In Vitro Propagation of Philodendron erubescens ‘Pink Princess’ and Ex Vitro Acclimatization of the Plantlets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical and Plant Materials
2.2. Effect of PGRs on Shoot Proliferation
2.3. Effect of Auxins on Root Proliferation
2.4. Ex Vitro Acclimatization of the Plantlets
2.5. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of PGRs on Shoot Proliferation
3.2. Effect of Auxins on Root Proliferation
3.3. Ex Vitro Acclimatization of the Plantlets
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Croat, T.B. A revision of Philodendron subgenus Philodendron (Araceae) for Mexico and Central America. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 1997, 84, 311–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo, S.J.; Bogner, J.; Boyce, P.C. The Genera of Araceae; Royal Botanical Gardens, Kew, The European Union by Continental Printing: Brussels, Belgium, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Mayo, S.J. A revision of Philodendron subgenus Meconostigma (Araceae). Kew Bull. 1991, 46, 601–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grayum, M.H. Revision of Philodendron subgenus Pteromischum (Araceae) for Pacific and Caribbean Tropical America. Syst. Bot. Monogr. 1996, 47, 1–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; McConnell, D.B.; Norman, D.J.; Henny, R.J. The Foliage Plant Industry. In Horticultural Reviews; Janick, J., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 45–110. [Google Scholar]
- Fahmy, G.E.; Arafa, A.M.S.; Ibrahim, I.A.; Zaynab, E.Z. In vitro propagation of Philodendron erubescens cv. Red Emerald. Ann. Agric. Sci. Moshtohor. 1998, 36, 1653–1666. [Google Scholar]
- Sreekumar, S.; Mukunthakumar, S.; Seeni, S. Morphogenetic response of six Philodendron cultivars in vitro. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2001, 39, 1280–1287. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.C.; Wang, C.Y.; Fang, J.Y. Micropropagation of self-heading Philodendron via direct shoot regeneration. Sci. Hortic-Amsterdam. 2012, 141, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Ahmed, I.; Nazir, H.; Ullah, I. Plant Tissue Culture: Current Status and Opportunities. In Recent Advances in Plant In Vitro Culture; Leva, A., Rinaldi, L.M.R., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Mongkolsawat, W.; Punjansing, T.; Loma-in, P. Effects of BA, TDZ, and NAA on growth of Philodendron ‘Birkin’ in vitro. PSRU J. Sci. Technol. 2023, 8, 27–36. (In Thai) [Google Scholar]
