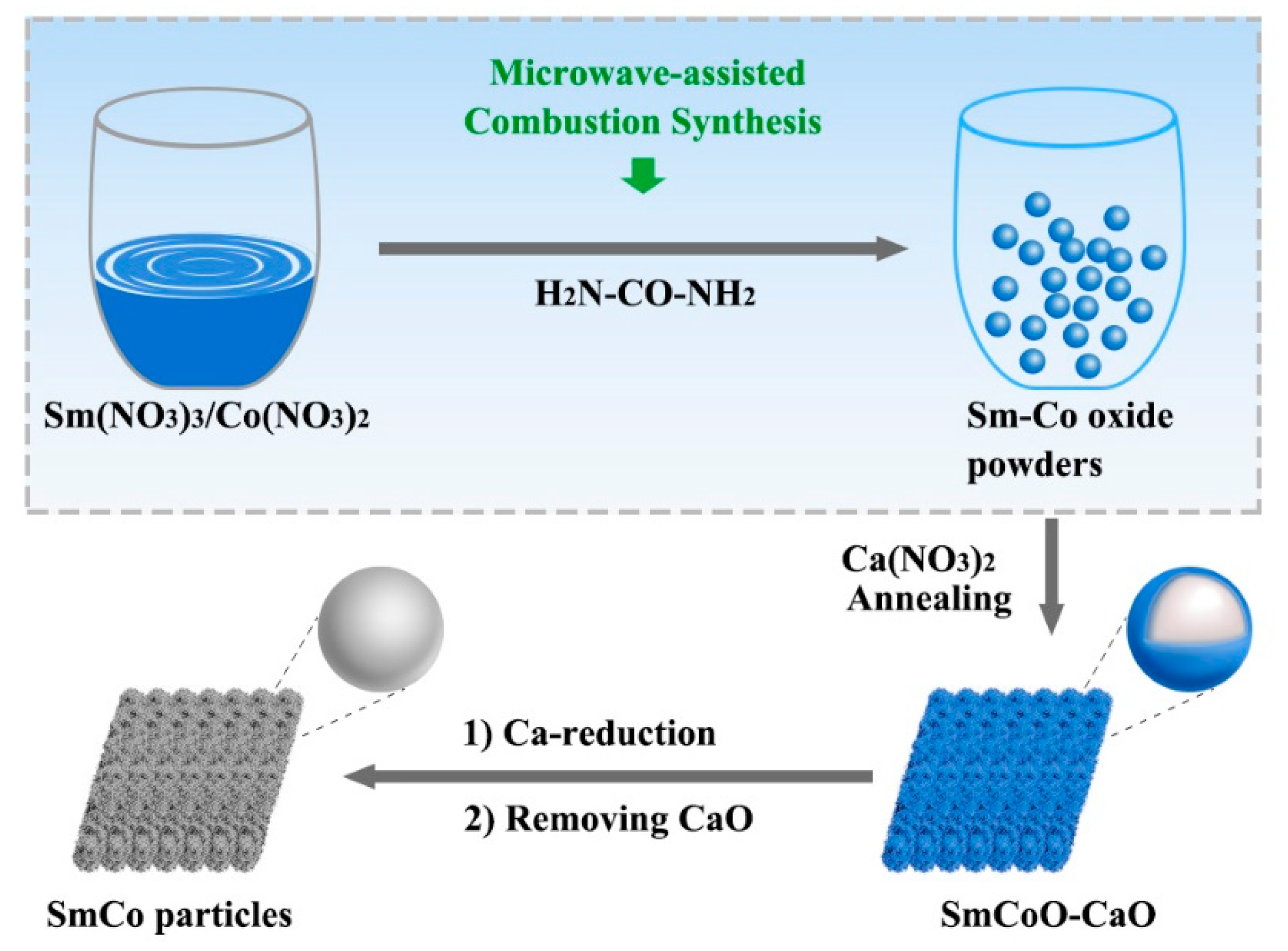
2. Experimental
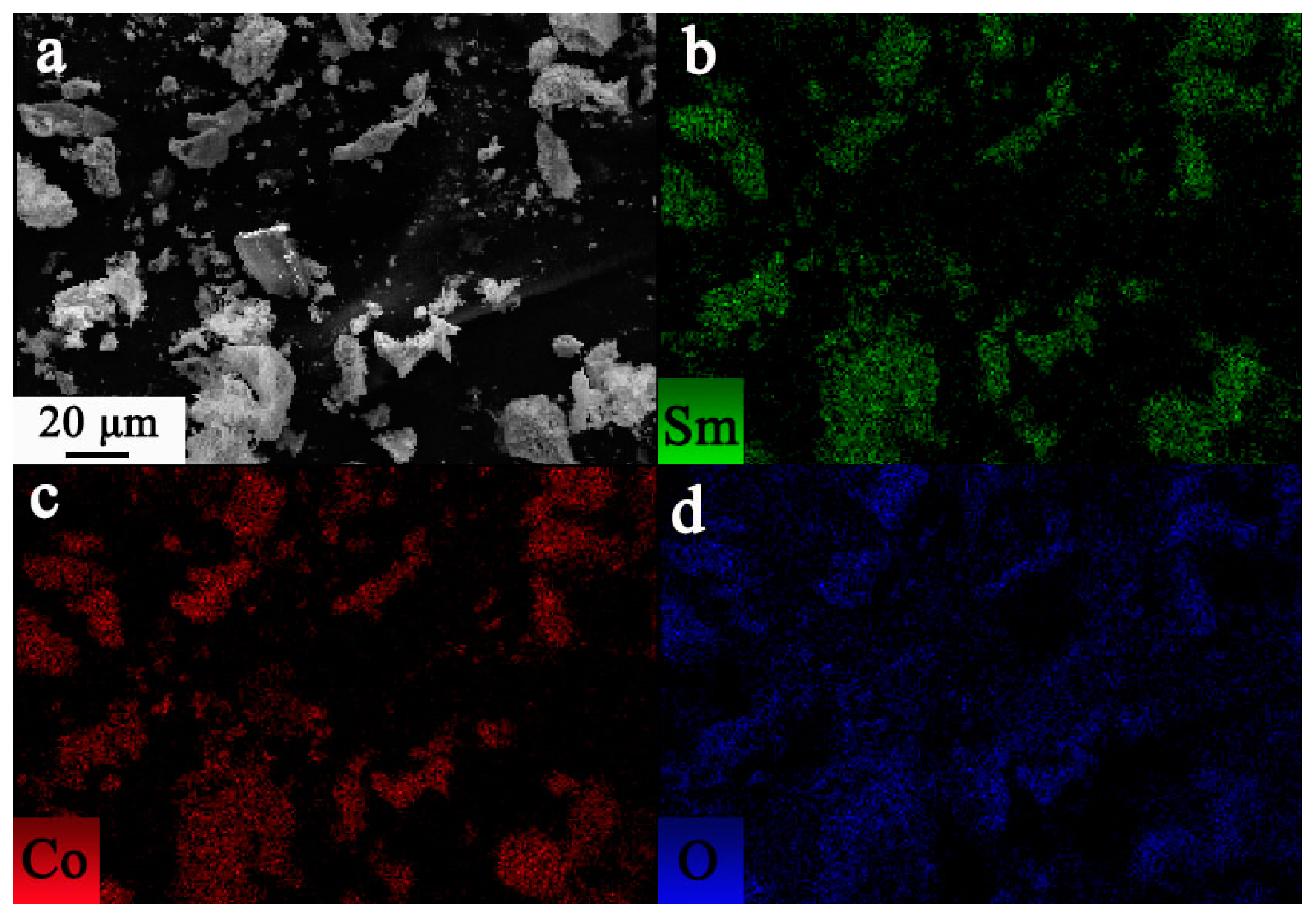
2.1. Synthesis of SmCo-O
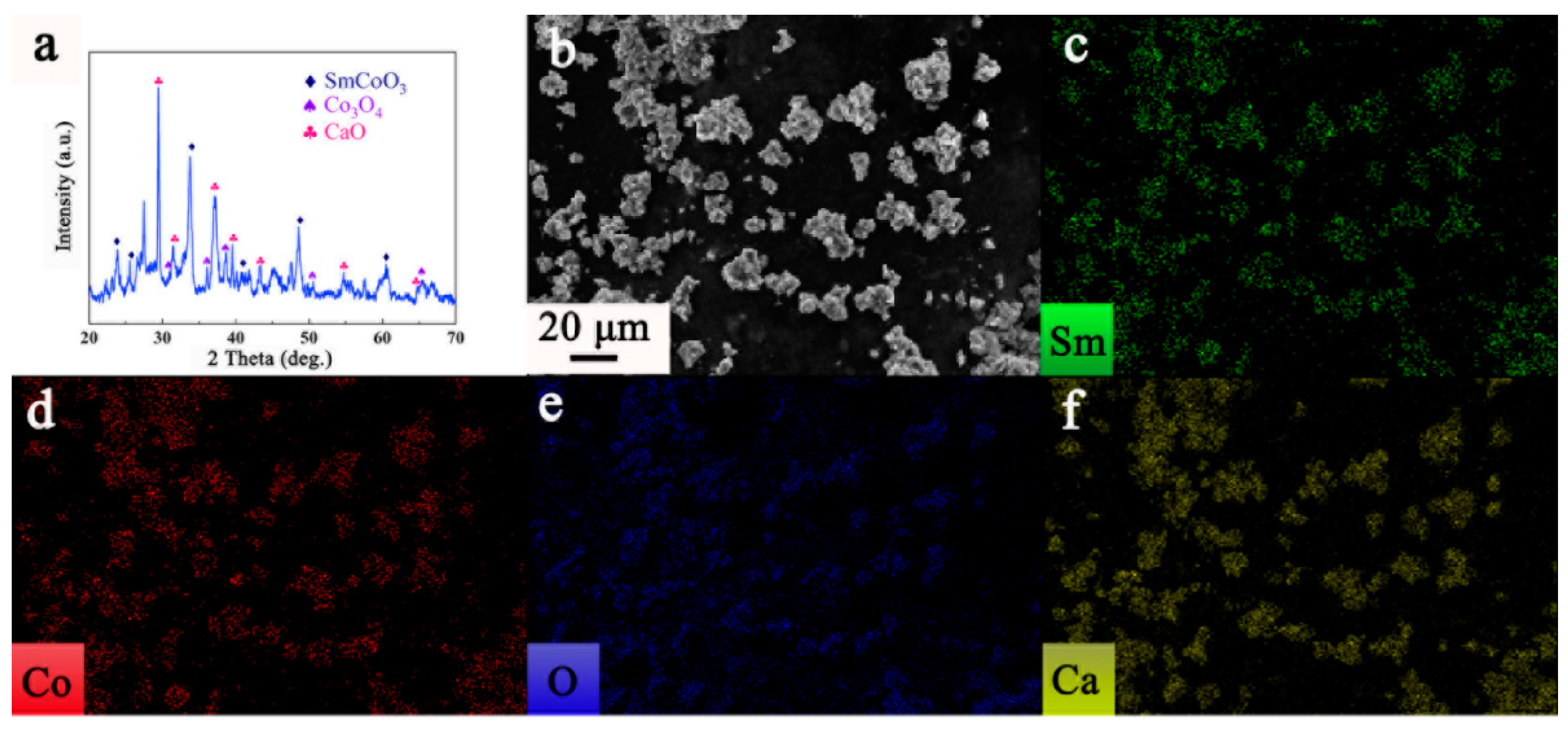
2.2. Synthesis of SmCo-O/CaO
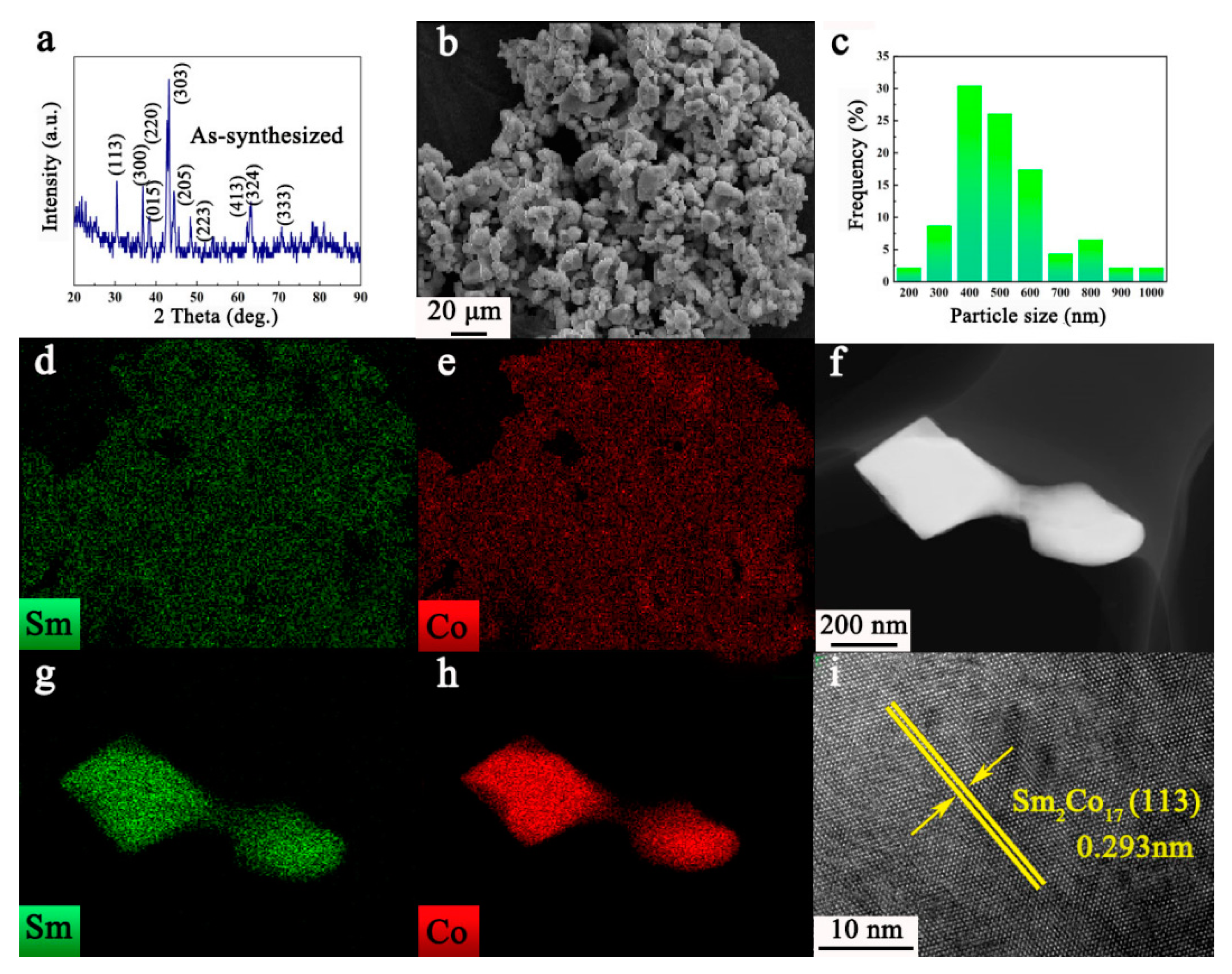
2.3. Synthesis of Sm2Co17
2.4. Characterization
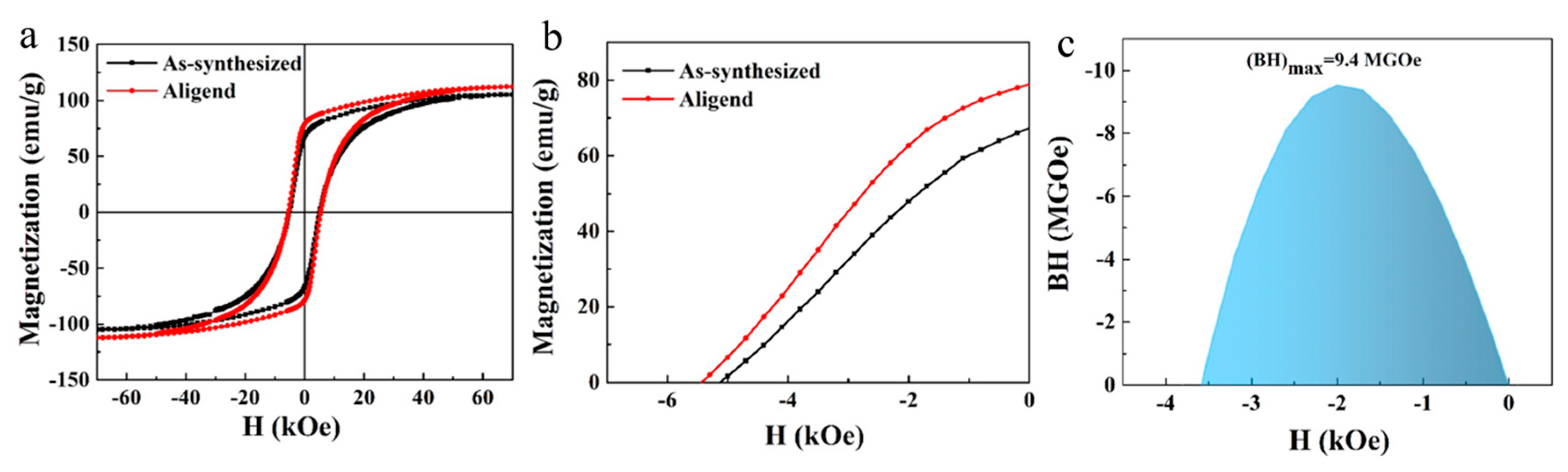
3. Results and Discussion
xSmCo + (y − x)/3Co3O4 + (1.5x + y + z)N2 + zCO2 + 2zH2O
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gorbachev, E.A.; Kozlyakova, E.S.; Trusov, L.A.; Sleptsova, A.E.; Zykin MAKazin, P.E. Design of modern magnetic materials with giant coercivity. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2021, 90, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, P.; Mazin, I.I.; Papaconstantopoulos, D.A. Calculation of magnetic anisotropy energy in SmCo5. Phys. Rev. B. 2003, 67, 214405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.F.; Gabay, A.M.; Hu, X.C.; Ni, C.; Hadjipanayis, G.C. Fabrication and microstructure evolution of single crystalline Sm2Co17 nanoparticles prepared by mechanochemical method. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2013, 117, 10291–10295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.-J.; Zhao, G.-P.; Tang, H.; Shen, L.-C.; Xiao, Y. Thickness-dependent coercivity mechanism and hysteresis loops in hard/soft magnets. Rare Met. 2020, 39, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.Y.; Wang, H.; Ma, Z.H.; Liu, X.; Dong, Y.; Liu, Z.Q.; Zhang, T.L.; Jiang, C.B. FePt/Co core/shell nanoparticle-based anisotropic nanocomposites and their exchange spring behavior. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 4061–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.Y.; Liu, W.Q.; Wang, Y.T.; Li, Y.Q.; Zhang, D.T.; Lu, Q.M.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, H.G.; Yue, M. Effects of shape anisotropy on hard-soft exchange-coupled permanent magnets. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, P.F.; Ming, W.Q.; Cao, X.; Huang, Y.Z.; Li, Z.M. On the structure of rare earth sesquioxide Sm2O3 in Sm2Co17-type magnets. Scr. Mater. 2023, 222, 115018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Mendoza-Garcia, A.; Baker, S.E.; McCall, S.K.; Yu, C.; Wu, L.H.; Sun, S.H. Stabilizing Fe nanoparticles in the SmCo5 matrix. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 5695–5698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Liu, J.P. Fabrication of bulk nanostructured permanent magnets with high energy density: Challenges and approaches. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 3674–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.L.; Xu, Z.C.; Peng, S.; Rong, C.B.; Liu, J.P.; Sun, S.H. A facile synthesis of SmCo5 magnets from core/shell Co/Sm2O3 nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 3349–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnasamy, C.N.; Huang, J.Y.; Lewis, L.H.; Latha, B.; Vittoria, C.; Harris, V.G. Direct chemical synthesis of high coercivity air-stable SmCo nanoblades. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 032505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaubey, G.S.; Poudyal, N.; Liu, Y.Z.; Rong, C.B.; Liu, J.P. Synthesis of Sm-Co and Sm-Co/Fe nanocrystals by reductive annealing of nanoparticles. J. Alloy Compd. 2011, 509, 2132–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.W.; Peng, S.; Rong, C.B.; Liu, J.P.; Zhang, Y.; Kramer, M.J.; Sun, S.H. Chemical synthesis of hard magnetic SmCo nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 16873–16876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.F.; Sepehri-Amin, H.; Zheng, L.Y.; Cui, B.Z.; Gabay, A.M.; Hono, K.; Huang, W.J.; Ni, C.; Hadjipanayis, G.C. Effect of ball-milling surfactants on the interface chemistry in hot-compacted SmCo5 magnets. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 6685–6691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, G.; Saravanan, P.; Babu, D.R. Effect of annealing on phase composition, structural and magnetic properties of Sm-Co based nanomagnetic material synthesized by sol-gel process. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 2158–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.H.; Zhang, T.L.; Wang, H.; Jiang, C.B. The synthesis of SmCo5 nanoparticles with small size and high performance by hydrogenation technique. Rare Met. 2018, 37, 1021–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, M.; Li, C.; Wu, Q.; Ma, Z.; Xu, H.; Palaka, S. A facile synthesis of anisotropic SmCo5 nanochips with high magnetic performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 343, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.H.; Yang, S.X.; Zhang, T.L.; Jiang, C.B. The