The Isolation, Identification, and Insecticidal Activities of Indigenous Entomopathogenic Nematodes (Steinernema carpocapsae) and Their Symbiotic Bacteria (Xenorhabdus nematophila) against the Larvae of Pieris brassicae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Survey and Sample Collection
2.2. In-Vivo Mass Multiplication of EPNs
2.3. Morphological Observations of Entomopathogenic Nematode
2.4. Isolation of Bacteria Associated with Entomopathogenic Nematode
2.5. Molecular Characterization of Entomopathogenic Nematode and Bacteria
2.6. Evaluation of EPNs Infectivity
3. Results
3.1. Entomopathogenic Nematode Occurrence in (Surveyed) Soils
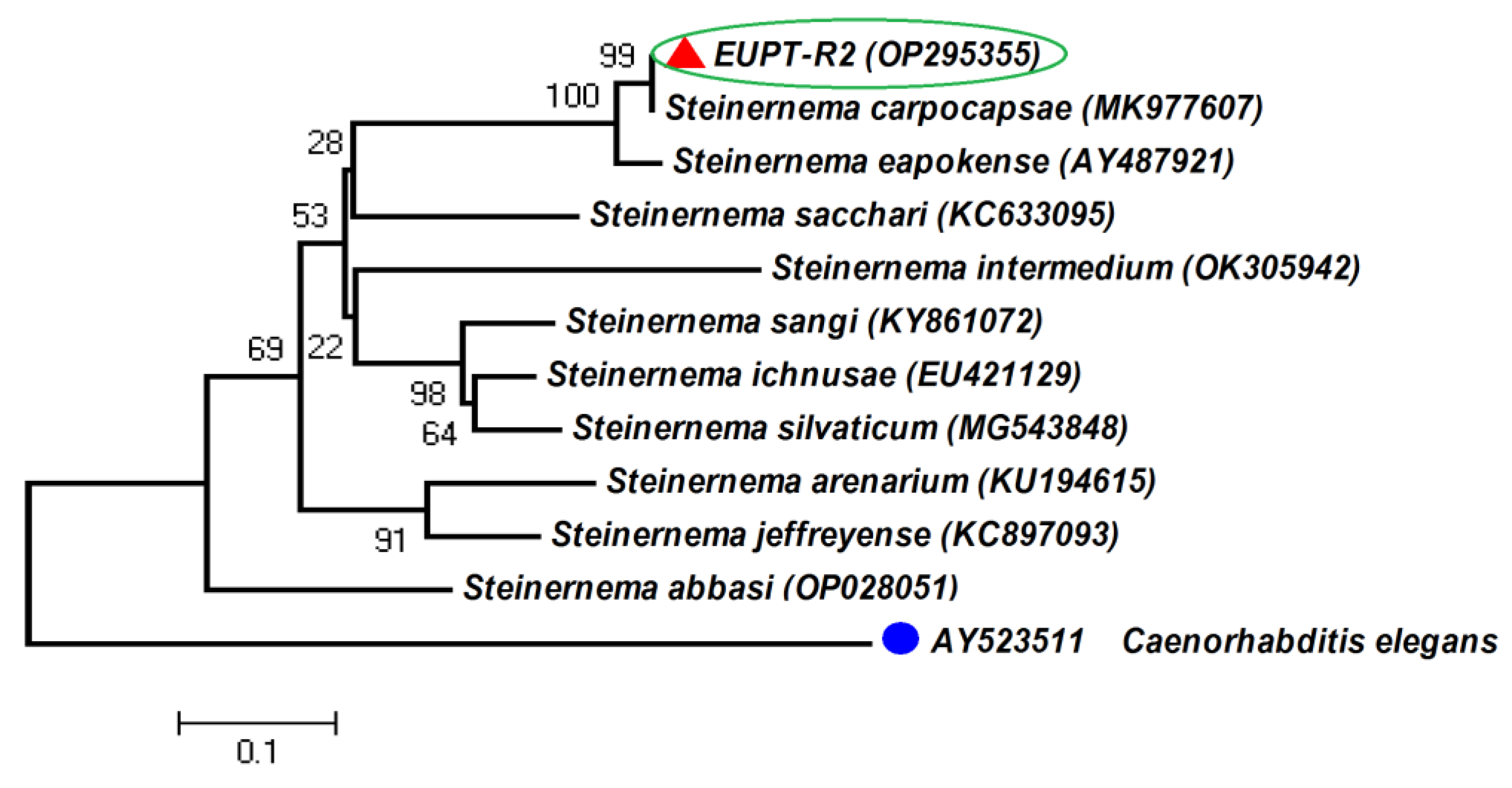
3.2. Morphological and Molecular Characterization of EPNs
