Changes in Soil Nematode and Microbial Community in Cucumber Root-Zone Soil Shaped by Intercropping with Amaranth
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Condition and Plant Materials
2.2. Cucumber-Amaranth Intercropping Experiment
2.3. Status of Cucumber Root-Knot Nematode Disease
2.4. Soil Chemical Properties Analysis
2.5. Soil Nematode Community Analysis
2.6. Soil Microbes-Related Parameters Analysis
2.7. Soil Microbial Community Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Properties and Cucumber RKN Disease
3.2. The Soil Nematode Community Shaped by Intercropping System
3.3. Soil Microbial Biomass and Community-Level Physiological Profiling
3.4. Intercropping System Altered Soil Microbial Community Composition
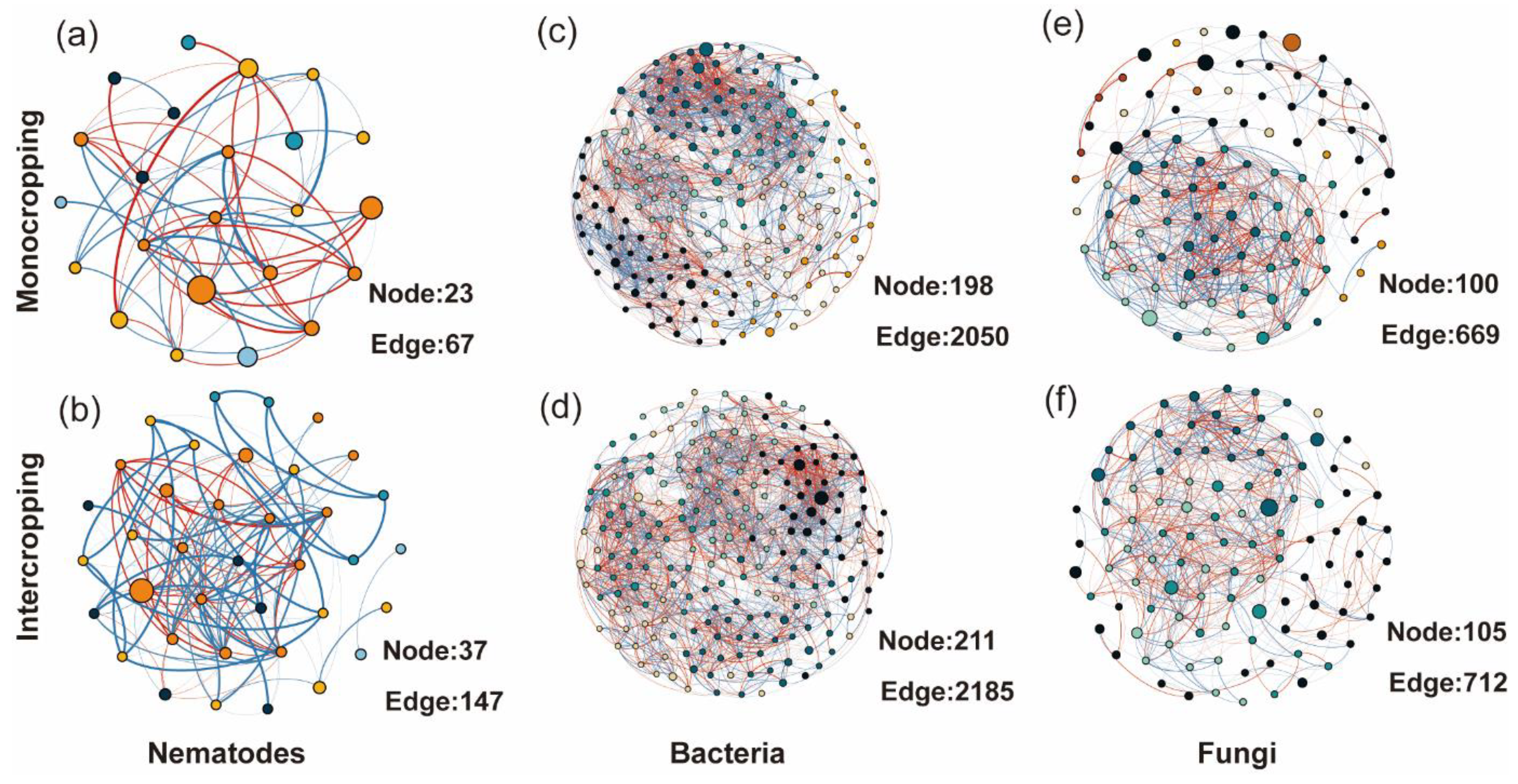
3.5. Co-Occurrence Network Soil Biota
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boudreau, M. Diseases in Intercropping Systems. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2013, 51, 499–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, M.A.; Yasin, H.S.; Gul, H.; Qin, R.; Mohi Ud Din, A.; Khalid, M.H.B.; Hussain, S.; Gitari, H.; Saeed, A.; Wang, J.; et al. Maize/Soybean Strip Intercropping Produces Higher Crop Yields and Saves Water under Semi-Arid Conditions. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1006720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooker, R.W.; Bennett, A.E.; Cong, W.-F.; Daniell, T.J.; George, T.S.; Hallett, P.D.; Hawes, C.; Iannetta, P.P.M.; Jones, H.G.; Karley, A.J.; et al. Improving Intercropping: A Synthesis of Research in Agronomy, Plant Physiology and Ecology. New Phytol. 2015, 206, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, M.S. Crop Strength through Diversity. Nature 2000, 406, 681–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Wu, M.; Xu, R.; Wang, X.; Pan, R.; Kim, H.-J.; Liao, H. Root Interactions in a Maize/Soybean Intercropping System Control Soybean Soil-Borne Disease, Red Crown Rot. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; de Boer, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, C.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X. Suppression of Soil-Borne Fusarium Pathogens of Peanut by Intercropping with the Medicinal Herb Atractylodes Lancea. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 116, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malézieux, E.; Crozat, Y.; Dupraz, C.; Laurans, M.; Makowski, D.; Ozier-Lafontaine, H.; Rapidel, B.; de Tourdonnet, S.; Valantin-Morison, M. Mixing Plant Species in Cropping Systems: Concepts, Tools and Models: A Review. In Sustainable Agriculture; Lichtfouse, E., Navarrete, M., Debaeke, P., Véronique, S., Alberola, C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 329–353. ISBN 978-90-481-2666-8. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Zwimpfer, E.; Hervé, M.R.; Bont, Z.; Erb, M. Neighbourhood Effects Determine Plant–Herbivore Interactions below-Ground. J. Ecol. 2018, 106, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Song, C.; Liu, X.; Zhou, L.; Yang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Du, Q.; Pang, T.; Fu, Z.; et al. Yield Advantage and Nitrogen Fate in an Additive Maize-Soybean Relay Intercropping System. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 987–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristok, C.; Poeschl, Y.; Dudenhöffer, J.