Improved Genetic Map and Localization of Quantitative Trait Loci for Quality Traits in Auricularia heimuer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strain and Culture Conditions
2.2. Nucleic Acid Extraction
2.3. Synthesis of Primers
2.4. PCR Amplification and Electrophoresis
2.5. Genotyping
2.6. High-Density Genetic Linkage Map Construction
2.7. Genetic Linkage Mapping Analysis
2.8. Genome Assembly Sequence Anchoring to Genetic Maps
2.9. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA)
2.10. TPA Data Analysis and QTL Localization
2.11. Candidate Gene Prediction
3. Results
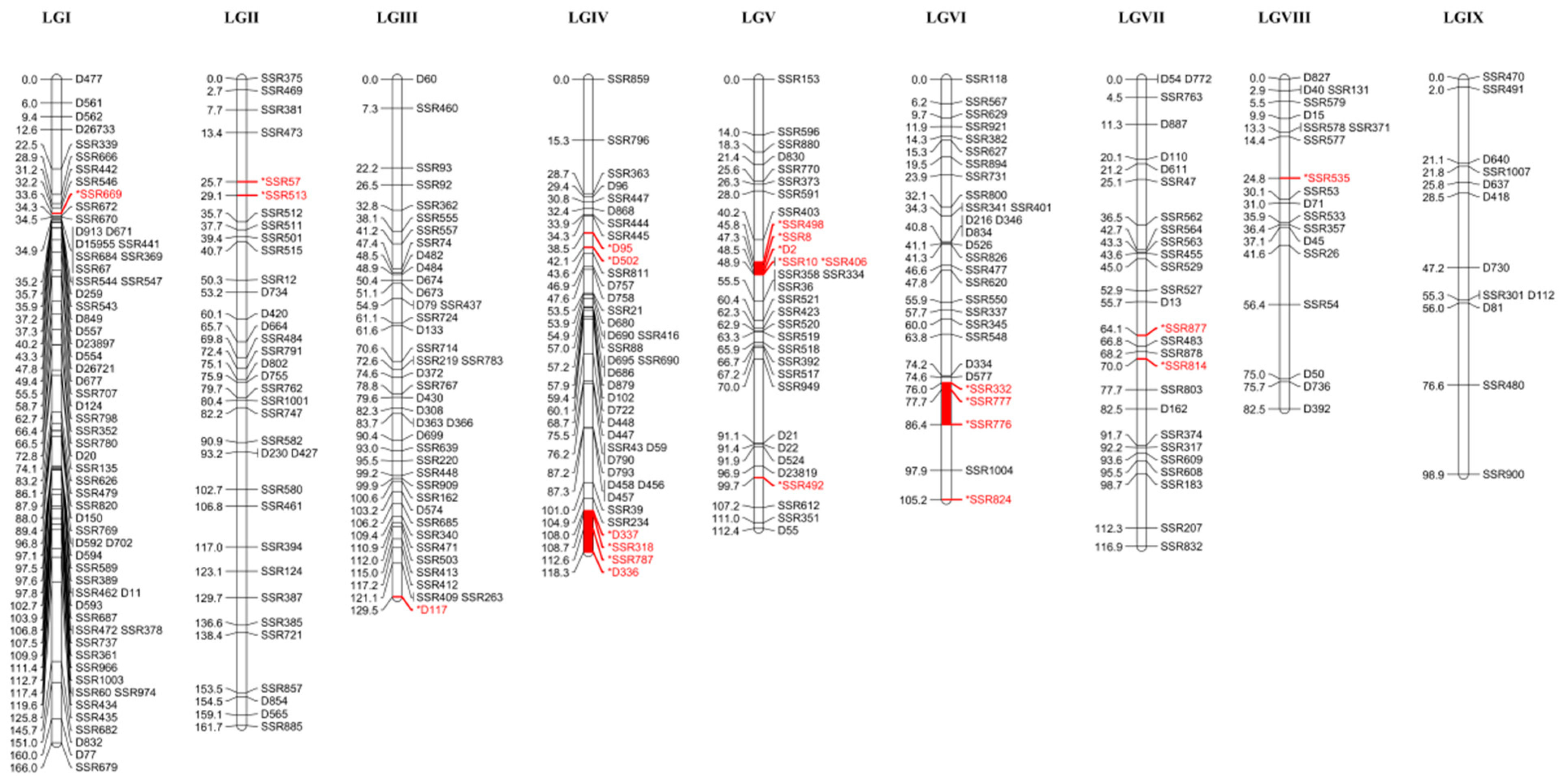
3.1. Construction of Genetic Linkage Map
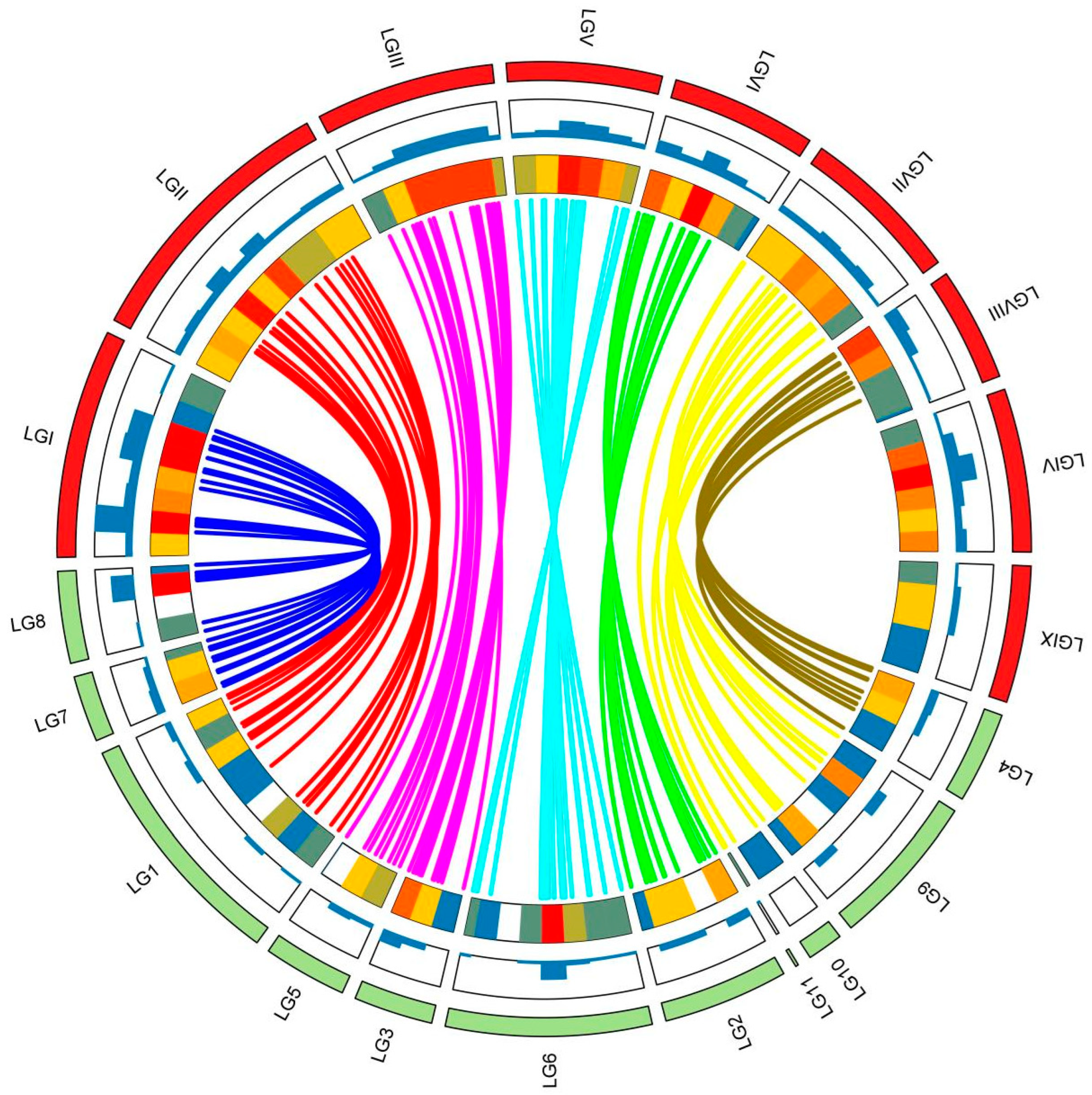
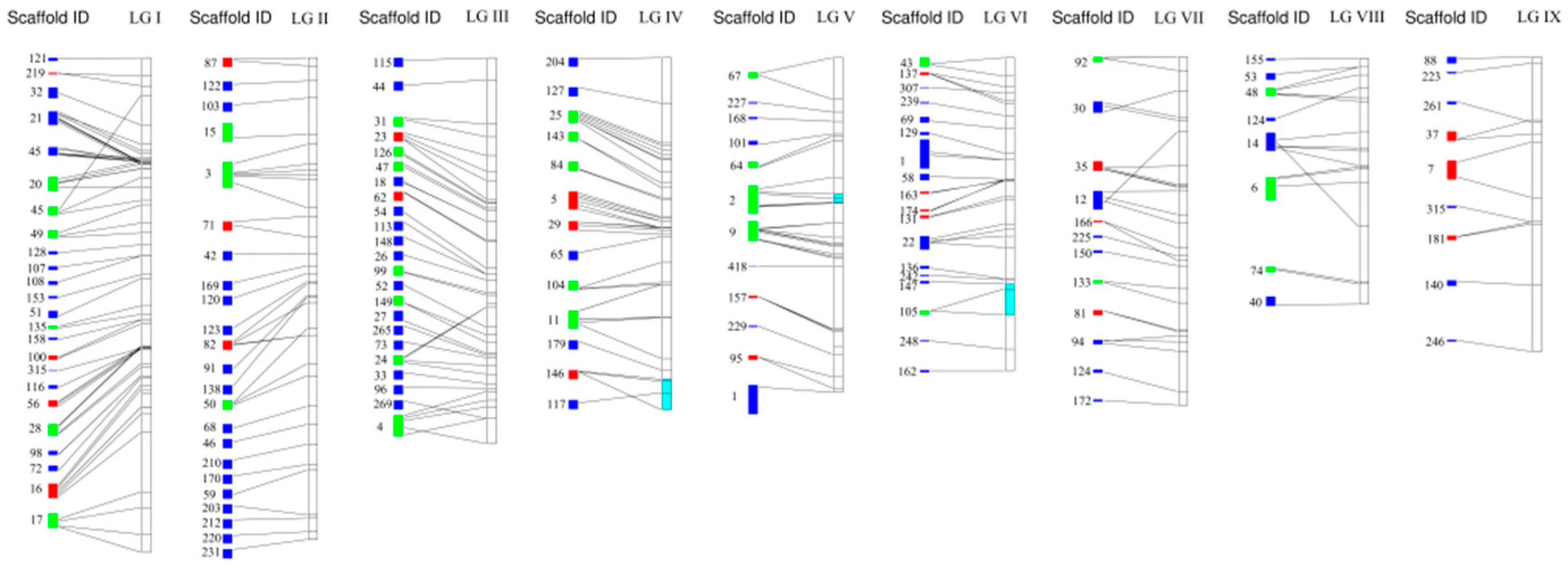
3.2. Comparative Analysis Genetic Linkage Map and Genomic Anchoring
3.3. Statistical Analysis of Quality-Related Traits of A. heimuer
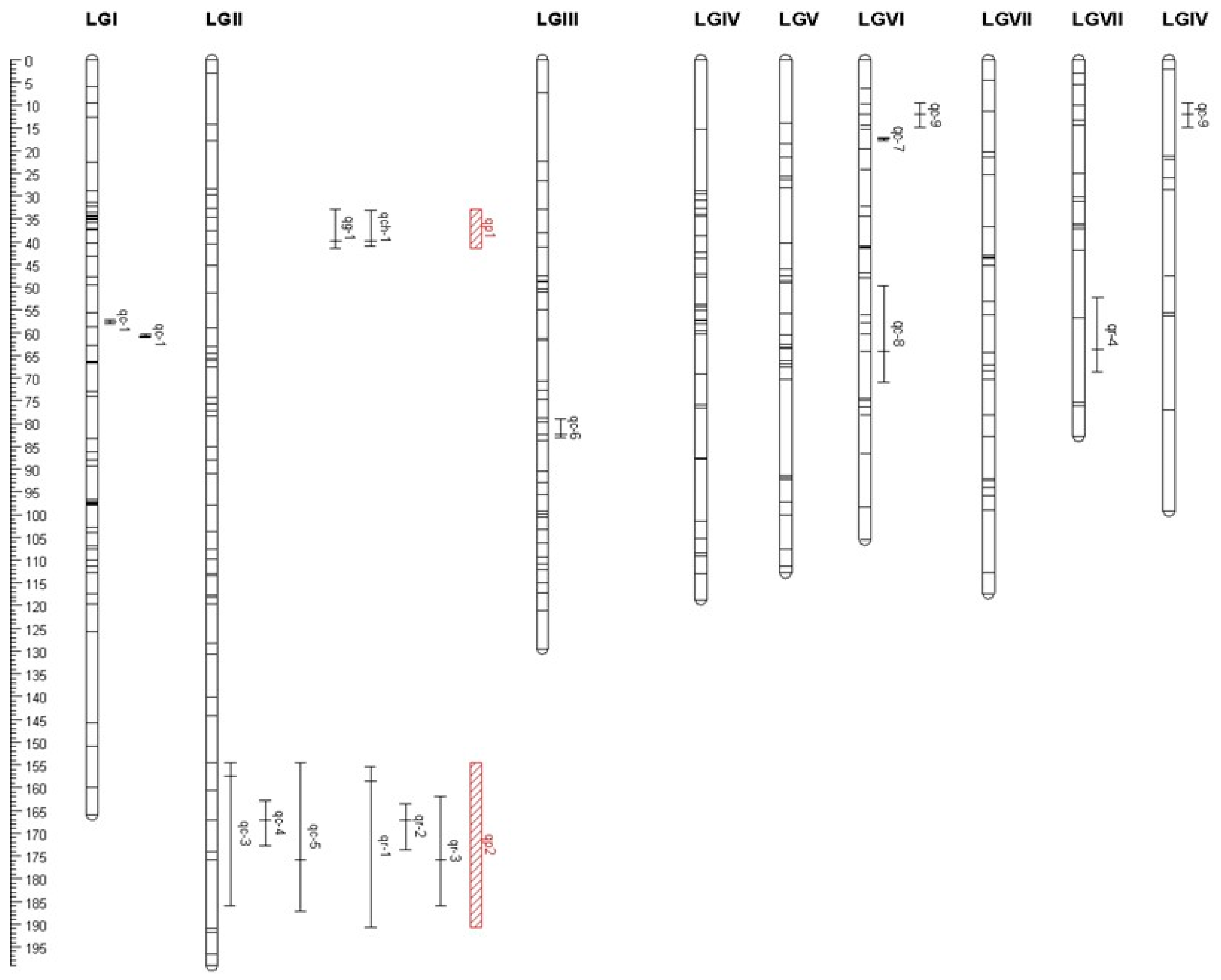
3.4. QTL Mapping Analysis of Fruiting Body Quality-Related Traits of A. heimuer
3.5. Candidate Gene Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. SSR and InDel Marker Development
4.2. Characterization and Anchoring of the New Genetic Linkage Map of A. heimuer
4.3. QTL Mapping for Fruiting Body Quality-Related Traits of A. heimuer
4.4. Candidate Gene Analysis for Fruiting Body Quality-Related Traits of A. heimuer
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, F. Taxonomy and Phylogeny of Auricularia (Auriculariales, Basidiomycota). Ph.D. Thesis, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.Y.; Wang, Y.X.; Wang, A.X.; Deng, W.M.; Wu, R.G. Regional Testing and Application Evaluation of ‘Xuemei No.1’ in Fujian. North. Hortic. 2017, 14, 160–165. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.Y.; Shi, L.Y.; Zhao, C.M.; Zhang, Y.L.; Guo, J.Y. Screening of High-quality Auricularia auricula Strains Suitable for Cultivation in Western Mountainous Areas of Hebei Province. Edible Fungi China 2019, 38, 19–22, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, F.J.; Bian, Y.B. Illustrating the Key Technology of Auricularia Auricula; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, F.J. The Cultivation Spread of Auricularia auricula from North to South in China. Edible Fungi China 2012, 31, 61–62. [Google Scholar]
