Abstract
The development of novel synthesis and assembly strategies is critical to achieving a ferromagnetic organic semiconductor with high Curie temperature. In this study, we report a high magnetic field (HMF)-modified solvothermal approach for the reduction in neutral perylene diimide (PDI) into the dianion species to prepare the PDI magnets comprising radical anions after subsequent oxidation processes. The PDI materials, assembled from the dianion solution by an HMF-modified reduction, exhibit a smaller crystallite size and an enlarged distance of the π-π stacking in the PDI aggregates. Furthermore, the PDI magnets obtained from the process under a 9T field reveal weakened ferromagnetism and the rapid degradation of electrical conductivity compared to those prepared without a magnetic field. Based on spectral and structural characterizations, such performance deterioration originates from the enhanced instability of the radical anions exposed to air, as well as the decreased crystallinity for the radical PDIs synthesized from the HMF-modified reduction process. This work demonstrates that magnetic fields offer an effective way in the material synthesis process to manipulate the structure and magnetic properties of the radical-based organic magnets.
1. Introduction
Conjugated molecular and polymeric semiconductors have attracted extensive interest in flexible electronics in the past decades [1,2,3]. Much effort has also been devoted to developing magnets and spintronic devices based on pure organic compounds [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11]. The mechanical flexibility, light weight, biocompatibility and low-temperature preparation of these materials offer them great potential to replace traditional magnets in certain applications, especially ferromagnetic semiconductors, simultaneously possess semiconducting properties and spontaneous ferromagnetic order, enabling the possibility of combining logic and storage operations as key elements for future spintronics.
Magnetic ordering of the organic and/or molecular magnets originates from the unpaired electrons in the s or p molecular orbitals. The study of organic magnets has focused on the radical-carrying compounds [6,8,12] and the charge-transfer complexes (e.g., thiophene-C60 and coronene-tetracyanoquinodimethane (TCNQ)) [13,14]. Since the 1980s, a number of polymeric magnets have been discovered, in which spin exchange interaction between the unpaired electrons (radicals) on pendant side chains of the conjugated backbones induces ferromagnetic order, usually at low temperatures [15,16]. Recently, Baek et al. obtained a polymeric magnet by self-polymerization of the TCNQ monomers [17]. The material exhibits a weak ferromagnetism at room temperature (RT). Notably, Jiang et al. have achieved a ferromagnetic organic semiconductor of the perylene diimide (PDI) radicals [18]. They utilized a solvothermal approach to reduce the neutral PDI into the PDI dianions, as well as a subsequent self-assembly and spontaneous oxidation process to fabricate stable radical anions. The resultant magnet exhibits a saturation magnetization of 1.2 emu/g and a Curie temperature (Tc) above 400 K. Despite many efforts, intrinsic ferromagnetic organic semiconductors that work at RT are still rare. In addition to molecular design, the development of novel synthetic strategies and molecular assembly methods to effectively control reaction pathways and the self-assembly/growth process is crucial for the improved performance of organic magnets [5,19,20].
As a type of important thermodynamic parameter, the magnetic field has been extensively utilized to manipulate the morphology, structure, and product phase during the synthesis and growth of the nanomaterials [21,22,23,24]. For instance, Ding et al. have demonstrated a magneto-hydrothermal approach to prepare pure and stable 1T-MoS2 nano-sheets. They found that the formation of the metallic 1T-MoS2 phase is facilitated under a high magnetic field (HMF) due to the higher magnetic susceptibility of 1T-MoS2 than diamagnetic 2H-MoS2 [25]. Qian et al. have synthesized the PVP-directed nickel nanowires via a magnetically assisted hydrothermal method, which also exhibited enhanced magnetization and excellent microwave absorption performance [26]. Furthermore, our group has achieved a large area highly oriented film structure of several semiconducting polymers by solution-phase deposition under a field of 9T [27,28]. The conjugated polymer backbones are aligned well with the applied field direction, leading to a remarkable enhancement of carrier transport properties. For the preparation of molecular-based magnets, it has been demonstrated that the magnetic field could be an effective tool to modulate electrical polarization and magnetic properties of multiferroic metal–organic framework (MOF) materials by tuning the reaction pathway and the coordination modes of organic ligands during synthesis [29,30]. Despite the aforementioned progress, the synthesis and structural manipulation of ferromagnetic organic semiconductors, modified by the HMF, have not been reported so far.
In this work, a detailed investigation is performed for the magnetic field effect on the reduction reaction of the conjugated PDI, as well as the structure and magnetic properties of the synthesized radical magnets. The pristine PDI (depicted in Figure 1a) is an N-type semiconductor [31,32], while its radical anions or dianions can be obtained by a chemical reduction process [33]. Due to the high sensitivity of the radicals (unpaired electrons) to the magnetic field [34,35], the applied HMF could regulate the reaction pathway, species selection, and molecular assembly of the PDI during a reduction/oxidation process in which the radicals are generated. We demonstrate that the electrical and magnetic properties of the PDI-based magnets can be manipulated effectively via a solvothermal approach under a high magnetic field. Notably, an enhanced instability of the radical anions is also observed on the PDI materials prepared from the dianion solutions via the HMF-modified reduction process. The enhanced instability of PDI anions corresponds well to the weakened ferromagnetism and the faster degradation of the conductivity of the products.