- Paek, K.Y.; Chakrabarty, D.; Hahn, E.J. Application of Bioreactor System for Large Scale Production of Horticultural and Medicinal Plants. In Liquid Culture Systems for In Vitro Plant Propagation; Hvoslef-Eide, A.K., Preil, W., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Koriesh, E.M.; Al-Manie, F.A. Growth and root formation of Philodendron oxycardium grown in vitro as affected by benzyladenine and indole acetic acid. Egypt. J. Hort. 2000, 27, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Han, B.H.; Park, B.M. In vitro micropropagation of Philodendron cannafolium. J. Plant Biotechnol. 2008, 35, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.M.S.; Ali, M.A.M.; Soliman, D.A. Effect of low cost gelling agents and some growth regulators on micropropagation of Philodendron selloum. J. Plant Production. Mansoura Univ. 2016, 7, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seliem, M.K.; El-Mahrouk, M.E.; El-Banna, A.N.; Hafez, Y.M.; Dewir, Y.H. Micropropagation of Philodendron selloum: Influence of copper sulfate on endophytic bacterial contamination, antioxidant enzyme activity, electrolyte leakage, and plant survival. South Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 139, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawaadh, A.A.; Dewir, Y.H.; Alwihibi, M.S.; Aldubai, A.A.; El-Hendawy, S.; Naidoo, Y. Micropropagation of lacy tree Philodendron (Philodendron bipinnatifidum Schott ex Endl.). HortScience. 2020, 55, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Ascencio, M.; Andrade-Rodriguez, M.; Guillen-Sanchez, D.; Sotelo-Nava, H.; Villegas-Torres, O.G. Establishment of in vitro aseptic culture of Philodendron xanadu Croat. Rev. Cienc. Agron. 2021, 52, e20197034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieber, J.J.; Schaller, G.E. Cytokinin signaling in plant development. Development 2018, 145, dev149344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, S.S.; Mekureyaw, M.F.; Pandey, C.; Roitsch, T. Role of cytokinins for interactions of plants with microbial pathogens and pest insects. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 10, 1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, R.J.N.; Kisiala, A. The roles of cytokinins in plants and their response to environmental stimuli. Plants 2020, 9, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jambor-Benczur, E.; Marta-Riffer, A. In vitro propagation of Philodendron tuxilanum Bunting with benzylaminopurine. Acta Agron. Hung. 1990, 39, 341–348. [Google Scholar]