- China Edible Fungi Association. Analysis of the results of the national edible mushroom statistical survey in 2020. Edible Fungi China 2022, 41, 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, F.J.; Zhang, Y.M.; Lu, L.X.; Fang, M. Research Progress on Genetics and Breeding of Auricularia auricula-judae. J. Fung. Res. 2015, 13, 125–128. [Google Scholar]
- Idrees, M.; Yaqoob, S.; Leo, S.F.; Khan, A.A.; Sun, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, D.; Fu, Y.; Li, Y. A Comparison of the Physical, Chemical, and Structural Properties of Wild and Commercial Strains of Button Mushroom, Agaricus bisporus (Agaricomycetes). Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2019, 21, 611–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Me, H.W.; Han, Y.; Li, Y.J.; Xue, Y.; Fu, T.T.; Liu, Y.; Hu, W.; Han, S.C.; Zhao, F.C.; Wu, H.J.; et al. Effect of Different Culture Substrates and Cultivation Mode on Sensory Quality of Auricularia auricular. J. Northeast For. Univ. 2017, 45, 51–56, 88. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.H. Texture Analysis and Nutrition Evaluation for Products of Auricularia heimuer Produced by Log Cultivation and Substituted Material Cultivation. Edible Fungi China 2019, 38, 50–56, 60. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Mu, Y.; Li, Y.J.; Wan, P.; Feng, L.; Lei, H. Effects of Geographical Environment and Genotype on Nutritional Contents, Texture and Microstructure of Auricularia auricula-judae. Food Sci. 2018, 39, 233–239. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Gong, W.; Li, C.; Shen, N.; Gui, Y.; Bian, Y.; Kwan, H.S.; Cheung, M.K.; Xiao, Y. RNA-Seq-based high-resolution linkage map reveals the genetic architecture of fruiting body development in shiitake mushroom, Lentinula edodes. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 1641–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, W.; Sonnenberg, A.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, J.; Huang, C. Genetic Linkage and Physical Mapping for an Oyster Mushroom (Pleurotus cornucopiae) and Quantitative Trait Locus Analysis for Cap Color. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e0095321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Yao, F.J.; Lu, L.X.; Fang, M.; Zhang, Y.M.; Khan, A.A.; Kong, X.H.; Yu, J.; Jiang, W.Z.; Kitamoto, Y. Map-based cloning of genes encoding key enzymes for pigment synthesis in Auricularia cornea. Fungal Biol. 2019, 123, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.Z.; Yao, F.J.; Lu, L.X.; Fang, M.