chemical synthesis of SmCo5 single-crystal particles with small size and high performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 304, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, T.; Iwamoto, T.; Inokuchi, M.; Toshima, N. Novel ferromagnetic materials of SmCo5 nanoparticles in single-nanometer size: Chemical syntheses and characterizations. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 95603–95611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Xu, B.; Rao, J.; Zheng, R.K.; Zhang, X.X.; Fung, K.K.; Wong, C.Y.C. Chemical synthesis of narrowly dispersed SmCo5 nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 7589–7591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.H.; Liang, J.M.; Ma, W.; Cong, L.Y.; Wu, Q.; Yue, M. Chemically synthesized anisotropic SmCo5 nano-magnets with a large energy product. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 12484–12488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Yu, C.; Su, D.; Yin, Z.Y.; Li, J.R.; Xi, Z.; Sun, S.H. A new strategy to synthesize anisotropic SmCo5 nanomagnets. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 8735–8740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zhang, T.L.; Xia, Z.C.; Wang, H.; Ma, Z.H.; Liu, X.; Xia, W.; Coey, J.M.D.; Jiang, C.B. Dispersible SmCo5 nanoparticles with huge coercivity. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 16962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.H.; Yue, M.; Wu, Q.; Li, C.L.; Yu, Y.S. Designing shape anisotropic SmCo5 particles by chemical synthesis to reveal the morphological evolution mechanism. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 10377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wen, Y.; Liu, B.L.; Xu, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.T. Microstructures and Photoluminescence property of flower-like ZnO nanopowders, synthesized by microwave-induced combustion technique. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 1, 190–198. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.P.; Lin, C.H.; Hsu, C.S. Preparation of ultrafine CeO2 powders by microwave-induced combustion and precipitation. J. Alloys Compd. 2005, 391, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangalaraja, R.V.; Mouzon, J.; Hedström, P. Microwave assisted combustion synthesis of nanocrystalline yttria and its powder characteristics. Powder Technol. 2019, 191, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Liu, B.; Huang, R.; Xia, Z.; Ge, S. Flash synthesis of flower-like ZnO nanostructures by microwave-induced combustion process. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, H.; Xiao, T.; Chaudhary, V.; Zhong, Y.; Ramanujan, R.V. High energy product chemically synthesized exchange coupled Nd2Fe14B/α-Fe magnetic powders. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 13956–13966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Tian, Y.L.; Yu, H.Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhong, X.C.; Liu, Z.W. Synthesis of hard magnetic NdFeB composite particles by recycling the waste using microwave assisted auto-combustion and reduction method. Waste Manag. 2019, 87, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.T.; Yang, Z.; Xu, H.B.; Cong, L.Y.; Li, C.L.; Xi, J.H.; Wu, Q.; Liu, W.Q.; Lu, Q.M.; Ming, Y. Microwave-assisted chemical synthesis of SmCo5 magnetic particles wit h high coercivity. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2023, 579, 170855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.H.; Tian, H.; Cong, L.Y.; Wu, Q.; Yue, M.; Sun, S.H. A flame-reaction methodfor the large-scale synthesis of high-performance SmxCoy nanomagnets. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 14509–14512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.H.; Zhang, T.L.; Jiang, C.B. A facile synthesis of high performance SmCo5 nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 264, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.L.; Wu, Q.; Ma, Z.H.; Xu, H.H.; Cong, L.Y.; Yue, M. A novel strategy to synthesize anisotropic SmCo5 particles from Co/Sm(OH)3 composites with special morphology. J. Mater. Chem. C. 2018, 6, 8522–8527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Cong, L.Y.; Yue, M.; Li, C.L.; Ma, Z.H.; Ma, X.Y.; Wang, Y.T. A unique synthesis of rare-earth-Co-based single crystal particles by “self-aligned” Co nano-arrays. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 13958–13963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Yu, C.; Baker, A.A.; McCall, S.K.; Yu, Y.S.; Su, D.; Yin, Z.Y.; Liu, H.; Li, J.R.; Sun, S.H. Chemical synthesis of magnetically hard and strong rare earth metal based nanomagnets. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 131, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Sun, S.H. Chemical synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles for permanent magnet applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 26, 6757–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Ma, X.; Lu, Y.; Wen, H.; Guo, G.; Li, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z. Microwave-Assisted Combustion Synthesized Sm2Co17 Magnetic Particles for Permanent Magnetic Application. Magnetochemistry 2024, 10, 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry10090063
Wang Y, Ma X, Lu Y, Wen H, Guo G, Li Y, Zhang P, Wang Y, Yang Z. Microwave-Assisted Combustion Synthesized Sm2Co17 Magnetic Particles for Permanent Magnetic Application. Magnetochemistry. 2024; 10(9):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry10090063
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yatao, Xiangyu Ma, Yani Lu, Hui Wen, Guozhe Guo, Yingying Li, Pengming Zhang, Yan Wang, and Zhi Yang. 2024. "Microwave-Assisted Combustion Synthesized Sm2Co17 Magnetic Particles for Permanent Magnetic Application" Magnetochemistry 10, no. 9: 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry10090063
APA StyleWang, Y., Ma, X., Lu, Y., Wen, H., Guo, G., Li, Y., Zhang, P., Wang, Y., & Yang, Z. (2024). Microwave-Assisted Combustion Synthesized Sm2Co17 Magnetic Particles for Permanent Magnetic Application. Magnetochemistry, 10(9), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry10090063





