The Effects of Calcium and Sulfur Fertilizers Accompanied by Different Side Elements on the Growth and Cd Uptake of Spinacia oleracea Grown in Cd-Contaminated Alkaline Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Set-Up
2.2. Leaf Chlorophyll Fluorescence and Actual Photochemical Efficiency
2.3. Plant Biomass and Nutrient Uptake
2.4. Soil Physicochemical Properties and Nutrient Content
2.5. Plant Cd Uptake and Soil Cd Content
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Leaf Fluorescence and Plant Growth
3.2. Plant Cd and Soil Cd Content
3.3. Soil Physicochemical Properties and Nutrient Condition
3.4. The Relationship between Plant Growth, Plant Cd Uptake, Soil Physicochemical Properties, and Nutrient Conditions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adriano, D.; Wenzel, W.; Vangronsveld, J.; Bolan, N. Role of assisted natural remediation in environmental cleanup. Geoderma 2004, 122, 121–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, B.; Umer, M.; Li, J.; Ma, Y.; Abbas, Y.; Ashraf, M.; Tahir, N.; Ullah, A.; Gogoi, N.; Farooq, M. Strategies for reducing cadmium accumulation in rice grains. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 286, 125557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Long, X.; Ye, H.; He, Z.; Calvert, D.; Stoffella, P. Cadmium tolerance and hyperaccumulation in a new Zn-hyperaccumulating plant species (Sedum alfredii Hance). Plant Soil. 2004, 259, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treesubsuntorn, C.; Hurakit, P.; Khaksar, G.; Thiravetyan, P. Effect of microorganisms on reducing cadmium uptake and toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 25690–25701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Tang, Z.; Song, J.; Huang, X.; Wang, P. Toxic metals and metalloids: Uptake, transport, detoxification, phytoremediation, and crop improvement for safer food. Mol. Plant 2022, 15, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, F.; Cai, L.; Coulter, J.; Cheema, S.; Wu, J.; Zhang, R.; Ma, W.; Muhammad, F. Cadmium toxicity in plants: Impacts and remediation strategies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 211, 111887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Meunier, J.; Miche, H.; Keller, C. Effect of silicon on reducing cadmium toxicity in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. cv. Claudio W.) grown in a soil with aged contamination. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 209–210, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S.; Ghosh, S.; Azahar, I.; Adhikari, A.; Shaw, A.; Konar, S.; Roy, S.; Hossain, Z. Sulfate improves cadmium tolerance by limiting cadmium accumulation, modulation of sulfur metabolism and antioxidant defense system in maize. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2018, 153, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Liu, H.; Nie, Z.; Rengel, Z.; Gao, W.; Li, C.; Zhao, P. Toxicity of cadmium and its competition with mineral nutrients for uptake by plants: A review. Pedosphere 2020, 30, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L. Safe Utilization of Slightly-Moderately Cadmium-Polluted Farmland Soil. Ph.D. Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2018. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Sun, L.; Tai, P.; Liu, W.; Li, X.; Hao, L. Effects of grafting on root-to-shoot cadmium translocation in plants of eggplant (Solanum melongena) and tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Li, T.; Xu, W.; Chai, Y. Distribution of cadmium in subcellular fraction and expression difference of its transport genes among three cultivars of pepper. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 216, 112182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Su, G.; Guo, X.; Yang, Y.; Yao, A.; Chou, R.; Tang, Y. Effects of different sulfur forms on cadmium uptake and accumulation in paddy rice. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2021, 40, 1208–1218. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Yang, R.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Xia, Y.; Xu, X. Foliar application of gibberellin inhibits the cadmium uptake and xylem transport in lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). Sci. Hortic. 2021, 288, 110410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaf, M.; Hao, Y.; Shu, H.; Mumtaz, M.; Chen, S.; Alyemeni, M.; Ahmad, P.; Wang, Z. Melatonin enhanced the heavy metal-stress tolerance of pepper by mitigating the oxidative damage and reducing the heavy metal accumulation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 454, 131468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pishkar, L.; Yousefi, S.; Iranbakhsh, A. Foliar application of Zinc oxide nanoparticles alleviates cadmium toxicity in purslane by maintaining nutrients homeostasis and improving the activity of antioxidant enzymes and glyoxalase system. Ecotoxicology 2022, 31, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, M.; Mukherjee, S.; Kumar, R.; Alansi, S.; Shah, A.; Kalaji, H.; Javed, T.; Raza, A. K and melatonin-mediated regulation of fructose-1, 6-bisphosphatase (FBPase) and sedoheptulose-1, 7-bisphosphatase (SBPase) activity improve photosynthetic efficiency, carbon assimilation and modulate glyoxalase system accompanying tolerance to cadmium stress in tomato seedlings. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 171, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, C.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Z. Increasing phosphate inhibits cadmium uptake in plants and promotes synthesis of amino acids in grains of rice. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Lan, Y.; Sun, S.; Fan, X. Response of alkaline functional fertilizer on Cd absorption and transportation in soil-rice system. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, R.; Lu, Y.; Bai, Z. Sustainable management of cadmium-contaminated soils as affected by exogenous application of nutrients: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 295, 113081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xiong, J.; Tao, L.; Cao, Z.; Tang, W.; Zhang, J.; Yu, X.; Fu, G.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Y. Regulatory mechanisms of nitrogen (N) on cadmium (Cd) uptake and accumulation in plants: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 135186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, R.; Wang, X.; Huo, W.; Chi, K.; Fan, H. Effect of different fertilizers on cadmium accumulation in Amaranshus mangostanus L. Soil Fertil. Sci. China 2018, 1, 37–42. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zou, R.; Wang, X.; Huo, W.; Chi, K.; Fan, H. Effects of different nitrogen fertilizers on cadmium accumulation of Amaranshus mangostanus L. in different soil types. Soil Fertil. Sci. China 2020, 3, 29–35. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hakeem, K.; Alharby, H.; Pirzadah, T. Exogenously applied calcium regulates antioxidative system and reduces cadmium-uptake in Fagopyrum esculentum. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 180, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, H.; Huang, D.; Guo, X.; Xu, C.; Zhu, H.; Li, B.; Liu, T.; Feng, R.; Zhu, Q. Sulfur fertilization integrated with soil redox conditions reduces Cd accumulation in rice through microbial induced Cd immobilization. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 824, 153868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thor, K. Calcium-Nutrient and Messenger. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Liu, J.; You, Z.; Huang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, C. Plasma membrane-associated calcium signaling modulates cadmium transport. New Phytol. 2023, 238, 313–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Shang, X. Ca alleviated Cd-induced toxicity in Salix matsudana by affecting Cd absorption, translocation, subcellular distribution, and chemical forms. J. Plant Physiol. 2023, 281, 153926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matraszek, R.; Hawrylak-Nowak, B.; Chwil, S.; Chwil, M. Macroelemental composition of cadmium stressed lettuce plants grown under conditions of intensive sulphur nutrition. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 180, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Pu, P.; Li, X.; Gong, Y.; An, D.; Zhang, L.; Lv, J. Sulfur application reduces cadmium uptake in edible parts of pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) by cadmium chelation and vacuolar sequestration. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 194, 110402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, G.; Yang, X.; Ke, X.; Huang, L.; Li, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Tao, M.; Hu, Z. Effects of sulfur supply on cadmium transfer and concentration in rice at different growth stages exposed to sulfur-deficient but highly cadmium-contaminated soil. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2023, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Mubsher, A.; Rizwan, M.; Usman, M.; Jafir, M.; Umair, M.; Alharby, H.; Bamagoos, A.; Alshamrani, R.; Ali, S. Effect of farmyard manure, elemental sulphur and EDTA on growth and phytoextraction of cadmium by spider plants (Chlorophytum comosum L.) under Cd stress. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Cao, F.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, G.; Wu, F. Modulation of Exogenous Glutathione in Phytochelatins and Photosynthetic Performance Against Cd Stress in the Two Rice Genotypes Differing in Cd Tolerance. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2010, 143, 1159–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, A.; Takeda, H.; Oyanagi, W.; Nishihara, E.; Murakami, M. Reduction of cadmium uptake in spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) by soil amendment with animal waste compost. J. Hazard Mater. 2010, 181, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Fang, B.; Yue, X.; Zou, J.; Chen, Y.; Su, N.; Cui, J. The research progress of vegetable Cd contamination and physiological blocking agents of Cd. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 2020, 43, 988–997. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Hou, H.; Zhao, L.; Sun, Z.; Li, H. Protective Effect of foliar application of sulfur on photosynthesis and antioxidative defense system of rice under the stress of Cd. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, U.; Rahman, M.; Ela, E.; Lee, K.; Kabir, A. Sulfur triggers glutathione and phytochelatin accumulation causing excess Cd bound to the cell wall of roots in alleviating Cd-toxicity in alfalfa. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingorance, M. Focused microwave-assisted digestion of vegetal materials for the determination of essential mineral nutrients. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2002, 373, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maereka, E.; Madakadze, R.; Mashingaidze, A.; Kageler, S.; Yakanda, C. Effect of nitrogen fertilization and timing of harvesting on leaf nitrate content and taste in mustard rape (Brassica juncea L. Czern). J. Food Agric. Environ. 2007, 5, 288–293. [Google Scholar]
- Ganesh, S.; Khan, F.; Ahmed, M.; Velavendan, P.; Pandey, N.; Mudali, U. Spectrophotometric determination of trace amounts of phosphate in water and soil. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 66, 2653–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asch, J.; Johnson, K.; Mondal, S.; Asch, F. Comprehensive assessment of extraction methods for plant tissue samples for determining sodium and K via flame photometer and chloride via automated flow analysis. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2022, 185, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, T.; Han, S.; Meng, Y.; Song, M.; Jiang, J. Occurrences and patterns of major elements in coal fly ash under multi-acid system during microwave digestion processes. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 359, 131950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Yang, Y.; Fan, M.; Huang, K.; Wang, L.; Lv, T.; Yi, X.; Chen, L.; Fang, Y. Inter- and Intra-Population Variation of Foliage Calcium and Magnesium in Two Chinese Pine Species. Plants 2023, 12, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Berbel, N.; Soria, R.; Ortega, R.; Lucas-Borja, M.; Miralles, I. Benefits of applying organic amendments from recycled wastes for fungal community growth in restored soils of a limestone quarry in a semiarid environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 151226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Molina, M.; Berns, A.; Macias, F.; Knicker, H. Biochemically altered charcoal residues as an important source of soil organic matter in subsoils of fire-affected subtropical regions. Geoderma 2016, 262, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazamias, G.; Roulia, M.; Kapsimali, I.; Chassapis, K. Innovative biocatalytic production of soil substrate from green waste compost as a sustainable peat substitute. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 203, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, C.; Lv, W.; Liao, X.; Brooks, M.; Li, Y.; Yu, C.; Yang, L.; Li, X.; Hu, W.; Dai, J.; et al. Green Manure Amendment Increases Soil Phosphorus Bioavailability and Peanut Absorption of Phosphorus in Red Soil of South China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, M.; Dong, Y.; Jiang, Y. Determination of Soil Exchangeable Base Cations by Using Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer and Extraction with Ammonium Acetate. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2012, 32, 2242–2245. [Google Scholar]
- Altaf, M.; Shahid, R.; Ren, M.; Naz, S.; Altaf, M.; Khan, L.; Lal, M.; Tiwari, R.; Shakoor, A. Melatonin Mitigates Cadmium Toxicity by Promoting Root Architecture and Mineral Homeostasis of Tomato Genotypes. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 22, 1112–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Sheng, H.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, Y. Remediation of Cd-contaminated acidic paddy fields with four-year consecutive liming. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 188, 109903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hseu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Tsai, C.; Tsui, C.; Cheng, S.; Liu, C.; Lin, H. Digestion methods for total heavy metals in sediments and soils. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2002, 141, 189–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Xu, C.; Wang, H.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, F.; Huang, D. Effects of three organic materials on the availability of cadmium in soil and cadmium accumulation and translocation in rice plants. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2020, 39, 2143–2150. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tlustos, P.; Szakova, J.; Hruby, J.; Hartman, I.; Najmanova, J.; Nedelnik, J.; Pavlikova, D.; Batysta, M. Removal of As, Cd, Pb, and Zn from contaminated soil by high biomass producing plants. Plant Soil Environ. 2006, 52, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Y.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Wang, L.; Liang, X.; Qin, X.; Zhao, L. Remediation effect of mercapto-palygorskite combined with manganese sulfate on cadmium contaminated alkaline soil and cadmium accumulation in pak choi (Brassica chinensis L.). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 813, 152636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Fu, H.; Liao, Q.; Huang, B.; Fan, X.; Liu, X.; Xin, J.; Huang, Y. Transcriptome analysis and physiological indicators reveal the role of sulfur in cadmium accumulation and transportation in water spinach (Ipomoea aquatica Forsk.). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 225, 112787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Li, L. Determination of Trace Elements K, Calcium Copper, Iron and Zinc in Spinach. Stud. Trace Elem. Health 2018, 35, 49–50. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Liu, L.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, Z.; Yin, F.; Jiao, N.; Fu, G. Mechanism of maize intercropping peanut improving iron nutrition to increase photosynthetic performance of peanut. J. Plant Nutr. 2020, 26, 901–913. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, J.; Coumar, M. Alteration of contamination threat due to dilution effect on metal concentration in maize-wheat biomass on sludge amended clayey soil. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yang, L.; Li, N.; Zhou, C.; Feng, H.; Yang, J.; Han, X. Cadmium toxicity reduction in rice (Oryza sativa L.) through iron addition during primary reaction of photosynthesis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 200, 110746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, D.; Xu, C.; Zhu, H.; Feng, R.; Zhu, Q. Fe fortification limits rice Cd accumulation by promoting root cell wall chelation and reducing the mobility of Cd in xylem. Ecotoxicol. Envirovn. Saf. 2022, 240, 113700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mleczek, M.; Kozłowska, M.; Kaczmarek, Z.; Magdziak, Z.; Goliński, P. Cadmium and lead uptake by Salix viminalis under modified Ca/Mg ratio. Ecotoxicology 2011, 20, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaswar, M.; Hussain, S.; Rengel, Z. Zinc fertilisation increases grain zinc and reduces grain lead and cadmium concentrations more in zincbiofortified than standard wheat cultivar. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 605–606, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, B.; Xia, H. Effect of cadmium on growth, photosynthesis, mineralnutrition and metal accumulation of bana grass and vetiver grass. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 106, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Hou, D.; O’Connor, D.; Pan, S.; Zhu, J.; Bolan, N.; Mulder, J. Exogenous phosphorus treatment facilitates chelation-mediated cadmium detoxification in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 121849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Lin, W. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer rates on the growth and nutrient utilization of calla lily intercropped with rubber trees. Soil Till. Res. 2021, 211, 105031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Liu, W.; Hong, H.; Lu, H.; Liu, J.; Jia, H.; Yan, C. Exogenous phosphorus enhances cadmium tolerance by affecting cell wall polysaccharides in two mangrove seedlings Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh and Kandelia obovata (S., L.) Yong differing in cadmium accumulation. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 126, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shen, J.; Liao, H. Acquisition or utilization, which is more critical for enhancing phosphorus efficiency in modern crops? Plant Sci. 2010, 179, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Juang, K. Alleviation effects of calcium and K on cadmium rhizotoxicity and absorption by soybean and wheat roots. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2015, 178, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, P.; Latef, A.; Abd_Allah, E.; Hashem, A.; Sarwat, M.; Anjum, N.; Gucel, S. Calcium and K supplementation enhanced growth, osmolyte secondary metabolite production, and enzymatic antioxidant machinery in cadmium-exposed chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
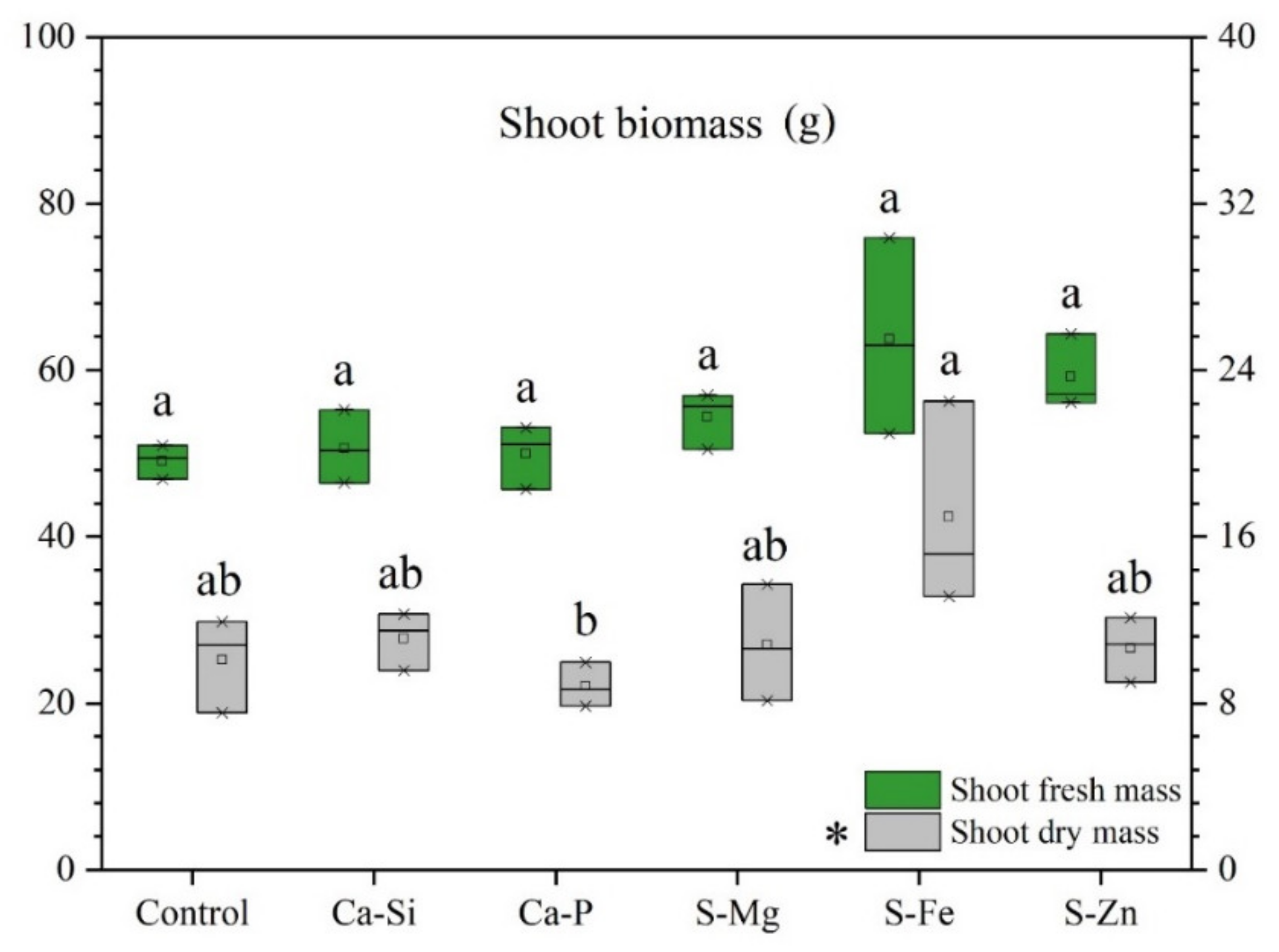

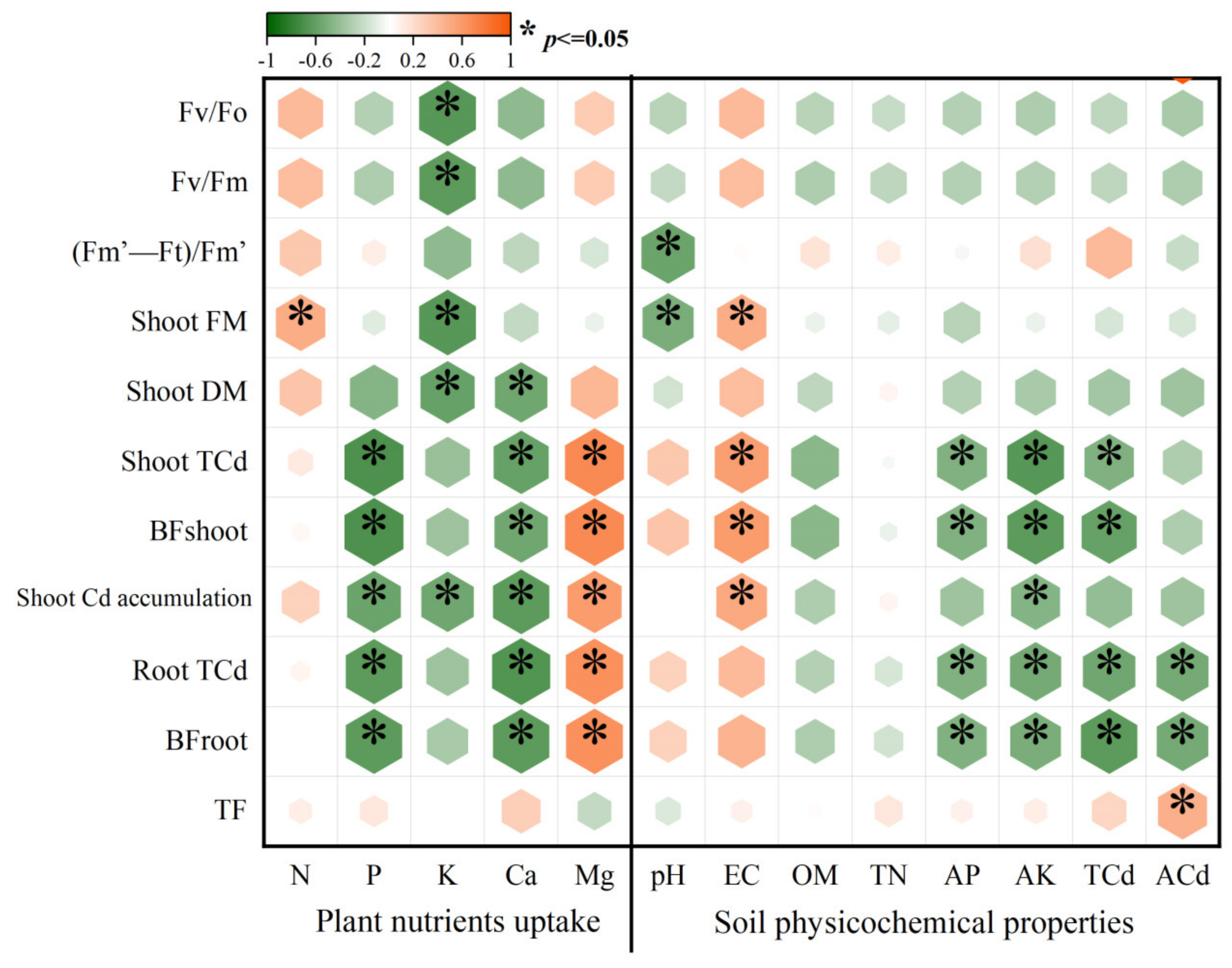
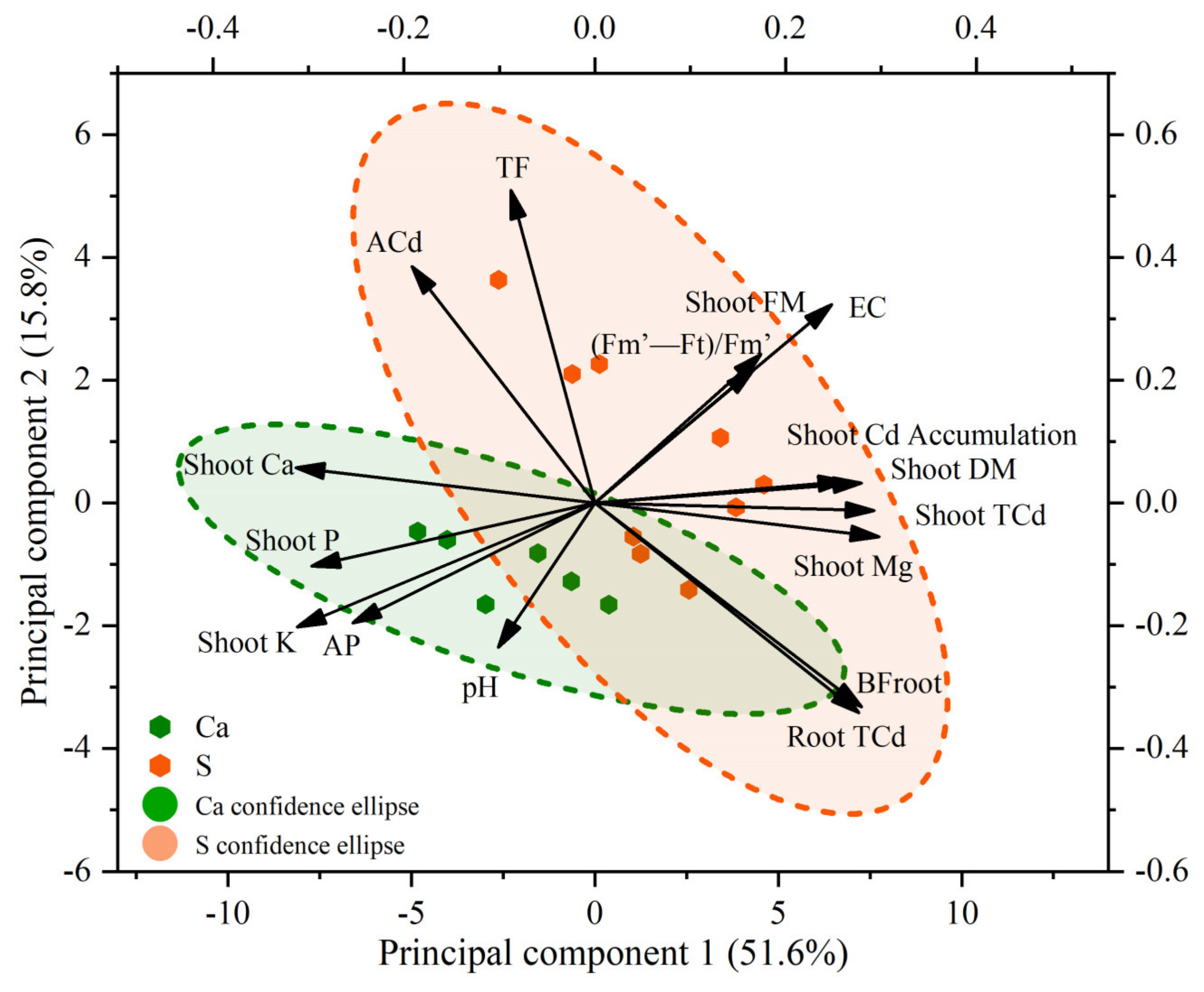
| Fv/Fo | Fv/Fm | Qy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 1.82 ± 0.09 a | 0.65 ± 0.01 a | 0.38 ± 0.03 b |
| Ca-Si | 1.86 ± 0.17 a | 0.65 ± 0.02 a | 0.45 ± 0.01 ab |
| Ca-P | 1.84 ± 0.19 a | 0.64 ± 0.03 a | 0.45 ± 0.01 ab |
| S-Mg | 2.13 ± 0.10 a | 0.68 ± 0.01 a | 0.47 ± 0.02 a |
| S-Fe | 2.33 ± 0.04 a | 0.70 ± 0.00 a | 0.48 ± 0.01 a |
| S-Zn | 2.11 ± 0.14 a | 0.68 ± 0.01 a | 0.47 ± 0.00 a |
| ANOVA | * |
| N | P | K | Ca | Mg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g kg−1 | mg kg−1 | g kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | |
| Control | 13.03 ± 1.21 a | 23.90 ± 1.85 c | 2.95 ± 0.23 ab | 119.69 ± 10.19 abc | 96.65 ± 12.44 a |
| Ca-Si | 14.17 ± 0.49 a | 56.57 ± 16.55 bc | 2.79 ± 0.11 ab | 123.54 ± 9.16 abc | 49.48 ± 19.80 ab |
| Ca-P | 12.27 ± 0.45 a | 160.00 ± 8.91 a | 3.41 ± 0.04 a | 150.83 ± 7.67 a | 12.34 ± 0.39 b |
| S-Mg | 13.05 ± 0.90 a | 64.20 ± 4.80 bc | 2.54 ± 0.13 bc | 118.59 ± 4.05 bc | 87.41 ± 1.94 a |
| S-Fe | 15.60 ± 0.41 a | 34.10 ± 11.30 bc | 1.88 ± 0.13 c | 94.08 ± 0.39 c | 87.99 ± 18.98 a |