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.M.; Meng, J.J.; Lu, J.; Ma, X.X.; He, Q.; et al. Affiliations expand. Genetic linkage map construction and quantitative trait loci mapping of agronomic traits in Gloeostereum incarnatum. J. Microbiol. 2021, 59, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.X.; Yao, F.J.; Wang, P.; Fang, M.; Zhang, Y.M.; Zhang, W.T.; Kong, X.H.; Lu, J. Construction of a genetic linkage map and QTL mapping of agronomic traits in Auricularia auricula-judae. J. Microbiol. Biol. Educ. 2017, 55, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Yao, F.J.; Wang, L.J.; Zhang, Y.M. Overview of Morphological Development about Auricularia auricula. North. Hortic. 2011, 19, 185–187. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Yao, F.J.; Zhang, Y.M.; Fang, M. Numerical classification of cultivated germplasm of Auricularia auricula-judae. Mycosystema 2014, 33, 984–996. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, F.J.; Zhang, Y.M. A New Auricularia auricula Cultivar ‘Qihei 1’. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2012, 39, 603–604. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.M.; Chen, Y.; Fang, M.; Wang, W.; Yao, F.J. A New Auricularia auricula Cultivar ‘Jihei 1’. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2013, 40, 601–602. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, M.; Yao, F.J.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.W.; Ren, Y.Y. A New Auricularia auricula Cultivar ‘Jihei 2’. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2013, 40, 1215–1216. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, F.J.; Lu, L.X.; Wang, P.; Fang, M.; Zhang, Y.M.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.T.; Kong, X.H.; Lu, J.; Honda, Y. Development of a Molecular Marker for Fruiting Body Pattern in Auricularia auricula-judae. Mycobiology 2018, 46, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, M.G.; Thompson, W.F. Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980, 8, 4321–4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yao, F.J.; Sun, W.J.; Fang, M.; Wu, C.S. Screening of reference genes for qRT-PCR amplification in Auricularia heimuer. Mycosystema 2020, 39, 1510–1519. [Google Scholar]