3.3. Identification and Molecular Characterization of the Endosymbiotic Bacteria
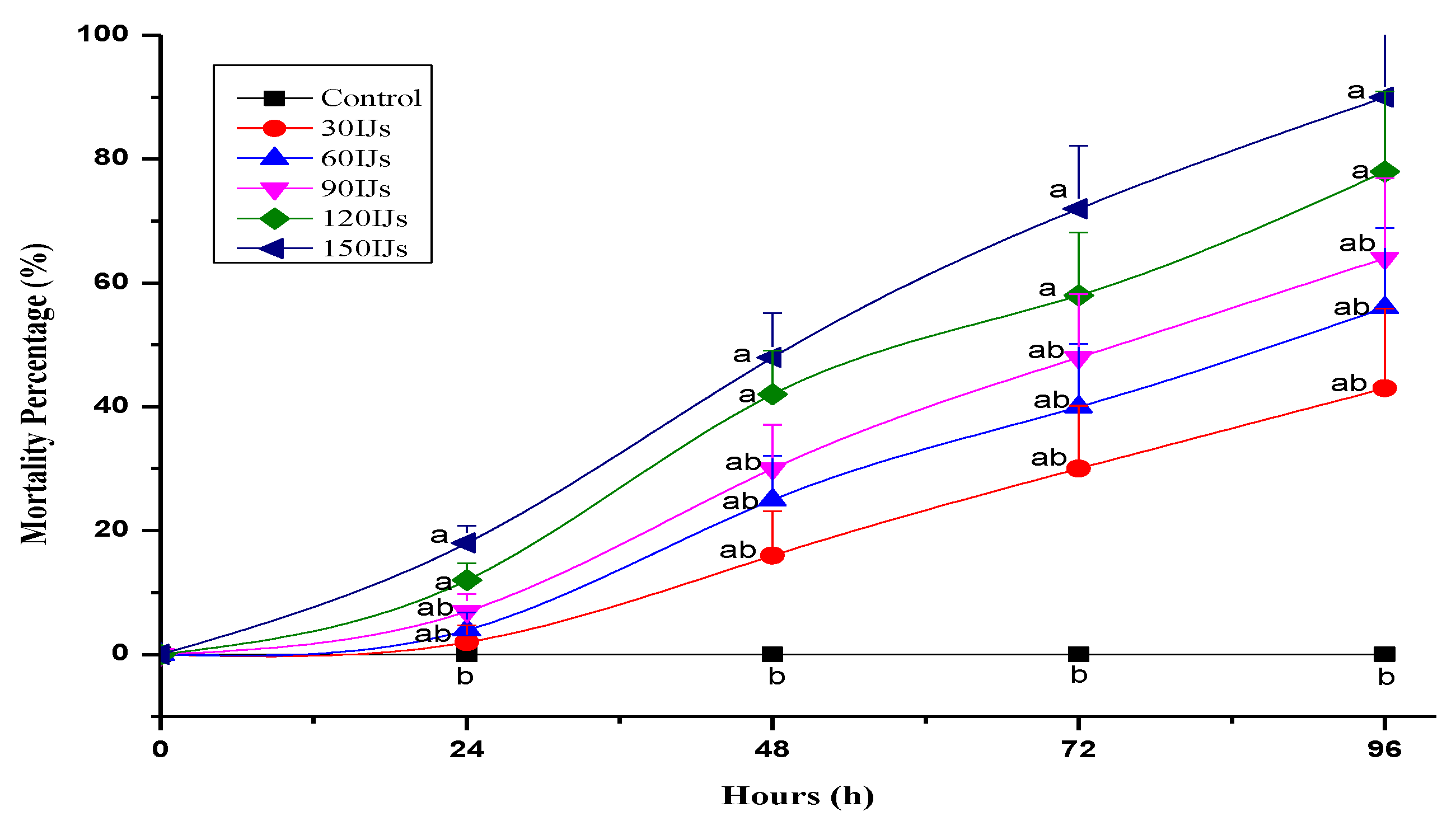
3.4. Entomopathogenic Capacity of Isolated EPN Species and Associated Bacterium
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dhaliwal, G.; Jindal, V.; Mohindru, B. Crop losses due to insect pests: Global and Indian scenario. Indian J. Entomol. 2015, 77, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, C.J.; Leroy, B.; Bellard, C.; Roiz, D.; Albert, C.; Fournier, A.; Barbet-Massin, M.; Salles, J.-M.; Simard, F.; Courchamp, F. Massive yet grossly underestimated global costs of invasive insects. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) Working Group I Contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; U.C.U.P.: Cambridge, UK, 2013.