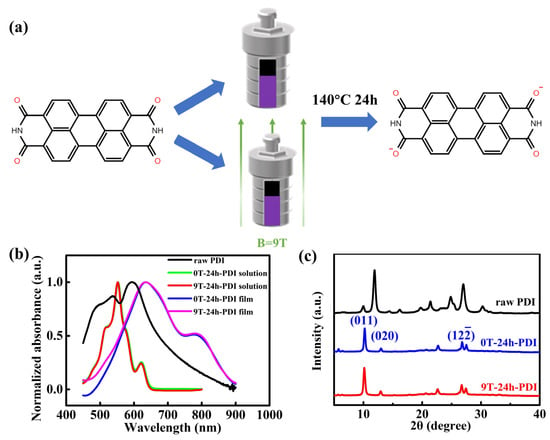
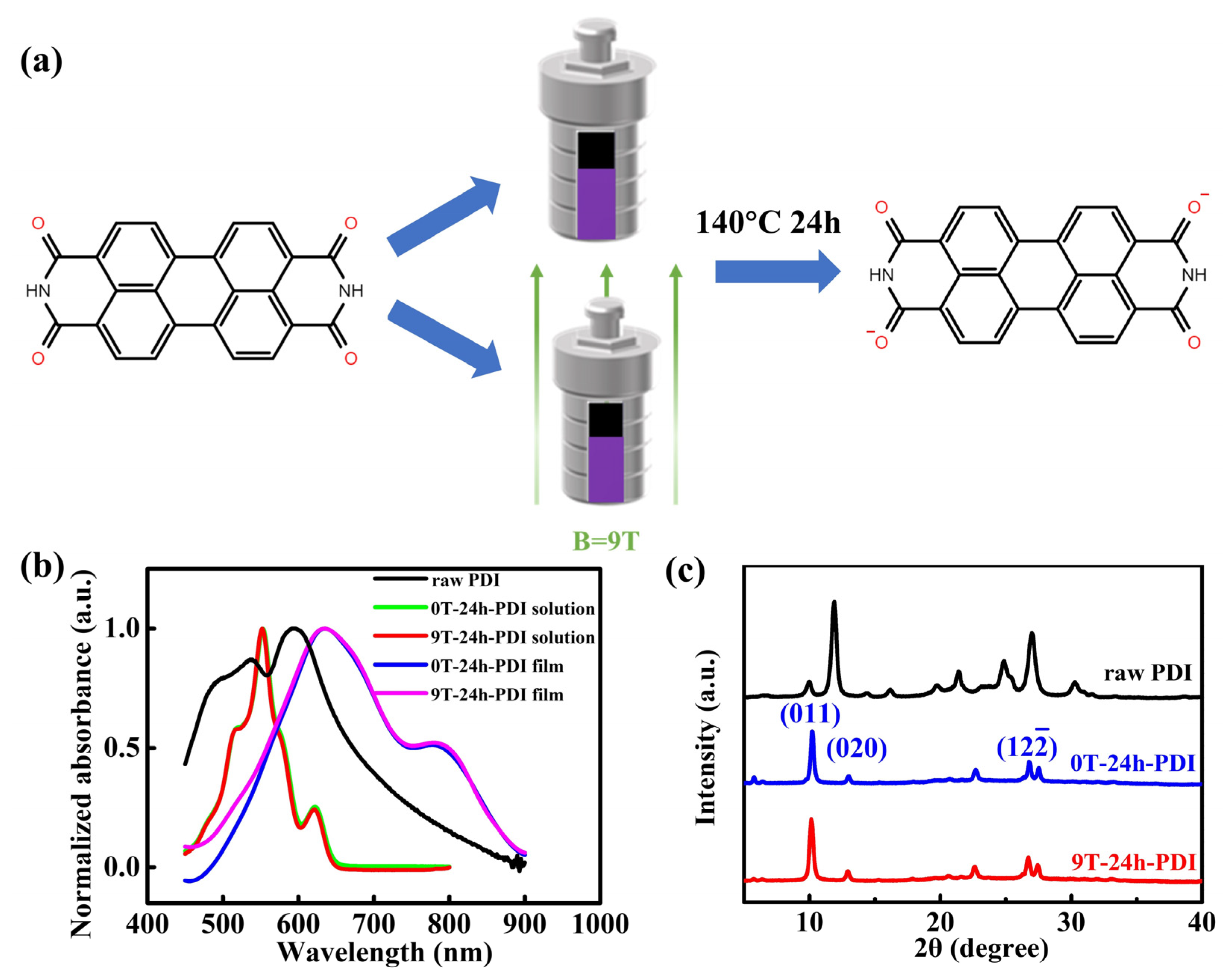
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic diagram of the preparation of the PDI solution via the solvothermal method with and without HMF, respectively. The molecular structure of the PDI is also shown; (b) UV-vis spectra of raw PDI solutions, the PDI dianion solutions produced from the reduction reaction under the field of 0 T and 9 T, as well as the as-prepared films cast from the 0T-24h-PDI and 9T-24h-PDI solutions, respectively. (c) XRD patterns of the raw PDI powder and the as-prepared powders of 0T-24h-PDI and 9T-24h-PDI.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material and Sample Preparation
The PDI (98%) was purchased from J & K Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China). and used as received. Hydrazine hydrate (98%) was purchased from Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China). A total of 10 mg PDI and hydrazine hydrate (5 mL) were sealed into a Teflon-lined stainless-steel autoclave (shown in Figure S1a). Subsequently, the autoclave was fixed in a homemade heater (shown in Figure S1b,c) and transferred to a 10 T superconducting magnet (AMI American Magnetics from AMI Inc., Oak Ridge, TN, USA), displayed in Figure S1d). The reduction reaction was performed by heating the autoclave at 140 °C in a homemade heater under an external magnetic field of 0 T, 3 T, 6 T, and 9 T for different durations. Additionally, a sample synthesis was conducted by heating an autoclave at 140 °C in a vacuum oven for 24 h (0 T). After the reaction, the autoclave was transferred into and opened in a N2 glove box (H2O and O2 ≤ 0.1 ppm). The powders were obtained by suction filtration of the PDI dianion solutions, and the films were drop cast from the above solutions on a clean SiO2/Si substrate in a nitrogen atmosphere. Finally, both the powders and the films were dried at 100 °C in the glove box to remove the residual solvent.
2.2. Structural Characterizations
The X-ray diffraction (XRD) measurements of the powder and film samples were performed using a Rigaku MiniFlex powder X-ray diffractometer (Akishima, Tokyo, Japan) using Cu-Kα radiation (λ = 1.54 Å). Two-dimensional (2D) grazing incidence X-ray diffraction (GIXRD) measurements were also conducted for the films at the beamline BL14B of the Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (SSRF) (Shanghai, China) with a photon energy of 10.0 keV. The incidence angle of the X-ray beam is 0.2°. Sample morphology was characterized by a scanning electron microscope (SEM, Hellons Nanolab 600 from Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). UV-vis-NIR absorption spectra were measured by a Shimadzu UV-3100 spectrophotometer from Shimadzu Inc. (Kyoto, Japan) in transmission geometry for the samples, which were deposited on quartz substrates and subsequently exposed to the air. Electron paramagnetic resonance spectra (EPR) were recorded by a Bruker EMX plus 10/12 from Bruker Inc. (Berlin, Germany) (9.1–9.9 GHz) equipped with Oxford EPR910 Liquid Helium cryostat (Abingdon, UK) for the samples deposited on quartz substrates with exposure to air. The solution samples for the absorption and EPR measurements were taken from the “as-reduced” PDI solutions without access to oxygen.
2.3. Electrical and Magnetic Properties’ Characterization
A magnetization measurement was performed on a superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) magnetometer (Quantum Design MPMS3-175 from Quantum Design Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) in the temperature range of 4.2–300 K. The samples for electrical characterization were prepared by casting the PDI dianion solution on the SiO2/Si substrates pre-patterned with interdigitated electrode arrays (30 nm Au/5 nm ITO) and subsequently oxidized in the glove box. The I-V curves and conductance were measured on a probe station by a Keithley 2612A source meter from Tektronix, Inc. (Beaverton, OR, USA) in a nitrogen atmosphere.
2.4. PDI-Based OFET Fabrication and Characterization
The pristine PDI was dissolved in o-dichlorobenzene. The solution (2 mg/mL) was stirred at 80 °C/12 h for complete dissolution in a N2 glove box, and then the intrinsic PDI solution above was cast on a clean SiO2/n+-Si substrate with a Au source/drain electrode array, which has a channel width (W) of 2.0 mm and a channel length (L) of 5 μm on it to fabricate bottom-gate/bottom-contact (BG/BC) FET device. The electrical characteristics of the devices were measured on a probe station by a Keithley 2612A source meter in a nitrogen atmosphere. The field effect mobility was calculated from the slope of the square root of drain current (ID) versus the gate voltage (VG) curves in a saturated regime according to the transistor equation as follows:
where Ci is the area capacitance of the dielectric (15 nF/cm2 for 230-nm SiO2) and VT is the threshold voltage.