- Kofler, R.; Schlotterer, C.; Lelley, T. SciRoKo: A new tool for whole genome microsatellite search and investigation. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1683–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Ooijen, J.W. JoinMap 4, Software for the Calculation of Genetic Linkage Maps in Experimental Populations; Kyazma BV: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Labbé, J.; Zhang, X.; Yin, T.; Schmutz, J.; Grimwood, J.; Martin, F.; Tuskan, G.A.; Le Tacon, F. A genetic linkage map for the ectomycorrhizal fungus Laccaria bicolor and its alignment to the whole-genome sequence assemblies. New Phytol. 2008, 180, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishman, L.; Kelly, A.J.; Morgan, E.; Willis, J.H. A genetic map in the Mimulus guttatus species complex reveals transmission ratio distortion due to heterospecific interactions. Genetics 2001, 159, 1701–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarti, A.; Lasher, L.K.; Reefer, J.E. A maximum likelihood method for estimating genome length using genetic linkage data. Genetics 1991, 128, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, F.; Aerts, A.; Ahren, D.; Brun, A.; Danchin, E.G.; Duchaussoy, F.; Gibon, J.; Kohler, A.; Lindquist, E.; Pereda, V.; et al. The genome of Laccaria bicolor provides insights into mycorrhizal symbiosis. Nature 2008, 452, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Nest, M.A.; Slippers, B.; Steenkamp, E.T.; De Vos, L.; Van Zyl, K.; Stenlid, J.; Wingfield, M.J.; Wingfield, B.D. Genetic linkage map for Amylostereum areolatum reveals an association between vegetative growth and sexual and self-recognition. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2009, 46, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remington, D.L.; Whetten, R.W.; Liu, B.H.; O’Malley, D.M. Construction of an AFLP genetic map with nearly complete genome coverage in Pinus taeda. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1999, 98, 1279–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.B. Precision mapping of quantitative trait loci. Genetics 1994, 136, 1457–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Basten, C.; Zeng, Z. Windows Qtl Cartographer 2.5; Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Voorrips, R.E. MapChart: Software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J. Hered. 