- Sosnowski, J.; Truba, M.; Vasileva, V. The impact of auxin and cytokinin on the growth and development of selected crops. Agriculture 2023, 13, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thao, N.T.P.; Ozaki, Y.; Okubo, H. Callus induction and plantlet regeneration in ornamental Alocasia micholitziana. Plant Cell Tissue Org. Cult. 2003, 73, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, A.W.; Bartel, B. Auxin: Regulation, action, and interaction. Ann. Bot. 2005, 95, 707–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.; Saher, A.; Javed, S.; Farooq, Q.; Shakir, M.; Zafar, T.; Komal, L.; Hussain, K.; Shabir, A.; Javed, A.; et al. A review on potential role of auxins in plants, current applications and future directions. J. Bio. Env. Sci. 2021, 18, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Gong, M.; Xu, X.; Li, H.; Deng, W. Roles of auxin in the growth, development, and stress tolerance of horticultural plants. Cells 2022, 11, 2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartabia, A.; Sarropoulou, V.; Grigoriadou, K.; Maloupa, E.; Declerck, S. In vitro propagation of Alkanna tinctoria Tausch.: A medicinal plant of the Boraginaceae family with high pharmaceutical value. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2022, 182, 114860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziv, M.; Ariel, T. Bud proliferation and plant regeneration in liquid-cultured Philodendron treated with ancymidol and paclobutrazol. J. Plant Growth Regul. 1991, 10, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, E.A.; Murthy, H.N.; Hahn, E.J.; Paek, K.Y. Micropropagation of Alocasia amazonica using semisolid and liquid cultures. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 2008, 44, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewir, Y.H.; Chakrabarty, D.; Hahn, E.J.; Paek, K.Y. A simple method for mass propagation of Spathiphyllum cannifolium using an airlift bioreactor. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 2006, 42, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, B.; LeClere, S.; Magidion, M.; Zolman, B.K. Inputs to the active indole-acetic acid pool: De novo synthesis, conjugate hydrolysis and indole-3-butyric acid β-oxidation. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2001, 20, 198–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez, G.; Alarcon, M.V.; Salguero, J. Differential responses of primary and lateral roots to indole-3-acetic acid, indole-3-butyric acid, and 1-naphthaleneacetic acid in maize seedlings. Biol. Plant. 