- Thackeray, S.J.; Henrys, P.A.; Hemming, D.; Bell, J.R.; Botham, M.S.; Burthe, S.; Helaouet, P.; Johns, D.G.; Jones, I.D.; Leech, D.I. Phenological sensitivity to climate across taxa and trophic levels. Nature 2016, 535, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, K.; Phillips, C.; Broome, K.; Green, C.; Toft, R.; Walker, G. Feasibility of eradicating the large white butterfly (Pieris brassicae) from New Zealand: Data gathering to inform decisions about the feasibility of eradication. In Island Invasives: Scaling Up to Meet the Challenge; Veitch, C.R., Clout, M.N., Martin, A.R., Russell, J.C., West, C.J., Eds.; Occasional Paper SSC; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 62, pp. 364–369. [Google Scholar]
- Feltwell, J. Large White Butterfly: The Biology, Biochemistry and Physiology of Pieris brassicae (Linnaeus); Springer Science & Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 18. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, W.; Javed, N.; Haq, I.-U.; Ahmed, S. Virulence potential of two entomopathogenic nematodes, their associated bacteria, and its metabolites to larvae of Pieris brassicae L.(Lepidoptera, Pieridae) in cabbage under greenhouse and field bioassays. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2022, 42, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meszka, B.; Broniarek-Niemiec, A.; Bielenin, A. The status of dodine resistance of Venturia inaequalis populations in Poland. Phytopathol. Pol. 2008, 47, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Matson, M.E.; Small, I.M.; Fry, W.E.; Judelson, H.S. Metalaxyl resistance in Phytophthora infestans: Assessing role of RPA190 gene and diversity within clonal lineages. Phytopathology 2015, 105, 1594–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Shukla, N.; Kabadwal, B.; Tewari, A.; Kumar, J. Review on plant-Trichoderma-pathogen interaction. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2018, 7, 2382–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozel, U.; Gozel, C. Entomopathogenic nematodes in pest management. In Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Environmentally Sound Pest Management; Gill, H.K., Goyal, G., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016; Volume 55. [Google Scholar]
- Mracek, Z. Use of entomoparasitic nematodes (EPANs) in biological control. In Advances in Microbial Control of Insect Pests; Upadhyay, R.K., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 235–264. [Google Scholar]
- Poinar, G.O., Jr. Description and biology of a new insect parasitic Rhabditoid, Heterorhabditis bacteriophora N. Gen., N. Sp.(Rhabditida; Heterorhabditidae N. Fam.). Nematologica 1975, 21, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitwood, B.G.; Chitwood, M.B. An introduction to nematology. Nature 1937, 139, 654. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, A.H.; Chaubey, A.K.; Askary, T.H. Global distribution of entomopathogenic nematodes, Steinernema and Heterorhabditis. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2020, 30, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, P.; Thakur, N.; Yadav, A.N. Endosymbiotic microbes from entomopathogenic nematode (EPNs) and their applications as biocontrol agents for agro-environmental sustainability. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2022, 32, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, R.A.; Wüthrich, D.; Kuhnert, P.; Arce, C.C.; Thönen, L.; Ruiz, C.; Zhang, X.; Robert, C.A.; Karimi, J.; Kamali, S. Whole-genome-based revisit of Photorhabdus phylogeny: Proposal for the elevation of most Photorhabdus subspecies to the species level and description of one novel species Photorhabdus bodei sp. nov., and one novel subspecies Photorhabdus laumondii subsp. clarkei subsp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 2664–2681. [Google Scholar]
- Sajnaga, E.; Kazimierczak, W. Evolution and taxonomy of nematode-associated entomopathogenic bacteria of the genera Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus: An overview. Symbiosis 2020, 80, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Kumar, M.; Ahuja, A.; Vinay, B.; Kommu, K.K.; Thakur, S.; Paschapur, A.U.; Jeevan, B.; Mishra, K.; Meena, R.P. Entomopathogenic nematodes: A sustainable option for insect pest management. In Biopesticides; Rakshit, A., Meena, V.S., Abhilash, P.C., Sarma, B.K., Singh, H.B., Fraceto, L., Parihar, M., Singh, A.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 73–92. [Google Scholar]