3. Results and Discussion
The PDI is prone to be chemically reduced due to its strong electron-withdrawing diimide groups [33,36]. Here, a reduction process of the raw PDI was performed using the solvothermal approach with excess hydrazine under the applied high magnetic field, as schematically illustrated in Figure 1a. UV–visible absorption spectra were utilized to probe the radical species produced from the reaction. As shown in Figure 1b, the raw PDI solution (0.01 mg/mL in ethanol) exhibits three absorption peaks at 490 nm, 537 nm, and 593 nm, respectively, ascribed to a neutral PDI aggregation in the solution [37,38]. A strong main peak around 554 nm is observed on the solutions after the reduction process under a field of 0 T and 9 T for 24 h (denoted as 0T-24h-PDI and 9T-24h-PDI solutions, respectively, thereafter), which is assigned to the PDI dianion species [36,39]. The change from the absorption spectra is accompanied by a transition from the red to purple color of the solutions after the reaction, as reflected in Figure S2. Furthermore, the as-prepared films cast from both the 0T-24h-PDI and 9T-24h-PDI solutions exhibit a wide shoulder at around 800 nm, which should be attributed to the contribution of the PDI radical anions [39,40]. It is interesting to note that the difference in absorption spectra is hardly discernable between the 0T-24h-PDI and 9T-24h-PDI solutions (similarly negligible spectral change is also shown on the films cast from two solutions). It is indicated that the application of a magnetic field does not influence the generation and components of the radical species during the reduction process of the PDI.
Figure 1c shows the X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of the raw PDI, the 0T-24h-PDI, and 9 T-24 h-PDI powders, respectively. Both the samples, fabricated from the reduction process, exhibit distinct differences in the XRD patterns (e.g., peak positions and intensity) from the raw PDI. However, both of the powders present highly similar diffraction patterns. Furthermore, the PDI powders via the solvothermal approach under the field of 3 T and 6 T (denoted as 3T-24h-PDI and 6T-24h-PDI, respectively) are prepared, respectively. As shown in Figure S3a, the XRD patterns of 3T-24h-PDI and 6T-24h-PDI are also identical to those of 0T-24h-PDI. It is, therefore, concluded that the magnetic field applied during the PDI reduction has a negligible effect on the phase structure of crystallites in the resultant powders, despite the fact that a phase change from a neutral PDI occurs. These observations are also consistent with the UV-vis results above. Nevertheless, the full width at half maximum (FWHM) of the (011) peak (around 10.2°) for the 9T-24h-PDI powder is slightly larger than that for the 0T-24h-PDI sample (shown in Figure S4). It corresponds to a reduced size of crystallites from 25.72 nm to 22.13 nm, determined using the Scherrer equation. Meanwhile, the size of crystallites of the 3T-24h-PDI and 6T-24h-PDI is calculated to be 24.17 nm and 22.15 nm from the FWHM of the (011) peak (Figure S3b), respectively. Furthermore, the PDI material via the HMF-modified solvothermal reaction for a prolonged time of 36 h (denoted as 9T-36h-PDI) is also prepared. As shown in Figure S5a, the powder exhibits almost identical XRD patterns as the 9T-24h-PDI, implying that the lattice structure of the PDI remains intact. However, the size of crystallites is calculated as 18.11 nm (from the data in Figure S5b), smaller than that of the 0T-24h-PDT and 9T-24h-PDI. The results clearly reveal that the self-assembly of the aggregates is suppressed in the PDI radical solutions synthesized under magnetic field conditions. To gain a deeper insight into packing ordering and crystallinity of the PDI from the HMF-modified reduction process, 2D grazing incident X-ray diffraction (GIXRD) is also performed on the as-prepared films cast