Abstract
In recent years, kenaf has gained significant global attention as a more cost-effective, adaptable, and manageable alternative to other fibre crops. India and China, with nearly 70% of the global kenaf production, have emerged as the leading producers of kenaf plants. While kenaf was traditionally valued for its paper production, it has evolved into a multipurpose crop with diverse industrial applications over the past two decades. Conventional soil-based cultivation methods for kenaf require up to six months for plant maturity. However, in vitro propagation techniques offer a promising alternative that enables faster growth and reduced labour costs. In vitro propagation can be achieved using solid and liquid media, with limited research available on the pure liquid culture method for kenaf. This review aims to introduce and compare the production of kenaf using solid and liquid media, with a specific focus on the emerging country of Malaysia, which seeks to harness the potential of kenaf cultivation for the 15th Sustainable Development Goal, “life on land”, and its contribution to the economy.
1. Introduction
Kenaf, Hibiscus cannabinus L., is a tall annual dicotyledonous herb that has gained widespread attention for its potential in diverse industries such as food and beverages, medicine, and cosmetics, and for its economic and horticultural importance [1]. Hibiscus cannabinus L. is a common wild plant in the African nations from the southern Sahara. The warm-season annual plant kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) is indigenous to tropical Africa and is from the Malvaceae botanical family [2]. This dicotyledonous herbaceous plant shares a kinship with cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.), hollyhock (Althaea rosea), okra (Hibiscus esculentus), and roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa). Short-day plants like kenaf have been used for producing fibre, energy, and feedstock. Kenaf is grown for various reasons, primarily due to its horticultural importance; for example, the delicate bast fibre found in its stem [3], its leaves, and its seeds are used in the medical field as they are rich in medicinal value including antioxidants, anticancer, hepatoprotective activities, analgesic, aphrodisiacs, and anti-inflammatory properties [4].
Kenaf has garnered significant interest worldwide due to its versatility and ease of cultivation compared to other fibre crops [5]. According to Hassan et al. [6], this plant exhibits a wider range of adaptability to environmental conditions, climates, and soil types, making it a superior source of cellulose. Additionally, kenaf possesses excellent moisture absorption properties and is both renewable and biodegradable. Kenaf fibres have been found to exhibit impressive tensile strengths and moduli, reaching up to 11.9 GPa and 60 GPa, respectively. Initially used in the production of fabrics, ropes, cords, and storage bags, these fibres are now combined with other materials to create composites employed in diverse industries such as construction, packaging, and furniture [7].
While kenaf’s significance was primarily attributed to paper production in the past, it has gained recognition as a multipurpose crop over the last two decades, owing to its wide range of industrial applications. Traditional soil-based cultivation methods require approximately six months for kenaf to reach maturity. However, one of the main challenges faced by kenaf producers is the management of pests and weeds [8]. Nevertheless, kenaf, with its rapid growth and high biomass production, has demonstrated the ability to tolerate soil conditions containing toxic elements [9].
Traditional breeding can enhance kenaf’s qualities, but to quickly increase the physical material qualities as a structural material, a thorough genetic transformation technique must be established. Plant regeneration from the initial callus can be produced by combining auxins and cytokinins. This method is commonly used for the genetic modification discovered in plants [10]. The cultivation strategies of kenaf in both solid medium and liquid medium should be researched as the kenaf industry is one of the agricultural sectors that contributes to Malaysia’s GDP (gross domestic product) [11]. According to Klaus and Wan-Mohtar [12], significant enhancements have been made in the techniques used for cultivating and domesticating crucial wild mushrooms, as there has been a notable increase in the emergence of industries dedicated to the commercial production of wild edible mushrooms, which applies for plants as well.
The global kenaf market is projected to cross USD 854 million by 2025. Thus, more research should be conducted on the horticultural aspects of this plant, especially the cultivation strategies. The goal of horticulture is to optimize plant growth and yield, waste utilization, and fungal–plant stimulants; improve plant quality; and enhance the overall aesthetic appeal of cultivated plants [13,14,15]. This review suggests a cheaper, safer, and faster method of kenaf production via in vitro propagation and compares the cultivation techniques of solid medium culture and liquid medium culture. This can contribute to the advancement in kenaf applications in various fields such as the food industry, biotechnological and medical fields for its fibre production, biomass production, and extraction of bioactive compounds [4]. One of the primary horticultural uses of kenaf is the fibre production that could be used in automotive industries [16], paper production, and textile industries [17]. The kenaf seed can be used in food production [18], and the biomass of kenaf has a broad application in fields such as medicine and food biotechnology [19].
Botanical Description of Kenaf
Kenaf is an annual herb with a stem height of 2 to 5 m; it is slender, with a cylindrical shape and thorny wild accessions. The leaves of the kenaf plant are alternate and simple, with filiform stipules, and pubescent with a length range of 5–8 mm. The petioles of the plant are between 3 and 30 cm long. The leaves of the kenaf plant have a blade that measures 1 to 19 cm in length and 0.1 to 20 cm in width. The blade is three- to seven-lobed in the lower part of the plant, while the upper part is usually not lobed or can be bract-like near the apex. The blade apex is acuminate, and the base is cuneate to cordate with dentate or serrate margins. The upper surface of the blade is glabrous, and there is a noticeable nectary at the base of the midrib that is approximately 3 mm long. The lower surface of the blade is hairy along the veins [20].
The flowers of kenaf plants are axillary, solitary flowers with short pedicels, a stiff epicalyx, and seven to eight bracteoles, as demonstrated in Figure 1. The bracteoles are large spreading yellow or pale yellow with a crimson or purple centre corolla. It also has a staminal column with many stamens (superior ovary with five carpels). The flower of the kenaf plant has five stigmatic branches emerging from the style after it passes through the staminal column. The fruit capsule has five locules and four to five seeds per locule. Kenaf is primarily a crop with self-pollination [21]. Moreover, photoperiod affects the flowering phase as well. The kenaf flowers are large, bell-shaped, open blossoms ranging in colour from light yellow to cream. The flower is 8–13 cm in diameter, short-stalked, and auxiliary. A single flower has several stamens, five petals, and five sepals. The flowers of kenaf are complete with indeterminate growth. It also contains a superior ovary. The opening and shutting of the flower take place on the same day [22].

Figure 1.
The morphology of Hibiscus cannabinus L. flower: (a) lapped, (b) spiral, (c) detached. (d) The morphology of kenaf fruit. The morphology of kenaf leaves: (e) lobed, (f) partially lobed, (g) unlobed. (h) The morphology of kenaf seeds (figure is original by author).
Kenaf seeds have various shapes such as kidney-shaped, sub-kidney-shaped, and triangular. Kenaf seeds need four to five weeks to mature [23]. Simple kenaf leaves have visible serrated edges on the stem and branches. Leaves start to develop into the cultivar-specific leaf form (entire or split) as the kenaf plant ages. Due to its capacity for rapid development, kenaf may reach heights up to 6 m and a stem diameter in the range of 25 to 51 mm in around 5 months. Kenaf is often sown in the spring and harvested in the early fall as a summer crop. Kenaf may be harvested in a tropical climate for about three to four months after seeding since it grows quickly [24]. Seeds can be kept in good condition for about 8 months when stored at ambient room temperature and humidity [5]. The seeds have various benefits and could be used in making edible oil or biodiesels. Figure 1 shows the morphology of kenaf parts.
Short days encourage the growth of kenaf, and kenaf grows well in temperate and tropical climates where the plant benefits from abundant solar radiation and rain. This lignocellulosic plant is fast-growing and can grow an average of 10 cm per day to a height of 4–6 m. The internal stick, which is 60–65% of the stem and bast, comprises about 35–45% of the stem, making up the entire stem of the kenaf plant. The external skin encloses lengthy fibres with a 2.5 mm length and width of 17 m, whereas the inner core is made up of short, porous fibres with a fibre length of 0.6 mm and width of 33 μm [22].
Within the kenaf stem, there are two distinct layers, each with unique features. The outer layer, also known as the bark or bast, is dense and fibrous. Meanwhile, the inner core is light and composed of wood, with a spongy pith at its centre. Figure 2 illustrates the cross-sectional area of a kenaf stem, providing a visual representation of these characteristics.
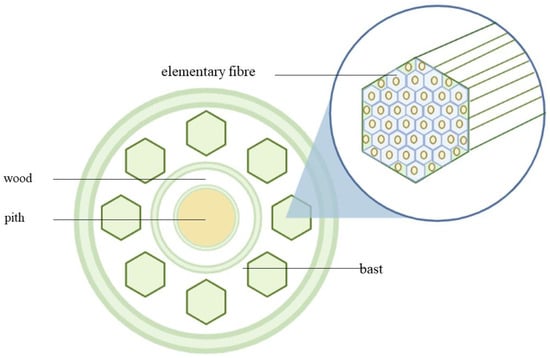
Figure 2.