| S-Zn | 14.56 ± 0.22 a | 70.93 ± 6.19 b | 2.43 ± 0.18 bc | 138.70 ± 2.75 ab | 37.27 ± 5.20 ab |
| ANOVA | *** | *** | ** | ** |
| Root TCd | BFshoot | BFroot | TF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg kg−1 | ||||
| Control | 2.92 ± 0.14 a | 2.01 ± 0.25 a | 1.53 ± 0.10 a | 1.31 ± 0.11 ab |
| Ca-Si | 2.40 ± 0.11 ab | 1.45 ± 0.08 a | 1.21 ± 0.05 ab | 1.20 ± 0.01 b |
| Ca-P | 1.69 ± 0.21 b | 1.22 ± 0.10 a | 0.84 ± 0.12 b | 1.49 ± 0.18 ab |
| S-Mg | 2.71 ± 0.12 a | 1.65 ± 0.16 a | 1.38 ± 0.09 a | 1.19 ± 0.05 b |
| S-Fe | 2.85 ± 0.29 a | 2.05 ± 0.19 a | 1.46 ± 0.15 a | 1.46 ± 0.26 ab |
| S-Zn | 1.48 ± 0.27 b | 1.40 ± 0.21 a | 0.74 ± 0.14 b | 1.92 ± 0.12 a |
| ANOVA | *** | * | ** | * |
| pH | EC | OM | TN | AP | AK | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g kg−1 | g kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | |||
| Control | 8.24 ± 0.06 a | 247.00 ± 4.04 a | 18.23 ± 0.42 | 1.12 ± 0.01 | 8.97 ± 0.12 b | 160.85 ± 2.72 |
| Ca-Si | 7.95 ± 0.08 ab | 186.00 ± 7.81 b | 18.88 ± 0.56 | 1.15 ± 0.01 | 9.92 ± 0.40 b | 168.22 ± 7.25 |
| Ca-P | 7.90 ± 0.06 ab | 188.83 ± 5.89 b | 19.82 ± 1.15 | 1.15 ± 0.10 | 17.85 ± 0.86 a | 181.77 ± 9.29 |
| S-Mg | 7.64 ± 0.06 b | 239.67 ± 5.49 a | 18.66 ± 0.76 | 1.17 ± 0.03 | 8.98 ± 0.05 b | 165.62 ± 1.89 |
| S-Fe | 7.77 ± 0.06 b | 254.00 ± 3.00 a | 19.02 ± 0.60 | 1.16 ± 0.01 | 9.22 ± 0.41 b | 162.68 ± 2.05 |
| S-Zn | 7.71 ± 0.11 b | 238.33 ± 3.71 a | 18.88 ± 0.80 | 1.14 ± 0.01 | 9.23 ± 0.43 b | 172.83 ± 9.81 |
| ANOVA | ** | *** | *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Suo, L.; Sun, Y.; Sun, N.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Zou, G.; Liao, S. The Effects of Calcium and Sulfur Fertilizers Accompanied by Different Side Elements on the Growth and Cd Uptake of Spinacia oleracea Grown in Cd-Contaminated Alkaline Soil. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9070835
Li Y, Xu X, Suo L, Sun Y, Sun N, Liu J, Li S, Zou G, Liao S. The Effects of Calcium and Sulfur Fertilizers Accompanied by Different Side Elements on the Growth and Cd Uptake of Spinacia oleracea Grown in Cd-Contaminated Alkaline Soil. Horticulturae. 2023; 9(7):835. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9070835
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yanmei, Xiangnan Xu, Linna Suo, Yanxin Sun, Na Sun, Jing Liu, Shunjiang Li, Guoyuan Zou, and Shangqiang Liao. 2023. "The Effects of Calcium and Sulfur Fertilizers Accompanied by Different Side Elements on the Growth and Cd Uptake of Spinacia oleracea Grown in Cd-Contaminated Alkaline Soil" Horticulturae 9, no. 7: 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9070835
APA StyleLi, Y., Xu, X., Suo, L., Sun, Y., Sun, N., Liu, J., Li, S., Zou, G., & Liao, S. (2023). The Effects of Calcium and Sulfur Fertilizers Accompanied by Different Side Elements on the Growth and Cd Uptake of Spinacia oleracea Grown in Cd-Contaminated Alkaline Soil. Horticulturae, 9(7), 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9070835