from the 0T-24h-PDI and 9T-24h-PDI solutions, as shown in Figure S6. Both kinds of films exhibit a strong () scattering along the direction of qz (shown in Figure S6a,b), which is assigned to the π-π stacking, indicating the face-on packing ordering. However, the cross-section profiles along qz (Figure S6c,d) reveal a small difference in the () peak position between the two films. Based on the Bragg formula (Supporting Information), the π-π stacking distance is calculated as 3.37 Å for the 9T-24h-PDI films, a slight increase from 3.32 Å for the 0T-24h-PDI films (inset of Figure S6c,d). Summarily, our results indicate that the magnetic field influences the reduction process and the properties of the resultant PDI solutions, which can, consequently, tune the molecular stacking and order of the crystallites assembled from the dianion solutions.
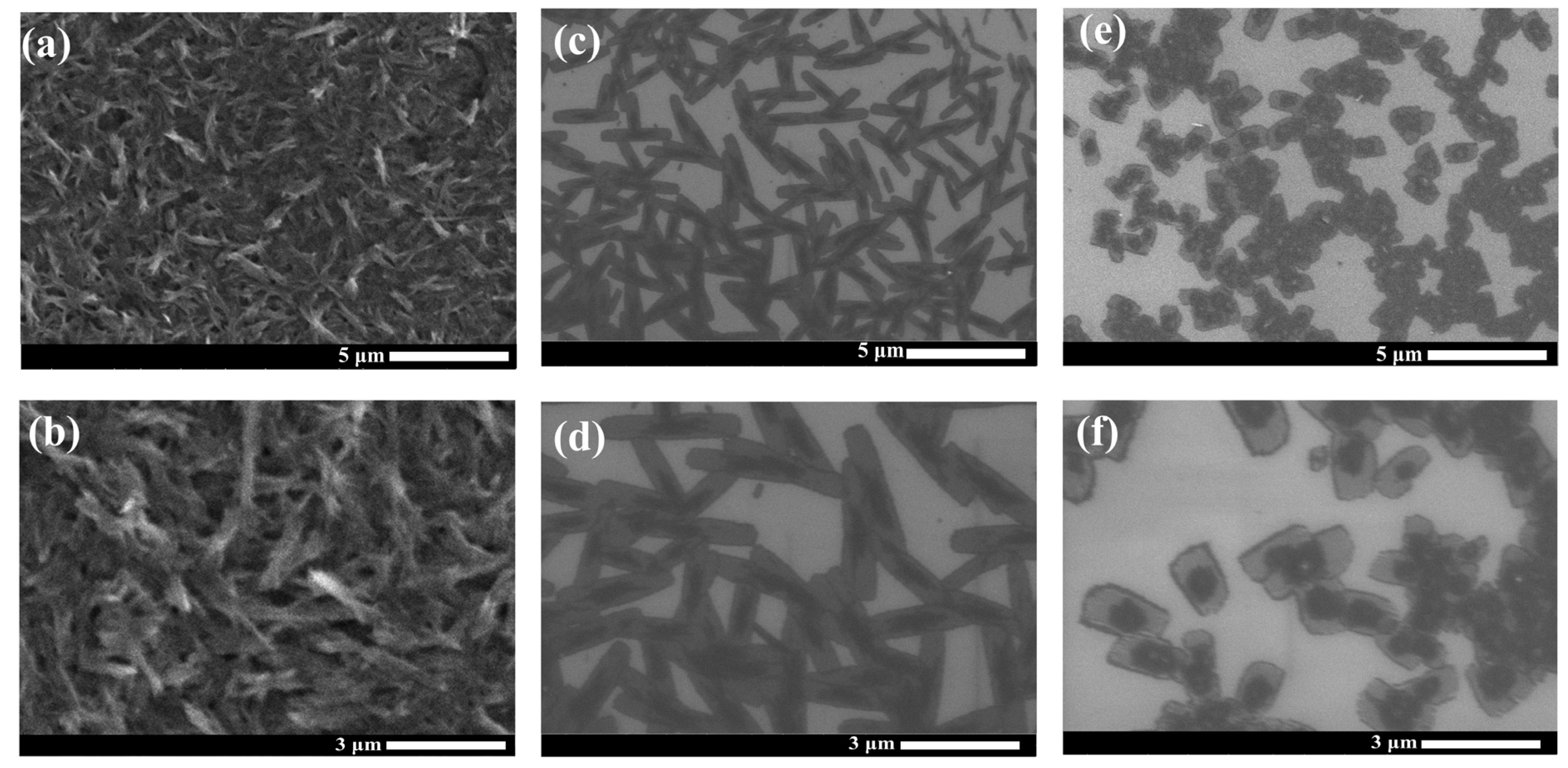
SEM was utilized to investigate the morphology of the PDI films obtained from different synthesis processes. The SEM images in Figure 2a,b exhibit the compact nanorod structure formed in the film of the raw PDI. These nanorods become clearly larger in size (3–5 μm long) and less compactly distributed in the film by self-assembly from the reduced PDI solution (shown in Figure 2c,d). Intriguingly, micro-plate structures are formed in the film cast from the solution prepared via the HMF-modified reduction process (Figure 2e,f). Distinct morphological change indicates that HMF enables the regulation of the self-assembly of the PDI aggregates by influencing the synthesis reaction of the PDI radical species, which is consistent with the XRD characterizations above. Similarly, effective morphological tuning of the nanomaterials has been observed in the magnetic field-assisted synthesis and assembly of the oxides/sulfides and carbon nanostructures [22,41,42]. Magnetic manipulation of the nanomorphology observed can be driven by the magnetic field effects (MFEs), such as the magnetic force or the anisotropy of magnetic energy on the reaction species, as well as the change in the Zeeman energy on the radicals [41]. In our case, such MFEs might affect the formation and structure of the pre-aggregates of the PDI radical molecules during the HMF-modified reduction, which would finally determine the assembly and growth of the crystallites in the subsequent solution cast process.
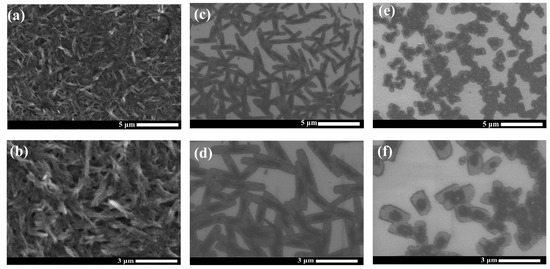
Figure 2.
SEM images of raw PDI films (a,b), 0T-24h-PDI films (c,d), and 9T-24h-PDI films (e,f). Dilute solutions were utilized for the deposition.
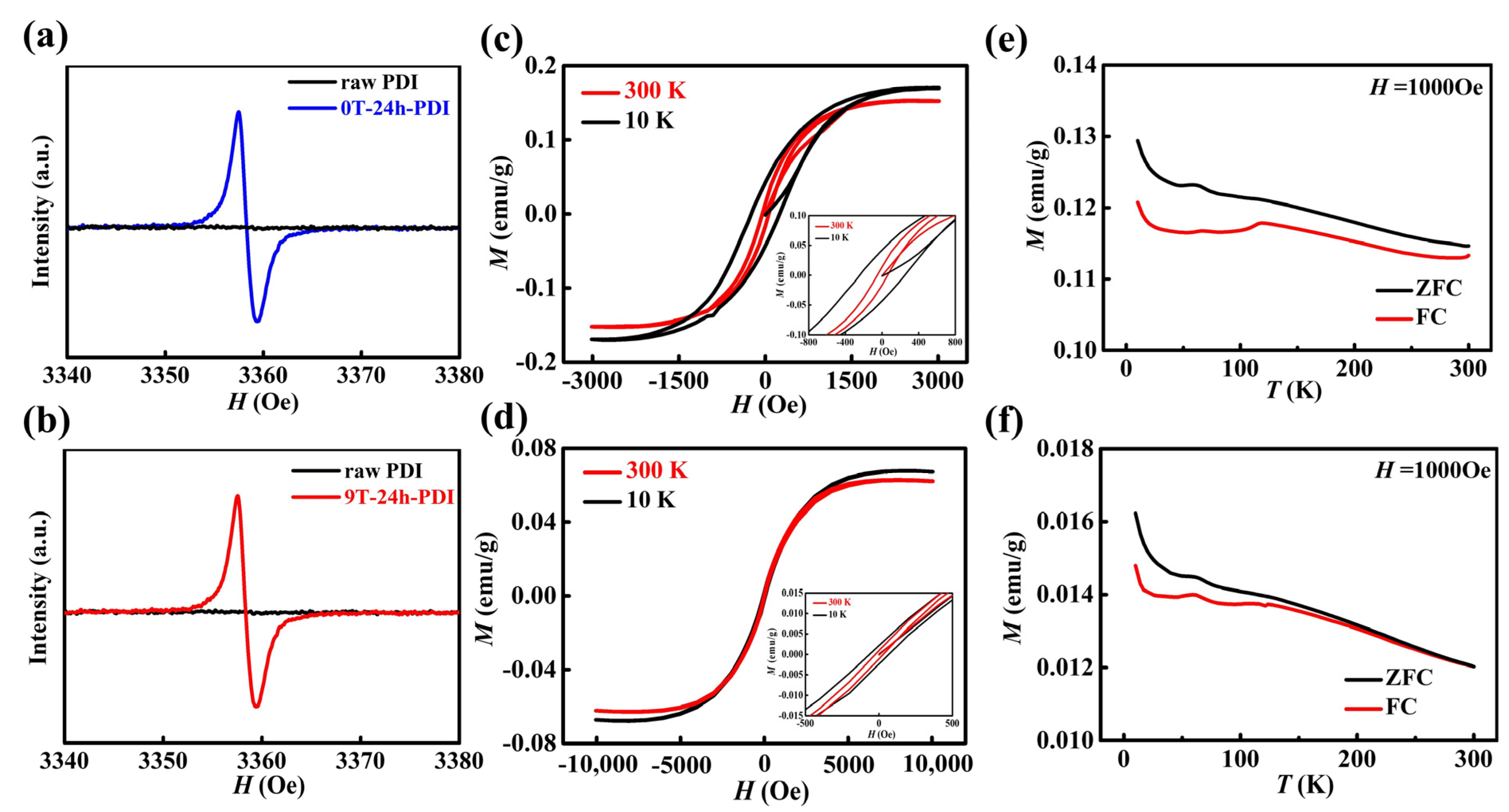
Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) measurements were performed to detect the formation of unpaired electrons and radical anions of the PDI samples [43,44]. As shown in Figure 3a,b, the neutral raw PDI exhibits no EPR signal, while an intense resonance absorption around g = 2.003 is observed on both as-prepared 0T-24h-PDI and 9T-24h-PDI films (also shown in Figure S7a), which is assigned to the unpaired electrons with spin S = 1/2. It clearly confirms that a high concentration of free radical anions is generated after the oxidation of the PDI dianions, while there is no EPR signal for the PDI solutions composed of the dianions (shown in Figure S7b) with a closed-shell structure. Magnetic properties were measured on the oxidized PDI powders prepared via the reduction process under HMF and free of HMF. As shown in Figure 3c, the magnetization-magnetic field (M-H) curves of the 0T-24h-PDI exhibit clear hysteresis loops at 10 K and 300 K, a ferromagnetic character. A fairly high saturated magnetization (Ms) of ca. 0.15 emu/g is extracted at 300 K, while the coercive field (Hc) of 249 Oe and 61 Oe is obtained at 10 K and 300 K, respectively (inset of Figure 3c). However, the PDI powder via a reduction process under 3T-HMF (3T-24h-PDI) exhibits an Ms of 0.12 emu/g and an