The cross-sectional area of Hibiscus cannabinus L. stem.
The dry weight of the stem to the core is 30:70. The bast and core of the kenaf plant differ significantly in terms of their physical properties, anatomical structures, chemical compositions, and mechanical properties. The values of the common fibre properties between bast fibre and the core parts differ due to the usage of different retting processes, plantation locations, and species variation, resulting in inconsistent kenaf fibre properties [25]. The bast fibre of the kenaf plant is made up of elementary fibres and microfibril. Cellulose is usually present in the microfibril. The cellulose is usually synthesized and deposited either continuously in a highly linear and parallel arrangement, referred to as the crystalline region, or in a low-ordered and loose orientation, referred to as the amorphous region. Cellulose whiskers, which are the nearly flawless crystalline section of microfibrils, can bring the physical characteristics of cellulose biogenesis closer to those of faultless crystals, as noted by Xu, J. et al. [26].
The mechanical features found in kenaf bast fibres could be used as a substitute for glass fibres and aramid, and utilized as reinforcement in polymer composites. The cellulose content of kenaf bast fibres is about 63.5%. Figure 3 shows the cross-sectional area of Hibiscus cannabinus L. bast fibre.
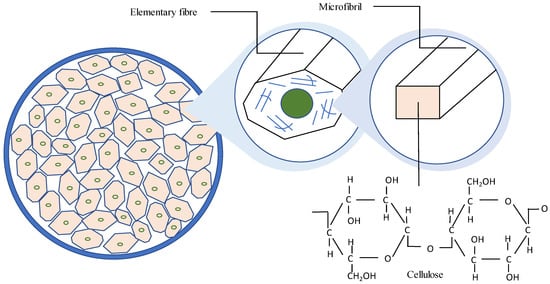
Figure 3.
The cross-sectional area of Hibiscus cannabinus L. bast fibre.
Kenaf fibres behave differently during pulping and papermaking due to their different morphological structures. Fibre properties affect the pulping conditions used in paper pulp manufacturing. The degree of milling required for the core pulp during the milling process is exceptionally high and may not be practical. On the other hand, the bast pulp is easily refined and does not compromise its strength. Due to the variation in quality between the bast and core fibres, it is recommended to separate and pulp each fraction independently. The refined bast pulp can then be blended with the unrefined core, depending on the desired properties of the final product. The selection of the pulping process is determined by the characteristics of the end product, as stated by Mohd et al. [27].
Some of the kenaf parts such as kenaf core, kenaf fibre, and kenaf stem are sold in various sizes from chips up to powder. The kenaf chip size is usually sieved in different mesh sizes and packed for selling. Figure 4 shows the kenaf core, kenaf fibre, and kenaf stem, packaged for commercialization.
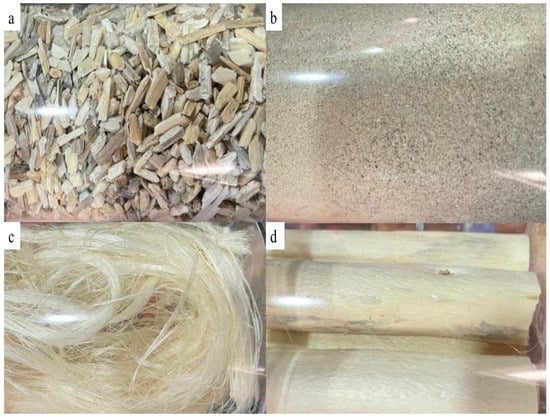

Figure 4.
(a) Hibiscus cannabinus L. core (chip), (b) Hibiscus cannabinus L. core (powder), (c) Hibiscus cannabinus L. fibre, (d) Hibiscus cannabinus L. stem (figure is original from author).
Different parts of the kenaf plant have unique characteristics and functions. The stem, for example, is sturdy and can be used to make durable textiles, while the leaves are a source of fibre that can be used to make paper. The bark is also rich in fibre and can be used for insulation or as a source of biofuel. Table 1 provides a general morphological description of the different parts of the kenaf plant. It highlights the various physical characteristics of each part, including size, shape, and colour. This information is crucial for understanding the plant’s potential uses and how to best utilize its various components.

Table 1.
General morphological description of kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) plant parts.
In addition to its many practical applications, kenaf is also a highly sustainable crop. It requires less water and pesticides than other crops and can be grown in areas that are not suitable for other types of agriculture. This makes it an attractive option for farmers and businesses looking to reduce their environmental impact.
2. Malaysian Kenaf Cultivation
Kenaf was introduced in Malaysia as a replacement for tobacco through a strategic industrial plan in the 1990s. Initially, the idea of using roselle as a substitute was considered, but kenaf was introduced to the National Tobacco Board in 2004–2005. After meticulous planning for about four years, kenaf crops were introduced to growers in 2006. The National Tobacco Board was later replaced by the National Kenaf and Tobacco Board (NKTB) in April 2010, with the government’s vision of establishing kenaf as the country’s third major commodity plant, alongside rubber and oil palm.
From 2011 to 2015, significant emphasis was placed on commercializing kenaf core and its related products. By 2015, kenaf cultivation covered an area of 2274 hectares, representing 45% of the intended cultivation area, with a production yield of 11,600 tons of dry stems. Each cropping season of kenaf typically takes 75 to 120 days from sowing to harvest. Figure 5 shows the kenaf plant cultivated in Malaysia.

Figure 5.
Hibiscus cannabinus L. plant cultivated in Pahang, Malaysia.
Following that, around October to January, the land is rehabilitated before the rice is planted. Unfortunately, climate change has caused unexpectedly heavy rainfalls. As a result of the waterlogged soil, kenaf crops have been either stunted or destroyed [32]. Figure 6 shows the milestones of Kenaf as a new commodity in Malaysia.

Figure 6.
The milestones of Hibiscus cannabinus L. as a new commodity in Malaysia.
Peninsular Malaysia is in the tropics, with a land area of 130,598 km2, and is situated between latitudes 1.20 and 6.40 north and 99.35 and 104.20 east (Table 2). Its rugged topography, monsoon winds, and intricate land–sea interactions all contribute to its hot, humid climate. The region experiences two distinct rainy seasons, namely, the southwest (SW) monsoon spanning from May to September, and the northeast (NE) monsoon between November and March. According to Noor et al. [33], the annual rainfall varies from 2000 to 4000 mm, and the number of wet days ranges from 150 to 200. According to the National Kenaf and Tobacco Board, kenaf is best grown in Malaysia from March to June, with crop harvesting taking place in July, since it grows best during that period because it thrives in hot conditions with moderate rainfall [34].

Table 2.
The data of cultivation areas for fibre and core extraction of Hibiscus cannabinus L. and cultivation areas for Hibiscus cannabinus L. seed production in Malaysia according to the National Kenaf and Tobacco Board.
The Malaysian government promoted kenaf cultivation as a source of income for small farmers in 2010. The northeast region of Peninsular Malaysia, including Pahang, Kelantan, and Terengganu, has been identified as a priority area for kenaf cultivation under the NKTB initiative to reduce poverty rates in these states. This initiative provided farmers with technical assistance, access to seeds, and subsidies for inputs such as fertilizer and pesticides. Government policies may have aided in the pioneering stages of kenaf cultivation in Malaysia in the states of Pahang, Kelantan, and Terengganu. This may be the reason for Pahang, Kelantan, and Terengganu having the highest kenaf cultivation area for kenaf core and fibre.
However, there are some fluctuations in the number of areas used for kenaf cultivation which might be due to farmers’ inability to continue planting kenaf as they reach their retirement age, their preference to grow tobacco, or their desire to avoid obtaining rashes while harvesting kenaf after the plant flowers [34]. Penang, Selangor, and Negeri Sembilan recorded the smallest cultivation area for fibre and core extraction in Malaysia as these states are urbanized areas. Urbanization and urban development can have a significant impact on soil fertility, frequently resulting in a decline in soil quality due to factors such as soil sealing, compaction, and pollutant contamination, such as in key Malaysian states such as Penang, Selangor, and Negeri Sembilan.
3. Growth Conditions and Challenges in Soil-Grown Kenaf
Sunlight, adequate temperature, moisture, air, and sufficient nutrients are vital for a plant that grows conventionally on land. According to Mohammed, H. [35], kenaf cultivars, photosynthesis, date of sowing, population of the plant, length of the growing season, and crop maturity are factors influencing the growth of kenaf plant in soil. Compared to other commercially grown fibre crops, kenaf has a wider range of climatic and soil adaptations. It thrives in both temperate and tropical climates and thrives in areas with high rainfall and solar radiation due to its wide range of ecological flexibility. Due to the extensive root system, which includes lengthy taproots and laterally spreading roots, this plant can respond well to changes in soil moisture. Moisture and high temperature are favourable for growth. Thus, kenaf can tolerate salinity and drought to a certain extent. Kenaf is a water-intensive crop, yet it is adaptable to varying levels of water availability, transpiration, and stomatal conductance. When water is not scarce, it exhibits high rates of transpiration and stomatal conductance, but it shows significantly lower rates when water is limited. However, an excess of stagnant water, particularly during the seedling phase, can significantly impede its growth [5].