2016, 60, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azza, M.E.S.; Khalafalla, M.M. In vitro shoot micropropagation and plant establishment of an ornamental plant dumb cane (Dieffenbachia compacta). Int. J. Curr. Res. 2010, 6, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Mariani, T.S.; Fitriani, A.; Teixeira da Silva, J.A.; Wicaksono, A.; Chia, T.F. Micropropagation of Aglaonema using axillary shoot explants. Int. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2011, 11, 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Hoang, N.N.; Kitaya, Y.; Shibuya, T.; Endo, R. Effects of supporting materials in in vitro acclimatization stage on ex vitro growth of wasabi plants. Sci. Hortic. -Amsterdam. 2020, 261, 109042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.M.; Chung, H.J.; Choi, J.S. Physico-chemical properties of organic and inorganic materials used as container media. Korean Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2000, 18, 529–535. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, M.M.; Seo, J.H.; Park, J.S.; Son, J.E. Physicochemical properties of mixtures of inorganic supporting materials affect growth of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) plantlets cultured photoautotrophically in a nutrient-circulated micropropagation system. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2012, 53, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
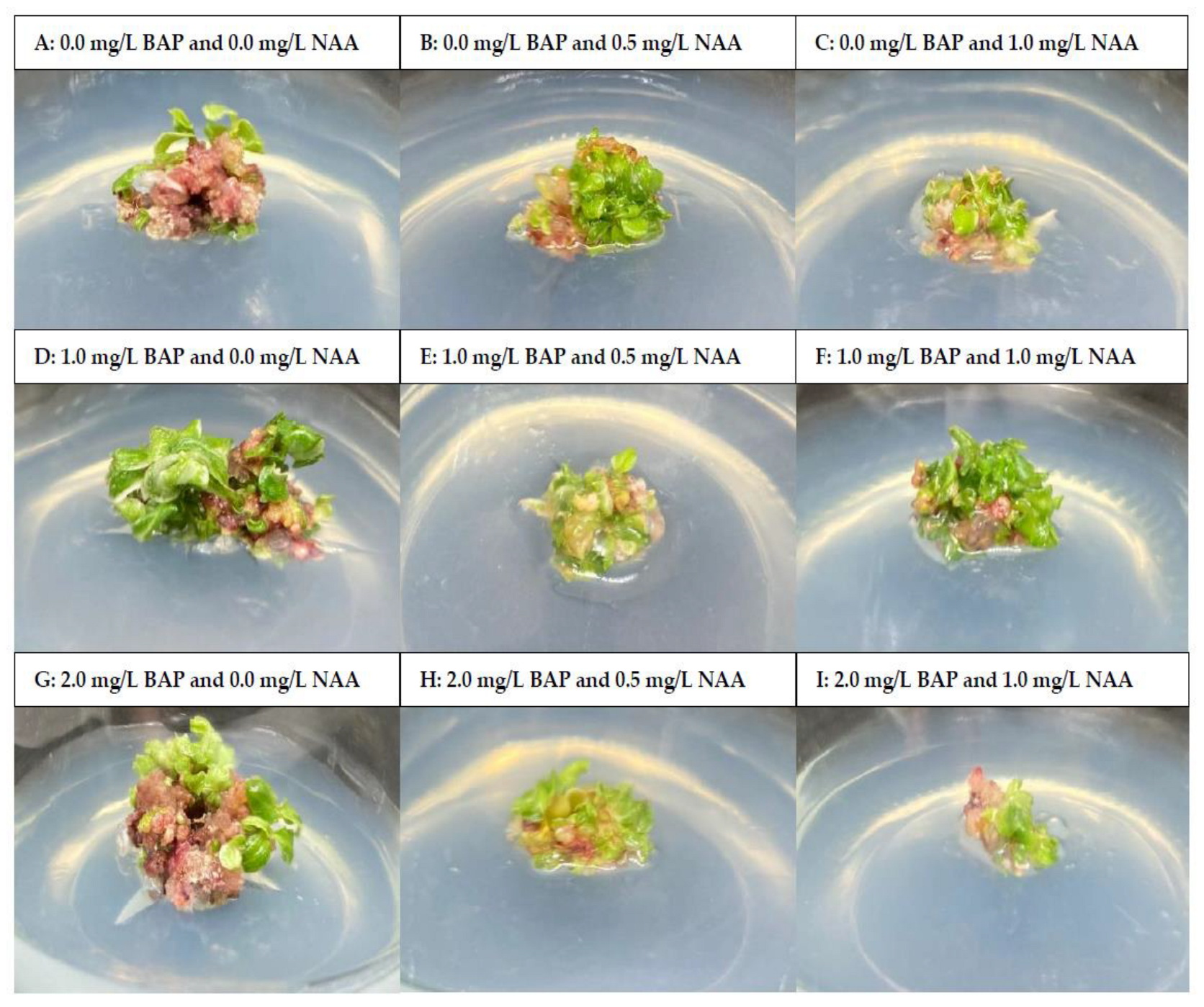


| Treatment | PGRs | Number of Shoots (Shoots/Explant) | Number of Leaves (Leaves/Explant) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BAP (mg/L) | NAA (mg/L) | |||
| 1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 4.4 ± 1.2 ab | 2.4 ± 0.5 b |
| 2 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 5.5 ± 1.9 ab | 2.6 ± 0.5 b |
| 3 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 4.2 ± 0.9 b | 2.4 ± 0.5 b |
| 4 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 7.7 ± 1.1 a | 4.1 ± 0.7 a |
| 5 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 7.0 ± 1.8 a | 3.8 ± 0.6 a |
| 6 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 6.6 ± 1.5 ab | 3.7 ± 0.7 a |
| 7 | 2.0 | 0.0 | 6.3 ± 1.4 ab | 3.5 ± 0.7 a |
| 8 | 2.0 | 0.5 | 6.4 ± 1.8 ab | 3.5 ± 0.7 a |
| 9 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 2.7 ± 1.1 b | 2.3 ± 0.5 b |
| BAP (mg/L) | NAA (mg/L) | Liquid MS Medium | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Shoots (Shoots/Explant) | Number of Leaves (Leaves/Explant) | ||