Hc of 213 Oe at 10 K, as well as weakened ferromagnetism at 300 K, as shown in the M-H curves in Figure S8a. The 6T-24h-PDI powder (shown in Figure S8b) displays a lower Ms and Hc than the 0T-24h-PDI and 3T-24h-PDI. Furthermore, the M-H curves of the 9T-24h-PDI powder (in Figure 3d) reveal a weak ferromagnetism at low temperatures and a super-paramagnetism at 300 K, respectively. The Ms of 0.063 emu/g at 10K can be achieved at a high field exceeding 5000 Oe, and a weak Hc of 68 Oe is observed. Figure S8c,d present the average values of Ms and Hc for the PDI magnets prepared under different field strengths. Both the values exhibit an obvious decline with the enhancement of the magnetic field applied, revealing a clear effect of HMF on the magnetic properties of the PDI magnets. Figure 3e,f display the magnetization versus temperature (M-T) curves of the 0T-24h-PDI and 9T-24h-PDI powders in the zero-field-cooled (ZFC) and field-cooled (FC) conditions. The bifurcation between the ZFC and FC curves starts from around 300 K and far above 300 K for two samples, respectively, indicating that the Tc of the 0T-24h-PDI is far above room temperature; however, the 9T-24h-PDI exhibits a lower Tc of around 300 K. It should be noted in Figure S9 that the raw PDI powder shows a linear M-H curve with a negative slope, a characteristic of diamagnetic behavior. Therefore, the above results clearly indicate that the ferromagnetism of the PDI originates from the generation of high concentrations of spin-carrying anions via the reduction and subsequent oxidation process. The spin exchange interaction between the neighboring PDI anions enables the emergence of magnetic order [18]. The lower magnetization and Tc, which is exhibited on the PDI materials from the magnetic field-modified reduction process, could be correlated with the lowered crystallinity and enlarged π–π stacking distance in the PDI aggregates, which might weaken the spin exchange interaction between the PDI anions [18]. However, the amount and stability of radicals in the reduced PDI solutions should be the key factor to affect the magnetic properties of the PDI (discussed as follows).
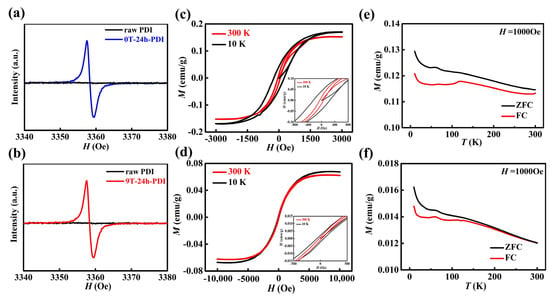
Figure 3.
(a,b) EPR spectra of the as-prepared 0T-24h-PDI (a) and 9T-24h-PDI (b) powders. The spectrum of the raw PDI is also shown. (c,d) Typical M-H curves of the 0T-24h-PDI (c) and 9T-24h-PDI (d) powders measured at 10 K and 300 K. (e,f) Temperature dependence of the ZFC and FC magnetization (M-T curves) of the 0T-24h-PDI (e) and 9T-24h-PDI (f) powders, respectively. A magnetic field of 1000 Oe is applied.
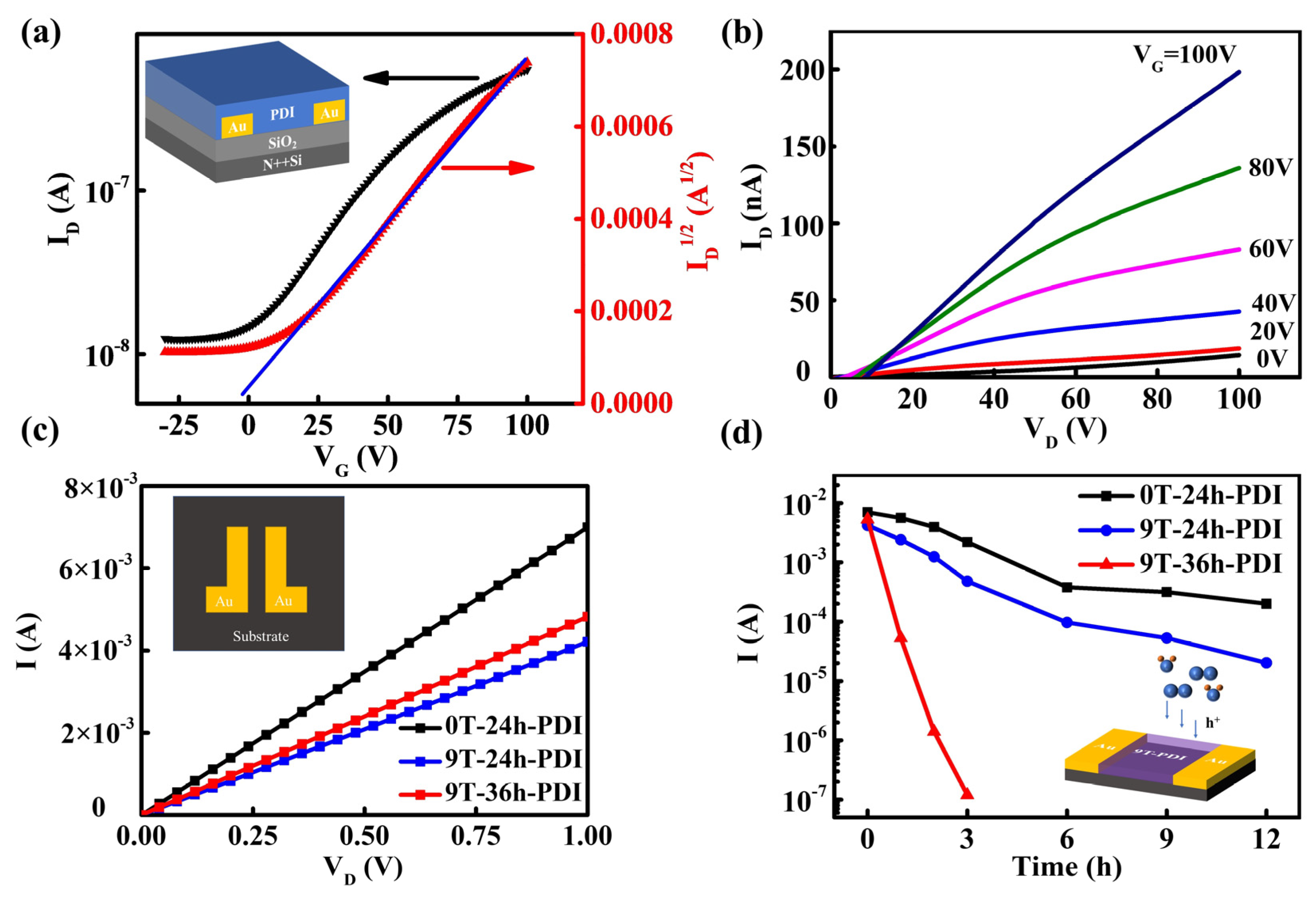
To investigate the electrical properties of the ferromagnetic PDIs, the FET devices based on the neutral PDI films in the bottom-gate/bottom-contact structure (displayed in the inset in Figure 4a) are fabricated. The neutral PDI film exhibits a clear N-type behavior (Figure 4b), with electron mobility of 1.8 × 10−5 cm2 V−1s−1 calculated from the transfer curves in Figure 4a. Considering the n-doping effect induced by the PDI radical anions, planar two-terminal device geometry was utilized to conduct electrical characterization of the radical PDI films. The inset in Figure 4c shows the image of the paired electrodes on which the films are deposited. Figure 4c displays the linear current-voltage (I-V) curves for all the samples. The as-prepared 0T-24h-PDI film (ca. 600 nm) exhibits a high electrical conductivity of 28.75 S/m, abruptly enhanced compared to the raw PDI films. It should be attributed to a high density of free carriers provided by radical anions after spontaneous oxidation of the PDI dianions. However, for the films prepared from the HMF-modified reduction process, the conductivity becomes lower, with 17.5 S/m and 20 S/m for the 9T-24h-PDI film and 9T-36h-PDI film, respectively. It could correspond to a decreased carrier density.