Research on kenaf’s water requirements has demonstrated that the plant needs a daily water supply of 12 mm during seed germination and initial crop establishment. Fluctuations in water levels can impact root length and fibre quality. Under optimal watering conditions, kenaf can reach a height of up to 3.2 m. Different cultivars have varying water needs at different growth stages due to physiological processes, environmental factors, and humidity. However, the high humidity and rainfall make kenaf susceptible to fungal diseases throughout the growing season. Pathogens such as Aphis gossypii Glover, Phytophthora, nematodes, and Dysderus cingulatus can damage young shoots, flower buds, and maturing fruits. Pesticide use is necessary for plant protection, especially against nematodes; Furadan spraying is recommended four weeks after germination.
Weed control is crucial in kenaf cultivation. Pre-emergence herbicides can manage emerging weeds. Common weeds in kenaf-growing regions include Digitaria ascendens, Borreria alata, Calapogonium sp., Cleome sp., Cynodon dactylon, and Cyperus rotundus. The Malaysian Agricultural Research and Development Institute (MARDI) suggests using flufenacet as a pre-emergence herbicide, while fluazifop-butyl is recommended for early post-emergence herbicide application. The efficacy of Bentazon as a late post-emergence herbicide against broadleaf weeds and sedges, considering potential resistance, has been evaluated [27].
Climate and soil characteristics affect the amount of nutrients that a crop needs. The crop kenaf is regarded as nutrient-demanding. The effects of various macronutrient intake levels have been studied in the past. Plant growth, biomass, and leaf production did not significantly differ among nitrogen (N) fertilizer concentrations. However, the production and growth of kenaf plants significantly improved when nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) were applied at a rate of 100 N to 200 P kg/ha. In Malaysia, application rates of 80 to 100 kg N/ha, 150 to 200 kg P/ha, and 100 kg K/ha are suggested by Mohd et al. [36]. The application of N alone had little impact on fibre production or quality, whereas the application of N and P together had marginally noticeable effects. Variations in soil properties across production regions were found to result in differences in the nutrient needs for kenaf cultivation.
Kenaf adapts to temperate climates, but not to frost. Since temperature affects both seed production and biomass and fibre yield, maintaining a temperature of more than 10 °C throughout the growing season maximizes the yield. Kenaf typically does not start to flower until the number of daylight hours drops below about 12.5 h. In addition to temperature, the photoperiod affects floral induction. Kenaf is a plant that grows naturally in Africa, spanning from the equator to a maximum latitude of 30° N and 30° S, and can grow up to 1.25 m in elevation. It is capable of adapting to regions with latitudes between 16° S and 41° N, where the seasonal temperatures range between 22.6 °C and 30.3 °C, and the average relative humidity falls between 68% and 82%.
Remarkably, the soil’s origin and composition do not impact kenaf cultivation, as it can grow in various soil types. Based on a study, kenaf can be grown on marginal lands and is more suited to poor soils than the majority of commercial crops. The main requirements are that the soil has good drainage and is free of nematodes, especially Meloidogyne spp., which has been determined to be a significant issue affecting the production of kenaf, resulting in the stunted growth and death of seedlings [5]. However, the water level, temperature, weed problems, and soil compositions can be resolved by using in vitro propagation methods. Kenaf plants which take an average of six months to grow can develop quicker and avoid weed and nematode problems.
4. Solid Culture of Kenaf Plants
In vitro propagation refers to the clonal multiplication of plants through techniques involving the cultivation of tissue, cells, and organs. This process entails cultivating aseptic explants of plant tissues and organs within enclosed containers, using precisely formulated culture mediums, all within a controlled setting [37]. Creating effective in vitro culture techniques including a system for effective plant propagation is crucial as any kenaf variety will become less pure over time, increasing its seed yields while decreasing its fibre yields. To establish an industrial plantation for high and consistent cellulosic fibre production, in vitro propagation techniques are necessary to rapidly produce a large quantity of genetically identical plants in a short period (Figure 7). Based on Ayadi et al. [5], in vitro shoot regeneration from shoot tips and nodes in MS medium demonstrated the highest shoot regeneration frequency (90.5%). Explants of shoot tips and nodes were taken from two-week-old seedlings and continued to grow on MS hormone-free media. Regenerated and extended shoots were exposed to five subcultures after 4–6 weeks to increase the rate of multiplication. In total, 70% of the healthy, completely formed shoots that were transplanted to the natural environment for acclimation under greenhouse conditions with sandy soil in pots survived [38]. More in vitro studies are needed as this is a disease-free plant cultivation technique [39]. A shorter period is taken for propagation compared to the conventional in vivo method. This method does not require land and can be planted in all seasons. This study would be a good alternative in helping countries or areas where there is no fertile soil for plants to grow for food production [40].

Figure 7.
Hibiscus cannabinus L. plant propagation in MS medium.
Due to the high labour expenses, conventional micropropagation techniques employing solid media are typically labour-demanding methods of making elite clones and are only useful for commercial purposes. The commercial facilities for conventional micropropagation of economically significant crop species are constrained due to the high production costs as well as the vast quantities required annually by producers. These are generally caused by complex and expensive equipment, high labour costs, low multiplication rates, the length of time required for multiplication before plantlets can be transplanted to the field, and low survival rates brought on by contamination hazards and acclimation. The use of micropropagation for scaling up potential horticultural species for commercialization was severely hampered by all of these drawbacks.
In the past, sterile tissue-cultured plants were cultivated in autoclavable vessels with a vented cover to allow for microbe-free gas exchange. Since species differ in their capacity to regenerate under selection, procedures must be adjusted to each targeted species, or even cultivar, as plants produced in such conditions tend to grow slowly. Stable transformants typically require a high level of replication. For the transformation vector to reach the cells intended for transformation, the cells should be dividing close to the tissue surface. In an experiment conducted in 2017, tissue culture plants were grown on semi-solid media with various amounts of MS nutrients and sucrose. The production of adventitious roots was reduced by MS media at 1 as opposed to MS medium at 0.5. Hence, at pH 5.7 and 3.5 mM MES (25 mg/L), respectively, solid and liquid media were produced using 0.5 Murashige and Skoog medium (½ MS) (half-strength MS micro- and macro-salts with 1 Gamborg’s B5 vitamins and 10,000 mg/L sucrose). Agar for plant tissue culture was utilized at 1% (w/v) under semi-solid growth conditions. Semisolid ½ MS resulted in the germination of hydroponic and semisolid culture seedlings. In order to evaluate genetically modified plants, 1% sucrose is frequently employed as the concentration; hence, this was utilized to germinate seeds on semi-solid media (½ MS plates) [41]. Differences in plant root weight between sucrose levels of 0.25 and 3% were found to be significant only in plants grown in liquid culture, while no such differences were observed in plants grown on a semi-solid medium [41].
The use of liquid culture with bioreactor technology has several benefits, including the ability to automate processes, save labour, and lower production costs by creating ideal conditions for growth that result in maximum yield and high-quality propagules, or to keep costs as low as possible by combining automated processes with basic, low-cost equipment. Local private micropropagation companies are increasingly adopting bioreactor technology for commercial purposes, and the results point to the system’s potential usefulness in plant propagation [28].
5. In Vitro Callus Formation
A callus can be created by a single differentiated cell, and several totipotent callus cells can regenerate the entire plant. In some cases, somatic embryogenesis in which mature somatic cells are employed to make embryos also affects callus cells. Consequently, it is believed that at least some types of callus development are influenced by cell dedifferentiation. It has also been acknowledged that calli are extremely diverse and can be classified into smaller groups depending on their macroscopic characteristics. For example, friable or compact calli are typically used to describe calli that do not appear to be regenerating organs. Figure 8 shows the types of kenaf callus without organ regeneration.

Figure 8.
Types of Hibiscus cannabinus L. callus without organ regeneration: (a) friable callus, (b) compact callus (figure by author).
The water content of the friable calli is higher due to their lack of lignified cell walls. This allows the cell clusters to easily separate. Compact calli have a firmer texture than friable calli. The cells are densely packed and do not separate easily. Callus texture can be used to determine the ability of the root and shoot organs to regenerate. Friable calli are more likely to develop shoots than compact calli [42]. Calli that display organ regeneration to a certain extent are called rooty, shooty, or embryonic calli, based on the organs they generate, according to research conducted by Ikeuchi et al. [43]. Figure 9 shows the types of callus induction.