2002, 93, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Xiao, J.; Huang, N.; Mccouch, S.R. Chromosomal regions associated with segregation distortion of molecular markers in F2, backcross, doubled haploid, and recombinant inbred populations in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol. Gen. Genet. 1997, 253, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y. A Sequence-Based Reference Genetic Linkage Map of Brassica Rapa. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Usdin, K. The biological effects of simple tandem repeats: Lessons from the repeat expansion diseases. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, S.T. Study on the linkage map construction and genome consolidation in Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn. Ph.D. Thesis, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, W.B. Quantitative Trait Loci Mapping of Important Agronomic Traits in Lentinula Edodes. Ph.D. Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Okuda, Y.; Ueda, J.; Obatake, Y.; Murakami, S.; Fukumasa, Y.; Matsumoto, T. Construction of a genetic linkage map based on amplified fragment length polymorphism markers and development of sequence-tagged site markers for marker-assisted selection of the sporeless trait in the oyster mushroom (Pleurotus eryngii). Appl. Environ. Microb. 2012, 78, 1496–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terashima, K.; Matsumoto, T.; Hayashi, E.; Fukumasa-Nakai, Y. A genetic linkage map of Lentinula edodes (shiitake) based on AFLP markers. Mycol. Res. 2002, 106, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.M. Density-Increasing of Genetic Map and QTL for Hybrid Population of Populus Adenopoda × P.Alba. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, Y.B.; Luo, X.C.; Wang, B.; Jin, D.M.; Zhou, Q. Electrophoretic karyotype analysis ofauricularia auricula. Mycosystema 2000, 19, 78–80. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Wu, F.; Si, J.; Zhao, Y.F.; Dai, Y.C. Whole genome sequence of Auricularia heimuer (Basidiomycota, Fungi), the third most important cultivated mushroom worldwide. Genomics 2019, 111, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, P.; Lu, L.; Lu, J.; Yao, F.; Zhang, Y. Genome Sequence Analysis of Auricularia heimuer Combined with Genetic Linkage Map. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larraya, L.; Peñas, M.M.; Pérez, G.; Santos, C.; Ritter, E.; Pisabarro, A.G.; Ramírez, L. Identification of incompatibility alleles and characterisation of molecular markers genetically linked to the A incompatibility locus in the white rot fungus Pleurotus ostreatus. Curr. Genet. 