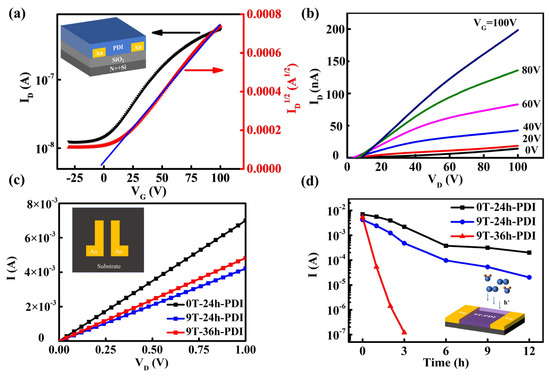
Figure 4.
(a,b) Typical transfer curves (a) and output curves (b) of a BG/BC FET device based on the neutral PDI film. The inset shows a schematic illustration of the FET structure. (c) I-V curves of the as-prepared 0T-24h-PDI films, 9T-24h-PDI films, and 9T-36h-PDI films measured in the N2 atmosphere. The inset depicts the Au electrode pairs with a gap distance of 5 μm, on which the PDI film is deposited. (d) The evolution of device current at the bias of 1.0 V with the air exposure time for different PDI films, which is extracted from the I-V curves in Figures S10–S12. The inset is the schematic diagram of the device structure used to “sensor” the air attack for the film.
Furthermore, the evolution of electrical properties of different PDI films is examined by prolonged exposure to ambient air. As shown in Figure 4d and Figures S10–S13, the current through the 0T-24h-PDI film measured at a bias of 1V exhibits only a slow decay with increased exposure time, while such current decay becomes more severe on the 9T-24h-PDI film (a 100-fold decrease in device current after air exposure for 12 h). Furthermore, the 9T-36h-PDI film shows an abrupt drop of device current by four orders of magnitudes upon a 3 h air exposure and exhibits a fast response of ca. 10−5 A/s within 180 s (shown in Figure S14). It is interesting to find out that the poorer stability of electrical properties happens on the samples prepared by the reduction process under HMF. Since the evolution of device current is correlated with the change in the carrier density of the films, which reflects the population and stability of free radicals [45], the observed instability of electrical properties should originate from the difference in chemical activity of the PDI radical anions influenced by the magnetic field-modified reduction process.
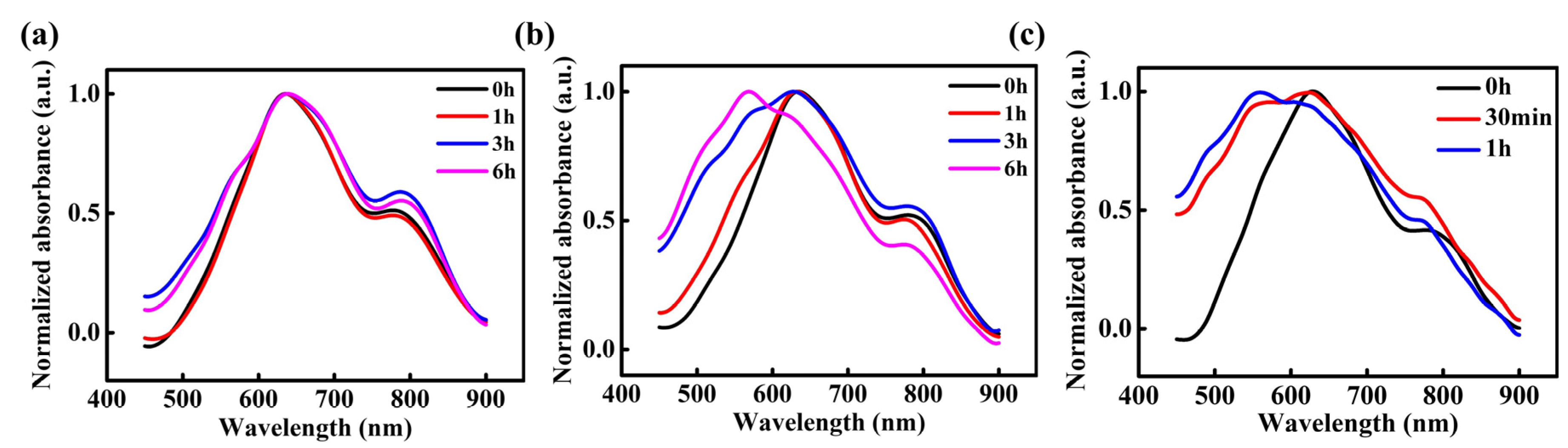
To explore the magnetic field effect on the stability of the radicals, in situ UV-vis absorption spectra were measured for three types of PDI films exposed to ambient air for different durations. As depicted in Figure 5a, the 0T-24h-PDI film exhibits a small decay of the 800 nm absorption peak attributed to the radical anions, as well as a slight enhancement of the neutral PDI absorption below 500 nm with the air exposure time. It indicates the good air stability of radical anions in this sample, which is in agreement with the electrical characterization results described above. In contrast, for the 9T-24h-PDI film, the absorption from radical anions decreases steadily; meanwhile, the absorption from the neutral PDI is enhanced dramatically with the prolonged air exposure (shown in Figure 5b), manifesting a greater sensitivity to the oxidation by oxygen and water from air [45]. Furthermore, as displayed in Figure 5c, the neutral PDI component becomes dominant in the absorption spectra after only 1h of air exposure, which arises from the fast conversion of the radical anions into the neutral PDI by an air attack. Our observations, therefore, corroborate that the accelerated degradation in conductivity is attributed to poorer stability of the radical anions in the PDI films fabricated from the HMF-modified reduction process. Such magnetic field-derived instability should also be one of the key origins for the weaker ferromagnetic properties of these films.