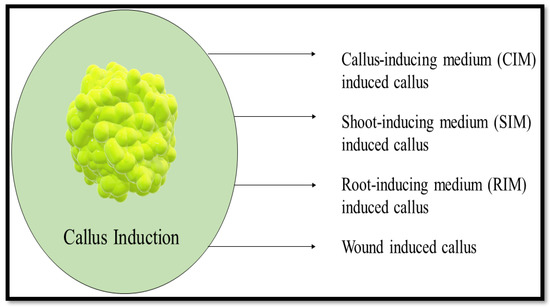
Figure 9.
Types of callus induction.
The proliferation of parent tissue leads to the formation of a callus, which is a dedifferentiated and disorganized mass of parenchyma cells. A good source of genetic viability and the development of accidental shoots is callus tissue. The quantities and combinations of plant hormones are the key determinants of embryogenic callus and plant regeneration [44]. In kenaf, plant regeneration via organogenesis from various explants employing various auxin and cytokinin combinations has been described. The potential of the explants, the use of the appropriate hormones, and optimal environmental conditions are all essential for the effective regeneration of plants in tissue culture. The usage of combined tissue culture and genetic modification techniques may result in the creation of kenaf plants with increased disease resistance [11].
Naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA), indole acetic acid (IAA), 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D), indole butyric acid (IBA), and benzyladenine (BA), a cytokinin, are commonly utilized for inducing callus and regenerating plants from leaf petiole and shoot explants. The addition of 2,4-D to the medium did not affect the formation of numerous shoots. However, an increase in the concentration of 2,4-D in the medium resulted in a decrease in multiple shoot regeneration. At higher concentrations of 2,4-D, fewer explants responded as more explants developed callus. The ability of 2,4-D and NAA to induce callus when combined with cytokinin may be a result of how they affect mitosis and DNA synthesis [45]. The morphology of the kenaf plant changed from a non-branching to a branching phenotype due to differences in some nitrogen bases.
NAA/IAA/2,4-D with BA induced the development of either abundant light to dark green coloration or fragile to nodular callus from leaf explants. Moreover, at higher concentrations of auxin, occasional root formation from leaf explants was observed. The use of BA led to indirect shoot organogenesis from the callus, resulting in the production of the highest number of shoots with the greatest frequency. Between kenaf V36 and kenaf G4, there was no discernible change in the induction of calluses or plant regeneration [45]. This outcome differed from a study that found Gossypium hirsutum callus induction to be strongly genotype-dependent [45]. In another study, callus initiation was seen in all hormone combinations studied, regardless of varietal differences, although shoot regeneration was significantly influenced by tobacco genotype. However, the combination of hormones had a very large impact on both the induction of calluses and plant regeneration [45].
For in vitro improvement, vegetative plant components, especially leaves, are preferred for explants because, upon regeneration, the parent genotype’s genetic homozygosity would be preserved. Surface sterilization is essential when using in vitro procedures on plant parts that will be cultivated on synthetic nutrient media. Since various fungi and bacteria are present in plants and plant components, it is vital to disinfect tissues with as little cellular harm as possible to the host tissue. The medium that contained 1.5 mg/L BA and 0.05 mg/L generated a disproportionately large number of calli masses (3–5 mm diameter). The cutting edge of the explants formed two to five nodular calli masses. Additionally, it was shown that the concentration of IBA and BA had an impact on callus induction, meaning that as IBA and BA levels rose, callus induction decreased. In research focusing on comparing the NAA and 2,4-D, it was found that IBA with BAP produced the highest callusing percentage and best callusing. The lowest callusing percentage was caused by IBA at higher concentrations, they further reported.
Except for the hormone-free media, most calli masses showed differentiation into plants after 9 weeks in all hormone combinations. But when compared to the other two combinations, medium with 1.5 mg/L BA, 0.05 mg/L IBA, and 0.3 mg/L GA3 exhibited a considerably higher amount of plant regeneration. The plant regeneration rate was 68.7%. They found that the MS basal medium with 1.0 mg/L of IBA and 0.5 mg/L of BAP provided the highest callusing percentage (95.0%) and the best callusing degree. Additionally, Broussonetia papyrifera demonstrated 100% callus induction when BA and IBA were combined.
It is consistent with the findings that IBA and BA can be combined to provide a good callus. Regenerated plants were cut out of the callus, grown in the same hormone mixture for 7 to 10 days, and then transplanted into the rooting media. In 4 to 6 weeks, almost all plants began to grow roots. After keeping in the MS media without hormones for 3 to 4 months, 2 to 4 cm tall plantlets were formed. Plants were transplanted to the field after one month of acclimatisation in plastic pots with autoclaved peat, clay soil, and sand (3:1:1) [44]. The process of kenaf breeding is sped up via advanced biotechnology, which also offers an innovation approach for germplasm multiplication and kenaf breeding. To create genetic variety for desirable features, tissue culture techniques can be used with plant breeding techniques. Conventional breeding efforts would be considerably improved by the creation of transgenic kenaf plants with pest and disease resistance.
According to a study, the organogenesis of kenaf using callus culture failed or was irreplicable. The demonstration of foreign gene expression in the kenaf callus did not result in plant regeneration. The selection of variant cells with greater resistance to abiotic stress has been carried out effectively using cell and tissue cultures, but no plants with the chosen features have been created. The production of unhealthy structures that either resist elongation or produce rosettes of deformed leaves, which typically do not produce normal shoots, severely limits plant regeneration in kenaf. To fully realize the potential of contemporary biotechnologies for kenaf enhancement, such constraints must be removed [11].
To encourage the growth of callus, seeds that had been sterilized were placed into MS media with 3% (w/v) sucrose, 0.3 mg/L 2,4-D, 0.3 mg/L Kinetin, and 0.3% (w/v) phytagel. They were then cultivated for a week at 22 °C with a 16 h light cycle. Hypocotyls from 10-day-old seedlings that had been produced aseptically were subsequently cut into 5 mm lengths or smaller fragments and placed onto MS media with 3% (w/v) sucrose, 2.0 mg/L 2,4-D, 2.0 mg/l kinetin, and 0.3% (w/v) phytagel. They were raised at 22 °C with a daily photoperiod of 16 h for one to four weeks. Cotyledons from seedlings that had been cultivated in an aseptic environment for 10 days were cut into 5 mm pieces and then put on MS, 1/2 MS, or Gamborg B5 medium with 2% (w/v) sucrose, 1.5 mg/L BA, 0–0.05 mg/L IBA, and 0.3% (calli were artificially induced for three weeks in the dark at 22 °C) [5].
6. Factors Influencing In Vitro Cultivation of Kenaf
6.1. Type of Media
According to Ayadi et al. [5], the highest shoot regeneration frequency of kenaf (90.5%) was obtained on the MS medium. Based on research conducted on the comparison of solid and liquid MS media for Typhonium flagelliforme, the liquid medium exhibited the most robust plant growth response for various growth parameters such as shoot height, number of leaves, shoot and root count, fresh weight, dry weight, total chlorophyll, chlorophyll a, and chlorophyll b [46].
6.2. Carbon Sources
Carbohydrates are a crucial component in the culture media for in vitro plant cell, tissue, and organ cultures, as they serve as nutrients and carbon sources to sustain osmotic potential and support various growth processes such as shoot proliferation, root induction, emission, embryogenesis, and organogenesis, despite not being entirely autotrophic. The carbon source used in culture media is determined by the genotype and growth stage, with a variety of carbon sources used ranging from reducing to non-reducing sugars. Sucrose is the most frequently used carbon source due to its significance as a significant transport sugar in many phloem saps. To encourage healthy and vigorous growth in vitro, a range of nutrients are needed, including macronutrients, micronutrients, PGRs, amino acids, vitamins, and nitrogen supplements. This is due to heterotrophy or mixotrophy in cultured cells, which results in a reliance on sugars to replace atmospheric carbon fixation by photosynthesis in vivo for growth. The type and carbon source concentration can have a big impact on the morphogenetic potential of plant tissues in micropropagation systems [47].
6.3. Plant Growth Regulators (PGRs)
The factors that have been found to affect the regeneration of embryogenic callus and plants are the combination and concentrations of plant hormones. Callus formation is aided by cytokinin and auxin. 1-Naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA), indole acetic acid (IAA), 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D), indole-3- butyric acid (IBA), and benzyl adenine (BA) are the most often used growth regulators for the development of calluses and plant regeneration from leaf petiole and shoot explants.