-H.; Ebeling, A.; Eisenhauer, N.; Vergara, F.; Wagg, C.; van Dam, N.M.; Weinhold, A. Plant Species Richness Elicits Changes in the Metabolome of Grassland Species via Soil Biotic Legacy. J. Ecol. 2019, 107, 2240–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, D.; Tilman, D. National Food Production Stabilized by Crop Diversity. Nature 2019, 571, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastogeer, K.M.G.; Tumpa, F.H.; Sultana, A.; Akter, M.A.; Chakraborty, A. Plant Microbiome—An Account of the Factors That Shape Community Composition and Diversity. Curr. Plant Biol. 2020, 23, 100161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, P.; Cesarz, S.; Liu, T.; Roscher, C.; Eisenhauer, N. Effects of Plant Species Diversity on Nematode Community Composition and Diversity in a Long-Term Biodiversity Experiment. Oecologia 2021, 197, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, R. Diversity in Biological Control. Crop Prot. 1991, 10, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detrey, J.; Cognard, V.; Djian-Caporalino, C.; Marteu, N.; Doidy, J.; Pourtau, N.; Vriet, C.; Maurousset, L.; Bouchon, D.; Clause, J. Growth and Root-Knot Nematode Infection of Tomato Are Influenced by Mycorrhizal Fungi and Earthworms in an Intercropping Cultivation System with Leeks. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 169, 104181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardgett, R.D.; van der Putten, W.H. Belowground Biodiversity and Ecosystem Functioning. Nature 2014, 515, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Chai, X.; Tariq, A.; Zeng, F.; Li, X.; Graciano, C. Intercropping Systems Modify Desert Plant-Associated Microbial Communities and Weaken Host Effects in a Hyper-Arid Desert. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 754453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Gao, L. Effects of Summer Cover Crop and Residue Management on Cucumber Growth in Intensive Chinese Production Systems: Soil Nutrients, Microbial Properties and Nematodes. Plant Soil 2011, 339, 299–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Hoogen, J.; Geisen, S.; Routh, D.; Ferris, H.; Traunspurger, W.; Wardle, D.A.; de Goede, R.G.M.; Adams, B.J.; Ahmad, W.; Andriuzzi, W.S.; et al. Soil Nematode Abundance and Functional Group Composition at a Global Scale. Nature 2019, 572, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Liu, T.; Whalen, J.K.; Wei, Z. Nematodes: An Overlooked Tiny Engineer of Plant Health. Trends Plant Sci. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongers, T.; Ferris, H. Nematode Community Structure as a Bioindicator in Environmental Monitoring. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1999, 14, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yang, H.; Zhang, W.; Bezemer, T.M.; Liang, W.; Li, Q.; Li, L. Interspecific Interactions between Crops Influence Soil Functional Groups and Networks in a Maize/Soybean Intercropping System. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 355, 108595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, B.; Wang, K.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Fei, H.; Pan, R.; Han, F. Plants Use Rhizosphere Metabolites to Regulate Soil Microbial Diversity. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 5267–5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbrich, T.C.; Rivas-Ubach, A.; Tiemann, L.K.; Friesen, M.L.; Evans, S.E. Plant Root Exudates and Rhizosphere Bacterial Communities Shift with Neighbor Context. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 172, 108753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad, P.; Gouzy, J.; Aury, J.-M.; Castagnone-Sereno, P.; Danchin, E.G.J.; Deleury, E.; Perfus-Barbeoch, L.; Anthouard, V.; Artiguenave, F.; Blok, V.C.; et al. Genome Sequence of the Metazoan Plant-Parasitic Nematode Meloidogyne incognita. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abad, P.; Favery, B.; Rosso, M.-N.; Castagnone-Sereno, P. Root-Knot Nematode Parasitism and Host Response: Molecular Basis of a Sophisticated Interaction. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2003, 4, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhtar, T.; Kayani, M.Z.; Hussain, M.A. Response of Selected Cucumber Cultivars to Meloidogyne incognita. Crop Prot. 2013, 44, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Li, R.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L.; Gu, X.; Fan, W.; Lucas, W.J.; Wang, X.; Xie, B.; Ni, P.; et al. The Genome of the Cucumber, Cucumis sativus L. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mndzebele, B.; Ncube, B.; Fessehazion, M.; Mabhaudhi, T.; Amoo, S.; du Plooy, C.; Venter, S.; Modi, A. Effects of Cowpea-Amaranth Intercropping and Fertiliser Application on Soil Phosphatase Activities, Available Soil Phosphorus, and Crop Growth Response. Agronomy 2020, 10, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mndzebele, B.; Ncube, B.; Nyathi, M.; Kanu, S.A.; Fessehazion, M.; Mabhaudhi, T.; Amoo, S.; Modi, A.T. Nitrogen Fixation and Nutritional Yield of Cowpea-Amaranth Intercrop. Agronomy 2020, 10, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awe, G.O.; Abegunrin, T.P. Effects of low input tillage and amaranth intercropp Effects of Low Input Tillage and Amaranth Intercropping System on Growth and Yield of Maize (Zea mays). Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2009, 4, 578–583. [Google Scholar]
- Pitan, O.O.R.; Esan, E.O. Intercropping Cucumber with Amaranth (Amaranthus cruentus L.) to Suppress Populations of Major Insect Pests of Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Prot. 2014, 47, 1112–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; La, S.; Zhang, X.; Gao, L.; Tian, Y. Salt-Induced Recruitment of Specific Root-Associated Bacterial Consortium Capable of Enhancing Plant Adaptability to Salt Stress. ISME J. 2021, 15, 2865–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.P.; Long, H.; Xu, J.H. PCR Assays for Rapid and Sensitive Identification of Three Major Root-Knot Nematodes, Meloidogyne incognita, M. Javanica and M. Arenaria. Acta Phytopathol. Sin. 2004, 34, 204–210. [Google Scholar]
- Houba, V.J.G.; Temminghoff, E.J.M.; Gaikhorst, G.A.; van Vark, W. Soil Analysis Procedures Using 0.01 M Calcium Chloride as Extraction Reagent. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2000, 31, 1299–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, P.L. Recommended Potassium Test. In Recommended Chemical Soil Test Procedures for the North Central Region, Bulletin 499; North Dakota Agricultural Experiment Station: Fargo, ND, USA, 1980; pp. 17–18. [Google Scholar]
- Jones Sr, J.B.; Wolf, B.; Mills, H.A. Microwave Digestion Using CEM Microwave Digestion System. In Plant Analysis Handbook; Micro-Macro Publishing: Athens, GA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Townshend, J.L. A Modification and Evaluation of the Apparatus for the Oostenbrink Direct Cottonwool Filter Extraction Method. Nematologica 1963, 9, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeates, G.W.; Bongers, T.; De Goede, R.G.M.; Freckman, D.W.; Georgieva, S.S. Feeding Habits in Soil Nematode Families and Genera—An Outline for Soil Ecologists. J. Nematol. 1993, 25, 315–331. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shannon, C.E.; Weaver, W. The Mathematical Theory of Communication, by CE Shannon (and Recent Contributions to the Mathematical Theory of Communication), W. Weaver; University of illinois Press: Champaign, IL, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Pielou, E.C. Ecological Diversity; Quarterly Review of Biology: Hoboken, NJ, Wiley, 1975.