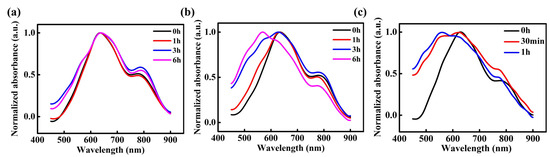
Figure 5.
UV-vis absorption spectra of the 0T-24h PDI film (a), 9T-24h-PDI film (b), and 9T-36h-PDI film (c) as a function of the air exposure time.
However, the origin of the instability of the radical anions is not clear presently. It is proposed to be related to the unidentified aspects of the radical dianions in the solution via the HMF-modified solvothermal approach. The issue needs further structural and electronic characterizations. From the energetic point of view, the application of a magnetic field is unfavorable energetically for the generation of radical dianions, which have a diamagnetic closed-shell structure (magnetic energy is promoted in the system). Therefore, the triplet/singlet ratio of the radicals, produced in the reduction process, might be modified remarkably [34], which could negatively influence the amount and stability of the resultant dianions and thus be correlated to deteriorated magnetic properties of the PDI magnets. The situation is different from the cases of the synthesis of the nanomaterials under HML [25,26], in which the formation of the product phases with a higher magnetic order is facilitated due to the lowering of magnetic energy upon the generation of these products under the magnetic field. On the other hand, the assembly and growth of the radical PDI aggregates could also be modulated via the solution cast of the dianion solution under HMF to study the MFE on the structure and magnetic properties of the PDI magnets. A lowering of magnetic free energy of the aggregates, arising from the interaction between the spin-carrying anions and HMF, will benefit the formation of a stable and enhanced ferromagnetic phase in the produced films.
4. Conclusions
In summary, a high magnetic field is applied during a solvothermal (reduction) reaction to modulate the synthesis and assembly of the radical organic magnet based on a semiconducting PDI. The XRD, GIXRD, and SEM measurements reveal the reduced crystallinity and a smaller-size nanorod structure on the produced PDIs. These materials also exhibit lowered saturation magnetization and Tc, as well as faster degradation of electrical conductivity, compared to the PDI magnets fabricated without a magnetic field. Notably, decreased stability of the radical anions against ambient air is observed on the PDI magnets synthesized via a magnetic field-modified reduction process. We propose that such radical instability is responsible for the weakened electrical and magnetic properties. Therefore, in addition to the capability for the effective tuning of the structure and properties of organic magnets in the synthesis (e.g., solvothermal reaction) process, a high magnetic field is expected to be utilized during the solution phase growth and assembly process to regulate and improve the ferromagnetism of organic radical magnets.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/magnetochemistry10050034/s1, Figure S1: (a) A photograph of an autoclave including a Teflon-lined tank and a non-magnetic stainless shell. (b,c) A photograph of a homemade heater (b) and the heater fixed with the autoclave (c). (d) A photograph of a superconducting magnet (containing a heater inside) used in this work; Figure S2: The photographs of the raw PDI solution (a) and the 9T-24h-PDI solution (b) prepared for UV–visible measurement; Figure S3: (a) XRD pattern of the as-prepared 3T-24h-PDI and 6T-24h-PDI powder; (b) the profile of the (011) reflection is shown in Figure S3a; Figure S4: XRD profiles of the (011) reflection for the samples of 0T-24h-PDI (a) and 9T-24h-PDI (b) shown in Figure 2d; Figure S5: (a) XRD pattern of the as-prepared 9T-36h-PDI powder; (b) the profile of the (011) reflection is shown in Figure S5a; Figure S6: (a,b) 2D GIXRD patterns of as-prepared films cast from the 0T-24h-PDI solution (a) and 9T-24h-PDI solution (b), respectively; (c,d) cross-section profiles along qz of the GIXRD patterns shown in Figure S6a,b; Figure S7: (a) g-factor spectrum of the as-prepared 9T-24h-PDI film and (b) EPR spectrum of the PDI dianion solution (9T-24h-PDI solution); Figure S8: (a,b) M-H curves of the 3T-24h-PDI (a) and 6T-24h-PDI (b) powders measured at 10 K and 300 K; (c,d) saturation magnetization (c) and coercive field (d) of the PDI magnets prepared by the solvothermal approach under an external magnetic field of 0 T, 3 T, 6 T, and 9 T; the data collected are based on at least five sample batches for each preparation condition (field strength); Figure S9: M-H curves of the raw PDI powder obtained at 300 K; Figure S10: I-V curves of the 0T-24h-PDI film exposed to ambient air for 1 h (a), 2 h (b), 3 h (c), 6 h (d), 9 h (e), and 12 h (f), respectively; Figure S11: I-V curves of the 9T-24h-PDI film exposed to ambient air for 1 h (a), 2 h (b), 3 h (c), 6 h (d), 9 h (e), and 12 h (f), respectively; Figure S12: I-V curves of the 9T-36h-PDI film exposed to ambient air for 1 h (a), 2 h (b), and 3 h (c); Figure S13: I-V curves of the 9T-36h-PDI film exposed to ambient air for 30 s (a), 60 s (b), 90 s(c), 120 s (d), 150 s (e), and 180 s (f), respectively; Figure S14: the device current at the bias of 1V of the 9T-36h-PDI film for different air exposure times, which is extracted from the I-V curves in Figure S13.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.Z.; data curation, H.Z.; formal analysis, Z.C.; funding acquisition, L.H. and F.Z.; investigation, X.L.; methodology, H.Z.; project administration, F.Z.; resources, H.Z.; software, Z.A.; supervision, L.H.; validation, Z.C.; visualization, L.H.; writing—original draft, H.Z.; writing—review and editing, F.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, Grant No. 12374127, 12074383, and 21972145) and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2021YFA1600202).