Based on Samanthi et al. [44], the addition of only 2,4-D to the medium did not affect the multiple-shoot formation. The role of 2,4-D and NAA in combination with cytokinin in inducing callus formation could be due to their involvement in DNA synthesis and mitosis. The use of NAA/IAA/2,4-D with BA led to the formation of fragile to nodular calli with a light-green to dark-green coloration from leaf explants. At high auxin concentrations, the observation of root formation directly from leaf explants was made. BA was used to achieve shoot organogenesis indirectly from the callus, regenerating maximum shoots with the greatest frequency. The medium containing 1.5 mg/L BA and 0.05 mg/L produced a disproportionately large number of calli masses (3–5 mm diameter). It was also discovered that IBA and BA concentrations influenced callus induction, with an increase in BA and IBA resulting in a decrease in callus induction. They also discovered that IBA at higher concentrations resulted in the lowest callusing percentage. Embryogenic calli formed at the ends of cut surfaces, and the majority of them had a compact yellow structure. These calli turned greenish after being transferred to the plant regeneration medium. Except for the medium without hormone, most calli masses showed differentiation into plants after 9 weeks in all hormone combinations. However, a medium containing 1.5 mg/L BA, 0.05 mg/L IBA, and 0.3 mg/L GA3 produced more plant regeneration than the other two combinations. It demonstrated 68.7% plant regeneration [45].
Based on a study conducted in 2021, a variety of BAP concentrations (0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, and 3.0 mg/L) were tested to determine the capability of explants to produce healthy calli. The results show 3.0 mg/L BAP induced the best growth of healthy calli. The shoot was successfully induced from the calli using a combination of BA, IBA, and GA3 PGRs [48].
6.4. Explants, Water, Temperature, pH, Humidity, and Photoperiodism
The largest proportion of shoot regeneration (49.60%) was seen in the hypocotyl explants, while no shoot regeneration was seen in the root tips [36]. The average temperature for the growth of kenaf is 25 °C because kenaf cannot frost with a pH of 4.4 to 6.5. Based on research conducted in 2014, although irrigation is not necessary for kenaf growth, it can improve the overall quality of the crop. Irrigated kenaf has shown a better growth rate, higher lignin content, thicker stems, and higher hemicellulose content than kenaf, which is not irrigated. Adequate irrigation has the potential to increase the kenaf yield volume twofold [49]. Kenaf grows in places with a relative humidity ratio of 68 to 82% and temperatures varying from 22.6 to 30.3 °C [31]. According to Zhang et al. [42], one of the most important factors influencing fibre production and quality in kenaf is the flowering stage, which is influenced by photoperiodism.
6.5. Type of Kenaf Variety Used
According to Nasreen et al. [10], selecting the appropriate kenaf variety is crucial, as research has shown that it can impact various factors including plant population, height, diameter, stick diameter, fibre and stick weight per plant, fibre and stick yield, and harvest index. Thus, the choice of the right kenaf variety is according to their respective unique traits. This statement was also supported by Alexopoulou et al. [8]. For high yields that would provide the largest economic returns, choosing the variety that is best suited for each location is a crucial factor. Numerous kinds have been produced that vary morphologically in their reaction to climatic circumstances, in their resistance to illnesses and enemies, in the quality of their fibre, and in the yields of their fibre.
7. Liquid Culture of Kenaf
Several factors, such as culture medium composition, environmental conditions such as photoperiod and temperature, and the type of vessels used, influence the process of in vitro plant regeneration. By using temporary immersion systems in liquid culture for plant propagation, the micropropagation efficiency and yield of healthy plants can be significantly increased, compared to growing cultures on semi-solid media. Various plant species have shown better results with pure liquid culture compared to solid or semi-solid medium culture, as supported by numerous studies. Nonetheless, some plant species may not be apt for liquid culture due to the occurrence of a physiological abnormality called hyperhydricity, despite the advantages of faster and more substantial multiplication provided by the liquid culture system [50].
To the best of our knowledge, no research has looked into the liquid culture techniques for kenaf micropropagation to date. Based on a study conducted by Ibraheem et al. [51], about ten times as many somatic embryos can be produced in liquid media compared to solid media. One of the widely known methods for cell culture in a liquid medium is using bioreactors. The primary goal of a bioreactor is to regulate numerous environmental chemical and physical elements to create the best possible circumstances for cell physiology and metabolism. Each bioreactor is different in terms of design and material choice; however, there are several universal guidelines. In general, sufficient oxygen transport, minimal shear stress, and effective mixing should be taken into account while building a plant cell or organ culture bioreactor in order to function [52].
8. Types of Bioreactors
Due to the development of the biotechnological field, various types of bioreactors are being used today. Some of the commonly used bioreactors with liquid media are bubble column bioreactors, modified column bioreactors with internal sections, mist bioreactors, balloon-type bubble bioreactors, trickle-bed bioreactors, RITA® system (Temporary Immersion Bioreactor System), and BioMINTTM reactors (Modular Temporary Immersion Bioreactor). The schematic diagrams in Figure 10 show the configuration of reactors for differentiated plant in vitro systems.
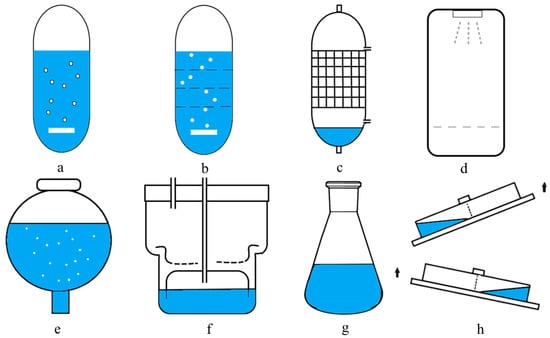
Figure 10.
Schematic diagrams of reactor configuration for the differentiated plant in vitro systems. (a) Bubble column bioreactor. (b) Modified column bioreactor with internal sections. (c) Trickle-bed bioreactor (d) Mist bioreactor. (e) Balloon-type bubble bioreactor. (f) RITA® system. (g) Shake flask system. (h) BioMINTTM reactor.
To confirm the sufficient supply of nutrients and to avoid the build-up of toxic metabolites, proper mixing is crucial. The time for mixing is an important parameter to be examined. In cell suspension culture, the biological performance of mixing, such as rate of growth and productivity, is frequently assessed. The ability of bioreactors to effectively mix materials is essential for controlling the temperature, pH, and substrate concentration. In a small-scale reactor, it is simple to maintain a uniform condition, but mixing frequently becomes a limitation with scaleup. Poor mixing frequently causes undesired concentration gradients and a reduction in the mass transfer efficiency in large-scale bioreactors. Increased agitation intensity cannot improve mixing in shear-sensitive plant cell cultures because excessive agitation would mechanically harm living cells.
The issue of oxygen transfer is a persistent concern in aerobic biological systems, as the essential nutrients required for cellular growth and metabolism are predominantly found in water. A well-mixed reactor is capable of providing a sufficient quantity of these nutrients. However, as oxygen is not readily soluble in aqueous solutions, its transfer often becomes a constraining factor in achieving the optimal performance of biological systems and scaling up. Both cell development and product synthesis would be negatively impacted by a limited oxygen supply. At a high cell density, a severe oxygen deficit is anticipated. High cell density sometimes results in a decline in the oxygen transfer coefficient, aggravating this issue. The geometrical and operational characteristics of the reactor vessel, the aeration rate, the agitation speed, the fluid hydrodynamics, the cell type, the media composition, the morphology, and the concentration are all very significant aspects of reactor design that must be considered in order to achieve a high volumetric oxygen transfer coefficient (kLa), which is influenced by a variety of factors and is essential for supplying oxygen to the medium [32,53]. Although plant cells use less oxygen than bacteria do, oxygen transport restrictions also provide a challenge for cell cultures with high cell densities. It is equally crucial to maintain an appropriate oxygen content in the culture broth. For the growth of cells and the production of products, varied dissolved oxygen concentrations may be ideal.
Plant cells are substantially larger and more susceptible to shear strain than microbe cells. In the literature, shear has primarily been viewed as a destructive force. Shear stress, duration, and power dissipation are factors related to shear-induced cell death and the growth stage of cells. Sparging can lead to shear damage at various points in the bioreactor, including the sparger’s bubble formation zone, the bulk liquid’s rising zone, and the suspension surface (both foam-covered and foam-free). To examine the impact of shear stress on plant cell cultures, a study using a plant cell bioreactor equipped with marine impellers of different diameters was conducted to quantitatively analyse its effect on cell growth and anthocyanin pigment synthesis in Perilla frutescens.
The conventional solution for shear-sensitive cell cultures involves reducing the agitation speed of the impeller to decrease the intensity of shear stress. However, this approach can result in insufficient mixing and potential conflicts with bettering the oxygen and heat transfer rates in high-viscosity cell culture broths. Additionally, low agitation rates may lead to the formation of cell aggregates of varying sizes at high biomass concentrations. To address the problem of rising air bubbles, an alternative option is to use membranes for indirect aeration to achieve bubble-free aeration. This approach relies on a diffusion-controlled oxygen supply, eliminating the need for bubbles. However, the oxygen transfer rate tends to be relatively low due to the limited length of the membrane, and the tubing pressure is also restricted. Consequently, this bioreactor design is best suited for small-scale cell cultures as it has limitations for large-scale operations [35].