| 0.0 | 0.0 | 5.0 ± 0.9 c | 3.3 ± 0.8 c |
| 1.0 | 0.0 | 11.2 ± 2.0 a | 4.7 ± 0.5 a |
| 0.5 | 8.1 ± 2.4 b | 4.0 ± 0.7 b | |
| 1.0 | 4.9 ± 1.2 c | 3.1 ± 0.7 c | |
| Treatment | Concentration (mg/L) | Number of Roots (Roots/Explant) | Root Length (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 0.0 | 0.0 e | 0.0 c |
| NAA | 0.5 | 0.0 e | 0.0 c |
| 1.0 | 1.5 ± 0.8 cd | 0.8 ± 0.3 bc | |
| 2.0 | 1.6 ± 0.9 cd | 1.2 ± 0.4 ab | |
| 3.0 | 1.4 ± 0.5 cd | 0.7 ± 0.3 bc | |
| IBA | 0.5 | 1.4 ± 0.5 cd | 1.6 ± 0.8 ab |
| 1.0 | 2.2 ± 1.2 bc | 1.6 ± 0.9 ab | |
| 2.0 | 2.6 ± 0.5 ab | 1.7 ± 1.0 ab | |
| 3.0 | 3.2 ± 0.8 a | 1.9 ± 0.6 a | |
| 2,4-D | 0.5 | 1.4 ± 0.5 cd | 0.8 ± 0.3 bc |
| 1.0 | 1.0 ± 0.0 d | 0.8 ± 0.2 bc | |
| 2.0 | 1.0 ± 0.0 d | 0.8 ± 0.3 bc | |
| 3.0 | 0.8 ± 0.4 de | 1.0 ± 0.3 b |
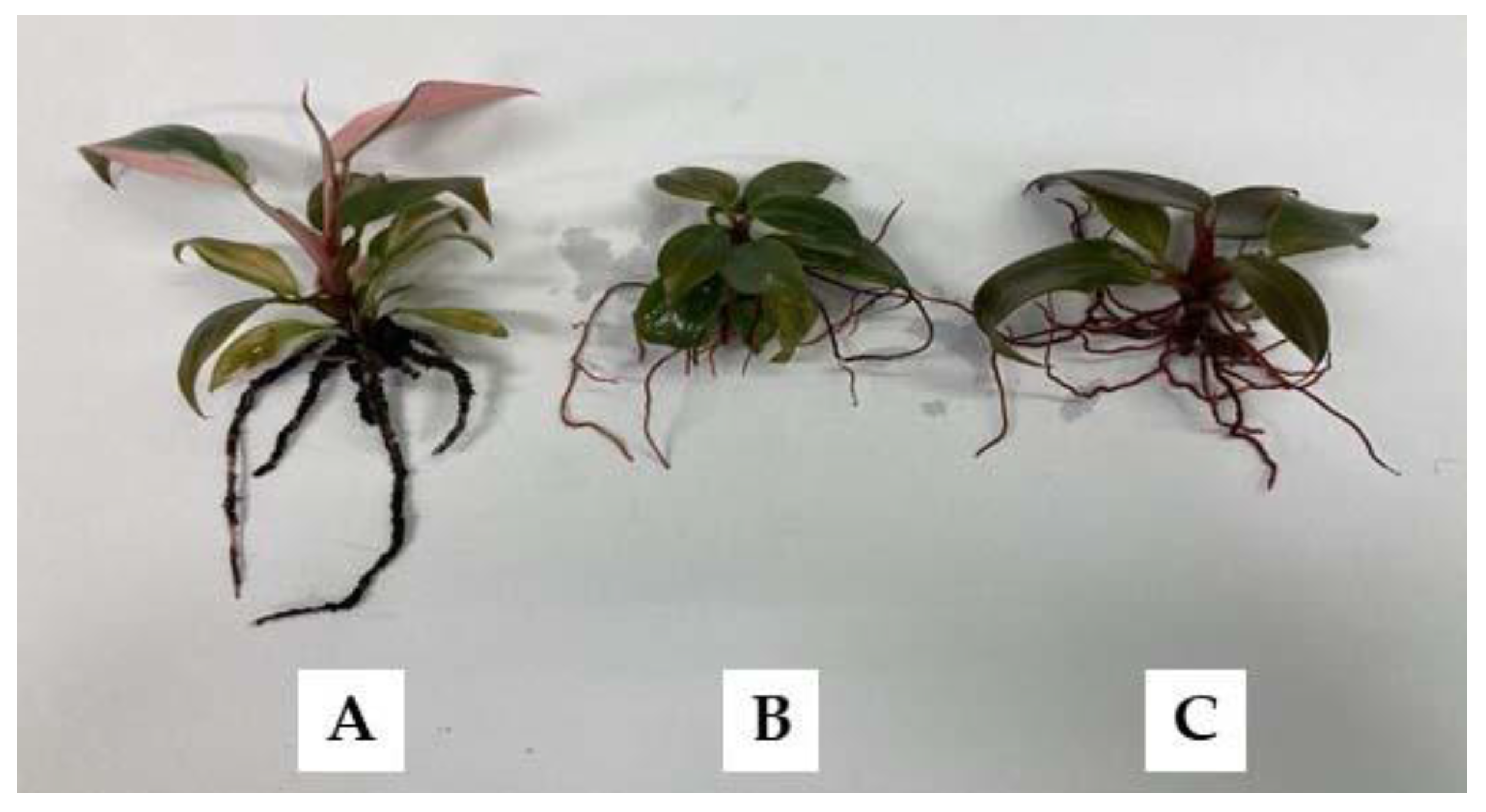
| Planting Material | Survival (%) | Plant Height (cm) | Number of Leaves (Leaves/Plantlet) | Number of Roots (Roots/Plantlet) | Root Length (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peat moss | 100 | 2.48 ± 0.4 a | 10.9 ± 1.3 a | 4.1 ± 1.6 b | 5.5 ± 1.0 b |
| Vermiculite | 100 | 1.82 ± 0.3 b | 7.1 ± 1.7 b | 8.0 ± 1.5 a | 6.7 ± 0.3 a |
| Perlite | 80 | 1.75 ± 0.4 b | 6.5 ± 1.3 b | 7.5 ± 1.2 a | 7.2 ± 0.6 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klanrit, P.; Kitwetcharoen, H.; Thanonkeo, P.; Thanonkeo, S. In Vitro Propagation of Philodendron erubescens ‘Pink Princess’ and Ex Vitro Acclimatization of the Plantlets. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 688. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9060688
Klanrit P, Kitwetcharoen H, Thanonkeo P, Thanonkeo S. In Vitro Propagation of Philodendron erubescens ‘Pink Princess’ and Ex Vitro Acclimatization of the Plantlets. Horticulturae. 2023; 9(6):688. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9060688
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlanrit, Preekamol, Haruthairat Kitwetcharoen, Pornthap Thanonkeo, and Sudarat Thanonkeo. 2023. "In Vitro Propagation of Philodendron erubescens ‘Pink Princess’ and Ex Vitro Acclimatization of the Plantlets" Horticulturae 9, no. 6: 688. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9060688
APA StyleKlanrit, P., Kitwetcharoen, H., Thanonkeo, P., & Thanonkeo, S. (2023). In Vitro Propagation of Philodendron erubescens ‘Pink Princess’ and Ex Vitro Acclimatization of the Plantlets. Horticulturae, 9(6), 688. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9060688