- Georgis, R.; Koppenhöfer, A.; Lacey, L.; Bélair, G.; Duncan, L.; Grewal, P.; Samish, M.; Tan, L.; Torr, P.; Van Tol, R. Successes and failures in the use of parasitic nematodes for pest control. Biol. Control. 2006, 38, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, N.; Tomar, P.; Kaur, S.; Kumari, P. Virulence of native entomopathogenic nematodes against major lepidopteran insect species of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). J. Appl. Biol. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, P.; Thakur, N.; Yadav, A.N. Indigenous entomopathogenic nematode as biocontrol agents for insect pest management in hilly regions. Plant Sci. Today 2021, 8, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepenekci, I.; Hazir, S.; Lewis, E.E. Evaluation of entomopathogenic nematodes and the supernatants of the in vitro culture medium of their mutualistic bacteria for the control of the root-knot nematodes Meloidogyne incognita and M. arenaria. Pest Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, H.; Stock, S.P.; Kim, S.-K.; Flores-Lara, Y.; Forst, S. New insights into the colonization and release processes of Xenorhabdus nematophila and the morphology and ultrastructure of the bacterial receptacle of its nematode host, Steinernema carpocapsae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5338–5346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, N.; Kaur, S.; Tomar, P.; Thakur, S.; Yadav, A.N. Microbial biopesticides: Current status and advancement for sustainable agriculture and environment. In New and Future Developments in Microbial Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Rastegari, A.A., Yadav, A.N., Yadav, N., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 243–282. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, N.; Tomar, P.; Kaur, S.; Jhamta, S.; Thakur, R.; Yadav, A.N. Entomopathogenic soil microbes for sustainable crop protection. In Soil Microbiomes for Sustainable Agriculture: Functional Annotation; Yadav, A.N., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Swizterland, 2021; pp. 529–571. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, N.; Tomar, P.; Sharma, S.; Kaur, S.; Sharma, S.; Yadav, A.N.; Hesham, A.E.-L. Synergistic effect of entomopathogens against Spodoptera litura (Fabricius) under laboratory and greenhouse conditions. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2022, 32, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco, R.A.; Lee, M.-M.; Stock, S.P. Soil sampling and isolation of entomopathogenic nematodes (Steinernematidae, Heterorhabditidae). J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 89, e52083. [Google Scholar]
- Bedding, R.; Akhurst, R. A simple technique for the detection of insect paristic rhabditid nematodes in soil. Nematologica 1975, 21, 109–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickle, W.R. Manual of Agricultural Nematology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- White, G. A method for obtaining infective nematode larvae from cultures. Science 1927, 66, 302–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, D.C. Ecology of Plant Parasitic Nematode; John Willey and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Seinhorst, J. Killing nematodes for taxonomic study with hot fa 4: 1. Nematologica 1966, 12, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hominick, W.; Briscoe, B.; del Pino, F.G.; Heng, J.; Hunt, D.; Kozodoy, E.; Mracek, Z.; Nguyen, K.; Reid, A.; Spiridonov, S. Biosystematics of entomopathogenic nematodes: Current status, protocols and definitions. J. Helminthol. 1997, 71, 271–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Man, J.G. Die, frei in der reinen Erde und im Süssen Wasser lebenden Nematoden der Niederländischen Fauna: Eine Systematisch-faunistische Monographie; EJ Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1884; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, N.; Tomar, P.; Kaur, J.; Kaur, S.; Sharma, A.; Jhamta, S.; Yadav, A.N.; Dhaliwal, H.S.; Thakur, R.; Thakur, S. Eco-friendly management of Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in tomato under polyhouse and field conditions using Heterorhabditis bacteriophora Poinar, their associated bacteria (Photorhabdus luminescens), and Bacillus thuringiensis var. kurstaki. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2023, 33, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Dudley, J.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA4: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1596–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, P.; Thakur, N.; Sharma, A. Infectivity of entomopathogenic nematode against the cabbage butterfly (Pieris brassicae L.) in polyhouse and in field condition. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2022, 32, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, W.S. A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J. Econ. Entomol. 1925, 18, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, A. Biocontrol of Maize Stem Borer (Chilo partellus) Using Entomopathogenic Nematodes. Master Thesis, Submitted to Maharana Pratap University of Agriculture & Technology (MPUAT), Udaipur, India, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Chand, P.; Parihar, A.; Maru, A.K.; Sharma, S. Mass production (in vivo) of the entomopathogenic nematode, Steinernema carpocapsae on greater wax moth, Galleria mellonella and rice moth, Corcyra cephalonica. Biodiversitas J. Biol. Divers. 2019, 20, 1344–1349. [Google Scholar]
- Weiser, J. Neoaplectana carpocapsae n. sp. (Anguillulata, Steinernematinae), novy cizopasník housenek obalece jablecného, Carpocapsa pomonella L. Vestn. Ceskoslovenske Spol. Zool. 1955, 19, 44–52. [Google Scholar]
- Poinar, G. Description and taxonomic position of DD-136 nematode (Steinernematidae Rhabditoidea) and its relationship to Neoaplectana carpocapsae Weiser. Proc. Helminthol. Soc. Wash. 1967, 34, 199. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, M.; Gupta, P. Occurrence of entomopathogenic nematodes in Himachal Pradesh, India and their pathogenicity against various insect species. Pest Manag. Econ. Zool. 2006, 14, 179–189. [Google Scholar]
- Lalramliana, Y.A.; Kumar, A. Occurrence of entomopathogenic nematodes (Rhabditida: Steinernematidae and Heterorhabditidae) in Meghalaya, NE India. Sci. Vis. 2010, 10, 89–100. [Google Scholar]
- Rana, A.; Bhat, A.H.; Chaubey, A.K.; Shokoohi, E.; Machado, R.A. Morphological and molecular characterization of Heterorhabditis bacteriophora isolated from Indian soils and their biocontrol potential. Zootaxa 2020, 4878, 77–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pervez, R.; Eapen, S.J.; Devasahayam, S.; Jacob, T. Natural occurrence of entomopathogenic nematodes associated with ginger (Zingiber officinale Rosc.) ecosystem in India. Indian J. Nematol. 2014, 44, 238–246. [Google Scholar]
- Torrini, G.; Landi, S.; Benvenuti, C.; De Luca, F.; Fanelli, E.; Troccoli, A.; Tarasco, E.; Bazzoffi, P. Morphological and molecular characterization of a Steinernema carpocapsae (Nematoda Steinernematidae) strain isolated in Veneto region (Italy). Redia 2014, 97, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Neira-Monsalve, E.; Wilches-Ramírez, N.C.; Terán, W.; del Pilar Márquez, M.; Mosquera-Espinosa, A.T.; Sáenz-Aponte, A. Isolation, identification, and pathogenicity of and its bacterial symbiont in Cauca-Colombia. J. Nematol. 2020, 52, e2020-89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalitha, K.; Venkatesan, S.; Balamuralikrishnan, B.; Shivakumar, M.S. Isolation and biocontrol efficacy of entomopathogenic nematodes Steinernema carpocapsae, Steinernema monticolum and Rhabditis blumi on lepidopteran pest Spodoptera litura. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2022, 39, 102291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Kim, Y.; Yi, Y. Identification and characterization of a symbiotic bacterium associated with Steinernema carpocapsae in Korea. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 1999, 2, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantoo, M.A.; Zaki, F. Biological control of cabbage butterfly, Pieris brassicae, by a locally isolated entomopathogenic nematode, Heterorhabditis bacteriophora SKUASTK-EPN-Hr-1 in Kashmir. SKUAST J. Res. 2014, 16, 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Gorgadze, O.; Fanelli, E.; Lortkhipanidze, M.; Troccoli, A.; Burjanadze, M.; Tarasco, E.; De Luca, F. Steinernema borjomiense n. sp.(Rhabditida: Steinernematidae), a new entomopathogenic nematode from Georgia. Nematology 2018, 20, 653–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, P.; Thakur, N. Biocidal potential of indigenous isolates of Entomopathogenic Nematodes (EPNs) against tobacco cutworm, Spodoptera litura Fabricius (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2022, 32, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabry, A.; Metwallya, H.; Abolmaatyb, S. Compatibility and efficacy of entomopathogenic nematode, Steinernema carpocapsae all alone and in combination with some insecticides against Tuta absoluta. Der. Pharm. Let. 2016, 8, 311–315. [Google Scholar]