- Yeates, G.W.; King, K.L. Soil Nematodes as Indicators of the Effect of Management on Grasslands in the New England Tablelands (NSW): Comparison of native and improved grasslands. Pedobiology. 1997, 41, 526–536. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, E.H. Measurement of Diversity. Nature 1949, 163, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongers, T. The Maturity Index: An Ecological Measure of Environmental Disturbance Based on Nematode Species Composition. Oecologia 1990, 83, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, D.S.; Powlson, D.S. The Effects of Biocidal Treatments on Metabolism in Soil—I. Fumigation with Chloroform. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1976, 8, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, E.D.; Brookes, P.C.; Jenkinson, D.S. An Extraction Method for Measuring Soil Microbial Biomass C. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.-H.; Dobbs, F.C. Comparison of Two Kinds of Biolog Microplates (GN and ECO) in Their Ability to Distinguish among Aquatic Microbial Communities. J. Microbiol. Methods 1999, 36, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, B.; Paulson, J.N.; Zheng, X.; Kolter, R. Simplified and Representative Bacterial Community of Maize Roots. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E2450–E2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardes, M.; Bruns, T.D. ITS Primers with Enhanced Specificity for Basidiomycetes-Application to the Identification of Mycorrhizae and Rusts. Mol. Ecol. 1993, 2, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. Fastp: An Ultra-Fast All-in-One FASTQ Preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast Length Adjustment of Short Reads to Improve Genome Assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian Classifier for Rapid Assignment of RRNA Sequences into the New Bacterial Taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, R.H.; Larsson, K.-H.; Taylor, A.F.S.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Jeppesen, T.S.; Schigel, D.; Kennedy, P.; Picard, K.; Glöckner, F.O.; Tedersoo, L.; et al. The UNITE Database for Molecular Identification of Fungi: Handling Dark Taxa and Parallel Taxonomic Classifications. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D259–D264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Andersen, G.L.; Knight, R. PyNAST: A Flexible Tool for Aligning Sequences to a Template Alignment. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 266–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I. QIIME Allows Analysis of High-Throughput Community Sequencing Data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly Accurate OTU Sequences from Microbial Amplicon Reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kembel, S.W.; Cowan, P.D.; Helmus, M.R.; Cornwell, W.K.; Morlon, H.; Ackerly, D.D.; Blomberg, S.P.; Webb, C.O. Picante: R Tools for Integrating Phylogenies and Ecology. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1463–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, M.E.J. Modularity and Community Structure in Networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 8577–8582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, J.; Cong, W.-F.; Bezemer, T.M. Legacies at Work: Plant-Soil-Microbiome Interactions Underpinning Agricultural Sustainability. Trends Plant Sci. 2022, 27, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikder, M.M.; Vestergård, M.; Kyndt, T.; Fomsgaard, I.S.; Kudjordjie, E.N.; Nicolaisen, M. Benzoxazinoids Selectively Affect Maize Root-Associated Nematode Taxa. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 3835–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Q. Soil Nematode Communities in Jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.) Rhizosphere Soil under Monoculture and Jujube/Wheat (Triticum aestivum Linn.) Intercropping Systems, a Case Study in Xinjiang Arid Region, Northwest of China. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2016, 74, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Banerjee, S.; Herzog, C.; Ramírez, A.C.; Dahlin, P.; van der Heijden, M.G.A. Impact of Land Use Type and Organic Farming on the Abundance, Diversity, Community Composition and Functional Properties of Soil Nematode Communities in Vegetable Farming. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 318, 107488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.; Sprunger, C.D. Soil Food Web Structure and Function in Annual Row-Crop Systems: How Can Nematode Communities Infer Soil Health? Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 178, 104553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leff, J.W.; Bardgett, R.D.; Wilkinson, A.; Jackson, B.G.; Pritchard, W.J.; De Long, J.R.; Oakley, S.; Mason, K.E.; Ostle, N.J.; Johnson, D.; et al. Predicting the Structure of Soil Communities from Plant Community Taxonomy, Phylogeny, and Traits. ISME J. 2018, 12, 1794–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, M.P.; Geisen, S. Trophic Regulations of the Soil Microbiome. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, P.; Zhou, H.; Chen, Z.; Suonan, J. Plant-Soil Mediated Effects of Long-Term Warming on Soil Nematodes of Alpine Meadows on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Biology 2022, 11, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.; Coulibaly, S.F.M.; Cheviron, N.; Mougin, C.; Hedde, M.; Maron, P.-A.; Recous, S.; Trap, J.; Villenave, C.; Chauvat, M. The Multi-Year Effect of Different Agroecological Practices on Soil Nematodes and Soil Respiration. Plant Soil 2023, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeates, G.W. Effects of Plants on Nematode Community Structure. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1999, 37, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikder, M.M.; Vestergård, M. Impacts of Root Metabolites on Soil Nematodes. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 10, 1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochola, J.; Coyne, D.; Cortada, L.; Haukeland, S.; Ng’ang’a, M.; Hassanali, A.; Opperman, C.; Torto, B. Cyst Nematode Bio-Communication with Plants: Implications for Novel Management Approaches. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 1150–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwamba, S.; Kihika-Opanda, R.; Murungi, L.K.; Losenge, T.; Beck, J.J.; Torto, B. Identification of Repellents from Four Non-Host Asteraceae Plants for the Root Knot Nematode, Meloidogyne incognita. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 15145–15156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, M.G.; Bradeen, J.M.; Kinkel, L.L. Effects of Plant Host Species and Plant Community Richness on Streptomycete Community Structure. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 83, 596–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, N.; Kinkel, L.L.; Kistler, H.C. Soil Fungal Communities Respond to Grassland Plant Community Richness and Soil Edaphics. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 70, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, C.R.; Copeland, J.; Wang, P.W.; Guttman, D.S.; Kotanen, P.M.; Johnson, M.T.J. Assembly and Ecological Function of the Root Microbiome across Angiosperm Plant Species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E1157–E1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bever, J.D.; Platt, T.G.; Morton, E.R. Microbial Population and Community Dynamics on Plant Roots and Their Feedbacks on Plant Communities. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 66, 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Li, X.; Xi, X.; Cong, W.-F. Crop Diversification Reinforces Soil Microbiome Functions and Soil Health. Plant Soil 2022, 476, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cheng, J.; Li, T.; Liao, Y. Response of Soil Fungal Communities to Continuous Cropping of Flue-Cured Tobacco. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Guo, X.; Guo, Q.; Tan, X.; Wang, Z. Long-Term Chili Monoculture Alters Environmental Variables Affecting the Dominant Microbial Community in Rhizosphere Soil. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 681953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bebber, D.P.; Richards, V.R. A Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Organic and Mineral Fertilizers on Soil Microbial Diversity. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 175, 104450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Wang, K.; Song, L.; Wang, X.; Wu, D. Daytime Warming Has Stronger Negative Effects on Soil Nematodes than Night-Time Warming. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, B.L.; Wall, D.H.; Adams, B.J.; Ayres, E.; Barrett, J.E.; Virginia, R.A. Long-Term Experimental Warming Reduces Soil Nematode Populations in the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 2052–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Bing, H.; Fang, L.; Wu, Y.; Yu, J.; Shen, G.; Jiang, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X. Diversity Patterns of the Rhizosphere and Bulk Soil Microbial Communities along an Altitudinal Gradient in an Alpine Ecosystem of the Eastern Tibetan Plateau. Geoderma 2019, 338, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagg, C.; Bender, S.F.; Widmer, F.; van der Heijden, M.G.A. Soil Biodiversity and Soil Community Composition Determine Ecosystem Multifunctionality. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5266–5270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Zhang, N.; Li, Y.; Zhu, C.; Qu, B.; Liu, H.; Li, R.; Bai, Y.; Shen, Q.; Falcao Salles, J. Bio-Organic Soil Amendment Promotes the Suppression of Ralstonia Solanacearum by Inducing Changes in the Functionality and Composition of Rhizosphere Bacterial Communities. New Phytol. 2022, 235, 1558–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, H.; Qi, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Han, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Li, H. Soil Nematode Community and Crop Productivity in Response to 5-Year Biochar and Manure Addition to Yellow Cinnamon Soil. BMC Ecol. 2020, 20, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topalović, O.; Hussain, M.; Heuer, H. Plants and Associated Soil Microbiota Cooperatively Suppress Plant-Parasitic Nematodes. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadfield, V.G.A.; Hartley, S.E.; Redeker, K.R. Associational Resistance through Intercropping Reduces Yield Losses to Soil-Borne Pests and Diseases. New Phytol. 2022, 235, 2393–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Song, M.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Gao, L.; Tian, Y. Changes in Soil Nematode and Microbial Community in Cucumber Root-Zone Soil Shaped by Intercropping with Amaranth. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9080924
Zhang X, Song M, Li J, Liu X, Gao L, Tian Y. Changes in Soil Nematode and Microbial Community in Cucumber Root-Zone Soil Shaped by Intercropping with Amaranth. Horticulturae. 2023; 9(8):924. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9080924
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xu, Mengyuan Song, Jiafan Li, Xingqun Liu, Lihong Gao, and Yongqiang Tian. 2023. "Changes in Soil Nematode and Microbial Community in Cucumber Root-Zone Soil Shaped by Intercropping with Amaranth" Horticulturae 9, no. 8: 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9080924
APA StyleZhang, X., Song, M., Li, J., Liu, X., Gao, L., & Tian, Y. (2023). Changes in Soil Nematode and Microbial Community in Cucumber Root-Zone Soil Shaped by Intercropping with Amaranth. Horticulturae, 9(8), 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9080924