Although liquid culture systems have several benefits over semi-solid culture systems, the commercial application of this method for the micropropagation of various plant species remains limited. Maintaining individual micro-shoots in an upright position during rooting is a significant hurdle in implementing a liquid culture system. It may result in abnormal root development. Recently, a two-piece scaffold has been developed to address this bottleneck issue. This scaffold comprises a grid structure that enables the micro-shoots to be inserted and kept upright during the rooting phase. This innovation streamlines the micropropagation process and minimizes the need for labour-intensive manual interventions. This root stand makes it simple to move plants without harming the plantlets, which raises the survival rate. A significant problem in plant tissue culture may be resolved by this ground-breaking design, which could also result in effective commercial micropropagation [29,54].
9. Challenges, Current Perspectives, and Future Work
9.1. Challenges in the Kenaf Industry
One of the major challenges faced by Malaysia’s kenaf industry is the sustainability of raw kenaf materials due to the lower supply and demand of raw kenaf materials (Figure 11). The lack of consumer awareness about the benefits of kenaf-based products is also another challenge faced in the kenaf industry. As a result, the demand is limited, hindering the industry’s growth. In addition, insufficient skilled labour is another one of the challenges faced in the local kenaf industry. The industry is facing a shortage of skilled labour, which is required for kenaf-based product cultivation, processing, and manufacturing. The lack of skilled labour is a significant impediment to the industry’s growth. Another issue confronting the industry is the low yield of kenaf. This is due to a variety of factors including insufficient soil fertility, pest infestations, and diseases. These factors influence the quality and quantity of kenaf production, which in turn influences the industry’s growth. More research and development are required to optimize the use of kenaf as a raw material. A significant challenge confronting the industry is a lack of adequate research and development, which limits the development of new products and the improvement in existing ones [6].
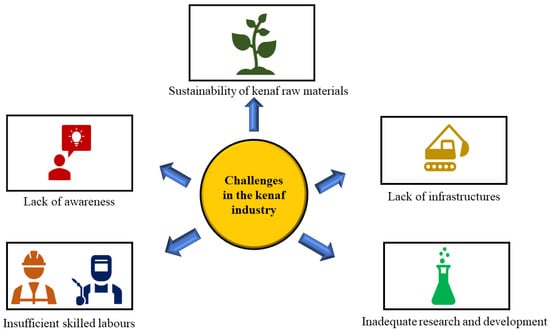
Figure 11.
Challenges in the kenaf industry.
9.2. Current Perspectives of the Kenaf Industry
Malaysia’s kenaf industry is still in its early stages, but it is rapidly expanding. Kenaf is a fibrous plant that is widely used in the production of paper, textiles, and biodegradable plastics. It is primarily grown in Malaysia for its fibre, which has been identified as a potential substitute for timber in the pulp and paper industry. The Malaysian government has recognized the Kenaf industry’s potential and has launched several initiatives to foster its growth. These initiatives include research and development funding, farmer subsidies, and the creation of a Kenaf industry development plan. Several companies in Malaysia are currently engaged in the Kenaf industry, including those that cultivate, process, and manufacture Kenaf-based products. These businesses are mostly concentrated in Malaysia’s northern states, such as Kedah and Perlis. However, the Kenaf industry in Malaysia continues to face challenges. One of the most significant challenges is a lack of farmer awareness of the potential of Kenaf cultivation. More research and development are also required to improve the yield and quality of kenaf fibres. Despite these obstacles, the Malaysian kenaf industry is estimated to thrive in the future, driven by rising demand for sustainable and ecofriendly materials.
9.3. Future Work of Kenaf
9.3.1. Kenaf Cultivation in a Bioreactor
The conventional method of cultivation can enhance the qualities of kenaf, but to increase the physical qualities as a structural material in a short time, a thorough genetic transformation technique must be established. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation, which uses the regeneration of plants from the callus that may be produced by the combination of the plant growth regulators auxin and cytokinin, is the most widely used method of genetic modification discovered in plants [55].
Plant cell suspension cultures are typically established using a sterile system that involves growing friable callus fragments in a sterile liquid medium. To initiate callus growth, tissue pieces are extracted from surface-sterilized plants and placed on solid growth media, resulting in the appearance of callus tissue on the explants within 2–6 weeks. Once established, a callus is cut from the explant and further subcultured to generate a cell suspension culture (Figure 12).
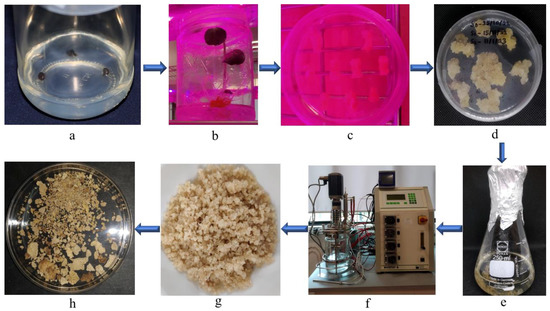
Figure 12.
Obtaining dried kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) callus via cell suspension culture. (a) Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) seed grown on solid media; (b) kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) seedling grown on solid media; (c) kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) callus induction; (d) kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) callus grown on media; (e) cell suspension culture of kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) in Erlenmeyer flask; (f) cultivation in stirred tank bioreactor; (g) filtration of kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) biomass; (h) dried kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) biomass.
It is recommended to research kenaf cultivation in liquid culture using bioreactors in the future as liquid cultures have been proven to have more advantages over solid cultures.
9.3.2. Optimization of Nitrogen Source on the In Vitro Growth of Kenaf
Nitrogen is an essential macronutrient for the growth and development of plants. It has been noted that callus growth, embryogenesis, and organogenesis are all significantly influenced by the total nitrogen content and the NH4+/NO3 ratio in the culture medium [41]. According to Anfinrud et al. [56], nitrogen is a component of amino acids, amides, nucleic acids, and proteins; it is one of the vital and restrictive nutrients that affects plant development. It is well known that nitrogen affects the morphogenesis and growth of tissue cultures. The availability and form of nitrogen are critical factors in tissue culture. Nitrate has traditionally been considered the most important form of nitrogen for tissue culture, but its use as the sole nitrogen source has not always been successful. It has been discovered that the optimal use of nitrate ions in tissue cultures requires a reduced nitrogen source, such as ammonium. The medium must also contain the appropriate nutrient levels to induce embryogenic calli. In plant tissue culture media, mineral nutrients make up the majority of the content, while ammonium (NH4+) and nitrate (NO3) are the primary inorganic nitrogen sources. KNO3 and NH4NO3 are commonly used forms of nitrogen in plant tissue culture media. The nitrogen availability in the growth medium has a significant impact on how plants respond to proteins, organic acids, secondary metabolites, and hormones, but no specific research has been reported on the optimization of nitrogen source level in the in vitro cultivation of kenaf.
9.3.3. Optimization of Production Yield of Kenaf Biomass Using Various Types of Kenaf Varieties
The kenaf plant has been proven to have slight variations among different varieties of Malaysia. Based on Mohd et al. [36], the selection of an appropriate genotype with rapid growth rates and high biomass production is crucial for successful commercial kenaf cultivation. The physiological characteristics of plants directly influence both their growth and production of biomass. The cultivars Everglade 71, HC2, HC78, Thai kenaf, V36, and V133 were suggested as commercially viable genotypes for the tropical climate of Malaysia. According to the findings of several studies, cultivars that are late bloomers and photoperiod-insensitive are best suited for Malaysia’s tropical climate. The accession V36 yielded 9.68 t/ha, which was the highest yield that could be reported. Malaysia offers the following kenaf cultivars: V4, V12, V25, V33, V34, V36, V40, V41, V43, and V72. According to Ibrahim et al. [28], the kenaf plant is made up of a variety of useful parts, including fibres, oil, proteins, and allelopathic chemicals. Other useful parts include the stalk, leaves, and seeds. Thus, several comparison studies can be conducted to identify the type of varieties which can produce the highest yields of different parts of the kenaf plant, for instance, the identification of kenaf varieties producing the maximum oil content in kenaf seeds, determining high-quality fibre-producing kenaf varieties, and determining the kenaf variety which contains high protein levels in the leaves.