1999, 34, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulongne-Oriol, M.; Spataro, C.; Cathalot, V.; Monllor, S.; Savoie, J. An expanded genetic linkage map of an intervarietal Agaricus bisporus var. bisporus × A. bisporus var. burnettii hybrid based on AFLP, SSR and CAPS markers sheds light on the recombination behaviour of the species. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2010, 47, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zygier, S.; Chaim, A.B.; Efrati, A.; Kaluzky, G.; Borovsky, Y.; Paran, I. QTLs mapping for fruit size and shape in chromosomes 2 and 4 in pepper and a comparison of the pepper QTL map with that of tomato. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2005, 111, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibov, S.T.; de Souza, C.J.; Garcia, A.A.; Garcia, A.F.; Silva, A.R.; Mangolin, C.A.; Benchimol, L.L.; de Souza, A.P. Molecular mapping in tropical maize (Zea mays L.) using microsatellite markers. 1. Map construction and localization of loci showing distorted segregation. Hereditas 2003, 139, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Linkage Group | Observed Length (cM) | Number of Markers | Average Marker Spacing (cM) | Largest Interval (cM) | >10 cM Interval | Number of Segregation Distortion Markers | SDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LGI | 166.0 | 63 | 2.635 | 19.9 | 1 | 1 | |
| LGII | 161.7 | 35 | 4.370 | 15.1 | 3 | 2 | |
| LGII | 129.5 | 41 | 3.160 | 14.9 | 1 | 1 | |
| LGIV | 118.3 | 39 | 3.032 | 15.3 | 2 | 6 | 1 |
| LGV | 112.4 | 32 | 3.513 | 21.1 | 4 | 6 | 1 |
| LGVI | 105.2 | 29 | 3.628 | 11.5 | 3 | 4 | 1 |
| LGVII | 116.9 | 27 | 4.329 | 13.9 | 2 | 2 | |
| LGVII | 82.5 | 19 | 4.342 | 18.6 | 3 | 1 | |
| LGIX | 98.9 | 12 | 8.241 | 22.3 | 4 | 0 | |
| Total | 1091.4 | 297 | 23 | 23 | 3 | ||
| Average | 121.3 | 33 | 3.79 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 0.3 |
| Project | New Mapping | Original Mapping |
|---|---|---|
| Number of chains | 9 | 11 |
| Number of markers | 297 | 130 |
| Average spacing (cM) | 3.79 | 7.14 |
| Estimated length (cM) | 1202.6 | 1018.4 |
| 20 cM of a marker | 100% | 99% |
| 10 cM of a marker | 99% | 92% |
| 5 cM of a marker | 92% | 72% |
