Observation of Zigzag-Shaped Magnetic Domain Boundaries in Granular Perpendicular Magnetic Recording Media Using Alternating Magnetic Force Microscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
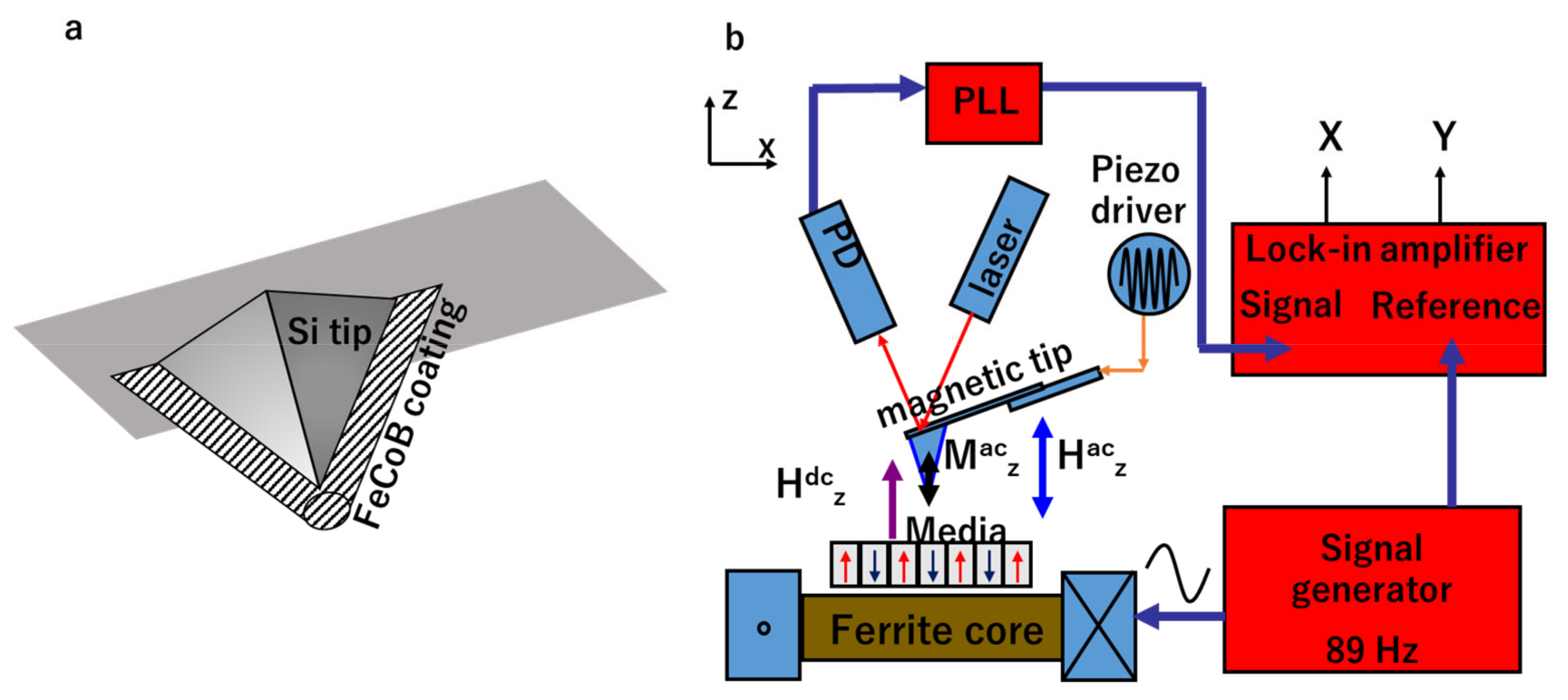
2. Experimental Protocol
3. Results and Discussion
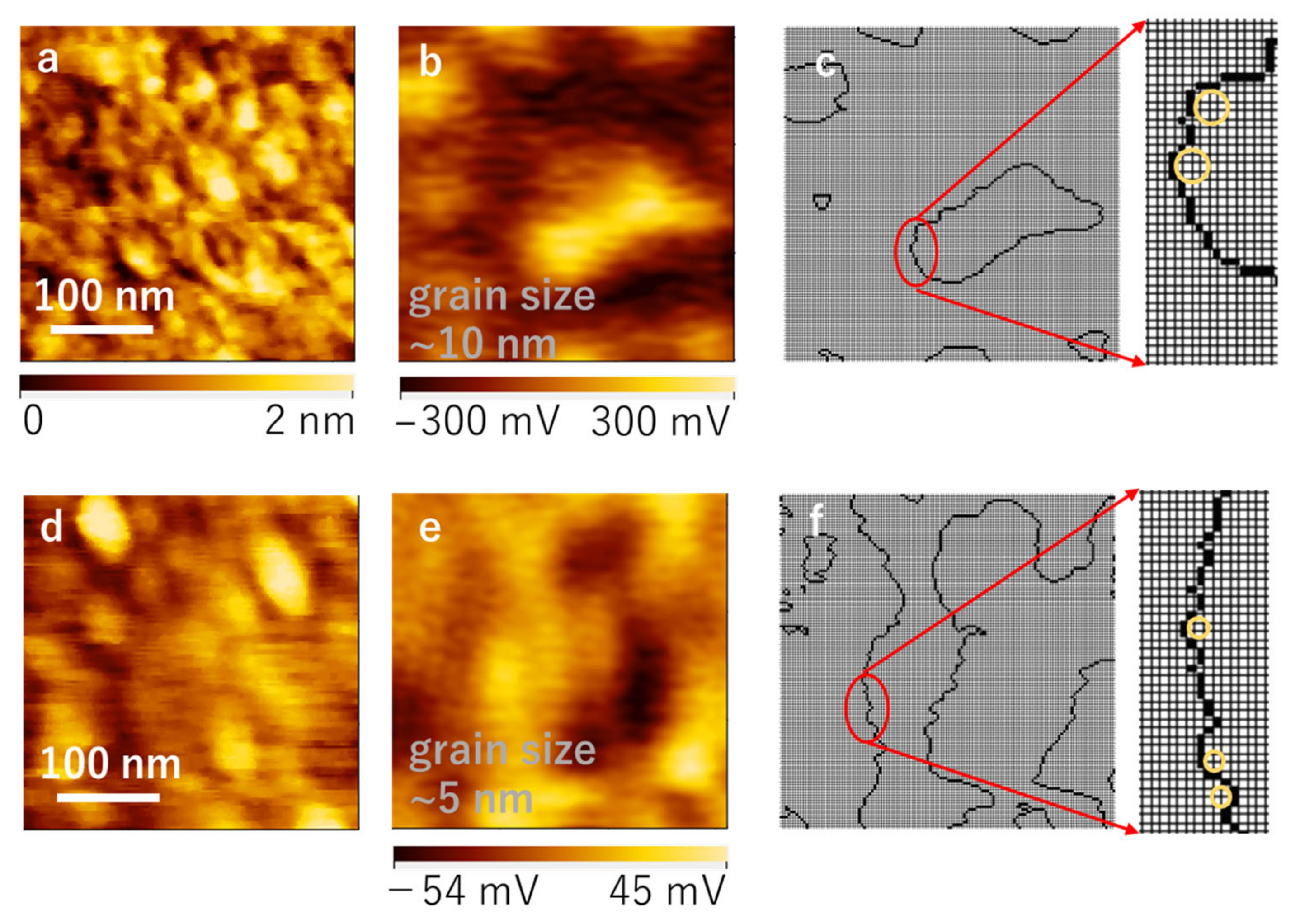
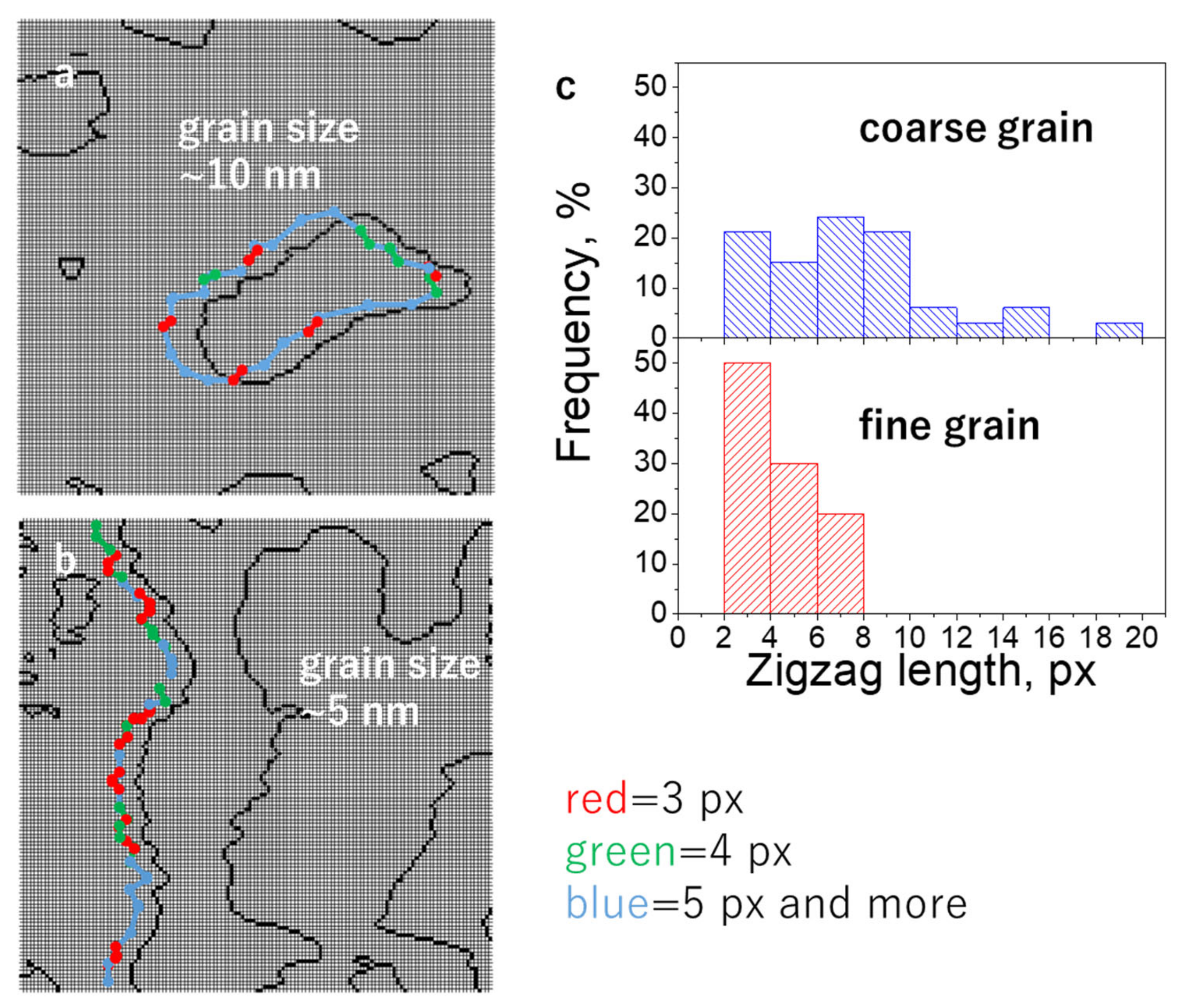
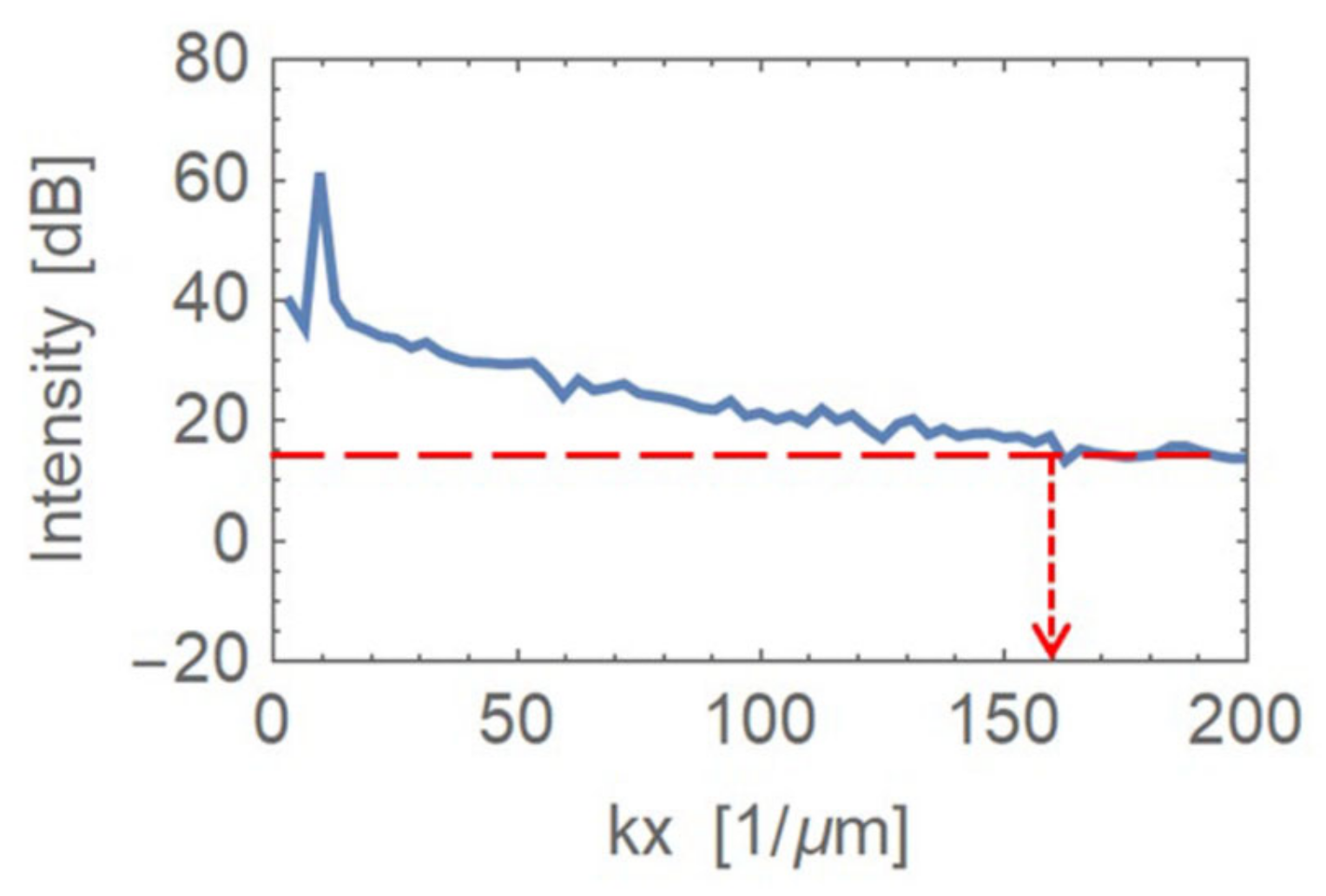
3.1. Granular Media
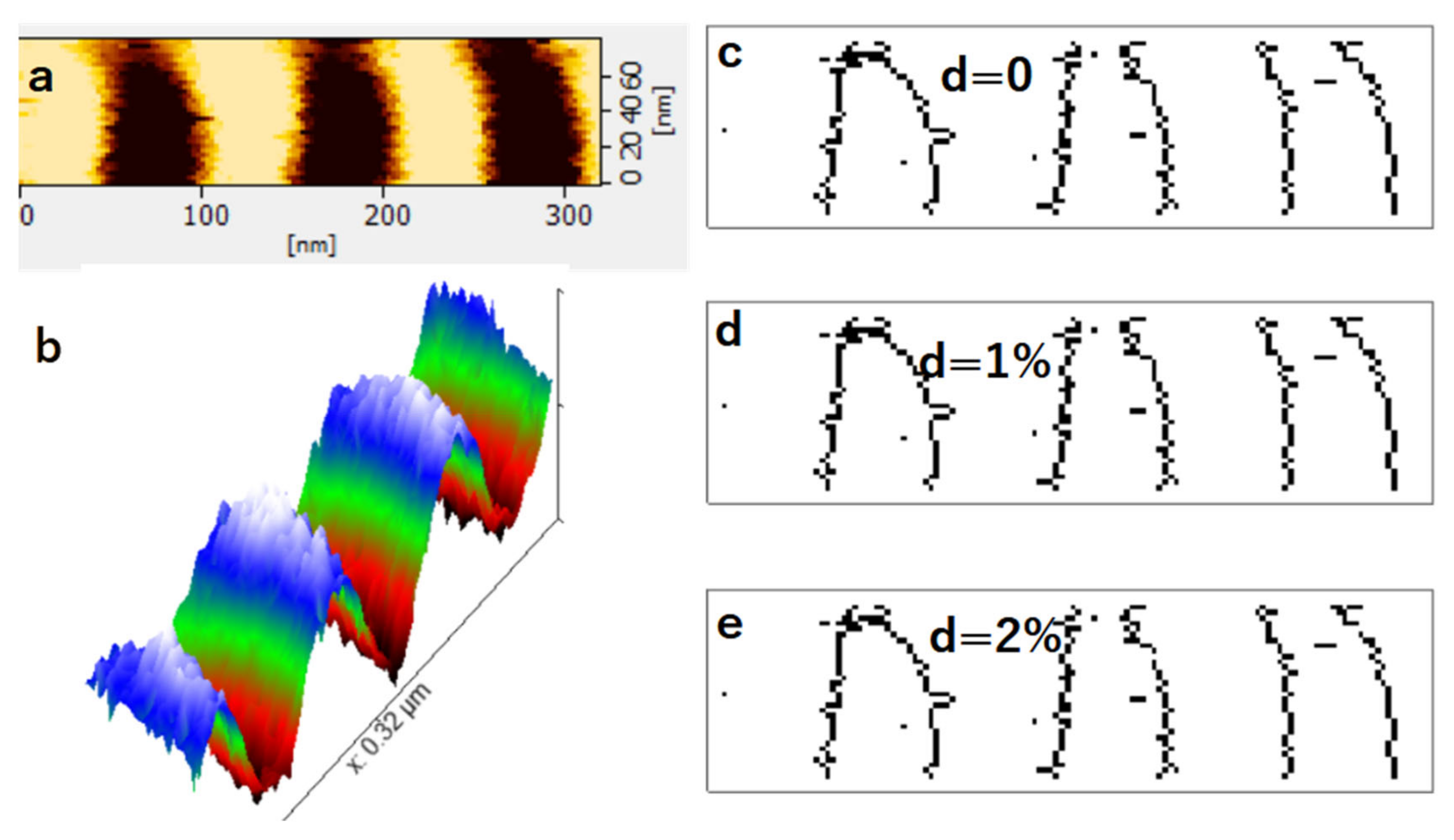
3.2. Recorded Media
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dwivedi, N.; Ott, A.K.; Sasikumar, K.; Dou, C.; Yeo, R.J.; Narayanan, B.; Sassi, U.; De Fazio, D.; Soavi, G.; Dutta, T.; et al. Graphene overcoats for ultra-high storage density magnetic media. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Futamoto, M.; Ohtake, M. Development of media nanostructure for perpendicular magnetic recording. J. Magn. Soc. Jpn. 2017, 41, 108–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, D.; Parker, G.; Mosendz, O.; Lyberatos, A.; Mitin, D.; Safonova, N.Y.; Albrecht, M. FePt heat assisted magnetic recording media. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2016, 34, 060801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.-H.; Victora, R.H. Heat-assisted magnetic recording—Micromagnetic modeling of recording media and areal density: A review. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 563, 169973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khunkitti, P.; Wannawong, N.; Jongjaihan, C.; Siritaratiwat, A.; Kruesubthaworn, A.; Kaewrawang, A. Micromagnetic simulation of L10-FePt-based exchange-coupled-composite-bit-patterned media with microwave-assisted magnetic recording at ultrahigh areal density. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Takahoshi, H.; Ito, H.; Rheem, Y.W.; Saito, H.; Ishio, S. Influence of inhomogeneous coercivities on media noise in granular perpendicular media investigated by using magnetic force microscopy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 283, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyachkin, A.; Sepehri-Amin, H.; Suzuki, I.; Tajiri, H.; Takahashi, Y.K.; Srinivasan, K.; Ho, H.; Yuan, H.; Seki, T.; Ajan, A.; et al. Transmission electron microscopy image based micromagnetic simulations for optimizing nanostructure of FePt-X heat-assisted magnetic recording media. Acta Mater. 2022, 227, 117744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noula Tefouet, J.D.; Yemele, D. Signal noise ratio and magnetic density in digital magnetic recording system: Analytical and numerical investigation. Int. J. Magn. Electromagn. 2021, 7, 034. [Google Scholar]
- Jongjaihan, C.; Kaewrawang, A. Micromagnetic simulation of L10-FePt-based transition jitter of heat-assisted magnetic recording at ultrahigh areal density. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulesh, N.; Bolyachkin, A.; Suzuki, I.; Takahashi, Y.K.; Sepehri-Amin, H.; Hono, K. Data-driven optimization of FePt heat-assisted magnetic recording media accelerated by deep learning TEM image segmentation. Acta Mater. 2023, 255, 119039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skomski, R.; Yan, M.L.; Xu, Y.F.; Sellmyer, D.J. Continuous/cluster-pinned recording media. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2007, 43, 2163–2165. [Google Scholar]
- Valcu, B.F.; Yeh, N.-H. Jitter in a Voronoi pattern media-effect of grain size distribution and reader width. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 2160–2162. [Google Scholar]
- Dengina, E.; Bolyachkin, A.; Sepehri-Amin, H.; Hono, K. Machine learning approach for evaluation of nanodefects and magnetic anisotropy in FePt granular films. Scripta Mater. 2022, 218, 114797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohashi, T.; Konoto, M.; Koike, K. High-resolution spin-polarized scanning electron microscopy (spin SEM). J. Electron Microscopy 2010, 59, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Kohashi, T. Magnetization analysis by spin-polarized Scanning Electron Microscopy. Scanning 2018, 2018, 2420747. [Google Scholar]