9.3.4. Production of Functional Food for Humans and Animal Feed
The advancement in bioreactors has garnered increasing attention due to their potential to enhance supply chains, foster circularity within the bioeconomy, promote food sustainability, and harness the beneficial properties of bio-based substances derived from food and waste products [57]. This aligns with the principles of the “One-Health” concept and the ongoing trend of digitalization. According to Wan-Mohtar et al. [58], given the considerable quantity of bioactive substances derived from kenaf, whether obtained from its foliage, seeds, or blossoms, this plant possesses the capability to be incorporated into the food sector as functional foods, capable of providing advantageous effects on health. Kenaf is a potential source of protein to maximize animal productivity and eradicate human malnutrition. This plant is regarded as a vegetable for human consumption along with other food substitutes. It is favoured primarily for the nutrients and phytochemical compounds that are present in the seeds and leaves. Additionally, phenolics, saponins, tocopherols, phytosterols, crude proteins, fatty acids, alkaloids, and phospholipids have all been reported to be present in kenaf. High levels of vitamin C, phosphorus, calcium, iron, and nitrogen are also present. Kenaf has a variety of medicinal properties that are extremely important to both human and animal health as kenaf contains bioactive compounds, including anticancer, antioxidant, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, anti-hypercholesterolemic, aphrodisiac, and hepatoprotective activities [13,25,42]. According to Muhammad et al. [32], the kenaf plant parts are not fully exploited, including kenaf seeds. Untapped potential exists for using kenaf seeds as a source of food-based products [19]. Based on Ryu et al. [41], kenaf is a plant rich in bioactive compounds, found in its leaves, seeds, and flowers, and it has the potential to be utilized as functional food in the food industry. Its various parts can be used to create medicinal teas, healthy beverages, edible flowers, food colorants, and antioxidant-rich edible flour. Kenaf also shows promise as a natural bio-preservative agent, capable of extending the shelf life of food products. Therefore, the potential of kenaf in the food industry should not be overlooked.
9.3.5. Phytoremediation of Heavy Metal Using Kenaf
Phytoremediation is a process that utilizes plants to remove organic or inorganic contaminants from soil, surface water, or groundwater. Studies have demonstrated the potential of kenaf as a plant for the phytoremediation of heavy metal contamination [59]. Arbaoui et al. [60] and Li et al. [61] reported that kenaf plants accumulated heavy metals in their roots, stems, and leaves. Moreover, Hibiscus cannabinus L. was found to be capable of boron phytoextraction and arsenic (As) phytoextraction in soils containing from 1 to 10 mg kg–1 of B and As, respectively. Although previous studies such as that by Nizam et al. [36] have focused on heavy metals such as Pb, Cd, and Zn, Zhao et al. [59] suggested that heavy metals such as As, Cd, Cu, Cr, Hg, Pb, Ni, and Zn are commonly found in the environment and pose a threat to public health. Therefore, bioremediation studies on various heavy metals using kenaf could be conducted and compared with the phytoremediation potential of other plants [62].
10. Conclusions
The demand for kenaf plants is increasing due to their versatility in various industries. However, there is limited research on kenaf propagation methods, such as solid culture and liquid culture cultivation. It is important to study these methods to determine the best way to propagate kenaf plants with less labour, in a shorter time, without land, and at a lower cost. Research on kenaf in vitro propagation is essential for achieving Sustainable Development Goal 15 (Life on Land). This field has the potential to create jobs, provide food, and address food scarcity issues, especially in countries with infertile land. This modern agricultural method could contribute to the economy of a country and improve the quality of life for its people.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.A.A.Q.I.W.-M., Z.I., N.M.S., S.R.A.U. and D.A.N.; Methodology, Z.I., N.M.S., S.R.A.U. and D.A.N.; Formal Analysis, D.A.G.V.; Investigation, Z.I., N.M.S., S.R.A.U. and D.A.N.; Resources, W.A.A.Q.I.W.-M.; Data Curation, D.A.G.V. and W.A.A.Q.I.W.-M.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, D.A.G.V. and W.A.A.Q.I.W.-M.; Writing—Review and Editing, D.A.G.V. and M.H.A.R.; Visualization, D.A.G.V.; Supervision, W.A.A.Q.I.W.-M.; Project Administration, W.A.A.Q.I.W.-M. and M.H.A.R.; Funding Acquisition, W.A.A.Q.I.W.-M. and M.H.A.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Strategic Research Fund, Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation (MOSTI), Malaysia (SRF21 P2P3) and [MOSTI001-2022SRF].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Highest appreciation to Ministry of Science Technology and Innovation for providing a research grant through Strategic Research Fund (SRF21 P2P3), project entitled Plant-based Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine [MOSTI001-2022SRF] and PV071-2022 “Pengawalan Penyakit Pokok Kelapa Sawit Menggunakan Cendawan Bukan Patogen”. We also thank the Lembaga Kenaf & Tembakau Negara (LKTN) for providing the seed materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Akinrotimi, C.; Okocha, P. Evaluations of genetic divergence in Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) genotypes using agro-morphological characteristics. J. Plant Sci. Agric. Res. 2018, 2, 2167-0412. [Google Scholar]
- Corinzia, S.A.; Scordia, D.; D’Agosta, G.; Cosentino, S.L.; Patanè, C. LAI and biomass of kenaf as affected by sowing time and plant density: A simple model simulates the time course in a Mediterranean environment. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 184, 114995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, L.; Li, C.; Huijuan, T.; Mingbao, L.; Gen, P.; Siqi, H.; Hui, J.; Yena, W.; Anguo, C. High-resolution genetic map construction and QTL analysis of important fiber traits in kenaf using RAD-seq. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 153, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.; Oh, K.K.; Azad, M.O.K.; Shin, M.H.; Wang, M.H.; Cho, D.H. Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) Leaves and Seed as a Potential Source of the Bioactive Compounds: Effects of Various Extraction Solvents on Biological Properties. Life 2020, 10, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekaya, A.; Hanana, M.; Mzid, R.; Hamrouni, L.; Khouja, M.L.; Hanachi, A. Hibiscus cannabinus L.—Kenaf: A Review Paper. J. Nat. Fibers 2016, 14, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Hassan, N.A.; Ahmad, S.; Chen, R.S.; Shahdan, D.; Haafiz, M. Tailoring lightweight, mechanical and thermal performance of PLA/recycled HDPE biocomposite foams reinforced with kenaf fibre. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 197, 116632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjmandi, R.; Yıldırım, I.; Hatton, F.; Hassan, A.; Jefferies, C.; Mohamad, Z.; Othman, N. Kenaf fibers reinforced unsaturated polyester composites: A review. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2021, 16, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexopoulou, E.; Papatheohari, Y.; Myrsini, C.; Monti, A. Origin, Description, Importance, and Cultivation Area of Kenaf. Green Energy Technol. 2013, 117, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, K.; Liu, B.; Zhao, T.; Wang, H.; Song, Y.; Ben, H.; Ragauskas, A.J.; Han, G.; Jiang, W. A facile degumming method of kenaf fibers using deep eutectic solution. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 19, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasreen, S.; Salim, M.; Paul, S. Effect of Variety and Seed Rate on the Yield of Kenaf. Int. J. Sustain. Crop Prod. 2014, 9, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Yan Yi, S. Application of Hibiscus cannabinus L. (kenaf) leaves extract as skin whitening and anti-aging agents in natural cosmetic prototype. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 167, 113491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaus, A.; Wan-Mohtar, W.A.A.Q.I. Cultivation Strategies of Edible and Medicinal Mushrooms in Wild Mushrooms; CRC Press: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Mohd Zaini, N.A.; Azizan, N.A.Z.; Abd Rahim, M.H.; Jamaludin, A.A.; Raposo, A.; Raseetha, S.; Zandonadi, R.P.; BinMowyna, M.N.; Raheem, D.; Lho, L.H.; et al. A narrative action on the battle against hunger using mushroom, peanut, and soybean-based wastes. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1175509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan Mohtar, W.H.M.; Wan-Mohtar, W.A.A.Q.I.; Zahuri, A.A.; Ibrahim, M.F.; Show, P.-L.; Ilham, Z.; Jamaludin, A.A.; Abdul Patah, M.F.; Ahmad Usuldin, S.R.; Rowan, N. Role of ascomycete and basidiomycete fungi in meeting established and emerging sustainability opportunities: A review. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 14903–14935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supramani, S.; Rejab, N.A.; Ilham, Z.; Wan-Mohtar, W.A.A.Q.I.; Ghosh, S. Basal stem rot of oil palm incited by Ganoderma species: A review. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2022, 164, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, F.; Zulkifli, R.; Ghazali, M.; Azhari, C. Kenaf Fiber Composite in Automotive Industry: An Overview. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2017, 7, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tholibon, D.; Tharazi, I.; Sulong, A.B.; Muhamad, N.; Ismial, N.; Radzi, M.; Radzuan, N.M.; Hui, D. Kenaf fiber composites: A review on synthetic and biodegradable polymer matrix. J. Kejuruter 2019, 31, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, R.; Noh, N.A.M.; Ibadullah, W.Z.W.; Zawawi, N.; Saari, N. Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) seed extract as a new plant-based milk alternative and its potential food uses. In Milk Substitutes-Selected Aspects; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sim, Y.Y.; Nyam, K.L. Hibiscus cannabinus L.(kenaf) studies: Nutritional composition, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and potential applications. Food Chem. 2021, 344, 128582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Snafi, A. Pharmacological Effects and Therapeutic Properties of Hibiscus Cannabinus L, A Review. Indo Am. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 5, 2176–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M. Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L., Malvaceae) Research and Development Advances in Bangladesh: A. Nutr. Food Process. 2019, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, M.; Ibrahim, A.; Xu, Y.; Niyitanga, S.; Li, Y.; Li, D.; Yang, X.; Zhang, L. Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) Breeding. J. Nat. Fibers 2020, 19, 4063–4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanthi, P.W.; Mohd Puad, A.; Suhaimi, N.; Kumar, S.M.; Nor Aini, A.S. In Vitro Studies on Callus Induction of Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.). Int. J. Microbiol. Appl. 2016, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Adebisi, M.; Esuruoso, O.; Adetumbi, J.; Abdul-Rafiu, A.; Kehinde, T.; Ajani, O.; Agboola, D. Shelf life of Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) seed stored under humid tropical conditions. Plant Breed. Seed Sci. 2014, 67, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kujoana, T.C.; Weeks, W.J.; Van der Westhuizen, M.M.; Mabelebele, M.; Sebola, N.A. Potential significance of kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) to global food and feed industries. Cogent Food Agric. 2023, 9, 2184014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Tao, A.; Qi, J.; Wang, Y. Bast fibres: Kenaf. In Handbook of Natural Fibres; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 71–92. [Google Scholar]
- Millogo, Y.; Aubert, J.-E.; Hamard, E.; Morel, J.-C. How Properties of Kenaf Fibers from Burkina Faso Contribute to the Reinforcement of Earth Blocks. Materials 2015, 8, 2332–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giwa Ibrahim, S.a.; Karim, R.; Saari, N.; Wan Abdullah, W.Z.; Zawawi, N.; Ab Razak, A.F.; Hamim, N.A.; Umar, R.U.A. Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) seed and its potential food applications: A review. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 2015–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, D.-H.; Irshad, M.; He, B.; Liu, S.; Lu, X.; Sun, Y.; Qiu, D. Role of reduced nitrogen for induction of embryogenic callus induction and regeneration of plantlets in Abelmoschus esculentus L. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020, 130, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunita, R.; Bagus, F.; Nova, B.; Rosadi, F.; Jamsari, A. Optimization of growth regulators to induce callus in chili [Capsicum annuum] cv. Berangkai. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 741, 012047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mamun, M.; Rafii, M.Y.; Misran, A.B.; Berahim, Z.; Ahmad, Z.; Khan, M.M.H.; Oladosu, Y. Combining ability and gene action for yield improvement in kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) under tropical conditions through diallel mating design. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marole, T.; Ligavha-Mbelengwa, M. The distribution, abundance and impact of the alien invasive species Hibiscus cannabinus following disturbance by fire of low intensity. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2016, 100, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, M.; Ismail, T.; Shahid, S.; Nashwan, M.; Ullah, S. Development of multi-model ensemble for projection of extreme rainfall events in Peninsular Malaysia. Hydrol. Res. 2019, 50, 1772–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainuddin, Z.; Pauzi, N.S.M.; Bahari, N.A.S. Establishment of in vitro Propagation of Hibiscus cannabinus L.(Kenaf). Sci. Herit. J. (GWS) 2021, 5, 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, H. Cost Benefit Analysis of Kenaf Cultivation for Producing Fiber in Malaysia. Arab. J. Bus. Manag. Rev. 2017, 7, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Mohd, H.; Arifin, A.; Nasima, J.; Hazandy, A.H.; Khalil, A. Journey of kenaf in Malaysia: A review. Sci. Res. Essays 2014, 9, 458–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, S.C.; Arigundam, U. In Vitro Propagation Strategies of Medicinally Important Berry Crop, Lingonberry (Vaccinium vitis-idaea L.). Agronomy 2020, 10, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Zinta, G.; Kanwar, K. Optimization of efficient direct organogenesis protocol for Punica granatum L. cv. Kandhari Kabuli from mature leaf explants. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. -Plant 2021, 57, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Leal, C.A.; Puente-Garza, C.A.; García-Lara, S. In vitro plant tissue culture: Means for production of biological active compounds. Planta 2018, 248, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnain, A.; Naqvi, S.A.H.; Ayesha, S.I.; Khalid, F.; Ellahi, M.; Iqbal, S.; Hassan, M.Z.; Abbas, A.; Adamski, R.; Markowska, D.; et al. Plants in vitro propagation with its applications in food, pharmaceuticals and cosmetic industries; current scenario and future approaches. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1009395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzle, K.; Cornish, K. Improved axenic hydroponic whole plant propagation for rapid production of roots as transformation target tissue. Plant Methods 2017, 13, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Weng, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Yong, H.; Hao, Z.; Li, X. Genome-wide association analysis of kernel row number in maize. Acta Agron. Sin. 2014, 40, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeuchi, M.; Sugimoto, K.; Iwase, A. Plant Callus: Mechanisms of Induction and Repression. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 3159–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Kwon, S.-J.; Kim, D.-G.; Lee, M.-K.; Kim, J.; Jo, Y.; Kim, S.; Jeong, S.; Kyung-yun, K.; Kim, S.; et al. Morphological characteristics, chemical and genetic diversity of kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) genotypes. J. Plant Biotechnol. 2017, 44, 416–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanthi, P.; Puad, A.M.; Suhaimi, N.; Kumar, S.; Aini, A. In vitro shoot regeneration from leaf explants of kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.). Sains Malays. 2013, 42, 1505–1510. [Google Scholar]
- Odahara, M.; Horii, Y.; Kimura, M.; Numata, K. Efficient callus induction and a temperature condition for flowering and seed setting in kenaf Hibiscus cannabinus. Plant Biotechnol. 2020, 37, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, B.; Asanakunov, B.; Shahin, L.; Jernigan, H.; Joshee, N.; Dhekney, S.A. Improving micropropagation of Mentha × piperita L. using a liquid culture system. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. -Plant 2019, 55, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, J.W.; Byrne, D.H. Improvement of peach embryo culture through manipulation of carbohydrate source and pH. HortScience 2003, 38, 582–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, I.B. Kenaf for biocomposite: An overview. J. Sci. Technol. 2014, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Norhisham, D.A.; Saad, N.M.; Ahmad Usuldin, S.R.; Vayabari, D.A.G.; Ilham, Z.; Ibrahim, M.F.; Wan-Mohtar, W.A.A.Q.I. Bioactivities of Kenaf Biomass Extracts: A Review. Processes 2023, 11, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibraheem, Y.; Pinker, I.; Böhme, M. A comparative study between solid and liquid cultures relative to callus growth and somatic embryo formation in Phoenix dactylifera L. cv. Zaghlool. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2013, 25, 883–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, M.; Eibl, R.; Zhong, J.-J. Hosting the plant cells in vitro: Recent trends in bioreactors. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 3787–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kho, K.; Sim, Y.Y.; Nyam, K.L. Antioxidant activities of tea prepared from kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L. KR9) leaves at different maturity stages. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2019, 13, 2009–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, M.R.; Piunno, K.; Saxena, P.K.; Jones, A.M.P. Improved in vitro rooting in liquid culture using a two piece scaffold system. Eng. Life Sci. 2020, 20, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miguel, S.; Michel, C.; Biteau, F.; Hehn, A.; Bourgaud, F. In vitro plant regeneration and Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of a carnivorous plant, Nepenthes mirabilis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anfinrud, R.; Cihacek, L.; Johnson, B.; Ji, Y.; Berti, M. Sorghum and kenaf biomass yield and quality response to nitrogen fertilization in the Northern Great Plains of the USA. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 50, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.L.; Yong, C.Y.; Dorotheo, E.U.; Assunta, M. Kenaf Malays. 2017. Available online: https://unfairtobacco.org/en/material/case-study-kenaf-in-malaysia/#/ (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Wan-Mohtar, W.A.A.Q.I.; Ilham, Z.; Rowan, N.J. Editorial: “The value of microbial bioreactors to meet challenges in the circular bioeconomy”. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1181822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, Y.; Lan, X.; Yang, Y.; Wu, X.; Du, L. Comprehensive assessment of harmful heavy metals in contaminated soil in order to score pollution level. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbaoui, S.; Evlard, A.; Mhamdi, M.E.W.; Campanella, B.; Paul, R.; Bettaieb, T. Potential of kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) and corn (Zea mays L.) for phytoremediation of dredging sludge contaminated by trace metals. Biodegradation 2013, 24, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Jin, G.; Luo, X.; An, X.; Li, P.; Zhu, G.; Chen, C. Comparative study on the potential of a kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus) variety for remediating heavy metal contaminated soils. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2018, 37, 2150–2158. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, K.S.; Ismail, M.; Zawawi, N. Nutritional Composition, Techno-functional properties and sensory analysis of pan bread fortified with kenaf seeds dietary fibre. J. Sains Malays. 2021, 50, 3285–3296. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).