| No. | Traits | Mean | Scope | Range | Standard Deviation | Variance | Coefficient of Variation | Kolmogorov–Smirnov Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hardness | 728.24 ± 20.83 | 190.44–1380.36 | 1189.92 | 46,845.32 | 46,845.32 | 30% | 0.431 |
| 2 | Springiness | 0.87 ± 0 | 0.74–0.95 | 0.21 | 0 | 0.00 | 3% | 0.289 |
| 3 | Cohesiveness | 0.75 ± 0.01 | 0.49–0.94 | 0.45 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 13% | 0.792 |
| 4 | Gumminess | 521 ± 17.36 | 137.40–1093.77 | 956.37 | 32,543.9 | 32,543.90 | 35% | 0.411 |
| 5 | Chewiness | 455.33 ± 15.41 | 105.96–995.82 | 889.86 | 25,640.79 | 25,640.79 | 35% | 0.259 |
| 6 | Resilience | 1 ± 0.03 | 0.33–1.67 | 1.34 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 33% | 0.444 |
| Traits | Loci | Linkage Map | Position (cM) | Adjacent Marker | LOD | Confidence Intervals (cM) | Additive Effect | Parental Genotype | R2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohesiveness | qc-1 | 1 | 57.5 | SSR707-D124 | 2.04 | 57.1–58.0 | −0.07 | A18-119 | 48 |
| qc-2 | 1 | 60.7 | D124-SSR798 | 3.00 | 60.4–61.0 | −0.07 | A18-119 | 49 | |
| qc-3 | 2 | 157.5 | SSR394-SSR124 | 2.70 | 154.4–185.9 | 0.04 | A14-5 | 13 | |
| qc-4 | 2 | 167.1 | SSR387 | 3.62 | 162.9–172.8 | 0.04 | A14-5 | 12 | |
| qc-5 | 2 | 175.8 | SSR721 | 2.55 | 154.6–187.0 | 0.03 | A14-5 | 9 | |
| qc-6 | 3 | 82.3 | D308 | 2.08 | 79.0–82.9 | 0.03 | A14-5 | 7 | |
| qc-7 | 6 | 17.3 | SSR627-SSR894 | 2.80 | 17.0–17.7 | −0.07 | A18-119 | 49 | |
| qc-8 | 6 | 63.8 | SSR548 | 2.09 | 49.5–70.5 | −0.03 | A18-119 | 7 | |
| qc-9 | 9 | 12.0 | SSR491-D640 | 2.29 | 9.3–14.9 | −0.07 | A18-119 | 41 | |
| Gumminess | qg-1 | 2 | 39.8 | SSR375-SSR469 | 2.30 | 32.9–41.5 | −92.46 | A18-119 | 9 |
| Chewiness | qch-1 | 2 | 39.8 | SSR375-SSR469 | 2.35 | 33.0–41.0 | −83.37 | A18-119 | 9 |
| Resilience | qr-1 | 2 | 158.5 | SSR394-SSR124 | 2.55 | 154.4–190.8 | 0.11 | A14-5 | 11 |
| qr-2 | 2 | 167.1 | SSR387 | 3.96 | 163.5–173.6 | 0.12 | A14-5 | 13 | |
| qr-3 | 2 | 175.8 | SSR721 | 3.33 | 161.9–185.9 | 0.11 | A14-5 | 11 | |
| qr-4 | 8 | 63.4 | SSR54-D50 | 2.15 | 52.1–68.4 | 0.13 | A14-5 | 16 |
| Multiple Effect Sites | Confidence Intervals (cM) | Loci | Confidence Intervals (cM) | Linkage Map | Trait | Parental Genotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qp-1 | 32.9–41.5 | qg-1 | 32.9–41.5 | LGII | Gumminess | A18-119 |
| qch-1 | 33.0–41.0 | LGII | Masticatory | A18-119 | ||