- Kasi, I.K.; Singh, M.; Waiba, K.M.; Monika, S.; Waseem, M.; Archie, D.; Gilhotra, H. Bio-efficacy of entomopathogenic nematodes, Steinernema feltiae and Heterorhabditis bacteriophora against the Cabbage butterfly (Pieris brassicae [L.]) under laboratory conditions. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2021, 31, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askary, T.H.; Ahmad, M.J. Efficacy of entomopathogenic nematodes against the cabbage butterfly (Pieris brassicae (L.)(Lepidoptera: Pieridae) infesting cabbage under field conditions. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2020, 30, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, W.; Javed, N.; Haq, I.U.; Ahmed, S. Pathogenicity of Entomopathogenic nematodes against cabbage butterfly (Pieris brassicae) Linnaeus (Lepidoptera: Pieridae) in laboratory conditions. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2021, 41, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, P.; Thakur, N. Isolation and evaluation of Heterorhabditis bacteriophora strain-S26 as biocontrol agents against Pieris brassicae L. under laboratory conditions. Indian J. Nematol. 2022, 52, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobanboa, S.; Bussaman, P.; Chandrapatya, A. Efficacy of Xenorhabdus sp.(X1) as biocontrol against for controlling mushroom mites (Luciaphorus sp.). Asian J. Food Agro-Ind. 2009, 2, S145–S154. [Google Scholar]
- Elbrense, H.; Elmasry, A.M.; Seleiman, M.F.; Al-Harbi, M.S.; Abd El-Raheem, A.M. Can symbiotic bacteria (Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus) be more efficient than their entomopathogenic nematodes against Pieris rapae and Pentodon algerinus larvae? Biology 2021, 10, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünal, M.; Yüksel, E.; Canhilal, R. Biocontrol potential of cell suspensions and cell-free superntants of different Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus bacteria against the different larval instars of Agrotis ipsilon (Hufnagel) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Exp. Parasitol. 2022, 242, 108394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüksel, E.; Ormanoğlu, N.; İmren, M.; Canhilal, R. Assessment of biocontrol potential of different Steinernema species and their bacterial symbionts, Xenorhabdus species against larvae of almond moth, Ephestia cautella (Walker). J. Stored Prod. Res. 2023, 101, 102082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Location/ Villages | Vegetations | Total No. of Samples | Samples Having EPNs | Samples without EPNs | Frequency of Occurrence (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chhupari | Peach, Apple, Pear, Cucumber and Plum | 05 | 01 | 04 | 25 |
| Rampur | Apple and Persimmon | 04 | - | 04 | - |
| Badiyara | Peach and Apple | 06 | 01 | 05 | 16.67 |
| Shimla | Apricot, Plum, Cherry, Apple, Pear, Peach | 05 | - | 05 | - |
| Fagu | Apple | 05 | 01 | 04 | 25 |
| Jabbal | Pear, Apple and Apricot | 06 | 02 | 04 | 33.33 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomar, P.; Thakur, N.; Sidhu, A.K.; Laskar, B.A.; Hashem, A.; Avila-Quezada, G.D.; Abd_Allah, E.F. The Isolation, Identification, and Insecticidal Activities of Indigenous Entomopathogenic Nematodes (Steinernema carpocapsae) and Their Symbiotic Bacteria (Xenorhabdus nematophila) against the Larvae of Pieris brassicae. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9080874
Tomar P, Thakur N, Sidhu AK, Laskar BA, Hashem A, Avila-Quezada GD, Abd_Allah EF. The Isolation, Identification, and Insecticidal Activities of Indigenous Entomopathogenic Nematodes (Steinernema carpocapsae) and Their Symbiotic Bacteria (Xenorhabdus nematophila) against the Larvae of Pieris brassicae. Horticulturae. 2023; 9(8):874. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9080874
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomar, Preety, Neelam Thakur, Avtar Kaur Sidhu, Boni Amin Laskar, Abeer Hashem, Graciela Dolores Avila-Quezada, and Elsayed Fathi Abd_Allah. 2023. "The Isolation, Identification, and Insecticidal Activities of Indigenous Entomopathogenic Nematodes (Steinernema carpocapsae) and Their Symbiotic Bacteria (Xenorhabdus nematophila) against the Larvae of Pieris brassicae" Horticulturae 9, no. 8: 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9080874
APA StyleTomar, P., Thakur, N., Sidhu, A. K., Laskar, B. A., Hashem, A., Avila-Quezada, G. D., & Abd_Allah, E. F. (2023). The Isolation, Identification, and Insecticidal Activities of Indigenous Entomopathogenic Nematodes (Steinernema carpocapsae) and Their Symbiotic Bacteria (Xenorhabdus nematophila) against the Larvae of Pieris brassicae. Horticulturae, 9(8), 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9080874