Data Availability Statement
Derived data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
A portion of this work was performed at the Steady High Magnetic Field Facilities (SM1 Superconducting Magnet), the High Magnetic Field Laboratory, and CAS. The technique assistance on the GIXRD experiments from the staff at BL14B station at Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facilities is also gratefully acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Forrest, S.R. The path to ubiquitous and low-cost organic electronic appliances on plastic. Nature 2004, 428, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.N.; Gasperini, A.; Bao, Z. Stretchable polymer semiconductors for plastic electronics. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2018, 4, 1700429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Qi, J.; Hu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Sun, S.; Sun, Y.; Gong, W.; Luo, L.; Zhang, L.; et al. Balancing the film strain of organic semiconductors for ultrastable organic transistors with a five-year lifetime. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.C.; Wang, H.; Ren, J.F.; Xie, S.J.; Timm, C. Spin-charge disparity of polarons in organic ferromagnets. Org. Electron. 2014, 15, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steelman, M.E.; Adams, D.J.; Mayer, K.S.; Mahalingavelar, P.; Liu, C.; Eedugurala, N.; Lockart, M.; Wang, Y.; Gu, X.; Bowman, M.K.; et al. Magnetic ordering in a High-Spin donor–acceptor conjugated polymer. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2206161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, H.; Herng, T.S.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Zeng, W.; Ding, J.; Loh, K.P.; Shen Wee, A.T.; Wu, J. Room-Temperature Magnets Based on 1,3,5-Triazine-Linked Porous Organic Radical Frameworks. Chem 2019, 5, 1223–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Z. Ferromagnetism in a periodic Anderson-like organic polymer at half-filling and zero temperature. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 73, 35118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Fan, Y.; Qin, W. Progress of organic magnetic materials. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2019, 62, 977501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wei, J.; Xie, S.; Hu, G. Spin filtering through a metal/organic-ferromagnet/metal structure. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 75, 165321. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, M.; Wei, M.; Ren, S.; Hao, X.; Qin, W. Organic chiral charge transfer magnets. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 4705–4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Li, H.X.; Zhang, H.Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.T.; Wang, C.; Ren, J.F.; Hu, G.C. Molecular rectification induced by magnetization alignment in organic-ferromagnetic devices. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2024, 26, 4329–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blundell, S.J.; Pratt, F.L. Organic and molecular magnets. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2004, 16, 771–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Gong, M.; Yuan, G.; Grossman, J.C.; Wuttig, M.; Ren, S. Room temperature multiferroicity of charge transfer crystals. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 9373–9379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, M.; Song, K.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Tian, Y.; Hao, X.; Qin, W. Organic multiferroic magnetoelastic complexes. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2003293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korshak, Y.V.; Medvedeva, T.V.; Ovchinnikov, A.A.; Spector, V.N. Organic polymer ferromagnet. Nature 1987, 326, 370–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajca, A.; Wongsriratanakul, J.; Rajca, S. Magnetic ordering in an organic polymer. Science 2001, 294, 1503–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, J.; Park, J.; Shin, D.; Choi, H.; Seo, J.; Yoo, J.; Baek, J. Organic ferromagnetism: Trapping spins in the glassy state of an organic network structure. Chem 2018, 4, 2357–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Mao, Z.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, D.; Jia, Y.; Hu, D.; Ma, Y. Room-Temperature ferromagnetism in perylene diimide organic semiconductor. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2108103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; Wuttig, M. Organic exciton multiferroics. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 724–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Li, H.; Hall, A.; Gao, W.; Gong, M.; Yuan, G.; Grossman, J.; Ren, S. All-polymeric control of nanoferronics. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1501264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Xia, G.; Chen, Q. Magnetochemistry and chemical synthesis. Chin. Phys. B 2019, 28, 37102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Watanabe, K. Magnetic-Field-Induced synthesis of magnetic γ-Fe2O3 nanotubes. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ren, Z.; Ren, W.; Cao, G.; Deng, K.; Zhong, Y. Magnetic-field-assisted solvothermal growth of single-crystalline bismuth nanowires. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 115602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Q.; Zeng, C.; Hou, B. Magnetic-Field-Induced growth of Single-Crystalline Fe3O4 nanowires. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Hu, L.; Dai, J.; Tang, X.; Wei, R.; Sheng, Z.; Liang, C.; Shao, D.; Song, W.; Liu, Q.; et al. Highly Ambient-Stable 1T-MoS2 and 1T-WS2 by hydrothermal synthesis under high magnetic fields. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 1694–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.; Meng, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Lin, Y.; Shi, X.; Sheng, Z.; Wang, H. Magnetic Field-Induced synthesis of One-Dimensional nickel nanowires for enhanced microwave absorption. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 10, 2201604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Chen, F.; Hu, L.; Zhang, K.; Dai, J.; Zhang, F. Effective controlling of film texture and carrier transport of a High-Performance polymeric semiconductor by magnetic alignment. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 5126–5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Fei, Y.; Ai, Z.; Hui, D.; Zhu, L.; Pan, G.; Zhang, F. The synergistic effect of processing solvents on magnetic manipulation of orientational order and carrier transport of semiconducting polymers. J. Mater. Chem. C 2023, 11, 6376–6385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Qu, Z.; Chen, Q. Tuning the structure and properties of a multiferroic metal–organic-framework via growing under high magnetic fields. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 13675–13678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Hu, L.; Qu, Z.; Hao, N.; Pi, L.; Ma, L. Magnetic field tuning of quantum spin excitations in a weakly coupled S=1/2 Heisenberg spin chain as seen from NMR. Phys. Rev. B 2019, 100, 125126. [Google Scholar]
- Usta, H.; Facchetti, A.; Marks, T.J. N-Channel semiconductor materials design for organic complementary circuits. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ye, P.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Xu, X.; Wu, X.; Dong, T.; Zhang, H.; Hou, J.; et al. Achieving High-Performance ternary organic solar cells through tuning acceptor alloy. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeman, C.J.I.; Kim, S.; Zhang, F.; Schanze, K.S. Direct observation of the reduction of aryl halides by a photoexcited perylene diimide radical anion. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 2204–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brocklehurst, B. Magnetic fields and radical reactions: Recent developments and their role in nature. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2002, 31, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zadeh-Haghighi, H.; Simon, C. Magnetic field effects in biology from the perspective of the radical pair mechanism. J. R. Soc. Interface 2022, 19, 20220325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifert, S.; Schmidt, D.; Würthner, F. An ambient stable core-substituted perylene bisimide dianion: Isolation and single crystal structure analysis. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wu, Y.; Fu, H.; Yao, J. Self-Assembly of perylenediimide nanobelts and their Size-Tunable exciton dynamic properties. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 2163–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ji, C.; Fan, Z.; Ma, R.; Yin, M. A facile design of thio-perylenediimides with controllable fluorescent, photodynamic and photothermal effects towards cancer theranostics. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 13126–13129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcon, R.O.; Brochsztain, S. Aggregation of 3,4,9,10-Perylenediimide Radical Anions and Dianions Generated by Reduction with Dithionite in Aqueous Solutions. J. Phys. Chem. A 2009, 113, 1747–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosztola, D.; Niemczyk, M.P.; Svec, W.; Lukas, A.S.; Wasielewski, M.R. Excited doublet states of electrochemically generated aromatic imide and diimide radical anions. J. Phys. Chem. A 2000, 104, 6545–6551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Zhang, R.; Chen, Q. Synthesis and assembly of nanomaterials under magnetic fields. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 14064–14105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Li, C.; Qian, Y.; Hu, L.; Fang, J.; Tong, W.; Nie, R.; Chen, Q.; Wang, H. Magnetic-induced graphene quantum dots for imaging-guided photothermal therapy in the second near-infrared window. Biomaterials 2020, 232, 119700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Pink, M.; Junghoefer, T.; Zhao, W.; Hsu, S.; Rajca, S.; Calzolari, A.; Boudouris, B.W.; Casu, M.B.; Rajca, A. High-Spin (S = 1) Blatter-Based diradical with robust stability and electrical conductivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 6059–6070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Li, J.; Fang, Y.; Deng, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, G.; Wang, Y.; Gu, X.; Jiang, S.; Lei, T. High-mobility semiconducting polymers with different spin ground states. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Sun, H.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, F.; Hu, D.; Jiao, F.; Qin, L.; Linseis, V.; Fabiano, S.; Crispin, X.; et al. High thermoelectric performance in n-Type perylene bisimide induced by the soret effect. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2002752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).