- Hirotsune, A.; Nemoto, H.; Takekuma, I.; Nakamura, K.; Ichihara, T.; Stipe, B.C. Improved grain isolation in [Co/Pd]n multilayer media for thermally assisted magnetic recording. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 1569–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcu, B.F.; Wu, X.; Albuquerque, G.; Papusoi, C.; Desai, M. Experimental determination of reader resolution using PRS patterns and application to media cluster size measurement. AIP Adv. 2017, 7, 056504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasyukov, D.; Ceccarelli, L.; Wyss, M.; Gross, B.; Schwarb, A.; Mehlin, A.; Rossi, N.; Tütüncüoglu, G.; Heimbach, F.; Zamani, R.R.; et al. Imaging stray magnetic field of individual ferromagnetic nanotubes. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 964–970. [Google Scholar]
- Favieres, C.; Vergara, J.; Madurga, V. Surface roughness influence on Néel-, Crosstie, and Bloch-type charged zigzag magnetic domain walls in nanostructured Fe films. Materials 2020, 13, 4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, H.; Ito, R.; Egawa, G.; Li, Z.; Yoshimura, S. Direction detectable static magnetic field imaging by frequency-modulated magnetic force microscopy with an AC magnetic field driven soft magnetic tip. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 07E330. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, D.; Saito, H.; Ishio, S. Near surface magnetic domain observation with ultra-high resolution. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 11163–11168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, D.V.; Staub, U.; Devidas, T.R.; Kalisky, B.; Nowack, K.; Webb, J.L.; Andersen, U.L.; Huck, A.; Broadway, D.A.; Wagner, K.; et al. 2024 roadmap on magnetic microscopy techniques and their applications in materials science. J. Phys. Mater. 2024, 7, 032501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarova, M.V.; Akaishi, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Rao, K.S.; Yoshimura, S.; Saito, H. High-resolution alternating magnetic force microscopy using an amorphous FeB-based tip driven by an inverse magnetostrictive effect: Imaging of the high-density magnetic recording media. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 546, 168755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarova, M.V.; Akaishi, Y.; Ikarashi, T.; Rao, K.S.; Yoshimura, S.; Saito, H. Alternating Magnetic Force Microscopy: Effect of Si doping on the temporal performance degradation of amorphous FeCoB magnetic tips. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 471, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Makarova, M.V.; Tanaka, H.; Sonobe, H.; Matsumura, T.; Saito, H. Observation of Zigzag-Shaped Magnetic Domain Boundaries in Granular Perpendicular Magnetic Recording Media Using Alternating Magnetic Force Microscopy. Magnetochemistry 2024, 10, 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry10120106
Makarova MV, Tanaka H, Sonobe H, Matsumura T, Saito H. Observation of Zigzag-Shaped Magnetic Domain Boundaries in Granular Perpendicular Magnetic Recording Media Using Alternating Magnetic Force Microscopy. Magnetochemistry. 2024; 10(12):106. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry10120106
Chicago/Turabian StyleMakarova, M. V., Hanamichi Tanaka, Hiroshi Sonobe, Toru Matsumura, and Hitoshi Saito. 2024. "Observation of Zigzag-Shaped Magnetic Domain Boundaries in Granular Perpendicular Magnetic Recording Media Using Alternating Magnetic Force Microscopy" Magnetochemistry 10, no. 12: 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry10120106
APA StyleMakarova, M. V., Tanaka, H., Sonobe, H., Matsumura, T., & Saito, H. (2024). Observation of Zigzag-Shaped Magnetic Domain Boundaries in Granular Perpendicular Magnetic Recording Media Using Alternating Magnetic Force Microscopy. Magnetochemistry, 10(12), 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry10120106