| qp-2 | 154.4–190.8 | qc-3 | 154.4–185.9 | LGII | Cohesiveness | A14-5 |
| qc-4 | 162.9–172.8 | LGII | Cohesiveness | A14-5 | ||
| qc-5 | 154.6–187.0 | LGII | Cohesiveness | A14-5 | ||
| qr-1 | 154.4–190.8 | LGII | Receptive | A14-5 | ||
| qr-2 | 163.5–173.6 | LGII | Receptive | A14-5 | ||
| qr-3 | 161.9–185.9 | LGII | Receptive | A14-5 |
| Loci | Linkage Map | Adjacent Marker | Scaffold Number | Mark Position | Predicted Gene Number | Gene Difference | Gene Name | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qc-1 | 1 | SSR707-D124 | 7 | 959,194–967,462 | 4 | 1 | g11733 | Hypothetical protein |
| qc-2 | 1 | D124-SSR798 | 7 | 967,462–1,068,450 | 33 | 13 (10) | ||
| qc-4 | 2 | SSR124-SSR387-SSR385 | 16 | 298,835–361,206–434,760 | 47 | 16 (10) | g3299 | Hypothetical protein |
| qc-5 | 2 | SSR385-SSR721 | 16 | 434,760–479,015 | 13 | 4 (1) | g3338 | Hypothetical protein |
| qc-8 | 6 | SSR548-SSR345 | 8 | 848,218–916,729 | 19 | 5 | ||
| qp-1 | 2 | SSR375-SSR469 | 4 | 1,513,685–1,569,878 | 19 | 1 | g8874 | Hypothetical protein |
| qr-2 | 2 | SSR124-SSR387-SSR385 | 16 | 398,835–361,206–434,760 | 47 | 16 (10) | g3299 | Hypothetical protein |
| qr-3 | 2 | SSR385-SSR721 | 16 | 434,760–479,015 | 13 | 4 (1) | g3338 | Hypothetical protein |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, J.; Fang, M.; Yao, F.; Lu, L.; Ma, X.; Meng, J.; Shao, K. Improved Genetic Map and Localization of Quantitative Trait Loci for Quality Traits in Auricularia heimuer. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9070763
Lu J, Fang M, Yao F, Lu L, Ma X, Meng J, Shao K. Improved Genetic Map and Localization of Quantitative Trait Loci for Quality Traits in Auricularia heimuer. Horticulturae. 2023; 9(7):763. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9070763
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Jia, Ming Fang, Fangjie Yao, Lixin Lu, Xiaoxu Ma, Jingjing Meng, and Kaisheng Shao. 2023. "Improved Genetic Map and Localization of Quantitative Trait Loci for Quality Traits in Auricularia heimuer" Horticulturae 9, no. 7: 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9070763
APA StyleLu, J., Fang, M., Yao, F., Lu, L., Ma, X., Meng, J., & Shao, K. (2023). Improved Genetic Map and Localization of Quantitative Trait Loci for Quality Traits in Auricularia heimuer. Horticulturae, 9(7), 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9070763





